Class 12 ISC Economics Specimen 2023
Maximum Marks: 80
Time Allowed: Three hours
(Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper.)
(They must NOT start writing during this time).
The Question Paper contains three sections.
Section A is compulsory for all candidates.
Candidates have to attempt all questions from either Section B or Section C.
There are internal choices provided in each section.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in the brackets [].
All calculations should be shown clearly.
All working, including rough work, should be done on the same page as, and
adjacent to, the rest of the answer.
Section-A
(i)
Indifference curve is convex to the origin due to:
(a) Axiom of transitivity.
(b) Law of DMU.
(c) Law of DMRS.
(d) Axiom of non-satiety.
Solution
Law of DMRS.
(ii)
When supply of a commodity increases by 24% following the rise in price by
8%, supply curve will be:
(a) positively sloped with positive intercept.
(b) positively sloped with negative intercept.
(c) horizontal.
(d) parallel to price axis.
Solution
positively sloped with positive intercept.
(iii)
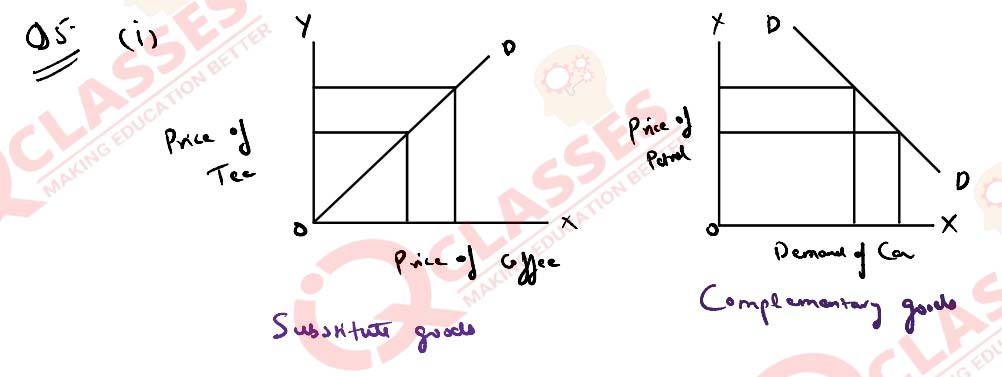
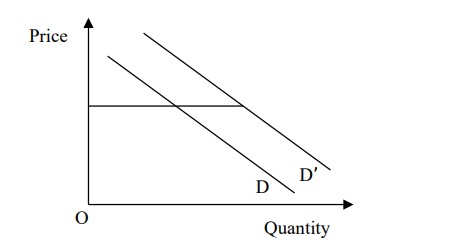 In the figure given above, D is demand curve for normal good. It shifts to D’
which is a case of:
In the figure given above, D is demand curve for normal good. It shifts to D’
which is a case of:
(a) extension of demand due to change in price level.
(b) increase in demand due to rice in expected future price of the commodity.
(c) contraction of demand due to increase in price of the substitute.
(d) increase in demand due to rise in price of the complimentary good.
Solution
increase in demand due to rice in expected future price of the commodity.
(iv)
A demand curve parallel to X axis signifies:
(a) perfectly elastic.
(b) perfectly inelastic.
(c) elastic.
(d) inelastic.
Solution
perfectly elastic.
(v)
Which one of the following is a pair of direct taxes?
(a) Excise duty and Wealth Tax
(b) Service Tax and Income Tax
(c) Excise Duty and Service Tax
(d) Wealth Tax and Income Tax
Solution
Wealth Tax and Income Tax
(vi)
Which one of the following is included in the calculation of National Income?
(a) Transfer Earnings
(b) Sale proceeds of Shares and Bonds
(c) Black Money
(d) None of the Above
Solution
None of the Above
(vii)
Indian Railways charges lower freight rates for transporting essential products
like food, coal etc., as compared to freight charges for other products like T.V.,
Air coolers etc. This is an example of:
(a) Price ceiling.
(b) Price discrimination.
(c) Price control.
(d) Floor pricing.
Solution
Price discrimination.
(viii)
A firm produces its profit maximising level of output only when:
(a) MR = AR
(b) MR > MC
(c) AR < MR
(d) MC=MR
Solution
MR > MC
(ix)
Complete the following table:
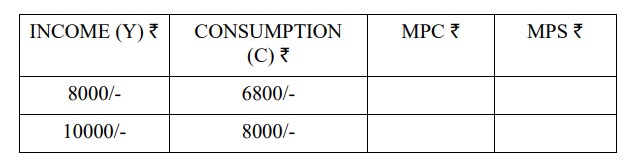
Solution
.jpg)
(x) What is investment multiplier?
Solution
.jpg)
(xi) Mention any two sources of receipts from tax revenue of government budget.
Solution
.jpg)
(xii)
State whether the following statement is True or False. Give one reason for your
answer.
Undistributed profits are not a part of domestic factor income
Solution
.jpg)
(xiii) An oligopolist has an indeterminate demand curve. What is the reason for this feature of Oligopoly?
Solution
.jpg)
(xiv) Why is AR=MR=P a horizontal straight line under perfect competition in the short run?
Solution
.jpg)
(xv) What does 0< c < 1 signify?
Solution
.jpg)
Section-B
(i) The following headline appeared in the newspaper –
“Crop damage in Himachal Pradesh sent tomato prices soaring in Delhi.”
Analyse the statement with reference to the relationship between price and
supply.
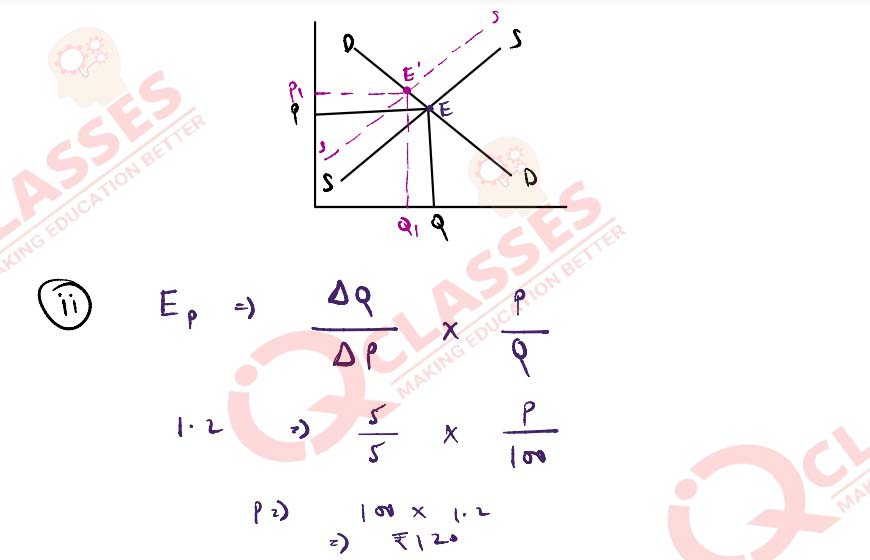
(ii) The initial demand for a commodity was 100 units. With a rise in price by ₹ 5,
the demand for the quantity decreases by 5 units. The elasticity of demand is 1‧2.
Calculate the price before the change in demand.
Solution

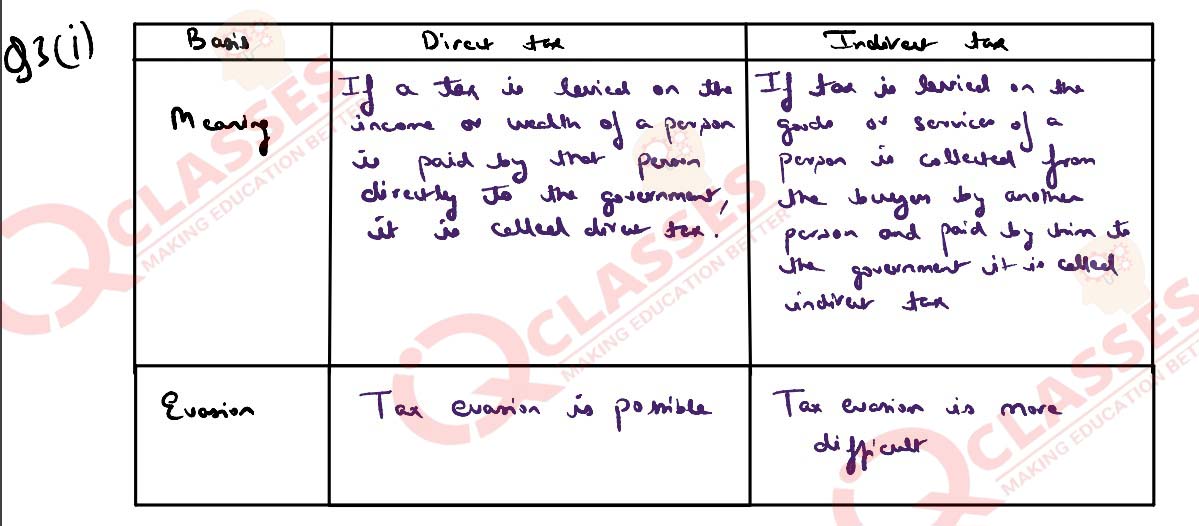
(i) State any two differences between a direct tax and an indirect tax.
(ii) Refunding and Debt conversion are two methods of Debt redemption. Briefly
explain these two methods of debt redemption.
Solution

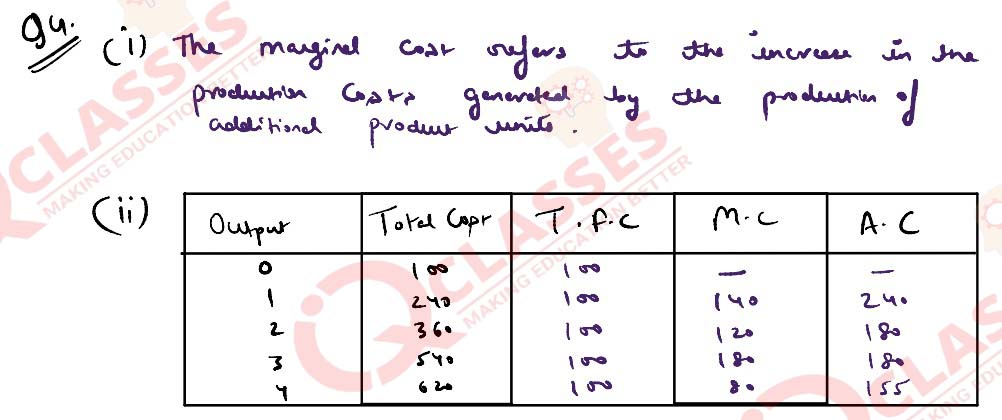
(i) What is marginal cost of a firm?
(ii) Calculate Total fixed cost, Marginal cost and Average Cost from the following
data:
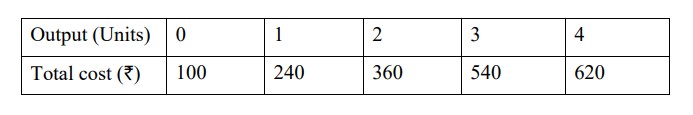
Solution
(i) Explain any two features of Perfect Competition.
(ii) What is meant by intense competition under Oligopoly?
OR
(i) Explain the equilibrium of a firm when it enjoys supernormal profit in the short
run under perfect competition.
Solution



(i) In the short run under perfect competition, a firm should produce if and only if
P or AR ≥ AVC. Justify.
(ii) Why do firms earn normal profit in the long run under Perfect competition?
Solution


(i) What is meant by inflation? Mention the types of Inflation.
(ii) Explain the role of ‘repo rate’ in controlling inflation.
Solution


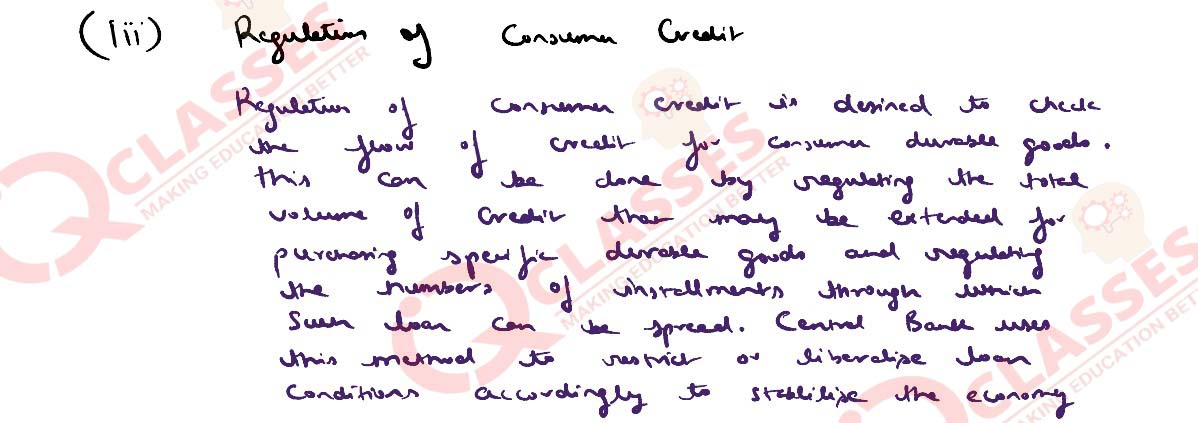
(i) Illustrate the process of credit creation by Commercial banks with the help of a
numerical example.
OR
(ii) How does Central bank control credit by using Qualitative methods?
Solution






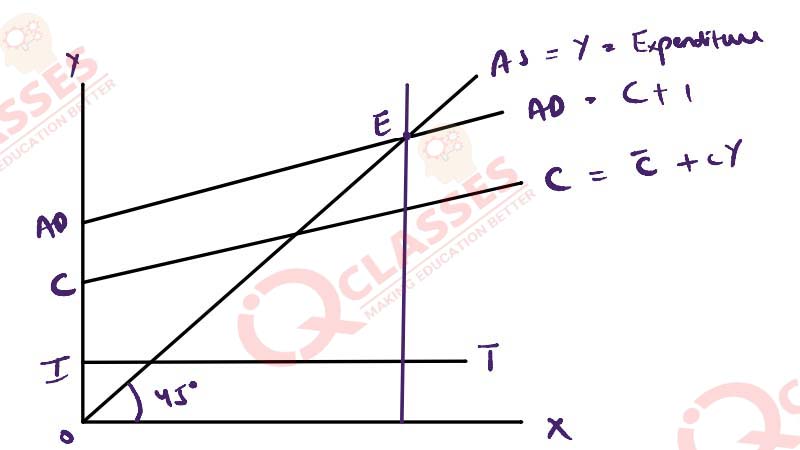
Explain the equilibrium level of income and output determination by Aggregate demand and Aggregate supply approach with the help of a diagram
Solution



Section-C
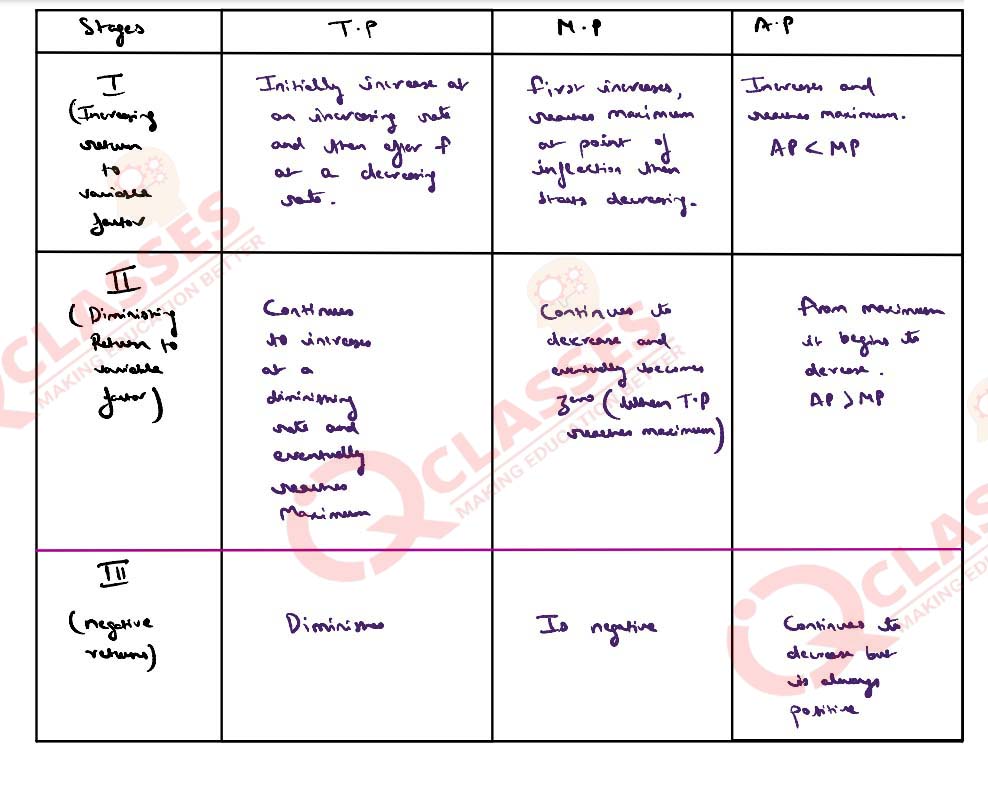
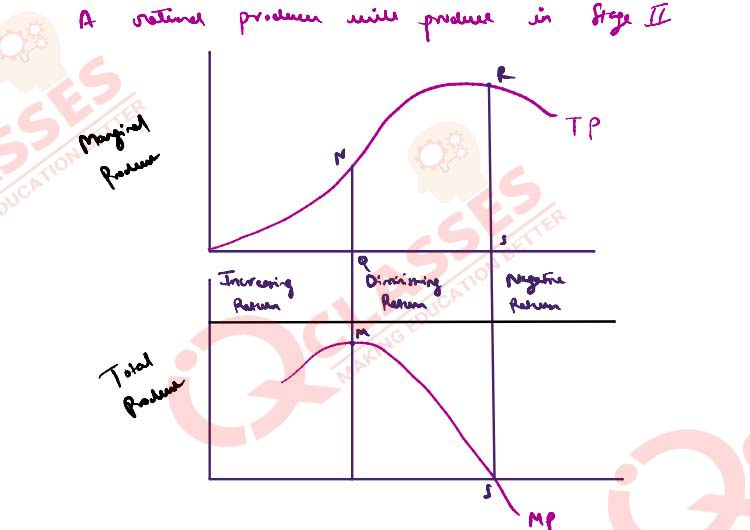
(i) State the law of variable proportions. Explain its three stages by using a diagram.
(ii) Briefly explain why the producer is comfortable in the second stage of
production.
Solution


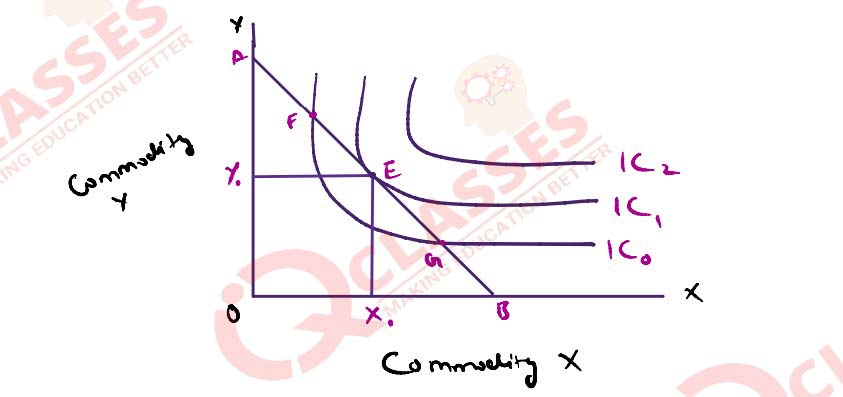
(i) Differentiate between total utility and marginal utility.
(ii) Explain the Consumer’s equilibrium through Indifference curve approach with
the help of a diagram
OR
(i) Differentiate between increase in demand and contraction of demand with the
help of diagrams.
(ii) Explain four properties of Indifference curves.
Solution



(i) What is the difference between GDPmp and NNPfc?
(ii) Calculate Domestic Income and National Income from the following
information:
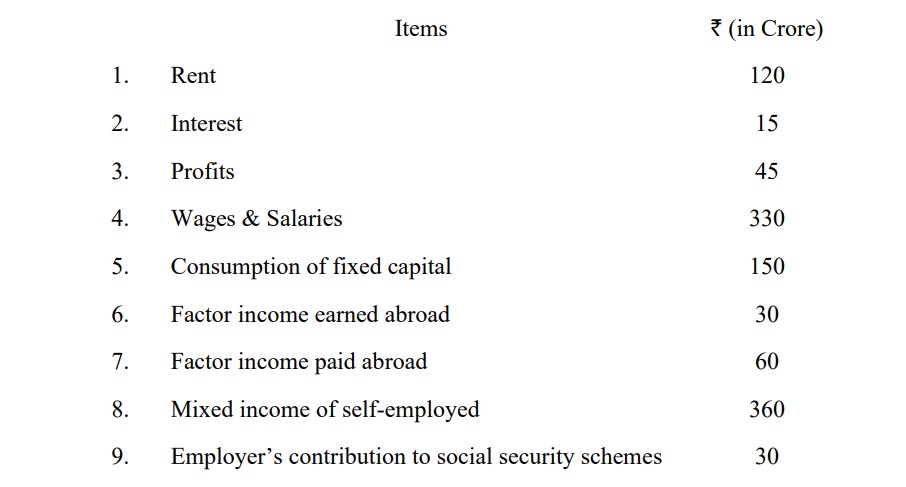
OR
(i) Differentiate between personal income and national income.
(ii) Calculate the GDPmp and NDPfc from the following data:

Solution






Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow
India is predominantly an agriculture based country. It is the second largest producer of
wheat in the world and wheat export is also an important component in its international
business transactions. Recently, Indian Government put a ban on the export of wheat to
other countries to control inflation in the country. This decision of Indian Government
may decrease the flow of foreign exchange in credit side of the balance of payments of
our country in comparison to the debit side of it. This may affect the Balance of Payment
as India has been following flexible exchange rate system, to some extent, since
1991-92.
(i) What is meant by balance of payments?
(ii) State any two causes of adverse balance of payments.
(iii) In the context of international business relations, what does flexible exchange
rate system mean?
(iv) What is meant by net exports?
(v) What economic variables are measured along x-axis and y-axis for the
determination of foreign exchange rate?
Solution



Add a comment