Class 12 ISC Chemistry Specimen 2023
Maximum Marks: 80
Time Allowed: Three hours
(Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper.)
(They must NOT start writing during this time).
This paper is divided into four sections – A, B, C and D.
Answer all questions.
Section A consists of one question having sub-parts of one mark each.
Section B consists of ten questions of two marks each.
Section C consists of seven questions of three marks each, and
Section D consists of three questions of five marks each.
Internal choices have been provided in one question each in Section B,
Section C and Section D.
All working, including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as, and
adjacent to the rest of the answer.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
Balanced equations must be given wherever possible and diagrams where they
are helpful.
SECTION A
Question 1(A)
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word(s) from those given in the
brackets:
[two, Williamson’s synthesis, three, anisole, toluene, Friedel-Crafts alkylation,
iodoform, sec-1
, mol-1L sec-1
, Lewis base, acetone, Lewis acid, chloroform,
formaldehyde]
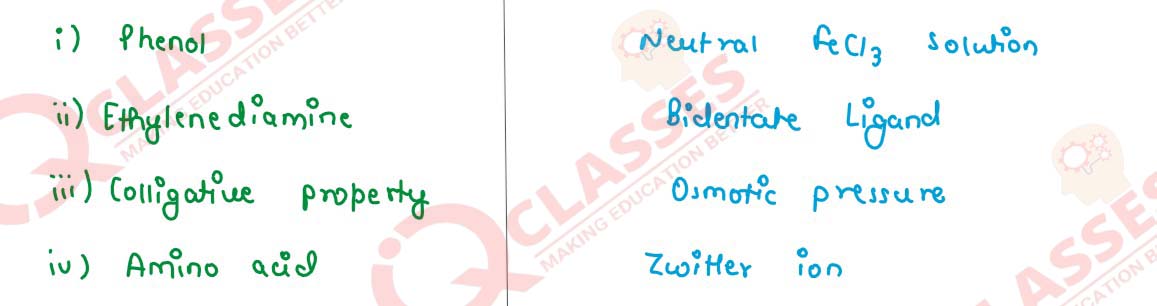
(i) Sodium phenoxide reacts with methyl chloride to give _______. The reaction is known as ________.
Solution
Anisole, Williamson’s synthesis
(ii) When the concentration of a reactant of first order reaction is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes ________ times. The unit of rate constant (k) for the first order reaction is ________.
Solution
3times,second-1
(iii) In coordination complexes, the central metal atom or ion behaves as ________ and the ligands behave as ________.
Solution
Lewis acid/Lewis bases
(iv) Calcium acetate on dry distillation gives ________ which gives _______ on heating with iodine and alkali.
Solution
Acetone/Iodoform
Select and write the correct alternative from the choices given below:
(i)
An alkyl isocyanide on complete reduction gives :
- Primary amine.
- Secondary amine.
- Tertiary amine.
- Carboxylic acid.
Solution
(b) Secondary amine
(ii)
For a spontaneous reaction E° cell and ∆G° will be respectively
- -ve and -ve
- -ve and +ve
- +ve and -ve
- +ve and +ve
Solution
(b)-ve and +ve
(iii)
Which of the following pairs of transition elements have exceptional
electronic configuration?
- Sc and Cu
- Fe and Ni
- Cr and Cu
- Mn and Zn
Solution
(c)Cr and Cu
(C)

Solution
(D)(i)
Assertion: Specific conductance of all electrolytes decreases on dilution.
Reason: On dilution, number of ions per unit volume decreases.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct
explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct
explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Solution

(D)(ii)
Assertion: Nitration of chlorobenzene leads to the formation of m-nitro
chlorobenzene
Reason: : Nitro (-NO2) group is a m-directing group
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct
explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct
explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Solution

SECTION B
Q2
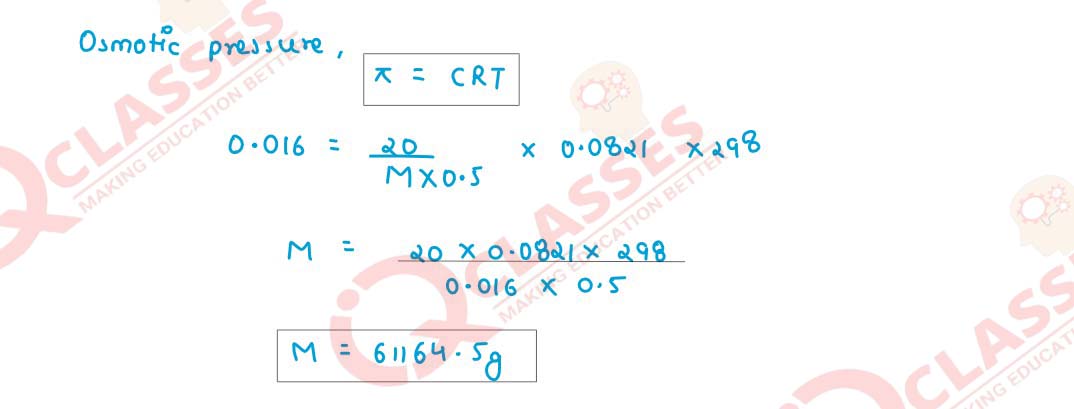
The osmotic pressure of 20g haemoglobin in 500ml of solution is 0·016atm at 25°C.
Calculate the molecular mass of haemoglobin.
Solution
Q3
Give reason for the following:
(i) Transition metals form large number of complex compounds.
(ii) Transition elements show variable oxidation states.
Solution

Q4
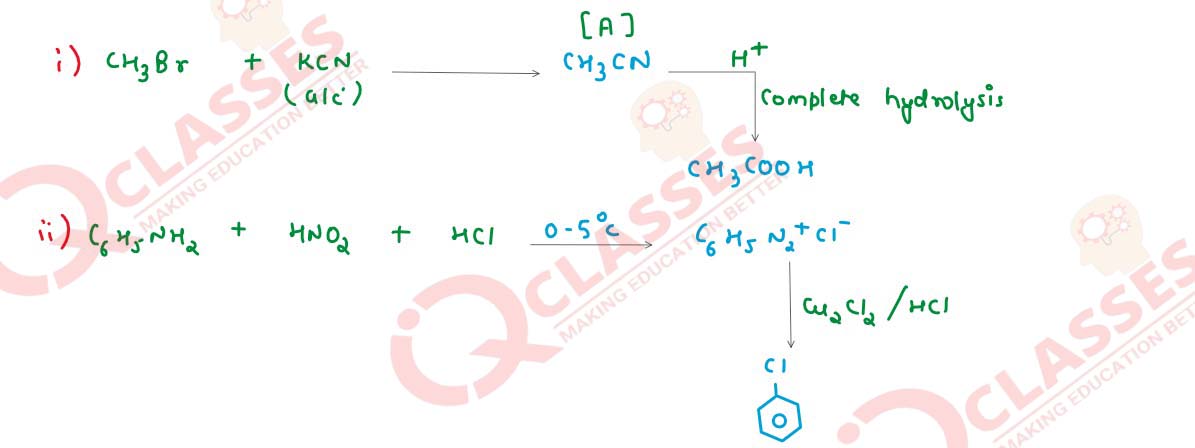
Identify compounds [A] and [B] in the following reactions.
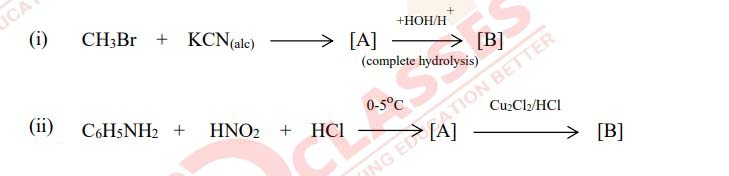
Solution
Q5
State reasons for the following:
(i) Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not soluble in water.
(ii) Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aromatic amines.
Solution

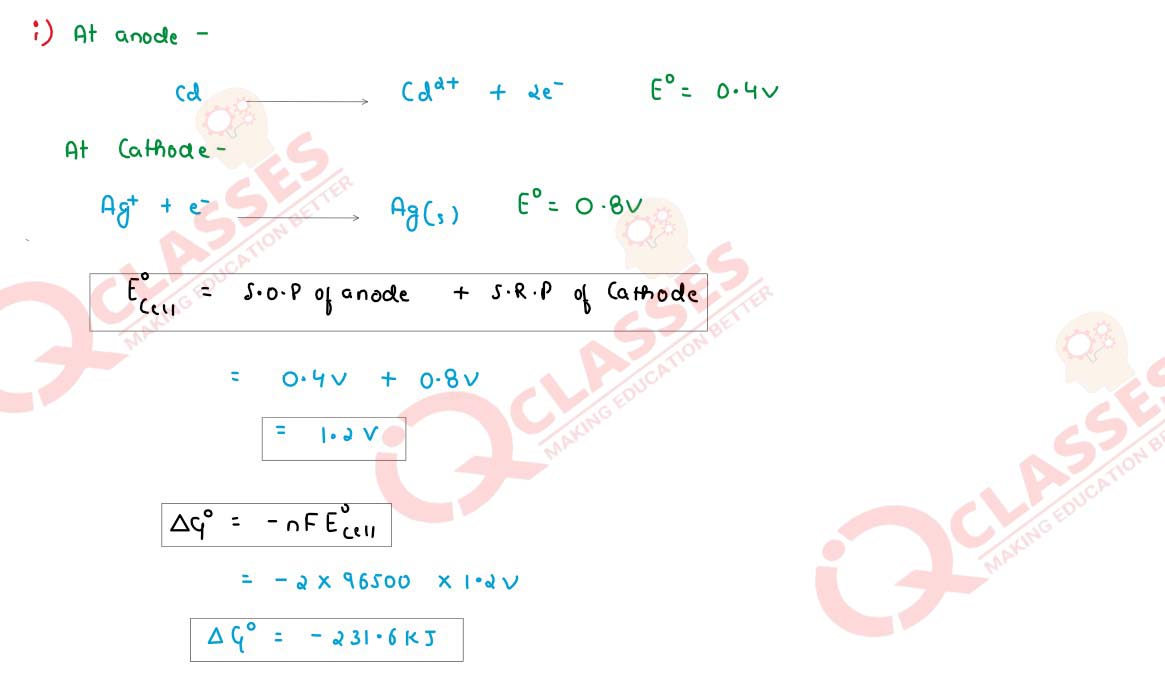
Q6
Calculate the standard free energy change (∆G°
) for the following chemical
reaction:
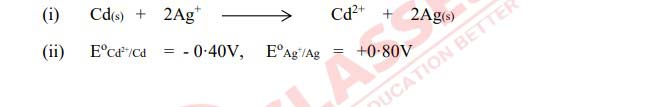
Solution
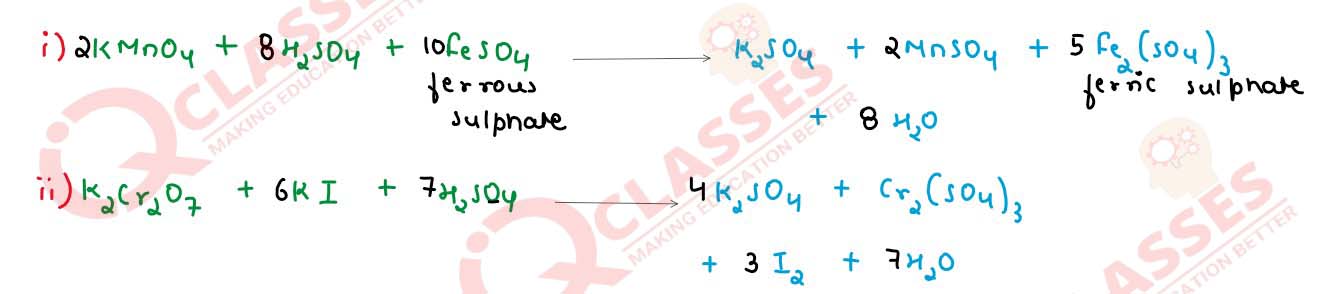
Q7
Complete and balance the following chemical equations
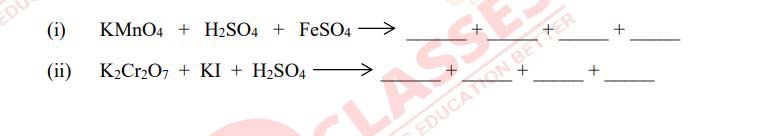
Solution
Q8
(i) How will the following be obtained? (Give chemical equation)
(a) Picric acid from phenol
(b) Ethanol from formaldehyde.
Solution
.jpg)
-1.jpg)
Q8(ii)
Write the chemical equations for the dehydration of ethanol with conc. H2SO4 at
140°C and 170°C
Solution
.jpg)
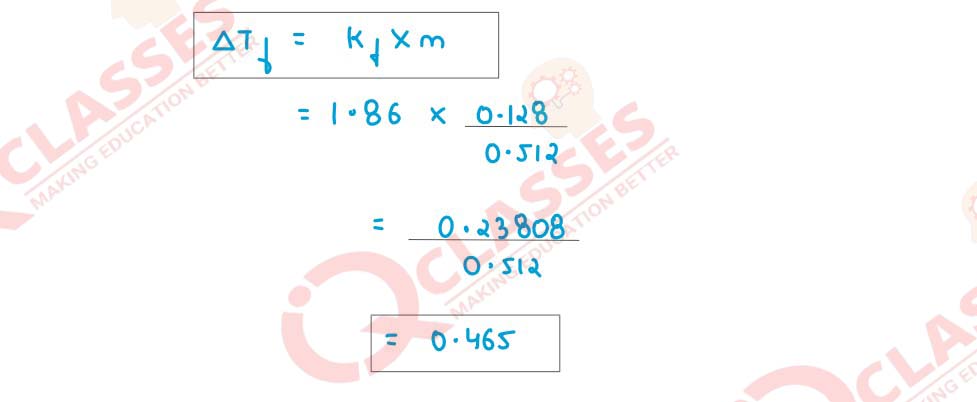
Q9
A solution of urea in water has boiling point 100·128°C. Calculate the freezing point of
the same solution. Molal constants for water are Kb = 0·512 K kg mol-1
and
Kf = 1·86 K kg mol-1
respectively.
Solution

Q10
Give one chemical test for each to distinguish between the following pair of compounds.
(i) Formaldehyde and acetic acid
(ii) Acetaldehyde and acetone
Solution


Q11
Why are Zn, Cd and Hg not regarded as transition elements?
Solution

SECTION C
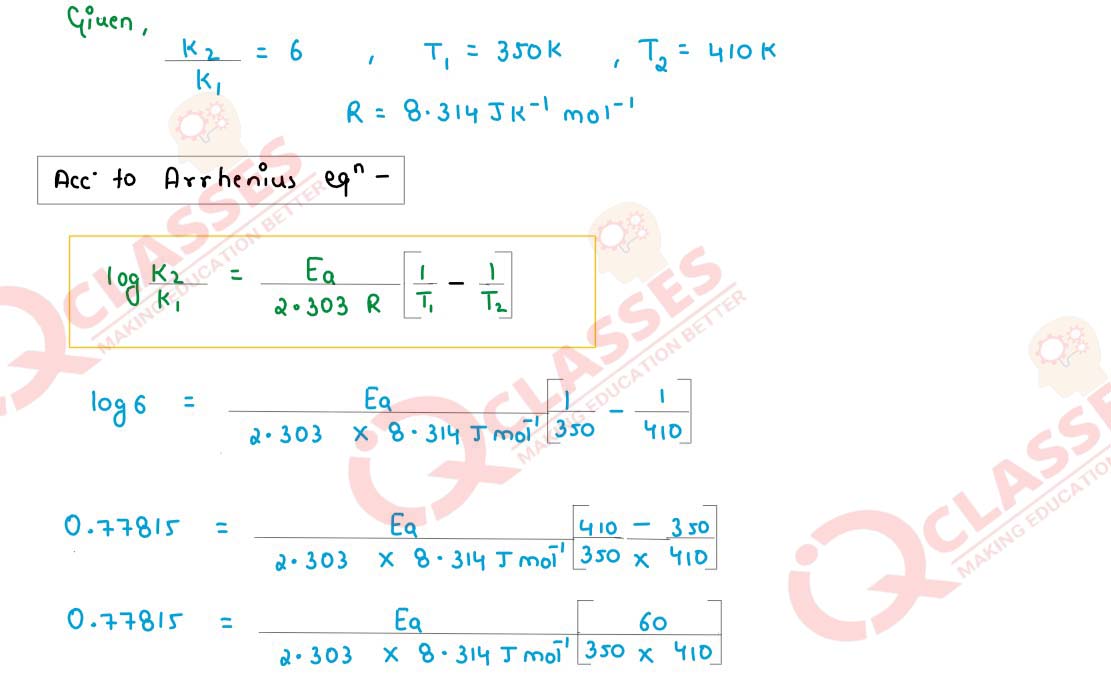
Q12
The rate constant for a first order reaction becomes six times when the temperature is
increased from 350 K to 410 K. Calculate activation energy (Ea) for the reaction.
Solution

Q13
An organic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aq.KCN produces compound ‘B’.
Compound ‘B’ on reduction with Na/C2H5OH gives compound ‘C’ with molecular
formula C2H7N. Compound ‘C’ reacts with NaNO2 and HCl to form compound ‘D’.
Compound ‘D’ on treatment with acetic acid in presence of conc. H2SO4 produces a sweet
smelling compound ‘E’.
(i) Identify the compounds ‘A’ to ‘E’.
(ii) Name the reaction for the formation of compound ‘E’ from compound ‘D’.
Solution
Q14
(i) Name the four bases present in DNA. Which one of these is not present in RNA?
(ii) Deficiency of which vitamin causes the following diseases.
(a) Scurvy
(b) Night blindness
Solution

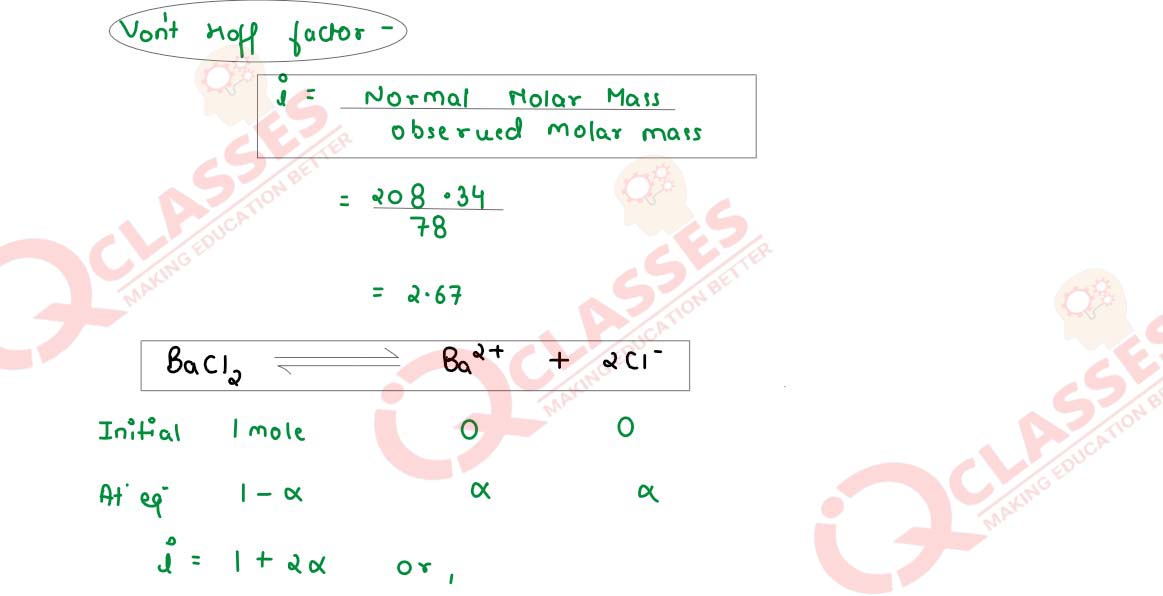
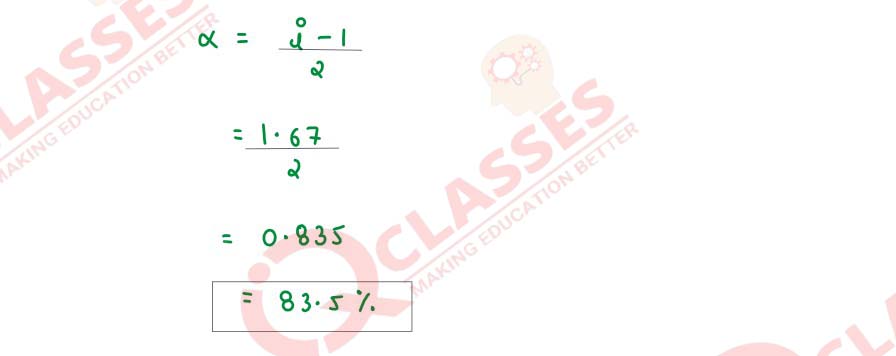
Q15
An aqueous solution containing 12·48g of barium chloride in 1000g of water boils at
373·0832K. Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of barium chloride.
Kb for H2O = 0·52K kg mol-1
, molecular mass of BaCl2 = 208·34 g mol-1
Solution

Q16
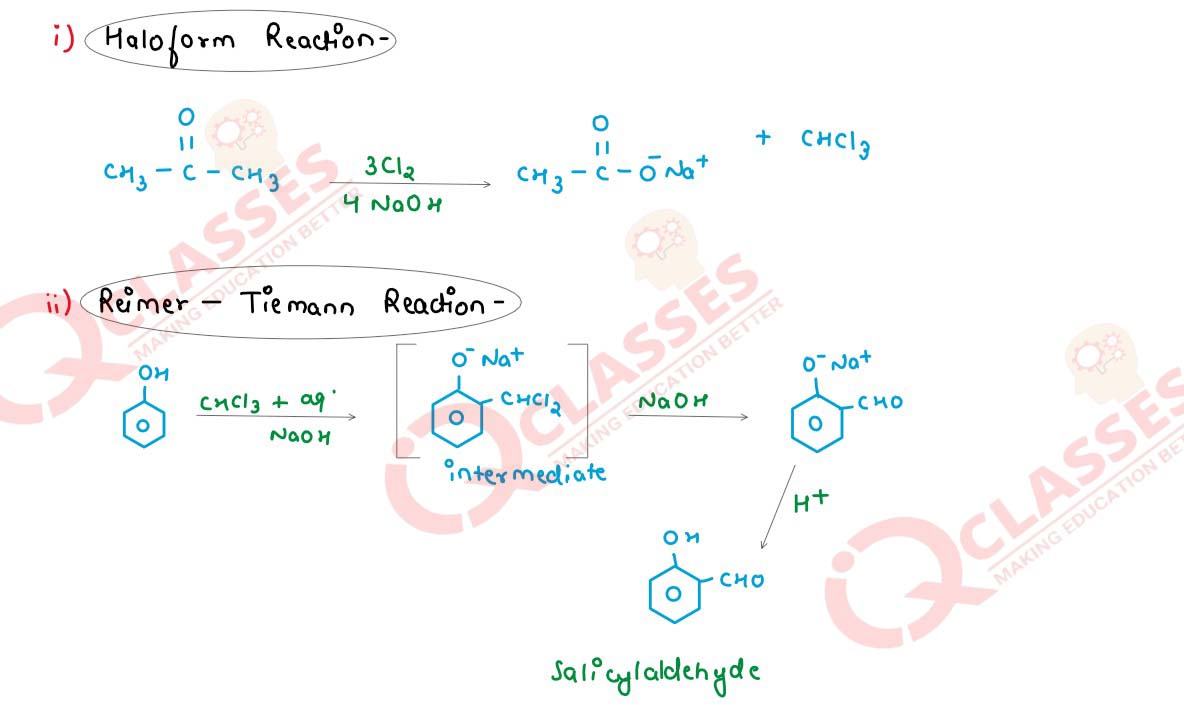
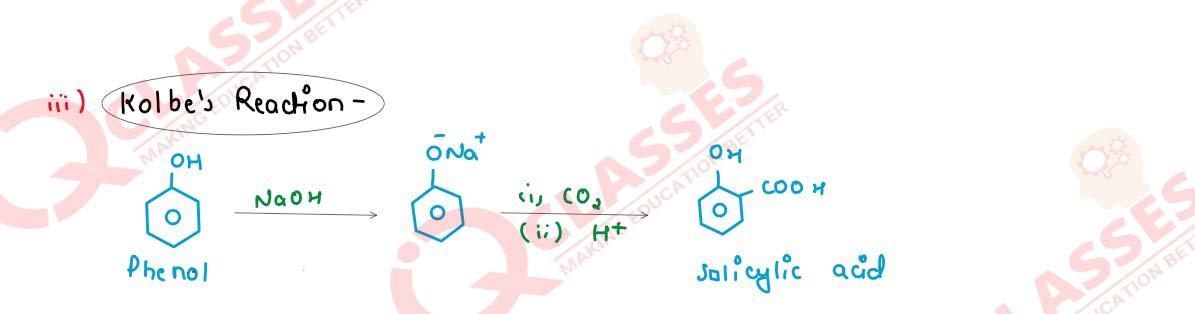
Write the chemical equation for the following named organic reactions.
(i) Haloform reaction
(ii) Reimer - Tiemann reaction
(iii) Kolbe - Schmidt reaction or Kolbe reaction
Solution
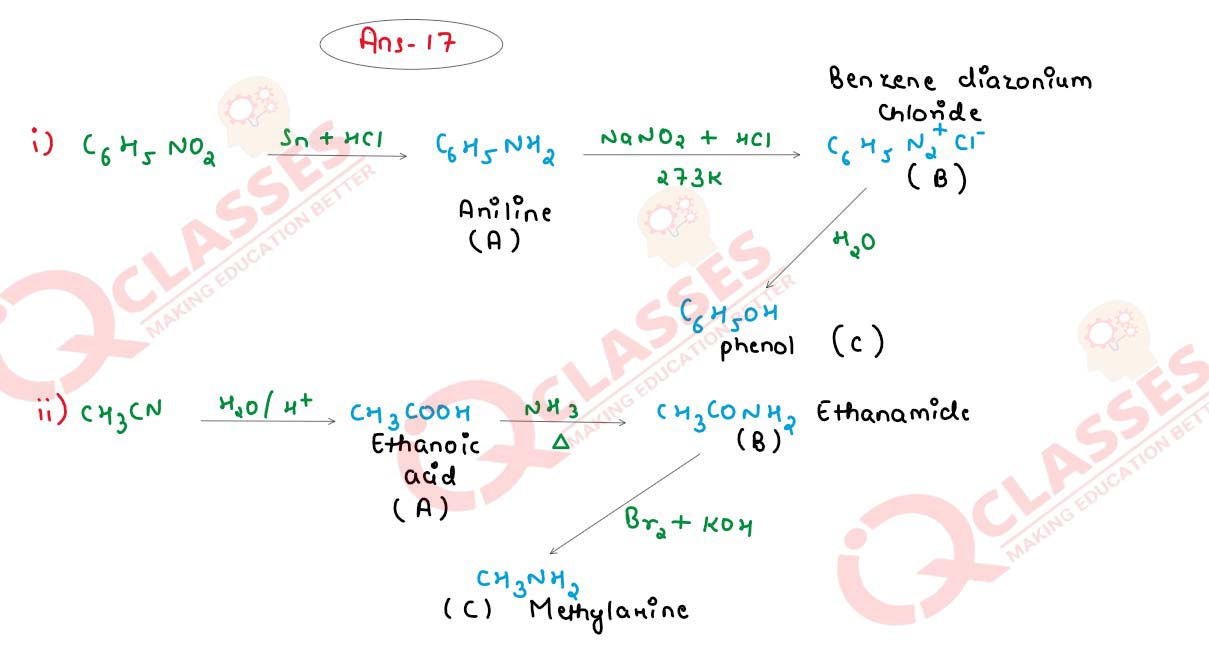
Q17
(i) Identify the compounds A, B and C in the following reactions:
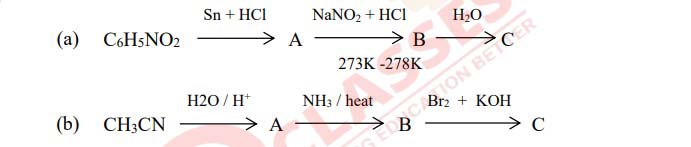
OR
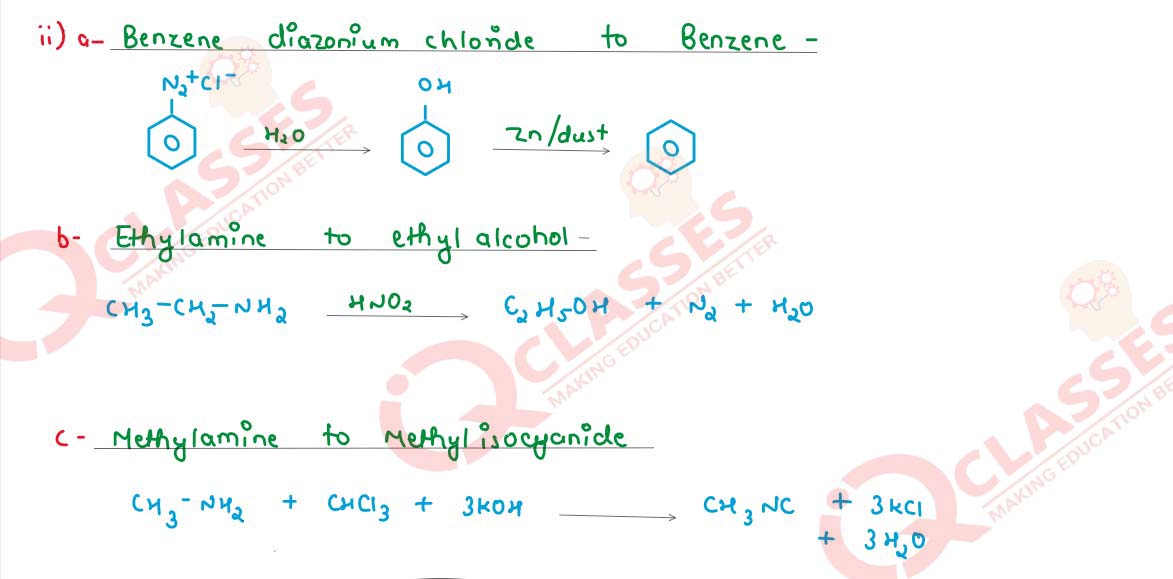
(ii) How will the following be converted? (Give chemical equations)
(a) Benzenediazonium chloride to Benzene
(b) Ethylamine to ethyl alcohol
(c) Methylamine to methyl isocyanide
Solution
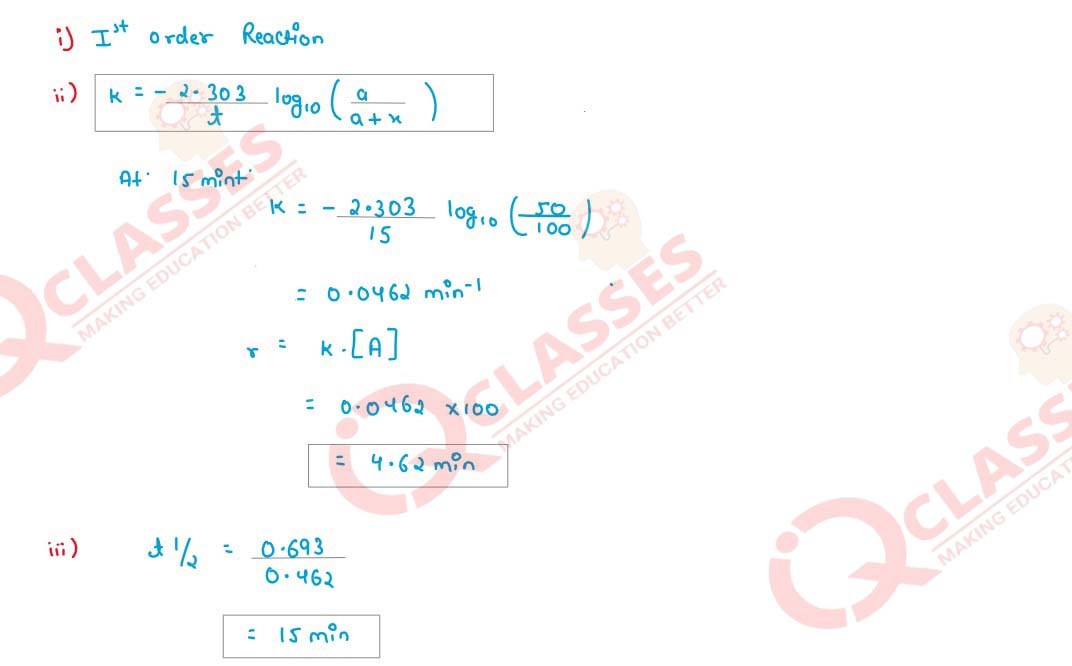
Q18
Suppose 50 bacteria are placed in a flask containing nutrients, so that they can multiply.
A study at 35° C gave the following results:
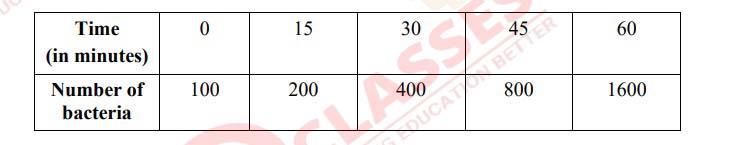
Answer the following questions:
(i) This multiplication of bacteria follows:
(a) Zero order reaction
(b) First order reaction
(c) Second order reaction
(d) Third order reaction
(ii) The rate constant for the reaction is:
(a) 0·0462 min-1
(b) 0·462 min-1
(c) 4·62 min-1
(d) 46·2 min-1
(iii) The half life period (t1/2) of the reaction is:
(a) 1500 minutes
(b) 150 minutes
(c) 15 minutes
(d) 1·5 minutes
Solution
SECTION D
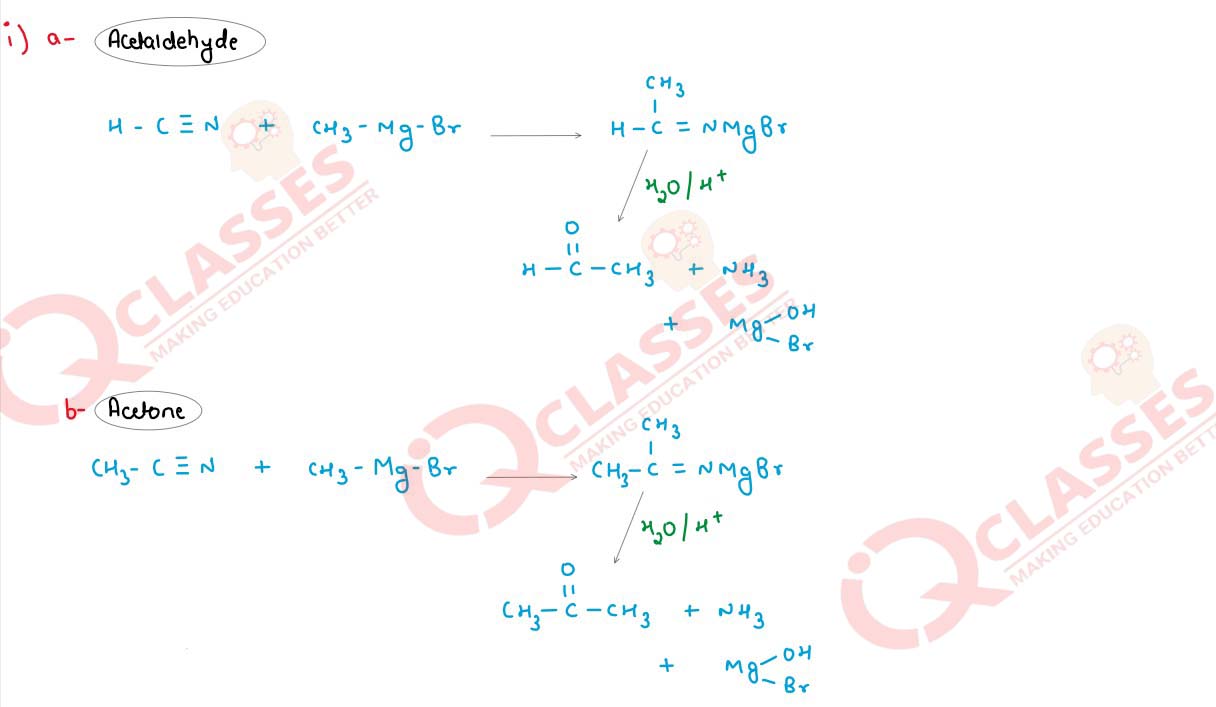
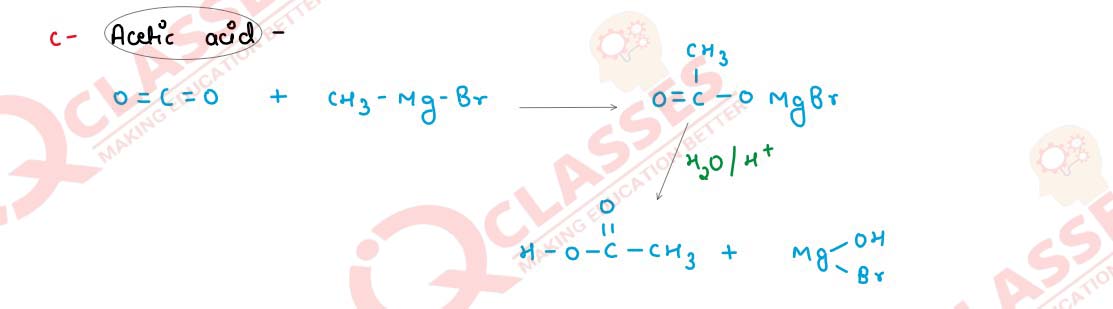
Q19(i)
Starting with methyl magnesium bromide, how will the following compounds be synthesised?
(a) Acetaldehyde
(b) Acetone
(c) Acetic acid
Solution
Q19(ii)
Explain the following:
(a) Chloroacetic acid is stronger acid than acetic acid.
(b) Formic acid reduces Tollen’s reagent but acetic acid does not.
Solution

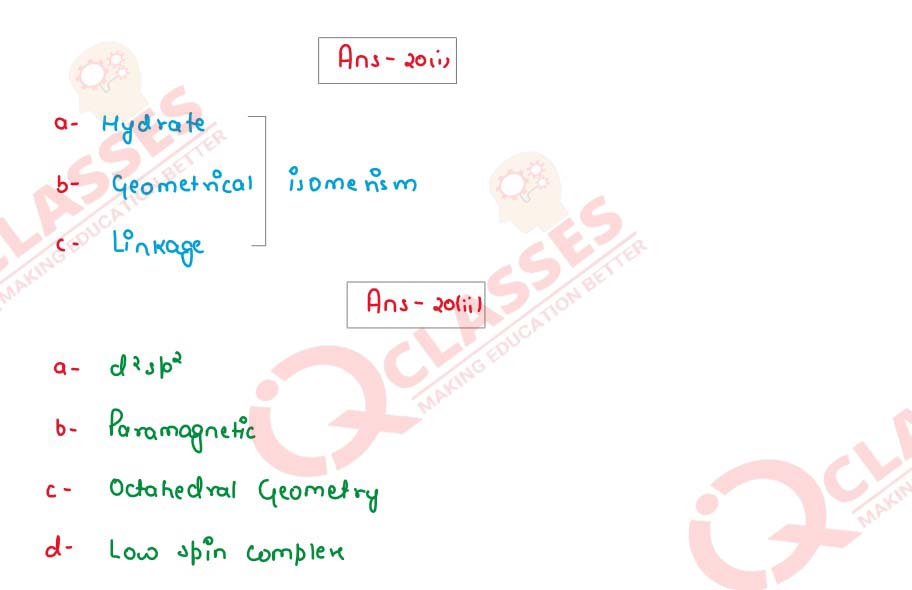
Q20
(i) Name the type of isomerism shown by the following pairs of coordination compounds.
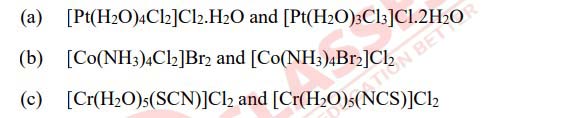
(ii) Consider the complex ion [Co(CN)6]3-
and answer the following questions:
(atomic number of Co = 27)
(a) Type of hybridisation of central metal atom
(b) Magnetic nature
(c) Geometry of the complex ion
(d) Low spin complex or high spin complex
Solution
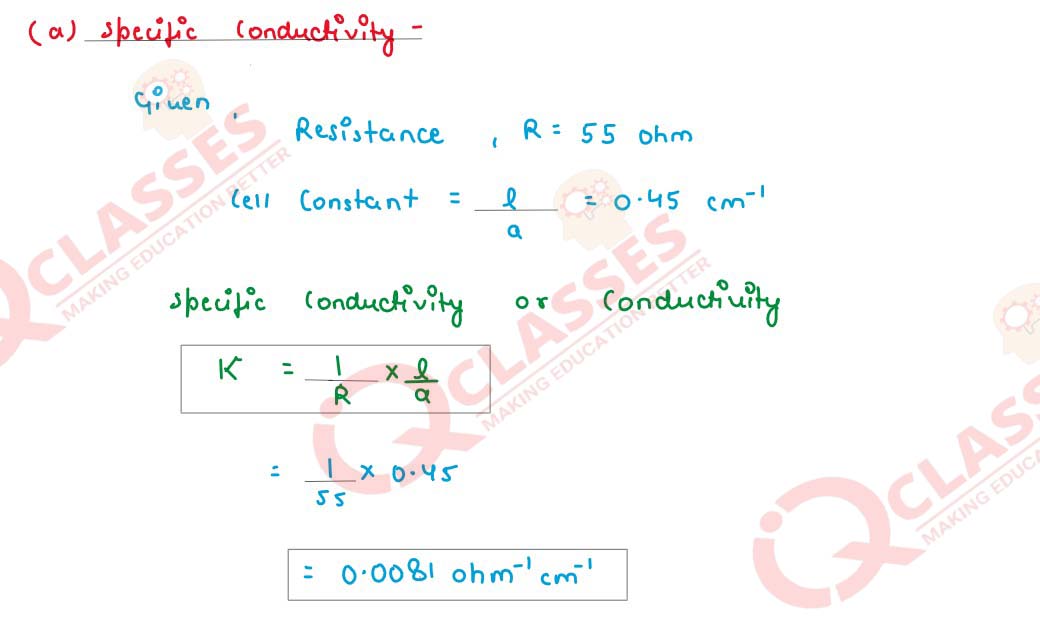
Q21
(i) A 0·06 molar CH3COOH solution offers a resistance of 55 ohms to a conductivity
cell at 25°C. If the cell constant is 0·45cm-1
and the molar conductance of
CH3COOH at infinite dilution is 398·5 ohm-1
cm2mol-1
. Calculate:
(a) Specific conductance
(b) Molar conductance
(c) Degree of dissociation
Calculate the number of coulombs of charge required to deposit 24·35g of
aluminium from a solution containing Al3+ ions.
(Atomic weight of Al = 27)
Solutions
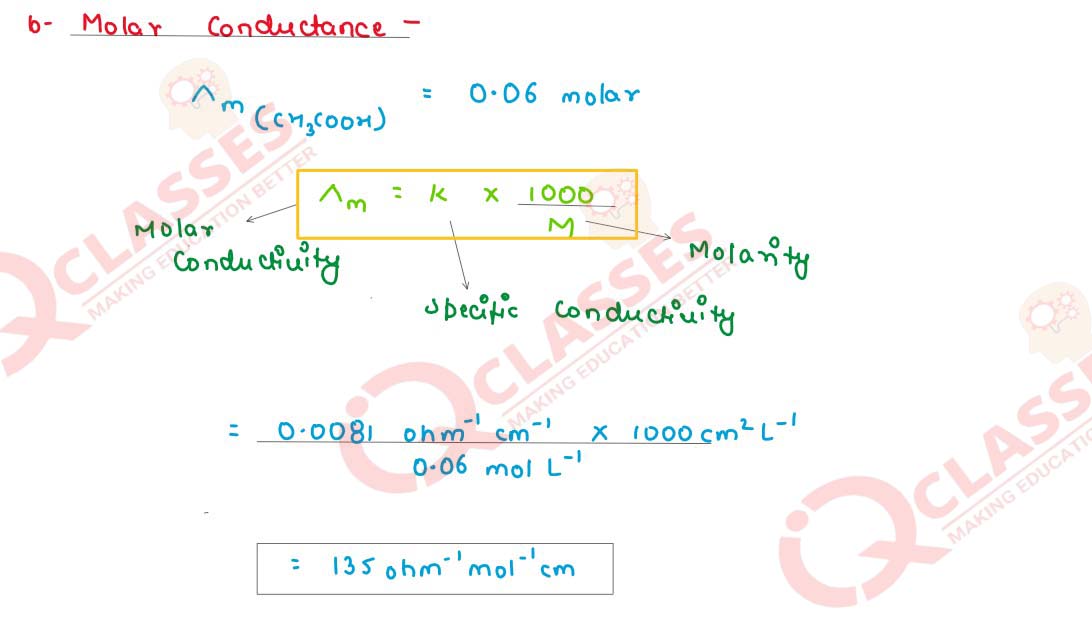

Q21(ii)
(i)Write the Nernst equation for the cell reaction given below and calculate the emf of the cell at
298K.
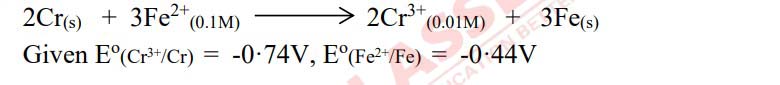
Calculate the molar conductance at infinite dilution (ꓥ∞m) for
NH4OH. Given that ꓥ∞m for Ba(OH)2, BaCl2 and
NH4Cl are 457 ohm-1cm2mol-1,240
ohm-1cm2mol-1and 129 ohm-1cm2mol-1
respectively.
Solutions
.jpg)
-1.jpg)
.jpg)

Add a comment