Q1
Define the term current and state its S.I. unit.
solutions
solutions

Q2
Define the term electric potential. State it’s S.I. unit.
solutions
solutions

Q3
How is the electric potential difference between the two points defined? State its S.I. unit.
solutions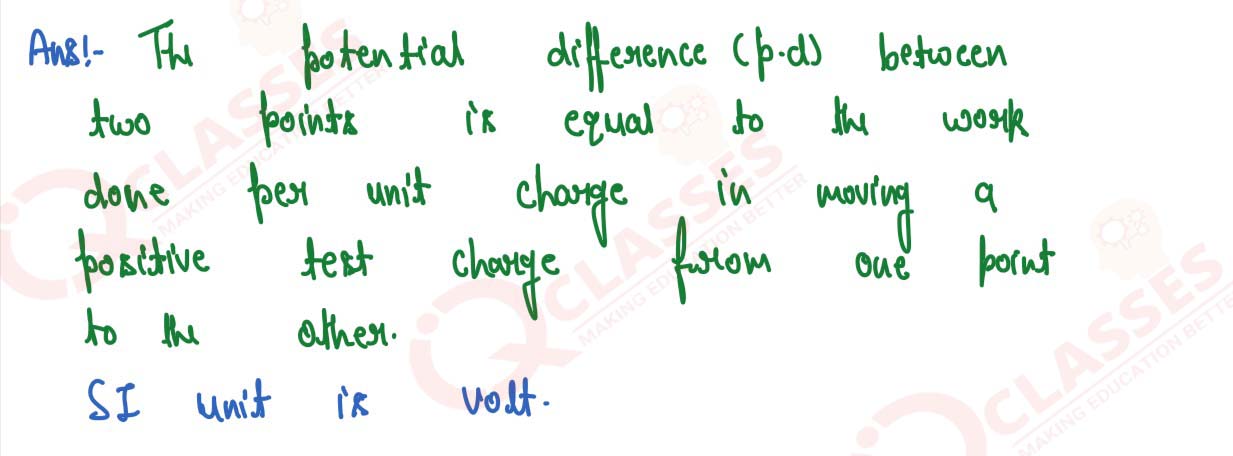
solutions

Q4
Explain the statement ‘the potential difference between two points is 1 volt’.
solutions
solutions

Q5
(a) State whether the current is a scalar or vector? What does the direction of current convey?
(b) State whether the potential is a scalar or vector? What does the positive and negative sign of potential convey?
solutions

(b) State whether the potential is a scalar or vector? What does the positive and negative sign of potential convey?
solutions


Q6
Define the term resistance. State its S.I. unit.
solutions
solutions

Q7
(a) Name the particles which are responsible for the flow of current in a metallic wire.
(b) Explain the flow of current in a metallic wire on the basis of movement of the particles named by you above in part (a).
(c) What is the cause of resistance offered by the metallic wire in the flow of current through it?
solutions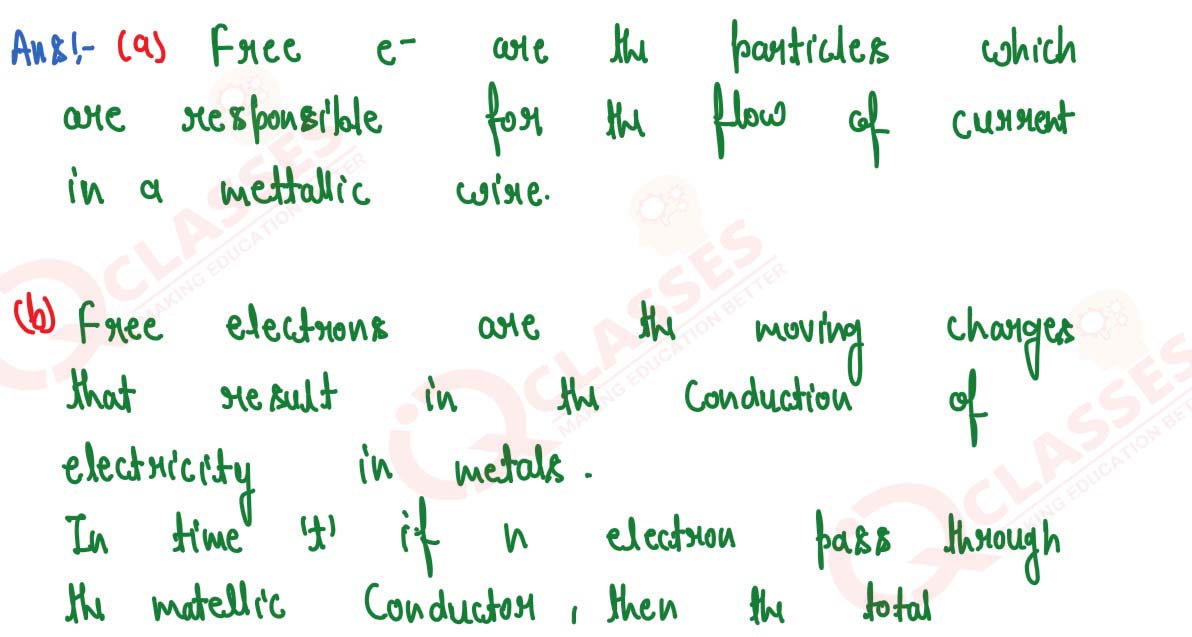


(b) Explain the flow of current in a metallic wire on the basis of movement of the particles named by you above in part (a).
(c) What is the cause of resistance offered by the metallic wire in the flow of current through it?
solutions



Q8
State Ohm’s law and draw a neat labelled circuit diagram containing a battery, a key, a voltmeter,
an ammeter, a rheostat and an unknown resistance to verify it.
solutions
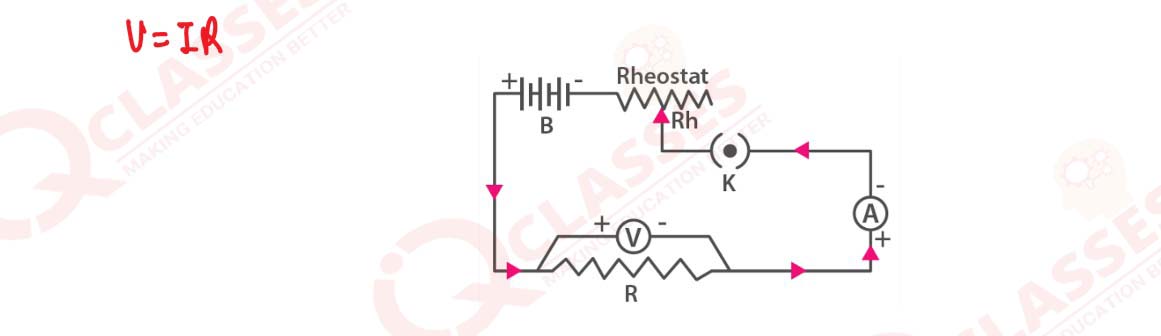
solutions


Q9
(a) Name and state the law which relates the potential difference and current in a conductor.
(b) What is the necessary condition for a conductor to obey the law named above in part (a)?
solutions

(b) What is the necessary condition for a conductor to obey the law named above in part (a)?
solutions


Q10
(a) Draw a V-I graph for a conductor obeying Ohm’s law.
(b) What does the slope of V-I graph for a conductor represent?
solutions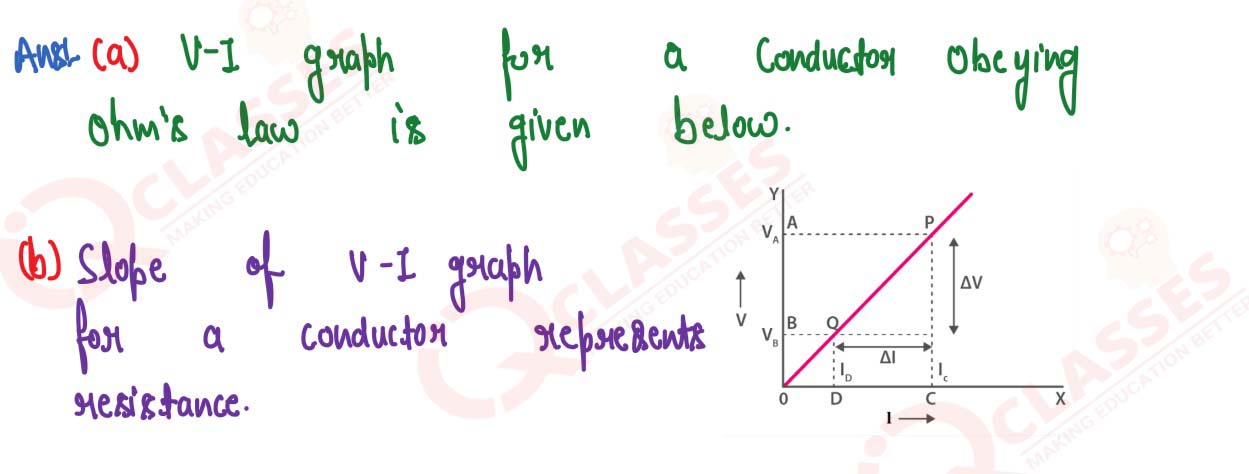
(b) What does the slope of V-I graph for a conductor represent?
solutions

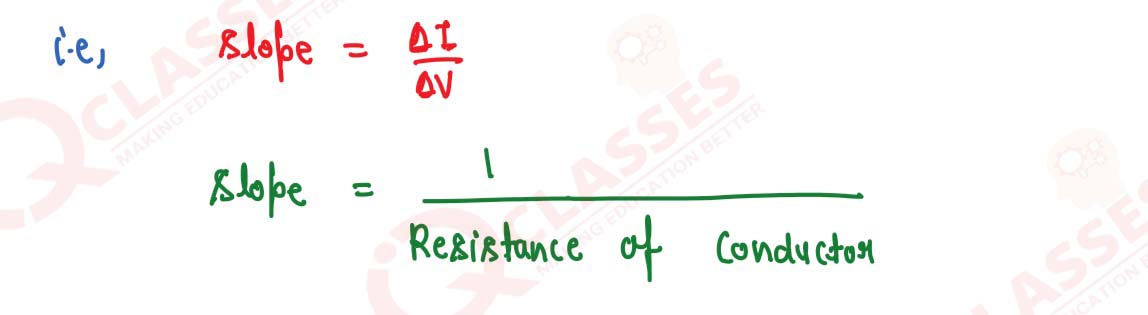
Q11
Draw a I-V graph for a linear resistor. What does its slope represent?
solutions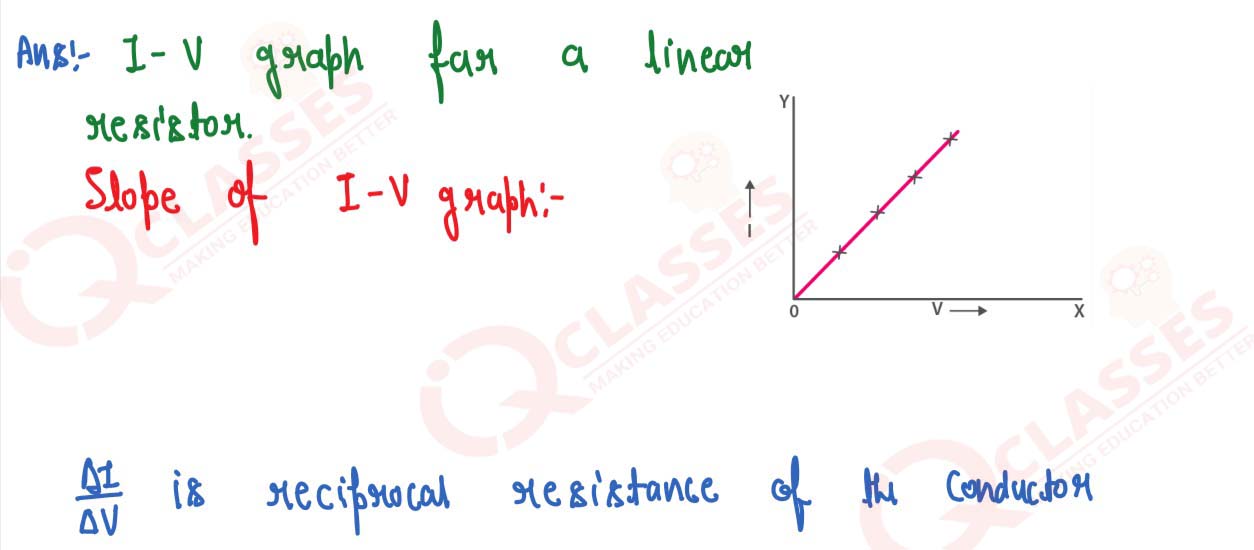
solutions


Q12
What is an ohmic resistor? Give one example of an ohmic resistor. Draw a graph to show its current –
voltage relationship. How is the resistance of the resistor determined from this graph?
solutions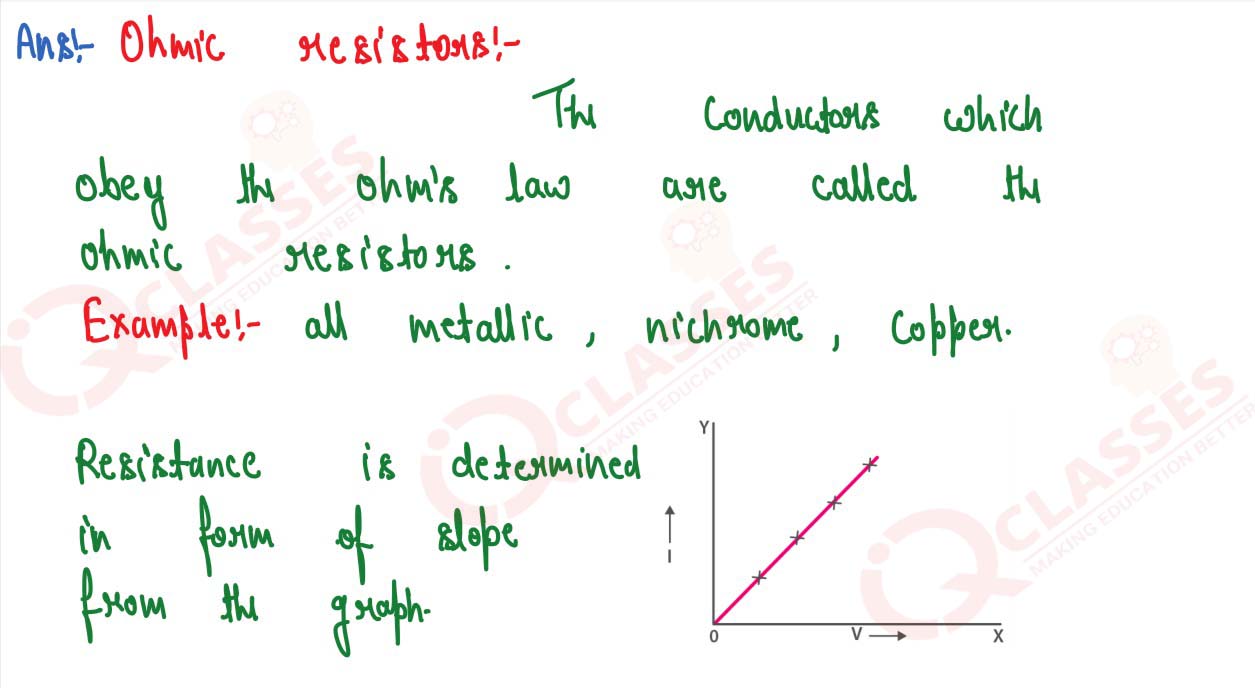
solutions

Q13
What are non-ohmic resistors? Give one example and draw a graph to show its current-voltage
relationship.
solutions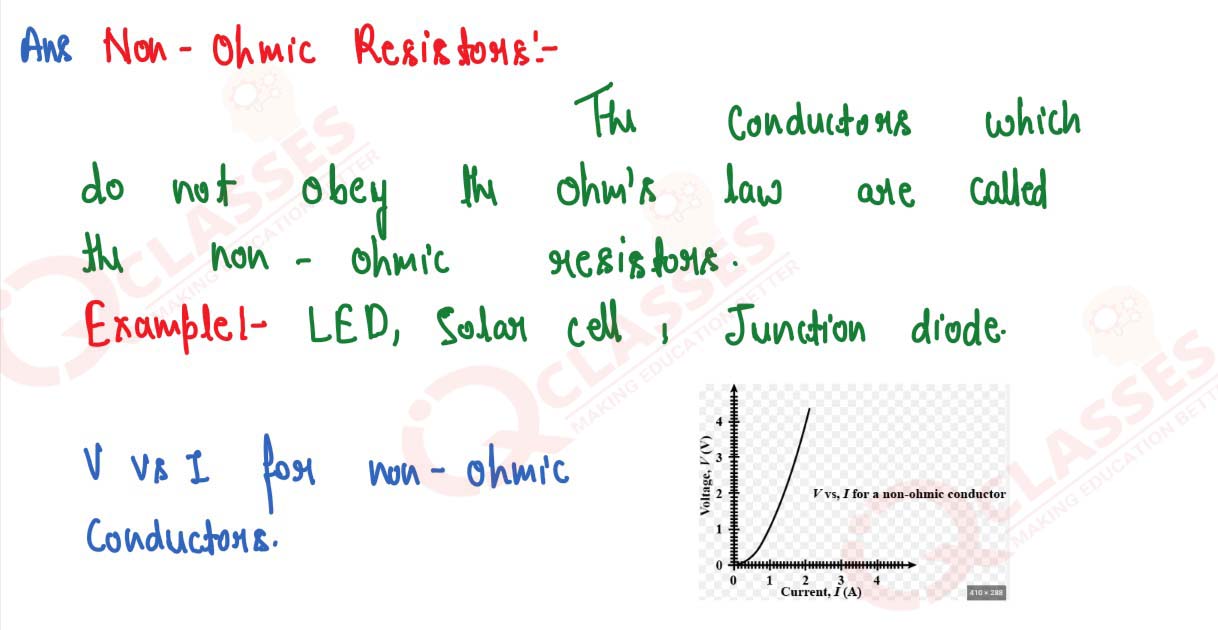
solutions

Q14
Give two differences between an ohmic and non-ohmic resistor
solutions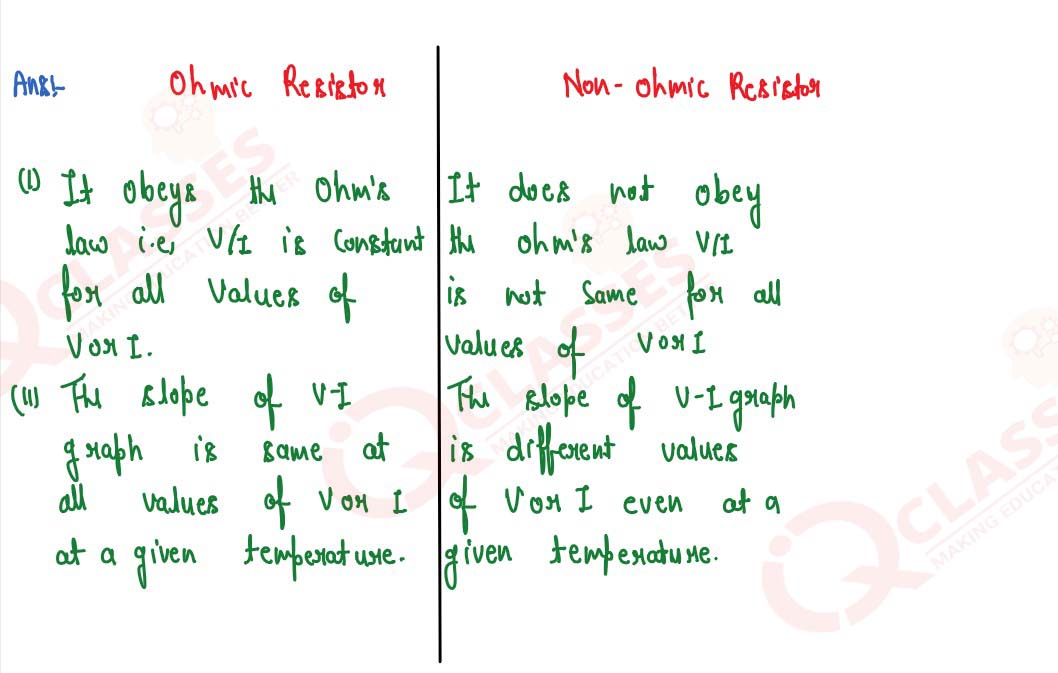
solutions

Q15
Fig. below shows the I-V characteristic curves for two resistors. Identify the ohmic and non-ohmic
resistors. Give a reason for your answer.
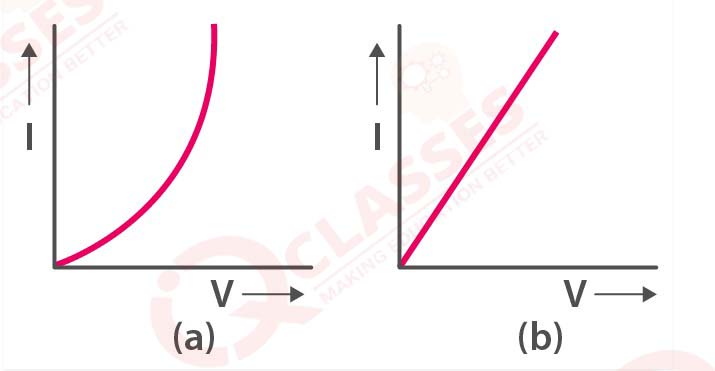
solutions

solutions

Q16
Draw a V – I graph for a conductor at two different temperatures. What conclusion do you draw from
your graph for the variation of resistance of conductor with temperature?
solutions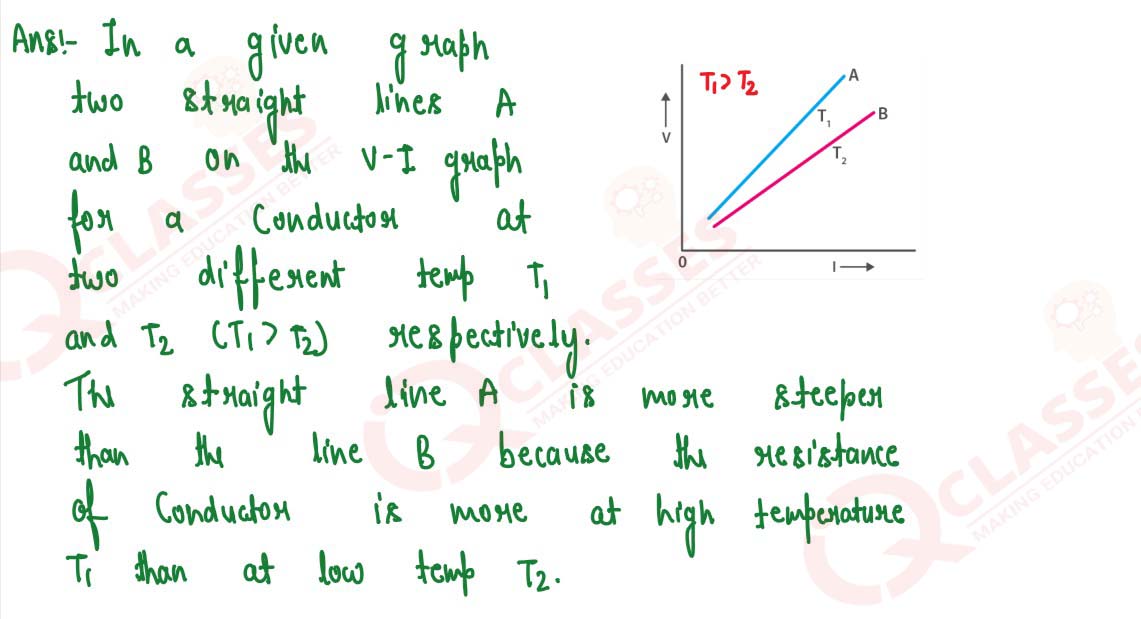
solutions

Q17
(a) How does the resistance of a wire depend on its radius? Explain your answer.
(b) Two copper wires are of same length, but one is thicker than the other. Which will have more resistance?
solutions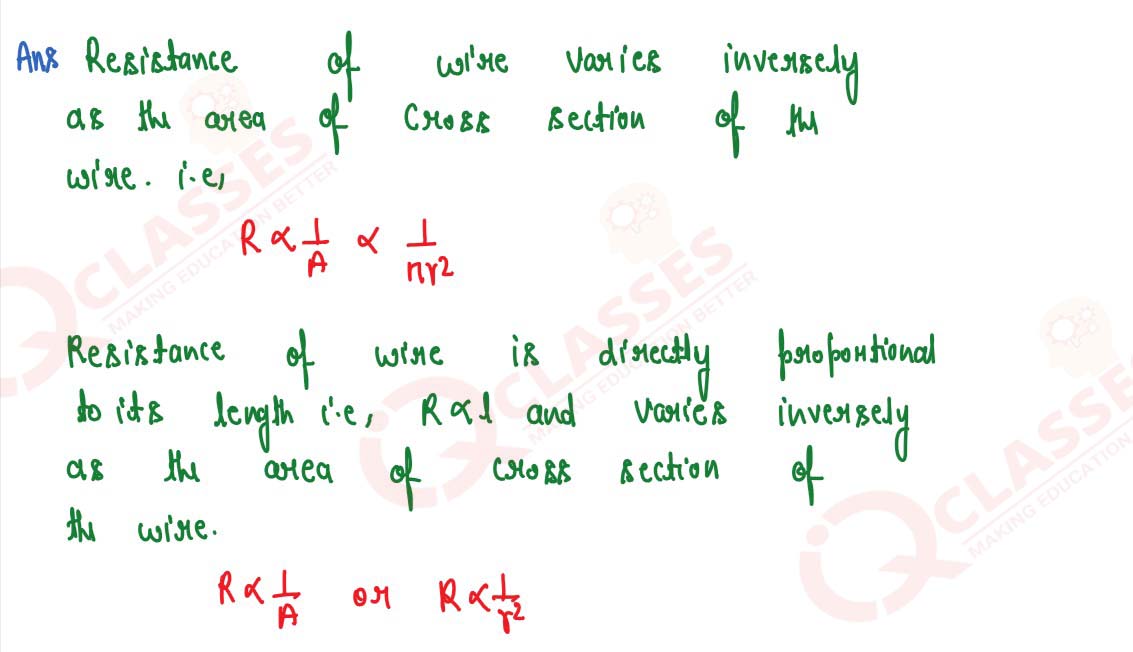

(b) Two copper wires are of same length, but one is thicker than the other. Which will have more resistance?
solutions


Q18
How does the resistance of a wire depend on its length? Give a reason of your answer.
solutions
solutions

Q19
How does the resistance of a metallic wire depend on its temperature? Explain with reason.
solutions
solutions

Q20
Two wires, one of copper and other of iron, are of the same length and same radius. Which will have
more resistance? Give reason.
solutions
solutions

Q21
Name three factors on which the resistance of a wire depends and state how it is affected by the
factors stated by you?
solutions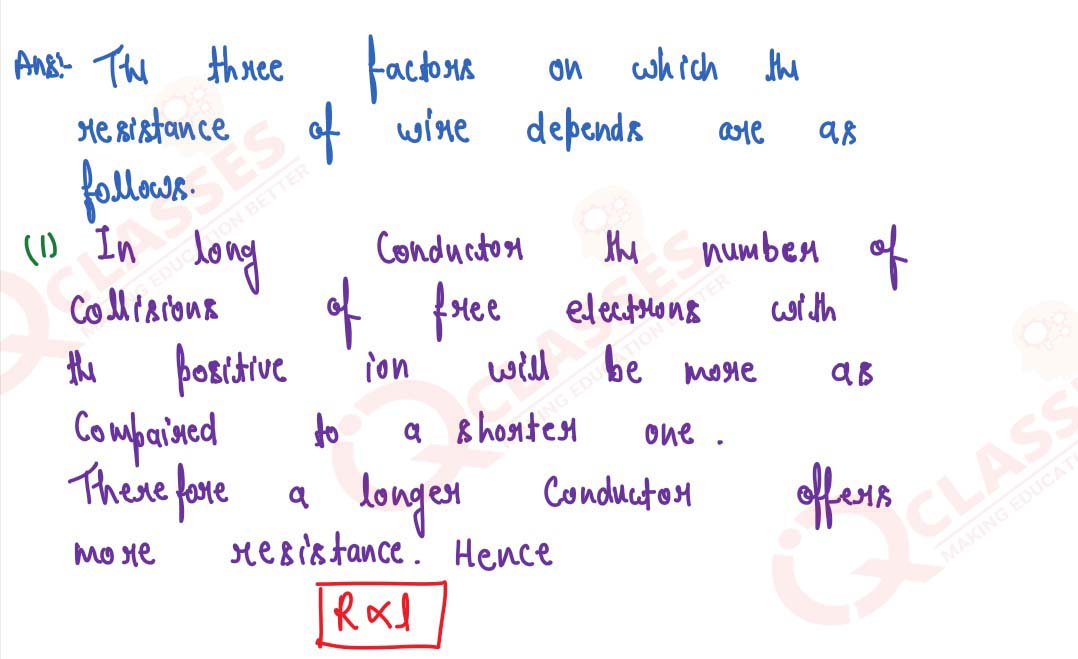
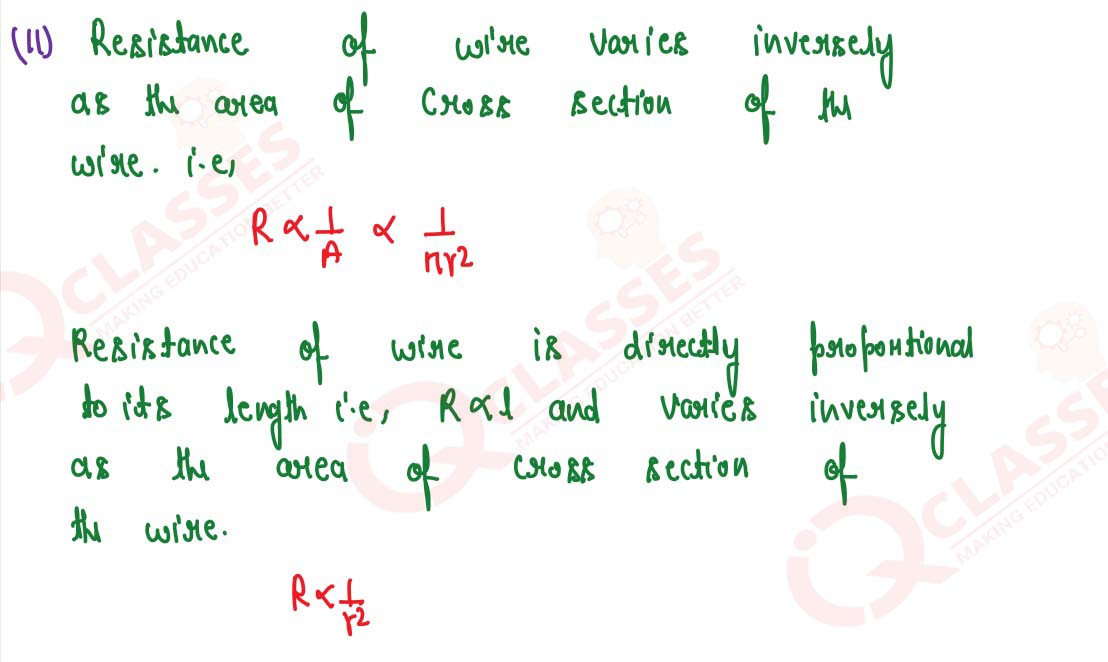

solutions



Q22
Define the term specific resistance and state its S.I. unit.
solutions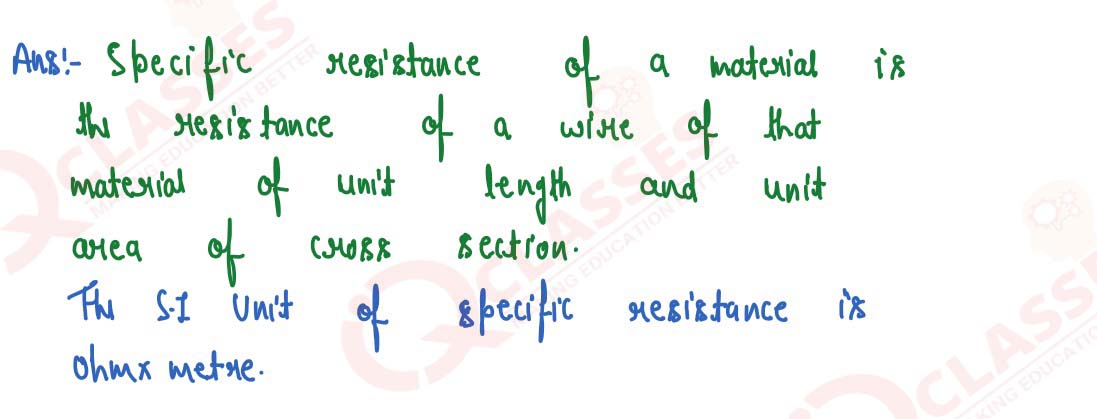
solutions

Q23
Write an expression connecting the resistance of a wire and specific resistance of its material.
State the meaning of symbols used.
solutions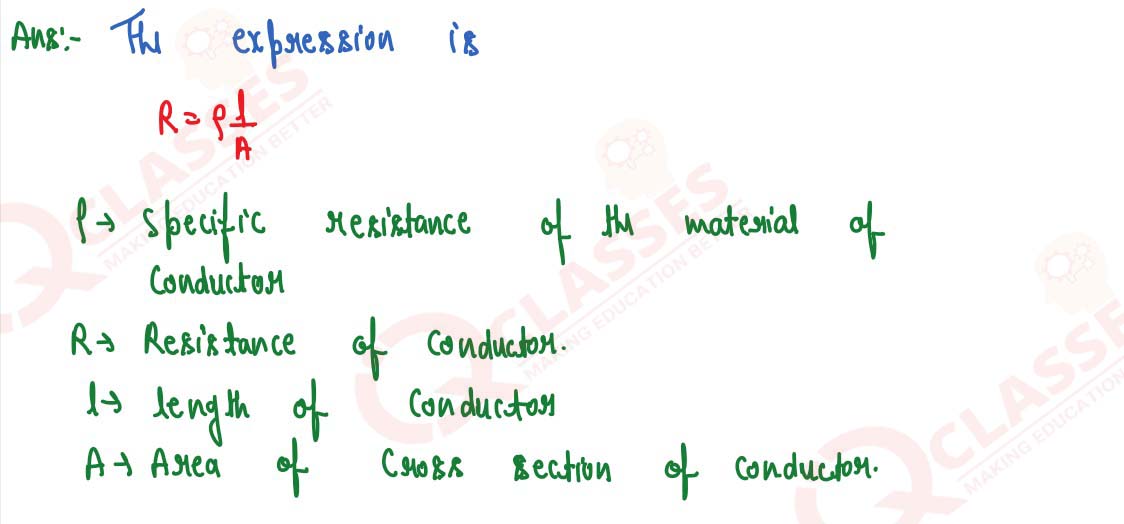
solutions

Q24
State the order of specific resistance of (i) a metal, (ii) a semiconductor and (iii) an insulator.
solutions
solutions

Q25
(a) Name two factors on which the specific resistance of a wire depends?
(b) Two wires A and B are made of copper. The wire A is long and thin while the wire B is Short and thick. Which will have more specific resistance?
solutions
(b) Two wires A and B are made of copper. The wire A is long and thin while the wire B is Short and thick. Which will have more specific resistance?
solutions

Q26
Name a substance of which the specific resistance remains almost unchanged by the increase in
temperature
solutions
solutions

Q27
How does specific resistance of a semi-conductor change with the increase in temperature?
solutions
solutions

Q28
How does (a) resistance, and (b) specific resistance of a wire depend on its (i) length, and (ii)
radius?
solutions
solutions

Q29
(a) Name the material used for making the connection wires. Give reason for your answer.
(b) Why should a connection wire be thick?
solutions
(b) Why should a connection wire be thick?
solutions

Q30
Name the material used for making a fuse wire. Give a reason.
solutions
solutions

MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE (Exercise 8a)
Q1
Which of the following is an ohmic resistance?
(a) LED
(b) Junction diode
(c) Filament of a bulb
(d) Nichrome wire
solutions
(a) LED
(b) Junction diode
(c) Filament of a bulb
(d) Nichrome wire
solutions

Q2
For which of the following substances, resistance decreases with increase in temperature?
(a) Copper
(b) Mercury
(c) Carbon
(d) Platinum
solutions
(a) Copper
(b) Mercury
(c) Carbon
(d) Platinum
solutions

NUMERICAL (8a)
Q1
Define the term current and state its S.I. unit.
solutions
solutions

Q1
In a conductor, 6.25 × 1016 electrons flow from its end A to B in 2 s. Find the current
flowing
through the conductor. (e = 1.6 × 10-19 C)
solutions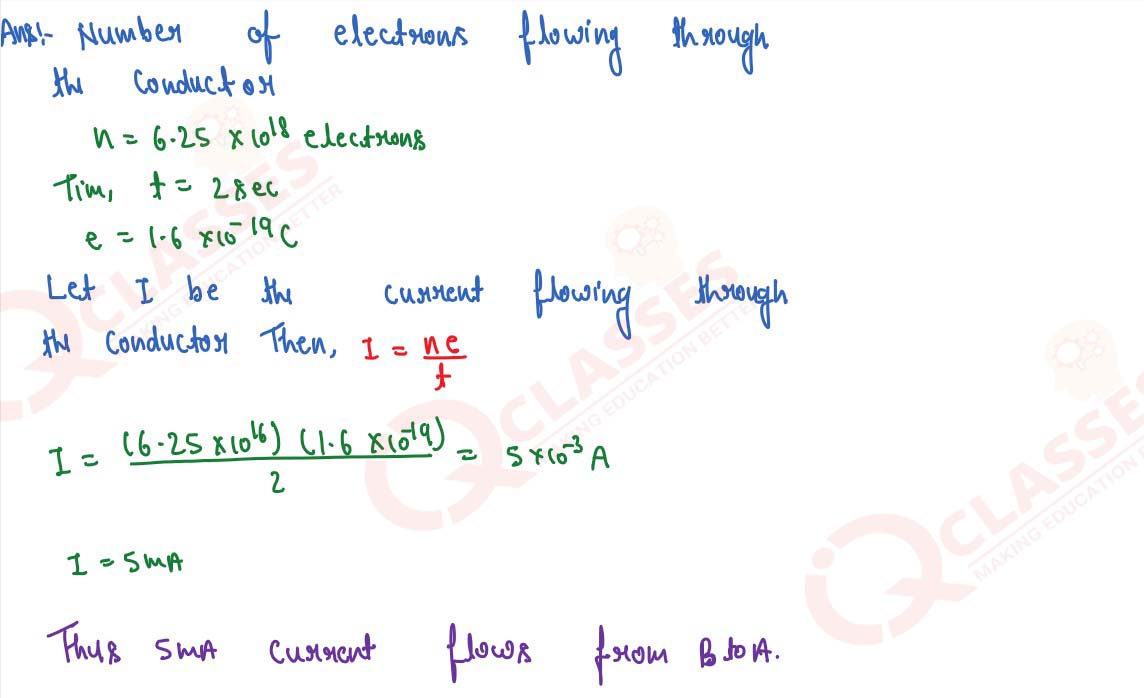
solutions

Q2
A current of 1.6 mA flows through a conductor. If charge of an electron is -1.6 x 10-19 coulomb,
find the number of electrons that will pass each second through the cross section of that conductor.
solutions
solutions

Q3
Find the potential difference required to flow a current of 200 mA in a wire of resistance 20 ohm.
solutions
solutions

Q4
An electric bulb draws 1.2 A current at 6.0 V. Find the resistance of filament of bulb while
glowing.
solutions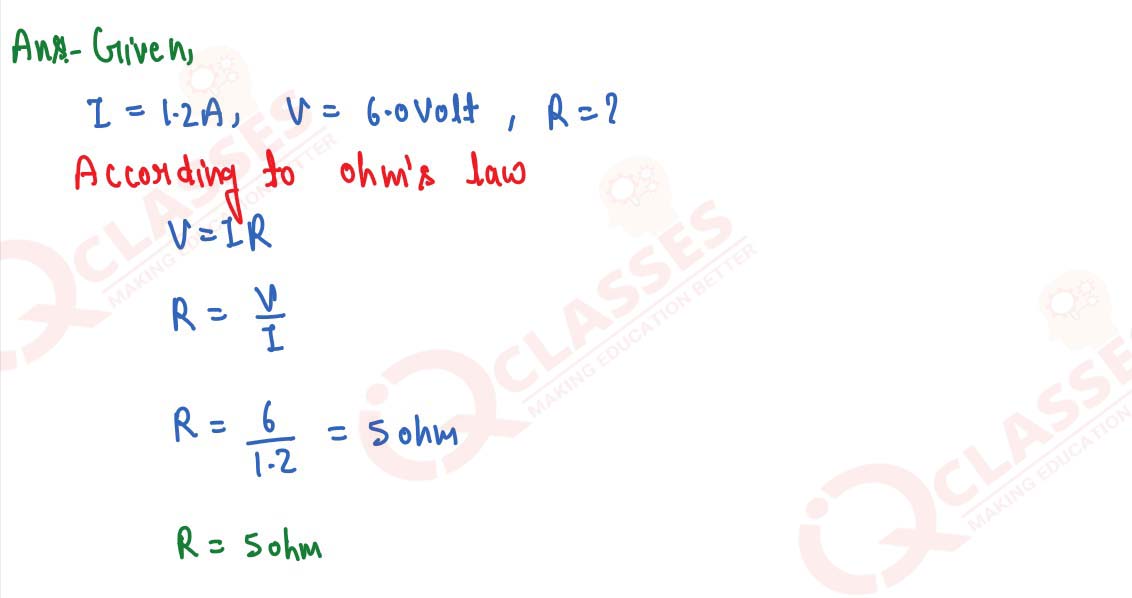
solutions

Q5
A car bulb connected to a 12 volt battery draws 2 A current when glowing. What is the resistance of
the filament of the bulb? Will the resistance be more, same or less when the bulb is not glowing.
solutions
solutions

Q6
Calculate the current flowing through a wire of resistance 5 Ω connected to a battery of
potential difference 3V.
solutions
solutions

Q7
In an experiment of verification of Ohm’s law, following observations are obtained.
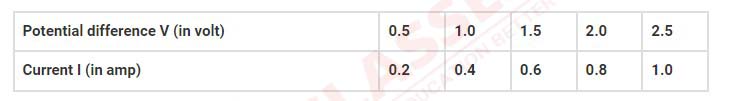
Draw a characteristic V-I graph and use this graph to find:
(a) potential difference V when the current I is 0.5 A.
(b) current I when the potential difference V is 0.75 V.
(c) resistance in circuit
solutions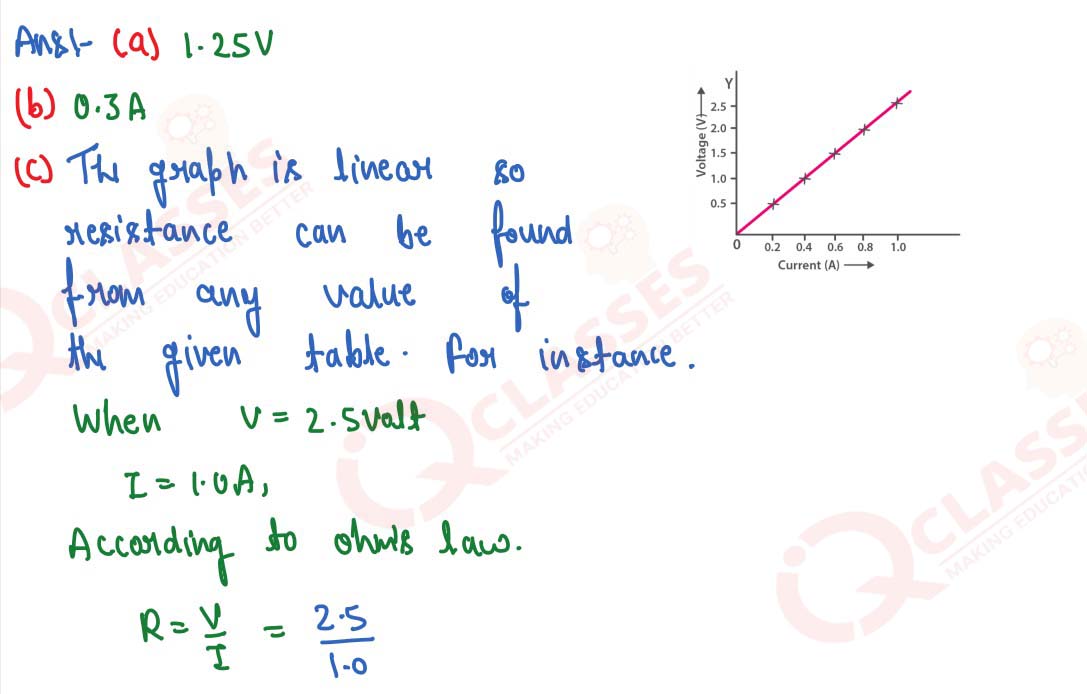


Draw a characteristic V-I graph and use this graph to find:
(a) potential difference V when the current I is 0.5 A.
(b) current I when the potential difference V is 0.75 V.
(c) resistance in circuit
solutions


Q8
Two wires of the same material and same length have radii 1 mm and 2 mm respectively. Compare (i)
their resistances (ii) their specific resistance.
solutions

solutions


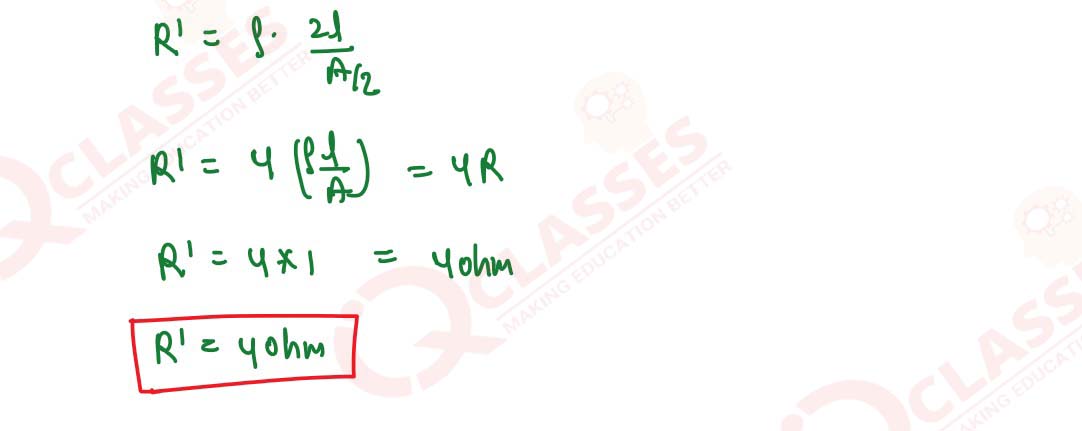
Q9
A given wire of resistance 1 Ohm is stretched to double its length. What will be its new resistance?
solutions
solutions


Q10
A wire of resistance 3 Ohm and length 10 cm is stretched to length 30 cm. Assuming that it has a
uniform cross-section, what will be its new resistance?
solutions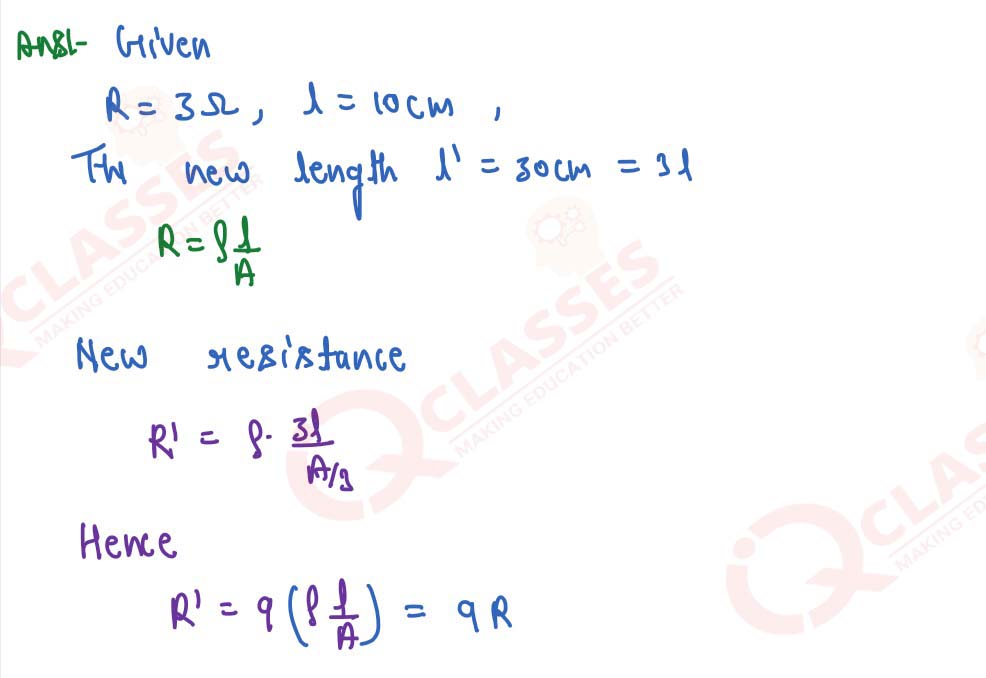
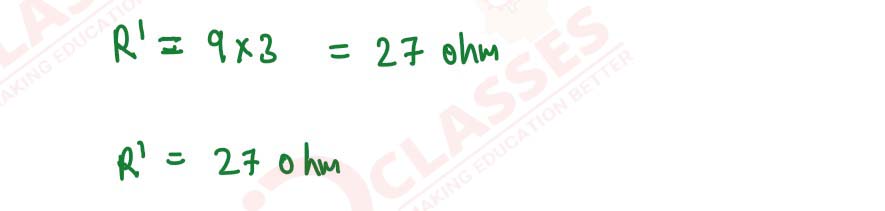
solutions

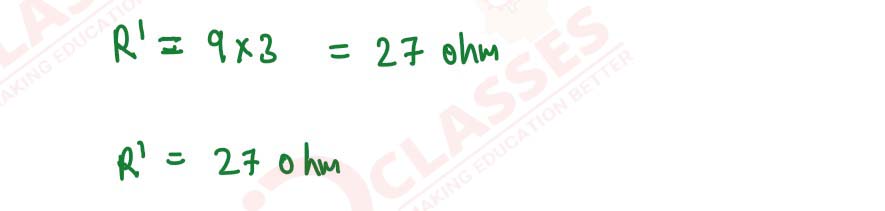
Q11
A wire of resistance 9 Ohm having length 30 cm is tripled on itself. What is its new resistance?
solutions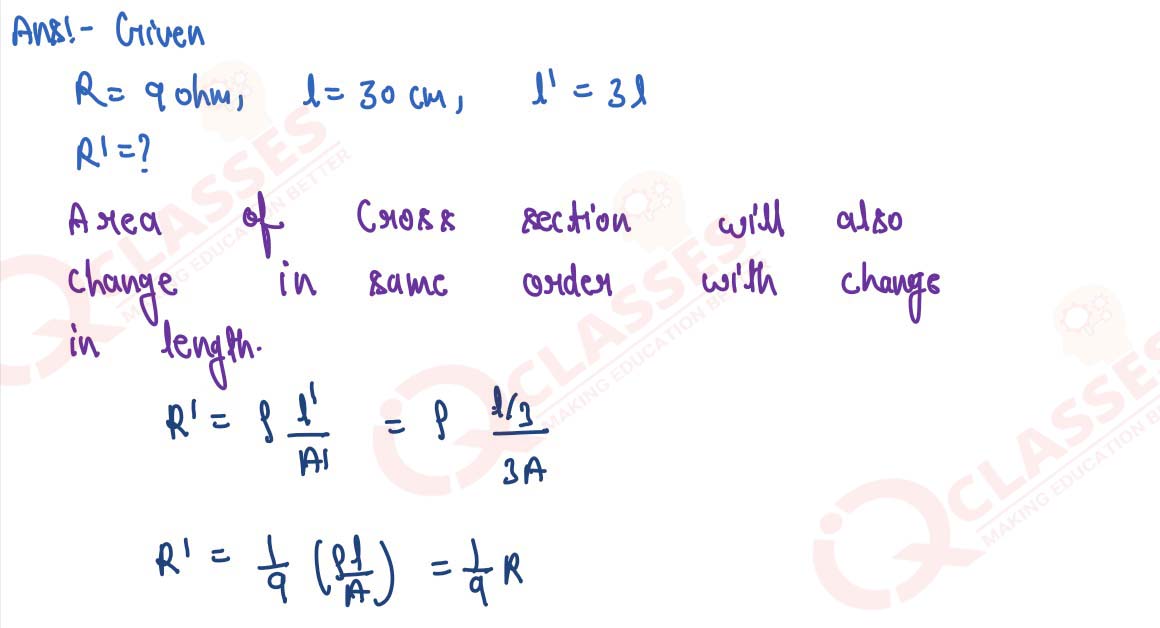

solutions


Q12
What length of copper wire of specific resistance 1.7 x 10-8 ohm m and radius 1 mm is
required so that its resistance is 1 ohm.
solutions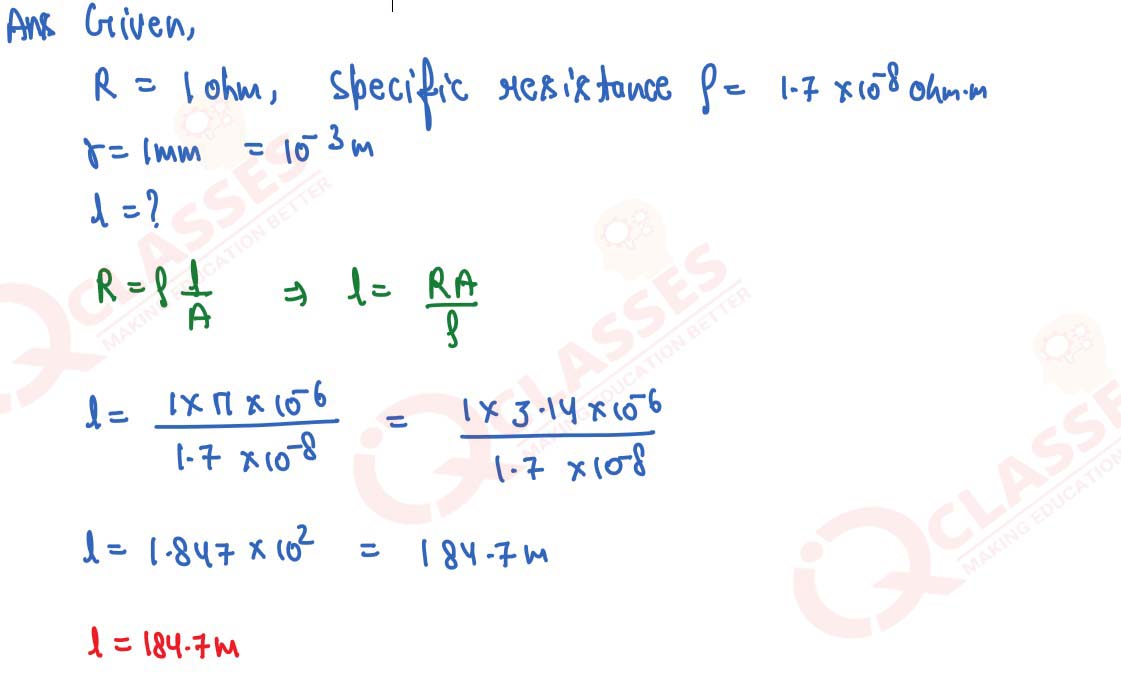
solutions

Q13
The filament of a bulb takes a current 100 mA when potential difference across it is 0.2 V. When the
potential difference across it becomes 1.0 V, the current becomes 400 mA. Calculate the resistance
of filament in each case and account for the difference.
solutions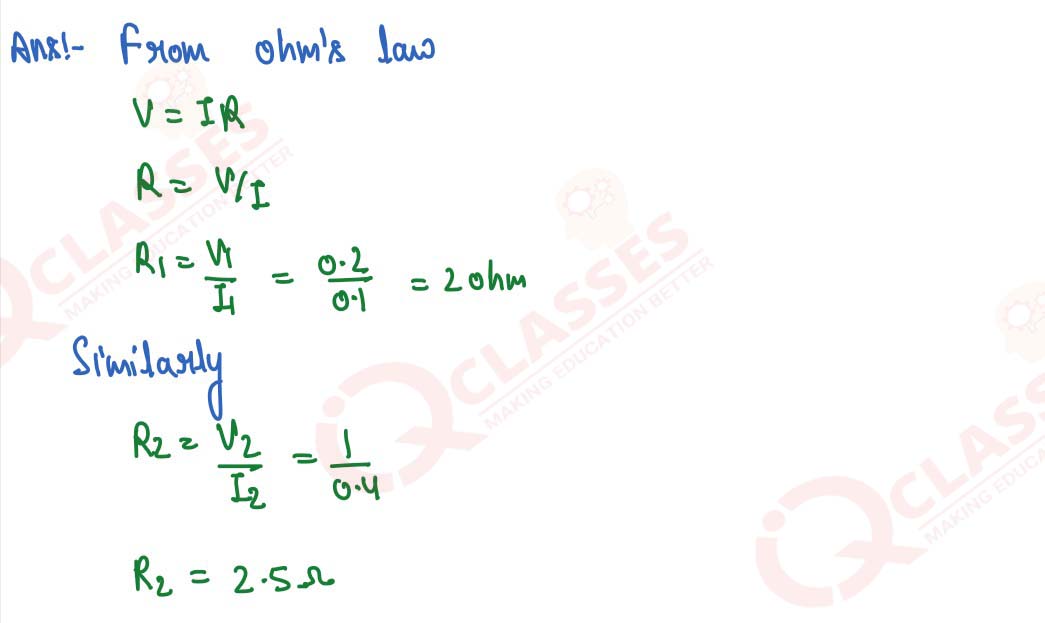

solutions

