Class 12 ISC term1 Economics Specimen 2022
BOARD -
CLASS -
SUBJECT -
ISC
12th
ECONOMICS
Paper Pattern for MCQ Term-I
TIME -
MARKS -
1 Hour 30 Minutes
80
Visit CISCE OFFICIAL PAGE for Regulations and Syllabus of Class 12th ISC
Solved Specimen Paper Semester-I 2021
Question 1 [Economics Specimen Paper Term-I 2021]
Q1. (1) What is the formula for calculating M.U.?
- TUN + TUN+1
- TUN - TUN+1
- TUN - TUN+1
- TUN - TUN-1
Solution
.jpg)
(2) When a consumer consumes two goods, then he will be in equilibrium at:
- MUx=Px
- M Ux⁄Px=Py⁄M Uy
- M Ux⁄Px=M Uy⁄Py
- none of these
Solution
.jpg)
(3) What relation do you notice between Price and Demand in the table given below:
| Price | Demand(Units) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 20 |
| 8 | 25 |
- Increase in demand
- Decrease in demand
- Extension in demand
- Contraction in demand
Solution
.jpg)
(4) When demand curve is parallel to X-axis, what would be its Elasticity of demand?
- E = ∞
- E = 1
- E = >1
- E = < 1
Solution
.jpg)
(5) Which of the given options shows the effects of Elasticity of demand?
- Nature of good
- Level of Income
- Availability of substitutes
- All
Solution
.jpg)
(6) What is the nature of relationship between price and demand in case of Elasticity of demand?
- Qualitative
- Quantitative
- Competitive
- None of these
Solution
.jpg)
(7) How will you calculate the Total product?
- ∑AP
- ∑TP
- ∑MP
- Any of these
Solution
.jpg)
(8) Which of the given options shows the application of increasing returns?
- Specialization
- Efficiency of factors
- Indivisibility of factors
- All
Solution
.jpg)
(9) When supply increases due to improvement in technology, it is known as
- Extension in supply
- Increase in Supply
- Contraction in supply
- Decrease in supply
Solution
.jpg)
(10) The Elasticity of Supply is always positive because there is:
- Direct relation between supply and price
- Inverse relation between demand and price
- Both(a)and (b)
- Neither (a) nor (b)
Solution
.jpg)
(11) Cost of exertion, pains and sacrifices is known as:
- Opportunity costs
- Production costs
- Real costs
- Explicit Costs
Solution
.jpg)
(12) What is the nature of the expenditure on raw material, power and labour?
- Fixed
- Variable
- Production costs
- Explicit
Solution
.jpg)
(13) What is the correct formula for calculating the Total variable cost?
- TVC = ∑MC
- TVC = TC – TFC
- TVC = AVC x Q
- All
Solution
.jpg)
(14) What is the relationship between AR and MR under Perfect competition?
- AR > MR
- AR < MR
- AR = MR
- AR ≠ MR
Solution
.jpg)
(15) Which of the following statements is true?
- AR=MR⁄Q
- TR= MR x Q
- TR = ∑MR
- All
Solution
.jpg)
(16) A competitive firm will be in equilibrium when:
- MR= MC and MC cuts MR from below
- AR = AC; AC cuts AR from above
- TR= TC
- None of these
Solution
.jpg)
(17) In a Perfectly competitive market, who decides the price?
- A firm
- An Industry
- Both A and B
- None of these
Solution
.jpg)
(18) What is determined at the point where market demand and market supply curves intersect each other?
- Equilibrium Price
- Equilibrium Quantity
- Both of these
- None of these
Solution
.jpg)
(19) What will be the effect upon equilibrium price, when an increase in demand is more than increase in supply?
- Equilibrium Price remains constant
- Equilibrium price rises
- Equilibrium price falls
- None of these
Solution
.jpg)
(20) What does Floor Price refer to?
- Controlled Price
- Maximum Ceiling Price
- Minimum Support Price
- Any of these
Solution
.jpg)
(21) An Indifference curve is convex to the origin because of:
- Increasing MRS
- Law of DMU
- Diminishing MRS
- Constant MRS
Solution
.jpg)
(22) AVC and AC curves cannot intersect each other because:
- MC starts falling
- TC- TVC =TFC which is constant
- TC does not increase
- None of the above
Solution
.jpg)
(23) Which of the given options is a reason of change in demand ?
- Change in Consumer’s Income
- Change in Prices of Related Goods
- Population increase
- All the above
Solution
.jpg)
(24) What is the basic reason for operation of the Law of Diminishing return?
- Scarcity of factors
- Imperfect substitution between factors
- Both (a) and ( b)
- None of the above
Solution
.jpg)
(25) What is the reason for the U shape of short run average cost curves?
- Law of Demand
- Law of DMU
- Law of variable proportions
- Law of supply
Solution
.jpg)
(26) The reason for decrease in demand is:
- Rise in price
- Increase in the price of substitute goods
- Increase in the price of complementary goods
- Decrease in income in case of inferior goods
Solution
.jpg)
(27) The demand for a certain brand of fruit juice is elastic because:
- It falls under luxuries
- Its consumption can be postponed
- Its substitutes are available in the market
- It is a multiple use product
Solution
.jpg)
(28) The reason for downward sloping demand curve is:
- Inverse relation between price and demand
- Inverse relation between income and demand
- Direct relation between price and demand
- Both (a) and (b)
Solution
.jpg)
(29) Which of the given options is the correct reason for a backward bending supply curve?
- Labour first prefers work over leisure and then leisure over work
- Labour first prefers leisure over work and then work over leisure
- Both (a) and (b)
- Neither (a) nor (b)
Solution
.jpg)
(30) What is the reason for the upward sloping supply curve?
- Direct relation between price and quantity
- Number of producers
- Profit maximisation
- All the above
Solution
.jpg)
(31) Cross elasticity of demand is _______ for substitute goods. An increase in the price of one commodity leads to _______ in the demand for another commodity.
- positive, increase
- negative, increase
- positive, decrease
- negative, increase
Solution
.jpg)
(32) Opportunity cost of a good is the ________.
- Anticipated cost
- Next best alternative
- Upcoming cost
- Real cost
Solution
.jpg)
(33) If the price of petrol increases, the demand for cars will:
- Increase
- Decrease
- Expand
- Vary
Solution
.jpg)
(34) What is Ex-ante demand also known as?
- Intended demand
- Actual demand
- Effective demand
- Unplanned demand
Solution
.jpg)
(35) The slope of the indifference curve is equal to:
- One
- Marginal utility
- Marginal rate of substitution
- None of these
Solution
.jpg)
(36) Price effect is:
- Income effect – Substitution effect
- Substitution effect – Income effect
- Income effect + Substitution effect
- Income effect + Substitution effect - Negative effect
Solution
.jpg)
(37) Social cost is:
- Implicit cost + Explicit cost
- Explicit cost+ Opportunity cost
- Private cost + External cost
- Private cost + Real cost
Solution
.jpg)
(38) _______ is an example of goods of Snob Appeal.
- Buying a Ferrari
- Buying basic utilities
- Buying a car insurance
- Opening a bank account.
Solution
.jpg)
(39) The short run refers to the period of time when output can be increased by increasing ____ while keeping _____ constant
- Capital, land
- Labour, capital
- Labour, land
- Land, entrepreneur
Solution
.jpg)
(40) When a fall in the price of the commodity results in increase in total expenditure, the elasticity of demand will be _______
- Ep = 1
- Ep = 0
- Ep < 1
- Ep>1
Solution
.jpg)
(41) The demand for a commodity refers to:
- desire for a commodity
- need for a commodity
- quantity demanded at the lowest prices during a particular period of time
- quantity demanded at various possible prices during a particular period of time
Solution
.jpg)
(42) The demand for labour is:
- independent of the demand for other inputs or resources.
- independent of the demand for the products produced by labour.
- independent of the availability of other inputs or resources
- derived from the demand for the products produced by labour.
Solution
.jpg)
(43) Giffen goods are:
- Normal goods, whose demand falls with a rise in their price
- Inferior goods, whose demand falls with a rise in their real income
- Inferior goods, whose demand falls with a fall in their price.
- Superior goods, whose demand falls with a rise in their real income
Solution
.jpg)
(44) Total utility refers to the total satisfaction derived by the consumer from the consumption of
- An additional quantity of a commodity.
- A minimum quantity of a commodity
- A maximum quantity of a commodity
- A specific quantity of a commodity
Solution
.jpg)
(45) Returns to a factor means:
- Quantity of only one factor is changed.
- Quantity of all factor inputs is changed.
- Fixed factors are changed but variable factors are kept constant.
- Fixed and Variable both factors are changed in equal proportion
Solution
.jpg)
(46) Economic cost refers to the sum of both explicit cost and implicit cost:
- Including excess profit
- Including normal profit.
- Including net profit.
- Including abnormal profit
Solution
.jpg)
(47) Monopolistic Competition is a form of market in which there are large number of sellers of a particular product, with each seller selling:
- Homogenous products.
- Differentiated products which are entirely distinct from each other
- Perfect substitutes
- Differentiated products which are close substitutes to the product.
Solution
.jpg)
(48) Normal profit is defined as that amount of profit that is high enough so that firms in the industry are induced to remain in the industry, yet low enough so that:
- New firms will want to enter the industry
- New firms will not want to enter the industry
- Old firms will want to expand their operations.
- Old firms will want to expand their operations.
Solution
.jpg)
(49) Firms maximise their profits by producing a level of output at which:
- MC = AFC
- MC = MR
- P= ATC
- MR =AVC
Solution
.jpg)
(50) The demand curve for the firm operating under perfect competition is:
- Upward sloping to the right
- Downward sloping to the right
- Perfectly horizontal li ne
- Perfectly vertical line
Solution
.jpg)
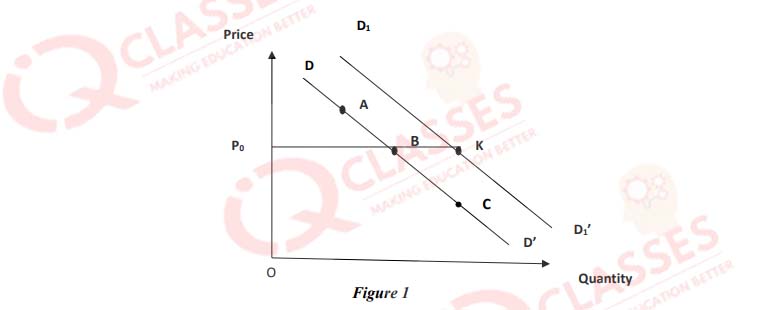
(51)
-
In figure 1, the:
- Movement from A to B is contraction of demand
- Movement from B to C is extension of demand
- Movement from A to C is contraction of demand
- Movement from C to B is extension of demand
Solution
1.jpg)
-
In figure 1, the movement from B to K
- is increase in demand
- indicates that demand rises at constant price
- takes place due to rise in demand caused by rise in money income of the consumer
- All of the above
Solution
2.jpg)
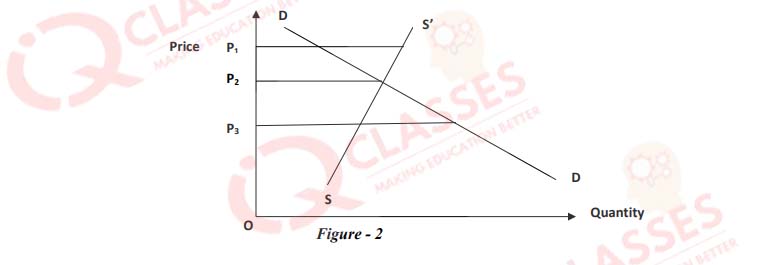
(52)
-
In figure 2, the Floor price is:
- OP1
- OP2
- OP3
- None of the above
Solution
1.jpg)
-
In figure 2, Ceiling price is:
- OP1
- OP2
- OP3
- None of the above.
Solution
2.jpg)
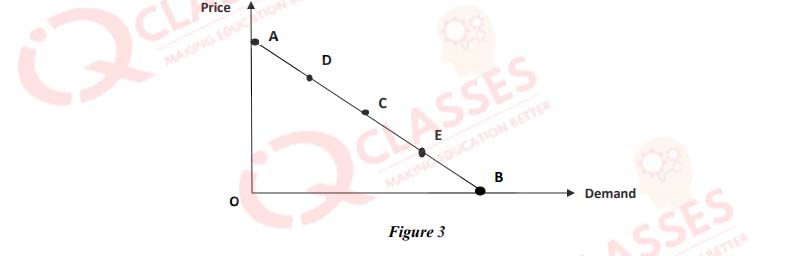
(53)
-
In figure 3, the demand is:
- Perfectly elastic at A, unit elastic at B and relatively inelastic at E
- Relatively elastic at D, perfectly elastic at C and unit elastic at E.
- Unit elastic at C, relatively inelastic at E and perfectly inelastic at B.
- Relatively inelastic at D, unit elastic at C and perfectly elastic at B.
Solution
.jpg)
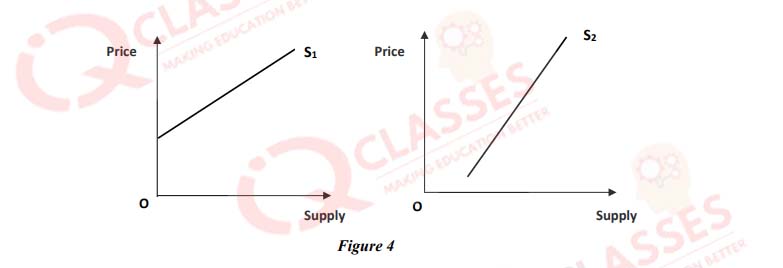
(54)
-
In figure 4:
- S1 supply curve indicates higher price elasticity of supply than S2
- S1 indicates relatively elastic supply and S2 is for inelastic supply
- S1 is for elastic supply and S2 indicates relatively inelastic supply
- All of the above
Solution
.jpg)
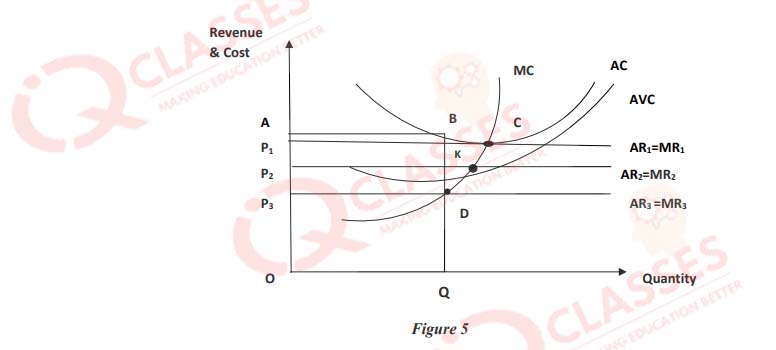
(55)
Choose the correct statements:
-
In figure 5:
- C is an equilibrium point, but D is not.
- C is shut down point, D is break-even point
- C is break-even point, D is shut down point.
- None of the above
Solution
.jpg)
-
In figure 5:
- Firm enjoys normal profit at point C.
- Firm enjoys normal profit at point D.
- Firm enjoys supernormal profit at B
- Firm enjoys supernormal profit at K
Solution
2.jpg)
-
In figure 5:
- Area ABDP3 represents loss.
- Area P3DBA represents total fixed cost.
- Area OP3DQ represents total variable cost.
- All of the above
Solution
3.jpg)
(56)
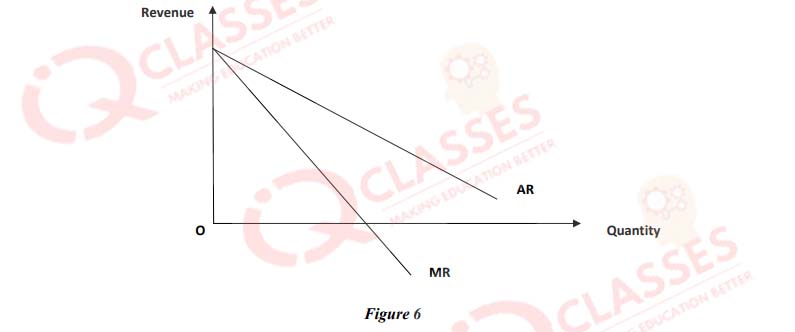
-
In figure 6, what is the slope of AR curve and MR curve?
- AR = 2MR
- MR = 2AR
- Slope of AR = 2 × Slope of MR
- Slope of MR = 2× slope of AR
Solution
.jpg)
(57)
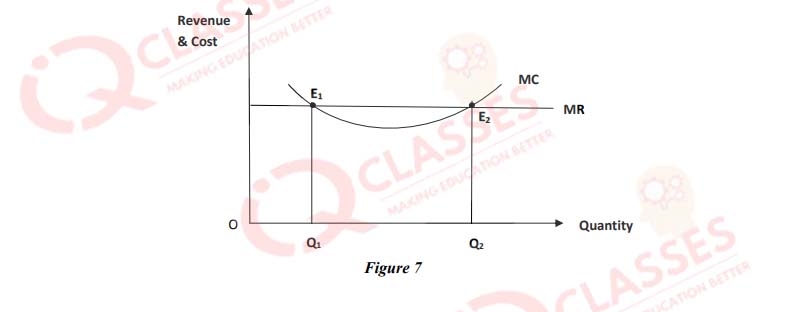
-
In figure 7, what is the condition of equilibrium?
- Necessary condition of equilibrium has been satisfied at E2 only
- Necessary and sufficient conditions of equilibrium have been satisfied at E2 only
- Sufficient condition has been satisfied at E1 only
- Necessary and sufficient conditions have been satisfied at E1 only
Solution
.jpg)
(58) When the price of a good falls by 7%, its quantity demanded rises from 40 units to 50 units. What will be the Price elasticity of demand for this good?
- 2.84
- 2.85
- 2.86
- 3.57
Solution
.jpg)
(59) When the price of a commodity falls by 2 per unit, its quantity demanded increases by 10 units. Its price elasticity of demand is (-) 1. Initial quantity demanded at previous price, `10, was –
- 49 units
- 50 units
- 51 units
- 52 units
Solution
.jpg)
(60) The price elasticity of demand for a commodity is (-) 1.5. When its price falls by 1, its quantity demanded rises from 30 units to 33 units. What was its previous price?
- 15.25
- 15.50
- 15.75
- None of the above
Solution
.jpg)
(61) A consumer buys 200 units of a good at a price of 5 per unit. When the price changes, he buys only 100 units. If price elasticity of demand is 2, the changed price will be:
- 5.75
- 6.25
- 6.75
- 7.25
Solution
.jpg)
(62) A consumer buys 80 units of a good at a price of 8 per unit. Price falls to 6 per unit. How much quantity will the consumer buy at a new price if ep = (-) 2?
- 100 units
- 110 units
- 120 units
- 130 units
Solution
.jpg)
(63) Based on the data given in the table, calculate the AFC and AVC
| Units of Output | 0 | 3 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cost () | 50 | 80 | 120 |
-
AFC for 0, 3 & 5 units will be -
- 0, 16.67, 10.00
- ∞, 16.00, 10.67
- 0, 16.00, 10.67
- ∞, 16.67, 10.00
Solution
1.jpg)
-
AVC for 0, 3 & 5 units will be –
- ∞, 10, 14
- 0, 10.1, 14.01
- ∞, 10.1, 14,01
- 0, 10, 14
Solution
2.jpg)
(64) Based on the data given in the table, calculate the TC and MC
| Output (Units) | AC | TC | MC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | --- | --- |
| 2 | 15 | --- | --- |
| 3 | 20 | --- | --- |
-
TC will be –
- 40, 60, 90 respectively
- 80, 60, 90 respectively
- 20, 30, 60 respectively
- 40, 60, 120 respectively
Solution
1.jpg)
-
MC will be –
- 0, 10, 20 respectively
- 20, 10, 30 respectively
- 10, 20, 30 respectively
- ∞, 10, 20 respectively
Solution
2.jpg)
(65) Based on the data given in the table below, find the product pricing\
| Output (Units) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR () | 0 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 |
-
The product price facing the firm is –
- 6
- 8
- 10
- None of the above
Solution
.jpg)
(66) Ramu is a sole producer and a seller of AC. He sells the product at a high price in Delhi and at a low price in Mussoorie.
-
What kind of a market structure is this?
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopsony
Solution
1.jpg)
-
He is able to sell the product at a higher price in Delhi because:
- Demand is elastic
- Demand is inelastic
- Unit elastic
- None of the above
Solution
2.jpg)
-
The characteristic of this market is:
- Price discrimination
- Product differentiation
- None of the above
- Both 1 and 2
Solution
3.jpg)
(67) A famous English economist believed that agricultural output would eventually stop growing, as more labour is added added to land that was fixed in quantity
-
Which law is applicable in the given context?
- Law of Variable proportion
- Law of Diminishing marginal utility
- Say’s law
- None of the above
Solution
1.jpg)
-
Which of the following statements is Correct in the given context?
- This law is applicable when the state of technology is given and remains unchanged
- This law is applicable in long run
- Variable factors are not equally efficient
- All inputs can vary
Solution
2.jpg)
-
Which of the following is a variable factor in the context of the statement given above?
- Land
- Labour
- Capital
- Entrepreneur
Solution
3.jpg)
(68) Due to the pandemic the prices of vegetables and fruits have increased but the demand for quantity has not fallen.
-
What is the reason for the demand remaining the same?
- Demand for food is inelastic since food is a necessity
- Demand for food is elastic
- Demand is for the inferior goods
- Demand is for the luxury goods
Solution
1.jpg)
-
What are the exceptions to the Law of Demand?
- Emergences
- Quality-Price relationship
- Veblen goods
- All of the above
Solution
2.jpg)
-
Which of the following statements pertains to Law of Demand?
- There is a direct relationship between price and quantity demanded
- There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
- There is a direct relationship between price and quantity demanded, other things remain the same
- There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, other things remain the same
Solution
3.jpg)