This paper is divided into four sections – A, B, C and D.
Answer all questions.
Section A consists of one question having sub-parts of one mark each.
Section B consists of seven questions of two marks each.
Section C consists of nine questions of three marks each, and
Section D consists of three questions of five marks each
.
Internal choices have been provided in two questions each in Section B,
Section C and Section D.
The intended marks for questions are given in brackets [ ].
All working, including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as and
adjacent to the rest of the answer.
Answers to sub parts of the same question must be given in one place only.
A list of useful physical constants is given at the end of this paper.
A simple scientific calculator without a programmable memory may be used for
calculations.
Section-A
Question
1
(A) Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word(s) from those given in the
brackets:
[ decreases, CN-ion, activation energy, catalyst, two, Fe2+ ion, carbon, lattice
energy, enzyme, five, double, halogen, triple, increases]
(i) In the Haber process, iron changes the _______ of reaction while
molybdenum increases the efficiency of the _________.
View
Solution
(ii) The number of ions that will be produced when potassium ferrocyanide,
K4[Fe(CN)6], dissolves in water is _________. This shows that
__________ is the ligand in the coordination compound
View
Solution
(iii) Haloalkenes undergo both nucleophilic and electrophilic reactions due to
the presence of __________bond and the __________ atom.
View
Solution
(iv) In case of alcohols, as the carbon chain length increases, the boiling
point ____________ and the solubility in water____________.
View
Solution
(B) Select and write the correct alternative from the choices given below:
(i) A potassium iodide (KI) solution containing starch turns blue on the
addition of chlorine. Which one of the following statements explain this?
(P) The reduction potential of Cl2 is more than that of I2.
(Q) The oxidation potential of Cl2 is more than that of I2.
(R) The product formed when Cl2 combines with starch is blue.
(S) The product formed when I2 combines with starch is blue.
(a) Only P and R
(b) Only Q and R
(c) Only Q and S
(d) Only P and S
View
Solution
(ii) Crystal field splitting energy (CFSE) for high spin d4
octahedral complex
is:
(a) -1·6 ∆o
(b) -1·2 ∆o
(c) -0·8 ∆o
(d) -0·6 ∆o
View
Solution
(iii) Acidified K2Cr2O7 solution turns green when
Na2SO3 is added to it. This
is due to formation of:
(a) CrO4
2-
(b) Cr2(SO3)3
(c) Cr2O3
(d) Cr2(SO4)3
View Solution
(iv) Which of the following product is formed when benzene diazonium
chloride is reduced by hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) in the presence of
cuprous ion as catalyst?
(a) Phenol
(b) Aniline
(c) Benzene
(d) Benzene cyanide
View
Solution
(v) Which of the following aqueous solution has lowest vapour pressure?
(a) 1M NaCl
(b) 1M K2SO4
(c) 1M Glucose
(d) 1M Sucrose
View Solution
(vi) Assertion: Adding water to two beakers ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing NaOH
and CH3COOH solutions respectively will increase the molar
conductance (ꓥm) of the solutions sharply in beaker ‘A’ and
slowly in beaker ‘B’.
Reason: Molar conductance (ꓥm) increases with a decrease in
concentration or upon dilution.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct
explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct
explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
View Solution
(vii) Assertion: Aniline is soluble in HCl while it is only slightly soluble
in
water.
Reason: Aniline cannot make hydrogen bonds with water but gets
protonated easily by acids.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct
explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct
explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
View
Solution
(C) Read the passage given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
During the winter season in a particular year, Kashmir experienced heavy
snowfall. It was an unexpected snowfall. Thousands of visitors were stranded
because it was dangerous to travel on snowy roads and vehicles could not move
as water froze in the car radiators. In such conditions officials decided to sprinkle
rock salt or CaCl2 on roads.
(i) Why was it decided to sprinkle rock salt or CaCl2 on the roads?
(ii) A mixture of ethylene glycol and water is used as coolant in car radiators.
Why?
(iii) How many grams of ethylene glycol (mol. wt. = 62 g mol-1
) should be
added to 10 kg of water so that the solution freezes at -10oC?
(Kf for water = 1ˑ86 K kg mol-1
)
View
Solution
Section-B
Question 2
(i) Arrange the following alcohols in order of decreasing activity towards Lucas’
reagent.
2-butanol, 2-methyl-2-propanol and 1-butanol
(ii) Ethanol has a higher boiling point than methoxymethane. Justify the statement.
View
Solution
Question
3
Give a reason for each of the following:
(i) The size of the trivalent cations in Lanthanoid series decreases steadily as the
atomic number increases.
(ii) The third ionization energy of manganese (Z = 25) is unexpectedly high.
View
Solution
Question
4
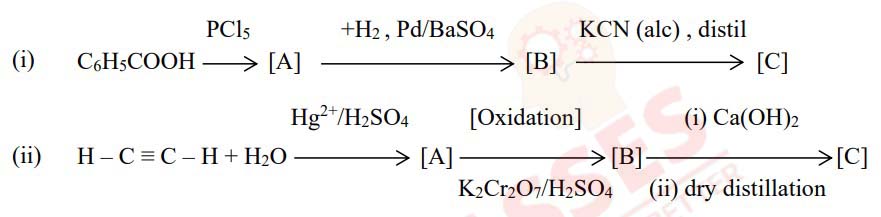
Give balanced chemical equations to convert the following:
(i) Benzene to biphenyl
(ii) Propene to propane -1-ol
View
Solution
Question
5
Account for the following:
(i) Salts of cuprous (Cu+
) ion are colourless whereas the salts of cupric (Cu2+) ion are
coloured.
(ii) Zinc is not regarded as a transition element. (at. no. of Zn = 30)
View
Solution
Question
6
Two compounds, D-2-chlorobutane and L-2-chlorobutane, are enantiomers of each
other.
Name one physical property that is:
(i) same for D-2-chlorobutane and L-2-chlorobutane.
(ii) different for D-2-chlorobutane and L-2-chlorobutane.
View
Solution
Question
7
(i) A rusted piece of iron undergoes electrochemical reactions. Write the chemical
reaction taking place at:
(a) the electrode that behaves as an anode.
(b) the electrode that behaves as a cathode.
(ii) Given that the standard reduction potential for Al3+/Al = -1ˑ66 V and
½ I2/I- = 0ˑ54V, what will be the standard potential of the cell made by using
Al3+
and I-
?
View
Solution
Question
8
(i) What happens when (write chemical reactions only)
(a) Diethyl ether is treated with phosphorous pentachloride.
(b) Ethyl alcohol is treated with methyl magnesium bromide.
OR
(ii) An organic compound [A] having molecular formula C6H6O gives a
characteristic colour with aqueous FeCl3 solution. [A] on treatment with CO2 and
NaOH at 400K under pressure gives [B] which on acidification gives compound
[C]. [C] reacts with acetyl chloride to give [D] which is a popular pain killer.
Identify the compounds [A], [B], [C] and [D].
View
Solution
Section-C
Question
9
John was making noodles in boiling water. When he added common salt (NaCl) to
boiling water, the water stopped boiling for a short while. If John had added 15ˑ0g of
NaCl to 250ˑ0g of water, calculate the boiling point of solution assuming that NaCl
dissociates completely in water. (Kb for water = 0ˑ512K kg mol-1
, molecular mass of
NaCl = 58ˑ44 g mol-1
)
View
Solution
Question
10
(i) Aromatic aldehydes do not give a reddish-brown precipitate on heating with
Fehling solution. Give a reason.
(ii) Why is benzaldehyde less reactive to electrophilic substitution reactions than
benzene?
View
Solution
Question
11
(i) Give a reason to explain why transition metals can act as a good catalyst.
(ii) Scandium (Z = 21) does not exhibit variable oxidation states and yet it is
regarded as transition element. Why?
View
Solution
Question
12
The data in the table given below was obtained in a series of experiments on the
rate of
the reaction between compounds [A] and [B] at a constant temperature:
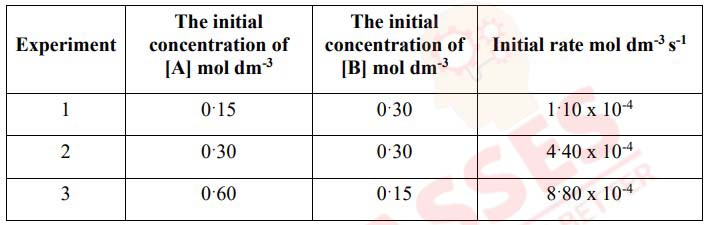
Show how this data can be used to deduce the rate expression for the reaction between
[A] and [B].
View
Solution
Question
13
Arrange the following compounds:
C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH,
(C2H5)3N, C2H5NH2.
(i) in the increasing order of their basic strength in water.
(ii) in a decreasing order of their basic strength in gas phase
View
Solution
Question
14
(i) What products are obtained when sucrose is subjected to acid hydrolysis?
(ii) Why are Vitamin B and Vitamin C essential for us?
(iii) On being heated, egg white becomes solid and opaque. Give a reason
View
Solution
Question
15
Water vapour and liquid water are in equilibrium in a container. At room
temperature,
the vapour pressure of water is 25 mm of Hg. The volume of water is V ml.
(i) What will be the vapour pressure of water if the volume of water is reduced to
V/4 ml without any change in temperature? Give a reason.
(ii) Will there be a change in vapour pressure if more water (at room temperature)
is added to the container? Give a reason.
View
Solution
Question
16
Question
17
(i) How will the following be obtained? (Give chemical equation)
(a) Picric acid from Phenol
(b) Ethyl acetate from ethanol
(c) Anisole from sodium phenoxide
OR
(ii) Explain the mechanism of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield the
corresponding alkene.
View
Solution
Section-D
Question
18
(i) The half-life period (t ½) for decay of radioactive 14C is 5730
years. An ancient
piece of wood has only 80% of the 14C found in a living tree. Calculate the age
of the piece of wood.
(ii) The rate of most of the reactions becomes double when the temperature is raised
from 298K to 308K. Calculate the activation energy. (R = 8ˑ314 J K-1 mol-1
)
View
Solution
Question
19
(i) Give a reason for each of the following:
(a) Formaldehyde does not undergo aldol condensation, but acetaldehyde
does.
(b) Chloroacetic acid is stronger acid than acetic acid.
(c) Both aldehydes and ketones undergo a number of nucleophilic addition
reactions.
(ii) An organic compound with the molecular formula C7H6O gets oxidised by
Tollens' reagent. It does not respond to Fehling test but can undergo the
Cannizzaro reaction.
Identify the compound. Show how you used the above information to identify
the compound.
View
Solution
Question
20
(i) When one mole of an isomer of the complex
[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 is treated with
AgNO3, it produces 1 mole of a white precipitate of AgCl.
Write the formula of this isomer of the complex and show how the metal-ligand
bonding differs in the isomers.
(ii) A coordination compound shows d2
sp3
hybridisation. Identify the nature of
ligand as weak or strong. What will be the geometry of the compound?
View
Solution
Question
21
(i)
(a) Calculate the value of Eo cell and ∆Go
that can be obtained from the
following cell under the standard conditions at 25oC
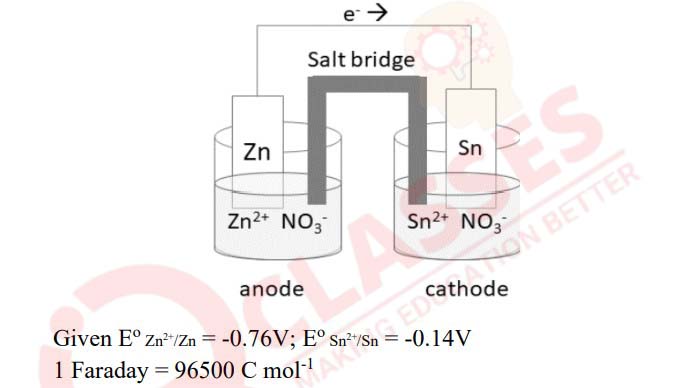
(b) How much electricity in Faraday is required for the complete reduction of
MnO4-
ions present in 500 ml of 0ˑ5 M solution to Mn2+?
OR
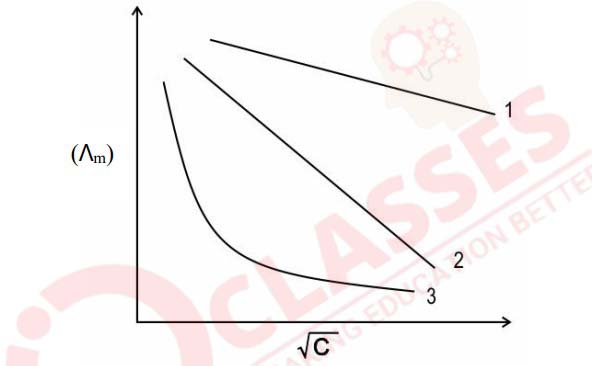
(a) The molar conductivity vs √C curve for Na2SO4, H2SO4,
and NH4OH are
shown below in random order
Identify the curve that corresponds to Na2SO4, H2SO4, and
NH4OH.
Justify your answer.
(b) The molar conductivity (ꓥm) of a dilute solution of methanoic acid is
34ˑ1 S cm2
/mol. Calculate its degree of dissociation.
(Given λ0
(H+
) = 349ˑ6 S cm2
/mol and λ
0
(HCOO-
) = 54ˑ6 S cm2
/mol)
View
Solution