Class 12 ISC term1 Chemistry Specimen 2022
BOARD -
CLASS -
SUBJECT -
ISC
12th
CHEMISTRY
Paper Pattern for MCQ Term-I
TIME -
MARKS -
1 Hour 30 Minutes
70
Visit CISCE OFFICIAL PAGE for Regulations and Syllabus of Class 12th ISC
Solved Specimen CHEMISTRY Paper Semester-I 2022
Question 1 [Chemistry Paper Term-I 2022]
Q.1 (1) Na and Mg crystallise in bcc and fcc structures respectively. The value of Z (number of atoms) for their crystals is:
- 8 and 14
- 2 and 4
- 14 and 8
- 6 and 4
Solution
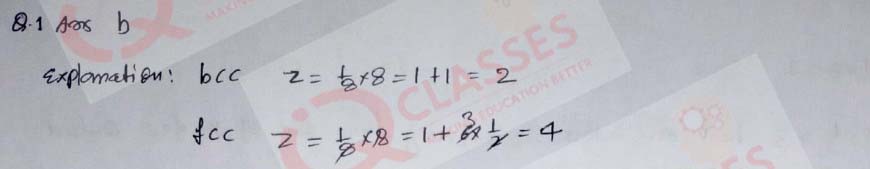
(2) Colligative properties depend on:
- The nature of solute particles in solution
- The number of solute particles in solution
- The nature of solute and solvent particles
- The physical properties of solute particles in solution
Solution

(3) On dilution, the specific conductance of a solution:
- Remains unchanged
- Increases
- Decreases
- First increases then decreases
Solution
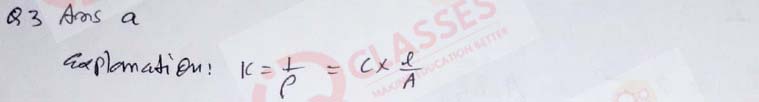
(4) The flux used in the extraction of iron from haematite ore is:
- Limestone
- Silica
- Coke
- Calcium phosphate
Solution
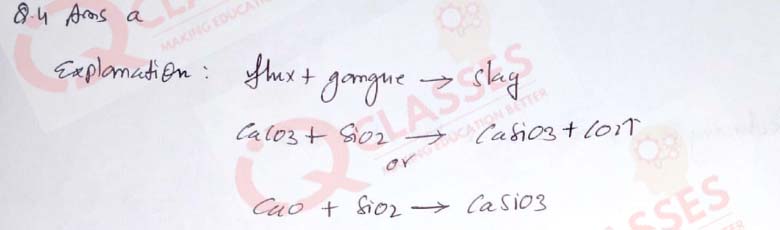
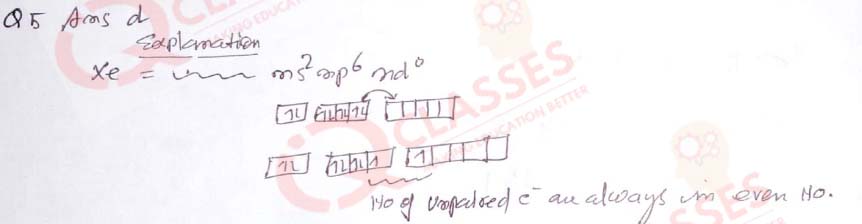
(5) Which of the following xenon fluoride of xenon cannot be formed?
- XeF2
- XeF4
- XeF6
- XeF3
Solution
(6) The gas obtained on heating iodoform with silver powder is:
- Propane
- Ethane
- Ethyne
- Ethene
Solution
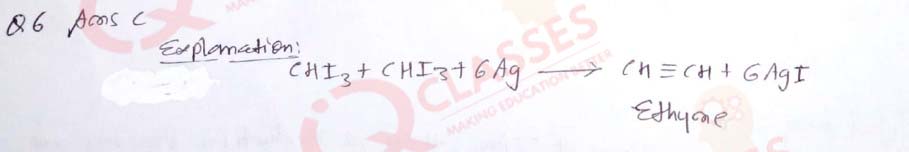
(7) Boiling point of ethyl alcohol is greater than diethyl ether due to:
- Vander Waals forces
- London forces
- Polarity
- Hydrogen bonding
Solution

(8) In a face centred cubic lattice, atom ‘A’ occupies the corner positions and atom ‘B’ occupies the face centred positions. If one atom of ‘B’ is missing from one of the face centred points, the formula of the compound will be:
- AB2
- A2B3
- A2B5
- A2B
Solution

(9) The standard reduction potential values of three metallic cations X, Y and Z are 0.52 V, - 3.03 V and -1.18 V respectively. The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is:
- Y > Z > X
- X > Y > Z
- Z > Y > X
- Z > X > Y
Solution

(10) If molality of the dilute solution of a non-volatile, non-dissociating and non-associating electrolyte is doubled, the value of molal elevation constant or Ebullioscopic constant (Kb) will be:
- doubled
- halved
- tripled
- unchanged
Solution
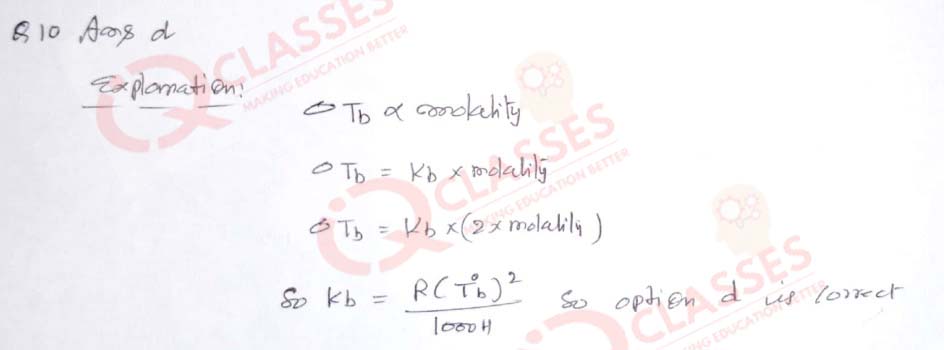
(11) Extraction of zinc from zinc blende is achieved by
- Electrolytic reduction
- Roasting, followed by reduction with carbon
- Roasting, followed by reduction with another metal
- Roasting, followed by self-reduction
Solution

(12) The most powerful oxidizing agent is:
- Fluorine
- Chlorine
- Bromine
- Iodine
Solution
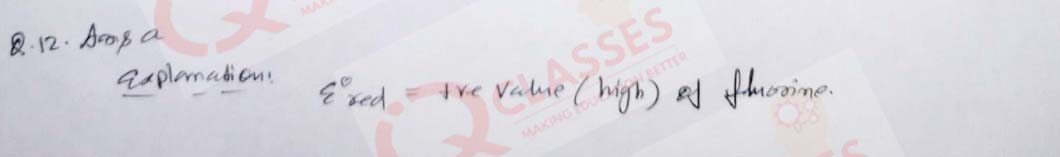
(13) During the course of SN1 reaction, the intermediate species formed is:
- A free radical
- A carbanion
- A carbocation
- An intermediate complex
Solution

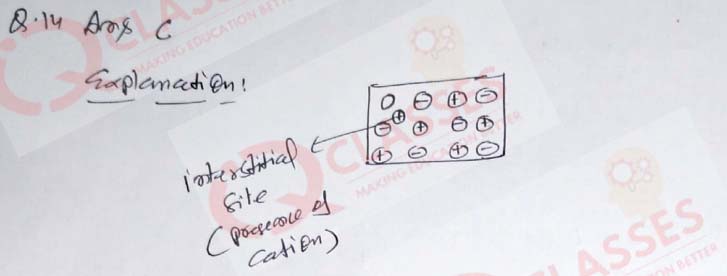
(14) Which type of defect has the presence of cations in the interstitial sites?
- Schottky defect
- Vacancy defect
- Frenkel defect
- Metal deficiency defect
Solution
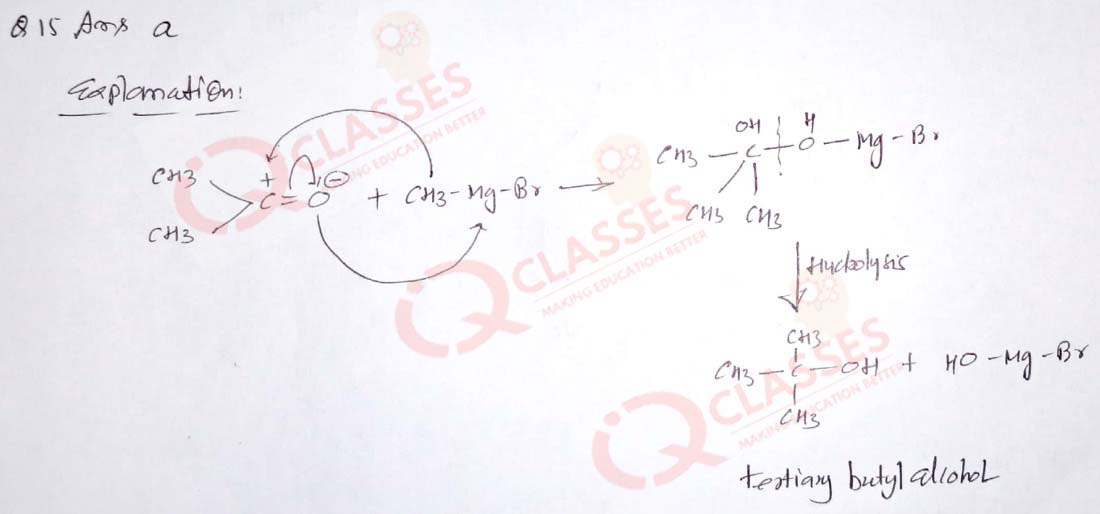
(15) Reaction between acetone and methyl magnesium chloride, followed by hydrolysis will give
- tert-butyl alcohol
- iso-butyl alcohol
- iso-propyl alcoho
- sec-butyl alcohol
Solution
(16) If 5.85 g of NaCl are dissolved in 90 g of water, the mole fraction of solute is:
- 0.2632
- 0.0102
- 0.0196
- 0.1045
Solution

(17) When zinc granule is dipped into copper sulphate solution, copper is precipitated because:
- Both copper and zinc have a positive reduction potential.
- Both copper and zinc have a negative reduction potential
- Reduction potential of zinc is higher than that of copper.
- Reduction potential of copper is higher than that of zinc.
Solution

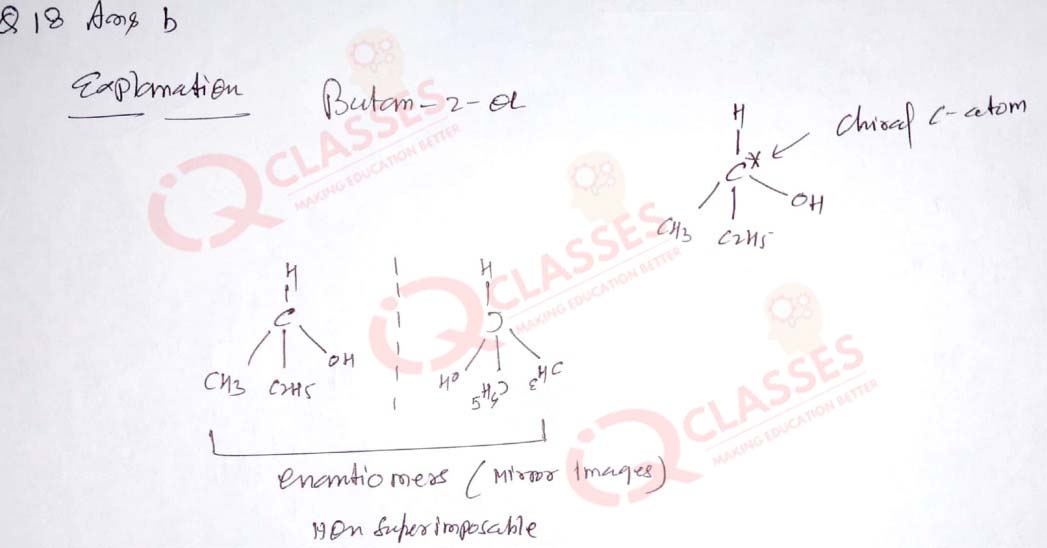
(18) The optically active compound is:
- Butan-1-ol
- Butan-2-ol
- Propan-1-ol
- 2-methyl-propan-1-ol
Solution
(19) Chlorine reacts with cold and dilute NaOH under ordinary conditions to give:
- NaCl and Cl2O
- NaCl and ClO2
- NaCl and NaClO
- NaCl and NaClO3
Solution
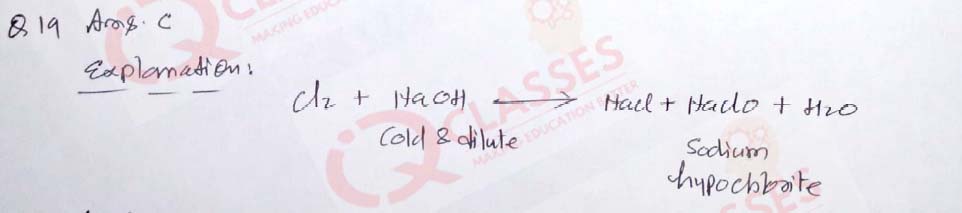
(20) Solutions which distil without any change in composition and temperature are called.
- Ideal
- Super saturated
- Azeotropic
- Isotonic
Solution

(21) The reaction: Sodium alkoxide + alkyl halide ---> Ether + Sodium halide is called:
- Wurtz reaction
- Kolbe’s reaction
- Perkin’s reaction
- Williamson’s synthesis
Solution

(22) Benzene diazonium chloride on hydrolysis gives:
- Benzene
- Phenol
- Chlorobenzene
- Benzyl alcohol
Solution

(23) The vacant space in body centred cubic lattice unit cell is:
- 32%
- 26%
- 48%
- 68%
Solution
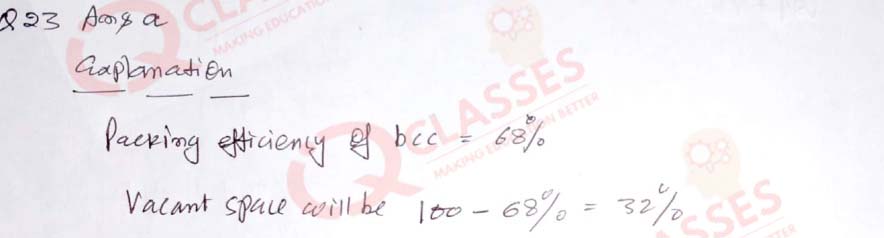
(24) For a spontaneous reaction ∆Go and Eo cell will be respectively:
- –ve and -ve
- +ve and +ve
- +ve and -ve
- –ve and +ve
Solution
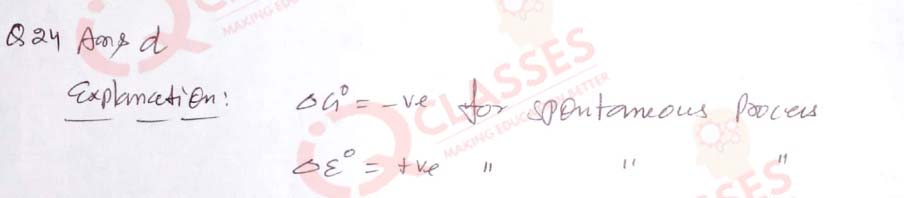
(25) A liquid is mixed with ethanol and few drops of conc. H2SO4 is added. A compound with a fruity smell is formed. The liquid is:
- HCHO
- CH3CHO
- CH3COOH
- CH3COCH3
Solution

(26) The chief ore of copper is copper pyrite (CuFeS2)
-
How is the sulphide ore concentrated?
- By Gravity separation process
- By Froth-floatation process
- By Electromagnetic separation process
- By Leaching process
-
Copper is purified by electrolytic refining of blister copper. The correct statement
about this process is:
- Impure copper strip is used as cathode
- Impurities do not settle as anode mud
- Pure copper deposits at cathode
- Acidified silver nitrate is used as electrolyte
Solution

(27) The reaction: CH3Br + OH- CH3OH + Br-
-
The expected mechanism of the above reaction is:
- SN1 mechanism
- SN2 mechanism
- SE1 mechanism
- SE2 mechanism
-
The above reaction is:
- Elimination reaction
- Nucleophilic addition reaction
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- Electrophilic substitution reaction
Solution

(28) For the extraction of metal, answer the following:
-
The smelting of iron ore in blast furnace involves all the processes except:
- Combustion
- Reduction
- Slag formation
- Sublimation
-
Which of the following metal is obtained by leaching the concentrated ore with
dilute sodium cyanide solution, followed by treatment with zinc?
- Aluminium
- Iron
- Copper
- Silver
Solution
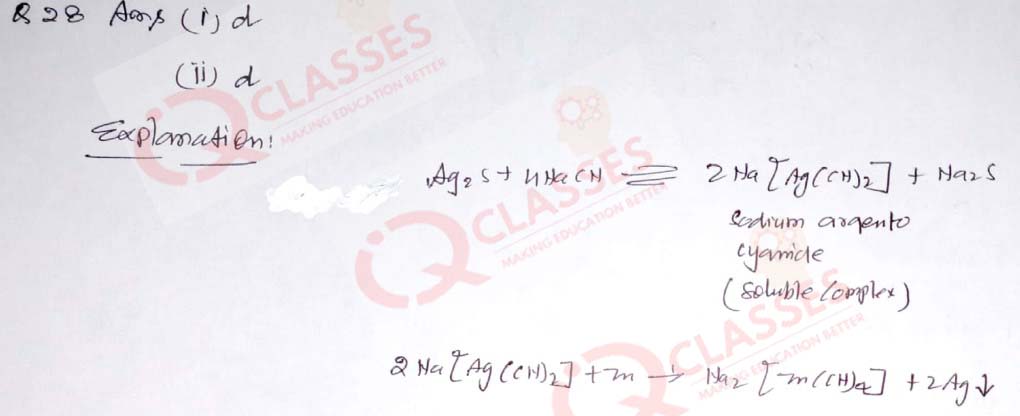
(29) Phenol is heated with alcoholic KOH and chloroform:
-
What is the name of the reaction?
- Cannizzaro reaction
- Gattermann reaction
- Reimer –Tiemann reaction
- Kolbe reaction
-
What is the main product formed in this reaction?
- Salicylaldehyde
- Salicylic acid
- Aniline
- Phenyl isocyanide
Solution
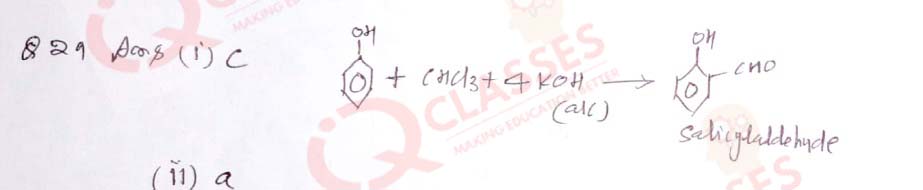
(30) For IF7 molecule
-
The structure of the given molecule is:
- Octahedral
- Octahedral
- Trigonal bipyramidal
- Pentagonal bipyramidal
-
The type of hybridization of the given molecule is:
- sp3 hybridisation
- sp3d3 hybridisation
- sp3d2hybridisation
- sp3d hybridisation
Solution
(31) Ethyl alcohol when reacts with PCl5 gives a compound (A). When compound (A) is treated with alc. KOH, compound (B) is formed along with KCl and H2O.
-
The compound (A) is:
- C2H4Cl2
- CH2CHO
- C2H5Cl
- CH3OH
-
The compound (B) is:
- C2H2
- C2H4
- C2H6
- C2H5OH
Solution
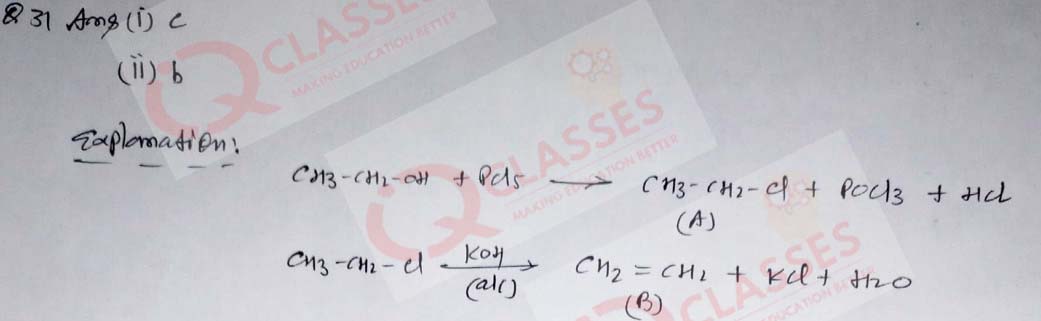
(32) Copper pyrite or chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) is the main ore of copper. The extraction of copper from its ore involves, concentration, partial roasting, removal of iron and self-reduction.
-
On heating the mixture of Cu2O and Cu2S, which one of the following will
be
obtained?
- Cu2SO3
- Cu + SO3
- CuO + CuS
- Cu + SO2
-
Iron is removed during the extraction of copper as:
- FeO
- FeS
- FeSiO3
- Fe2O3
Solution

(33) Conversion of Chlorobenzene into phenol.
-
Which of the following statements is correct for the above conversion?
- Heating it with alc. KOH at room temperature
- Heating it with aqueous NaOH at 623 K under pressure followed by acidification with dilute HCl
- Heating it with CuCN followed by acidification with dilute HCl
- Heating it with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether
-
What is the name of the above reaction?
- Dow process
- Wurtz reaction
- Sandmeyer’s reaction
- Kolbe’s reaction
Solution

(34) With reference to XeF6 molecule, answer the following questions.
-
What is the hybridisation of Xe atom in the given molecule?
- sp3d3
- sp3d2
- sp3
- sp3d
-
What is the geometry of this molecule?
- Distorted octahedral
- Square planer
- Pyramidal
- Tetrahedral
Solution
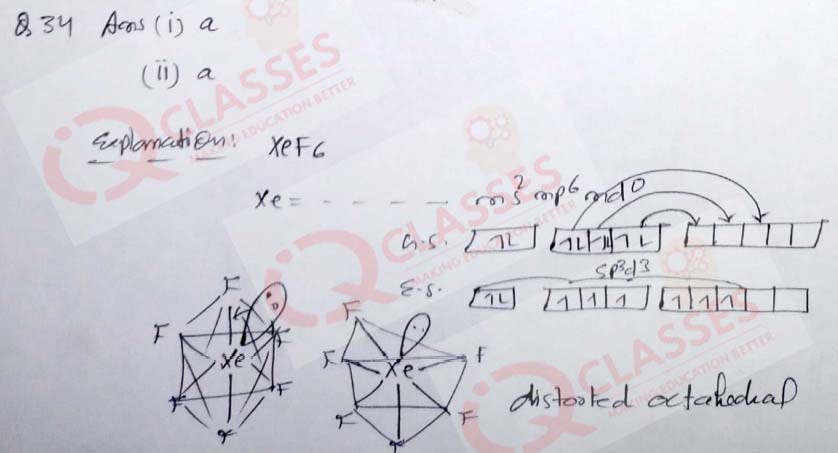
(35) An unknown alcohol is treated with Lucas reagent to determine whether the alcohol is primary, secondary or tertiary.
-
Which alcohol reacts fastest and by what mechanism?
- Tertiary alcohol by SN2
- Secondary alcohol by SN1
- Tertiary alcohol by SN1
- Secondary alcohol by SN2
-
What is the chemical composition of the Lucas reagent used above?
- Anhydrous zinc chloride in concentrated HCl
- Anhydrous zinc chloride in concentrated HCl
- LHAnhydrous lead chloride in concentrated HCl
- Anhydrous barium chloride in concentrated HCl
Solution

(36) Ozone is prepared from oxygen:
-
Which method is used in the above preparation?
- Oxidation at high temperature
- Oxidation using catalyst
- Silent electric discharge
- Reduction at high temperature
-
The ozone obtained above acts as a:
- reducing agent
- oxidising agent
- decomposer
- dehydrating agent
Solution

(37) Copper metal crystallises with face centred cubic unit cell. If the edge length of copper atom is 361.5 pm. (Atomic weight of Cu = 63.5, NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 )
-
The density of copper metal is:
- 7.86 g/cm3
- 8.93 g/cm3
- 9.76 g/cm3
- 10.5 g/cm3
-
The radius of copper metal is:
- 180.75 pm
- 156.53 pm
- 127.79 pm
- 104.86 pm
Solution

(38) An aqueous solution containing one gram of urea (molecular weight = 60) boils at 100.25oC. The same solution freezes at -0.894oC. The aqueous solution containing 3 gram of glucose (Molecular weight = 180) in the same volume of solution:
-
What is the boiling point of glucose?
- 100.75oC
- 100.50oC
- 100.25oC
- 100.08oC
-
What is the freezing point of glucose?
- +0.894oC
- -0.894oC
- +0.447oC
- -0.447oC
Solution
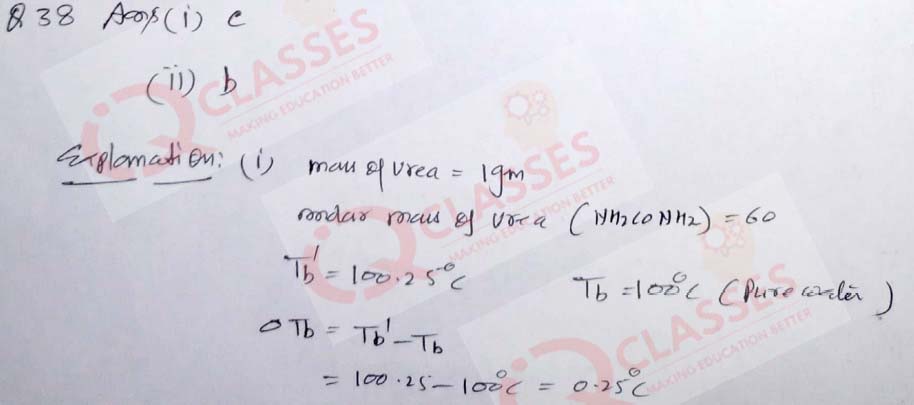


(39) When two Faradays of electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of CuSO4 and an aqueous solution of AgNO3. (Atomic weight of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1 , Ag = 108 g mol-1 )
-
The mass of copper deposited at the cathode is:
- 127.02 g
- 63.50 g
- 31.75 g
- 15.87 g
-
The mass of silver deposited at the cathode is:
- 54 g
- 108 g
- 216 g
- 270 g
Solution
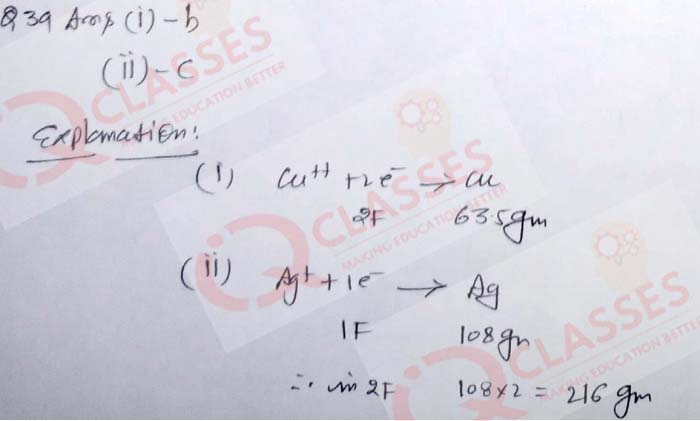
(40) Gold has cubic crystal whose unit cell has an edge length of 407.9 pm. Density of gold is 19.3 g cm-3 . Atomic weight of gold is 197 g mol-1 . (NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 )
-
The number of atoms (Z) in a unit cell of gold is:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
The type of crystal structure of gold is:
- Simple cubic unit cell
- Body centred cubic unit cell
- Face centred cubic unit cell
- Side centred cubic unit cell
Solution

(41)
A solution of sucrose (molecular weight 342 g mol-1
) has been prepared by dissolving
68.4 g of sucrose in 1000 g of water.
(Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1)
-
The freezing point of the solution obtained will be:
- -0.52 oC
- +0.52 oC
- -0.372 oC
- +0.372 oC
-
The molality of sucrose solution will be:
- 0.1
- 0.2
- 0.3
- 0.4
Solution

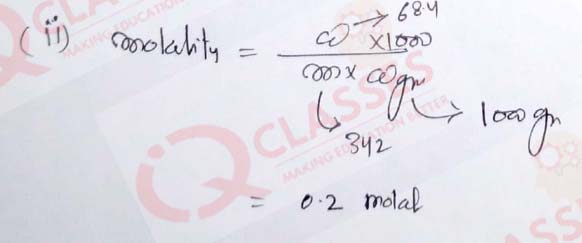
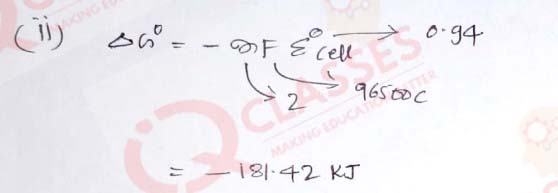
(42)
The standard electrode potential for the reaction is:
Ag++ e---->Ag(s); EoAg+/Ag = +0.80 V
Sn2++ 2e---->Sn(s); EoSn2+/Sn = -0.14 V
-
The Eocell will be:
- 0.66 V
- 0.88 V
- 0.94 V
- 1.08 V
-
The value of standard Gibbs energy (∆Go) will be:
(F = 96,000 C mol-1)- -181.42 kJ
- -90.71 kJ
- -45.36 kJ
- -22.68 kJ
Solution

(44) A metal has face centred cubic lattice. The edge length of the unit cell is 404 pm. The density of the metal is 2.72 g/cm3 . (NA = 6.023 x 1023 mol-1 )
-
The molar mass of the metal is:
- 20 g mol-1
- 27 g mol-1
- 30 g mol-1
- 40 g mol-1
-
The radius of the metal atom in centimetre (cm) is:
- 103.29 x 10-10 cm
- 125.63 x 10-10 cm
- 142.81 x 10-10 cm
- ) 142.81 x 10-10 cm
Solution

(45)
A binary solution contains 92 g ethyl alcohol and 72 g water.
(Atomic weight of C = 12, H =1, O =16)
-
Mole fraction of ethyl alcohol is:
- 0.40
- 0.80
- 0.66
- 0.33
-
Mole fraction of water is:
- 0.33
- 0.66
- 0.20
- 0.80
Solution

(45) The limiting molar conductivities (˄∞m) for NaCl, KBr and KCl are 126, 152 and 150 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 respectively
-
The molar conductivity at infinite dilution for NaBr is:
- 128 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
- 176 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
- 278 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
- 302 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
-
The law applied to determine the molar conductivity of infinite dilution is known
as:
- Faraday’s Law
- Avogadro’s Law
- Kohlrausch’s Law
- Ohm’s Law
Solution
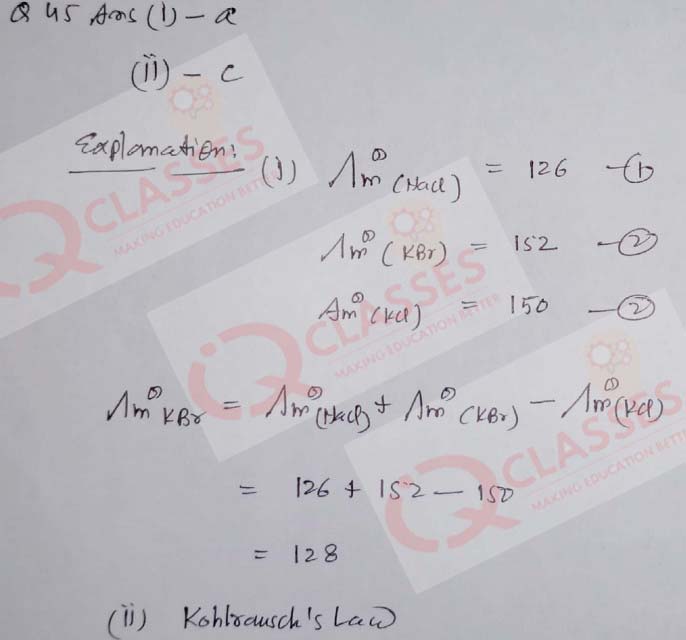
(46)
Assertion: Haloalkanes when treated with alcoholic KCN forms alkane nitrile as a major
product.
Reason: Potassium cyanide is a covalent compound.
- Assertion is false but reason is true.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Solution

(47)
Assertion: Iron is found free in nature.
Reason: Iron is highly reactive element
- Assertion is false but reason is true
- Assertion is true but reason is false
- Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not correct explanation of the assertion
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Solution
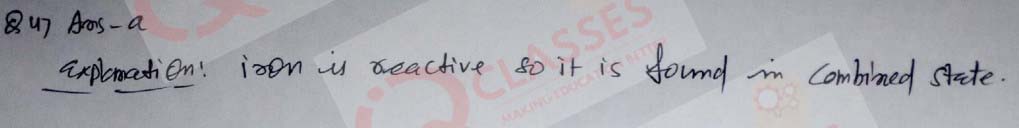
(48)
Assertion:Ethers are more volatile than alcohols having the same molecular formula.
Reason: Alcohols have intermolecular hydrogen bond.
- Assertion is false but reason is true
- Assertion is true but reason is false
- Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not correct explanation of the assertion
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
Solution
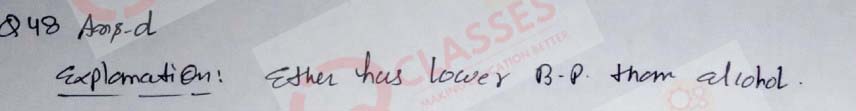
(49)
Assertion: SO2 decolorises pink colour of acidified KMnO4 solution.
Reason: SO2 is an oxidising agent
- Assertion is false but reason is true.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Solution

(50)
Assertion:Sulphide ores are concentrated by froth floatation process.
Reason: Sulphide ores are wetted by pine oil forming the froth while impurities are vetted
by water.
- Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
- Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
- Assertion is correct and the reason is wrong
- Both assertion and reason are wrong
Solution
