Class 10 CBSE Term2 Science Specimen 2022
BOARD -
CLASS -
SUBJECT -
CBSE
10th
SCIENCE
Paper Pattern for MCQ Term-I
TIME -
MARKS -
2 Hour
40
Visit CBSE OFFICIAL PAGE for Regulations and Syllabus of Class 12th CBSE
Solved Specimen Paper Semester-2 2022
Section-A
Question 1
The table shows the electronic structures of four elements.
| ELEMENT | ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE |
|---|---|
| P | 2,6 |
| Q | 2,8,1 |
| R | 2,8,7 |
| S | 2,8,8 |
a. Identify which element(s) will form covalent bonds with carbon.
b. “Carbon reacts with an element in the above table to form several
compounds.” Give suitable reason.
Solution
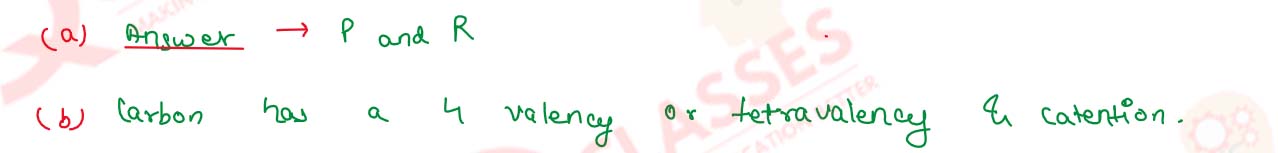
Question 2
The diagram below shows part of the periodic table.
a. Which elements would react together to form covalent compounds?
b. Between the two elements W and Z, which will have a bigger atomic
radius? Why?
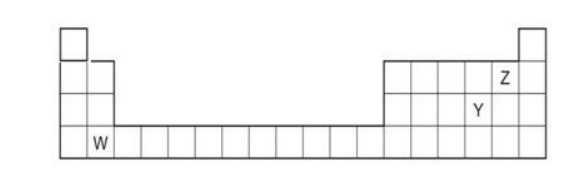
Solution

Question 3
a. Trace the path a male gamete takes to fertilise a female gamete after being
released from the penis.
b. State the number of sets of chromosomes present in a zygote.
Solution

Question 4
Rajesh observed a patch of greenish black powdery mass on a stale piece of
bread.
a. Name the organism responsible for this and its specific mode of asexual
reproduction.
b. Name its vegetative and reproductive parts.
Solution

Question 5
Mustard was growing in two fields- A and B. While Field A produced brown
coloured seeds, field B produced yellow coloured seeds.
It was observed that in field A, the offsprings showed only the parental trait for
consecutive generations, whereas in field B, majority of the offsprings showed
a variation in the progeny.
What are the probable reasons for these?
Solution

OR
In an asexually reproducing species, if a trait X exists in 5% of a population and trait Y exists in 70% of the same population, which of the two trait is likely to have arisen earlier? Give reason.
Solution
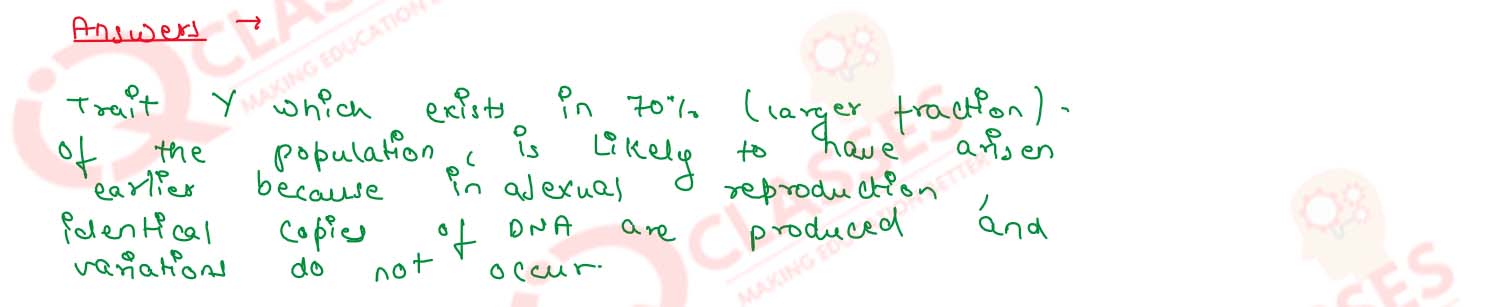
Question 6
A simple motor is made in a school laboratory. A coil of wire is mounted on an
axle between the poles of a horseshoe magnet, as illustrated.
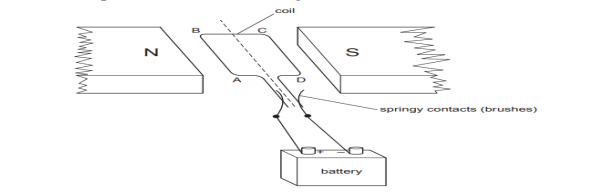 In the example above, coil ABCD is horizontal and the battery is connected as
shown.
In the example above, coil ABCD is horizontal and the battery is connected as
shown.
a. For this position, state the direction of the force on the arm AB.
b. Why does the current in the arm BC not contribute to the turning force on
the coil?

Solution

OR
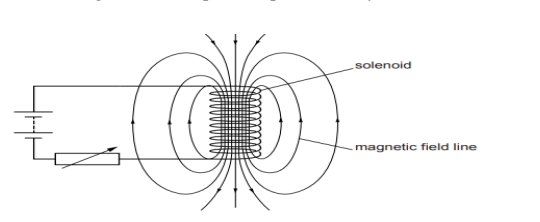
A circuit contains a battery, a variable resistor and a solenoid. The figure
below shows the magnetic field pattern produced by the current in the
solenoid.
a. State how the magnetic field pattern indicates regions where the magnetic
field is stronger.
b. What happens to the magnetic field when the current in the circuit is
reversed?
Solution

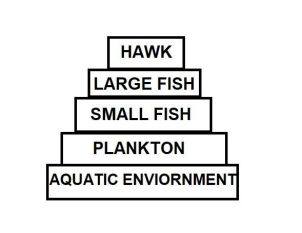
Question 7
DDT was sprayed in a lake to regulate breeding of mosquitoes. How would it affect the trophic levels in the following food chain associated with a lake? Justify your answer.
Solution

OR
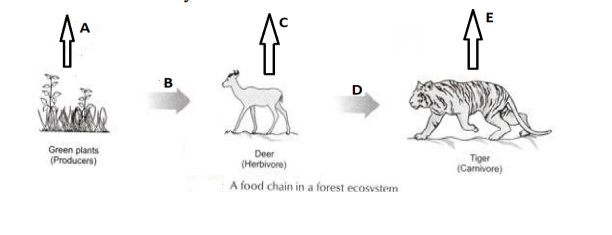
In the following food chain, vertical arrows indicate the energy lost to the environment and horizontal arrows indicate energy transferred to the next trophic level. Which one of the three vertical arrows (A, C and E) and which one of the two horizontal arrows (B and D) will represent more energy transfer? Give reason for your answer.
Solution

Section-B
Question 8
Choose an element from period 3 of modern periodic table that matches the
description given below in each instance. Give reason for your choice.
a. It has a similar structure to diamond.
b. It has same valency as Lithium.
c. It has variable valency and is a member of the Oxygen family (group 16).
Solution

Question 9
a. How many isomers are possible for the compound with the molecular
formula C4H8? Draw the electron dot structure of branched chain isomer.
b. How will you prove that C4H8 and C5H10 are homologues?
Solution

OR
A carbon compound ‘A’ having melting point 156K and boiling point 351K, with molecular formula C2H6O is soluble in water in all proportions. a. Identify ‘A’ and draw its electron dot structure. b. Give the molecular formulae of any two homologues of ‘A’.
Solution
Question 10
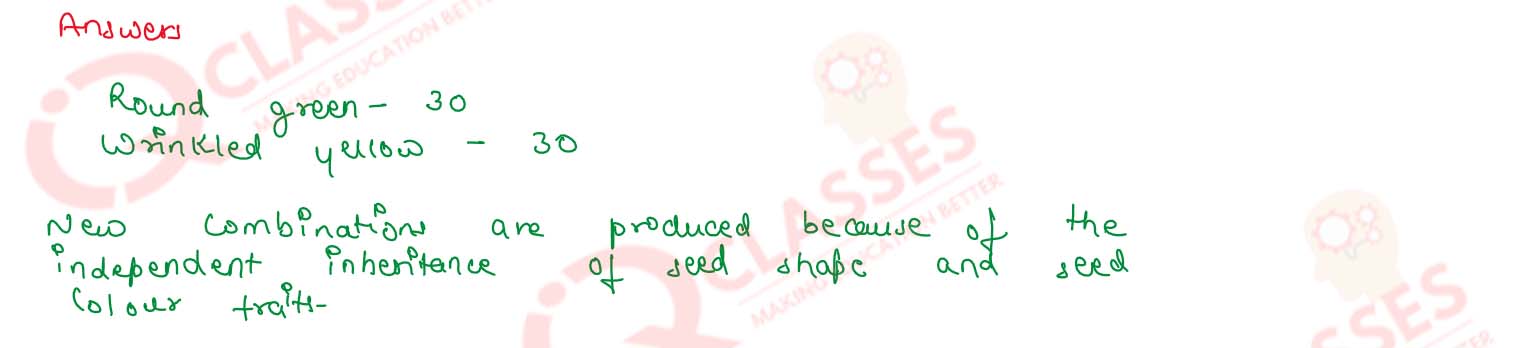
Two pea plants - one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total 160 seeds are produced in F2 generation? Explain with reason.
Solution
Question 11
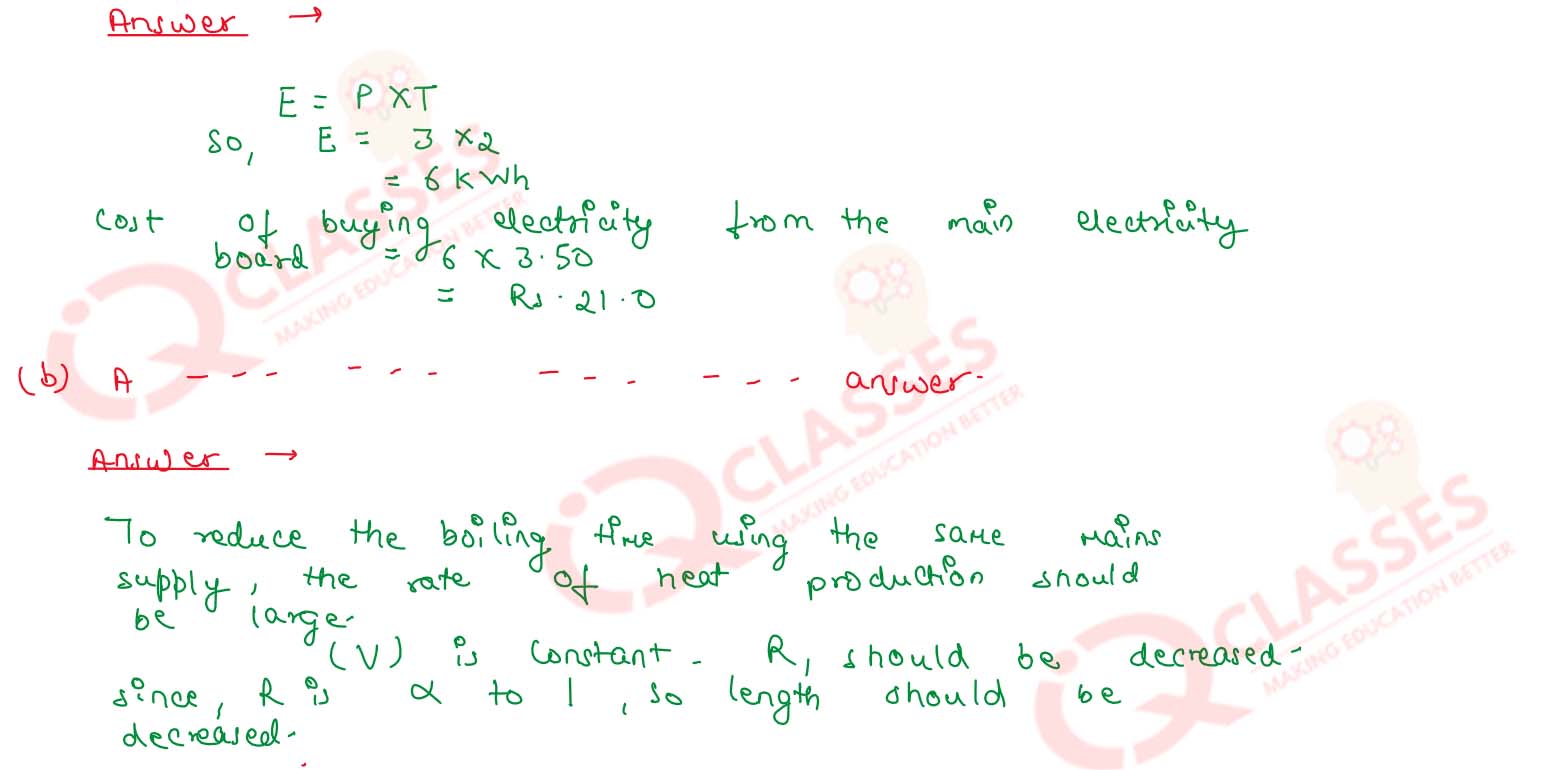
a. It would cost a man Rs. 3.50 to buy 1.0 kW h of electrical energy from the Main Electricity Board. His generator has a maximum power of 2.0 kW. The generator produces energy at this maximum power for 3 hours. Calculate how much it would cost to buy the same amount of energy from the Main Electricity Board.(1 Mark) b. A student boils water in an electric kettle for 20 minutes. Using the same mains supply he wants to reduce the boiling time of water. To do so should he increase or decrease the length of the heating element? Justify your answer.(2 Marks)
Solution
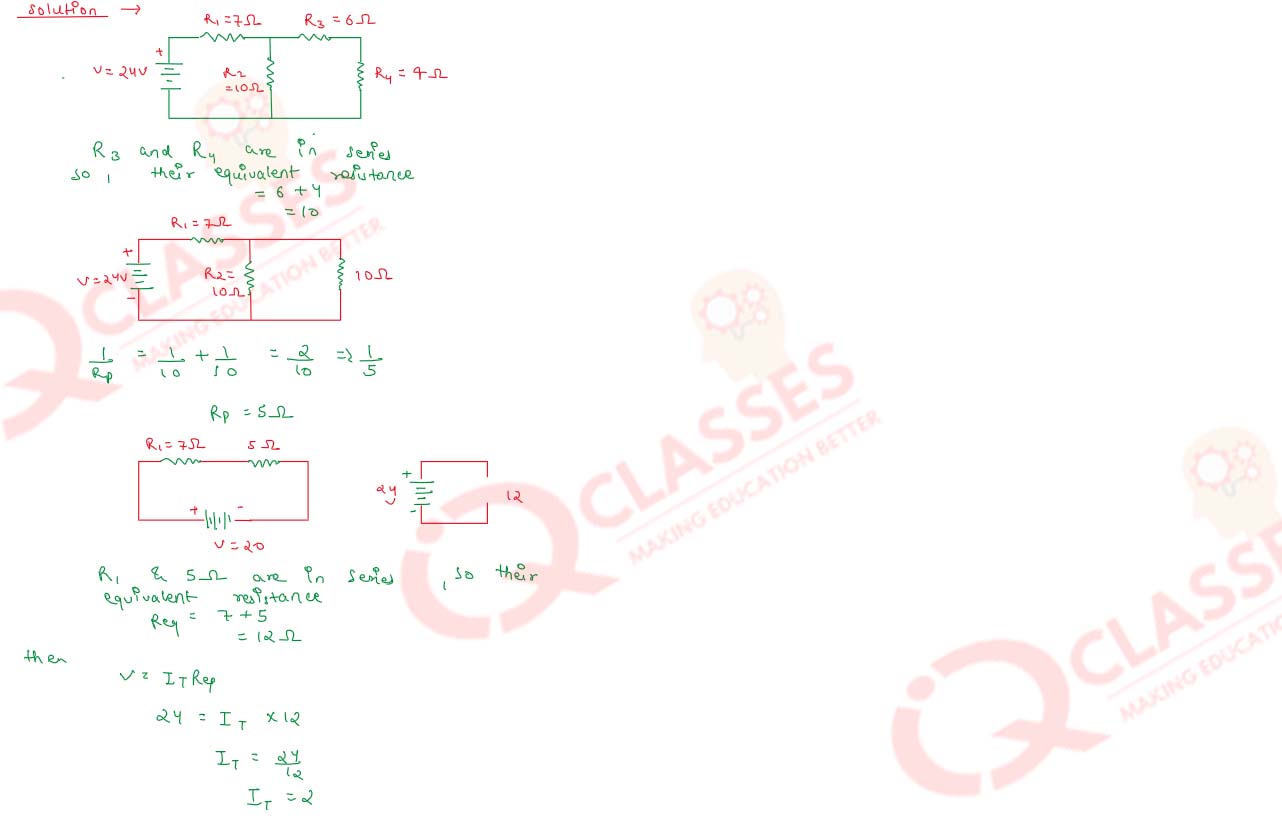
Question 12
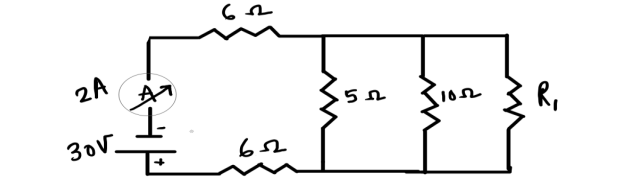
In the above circuit, if the current reading in the ammeter A is 2A, what would be the value of R1?
Solution

OR
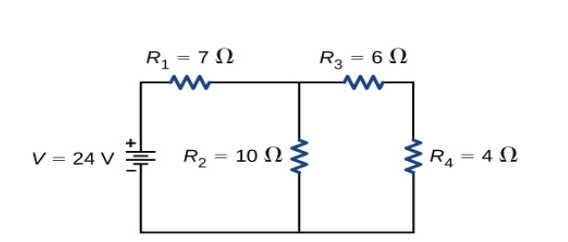
Calculate the total resistance of the circuit and find the total current in the circuit.
Solution
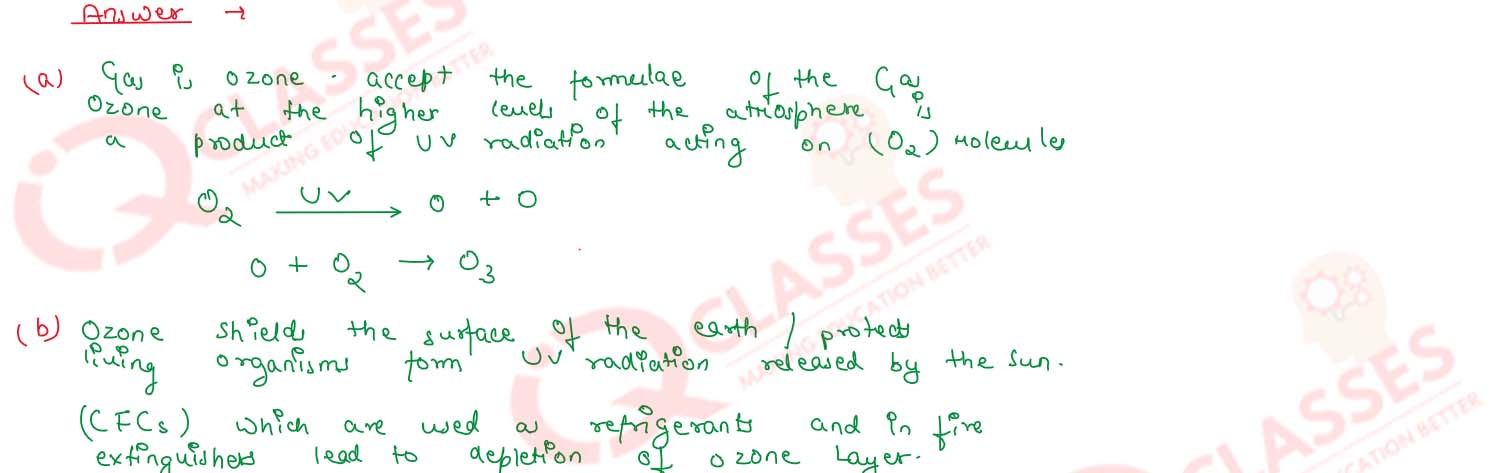
Question 13
Gas A, found in the upper layers of the atmosphere, is a deadly poison but is
essential for all living beings. The amount of this gas started declining sharply
in the 1980s.
a. Identify Gas A. How is it formed at higher levels of the atmosphere?
b. Why is it essential for all living beings? State the cause for the depletion
of this gas
Solution
Section C
Question 14
Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He
crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants
in F1 generation.
a. What will be set of genes present in the F1 generation?
b. Give reason why only tall plants are observed in F1 progeny.
c. When F1 plants were self - pollinated, a total of 800 plants were produced.
How many of these would be tall, medium height or short plants? Give the
genotype of F 2 generation.
Solution
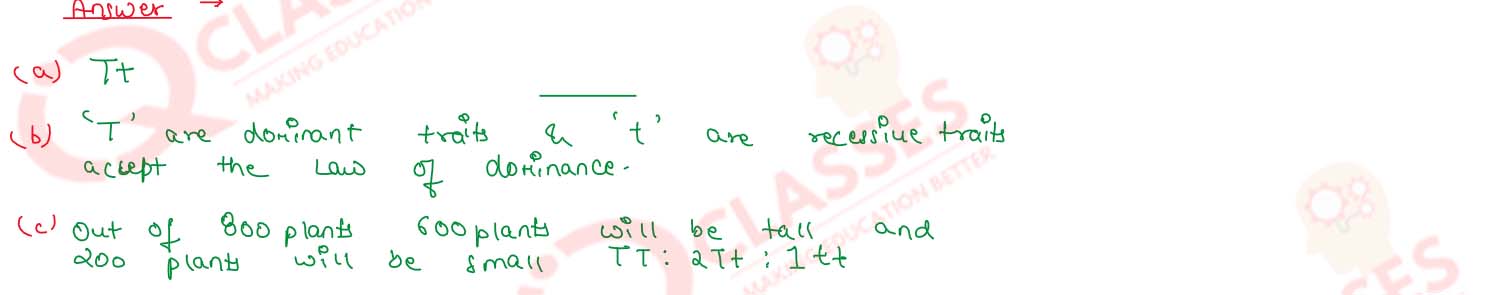
OR
When F1 plants were cross - pollinated with plants having tt genes, a total of 800 plants were produced. How many of these would be tall, medium height or short plants? Give the genotype of F 2 generation.
Solution

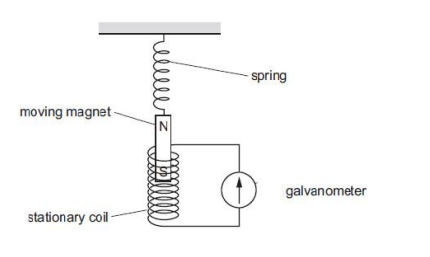
Question 15
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as
shown in the figure below.
A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the
stationary coil.
He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following
questions.
a. What is the principle which Ansari Sir is trying to demonstrate?
b. What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the
coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
c. Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State
two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the
galvanometer.

Solution

OR
Is there any difference in the observations in the galvanometer when the Magnet swings in and then out of the stationary coil? Justify your answer.
Solution
