Section-A
(Attempt all questions from this Section.)
Question 1
Choose one correct answer to the questions from the given options:
(Do not copy the question, write the correct answers only.)
(i) Loss of water as droplets from the hydathodes is called:
(a) Transpiration
(b) Bleeding
(c) Guttation
(d) Evaporation
Solution
Option b: Centromere - point of attachment of sister chromatids
(ii) Synthesis phase in the cell cycle is called so, because of the synthesis of more:
(a) Glucose
(b) Proteins
(c) RNA
(d) DNA
Solution
Option c: Photophosphorylation - conversion of ADP into ATP
(iii) While playing with his friends, Peter inserted a stick into his ear. He lost his
hearing due to the rupture of:
(a) Ear drum
(b) Pericardium
(c) Cornea
(d) Pinna
Solution
Option d: Guttation - takes place through hydathodes present on the margins of the leaf
(iv) The prime source of Chloro fluorocarbons is:
(a) Vehicular emissions
(b) Refrigeration equipment
(c) Sewage
(d) Effuents
Solution
Option b: Vasopressin - Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) which is responsible for reabsorption of water
from the kidney tubules
(v) Oxygenated blood to heart is supplied by:
(a) Hepatic artery
(b) Coronary artery
(c) Renal artery
(d) Pulmonary artery
Solution
Option b: Potassium ions - K+ ion concentration theory which regulates the stomatal opening and
closure
(vi) Assertion (A): There is frequent urination in summer than in winter.
Reason (R): In summer we lose a lot of water as sweat, so the kidneys reabsorb
more water. Hence, urine formed is less in summer than in winter
(a) Both A and R are True
(b) Both A and R are False
(c) A is True and R is False
(d) A is False and R is True
Solution
Option d: Boy - X+Y = Boy X+X = Gir
(vii) The age restrictions for marriage for boys and girls by law in India is:
(a) Boys 18 years, Girls 21 years
(b) Boys 17 years, Girls 16 years
(c) Boys 21 years, Girls 18 years
(d) Boys 20 years, Girls 17 years
Solution
Option a: Stapes - Stirrup transmits the vibration to the membrane of the oval window
(viii) Hari is fond of watching the fish in an aquarium. So, he set up an aquarium in his
house. Along with a number of fresh water fish, he also placed a clown fish which
is a salt water fish. After few hours, the clown fish was found dead and floating on
water. This was due to:
(a) Endosmosis
(b) Exosmosis
(c) Osmoregulation
(d) Excretion
Solution
Option d: P,Q and R
(ix) The solvent used for dissolving chlorophyll while testing a leaf for starch is:
(a) Sodium hydroxide
(b) Lime water
(c) Water
(d) Ethyl alcohol
Solution
Option c: Ciliary muscles - alter the shape of the lens
(x) The structure related to storage and maturation of sperms in a human male is:
(a) Epididymis
(b) Epidermis
(c) Epithelium
(d) Endothelium
Solution
Option b: R and S - Haemophilia, colour blindness and albinism are examples of genetic or inherited
disorders
(xi) A sequence of DNA has 200 nitrogenous base pairs, of which 100 are Thymine Adenine pairs. What is the number of Cytosine-Guanine pairs in this sequence:
(a) 50
(b) 200
(c) 100
(d) 25
Solution
Option c: Osmosis takes place through a selectively permeable membrane
(xii) The stress hormone in plants which functions during a drought is:
(a) Auxins
(b) Abscisic acid
(c) Ethylene
(d) Cytokinins
Solution
Option a: Sperms being haploid will have 23 chromosomes
(xiii) Compressed natural gas (CNG) is proposed to be a better alternative to fossil fuel
Which of the following reasons makes it a better alternative?
P. Combustion leaves little or no residue
Q. Absence of Carbon in CNG
R. Easily available
(a) Only P
(b) Only Q
(c) Only P and R
(d) Only Q and R
Solution
Option a: Both A and R are True
(xiv) The ground substance present in chloroplast is:
(a) Stoma
(b) Stroma
(c) Grana
(d) Thylakoids
Solution
Option a: 1 year (per year)
(xv) Lata wanted to cross the road. She looked on either side of the road and then
walked across to the other side of the road.
Which of the following is / are involved in the process described above?
1. Cerebrum
2. Cerebellum
3. Skeletal muscles
4. Medulla Oblongata
(a) Only 3
(b) Only 1 and 3
(c) Only 1, 3 and 4
(d) Only 1, 2 and 3
Solution
Option b: Peppered Moth (Biston betularia)
Question 2
(i) Name the following:
(a) The respiratory pigment in Erythrocytes.
(b) The tissue that transports manufactured food from the leaves to all the parts of
the plant.
(c) The type of gene, which in the presence of a contrasting allele, is not expressed.
(d) The duct which carries urine from the urinary bladder to outside the body.
(e) The collective term for the protective membranes of the brain.
(ii) Arrange and rewrite the terms in each group in the correct order so as to be in a
logical sequence beginning with the term that is underlined.
(a) Snake, Grass, Frog, Grasshopper
(b) Cochlea, Malleus, Pinna, Stapes
(c) Fibrin, Thrombin, Fibrinogen, Platelets
(d) Endodermis, Cortex, Xylem, Epidermis
(e) Embryo, Foetus, Blastocyst, Morula
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
The technical term for short sightedness is (a) __________. This defect is caused
because the eyeball is (b) __________ from front to back or the lens is too
(c) __________. It can be corrected by using a suitable (d) __________ lens. The
power of the lens is mentioned in (e) __________
(iv) Choose the odd one out from the following terms and name the category to which
the others belong:
(a) Newspapers, Vegetable peels, Electric bulbs, Animal excreta
(b) Renal pelvis, Renal artery, Renal Cortex, Renal medulla
(c) Urochrome, Urea, Keratin, Uric acid
(d) Oval window, Cochlea, Auditory canal, Round window
(e) ADH, TSH, ACTH, NADP
(v) Match the items given in Column I with the most appropriate ones in Column II and
rewrite the correct matching pairs.
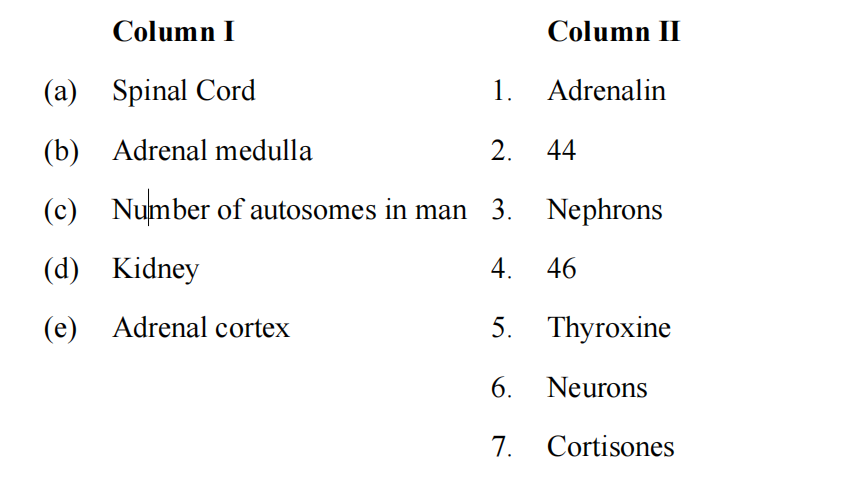
Solution
(i) Name the following:
(a) Root hair
(b) Astigmatism
(c) Chemotropism
(d) Urea
(e) Implantation
(ii) Arrange in logical sequence:
(a) Australopithecus, Homo erectus, Neanderthal man, Cro-Magnon
(b) Aqueous humour, Pupil, Vitreous humour, Retina
(c) Receptor, Sensory neuron, Motor neuron, Effector
(d) Bowman's capsule, Proximal convoluted tubule, Loop of Henle, Dis
tal convoluted tubule
(e) Soil water, Ascent of sap, Leaves, Water vapour
(iii) Fill in the blanks:
(a) photosynthesis
(b) destarch
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) brown
(e) blue-black
(iv) Odd one out:
(a) Odd: Albumin Others: blood clotting components
(b) Odd: Glomerulus Others: lymphatic organs
(c) Odd: Monocytes Others: granular WBCs
(d) Odd: Styrofoam Others: biodegradable wastes
(e) Odd: Pulmonary artery Others: carry oxygenated blood
(v) Match the following:
(a) Leydig cells - 3. Testosterone
(b) Stoma - 4. Diffusion of respiratory gases
(c) Ova - 5. Haploid cells
(d) Cranial nerves - 2. 12 pairs
(e) Cretinism - 1. Lack of thyroxine in children
Section-B
(Attempt any four questions from this Section.)
Question 3
(i) The gene of red hair is recessive to the gene for black hair. What will be the hair
colour of a person if he inherits a gene for red hair from his mother and a gene for
black hair from his father?
(ii) State Mendel’s Law of Dominance.
(iii) What are Homologous chromosomes?
(iv) Differentiate between Phenotype and Genotype.
(v) Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a duplicated chromosome.
Solution
(i) NADP - Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
(ii) Two adaptations in roots for absorption of water from the soil:-
• Huge surface area provided by rootlets and root hair
• Root hairs contain cell sap of a higher concentration than that of the surrounding water
(iv) Two examples of water pollutants:
• Sewage, effluents, oil spills, household detergents (any 2)
(v) (a) Phenomenon depicted - Thigmotropism
(b) Thigmotropism - it refers to the growth movement of plant parts in response to touch stimulus
(c) Part marked X - tendril
Question 4
(i) Mention the exact location of Corpus callosum.
(ii) What are the two hormones secreted by Corpus luteum?
(iii) Differentiate between Menarche and Menopause.
(iv) What is the significance of placenta in the growth of foetus?
(v) Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a human gamete that has the sex chromosome.Y
Solution
(i) Surgical of contraception in human females - Tubectomy
(ii) Two effects of acid rain on the environment:
• Fish and other aquatic animals are harmed due to increased acidity of the water in such lakes,
rivers etc.
• Damage to vegetation by pollution of the soil.
• Decay of building material and paints.
(iii) Two advantages of transpiration:
• Cooling effect - Evaporation reduces temperature of leaf surface. Therefore, transpiration is useful
to plants on hot sunny days.
• Suction force - Transpiration helps in the ascent of sap by producing a suction force acting from
the top of a plant.
(iv) Two objectives of Swachh Bharat Abhiyan:
• To clean the streets, roads and infrastructure of the country's cities and towns.
• To eliminate open defecation through the construction of individual, cluster and community
toilets.
• To achieve efficient solid and liquid waste management systems.
(v) (a) Cerebrum helps Mohan to concentrate.
(b) Sense organ engaged - eyes
(c) Cerebellum co-ordinates all the voluntary muscles of the body
Question 5
(i) Explain the term – Photsynthesis.
(ii) Write the overall chemical equation of Photosynthesis.
(iii) A potted plant having variegated leaves was exposed to sunlight for 3 hours. One of
the leaves was plucked and tested for starch. What will be your observation after the
starch test?
(iv) The initial food prepared by a green plant is A, which is later converted to food B by
polymerization. Name food A and food B.
(v) Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
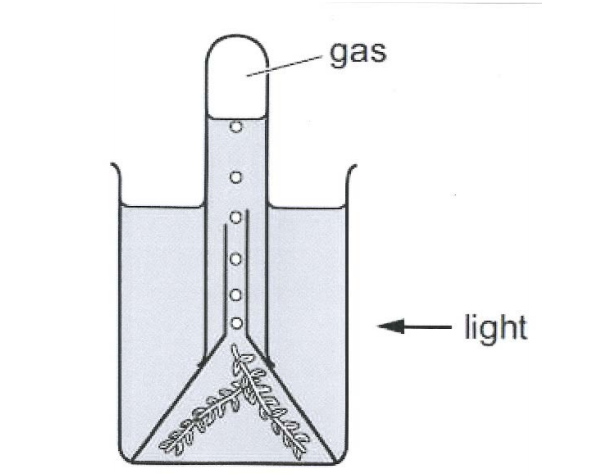
(a) Name the gas released when the setup was placed in sunlight.
(b) Give an example of an aquatic plant that can be used in the above experiment.
(c) What will happen if a pinch of Sodium bicarbonate is added to the water?
Solution
(i) Mixed nerves are those that contain both sensory and motor fibres.

(iii) Two factors responsible for high birth rate in India:
• Illiteracy - Most of the rural population, which forms the bulk of our society are still illiterate,
ignorant and superstitious. They do not know the functioning of the human reproductive system.
• Desire for a male child -Most of the Indian families still hold the view that a male child is essential
for keeping up the name of the family.
(iv) Exact location of:
(a) Pericardium - double walled membranous covering surrounding the heart.
(b) Bicuspid valve - at the aperture between the left auricle and the left ventricle.
(v) (a) Seed shape:
• Dominant - Round
• Recessive - Wrinkled
(b) 3:1 represents:
• 3 - Round offsprings
• 1 - Wrinkled offspring
(c) Mendel’s Law of Dominance - Out of a pair of contrasting characters present together, only one
is able to express itself while the other remains suppressed. The one that expresses is the dominant
character and the one unexpressed is the recessive.
Question 6
(i) Give the exact location of genes.
(ii) Differentiate between Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis.
(iii) Mention two significant features of the stage Anaphase during Mitosis.
(iv) How many daughter cells are formed at the end of Mitosis and Meiosis?
(v) Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
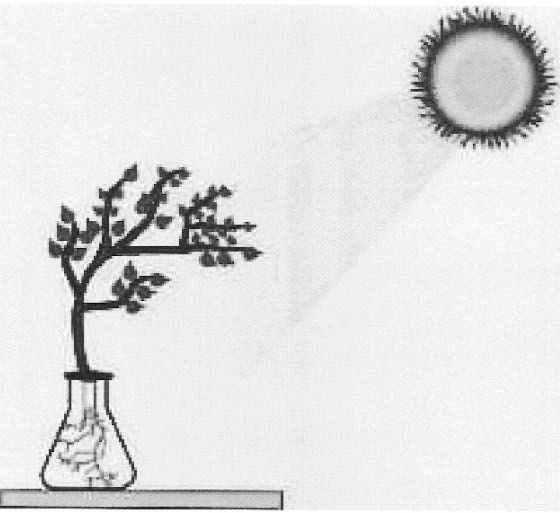
(a) Name the phenomenon depicted by the shoot in the above diagram.
(b) Which plant hormone plays an important role in the above movement?
(c) Name one stimulus which gives a positive response for the roots but negative
response for the shoot.
Solution
(i) Diapedesis - is defined as the process by which amoeboid white blood corpuscles squeeze through
the walls of the capillaries into the tissues (dia: across, pedesis: oozing out)
(iii) Carbon monoxide is dangerous when inhaled in excess as haemoglobin has very strong affinity for
carbon monoxide forming a stable compound carboxyhaemoglobin (HbCO). This cuts down the
capacity of the blood of transporting oxygen, sometimes resulting in death. This is known as carbon
monoxide poisoning.
(iv) (a) Process for the release of ovum - ovulation
(b) Structure marked 2 - Corpus luteum
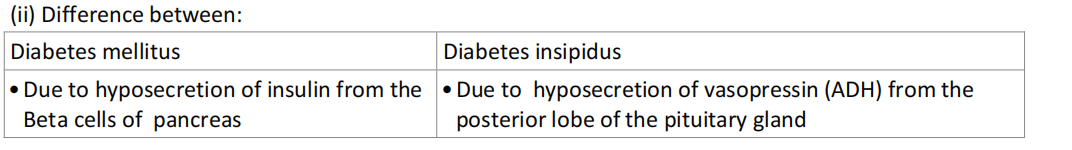
(v) Structure of a chloroplast:
Question 7
(i) What is the scientific name for man?
(ii) What are vestigial organs? Give one example.
(iii) State two structural differences between an artery and vein.
(iv) Mention any two features of the Cro-Magnon man.
(v) Study the picture given below and answer the questions that follow:

(a) Name the category of waste that is being disposed.
(b) Give an example of such a waste.
(c) Are they hazardous to humans and animals? Give a suitable reason to justify
your answer.
Solution
(i) Hormone - It is a secretion from some glandular part of the body, which is poured directly into
blood and which acts on the target organs or cells of the same individual, bringing about coordination
between distant parts of the body.
(ii) (a) Static equilibrium - utriculus and sacculus (vestibule)
(b) Dynamic equilibrium - ampulla (semi-circular canals)

(iv) Two limitations of Ganong's Potometer:
• Introducing the air bubble is not very easy
• The twig may not remain fully alive for a long time.
(v) (a) Mahesh is suffering from - Myopia (short-sightedness)
(b) The image of distant objects is formed in front of the retina in this defect.
(c) This defect can be corrected by suitable concave (diverging) lens for his spectacles which causes
the light rays to diverge before they strike the lens of the eye.
Question 8
(i) Define – Osmosis.
(ii) Name the two sensory cells in retina meant for light adaptation.
(iii) Mention one function each for – Cerebrum and Cerebellum.
(iv) State any two objectives of Swachh Bharat Abhiyan.
(v) Given below is the diagram of human blood smear. Answer the questions that follow:
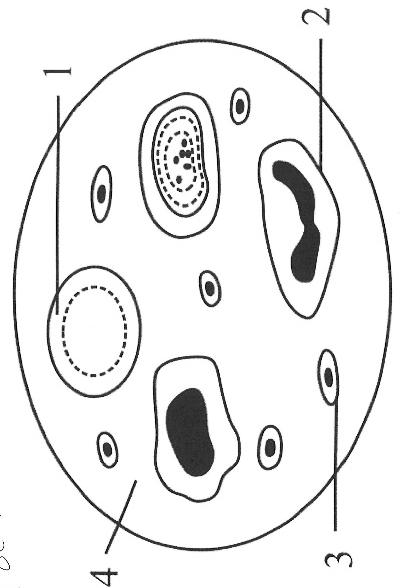
(a) Mention one structural difference between 1 and 2.
(b) What is the function of part 3?
(c) Name the part labelled 4.
Solution
(i) Ultrafiltration - The blood flows through the glomerulus under great pressure because the efferent
(outgoing) arteriole is narrower than the afferent (incoming) arteriole. This high pressure (hydrostatic
pressure) causes the liquid part of the blood to filter out from the glomerulus into the renal tubule,
which is termed as ultrafiltration.
(ii) (a) Clotting of blood - calcium
(b) Synthesis of thyroxine - iodine
(iii) Two harmful effects of noise pollution:
• It interferes in communication and interrupts concentration of thought and disturbs peace of
mind.
• It lowers the efficiency of work, disturbs sleep and leads to nervous irritability.
(iv) RBCs are efficient in their functions because:
• Loss of nucleus makes the red blood cells biconcave, thus increasing their surface area volume
ratio for absorbing more oxygen. It also increases the space between them so that more RBCs can
be accommodated in the same space.
• Loss of mitochondria means that the red blood cells cannot use oxygen for themselves as cellular
respiration occurs in mitochondria. Thus, all the oxygen absorbed is transported and delivered to
the tissues unconsumed. It also allows full transport of glucose in blood plasma, unused by the
RBCs.
(v) (a) Stage represented - Early Anaphase
(b) Reason - As the two sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and are drawn apart
towards opposite poles pulled by contraction of spindle fibres.
(c) Number of chromosomes - 4









