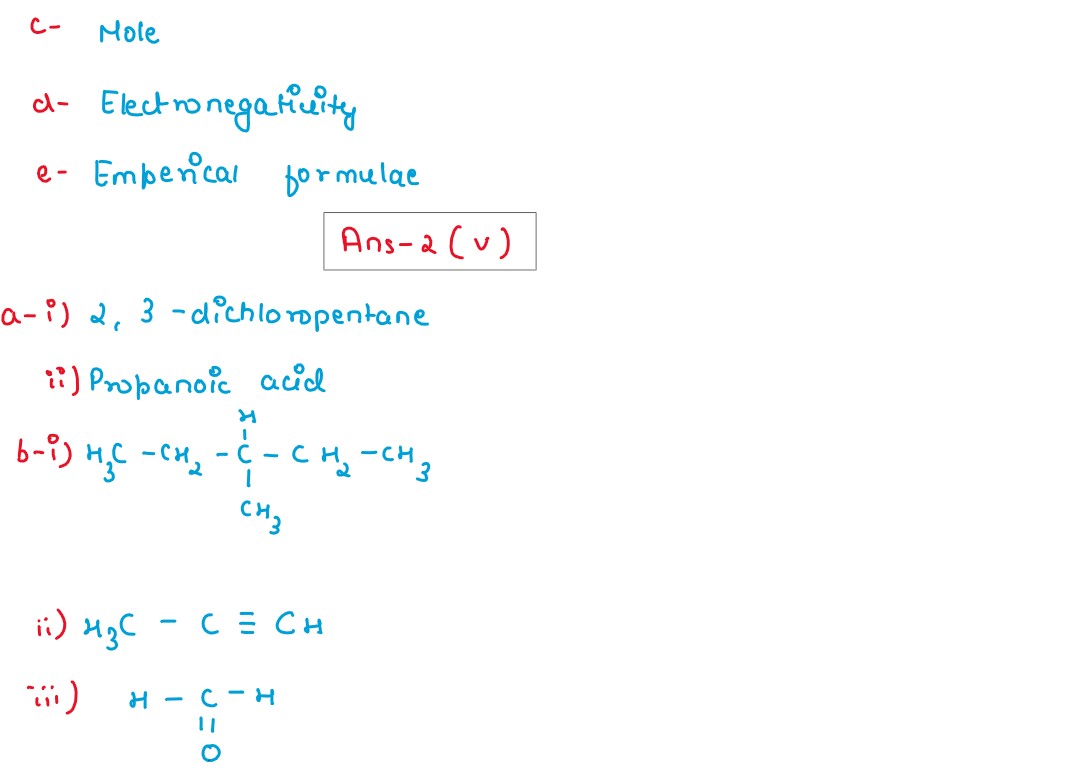
(i) The following sketch represents the electroplating of an Iron cup with Nickel metal. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
(a) During electroplating the iron cup is placed at the cathode. Why?
(b) Name the ion that must be present in the electrolyte.
(c) State one condition that is necessary to ensure that the deposit is smooth, firm and even.
(d) Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
(e) What change would you observe at the anode?
(ii) Match the Column A with Column B:

(iii) Complete the following sentences by choosing the correct:
(a) The salt that can be prepared by Direct Combination is ___ [FeCl2/FeCl3].
(b) The metallic oxide which can be reduced by using common reducing agent is ____ [Fe2O3/Al2O3].
(c) The metal nitrate which on thermal decomposition forms a black residue is ____. [zinc nitrate / copper nitrate]
(d) During the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution, if ______ electrodes, the colour of the electrolyte does not fade. [copper / platinum]
(e) The process of heating the concentrated ore in a limited supply or absence of air is _____. [roasting / calcination ]
(iv) State the terms for the following:
(a) The group obtained by removing one hydrogen atom from the parent alkane.
(b) Two metal plates or wires through which the current enters and leaves the electrolytic cell.
(c) The amount of substance which contains the same number of units as the number of atoms in carbon-12.
(d) The tendency of an atom to pull a shared pair of electrons towards itself in a compound.
(e) The formula which represents the simplest ratio between the atoms of elements present in a compound.
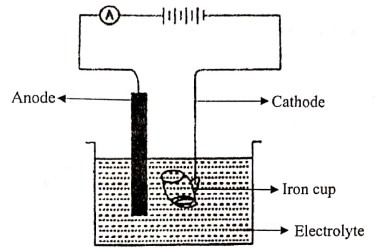
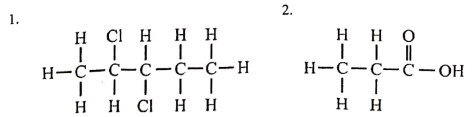
(v) (a) Give the IUPAC names of the organic compounds represented by the structural formulae given below:
(b) Draw the structural diagram for the following organic compounds:
1. 3-methyl pentane
2. propyne
3. methnal
Solution
 ,
, ,
,