Q1
At what voltage and frequency is the electric power generated at the power generating station?
solutions
solutions

Q2
(a) At what voltage is the electric power from the generating station transmitted? Give reasons for
your answer.
(b) What is the nature of the current transmitted from the power station?
solutions
(b) What is the nature of the current transmitted from the power station?
solutions

Q3
The voltage of power generated at the generating stations is first stepped up before its
transmission. Give reason.
solutions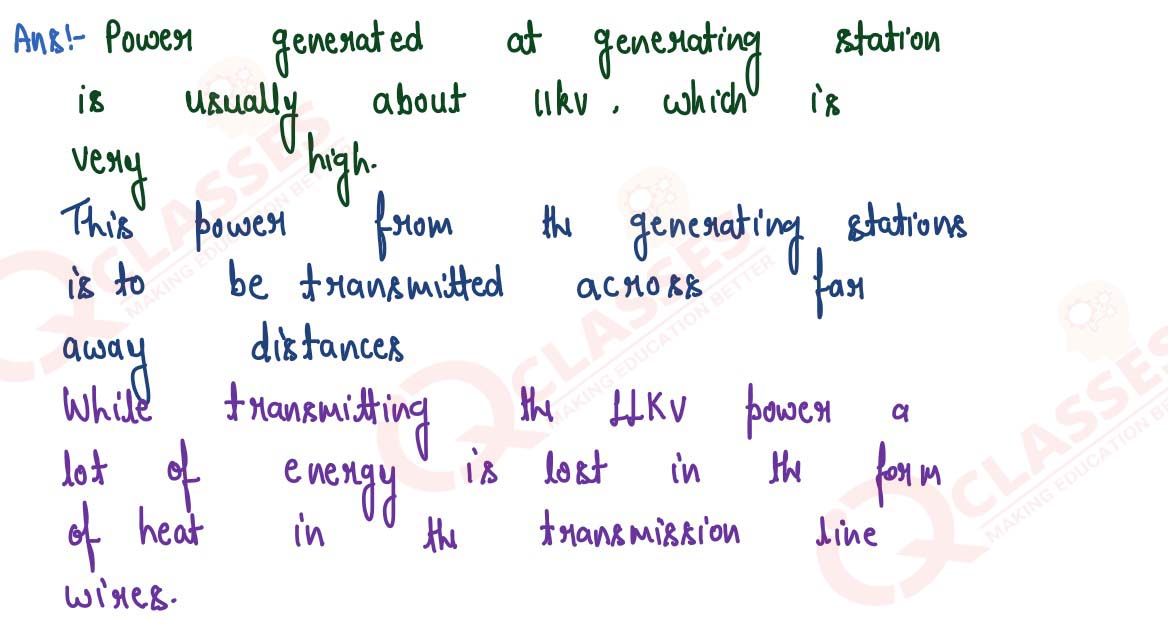
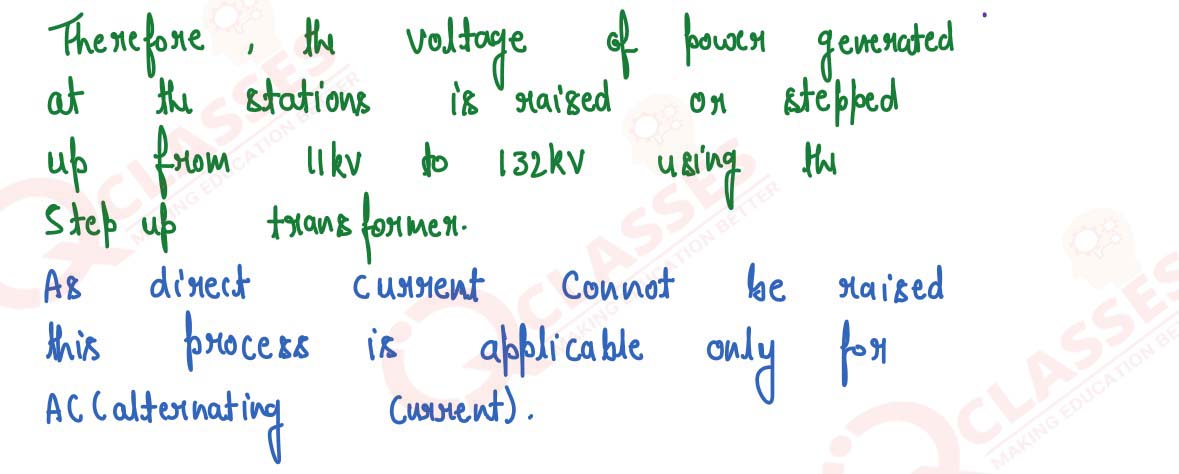
solutions


Q4
Explain with the aid of a simple diagram, the transmission of electric power from the generating
station to your house.
solutions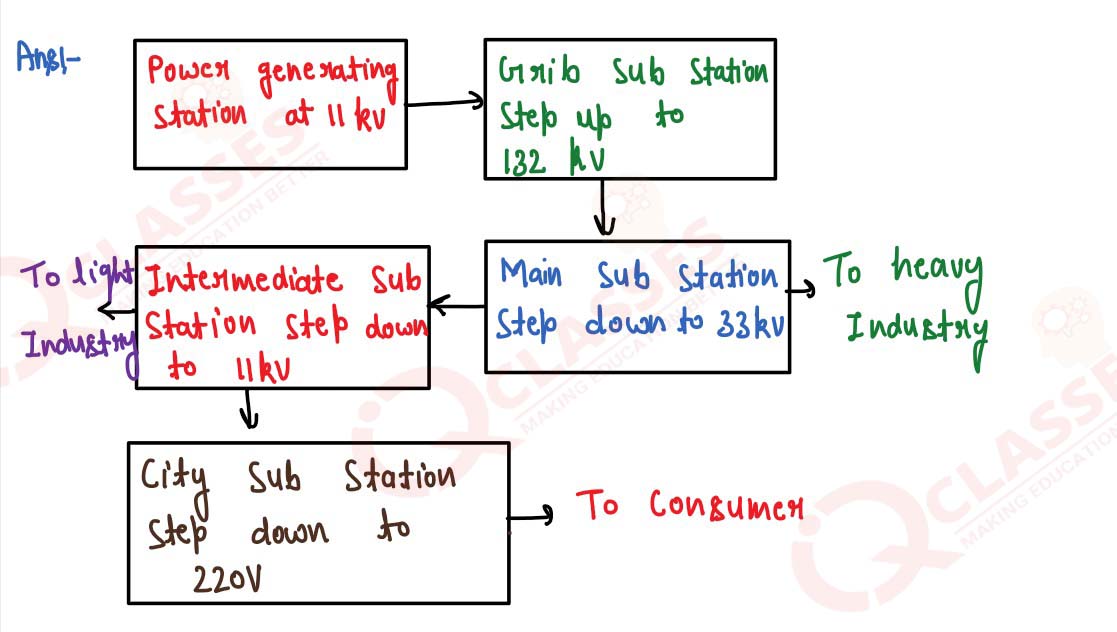


solutions



Q5
At what voltage and frequency is the a.c. supplied to our houses?
solutions
solutions

Q6
Name the device used to (a) Increase the voltage at the generating station (b) Decrease the voltage
at the sub-station for its supply.
solutions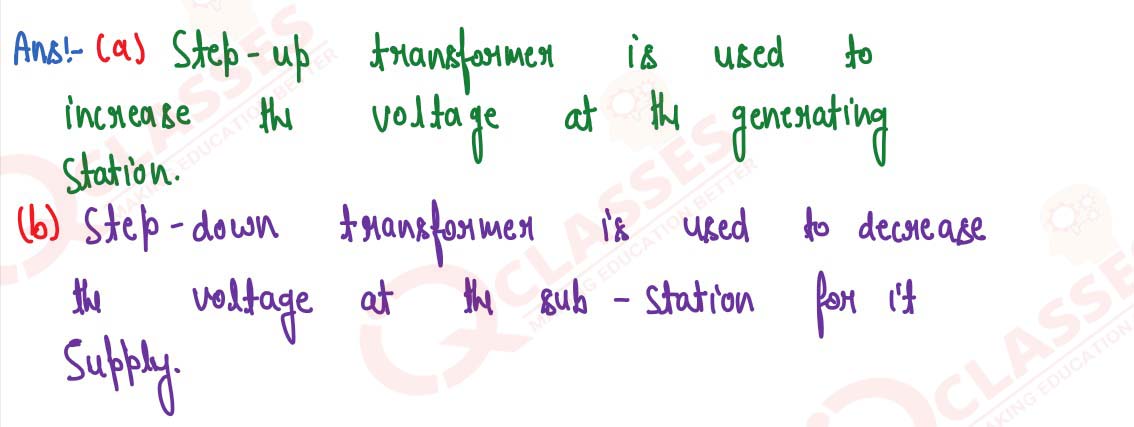
solutions
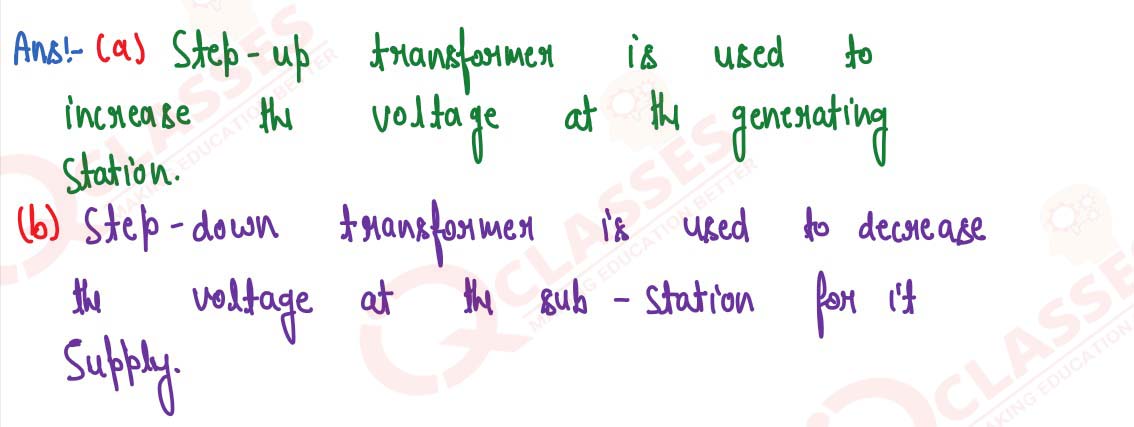
Q7
(a) Name the three connecting wires used in a household circuit.
(b) Which two wires mentioned in part (a) are at the same potential?
(c) In which of the wire stated in part (a) the switch is connected?
solutions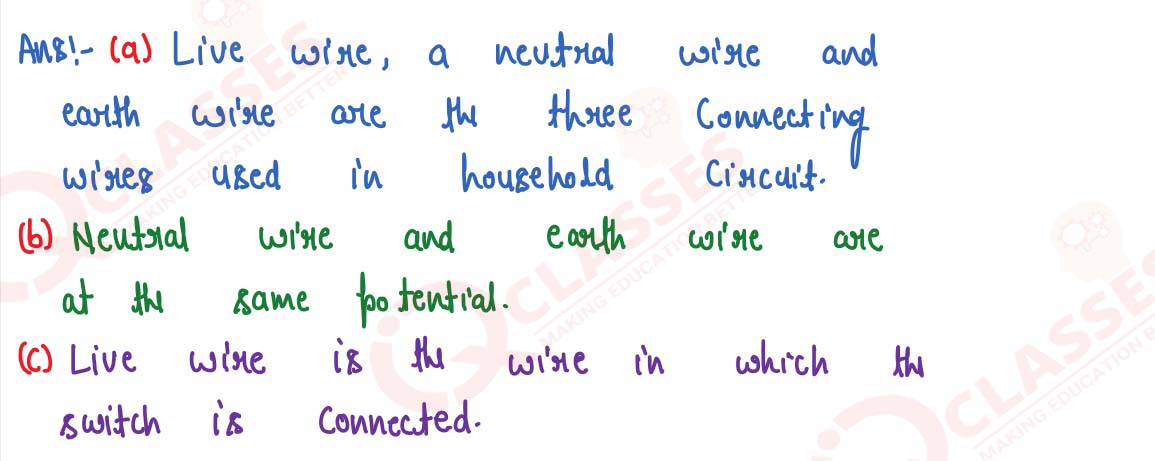
(b) Which two wires mentioned in part (a) are at the same potential?
(c) In which of the wire stated in part (a) the switch is connected?
solutions

Q8
What is the pole fuse? Write down it’s current rating.
solutions
solutions

Q9
State the function of each of the following in a house circuiting:
(a) kWh meter, (b) the main fuse, and (c) the main switch
solutions

(a) kWh meter, (b) the main fuse, and (c) the main switch
solutions


Q10
In what unit does the electric meter in a house measure the electrical energy consumed? What is its
value in S.I. unit?
solutions
solutions

Q11
Where is the main fuse connected in a house circuit?
solutions
solutions

Q12
State one advantage of using the main switch in house wiring.
solutions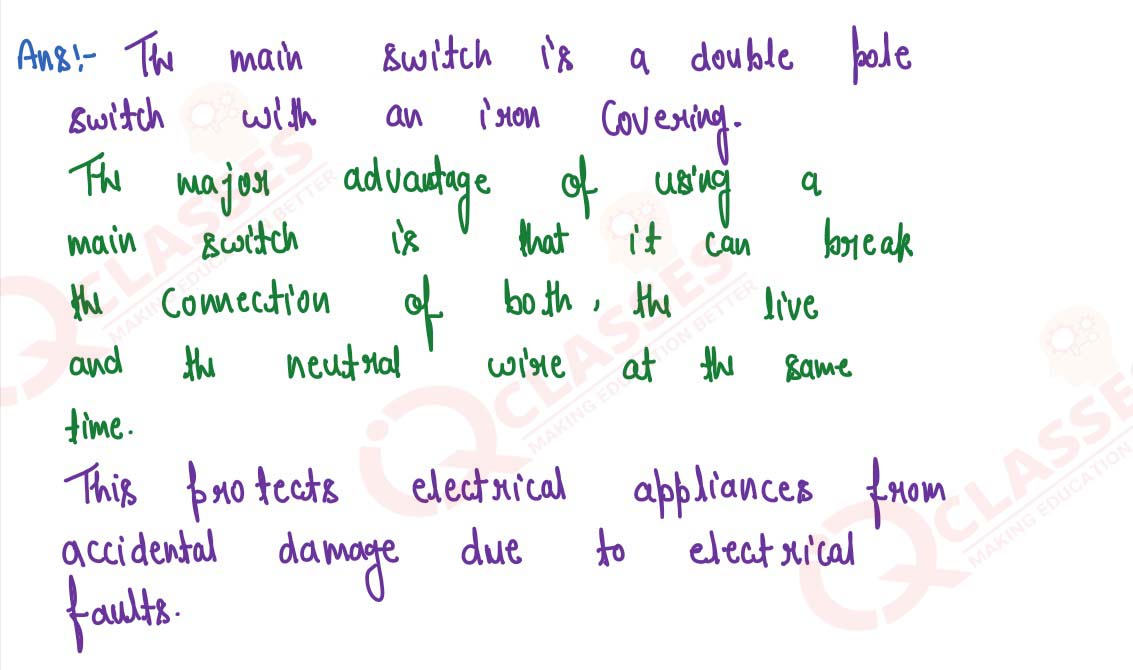
solutions

Q13
Draw a circuit diagram to explain the ring system of house wiring. State two advantages of it.
solutions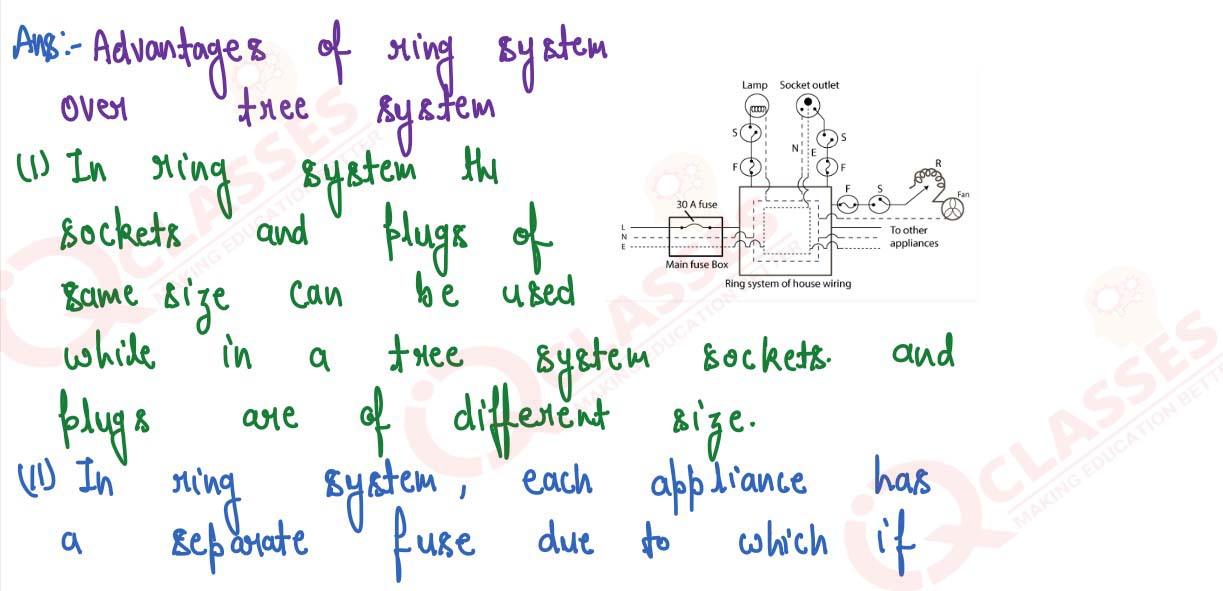

solutions


Q14
Draw a labelled diagram with the necessary switch, regulator, etc. to connect a bulb and a fan with
the mains. In what arrangement are they connected to the mains: series or parallel?
solutions
solutions

Q15
How should the several electric lamps be connected with the mains so that the switching on or off a
lamp has no effect on the operation of other lamps?
solutions
solutions

Q16
Fig.9.12 shows three bulbs A, B and C each of rating 100 W, 220 V connected to the mains of 220 V.
Answer the following:
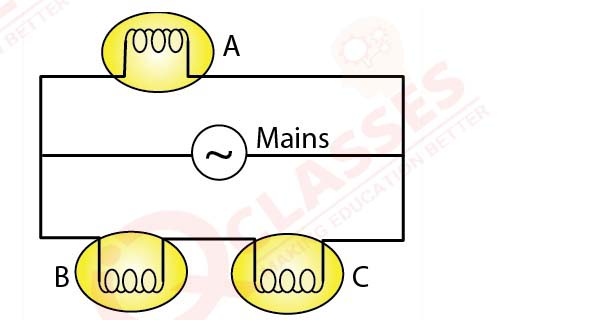
(a) How is the bulb A connected with the mains? At what voltage does it glow?
(b) How are the bulbs B and C connected with the mains? At what voltage does the bulb B glow?
(c) How is the glow of bulbs A and C affected if bulb B gets fused?
(d) How is the glow of bulbs B and C affected if bulb A gets fused?
solutions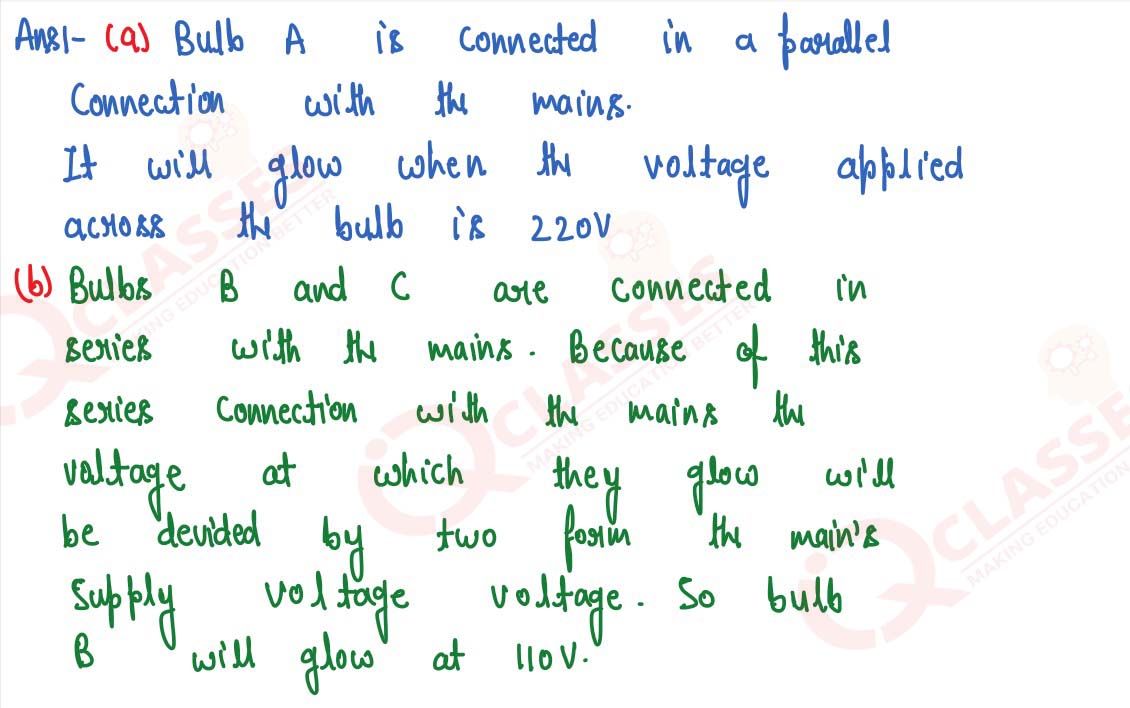


(a) How is the bulb A connected with the mains? At what voltage does it glow?
(b) How are the bulbs B and C connected with the mains? At what voltage does the bulb B glow?
(c) How is the glow of bulbs A and C affected if bulb B gets fused?
(d) How is the glow of bulbs B and C affected if bulb A gets fused?
solutions


Q17
Two sets A and B each of four bulbs are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set
A is fused, the other three bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other
bulbs continue to glow.
(i) Explain the difference in the two sets,
(ii) Which set of arrangement is preferred in the housing circuit and why?
solutions
(i) Explain the difference in the two sets,
(ii) Which set of arrangement is preferred in the housing circuit and why?
solutions

MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE (Exercise 9a)
Q1
The main fuse is connected in:
(a) Live wire
(b) Neutral wire
(c) Both the live and earth wires
(d) Both earth and the neutral wire.
solutions
(a) Live wire
(b) Neutral wire
(c) Both the live and earth wires
(d) Both earth and the neutral wire.
solutions

Q2
The electrical appliances in a house are connected in:
(a) Series
(b) Parallel
(c) Either in series or parallel
(d) Both in series and parallel
solutions
(a) Series
(b) Parallel
(c) Either in series or parallel
(d) Both in series and parallel
solutions

Q3
The electrical meter in a house records the consumption of:
(a) Charge
(b) Current
(c) Energy
(d) Power
solutions
(a) Charge
(b) Current
(c) Energy
(d) Power
solutions
