Class 12 ISC Physics Specimen 2024
Maximum Marks: 70
Time Allowed: Three hours
(Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper.
They must NOT start writing during this time).
This paper is divided into four sections – A, B, C and D.
Answer all questions.
Section A consists of one question having sub-parts of one mark each.
Section B consists of seven questions of two marks each.
Section C consists of nine questions of three marks each, and
Section D consists of three questions of five marks each
.
Internal choices have been provided in two questions each in Section B,
Section C and Section D.
The intended marks for questions are given in brackets [ ].
All working, including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as and
adjacent to the rest of the answer.
Answers to sub parts of the same question must be given in one place only.
A list of useful physical constants is given at the end of this paper.
A simple scientific calculator without a programmable memory may be used for
calculations.
Section-A
Question
1
(A) In questions (i) to (vii) below, choose the correct alternative (a), (b), (c) or (d) for
each of the questions given below:
(i) Two bulbs of power ratings 100 W and 40 W, designed to operate on the
same voltage, are connected in parallel to a battery source as shown in
Figure 1 below. Currents flowing across points 1,2 and 3 are I1, I2 and I3
respectively.
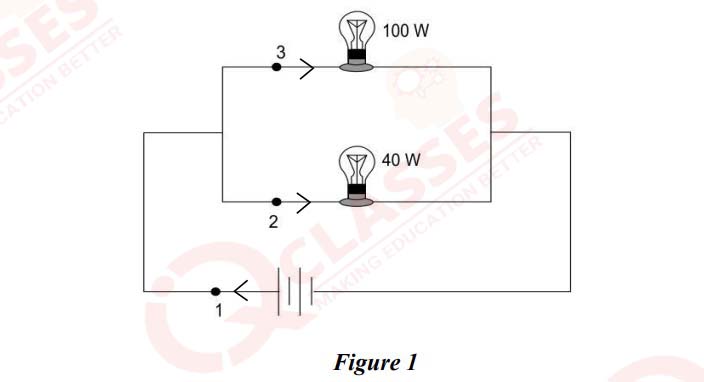
Choose the correct option.
(a) I1 > I2 > I3
(b) I1> I2
< I3 (c) I1 < I2=I3 (d) I1> I2 = I3
A circular coil having N turns of radius R carries a current I and produces a
magnetic field T at its centre O.
If this coil is opened and rewound such that the radius of the newly formed
coil is 2R, and the same current I passed through it, the magnetic field at the
centre O will be:
(a) 2T
(b) T
(c) T/2
(d) T/4
(iii) Assertion: Magnetic lines of force do not intersect each other.
Reason: At the point of intersection, the magnetic field will have two
directions.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct
explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct
explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true and Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false and Reason is true.
(iv) The focal length of a double convex lens is equal to the radius of curvature
of either surface. The refractive index of its material is:
(a) 3/2
(b) 1
(c) 4/3
(d) Zero
(v) Which one of the following statements is correct in case of
Fraunhofer’s single slit diffraction experiment?
(a) All bright fringes are of same intensity.
(b) Central bright fringe is the brightest.
(c) Central fringe is a dark fringe.
(d) Angular width of central fringe increases with an increase in
wavelength of the incident monochromatic light.
(vi) The de Broglie wavelength of a moving particle varies:
(a) directly with its velocity.
(b) directly with its momentum.
(c) directly with its kinetic energy.
(d) inversely with its linear momentum.
(vii) Which one of the following statements is correct with reference to
Semiconductor Physics?
(a) N type semiconductor has a majority of holes.
(b) To convert a pure semiconductor into a P type semiconductor,
Phosphorous is used as a dopant.
(c) In energy band diagram of a metal, forbidden band is absent.
(d) Resistance of a semiconductor increases on increasing its temperature.
(B) Answer the following questions briefly:
(i) State any one advantage of a full wave rectifier over that of a half wave
rectifier.
(ii) State the condition for a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
(iii) Name the rule used to determine the direction of induced current in the case
of a straight conductor moving in a magnetic field.
(iv) With what type of source of light are plane wavefronts associated?
(v) Write an expression for the torque acting on an electric dipole kept in a
uniform electric field in vector form.
(vi) In Young’s double slit experiment, what should be the path difference
between two overlapping waves to form a bright band / fringe?
(vii) What are isotones?
SECTION B
Q2
(i) (a) State Gauss’ theorem.
(b) What is the SI unit of electric flux?
OR
(ii) Calculate the equivalent capacitance C´ if n identical capacitors each of
capacitance C are connected in series.
Q3 A hollow charged metallic sphere of radius R carries a charge Q. How much work has to be done in moving a charge q on its surface through a distance d? Explain
Q4 (i) What is meant by pair annihilation? (ii) Give any one example where energy is converted to matter.
Q5
(i) Figure 2 given below shows a part of Wheatstone bridge circuit. With the help of
Kirchhoff’s loop rule, calculate the current flowing through the 4Ω resistor.
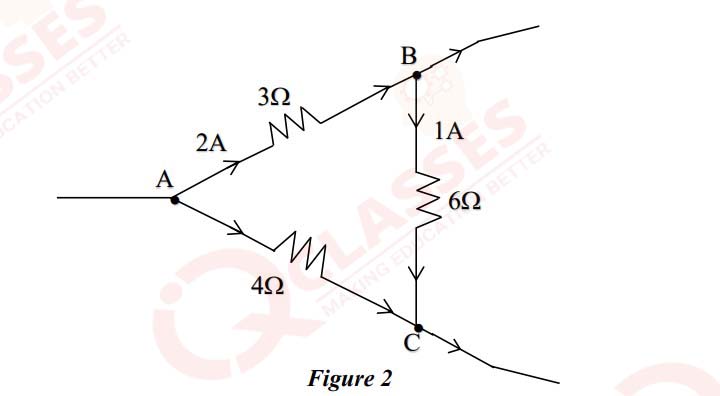
OR
(ii) In an experiment conducted to determine the internal resistance of a cell, its emf
is balanced against a p.d. across 110cm of the potentiometer wire. The balancing
length becomes 100cm when the cell is shunted by a resistance of 10Ω. Calculate
the internal resistance of the cell.
Q6
(i) On which principle do optical fibres work?
(ii) What is a thin prism?
Q7
(i) State any one application of microwaves.
(ii) Which one of the following rays/waves is NOT an electromagnetic wave?
X rays; UV rays; γ rays; matter waves.
Q8
(i) What is motional emf?
(ii) A 220V ac voltage is to be converted to 33,000V ac voltage. What kind / type of
transformer will you use?
SECTION-C
Q9 Obtain an expression for intensity of electric field at a point in broadside position of an electric dipole
Q10
(i) In Figure 3 shown below, all the cells are identical. The external resistance R is
also same in both the circuits.
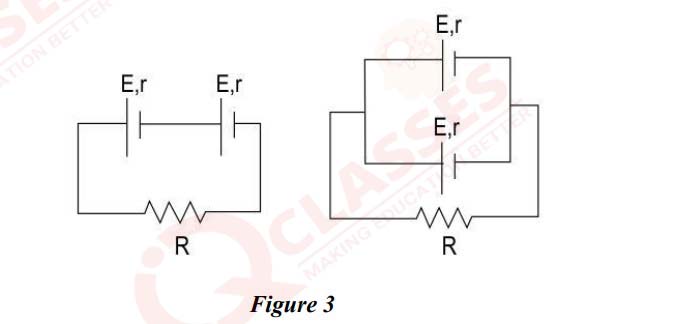
If the same current flows through the resistor R in both the circuits, calculate the
relation between r, the internal resistance of each cell and the external resistance R.
OR
(ii) The drift velocity of electrons in a conductor connected to a battery is given by
vd = -eEτ/m.
Here, e is the charge of the electron, E is the electric field, τ is the average time
between collisions and m is the mass of the electron.
(a) How does the drift velocity change with an increase in the potential
difference across the conductor?
(b) A copper wire of length 'l' is connected to a source. If the copper wire is
replaced by another copper wire of the same area of cross-section but of
length '4l', how will the drift velocity change? Explain.
Q11
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a potential difference
of 200 mV.
(i) How will you convert this galvanometer into an ammeter of the range 0 – 2A?
(ii) Define an ampere in terms of force between two current carrying conductors
Q12
(i) (a) Draw the ray diagram of a compound microscope t when the final image lies
at the least distance of distinct vision, D.
(b) Write an expression for magnifying power of an astronomical telescope when
final image lies at infinity. (No derivation required)
OR
(ii) For refraction at convex spherical surface of denser medium η2 surrounded by a
rarer medium of refractive index η1, derive a formula connecting object distance u,
image distance v, and radius of curvature R for the object in rarer medium and a real
image formed inside the denser medium.
Q13 Using Huygen’s wave theory, prove Snell’s Law for refraction of light.
Q14
(i) A certain metal emits photoelectrons with a green light but not with a yellow light.
If this surface is illuminated with blue light and red light, which one of the two will
cause photoelectric emission? Give a reason for your answer.
(ii) What conclusion can be drawn from this phenomenon regarding the nature of light?
Q15
A lens of focal length f is divided into two equal parts as shown in Figure 4A below. These
parts are then arranged as shown in Figure 4B below.
In terms of the original focal length f,
(i) What is the focal length of the lens L1 ?
(ii) What is the focal length of the final combination?
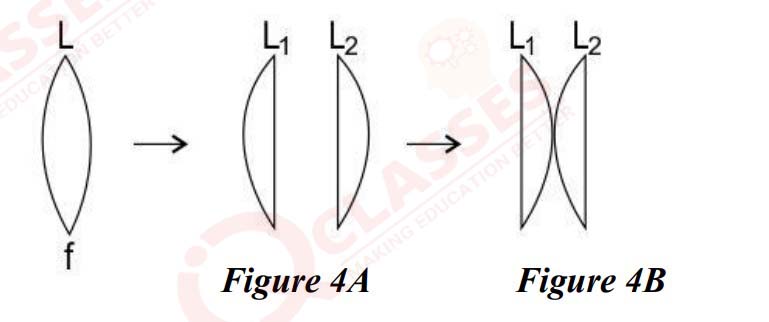
Q16 Using Ampere circuital law, obtain an expression for magnetic field B near a long current carrying straight conductor.
Q17
Young’s double-slit experiment is performed by a student. The examiner gives the
following instructions to the student. State whether the responses of the student, in each
case, are correct or incorrect. Give a reason for your answer.
(i) EXAMINER: The fringes on the screen are too crowded. Increase the distance
between the fringes.
STUDENT increases the distance between the two slits (thinking that distance
between the fringes increases on increasing the distance between slits).
(ii) EXAMINER: Bright fringes are not very bright. Increase their brightness.
STUDENT moves the source of light towards the two slits.
(iii) EXAMINER: Compare the distance between central and first maxima with the
distance between second and third maxima.
STUDENT measures and states that the distance between central and first maxima
is MORE than that between second and third maxima
SECTION D
Q18
(i) (a) A closed loop of area 1 m2
and resistance of 10Ω is free to rotate about an axis
passing through its plane and the centre. If the loop is placed at right angles to
a magnetic field B = 0.2 Wb/m2
and turned through 180° in 0.02 second, then
determine (I) induced emf and (II) induced current in the loop.
(b) A wire is wound into a solenoid of length l and radius r. It has a self-inductance
of L. By what factor does the self-inductance change, if the same wire is wound
into a solenoid of half the length and half the radius?
OR
(ii) (a) In a series LCR circuit connected to an alternating voltage source of 220V50Hz, the readings of
voltmeters across resistor, capacitor and inductor are
70V, 415V, 210V respectively.
If the value of the resistance R =100Ω, calculate
(1) current in the circuit.
(2) value of L.
(3) value of C.
(b) If the capacitance in an LC series circuit is doubled, by what value should the
inductance be changed to keep its resonant frequency constant?
Q19
(i) (a) Uranium undergoes nuclear fission as shown in the following nuclear reaction.
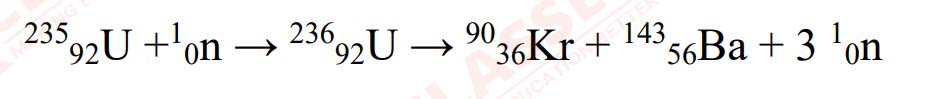
Calculate the energy released during the fission reaction.
(b) Write any one balanced equation to represent nuclear fusion.
(c) In Rutherford's α-particle scattering experiment, it was observed that most
of the α-particles did not deflect; some showed a deflection of more than 90°
and some were deflected by even 180°
(1) What hypothesis was made to justify the deflection of α-particle by more
than 90°?
(2) State any one postulate of Bohr’s theory
OR
(ii) (a)
(1) Define unified atomic mass unit.
(2) Write its energy equivalent.
(3) What is the physical significance of binding energy per nucleon of a
nucleus?
(b) The wavelength of the first line of Balmer series (Hα ) is 656·3nm. Calculate
the value of the Rydberg’s constant.
Q20
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
A rain sensor is a device used for sensing rain. They are used to automatically activate
windscreen wipers to remove water from the windshields An IR LED is used to shine
infrared light onto the windshield at an angle of 45°, which is then detected using an IR
photodiode.
(i) Name the two semiconductor diodes used in the rain sensor.
(ii) What kind of biasing is used in each of these diodes?
(iii) Draw the symbol of LED.
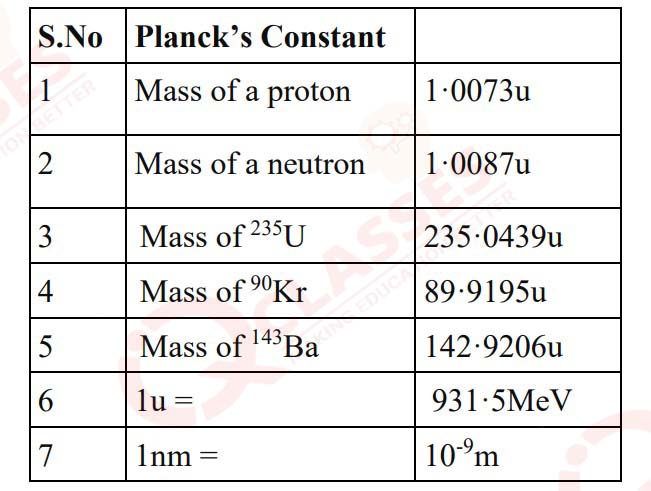
Useful Constants & Relations:

Add a comment