Class 12 ISC term1 Physics Specimen 2022
BOARD -
CLASS -
SUBJECT -
ISC
12th
PHYSICS
Paper Pattern for MCQ Term-I
TIME -
MARKS -
90 min
70
Visit CISCE OFFICIAL PAGE for Regualtions and Syllabus of Class 12th ISC
Solved Specimen Paper Semester-I 2021
Q.1 The ratio of forces between two small spheres having a constant charge 'q' when placed in air to when placed in a medium of dielectric constant K, is;
- 1: K
- K : 1
- 1: K2
- K2 :1
Solution
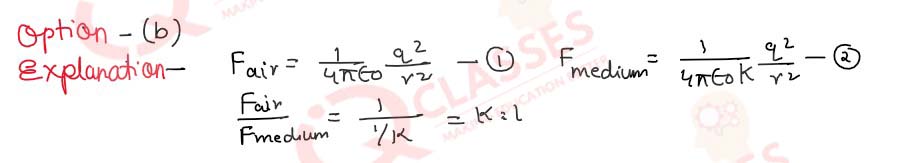
Q.2 When a soap bubble is given a positive charge, then its radius:
- Decreases
- Increases
- Remains unchanged
- Nothing can be predicted as information is insufficient
Solution

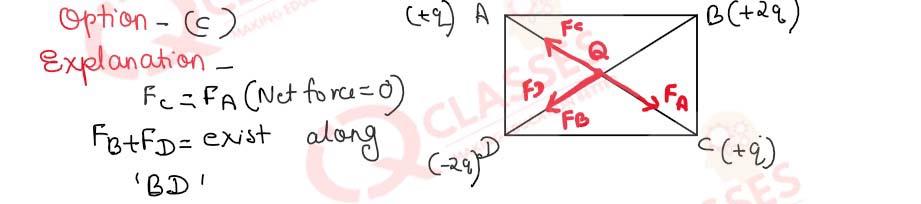
Q.3 Four charges are arranged at the corners of a square ABCD , as shown in the adjoining figure. The force on the charge 'Q' kept at the centre 0 is:
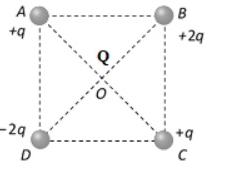
- Zero
- Along the diagonal AC
- Along the diagonal BD
- Perpendicular to side AB
Solution
Q.4 The surface charge density of a conductor, in the absence of another conductor:
- Is proportional to the charge on the conductor and its surface area
- Inversely proportional to the charge and directly proportional to the surface area
- Directly proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the surface area
- Inversely proportional to the charge and the surface area
Solution

Q.5 Which of the following is not the characteristic of resonance in an LCR series circuit?
- XL = XC
- ωL = 1 / ωC
- 2πfL = 2πfC
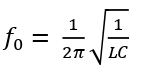
Solution

Q.6 A graph showing variation in impedance Z of a series LCR circuit, with frequency f of alternating emf applied to it is shown below. What is the minimum value of this impedance?
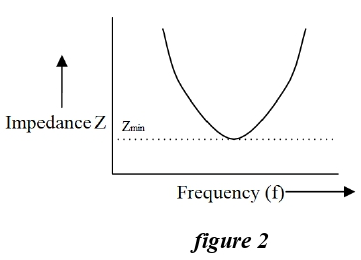
- R
- Z = √ R2 + (XL - XC)2
- Zmin =
- XL = XC
Solution
Q.7 An electric dipole of moment p⃗ is placed in a uniform electric field E⃗. It has maximum (negative) potential energy when the angle between p⃗ and E⃗ is:
- π/2
- zero
- π
- 3&pi / 2
Solution
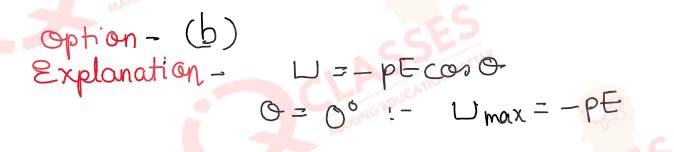
Q.8 A charge placed at a distance from a short electric dipole in the end-on position experiences a force F. If the distance is halved, then the force will become:
- 4F
- 8F
- F/4
- F/8
Solution
Q.9 In figure 3 given below, Electric field intensity 'E' at a point P, at a perpendicular distance `r' from an infinitely long line charge X'X having linear charge density is given by:
- E = (1⁄ 4π∊0)2λ ⁄r2
- E = (1⁄ 4π∊0)2λ ⁄r
- E = (1⁄ 4π∊0)λ ⁄r2
- E = (1⁄ 4π∊0)λ ⁄r
Solution
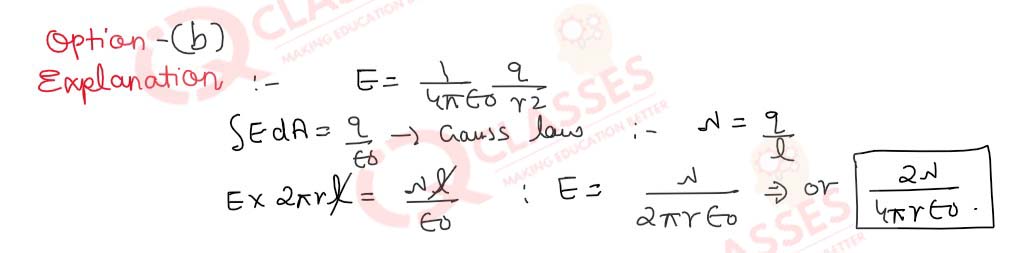
Q.10 Three capacitors, each of capacitance C, are connected in series. Their equivalent capacitance is Cs. The same three capacitors are now connected in parallel. Their equivalent capacitance becomes Cp. The ratio of Cp to Cs is:
- 9 : 1
- 1 : 9
- 3 : 1
- 1 : 3
Solution
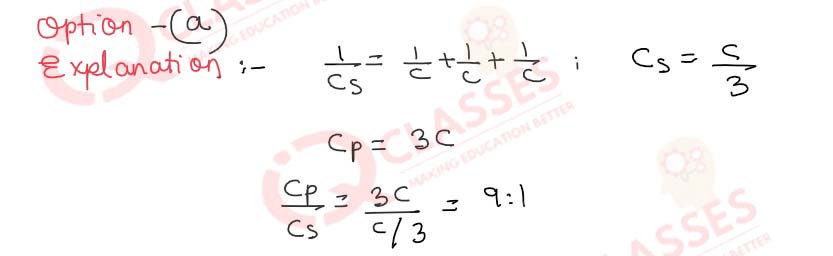
Q.11 The charges q1 = 3μF, q2 = 4μF and q3 = -7μF are placed on the circumference of a circle of radius 1.0m as shown in the figure below. What is the value of charge q4 placed on the same circle if the potential at the centre is?
- -4μF
- -3μF
- 7μF
- 0
Solution

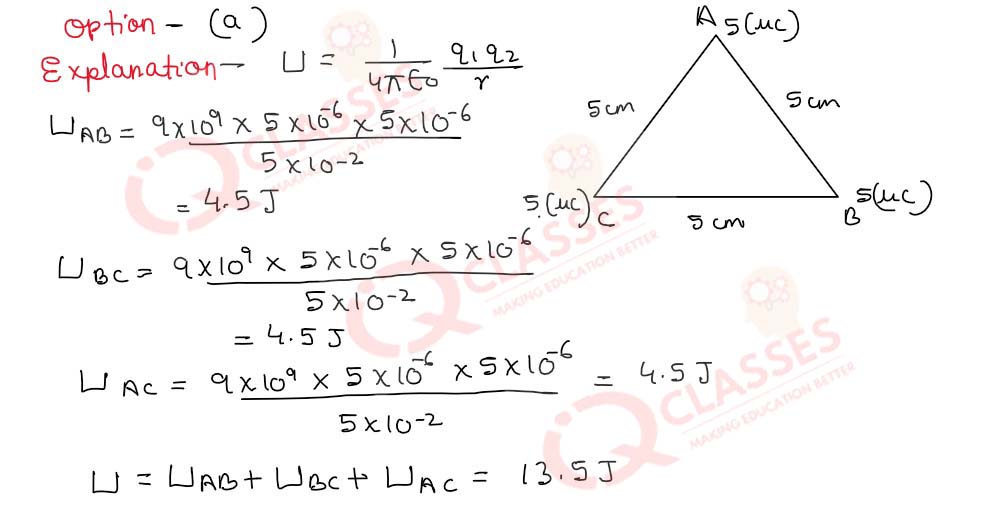
Q.12 Three equal charges of 5.0micro-coulomb each, are placed at the three vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 5.0cm each. The electrostatic potential energy of the system of charges is:
- 13.5 J
- 17.5 J
- 27 J
- 15J
Solution
Q.13
Three capacitors C1 =3μF, C2 = 6μF and C3 = 10μF are
connected to a 50V battery as shown in the figure below:
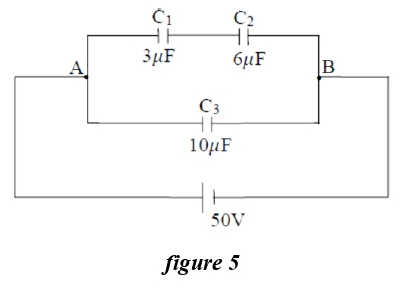 The equivalent capacitance of the circuit between point A and B and the charge on C1 are...
The equivalent capacitance of the circuit between point A and B and the charge on C1 are...
- 12μF, 150C
- 4.75μF, 100C
- 12μF, 100C
- 4.75μF, 150C
Solution

Q.14 A substance behaves like a magnet only if there are:
- at least some tiny current loops within the magnet
- stationary charges within the magnet
- magnet within the magnet
- none of these
Solution

Q.15 A straight long wire is turned into a loop of radius R = 10 cm, as shown in figure 6 below. If a current I = 16 A is passed through the wire, then the magnetic field at the centre of the loop is:
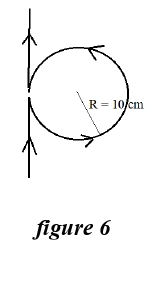
- 3.4 x 10-5T
- 6.8 x 10-5T
- 1.7 x 10-5T
- 5.1 x 10-5T
Solution

Q.16 The current in the circuit shown in figure 7 below, will be:
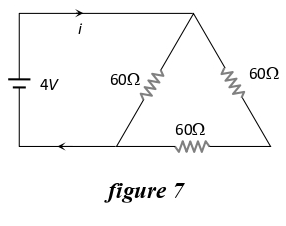
- 1/45A
- 1/15A
- 1/10A
- 1/5A
Solution
Q.17 A cell of e.m.f. E is connected to an external resistance R. The potential difference across [1] cell is V. The internal resistance of cell will be:
- (E-V)R ⁄ E
- (E-V)R ⁄ V
- (V-E)R ⁄ V
- (V-E)R ⁄ E
Solution
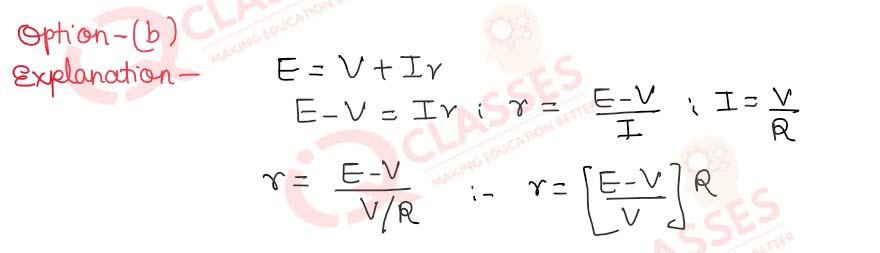
Q.18 The figure 8 given below shows currents in a part of an electric circuit. The current i is:
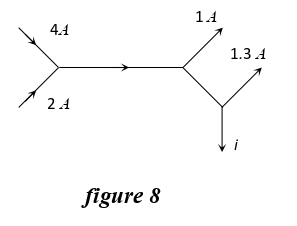
- 1.7 A
- 3.7 A
- 2.7 A
- 4.7 A
Solution
Q.19 n identical cells each of e.m.f. E and internal resistance r are connected in parallel. An external resistance R is connected in series to this combination. The current through R is:
- nE ⁄ R+nr
- nE ⁄ nR+r
- E ⁄ R+nr
- nE ⁄ R+r
Solution

Q.20 The circuit shown in figure 9 below is used to compare the e.m.f. of two cells E1 and EE2where E2 > E1. The null point is at C when the galvanometer is connected to E1. When the galvanometer is connected to E2, the null point will be:.
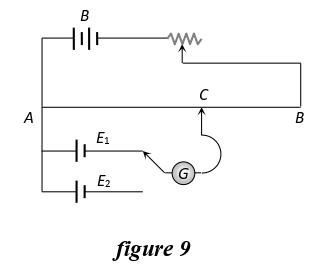
- To the left of C
- To the right of C
- At C itself
- At C itself
Solution

Q.21 Figure 10 given below shows a graph of emf ‘ε’ generated by an ac generator verses time. What is the frequency of the emf?
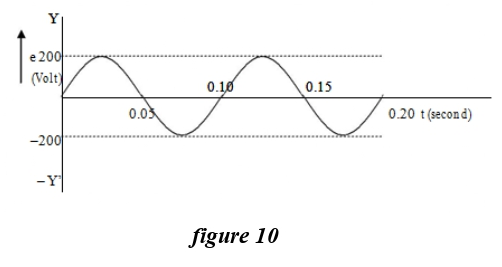
- 10 Hz
- 0.10 Hzv
- 20 Hz
- 50 Hz
Solution
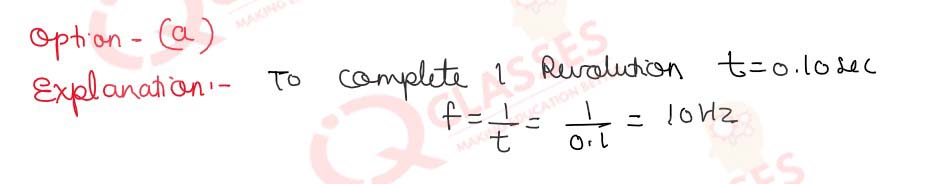
Q.22 If m, e, τ and n respectively represent the mass, charge, average relaxation time and density of the electron, then what will be the resistance of a wire of length l and area of cross-section A?
- ml⁄ne2τ A
- mτ 2A⁄ne2l
- ne2τ A ⁄2ml
- ne2 A ⁄2mτl
Solution
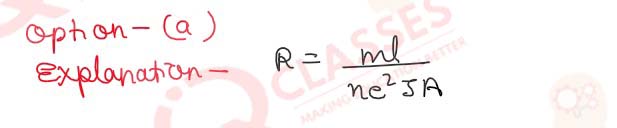
Q.23 The drift velocity of a current carrying conductor is v. What will be the drift velocity if the current flowing through the wire is doubled?
- v / 4
- v / 2
- 2v
- 4v
Solution
Q.24 The resistance of a wire is 10Ω. It is stretched so that its length becomes four times. What will be the new resistance of the wire?
- 40Ω
- 160.0Ω
- 120Ω
- 80.0Ω
Solution

Q.25 What is the angle between the current element 𝑑𝑙⃗ and the magnetic flux density B⃗ at point ‘P’ in the figure 11 given below?
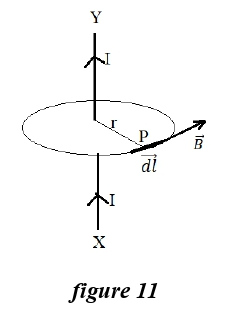
- Parallel to each other
- Perpendicular to each other
- Normal to each other
- Any angle between them is possible
Solution
Q.26 An A.C. generator generating an e.m.f of ε = 300 sin (100π) t is connected to a series combination of 16µ F capacitor, 1H inductor and 100 Ω resistor. What is the frequency of A.C.?
- 100 Hz
- 50 Hz
- 300 Hz
- 25 Hz
Solution
Q.27 Four identical cells each having an e.m.f. of 4V are connected in parallel. What will be the e.m.f. of this combination?
- 1 V
- 16 V
- 1/4V
- 4 V
Solution

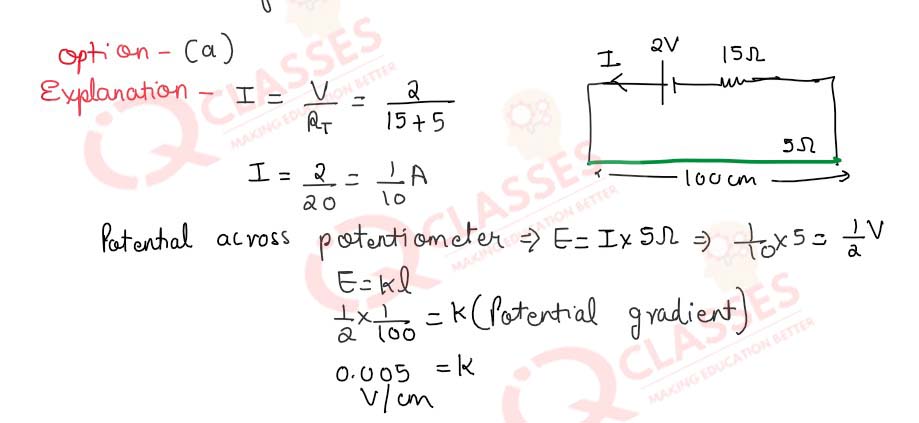
Q.28 A 2 volt battery, a 15Ω resistor and a potentiometer of 100 cm length, all are connected in series. If the resistance of potentiometer wire is 5Ω, then the potential gradient of the potentiometer wire is…
- 0.005 V/cm
- 0.05 V/cm
- 0.02 V/cm
- 0.2 V/cm
Solution
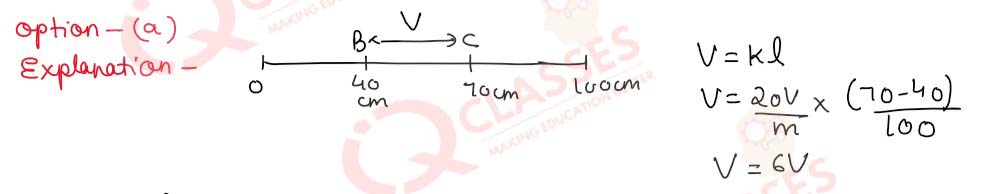
Q.29 The potential gradient along the length of a uniform wire is 20 volt/metre. B and C are the two points at 40cm and 70cm point on a meter scale fitted along the wire. What is the potential difference between B and C?
- 6 V
- 0.4 V
- 0.6 V
- 4 V
Solution
Q30. In an experiment of meter bridge, a null point is obtained at the centre of the bridge wire. When a resistance of 5 is connected in one gap, what is the value of resistance in the other gap?
- 10Ω
- 5Ω
- 1/5Ω
- 500Ω
Solution
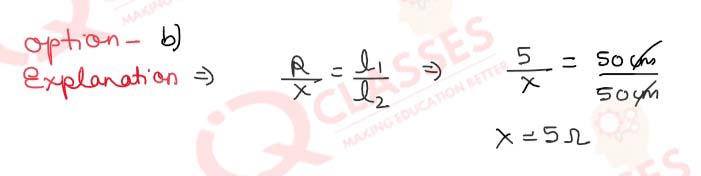
Q.31 What is the locus of an electron, projected perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field?
- Circle
- Right bisector
- Parabola
- Straight line
Solution

Q.32 Which of the following is the right expression to define the magnetic field B?
- F⃗ = q(v⃗ x B⃗)
- F⃗ = B(I⃗ x l⃗)
-
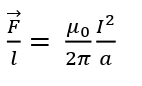
- B = μ n i
Solution
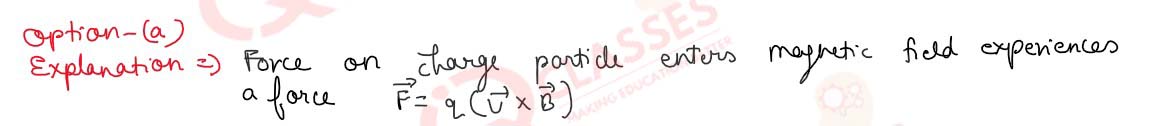
Q.33 What is the SI (base unit) unit of permeability?
- kg m s-2A-2
- kg m2s-2A-2
- kg m2 s A-2
- kg m s2A-2
Solution
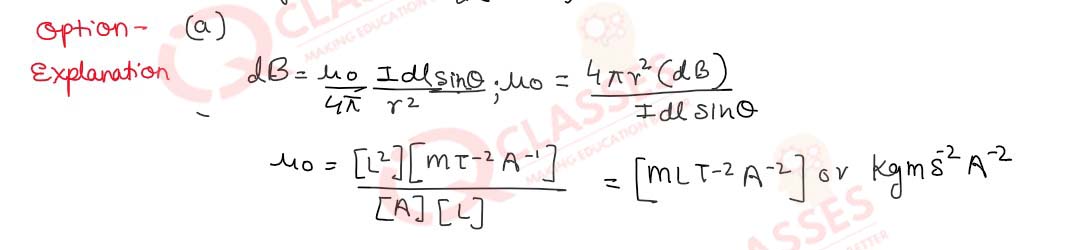
Q.34 The loss of power in a transformer can be reduced by:
- Increasing the number of turns in primary.
- Using solid core made of steel
- Increasing ac voltage applied to primary.
- Using a laminated core of soft iron
Solution

Q.35 Which is the most harmful radiation entering the atmosphere of earth from outer space?
- X - Rays
- Visible rays
- Gamma radiations
- Radio waves
Solution

Q.36 Radio waves and gamma waves are both transverse in nature and electromagnetic in character and have the same speed in vacuum. In what respects are they different?
- Frequency
- wavelength
- Both, (a) and (b)
- None of these
Solution

Q.37 Which of the following groups belongs only to the electromagnetic spectrum?
- alpha rays, beta rays, gamma rays
- ultra-sonic rays, radio waves, infra red rays
- gamma rays, cathode rays, X-rays
- X-rays, radio waves, infra red rays
Solution

Q.38 Which electromagnetic radiation has wavelength greater than that of X-rays and smaller than that of visible light?
- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infra Red Rays
- Ultra Violet Rays
Solution

Q.39 (i) A parallel plate capacitor of plate area A=600cm2and plate separation d=2.0 mm is connected to a dc source of 200V (i)What is the magnitude of the uniform electric field E between the plates?
- E = 1.0 x 105 V/m
- E = 1.0 x 107 V/m
- E = 0.5 x 105 V/m
- E = 0.5 x 107 V/m
Solution
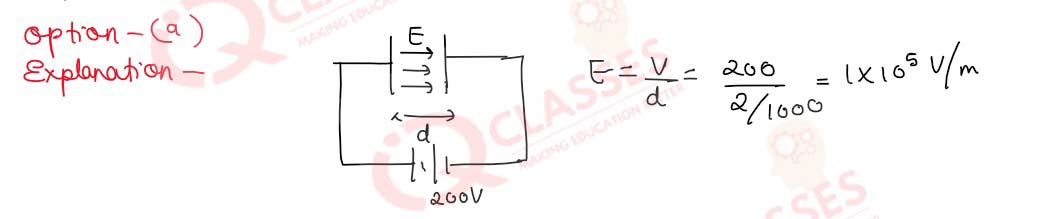
Q.39 (ii) What is the charge density σ on any one of the two plates?
- σ = =8.85 x 10-7 C/m2
- σ = 8.85 x 10-9 C/m2
- σ = 4.45 x 10-7 C/m2
- σ = 4.45 x 10-9 C/m2
Solution
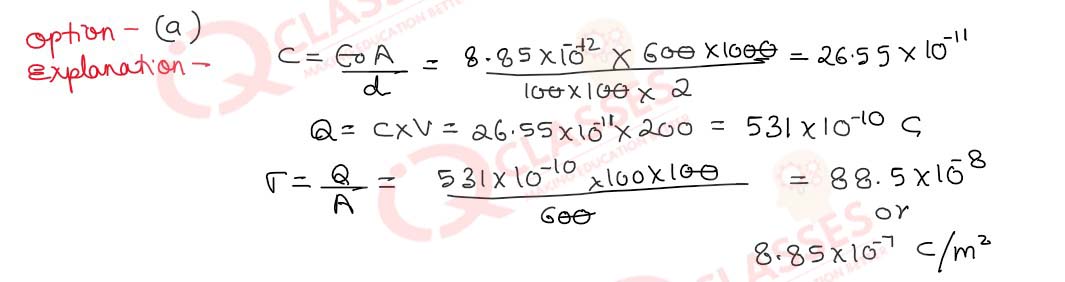
Q.40 (i)
A torch bulb rated as 4.5 W, 1.5 V is connected as shown in figure 12 given below. 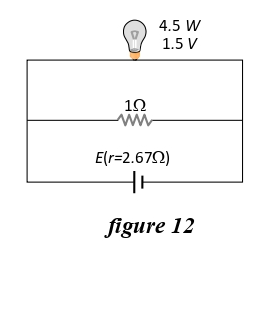 (i)What should be the e.m.f.
of the cell required to make this bulb glow at full intensity?
(i)What should be the e.m.f.
of the cell required to make this bulb glow at full intensity?
- 4.5 V
- 1.5 V
- 2.67 V
- 13.5 V
Solution
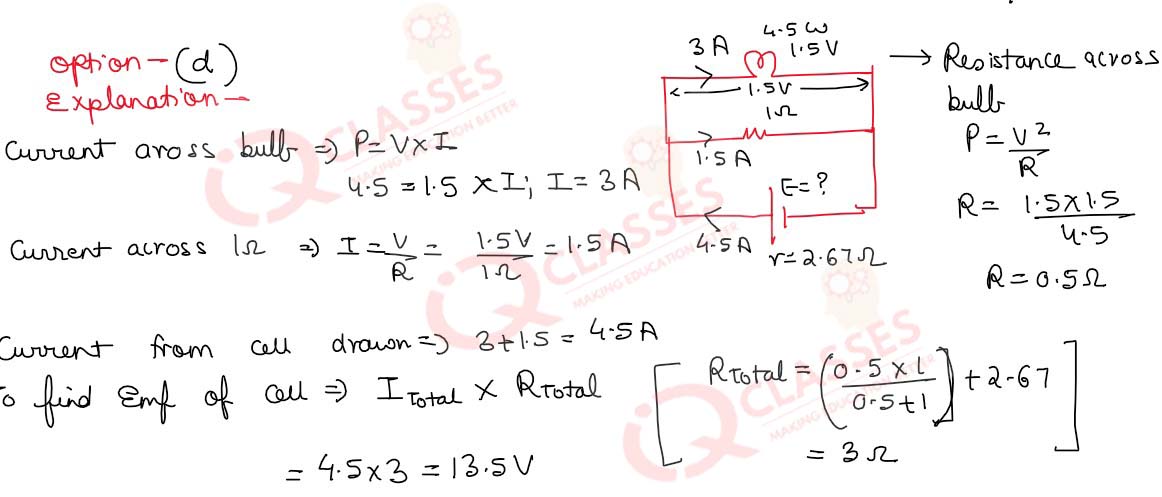
Q.40(ii) What is the current passing through 1Ω resistor?
- 4.5 A
- 1.5 A
- 2.67 A
- 13.5 A
Solution
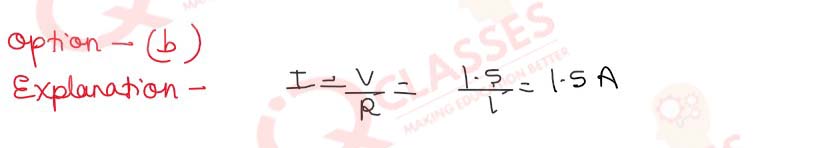
Q.41 (i) The specific resistance of manganin is 50 x 10-8 Ω mThe resistance of a cube of length 50m will be:
- 10-6 Ω
- 2.5 x 10-5Ω
- 2 x 10-6 Ωm
- 50 x 1010 Ωm
Solution
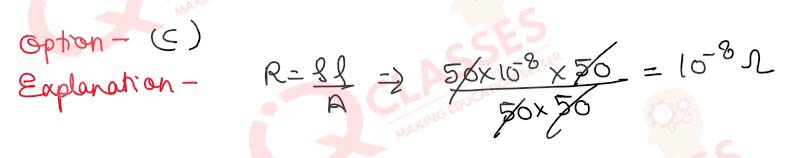
Q.41(ii) The specific resistance of the combination of two cubes of length 50m in series will be:
- 10-6 Ω
- 2.5 x 10-5Ω
- 2 x 10-6 Ωm
- 50 x 1010 Ωm
Solution

Q.42 (i)
A metallic rod CD rests on a thick metallic wire PQRS with arms PQ and RS parallel
to each other, at a distance l = 50 cm, as shown in figure 13 below. A uniform
magnetic field B = 0.1T acts perpendicular to the plane of this paper, pointing
inwards into the plane. (i.e. away from the reader).The rod is now made to slide towards right, with a
constant velocity of v= 5.0 m/s.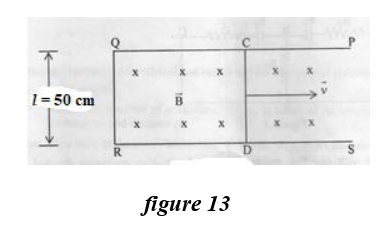 (i)How much emf is induced
between the two ends of the rod CD?
(i)How much emf is induced
between the two ends of the rod CD?
- 25.0 V
- 0.25 V
- 2.50 V
- .025 V
Solution
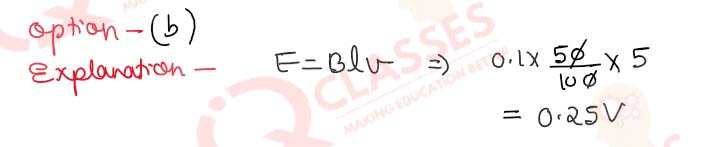
Q.42(ii) What is the direction in which the induced current flows?
- Along ‘CQRDC’
- Along the direction of motion of the conductor
- Along ‘CDRQC’
- Against the direction of motion of the conductor
Solution

Q.43 (i)
Study the diagram given below: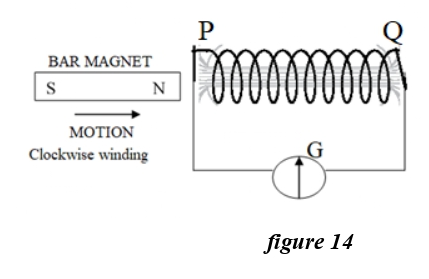 (i)The direction of the current
at end ‘P’ will be:
(i)The direction of the current
at end ‘P’ will be:
- Anti clockwise
- Clockwise
- Towards the magnet
- away from the magnet
Solution

Q.43(ii) The magnetic poles induced at the end ‘Q’ of the coil will be:
- North pole
- South pole
- Anti clockwise
- No pole
Solution

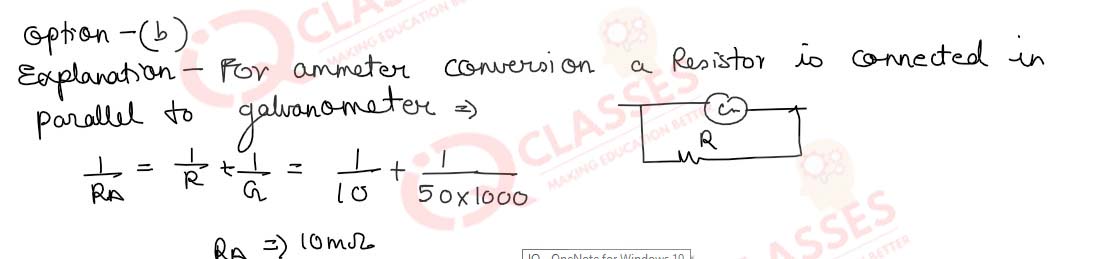
Q.44 (i) The resistance of a galvanometer is 50 Ω. It is converted into a voltmeter or an ammeter. Calculate the resistance of the voltmeter and ammeter to an accuracy of 2sf. Only with the mention below in the subparts.(i)A voltmeter using a 10 k Ω resistor is:
- 10050 Ω
- 10.050 kΩ
- 10000 Ω
- 10 kΩ
Solution

Q.44(ii) An ammeter using a 10 m Ω resistor is:
- 50 Ω
- 10 m Ω
- 0.0999 Ω
- 50. 0999 Ω
Solution
Q.45 (i)Two bulbs B1 and B2 are
connected in series with an source of emf 250V as shown in the figure 15 below. The labels on the bulbs
read 250V, 80W and 250V, 100W respectively
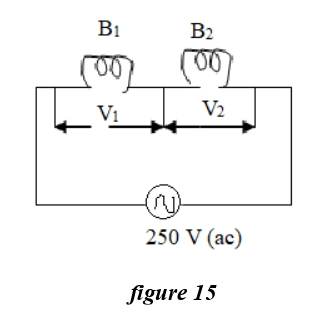 (i)What will
be the ratio of the resistance of the bulbs R1/R2?
(i)What will
be the ratio of the resistance of the bulbs R1/R2?
- 5 : 4
- 4 : 5
- 1: 1
- 5 : 3
Solution
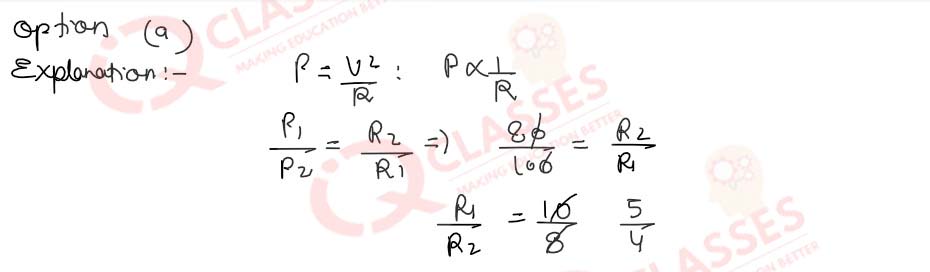
Q.45(ii)What will be the ratio of the power consumed (P1/P2) when connected in series?
- 5 : 4
- 4 : 5
- 1: 1
- 5 : 3
Solution
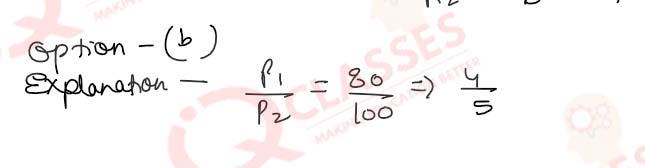
Q.45(iii)What is the ratio of the pd across the bulbs (V1/V2)?
- 5 : 4
- 4 : 5
- 1: 1
- 5 : 3
Solution
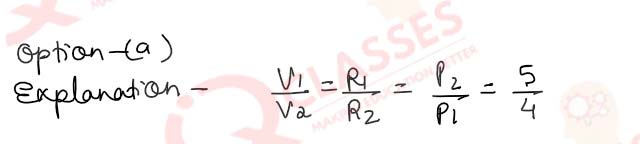
Q.46 (i) A 2 µF capacitor, 100 Ω resistor and 8 H inductor are connected in series with an ac source. At a certain frequency of about 40 Hz for this ac source, the current drawn in the circuit is maximum. If the peak value of e.m.f. of the source is 200V(i)What is the peak value of current in the circuit?
- 1.4 A
- 2.2 A
- 2.0 A
- 1.8 A
Solution
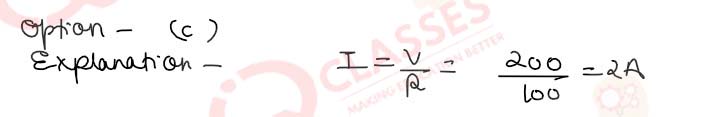
Q.46(ii)What is the phase relation between voltages across inductor and resistor?
- π/2 radian
- π/3 radian
- π/4 radian
- π radian
Solution
Q.46(iii)What is the phase difference between voltages across inductor and capacitor?
- π/2 radian
- π/3 radian
- π/4 radian
- π radian
Solution

Q.47 (i)Given below is a neat, labelled diagram to
obtain balancing condition of Wheatstone
bridge.  (i)Why is the key ‘K’ pressed before the key K1?
(i)Why is the key ‘K’ pressed before the key K1?
- There is no such requirement
- To avoid a back emf in the closed loops
- There is no current till the key ‘K’ is pressed
- None of these
Solution

Q.47(ii) What is the relation between the potential at ‘B’ and ‘D’, when the bridge is balanced?
- 𝑉𝐵 > 𝑉D
- 𝑉𝐵 < 𝑉D
- 𝑉𝐵 = 𝑉D
- 𝑉𝐵 ≥ 𝑉D
Solution

Q.47(iii)What is the galvanometer current when the bridge is balanced?
- Ig flows from ‘B’ to ‘D’
- Igflows from ‘D to ‘B’
- Ig has no significance in this case
- Ig=0
Solution

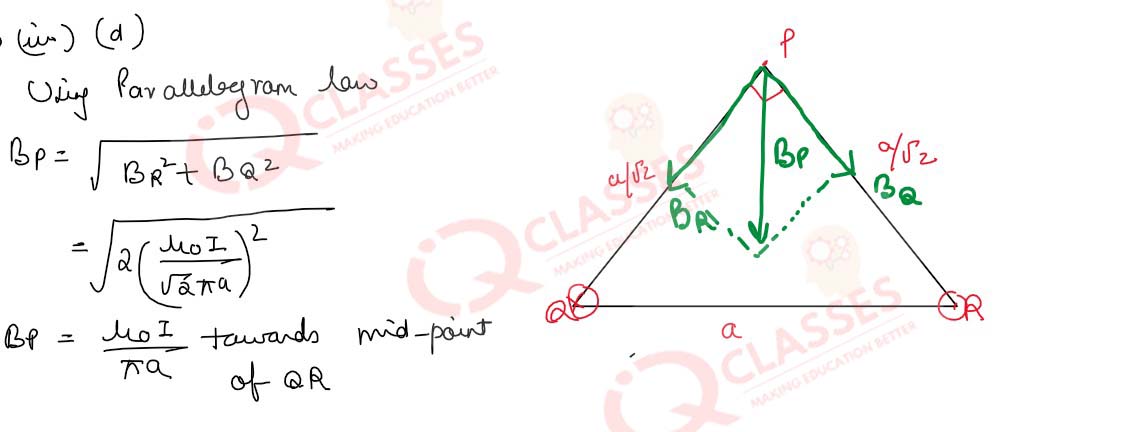
Q.48 (i)Figure 17 shows a right-angled isosceles
triangle PQR having its base equal to ‘a’.A current of 1.0 A is passing downwards along a thin straight
wire cutting the plane of a paper normally as shown at Q. Likewise, a similar wire carries an equal
current moving normally upwards at R. Assume the wire is to be infinitely long.
 (i)The
magnitude and the direction of the magnetic induction B at P due to wire at ‘Q’:
(i)The
magnitude and the direction of the magnetic induction B at P due to wire at ‘Q’:
Solution
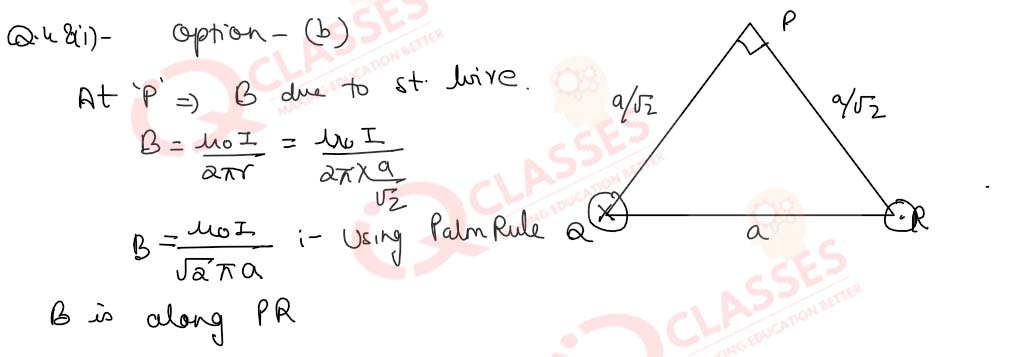
Q.48(ii) The magnitude and the direction of the magnetic induction B at P due to wire at ‘R’:
Solution

Q.48(iii)The net magnitude and the direction of the magnetic induction B at P:
Solution
Q.49 (i)An alternating e.m.f of 100V is applied to a circuit containing a resistance of 40 Ω and an inductance L in series. The current is found to lag behind the voltage by an angle a = tan-1 ¾(i)The inductive reactance in this case is:
- 40 Ω
- 30 Ω
- 50 Ω
- 10√5 Ω
Solution
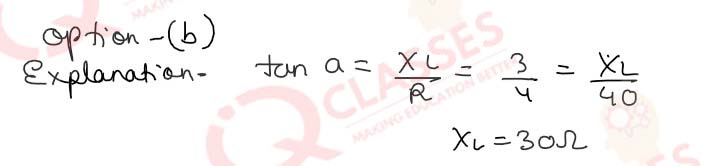
Q.49(ii) The impedance of the circuit is:
- 40 Ω
- 30 Ω
- 50 Ω
- 10√5 Ω
Solution
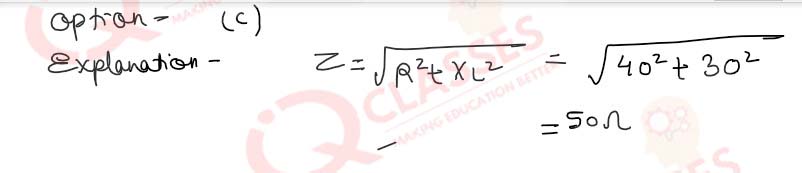
Q.49(iii)The current flowing through the circuit is:
- 2.5A
- 3.33A
- 2.0A
- 2√5 A
Solution
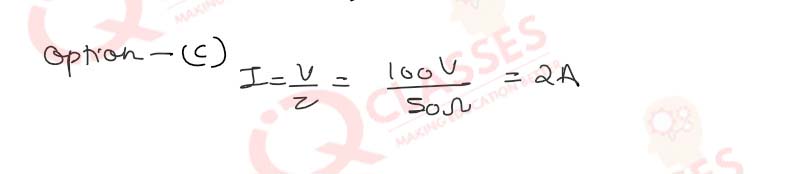
Q.49(iv)If the inductance has a value of 0.096 H, and π = 3.14, the approximate frequency of the applied e.m.f.
- 40 Hz
- 50 Hz
- 30 Hz
- None of these
Solution
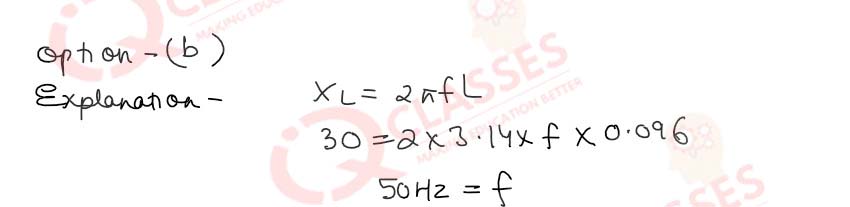
Q.50 (i)The teacher of Priti's school took the students on a study trip to a power generating station, located nearly 250 km away from the city. The teacher explained that electrical energy is transmitted over such a long distance to their city, in the form of alternating current (ac) raised to a high voltage. At the receiving end in the city, the voltage is reduced to operate the devices. As a result, the power loss is reduced. Priti listened to the teacher and asked questions about how the ac is converted to a higher or lower voltage. (i)What is the device used to change the alternating voltage to a higher or lower value?
- Transformer
- Rectifier
- Ammeter
- Voltmeter
Solution

Q.50(ii)What is the cause for power dissipation in the device referred to above?
- Hysteresis
- Eddy current
- Flux loss
- All of these
Solution
Q.50(iii)In the device used above, what is the relation between the power output and power input for an ideal case?
- Power output is less than power input.
- Power output is greater than power input
- Power output is equal to power input
- It depends upon the situation
Solution

Q.50(iv)What source input should be used in this device?
- A C source
- D C source
- Half wave rectifier
- Full wave rectifier
Solution




