Code is copied!
Question 7
Define a class to accept a number and check whether it is a SUPERSPY number or not. A number is called SUPERSPY if the sum of the digits equals the number of the digits.
Example l: Input: 1021
output: SUPERSPY number [SUM OF THE DIGITS = 1+0+2+1 =4, NUMBER OF DIGITS =4 ]
Example 2: Input: 125
output: Not an SUPERSPY number [1+2+5 is not equal to 3]
Solution:
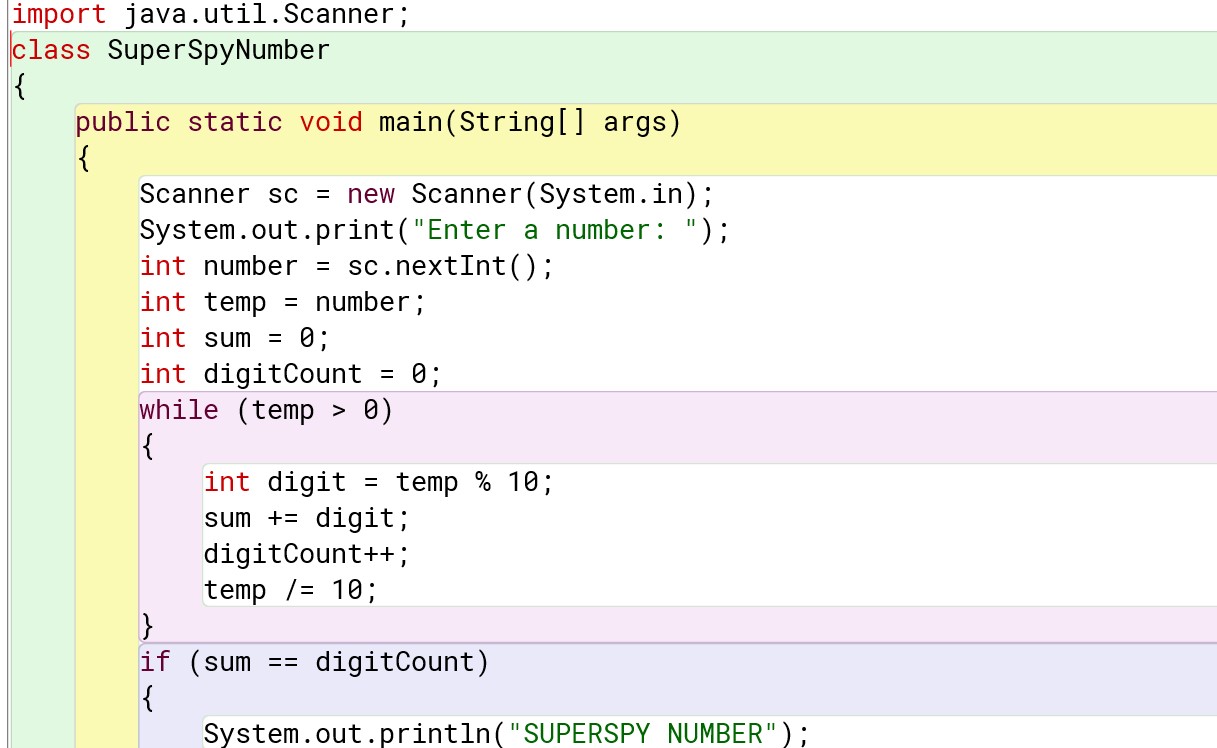 ,
,
import java.util.Scanner;
class SuperSpyNumber
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = sc.nextInt();
int temp = number;
int sum = 0;
int digitCount = 0;
while (temp > 0)
{
int digit = temp % 10;
sum += digit;
digitCount++;
temp /= 10;
}
if (sum == digitCount)
{
System.out.println("SUPERSPY NUMBER");
} else
{
System.out.println("NOT A SUPERSPY NUMBER");
}
}
}
Define a class to accept a number and check whether it is a SUPERSPY number or not. A number is called SUPERSPY if the sum of the digits equals the number of the digits.
Example l: Input: 1021
output: SUPERSPY number [SUM OF THE DIGITS = 1+0+2+1 =4, NUMBER OF DIGITS =4 ]
Example 2: Input: 125
output: Not an SUPERSPY number [1+2+5 is not equal to 3]
Solution:
 ,
,
import java.util.Scanner;
class SuperSpyNumber
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = sc.nextInt();
int temp = number;
int sum = 0;
int digitCount = 0;
while (temp > 0)
{
int digit = temp % 10;
sum += digit;
digitCount++;
temp /= 10;
}
if (sum == digitCount)
{
System.out.println("SUPERSPY NUMBER");
} else
{
System.out.println("NOT A SUPERSPY NUMBER");
}
}
}