Class XII ISC Chapter Probability Exercise 10.1
Access a comprehensive collection of probability questions, specially designed to help you grasp and apply this important mathematical topic. Our question bank covers various types of Integration, including first-order, second-order, homogeneous, and non-homogeneous equations, along with real-world applications in physics, engineering, and other fields. These practice questions will help you reinforce your problem-solving skills, deepen your conceptual understanding, and prepare effectively for exams. Whether you're a student or a learner aiming to master probability, our collection offers the perfect resource for practice and success.
class 12 Probability exercise2-1
Probability
Select Exercise
Q1 Given P(A)=3/5 P(B)=1/5 , Find P(A or B), given that A and B are mutually exclusive events.
Solution
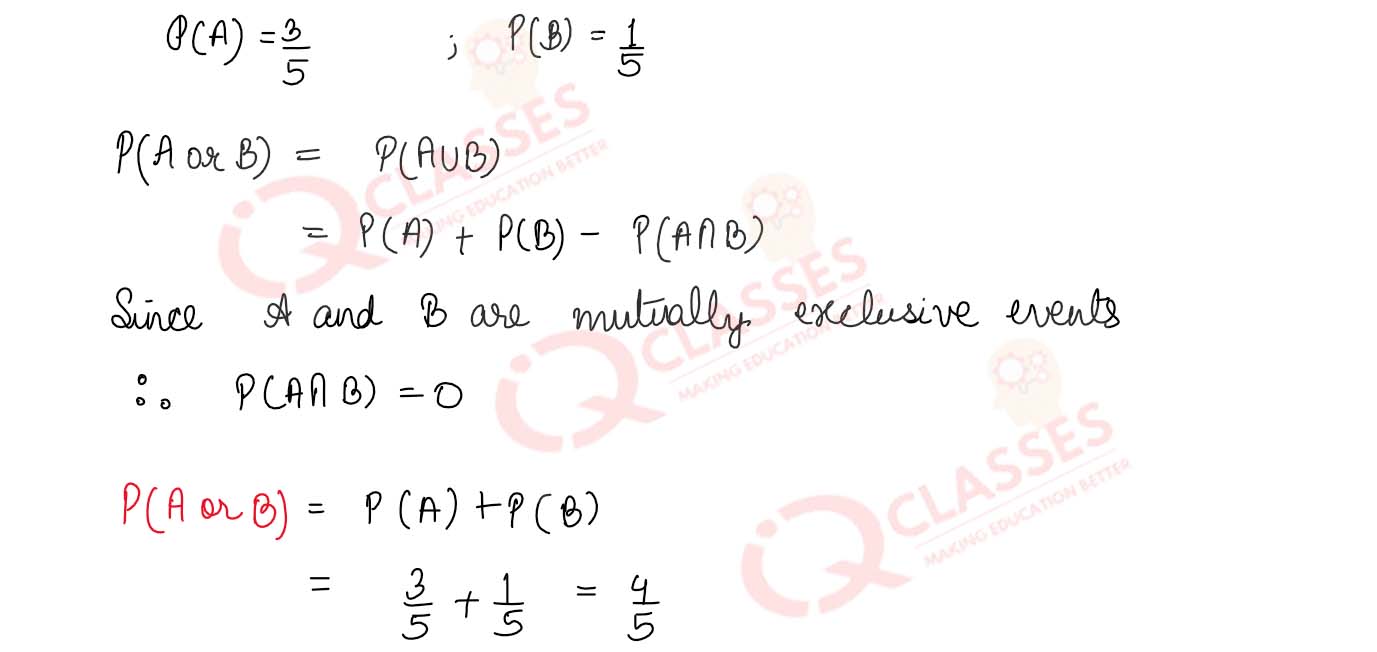
Q2 The probability of an event A occurring is 0.5 and of B is 0.3. If A and B are mutually exclusive events, then find the probability of neither A nor B occurring.
Solution
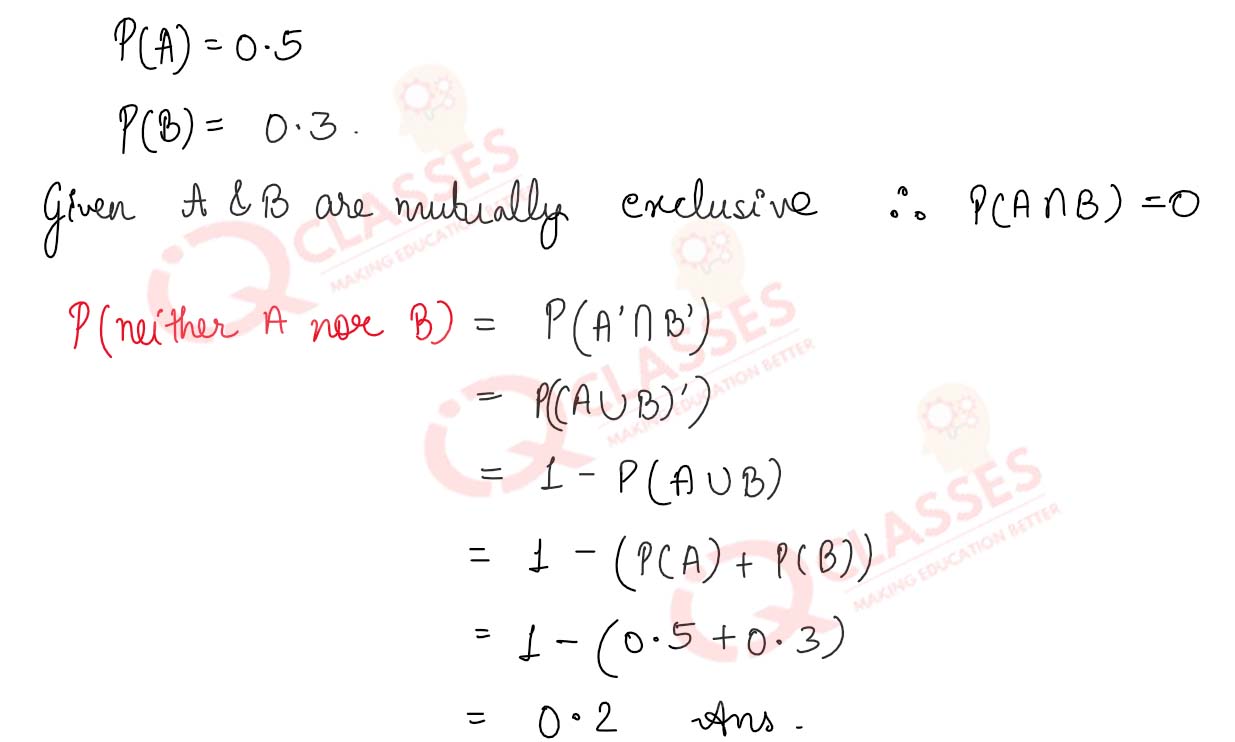
Q3
If A and B are mutually exclusive events, P (A) = 0.35 and P (B) = 0.45, then find
(i) P(A')
(ii) P(B’)
(iii) P(A U B)
(iv) P(A ∩ B)
(v) P(A ∩ B’)
(vi) P(A’ ∩ B’)
Solution
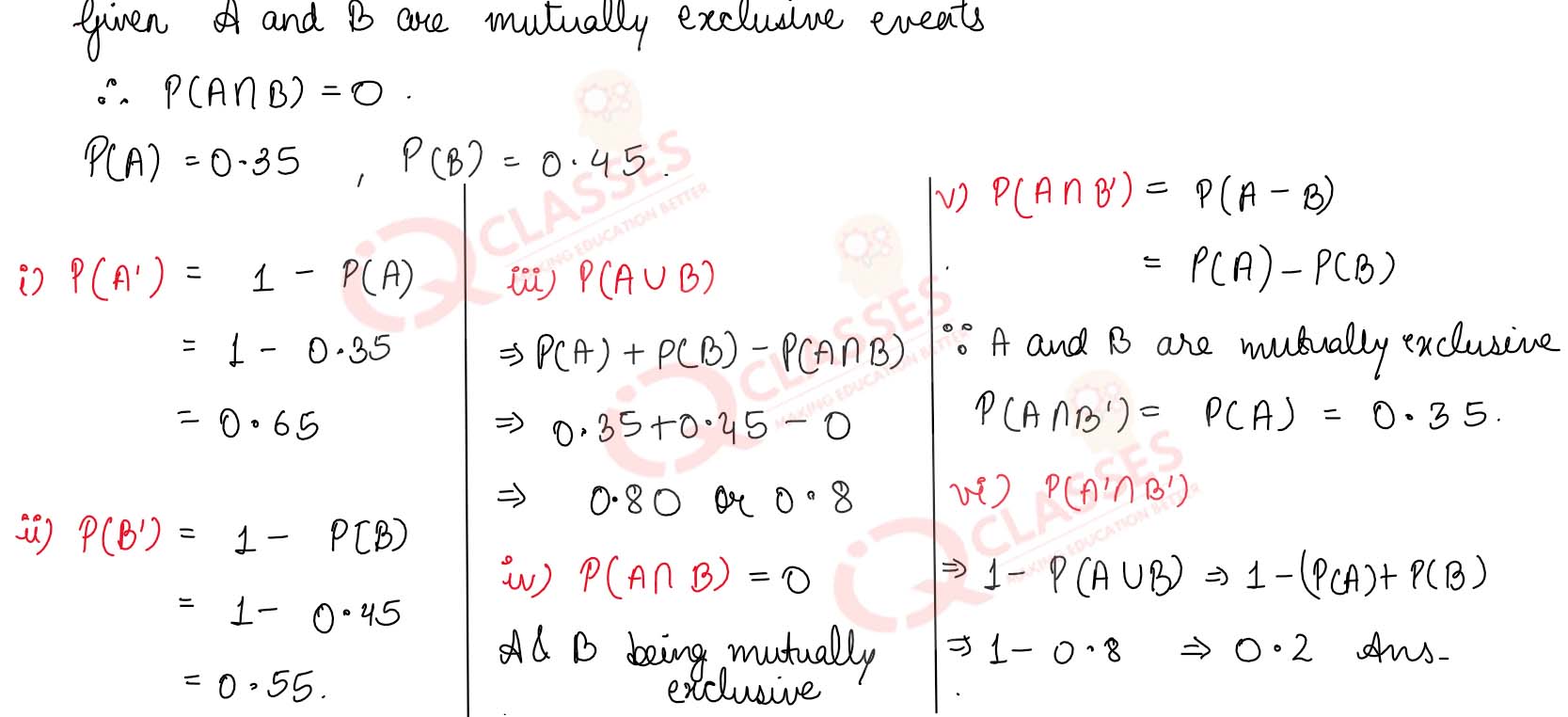
Q4
If E and F are events such that P(E) = 1/4, P(F) = 1/2 and P(E and F) = 1/8 find
(i) P(E or F) (ii) P(not E and not F).
Solution
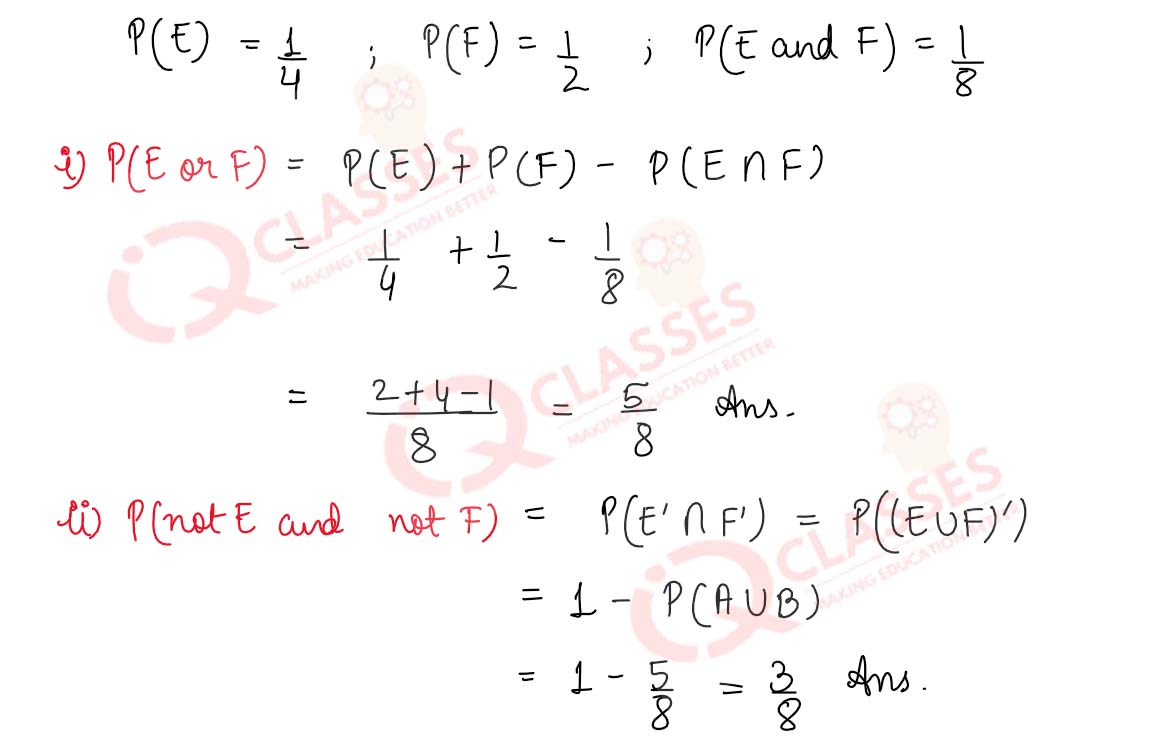
Q5
A and B are events such that P(A)
= 0.42, P(B) = 0.48 and P(A and B) = 0.16. Determine
(i) P(not A)
(ii) P(not B)
(iii) P(A or B).
Solution

Q6 A and B are two mutually exclusive event of an experiment. If P(not A) = 0.65, P(A U B) = 0.65 and P(B) = p, find the value of p.
Solution

Q7 E and F are two events associated with a random experiment for which P(E) = 0.60, P(E or F) = 0.85, P(E and F) = 0.42. Find P(F).
Solution

Q8 If A, B and C are mutually exclusive and exhaustive events and it is known that P(A U B) = 0.63, calculate P(C).
Solution
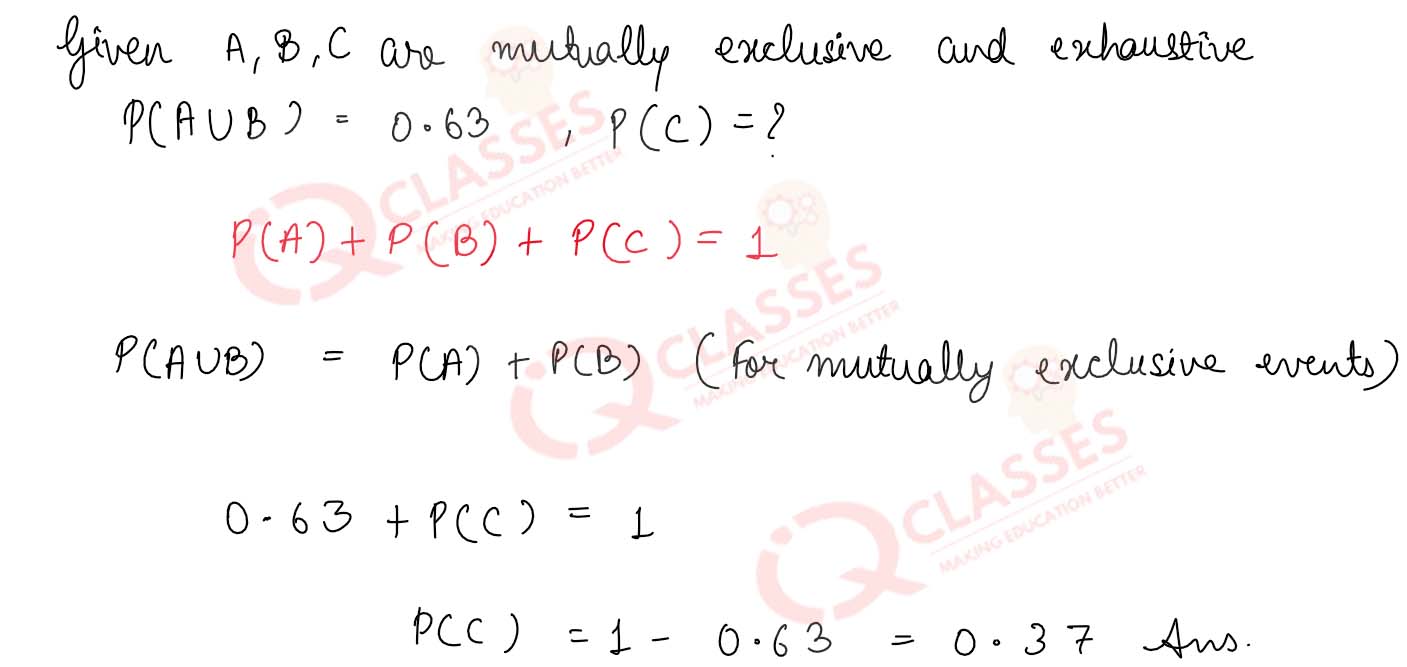
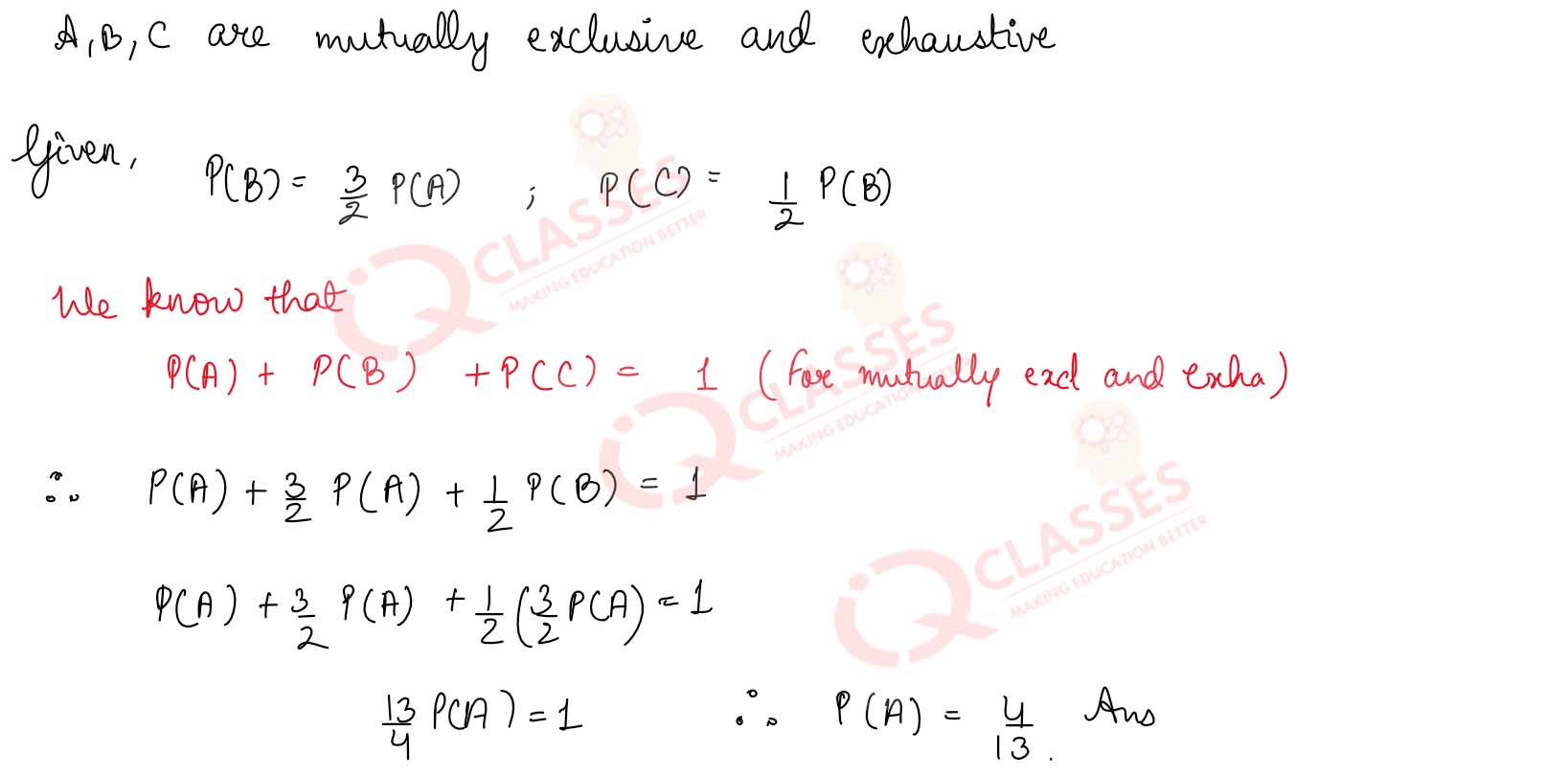
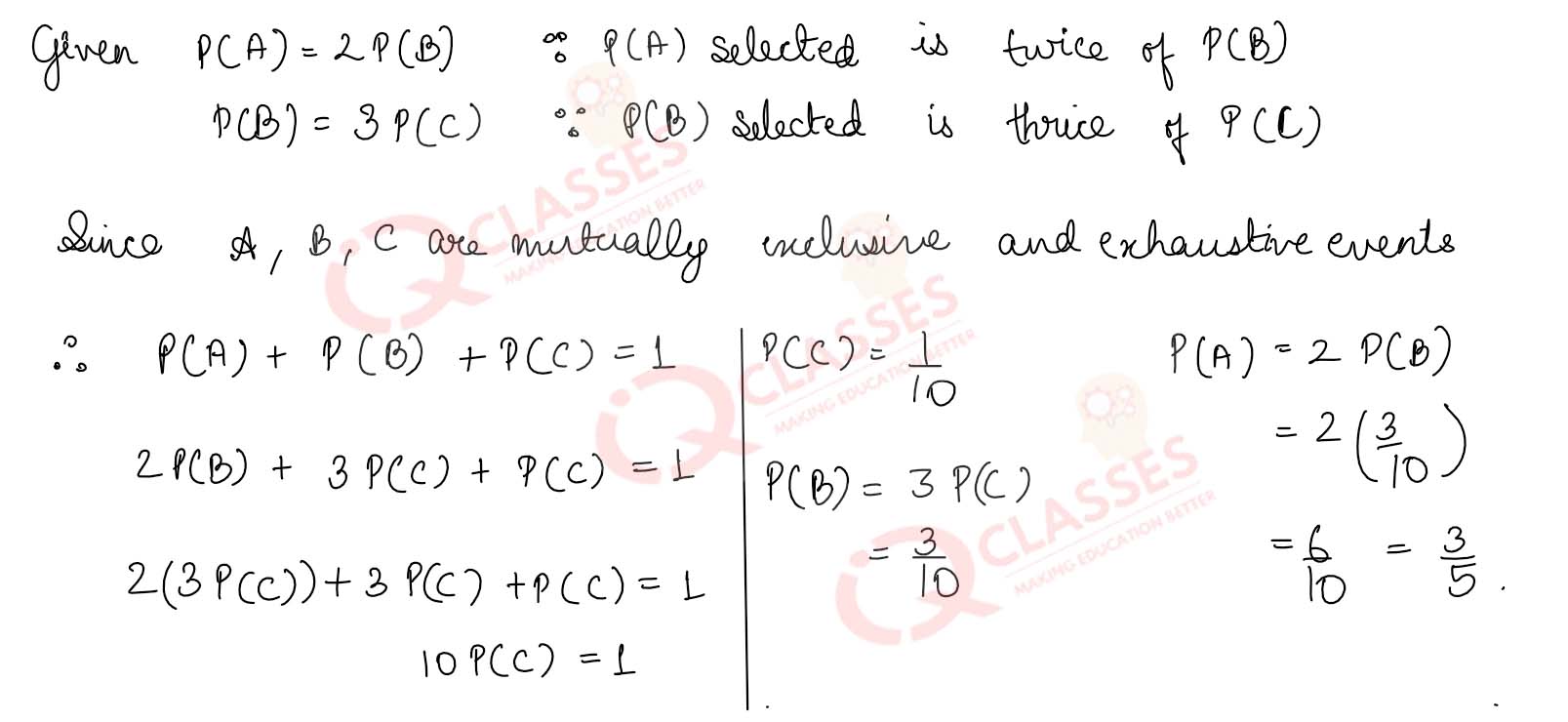
Q9
A, B, C are three mutually exclusive and exhaustive events associated with a random
experiment. Find P(A), it being given that P(B) =
3
/
2
P(A) and P(C) =
1
/
2
P(B).
Solution
Q10 A and B are two candidates seeking admission in an engineering college. The probability that A is selected is 0.5 and the probability that both are selected is atmost 0.3 . It is possible that the probability of B getting selected is 0.7?
Solution

Q11 The probability of an event A occurring is 2/3 and the probability of event B not occurring is 5/9 . If the probability of getting success in atleast one of the two events is 4/5, what is the probability of success in both the events?
Solution

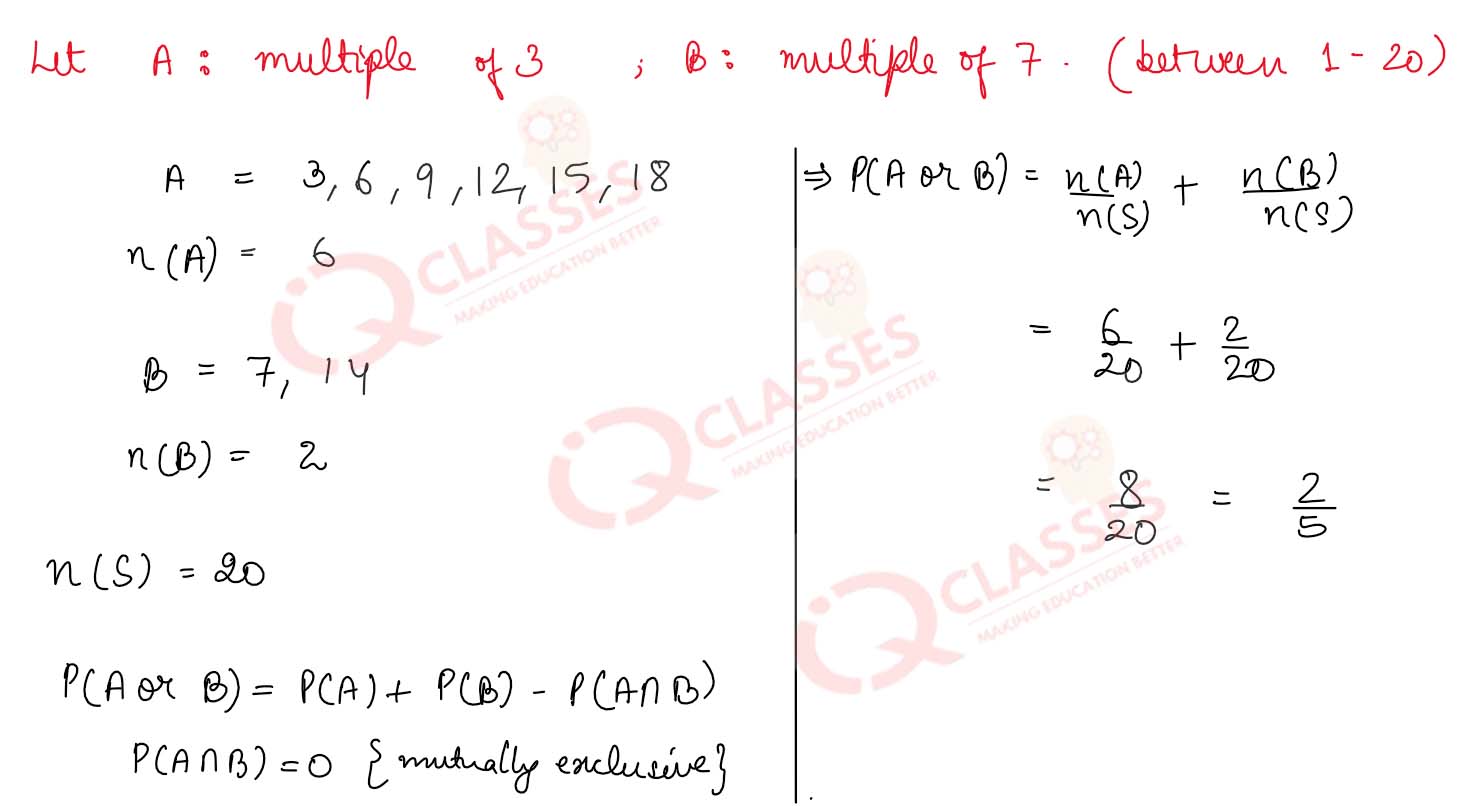
Q12 Tickets numbered from 1 to 20 are mixed up together and when a ticket is drawn at random What is the probability that the ticket has a number which is multiple of 3 or 7?
Solution
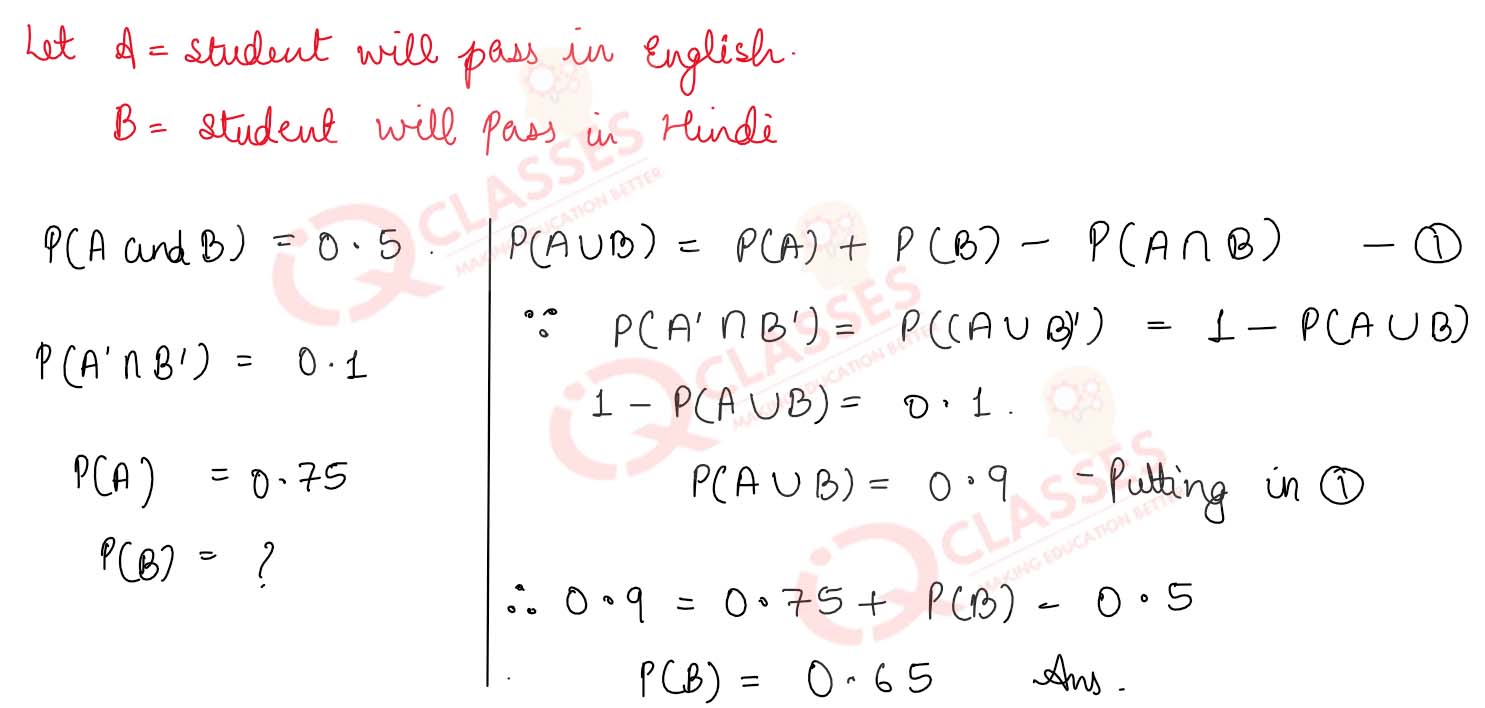
Q13 The probability that a student will pass the final examination in both English and Hindi is 0.5 and the probability of passing neither is 0.1 . If the probability of passing the English is 0.75 . What is the probability of passing Hindi examination
Solution
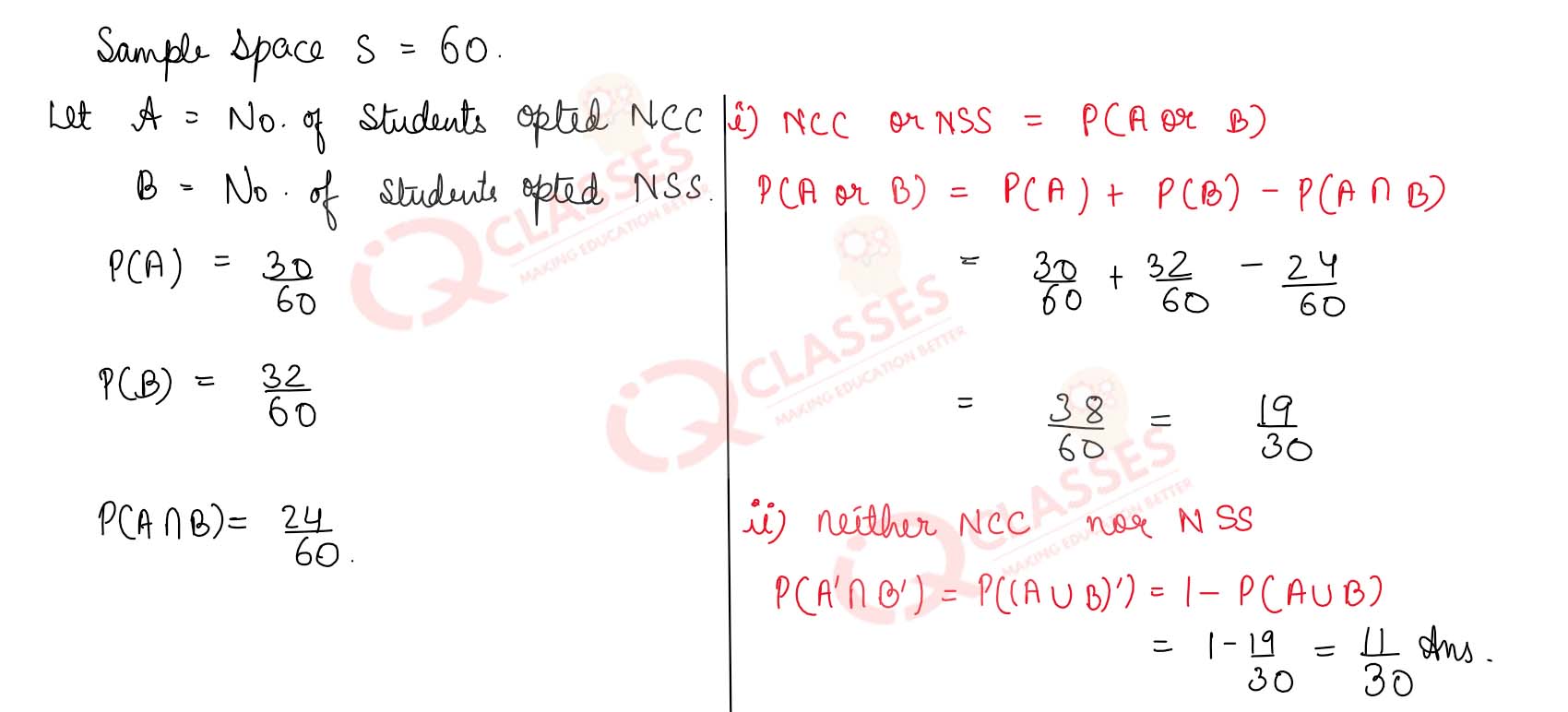
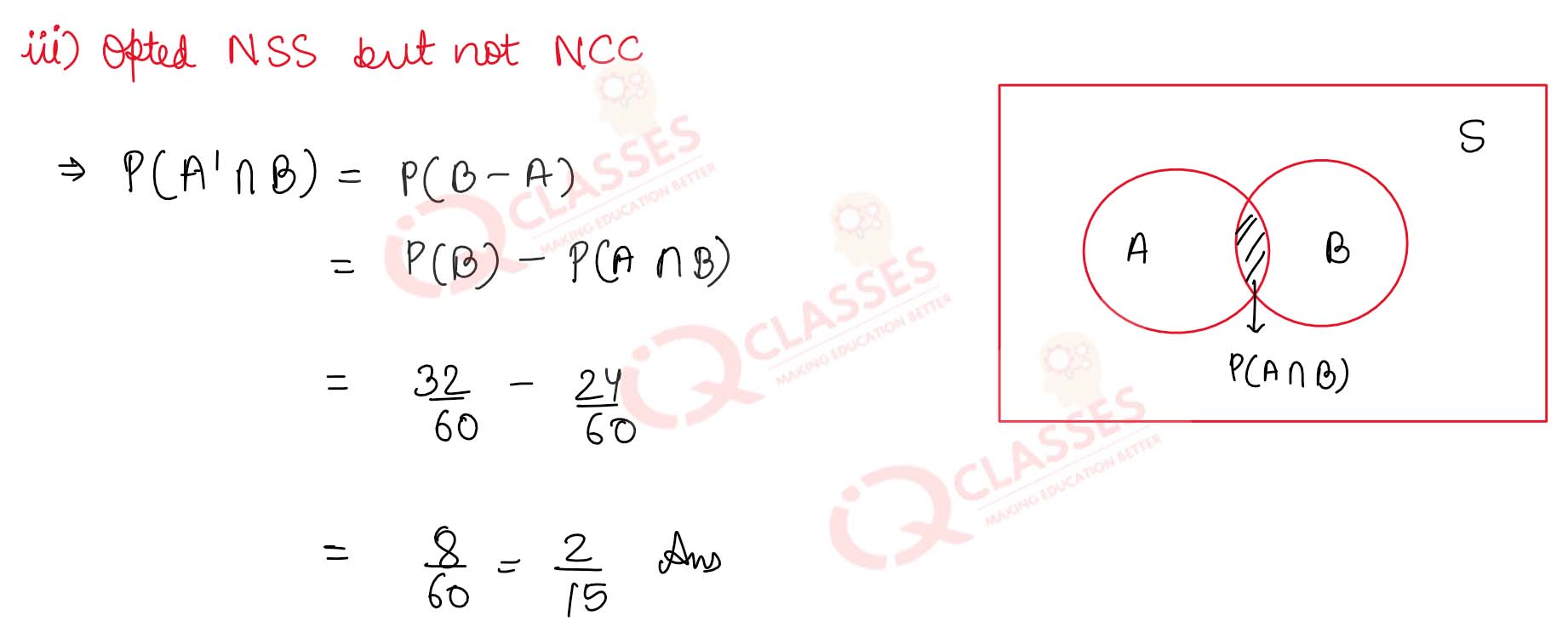
Q14
In a class of 60 students, 30 opted for NCC, 32 opted for NSS and 24 opted for both NCC and NSS. If one
of these students is selected at random find the probability that
(i) the student opted for NCC or NSS.
(ii) the student has opted neither NCC nor NSS.
(iii) the student has opted NSS but not NCC.
Solution
Q15 For a post, three persons A, B and C appear in an interview. The probability of A being selected is twice that of B and the probability of B being selected is thrice that of C. If the post is filled , what is the probabilities of A, B and C being selected?
Solution
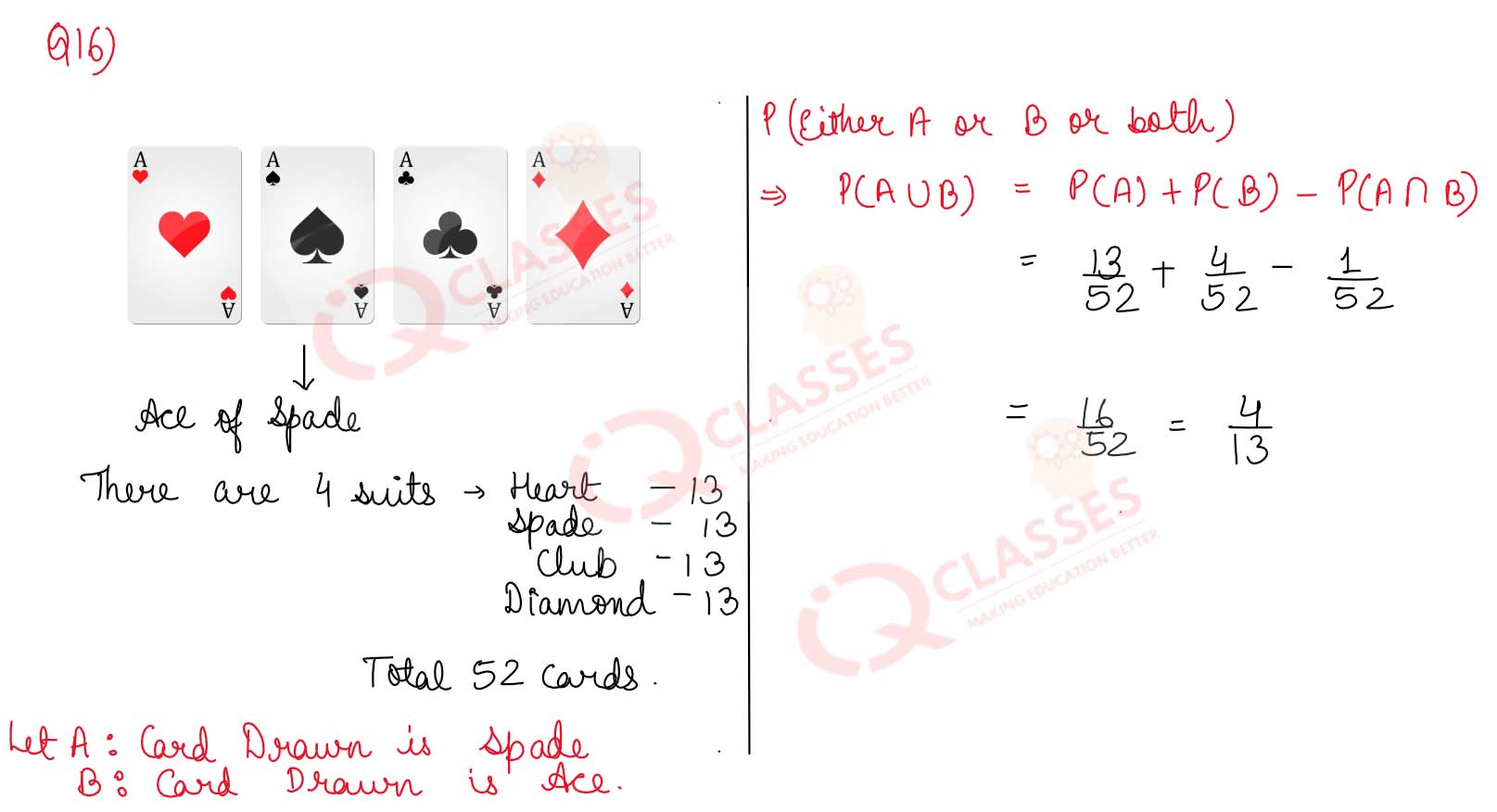
Q16 A card is drawn from a well shuffled pack of playing cards . What is the probability that it is either a spade or an ace or both?
Solution
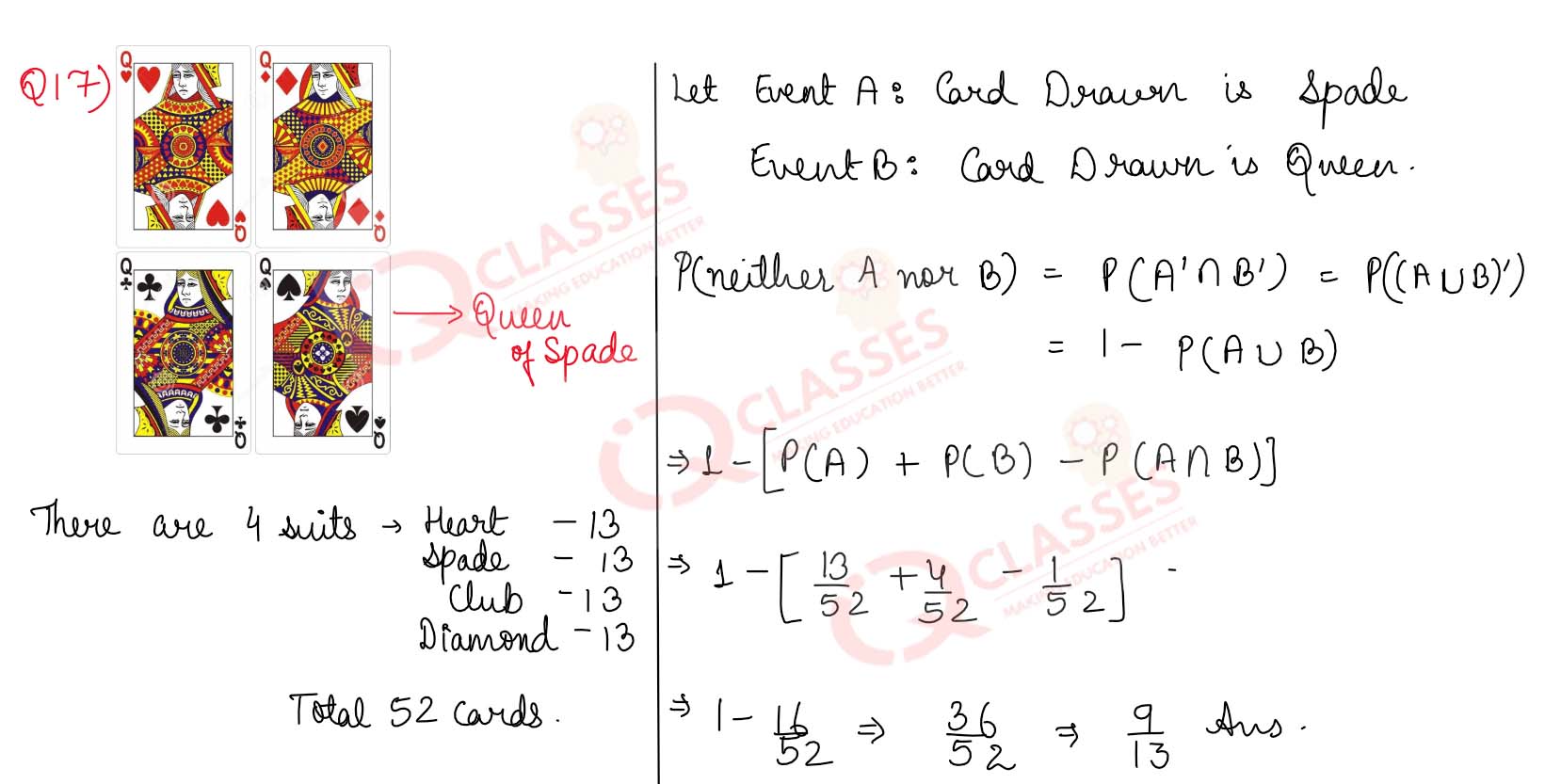
Q17) A card is drawn at random from a pack of 52 playing cards. What is the probability that the card drawn is neither a spade nor a queen?
Solution
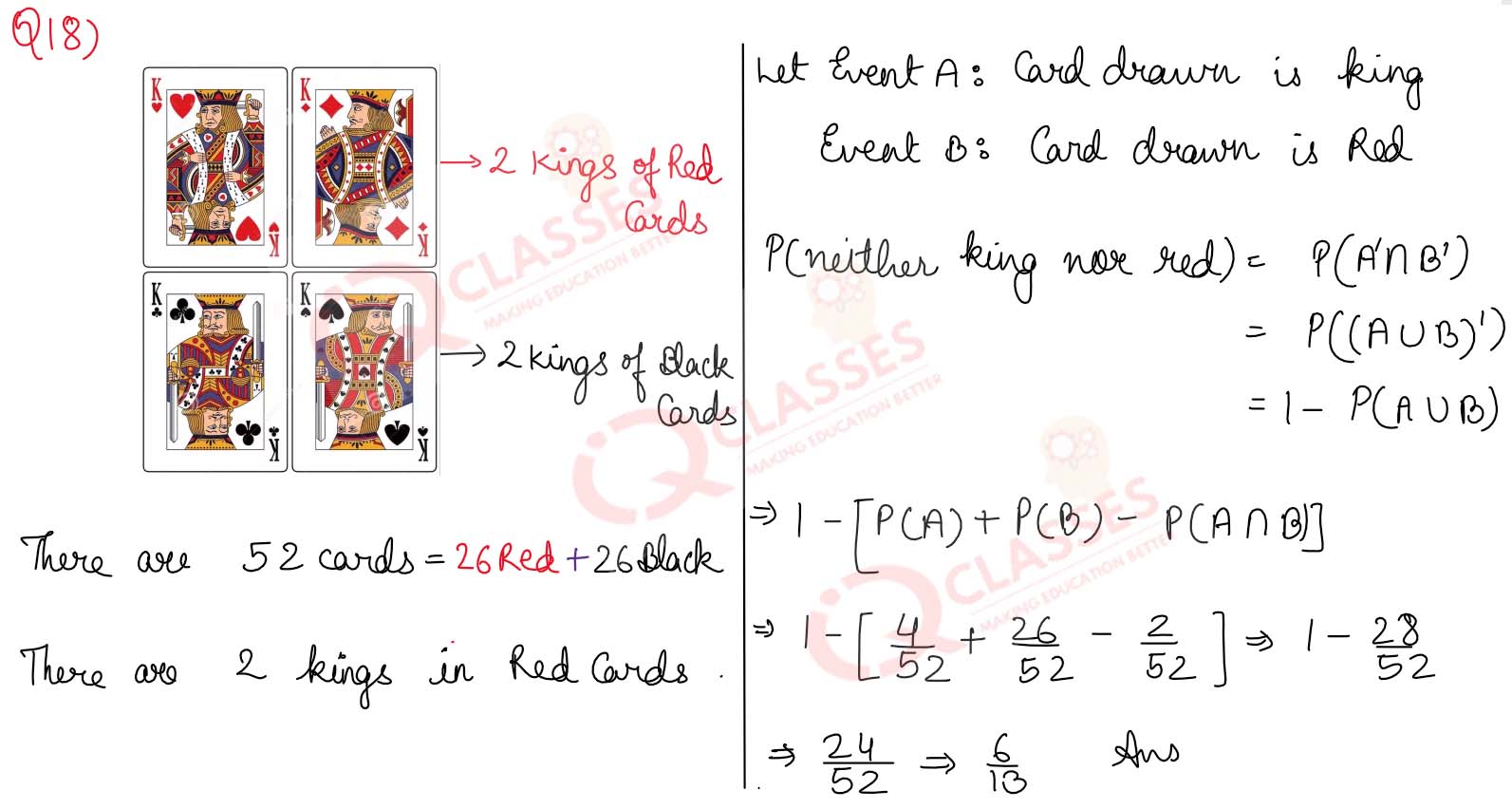
Q18) A card is drawn at random from well shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability that it is neither a king nor a red card.
Solution
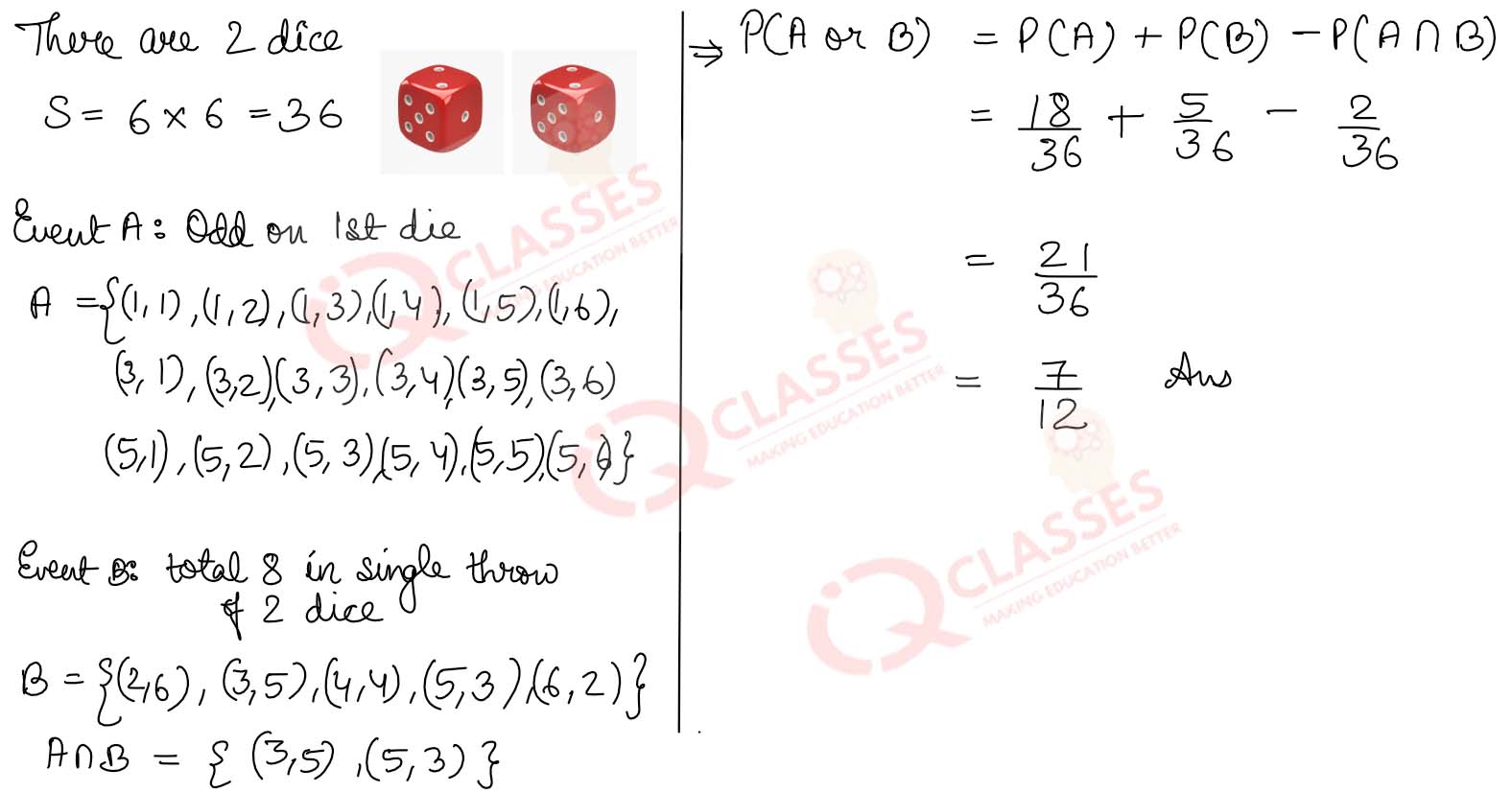
Q19 Find the probability of getting an odd number on the first die or a total of 8 in a single throw of two dice.
Solution
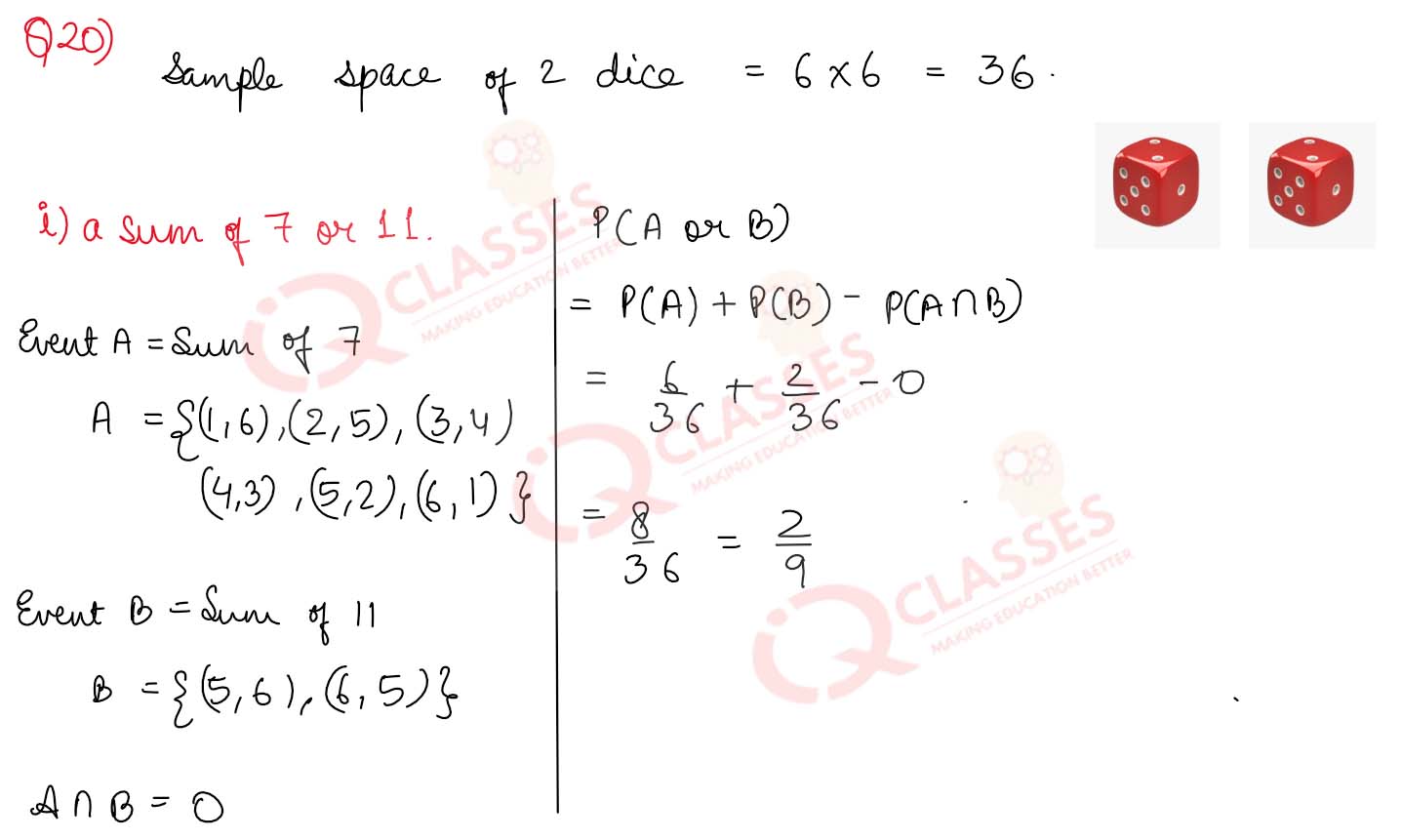
Q20
If two dice are thrown simultaneously, find the probability of getting
(i) a sum of 7 or 11
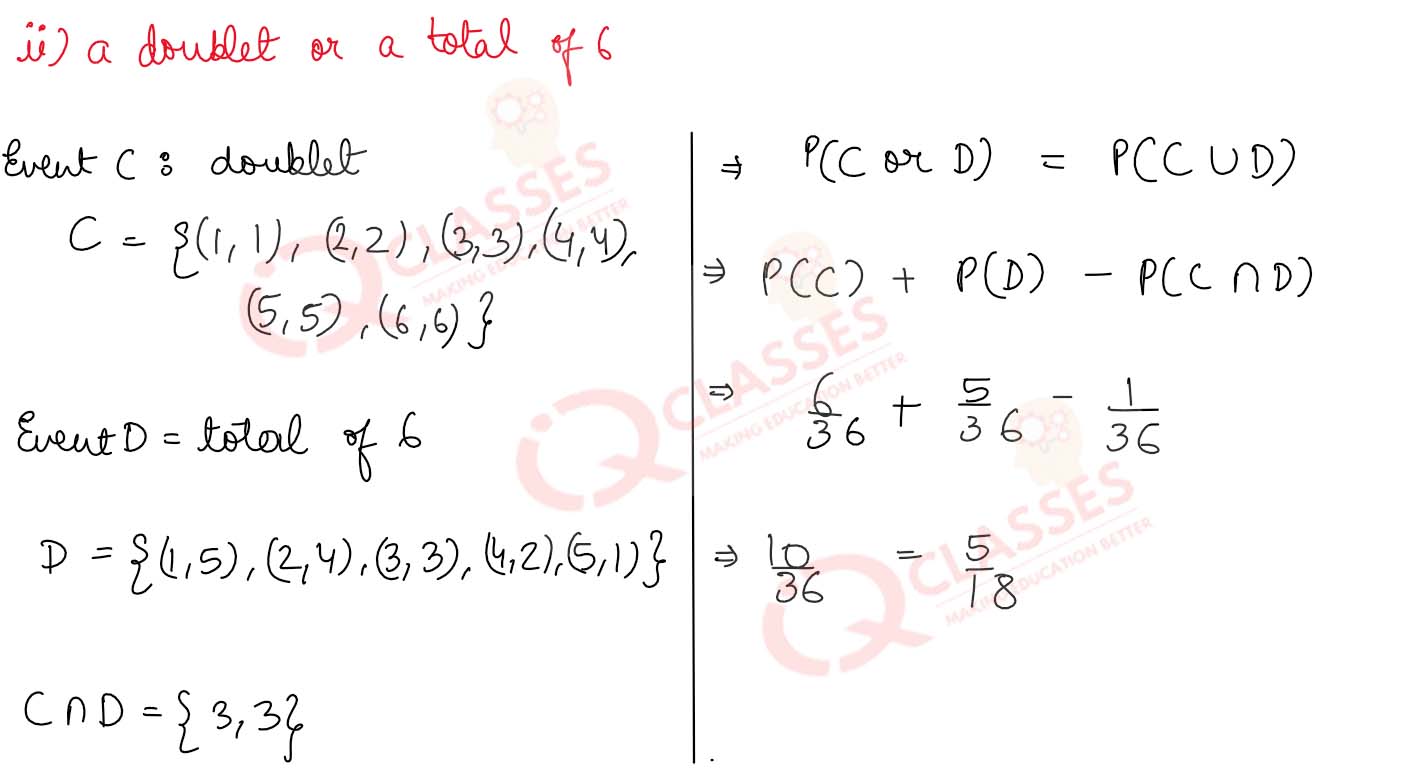
(ii) a doublet or a total of 6.
Solution
Q21
The probabilities that a student will get A, B, C or D grade are 0.4, 0.35 , 0.15 and 0.1
reapectively. Find the probability that she will get
(i) B or C grade (ii) atmost C grade.
Solution

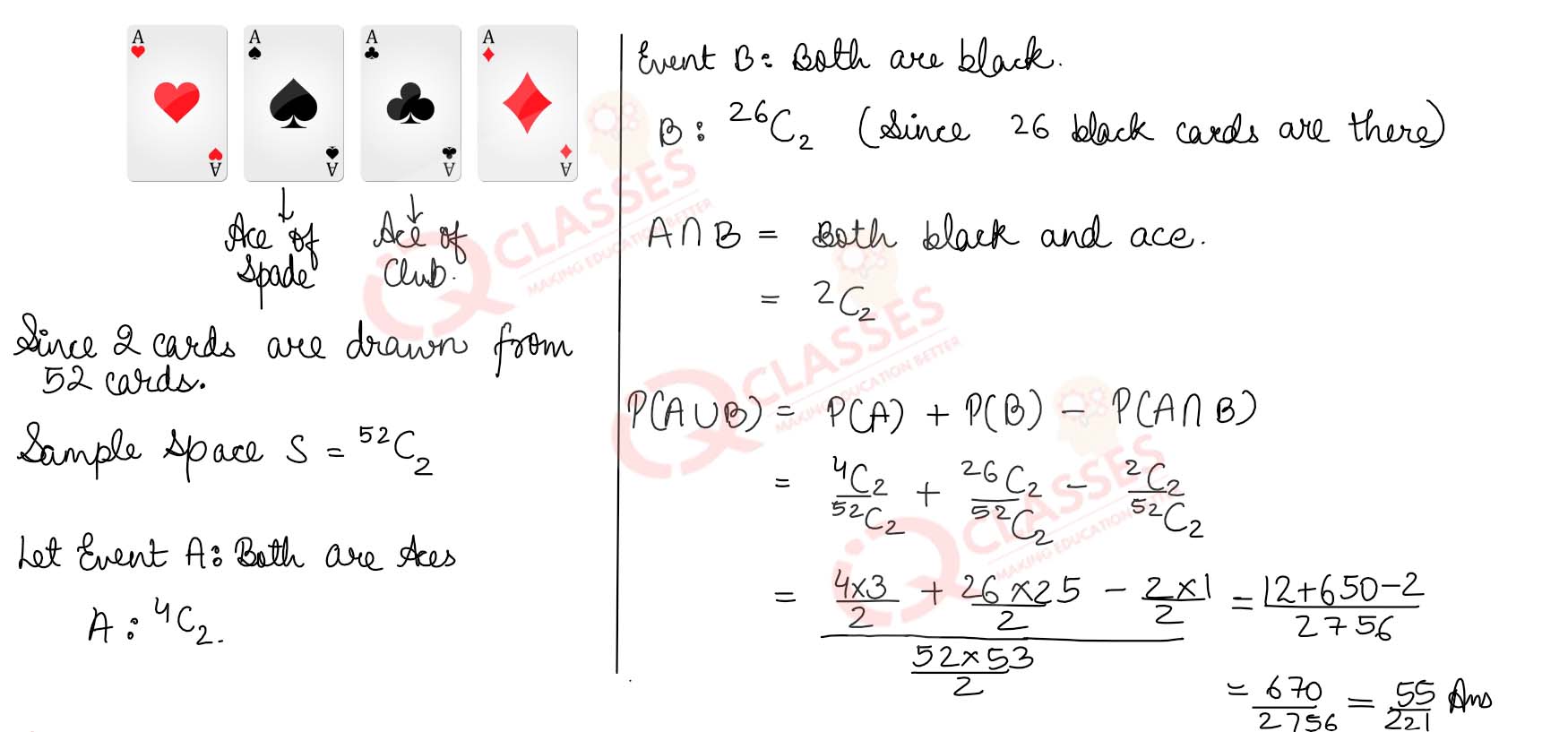
Q22 Two cards are drawn at random from a pack of 52 cards. What is probability that the cards are either both aces or both black cards.
Solution
Q23 A basket contains 20 apples and 10 oranges out of which 5 apples and 3 oranges are defective. If a person takes out 2 fruits at random , find the probability that either both are apples or both are good.
Solution



Add a comment