Q1
What is a lens?
solutions
solutions

Q2
Name the two kinds of lens? Draw diagrams to illustrate them.
solutions
solutions

Q3
State difference between a convex and a concave lens in their —
(a) appearance, and
(b) action on the incident light.
solutions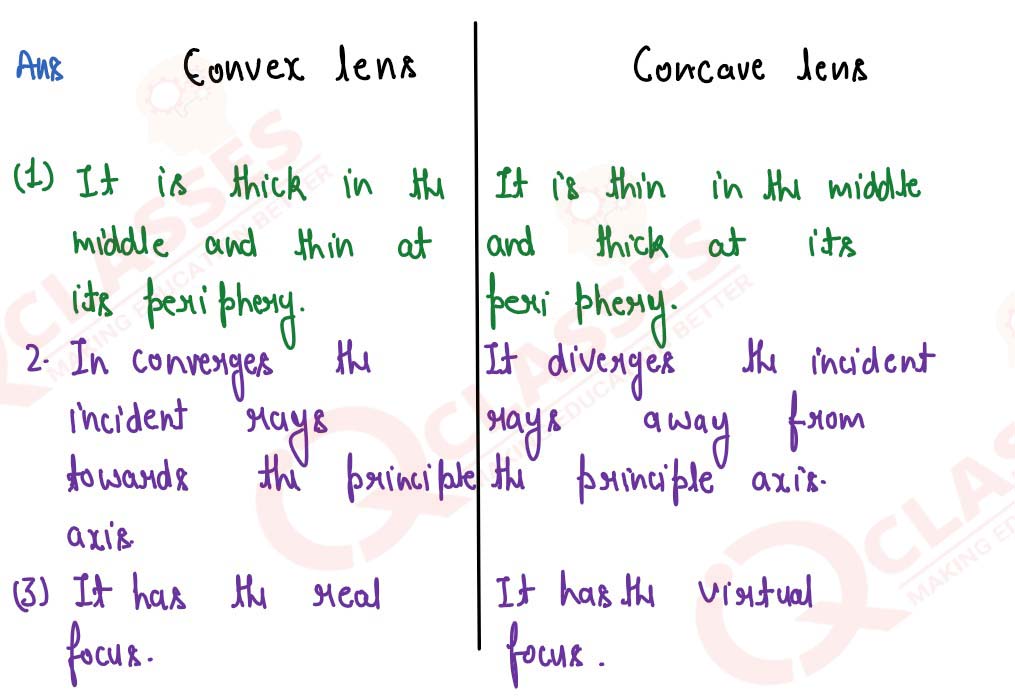
solutions

Q4
Which lens is converging —
(i) an equiconcave lens or an equiconvex lens?
(ii) a concavo-convex lens or a convexo-concave lens?
solutions
(i) an equiconcave lens or an equiconvex lens?
(ii) a concavo-convex lens or a convexo-concave lens?
solutions

Q5
Out of the two lenses, one concave and the other convex, state which one will show the divergent action on a light beam. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
solutions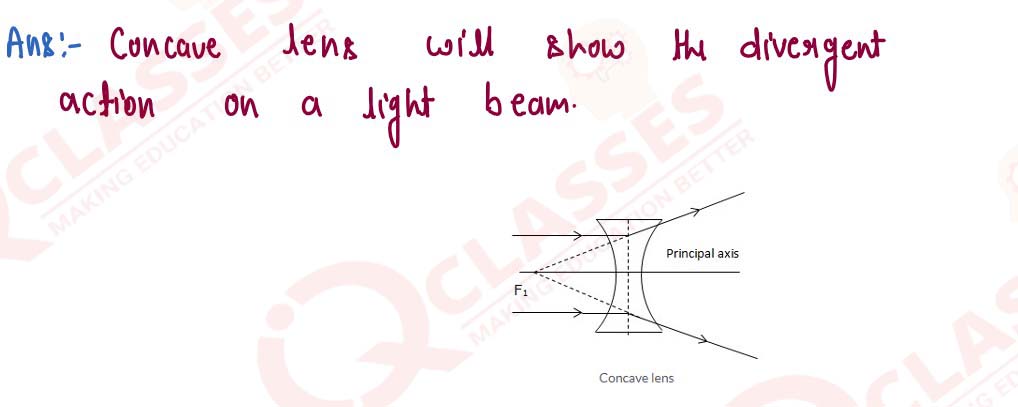

solutions


Q6
Show by a diagram the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a convex lens by treating it as a combination of a glass slab and two triangular glass prisms.
solutions
solutions

Q7
Show by a diagram the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a concave lens by treating it as a combination of a glass slab and two triangular glass prisms
solutions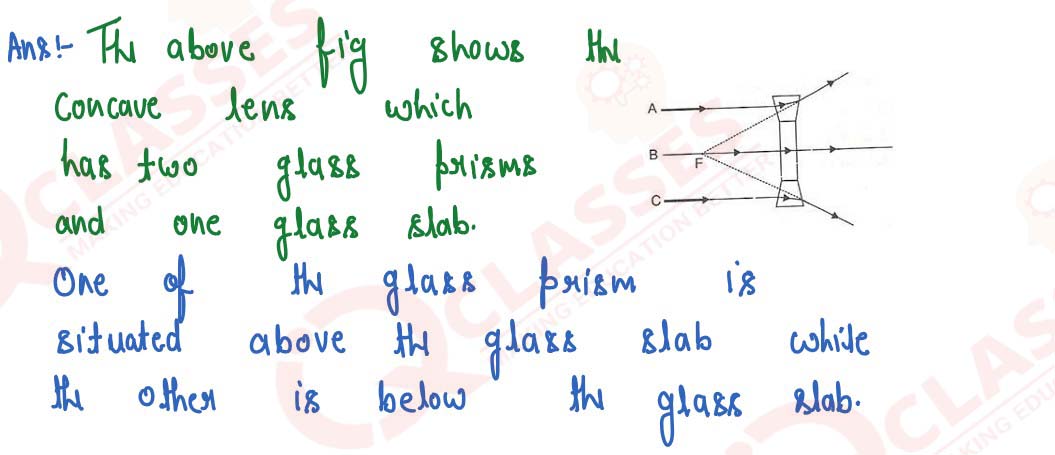
solutions

Q8
How does the action of the convex lens differ from that of a concave lens on a parallel beam of light incident on them? Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
solutions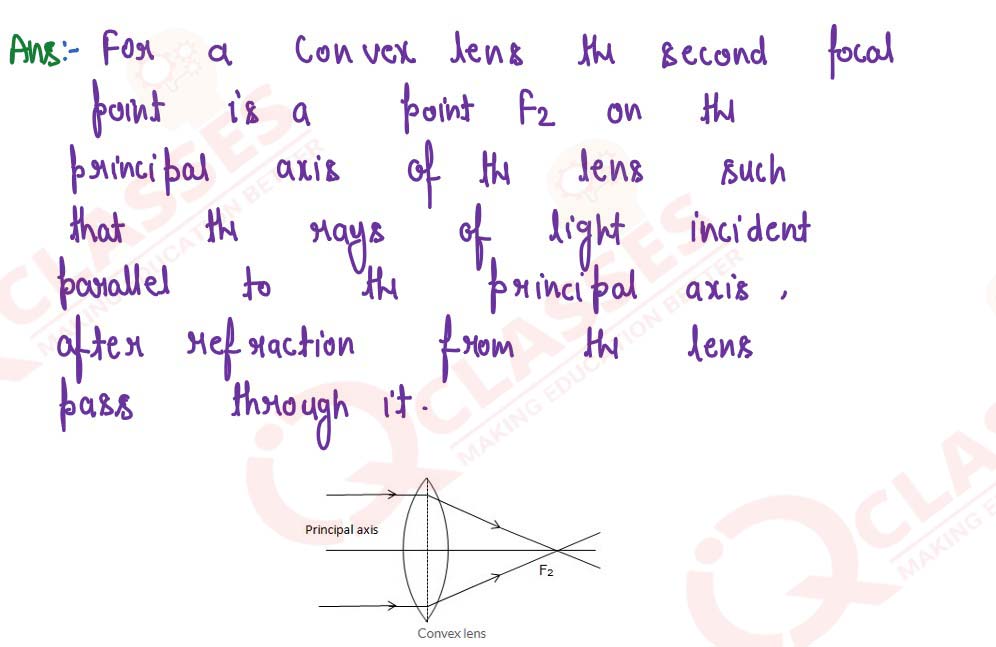
solutions

Q9
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
solutions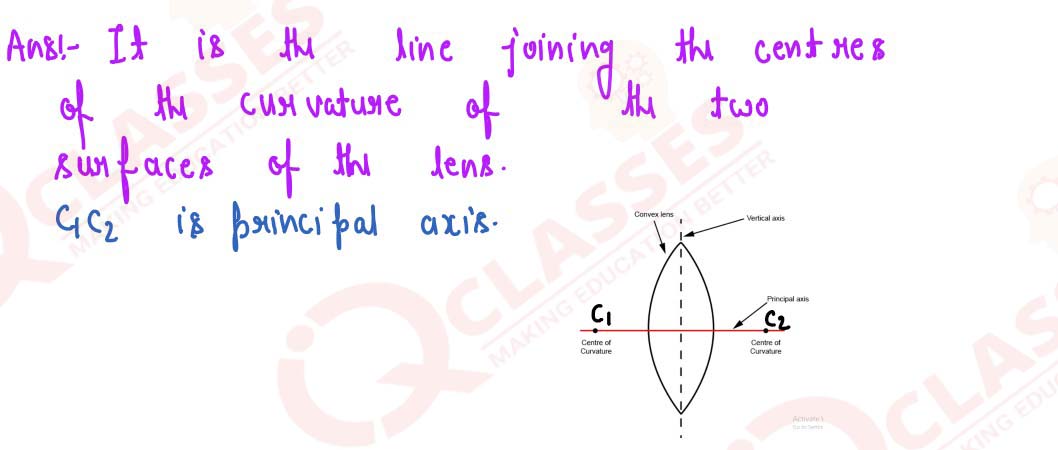
solutions

Q10
Explain the optical centre of a lens with the help of proper diagram(s).
solutions
solutions

Q11
A ray of light incident at a point on the principal axis of a convex lens passes undeviated through the lens.
(a) What special name is given to this point on the principal axis?
(b) Draw a labelled diagram to support the answer in part (a).
solutions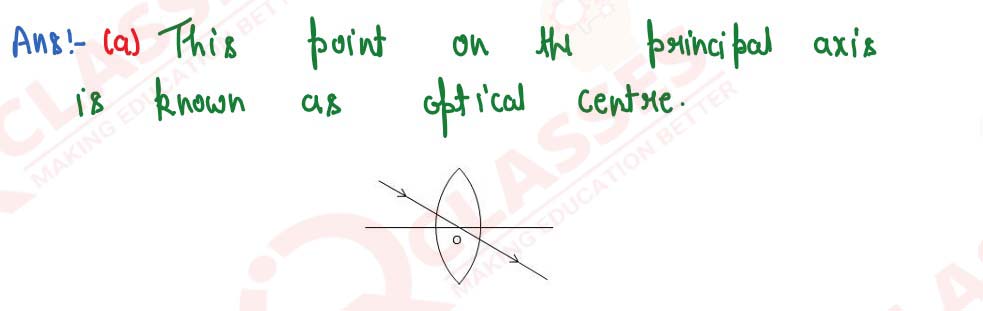
(a) What special name is given to this point on the principal axis?
(b) Draw a labelled diagram to support the answer in part (a).
solutions

Q12
State the condition when a lens is called equiconvex or equi-concave.
solutions
solutions

Q13
Define the term principal foci of a convex lens and illustrate your answer with the aid of proper diagrams.
solutions
solutions

Q14
Define the term principal foci of a concave lens and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
solutions
solutions

Q15
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a concave lens.
solutions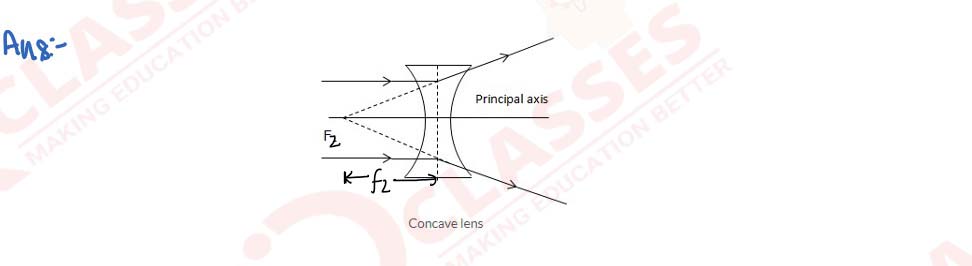


solutions



Q16
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
solutions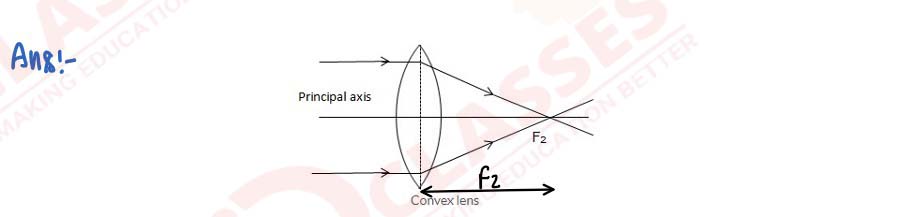
solutions

Q17
A ray of light, after refraction through a concave lens emerges parallel to the principal axis.
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the incident ray and its corresponding emergent ray.
(b) The incident ray when produced meets the principal axis at a point F. Name the point F
solutions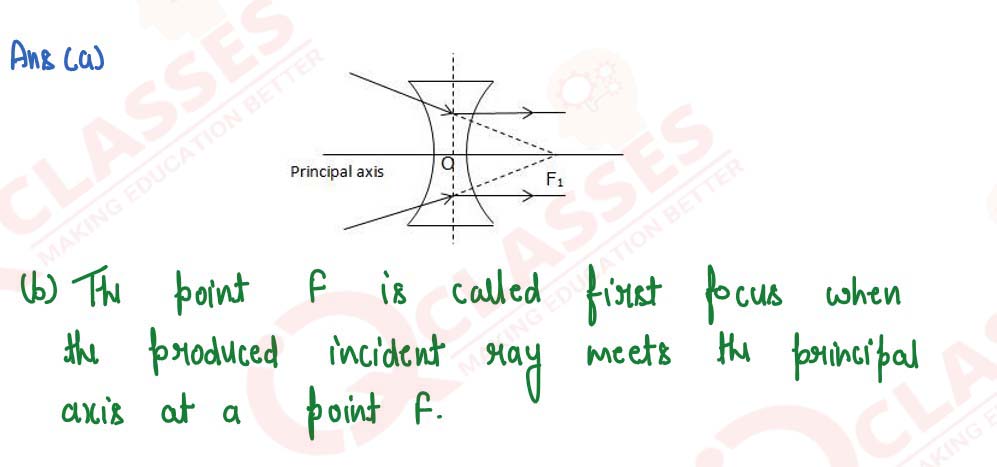
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the incident ray and its corresponding emergent ray.
(b) The incident ray when produced meets the principal axis at a point F. Name the point F
solutions

Q18
A ray of light, after refraction through a convex lens emerges parallel to the principal axis.
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show it.
(b) The incident ray passes through a point F on the principal axis. Name the point F.
solutions
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show it.
(b) The incident ray passes through a point F on the principal axis. Name the point F.
solutions

Q19
A beam of light incident on a convex lens parallel to its principal axis converges at a point F on the principal axis. Name the point F. Draw a ray diagram to show it.
solutions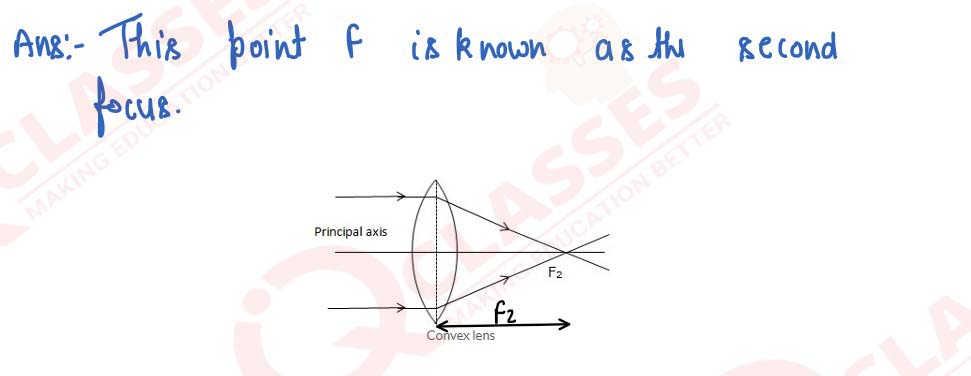
solutions

Q20
A beam of light incident on a thin concave lens parallel to its principal axis diverges and appears to come from a point F on the principal axis. Name the point F. Draw a ray diagram to show it.
solutions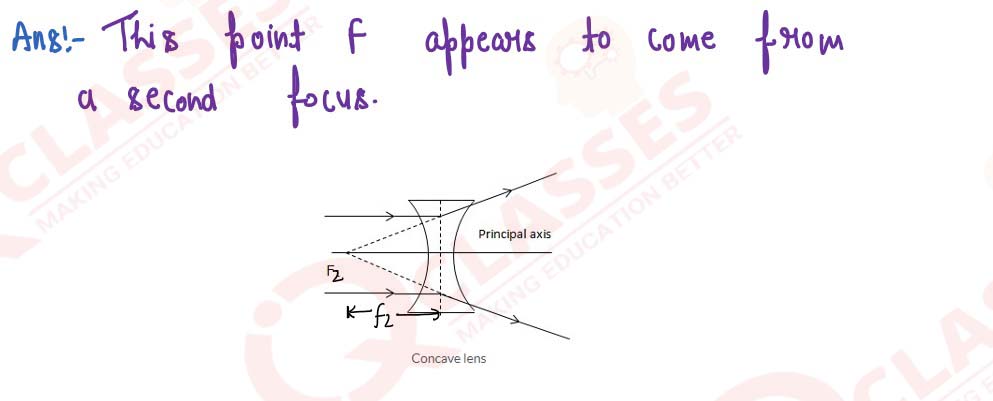
solutions

Q21
Define the term focal length of a lens.
solutions

solutions


Q22
What do you mean by focal plane of a lens?
solutions
solutions

Q23
State the condition for each of the following :
(a) a lens has both its focal lengths equal.
(b) a ray passes undeviated through the lens.
solutions
(a) a lens has both its focal lengths equal.
(b) a ray passes undeviated through the lens.
solutions

Q24
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a
(i) convex lens,
(ii) concave lens.
solutions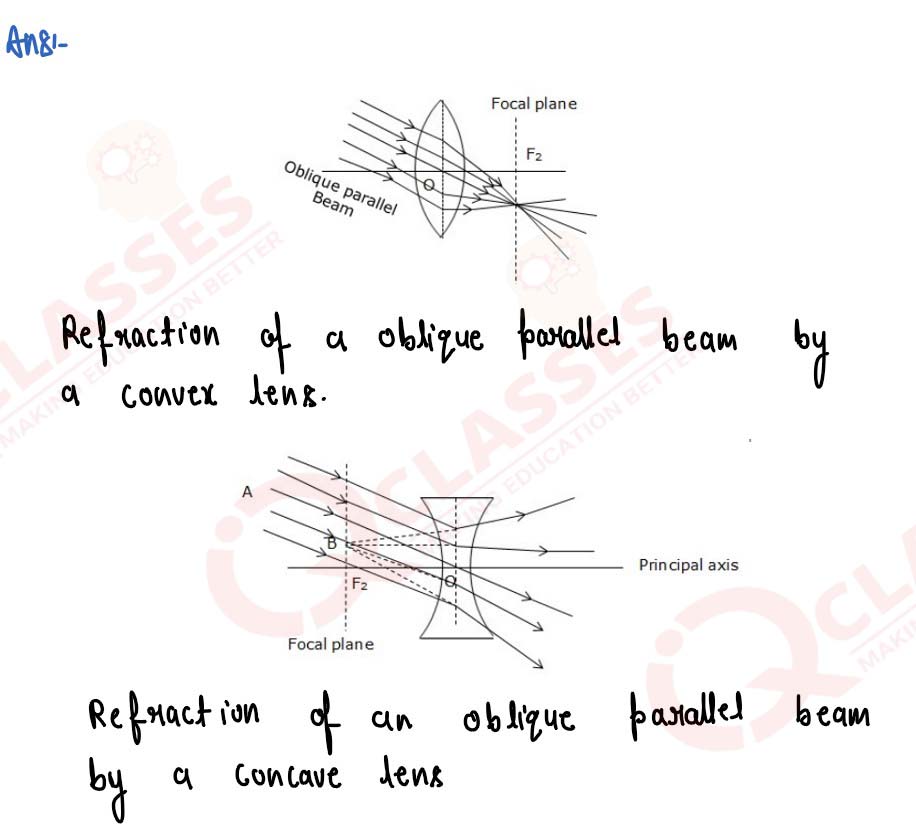
(i) convex lens,
(ii) concave lens.
solutions

Q25
The diagram below shows a lens as a combination of a glass slab and two prisms.
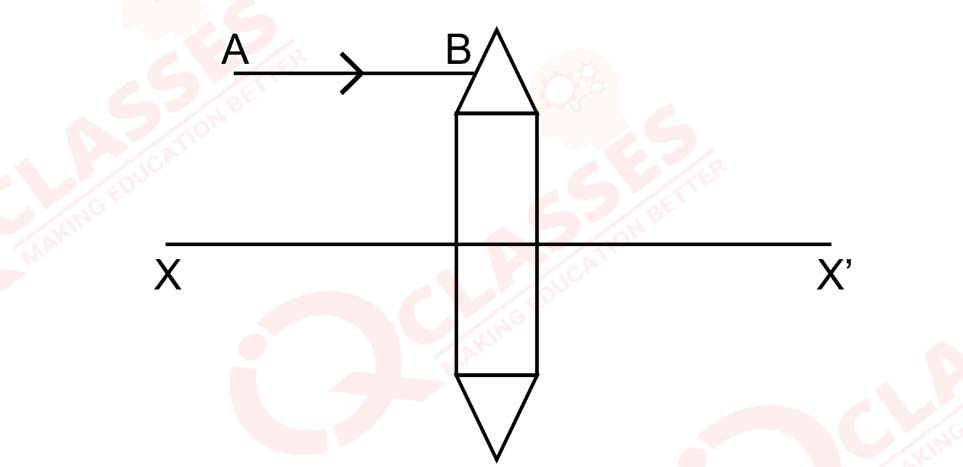
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray AB after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. Label the point as F. What is this point called?
solutions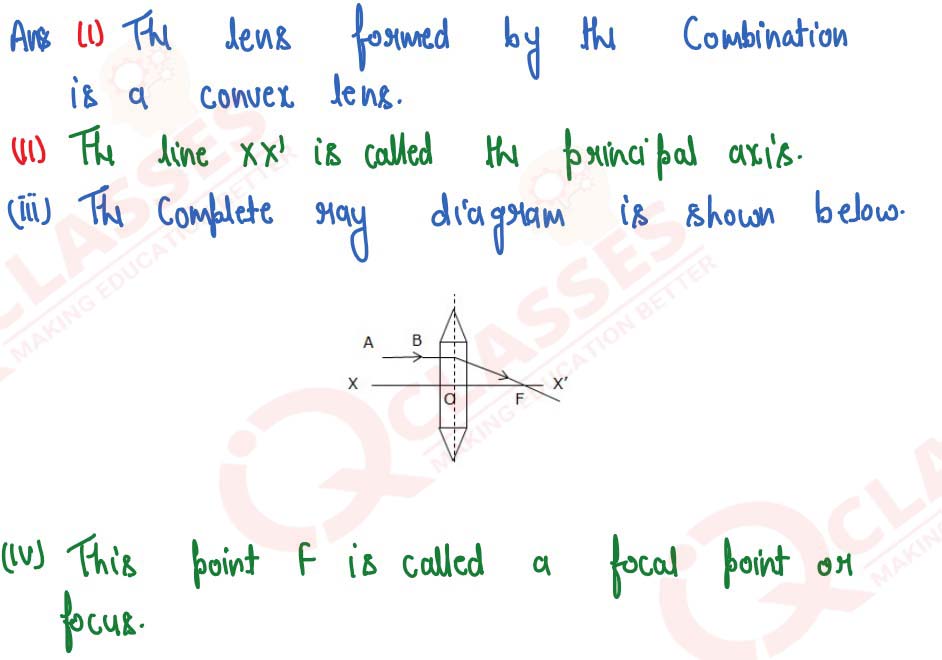

(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray AB after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. Label the point as F. What is this point called?
solutions

Q26
The diagram below shows a lens as a combination of a glass slab and two prisms.
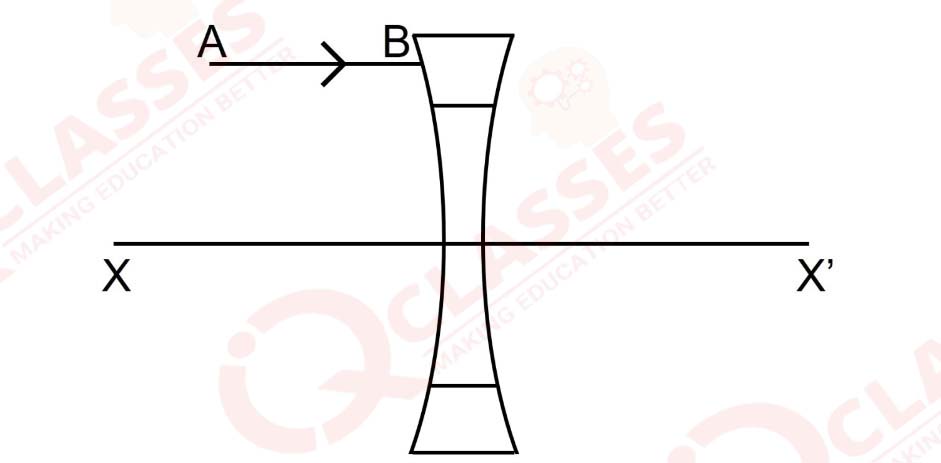
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray AB after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX’. Label it as F. What is this point called?
solutions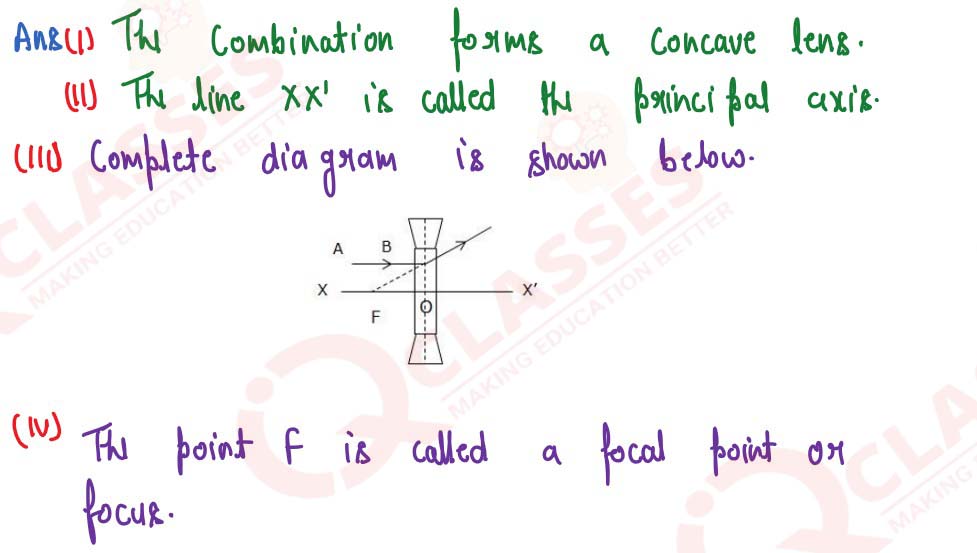



(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray AB after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX’. Label it as F. What is this point called?
solutions



Q27
In figure (a) and (b), F1 and F2 are the positions of the two foci of thin lenses. Draw the path taken by the light ray AB after it emerges from each lens.
(a) Figure a
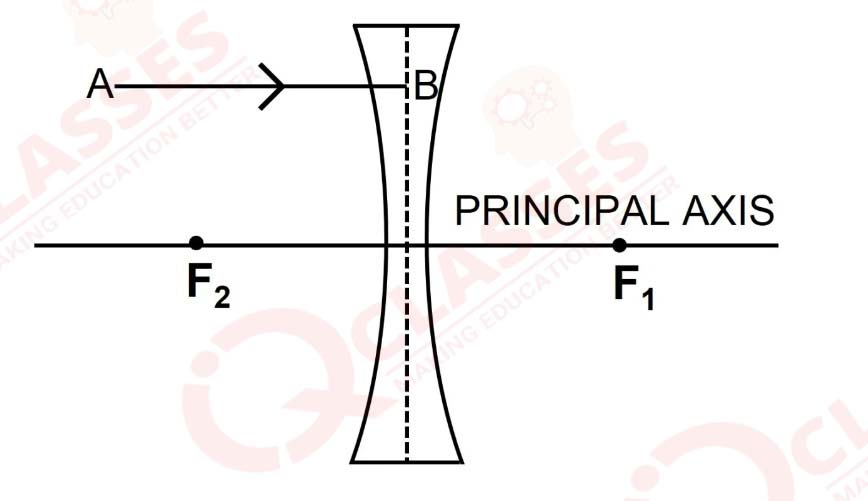
(b) Figure b
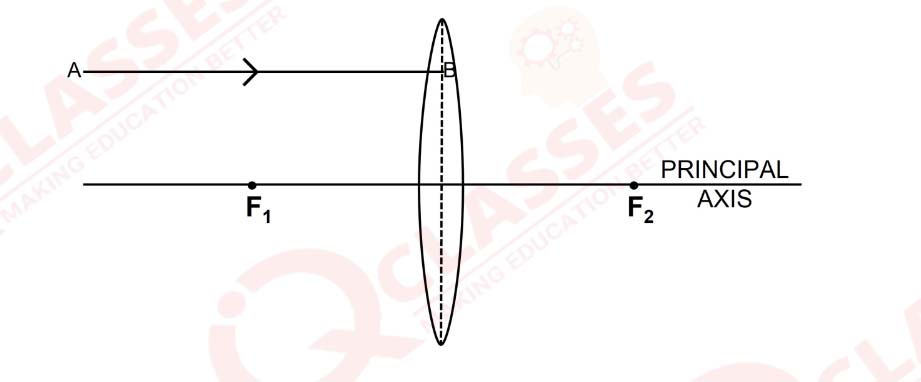
solutions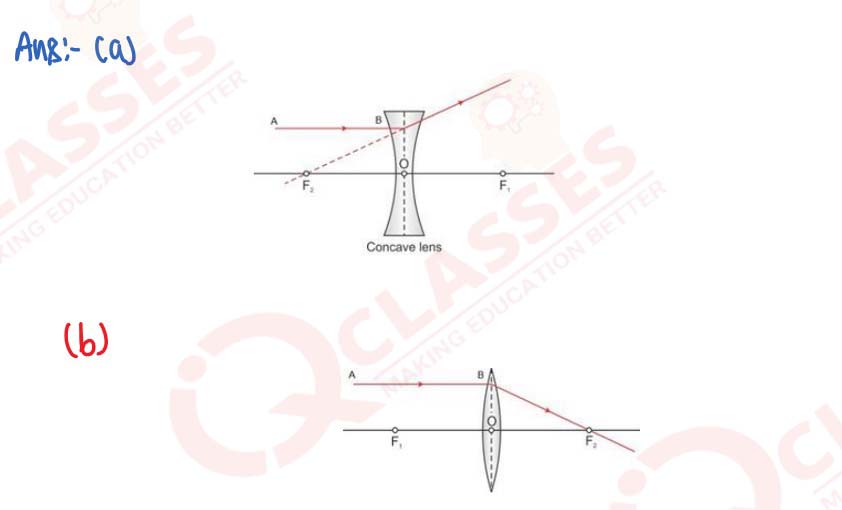
(a) Figure a

(b) Figure b

solutions

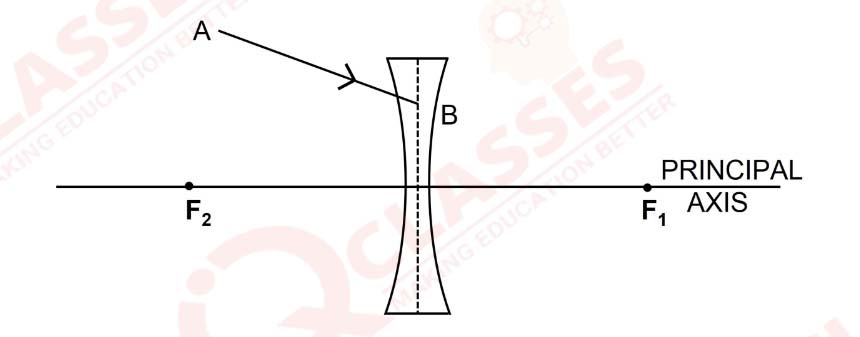
Q28
In figure (a) and (b), F1 and F2 are the two foci of thin lenses and AB is the incident ray. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray AB after refraction through the lens.
(a) Figure a
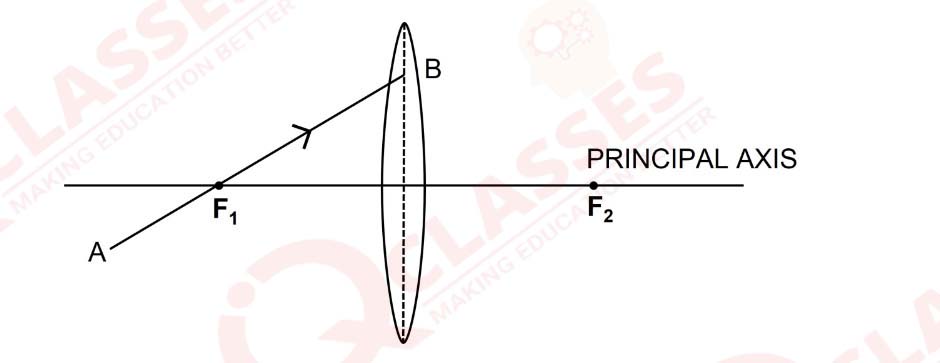
(b) Figure b
solutions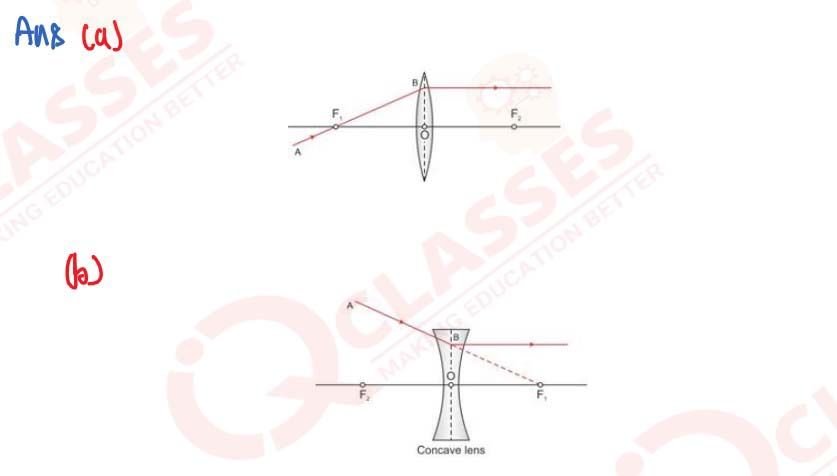
(a) Figure a

(b) Figure b

solutions

Q29
Complete the following sentences —
(a) If half part of a convex lens is covered, the focal length __________ change, but the intensity of image _________.
(b) A convex lens is placed in water. Its focal length will ________.
(c) The focal length of a thin convex lens is _________ than that of a thick convex lens.
solutions
(a) If half part of a convex lens is covered, the focal length __________ change, but the intensity of image _________.
(b) A convex lens is placed in water. Its focal length will ________.
(c) The focal length of a thin convex lens is _________ than that of a thick convex lens.
solutions

Multiple Choice type Questions :
Q1
A ray of light after refraction through a lens emerges parallel to the principal axis of the lens. The incident ray either passes through :
1. its optical centre
2. its first focus
3. its second focus
4. the centre of curvature of the first surface
solutions
1. its optical centre
2. its first focus
3. its second focus
4. the centre of curvature of the first surface
solutions

Q2
A ray of light incident on a lens parallel to its principal axis, after refraction passes through or appears to come from:
1. its first focus
2. its optical centre
3. its second focus
4. the centre of curvature of its second surface.
solutions
1. its first focus
2. its optical centre
3. its second focus
4. the centre of curvature of its second surface.
solutions
