11-1
What are alcohols and how are they classified?
Solution
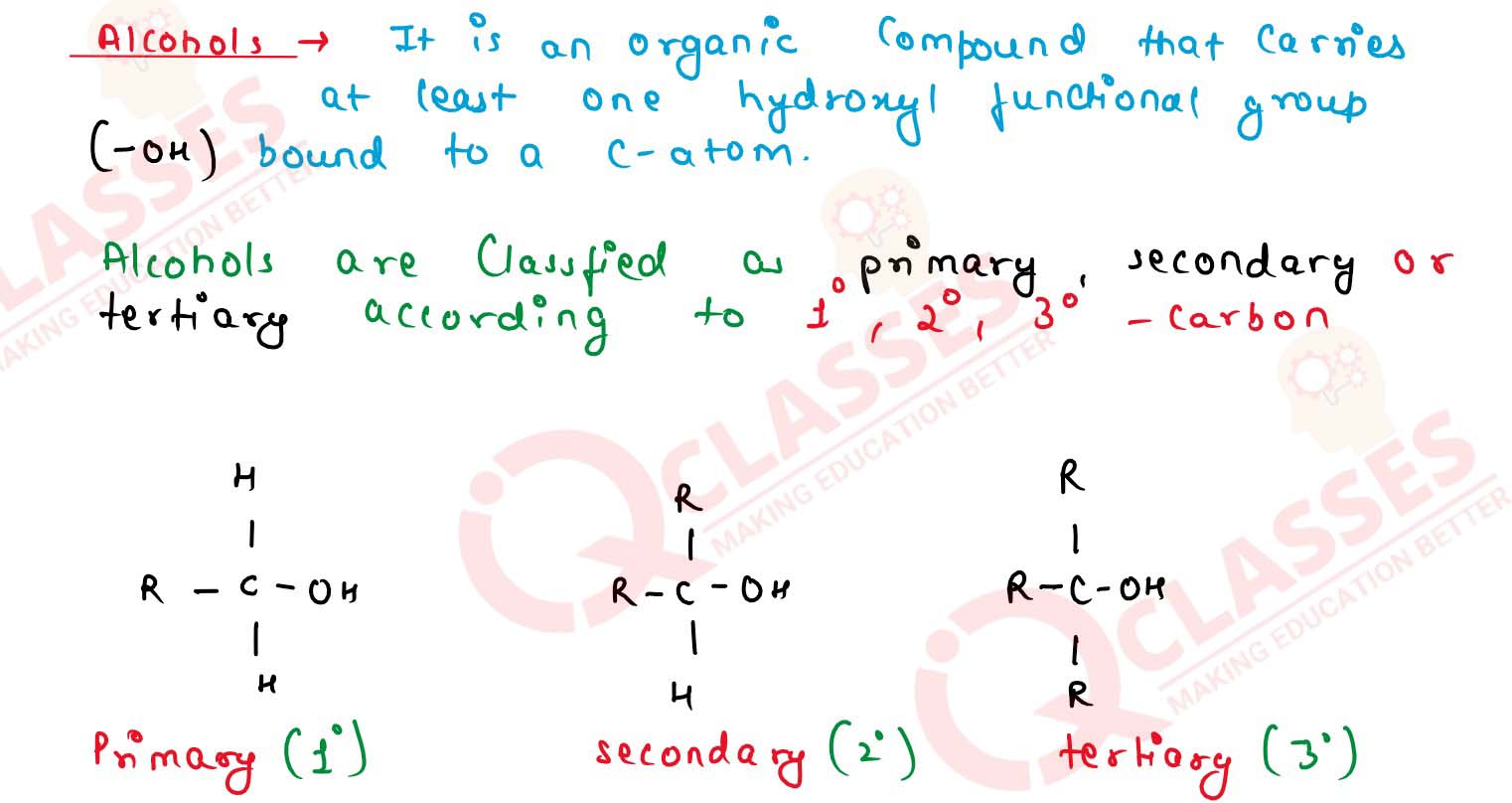

11-2
Give one example each of a 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols.
Solution
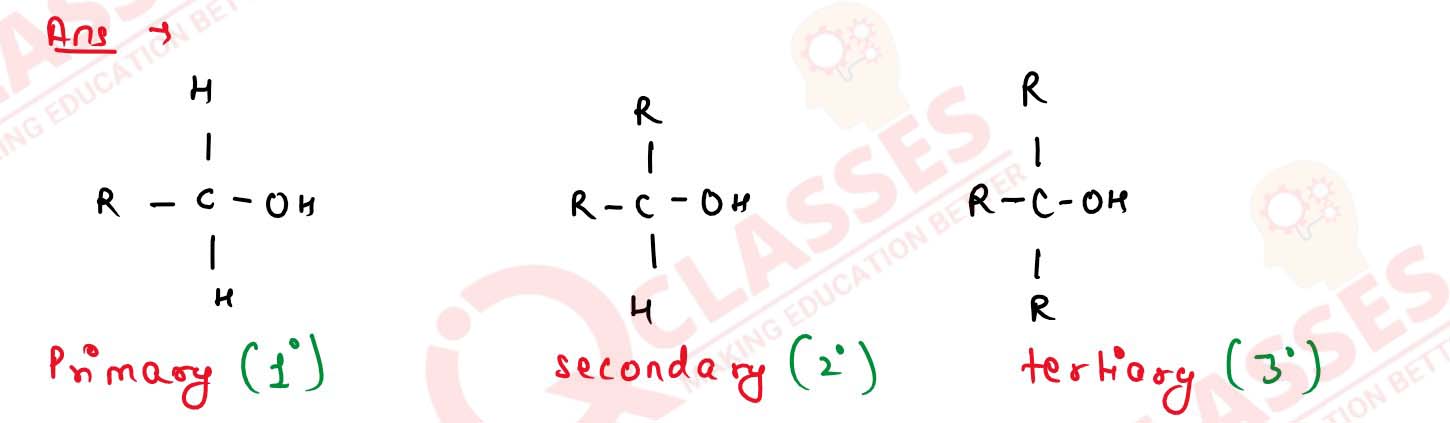

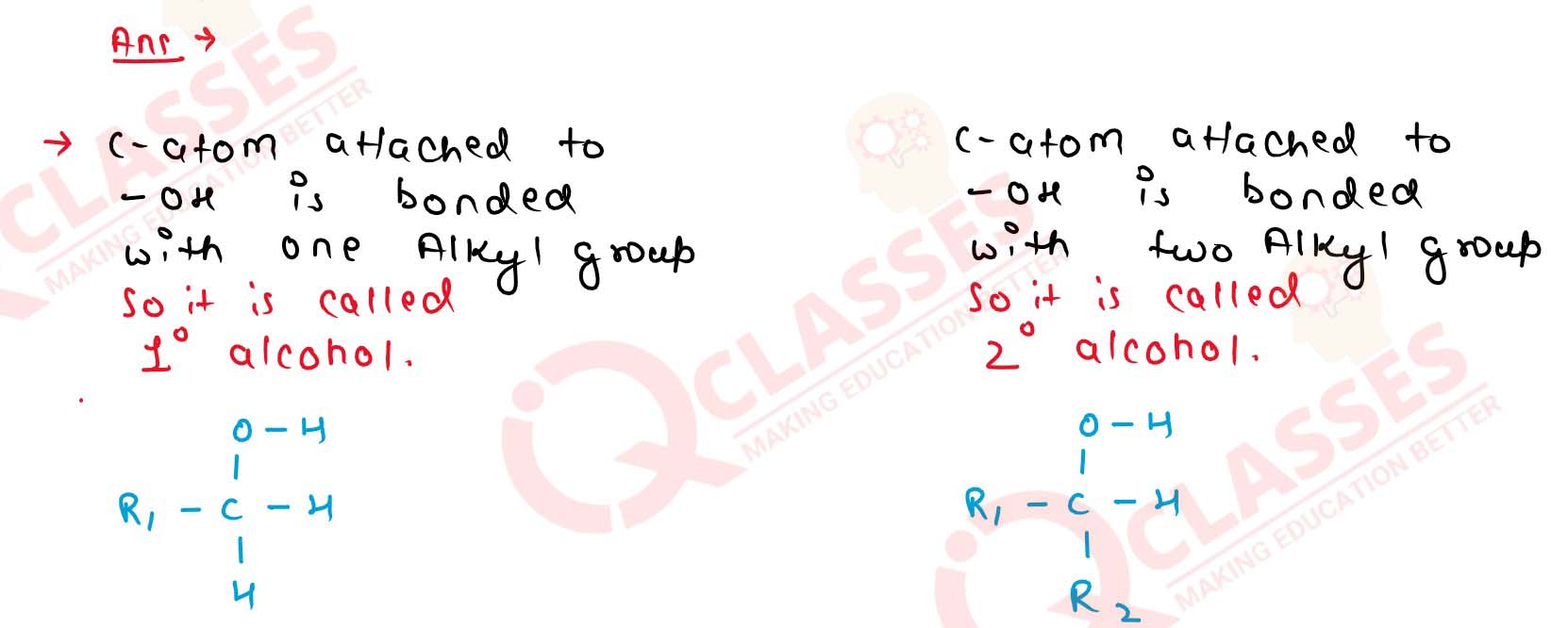
11-3
What is the main structural difference between 1° and 2°
alcohols? Explain with examples.
Solution

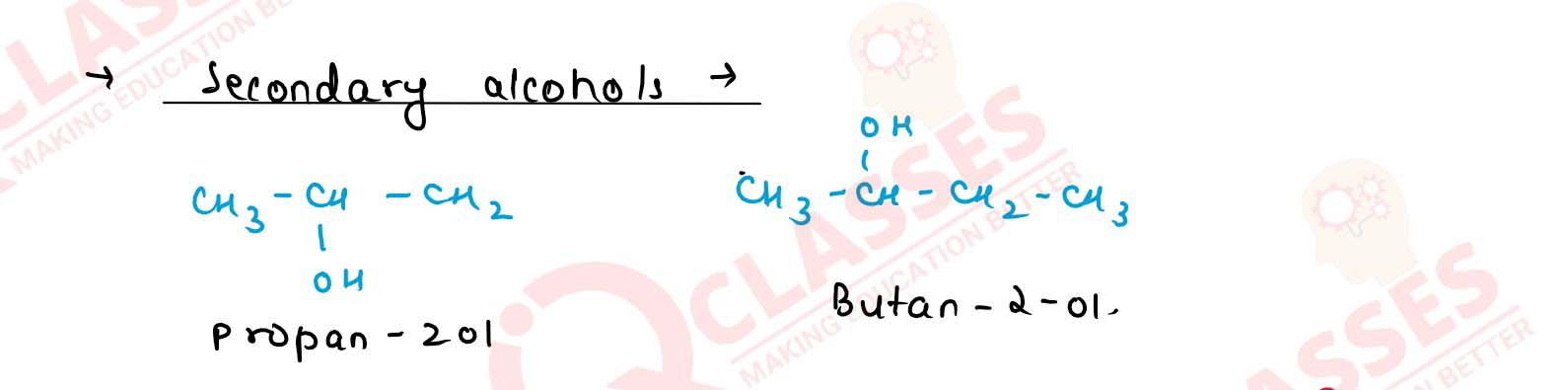


11-4
What are phenols and how do they differ from alcohols?
Solution


11-5
How are phenols classified?
Solution


11-6
Write the structural formulae and I.U.PA.C. names of the
following:
(a) Glycerol
(b) o-cresol
(c) Catechol
(d) Pyrogallol Solution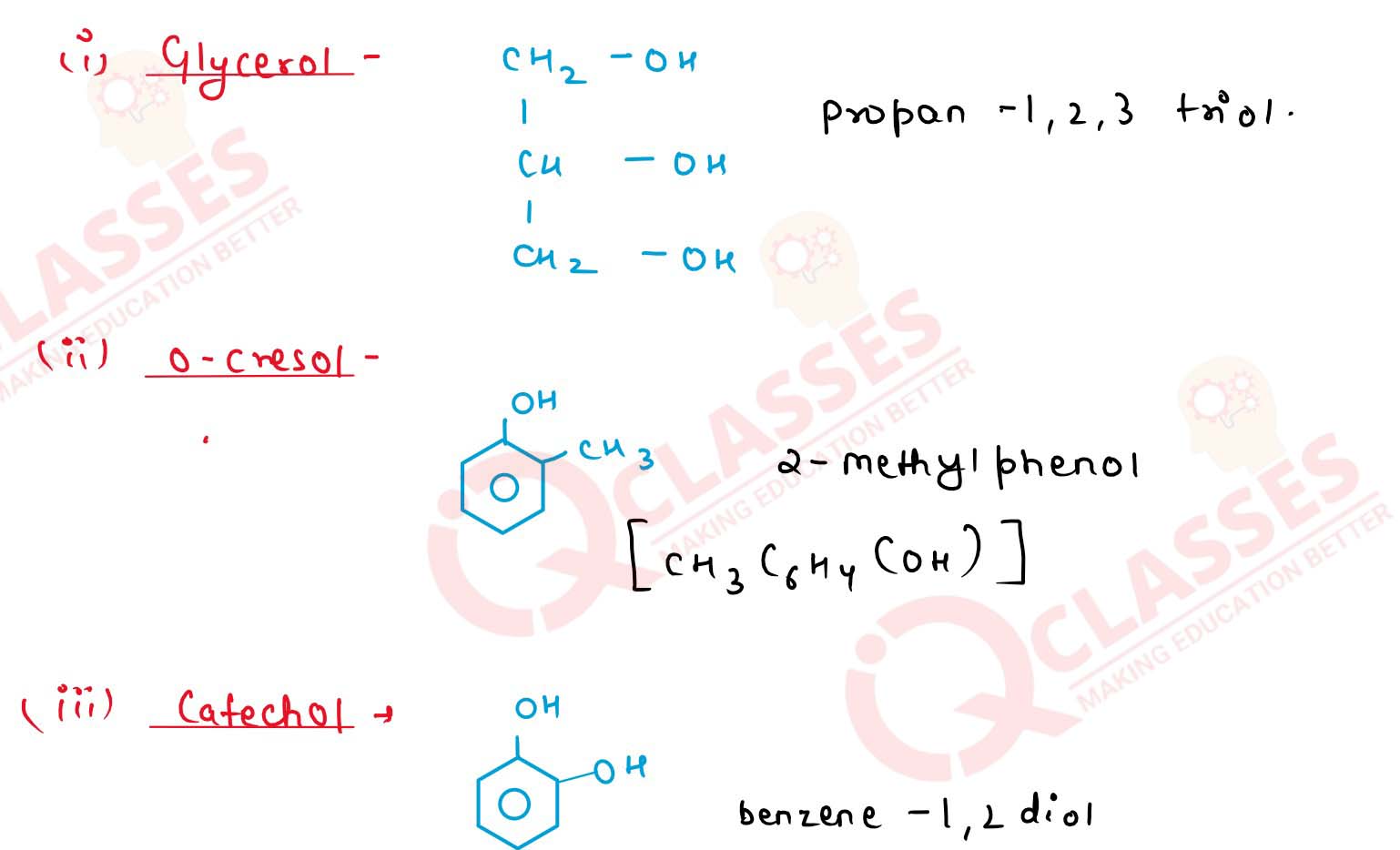
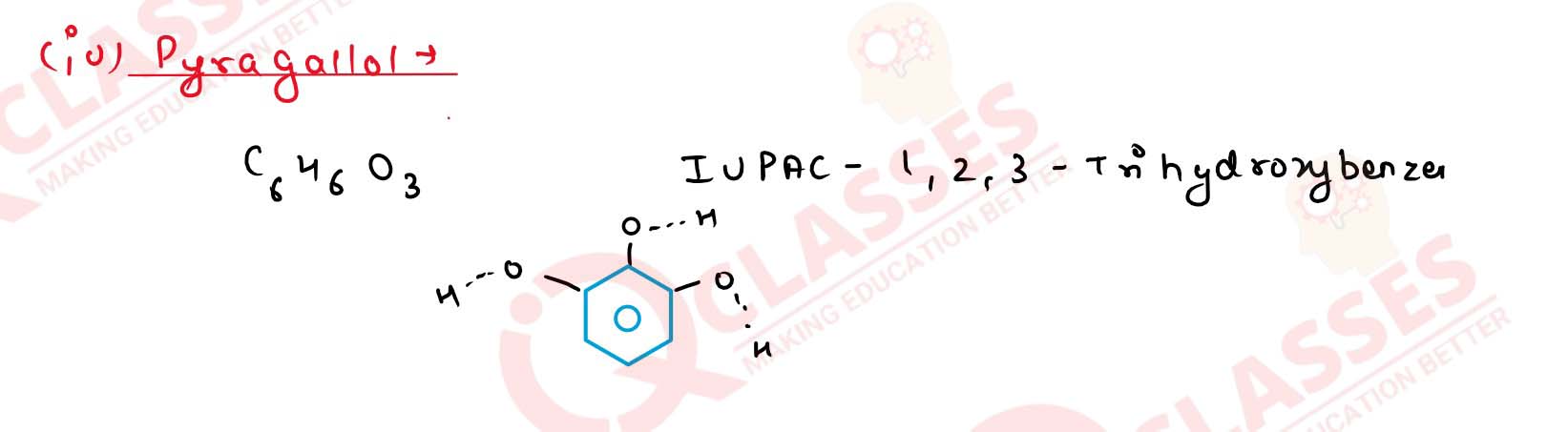
(a) Glycerol
(b) o-cresol
(c) Catechol
(d) Pyrogallol Solution


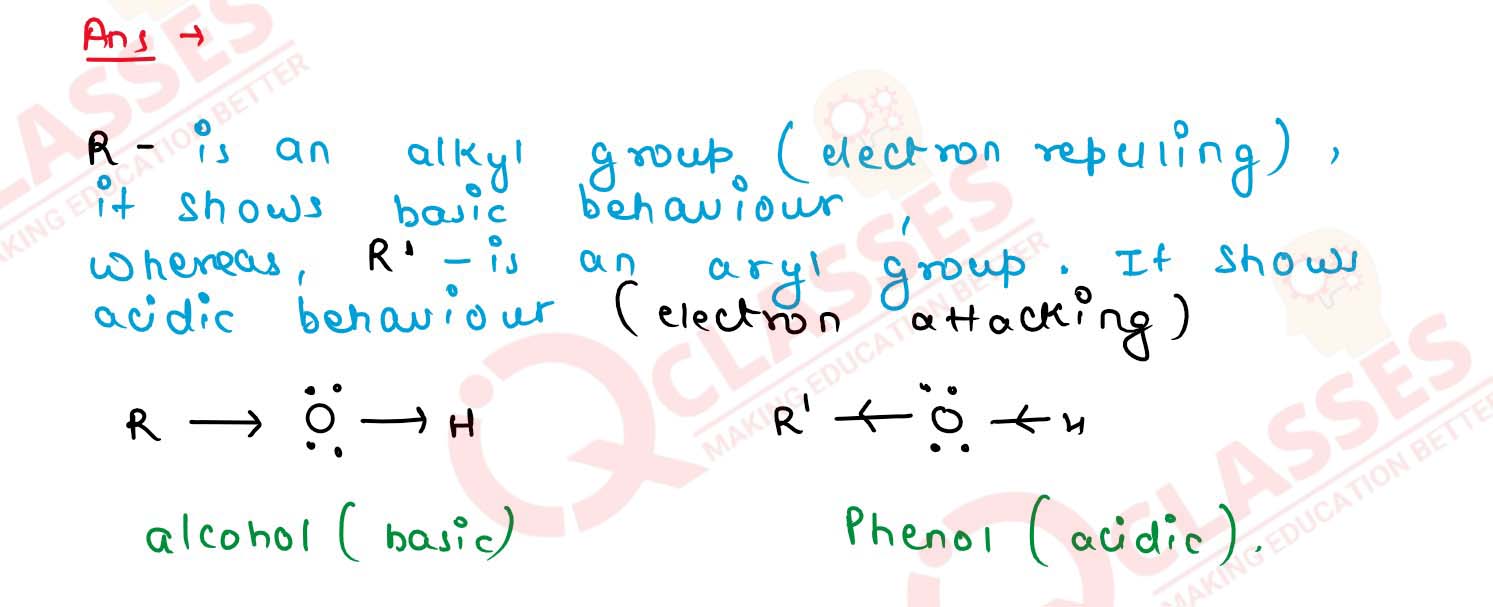
11-7
Of the two hydroxy organic compounds ROH and R’OH, the
first one is basic and the other is acidic in behavior. How is R
different from R'?
Solution

11-8
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds :
 Solution
Solution

 Solution
Solution

11-9
Classify the following as primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols.
(i) n-propyl alcohol
(ii) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iii) Butan-1-ol
(iv) Butan-2-ol
(v) iso-butyl alcohol
(vi) Benzyl alcohol
Solution
(i) n-propyl alcohol
(ii) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iii) Butan-1-ol
(iv) Butan-2-ol
(v) iso-butyl alcohol
(vi) Benzyl alcohol
Solution

11-10
Write down the structural formulae of all the isomeric alcohols having the molecular formula
C4H10O.
Solution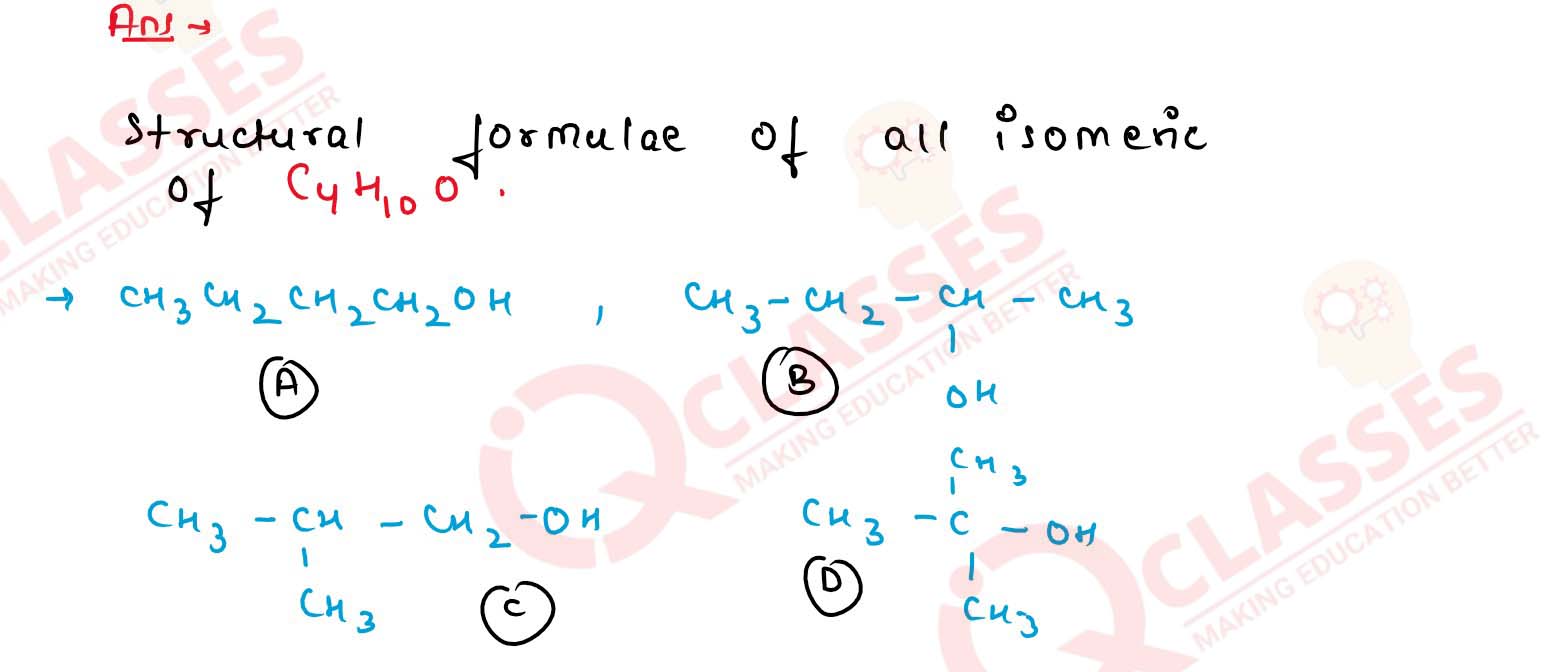
Solution

11-11
Alcohols are generally soluble , Explain
Solution


11-12
Why do alcohols have higher boiling points than the corresponding haloalkanes and hydrocarbons?
Solution


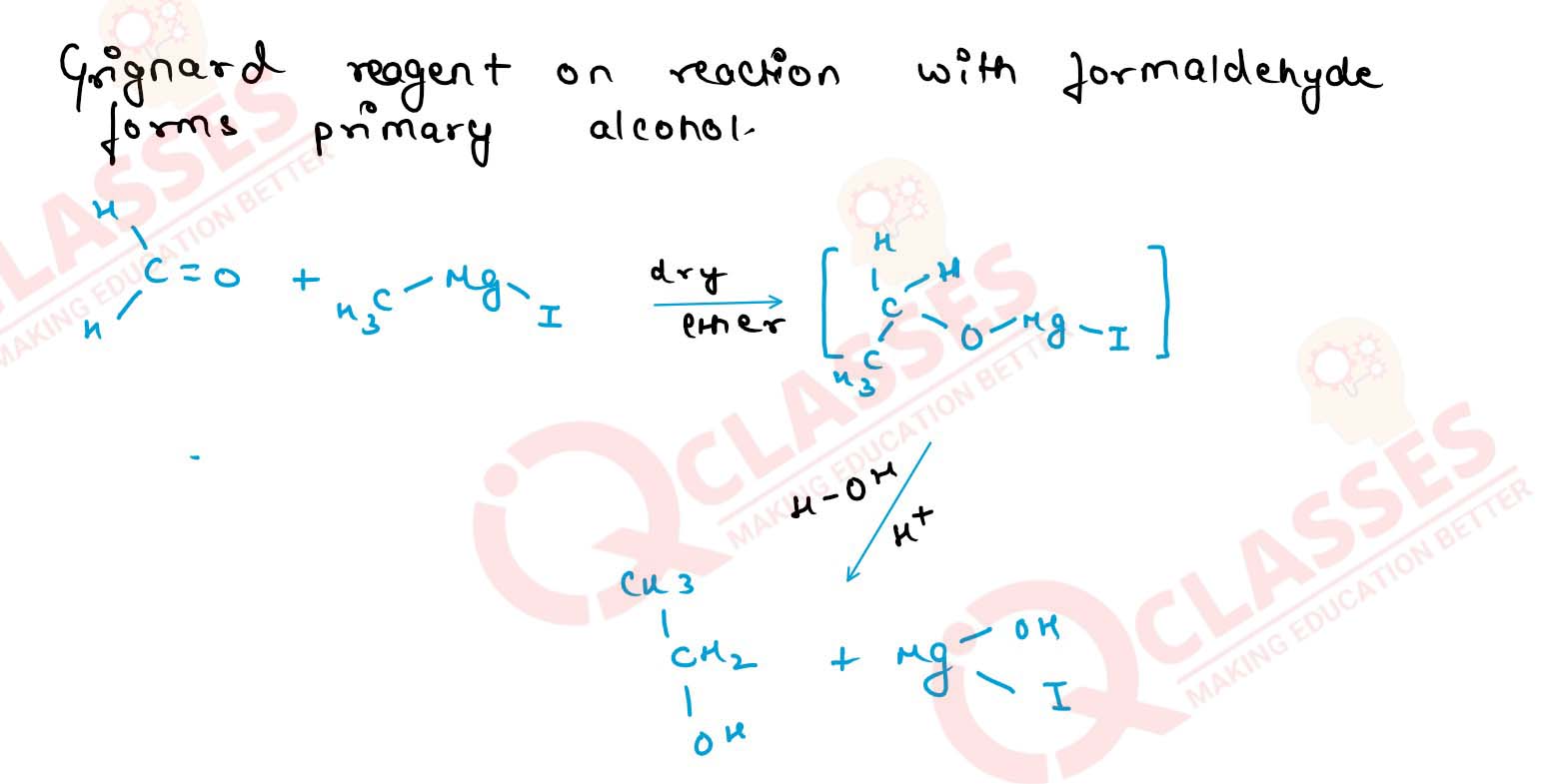
11-13
Write the equation involved in the preparation of secondary butyl alcohol using a Grignard reagent. Name
the reactants.
Solution

11-14
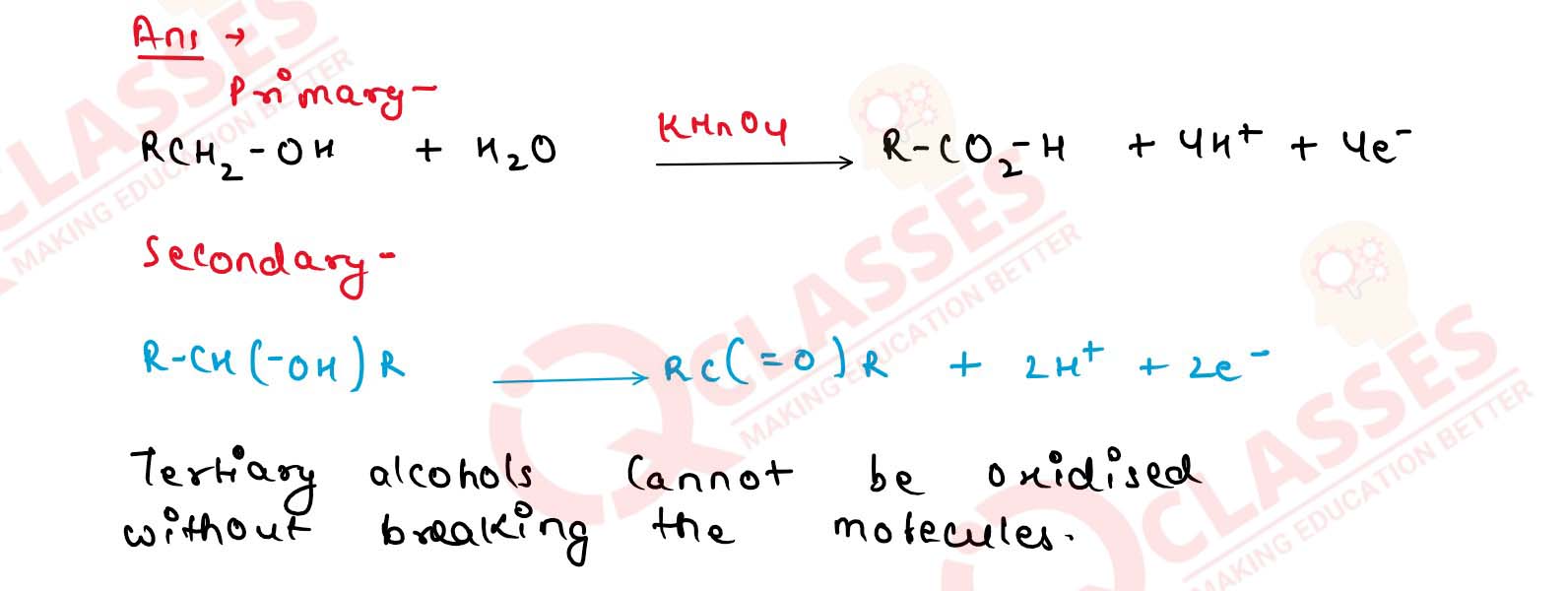
What happens when Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are oxidised using alkaline KMnO4?
Solution

11-15
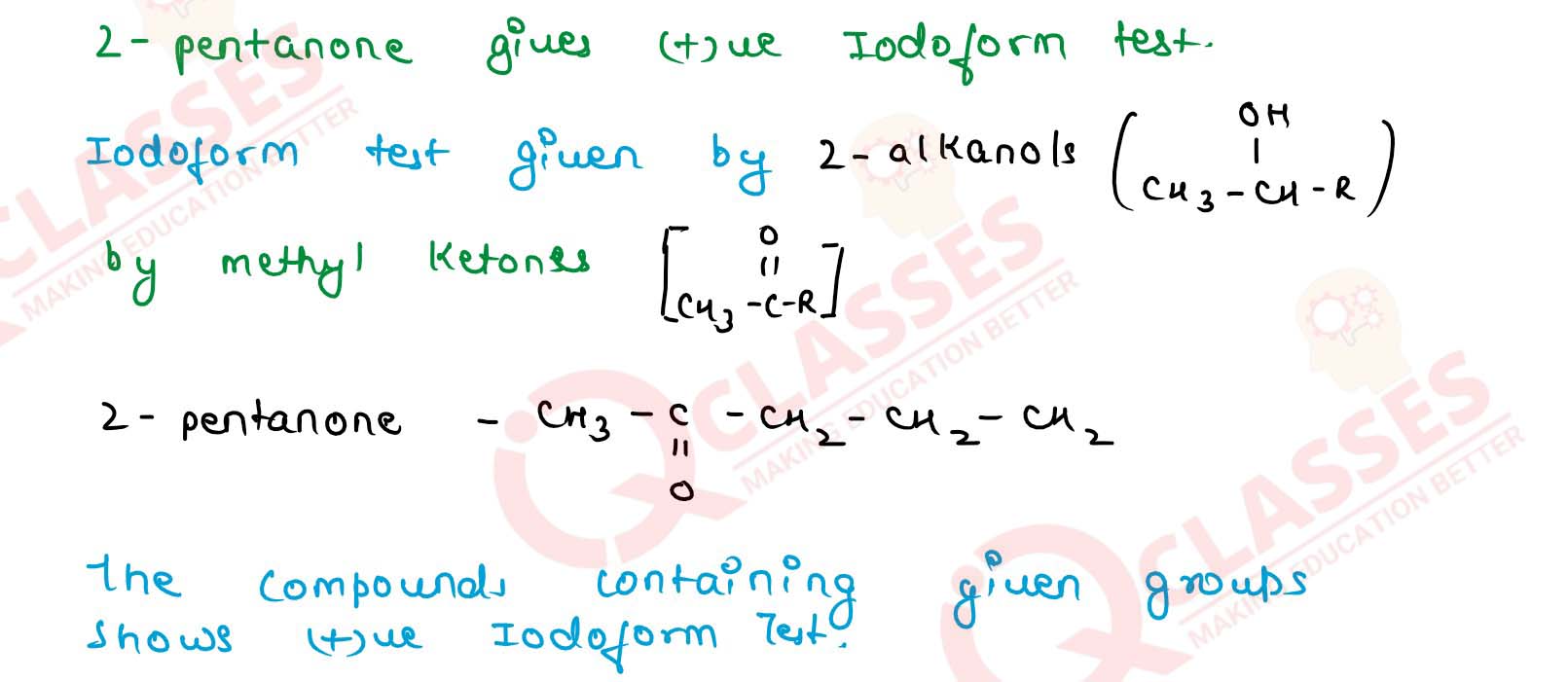
What type of compounds give iodoform test?
Solution

11-16
Explain the mechanism of the following reaction :
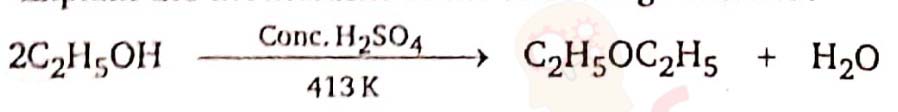 Solution
Solution
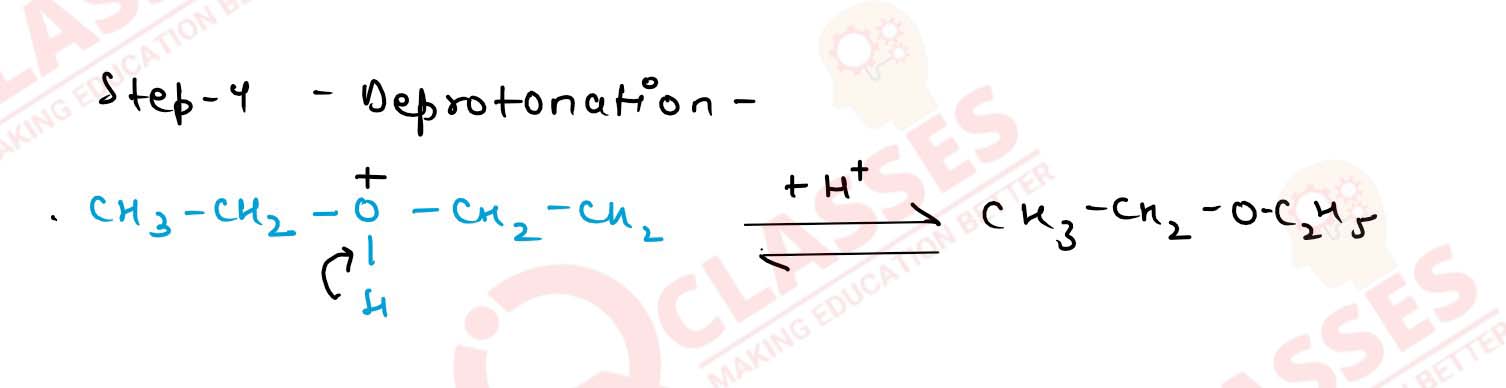
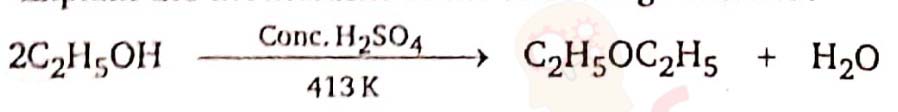 Solution
Solution


11-17
How would you obtain
(i) propan-2-o] from propanone;
(ii) butan-2-ol from ethanol;
(iii) propan-2-ol from ethanol;
(iv) tert-buty] alcohol from acetone;
(v) ethane-1, 2-diol from ethanol? Solution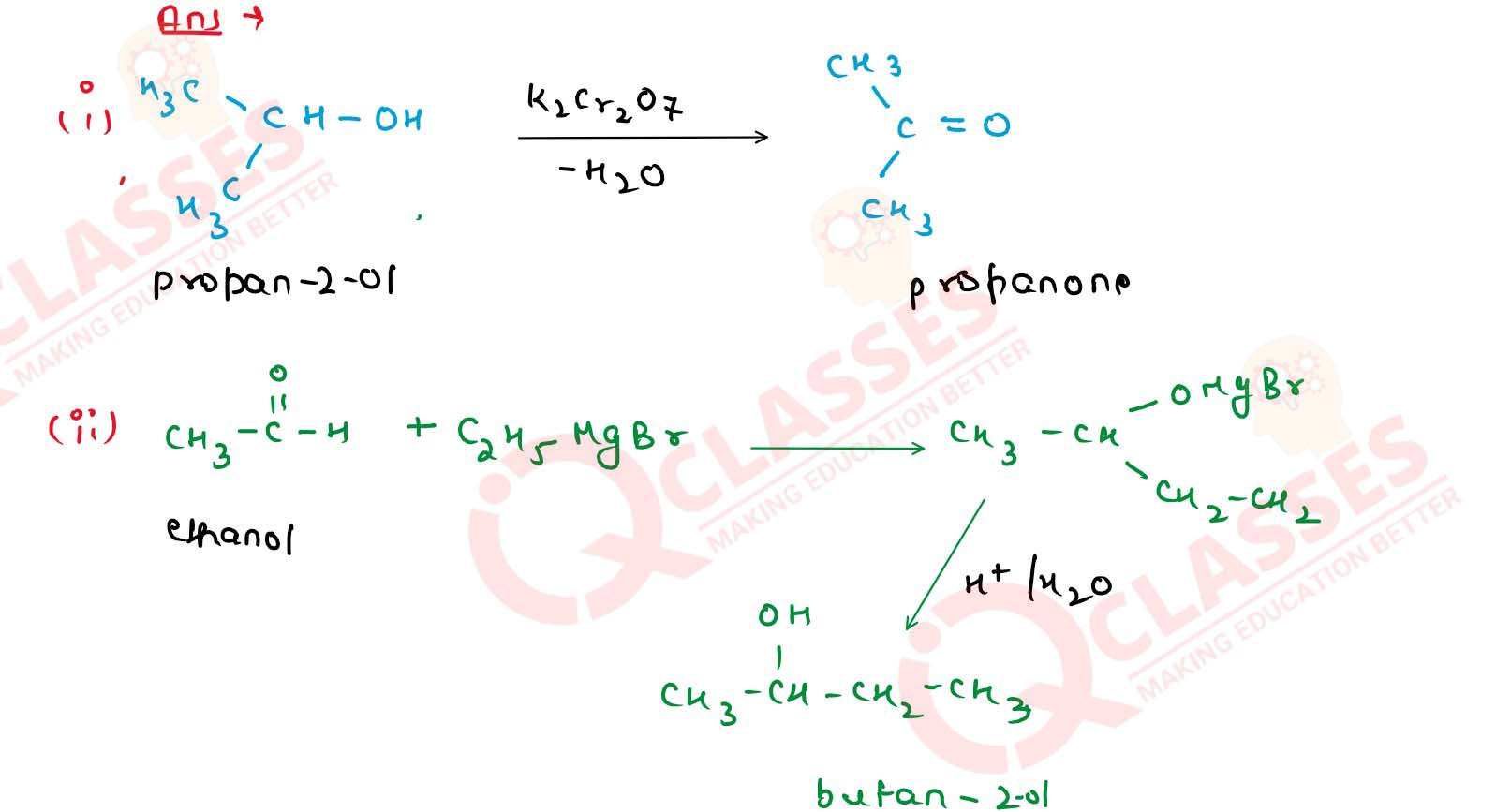
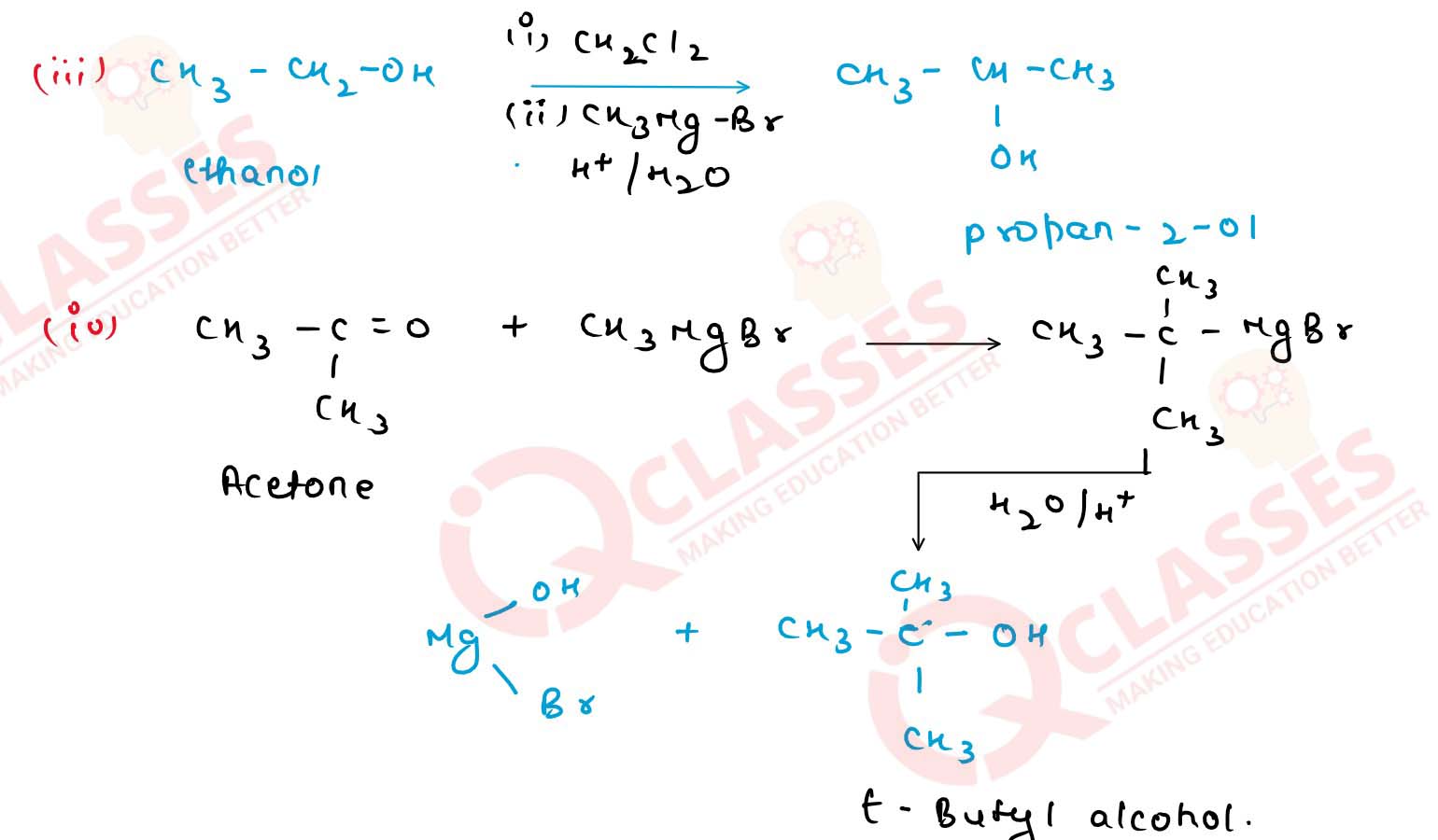
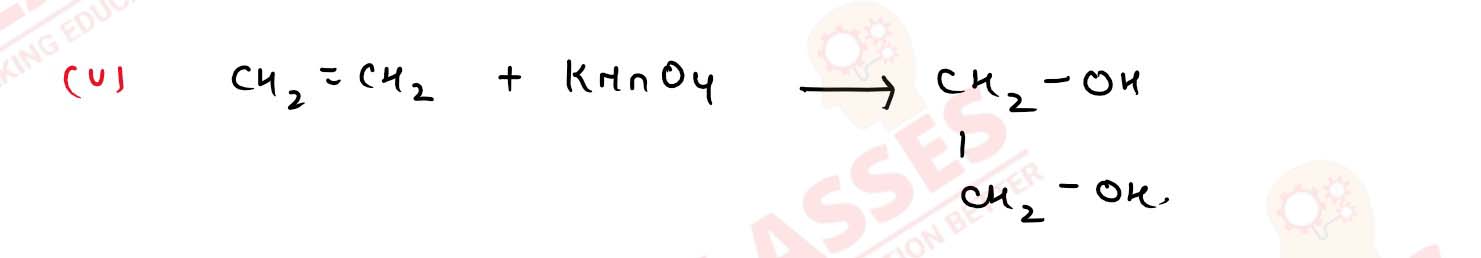
(i) propan-2-o] from propanone;
(ii) butan-2-ol from ethanol;
(iii) propan-2-ol from ethanol;
(iv) tert-buty] alcohol from acetone;
(v) ethane-1, 2-diol from ethanol? Solution


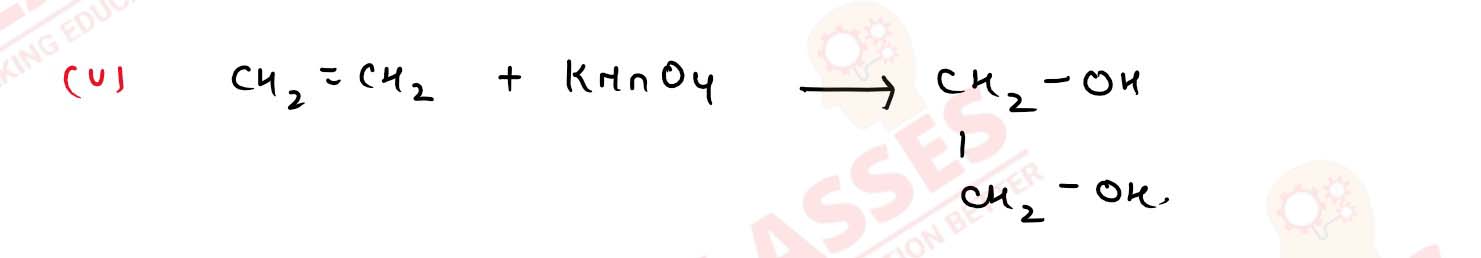
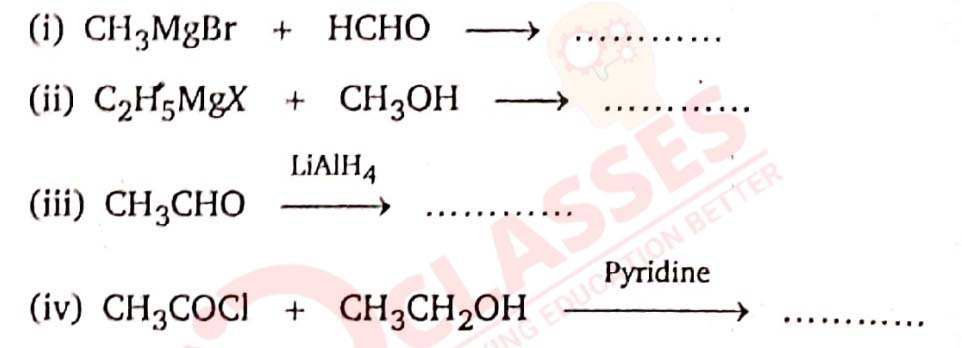
11-18
Complete the following chemical equations.
 Solution
Solution
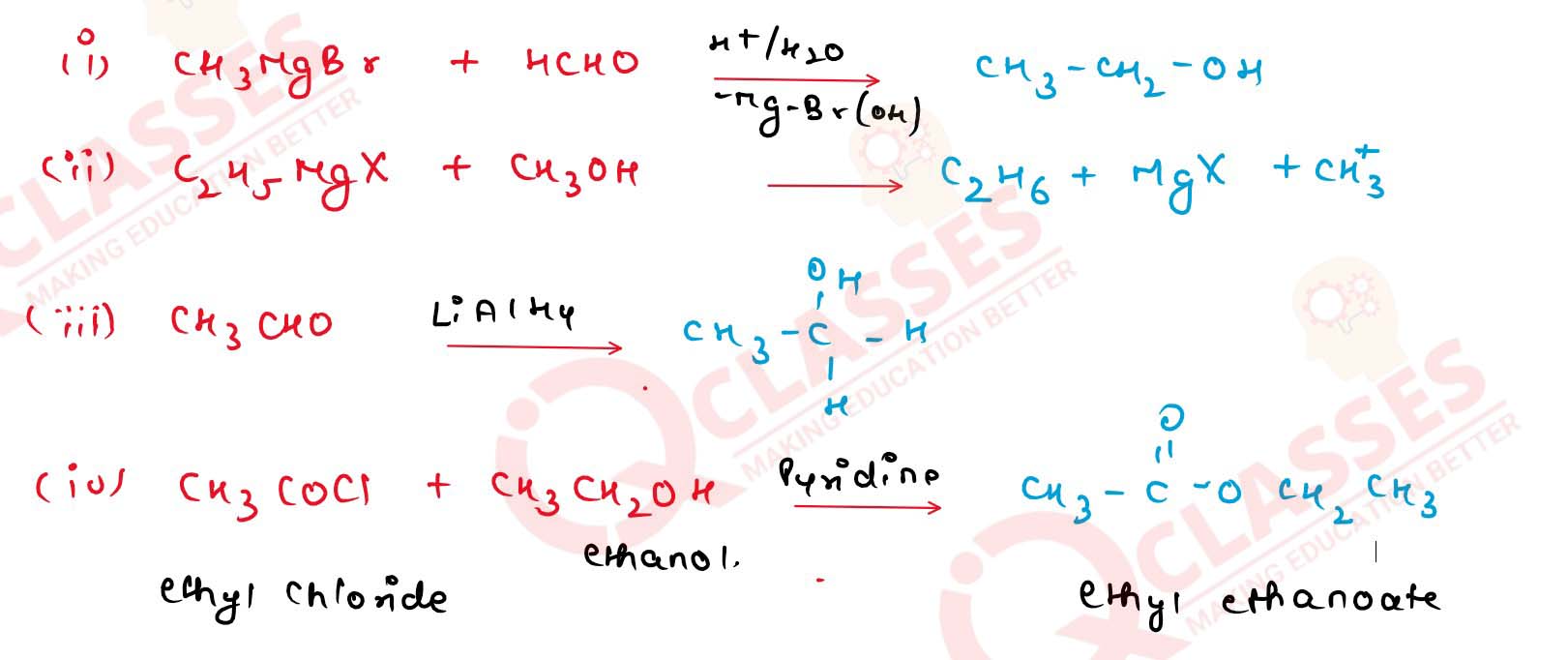
 Solution
Solution

11-19
With the help of chemical equations, show how would you
carry out the following conversions :
(i) Ethanol] to methanol.
(ii) Isopropyl alcohol to tert-butyl alcohol.
(iii) Methyl alcohol to n-propyl alcohol.
(iv) n-propyl alcohol to tert-butyl alcohol. Solution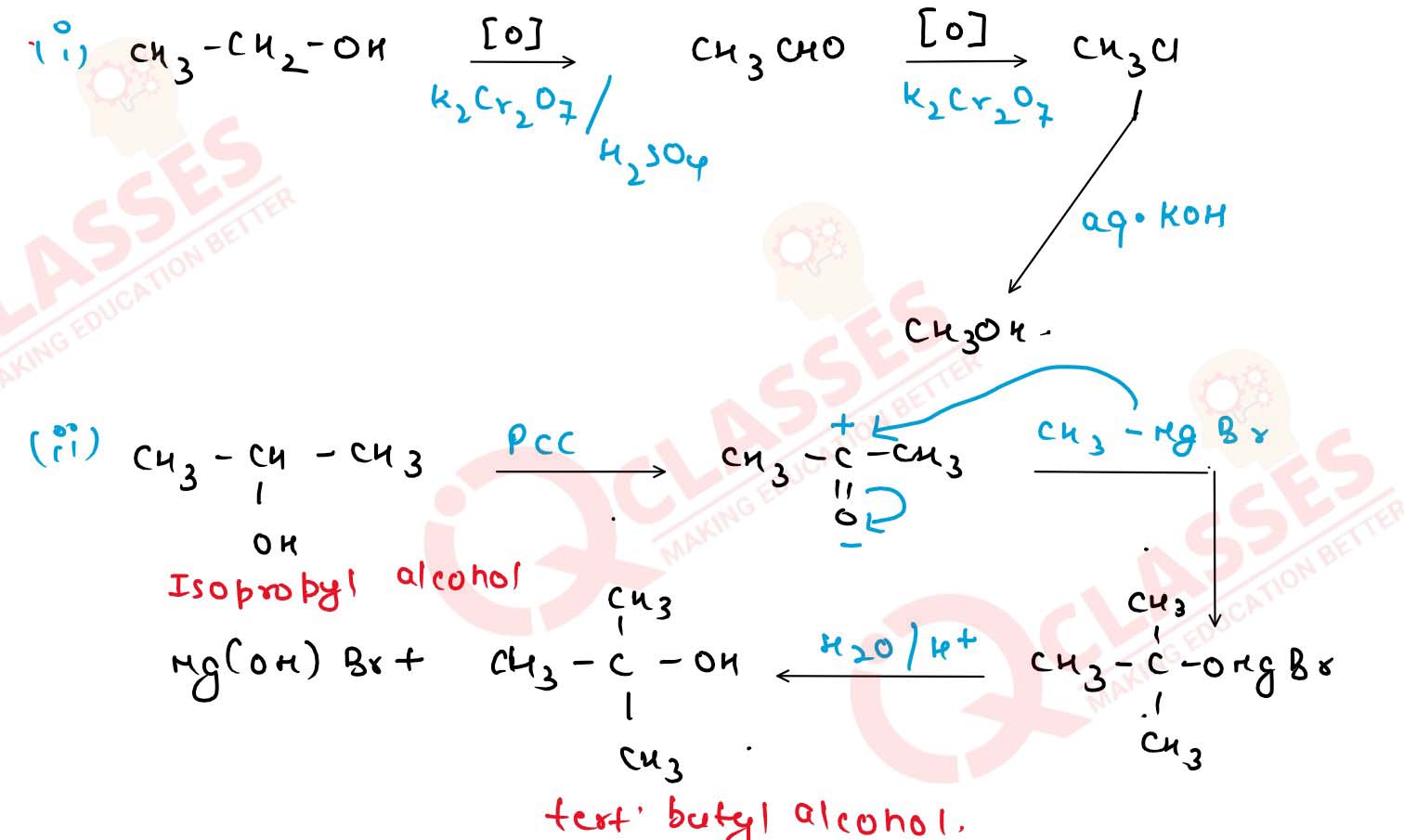
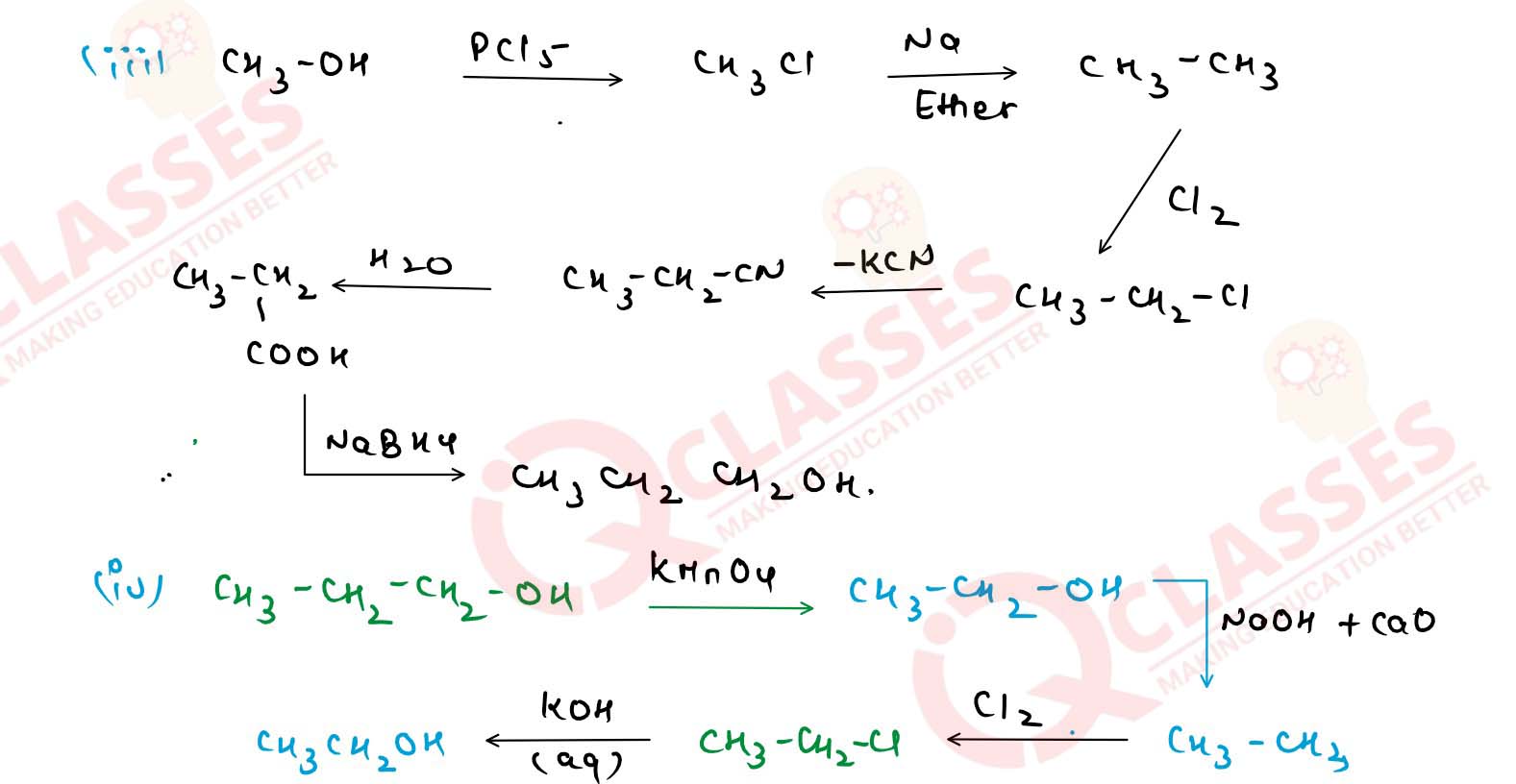
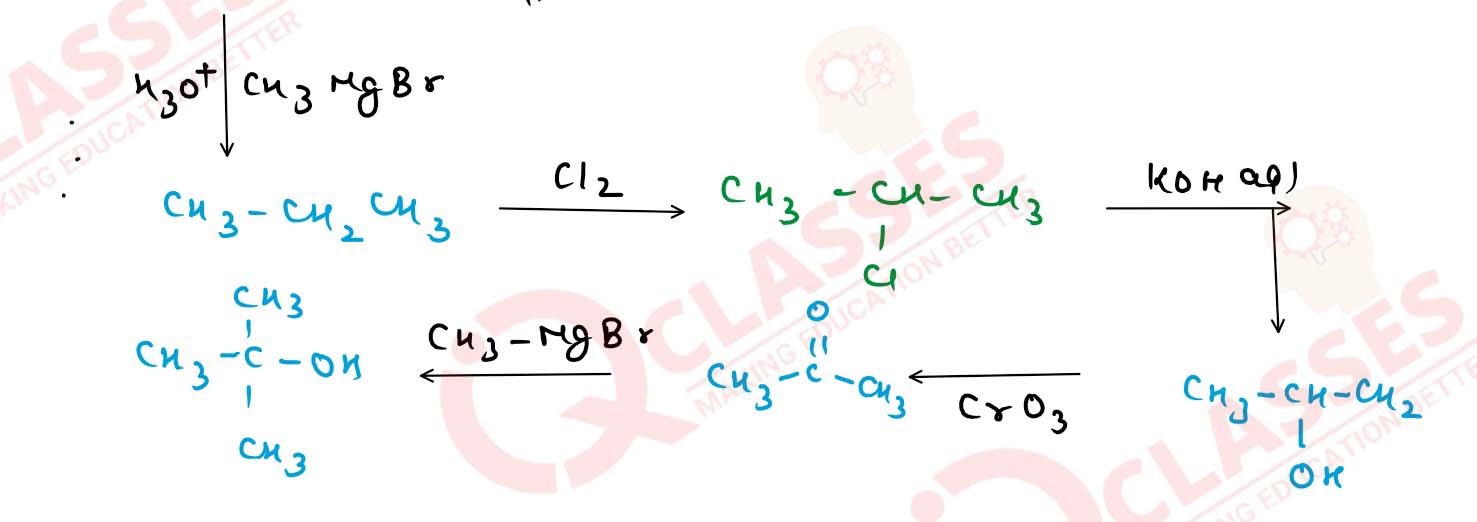
(i) Ethanol] to methanol.
(ii) Isopropyl alcohol to tert-butyl alcohol.
(iii) Methyl alcohol to n-propyl alcohol.
(iv) n-propyl alcohol to tert-butyl alcohol. Solution



11-20
Arrange the following in the decreasing order of acidic
strength ;
H2O, CH3OH, CH3CH2OOH, (CH3)2CHOH,
(CH3)3C.OH.
Solution
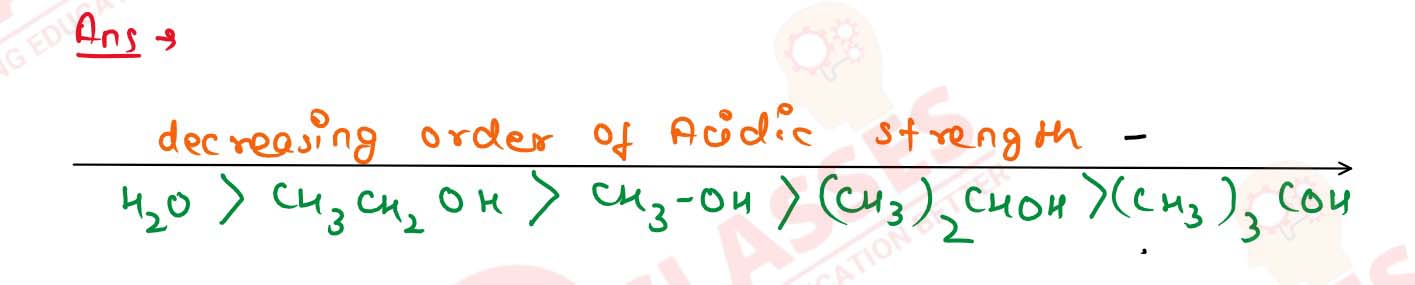
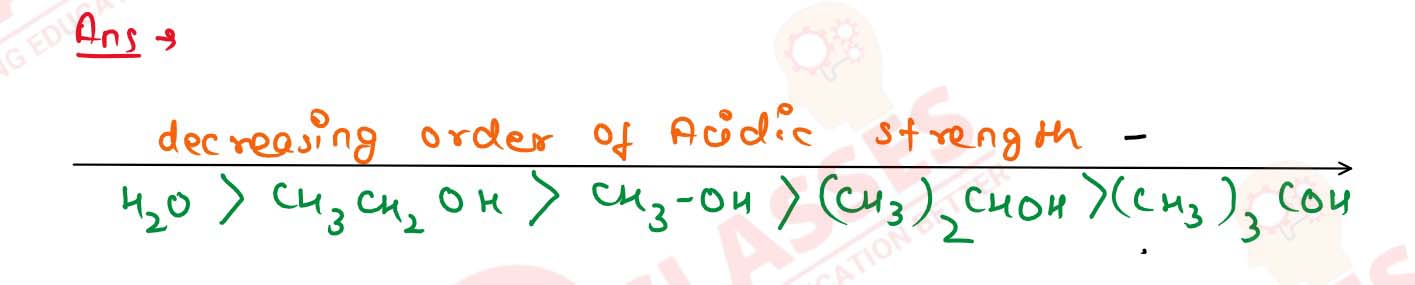
11-21
Starting from ethyl alcohol, how would you obtain the following?
(i) Iodoform
(ii) Acetaldehyde
(iii) Diethyl ether
(iv) Ethylene
(v) Ethyl acetate.
Solution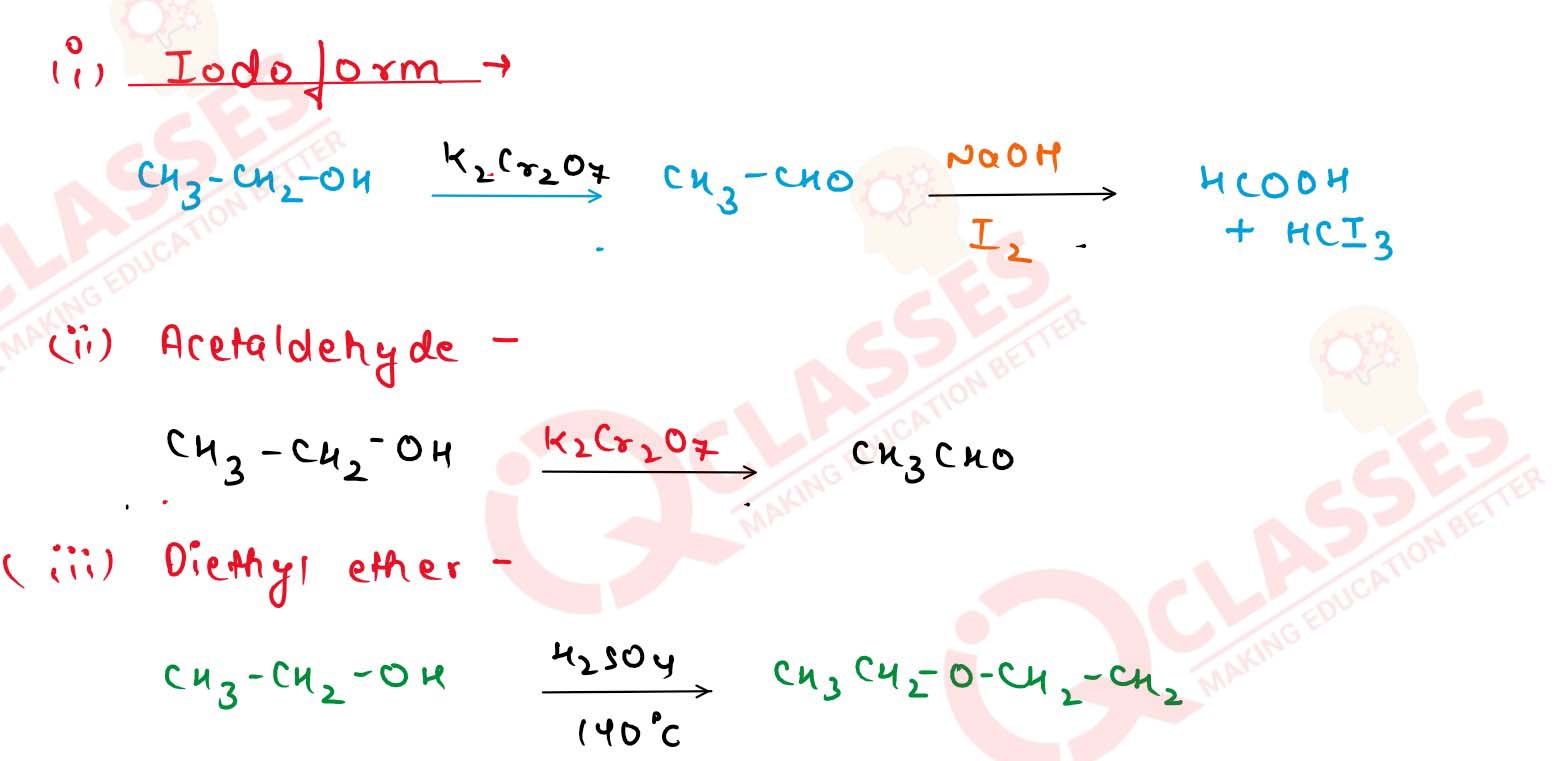
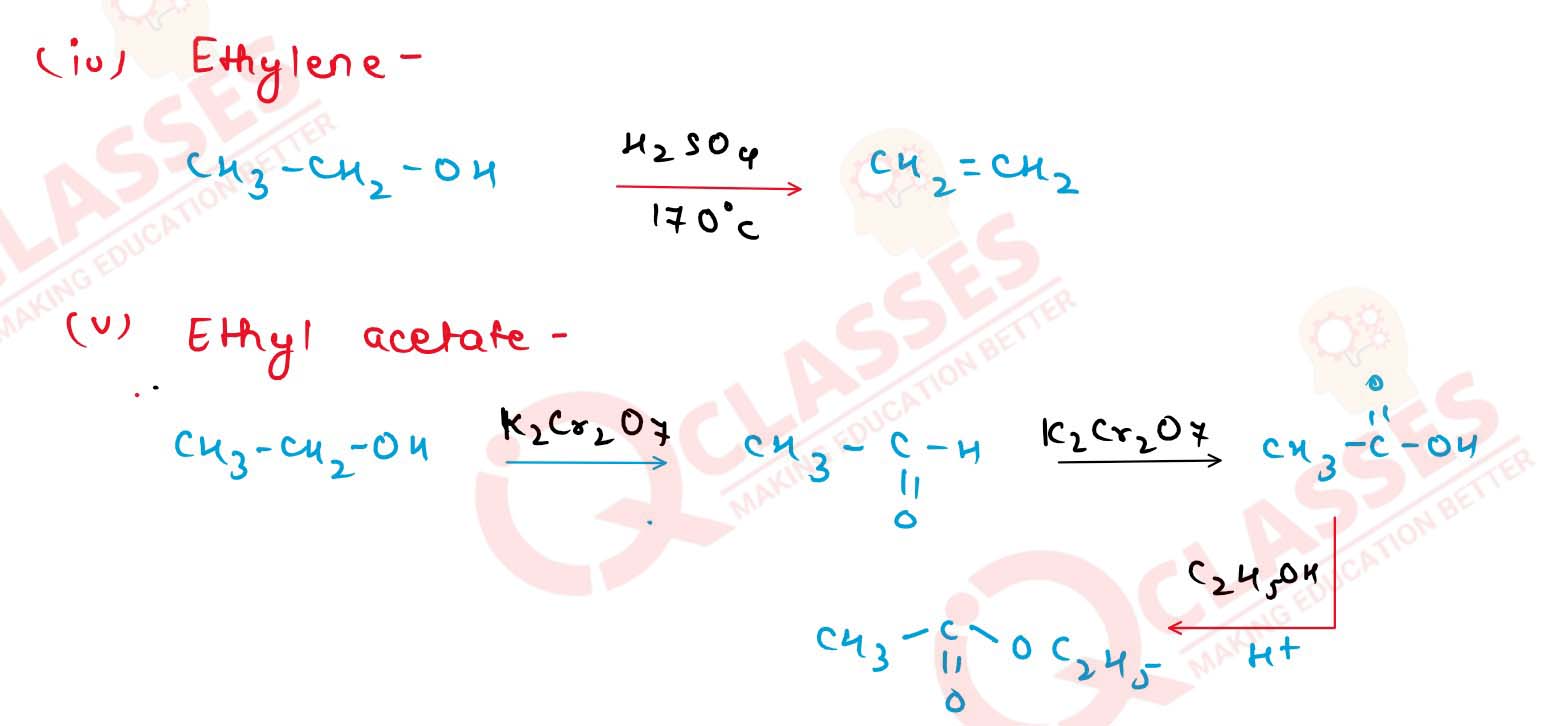
(i) Iodoform
(ii) Acetaldehyde
(iii) Diethyl ether
(iv) Ethylene
(v) Ethyl acetate.
Solution


11-22
Explain the following :
(i) Alcohols are freely soluble in water but alkyl halides are not.
(ii) Boiling point of an alcohol is higher than that of the corresponding alkane.
(iii) The solubility of alcohols in water decreases with increase in molecular mass,
(iv) Alcohols act as weak bases, Solution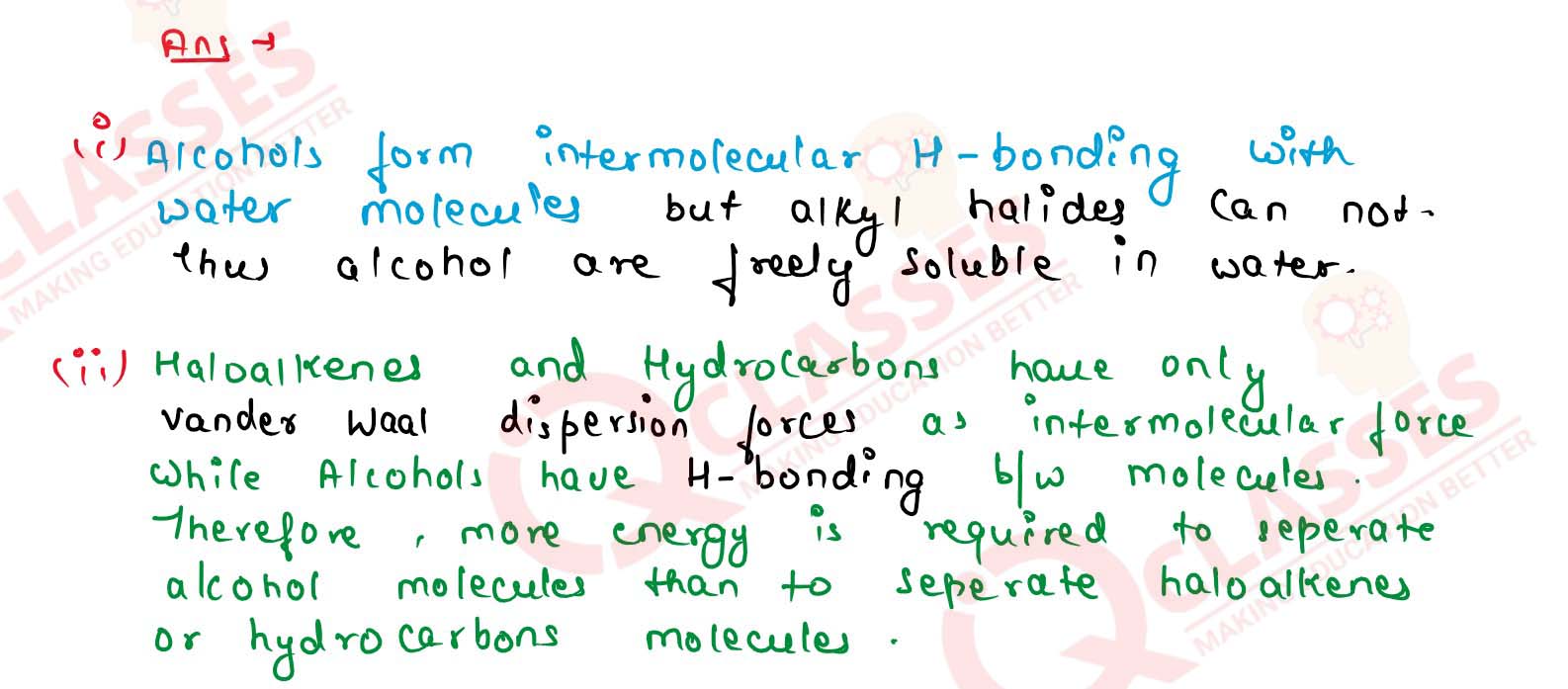

(i) Alcohols are freely soluble in water but alkyl halides are not.
(ii) Boiling point of an alcohol is higher than that of the corresponding alkane.
(iii) The solubility of alcohols in water decreases with increase in molecular mass,
(iv) Alcohols act as weak bases, Solution
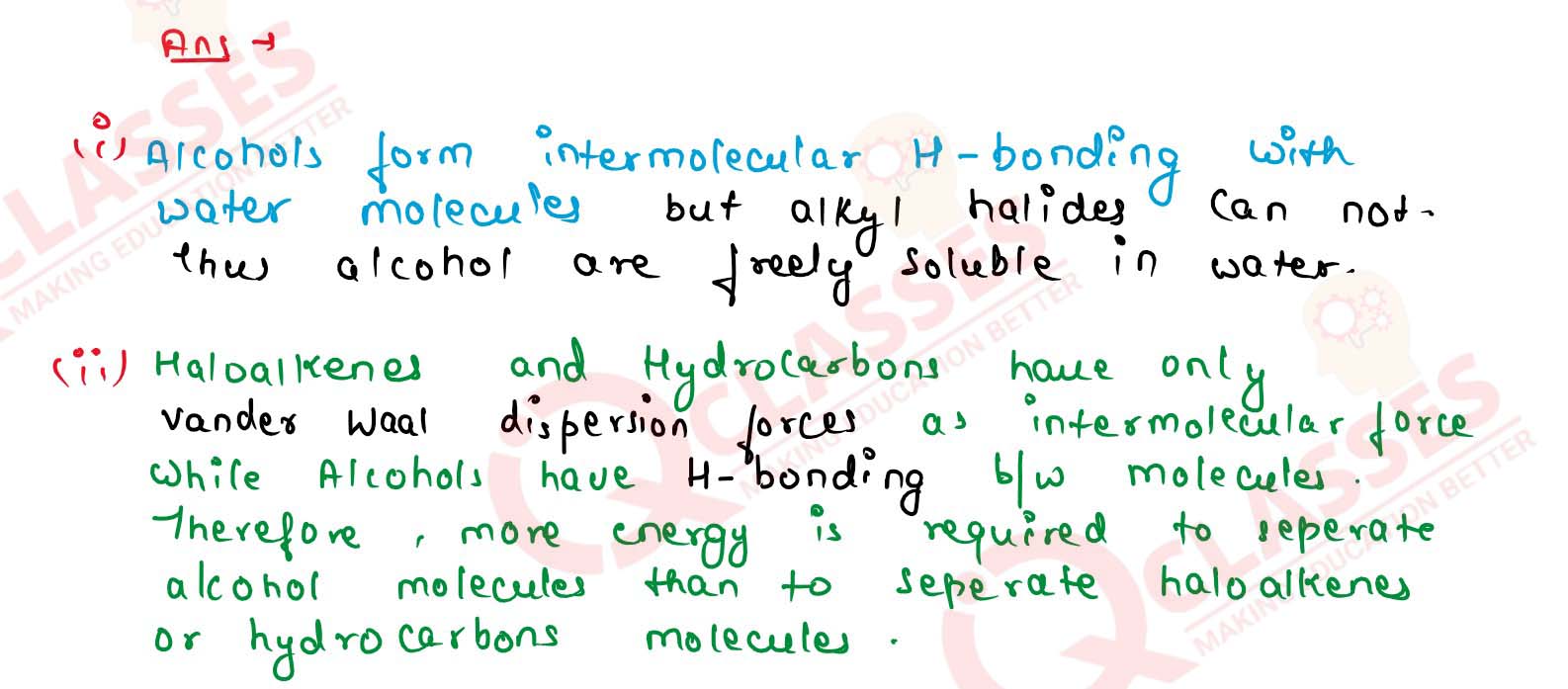

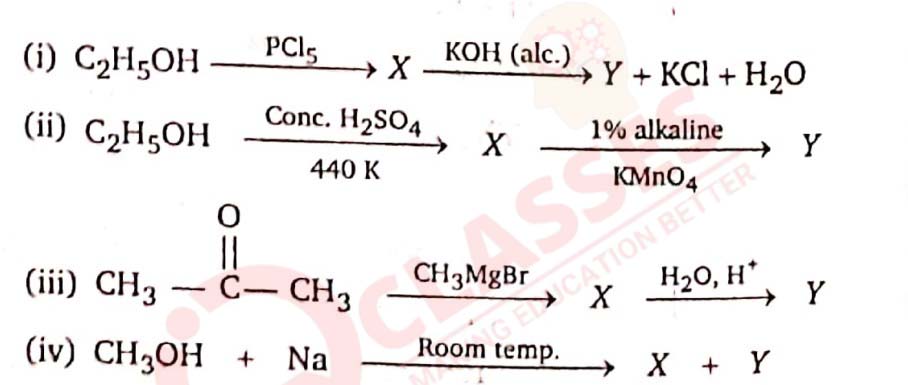
11-23
Identify the compounds X and Y in each of the following reactions.
 Solution
Solution
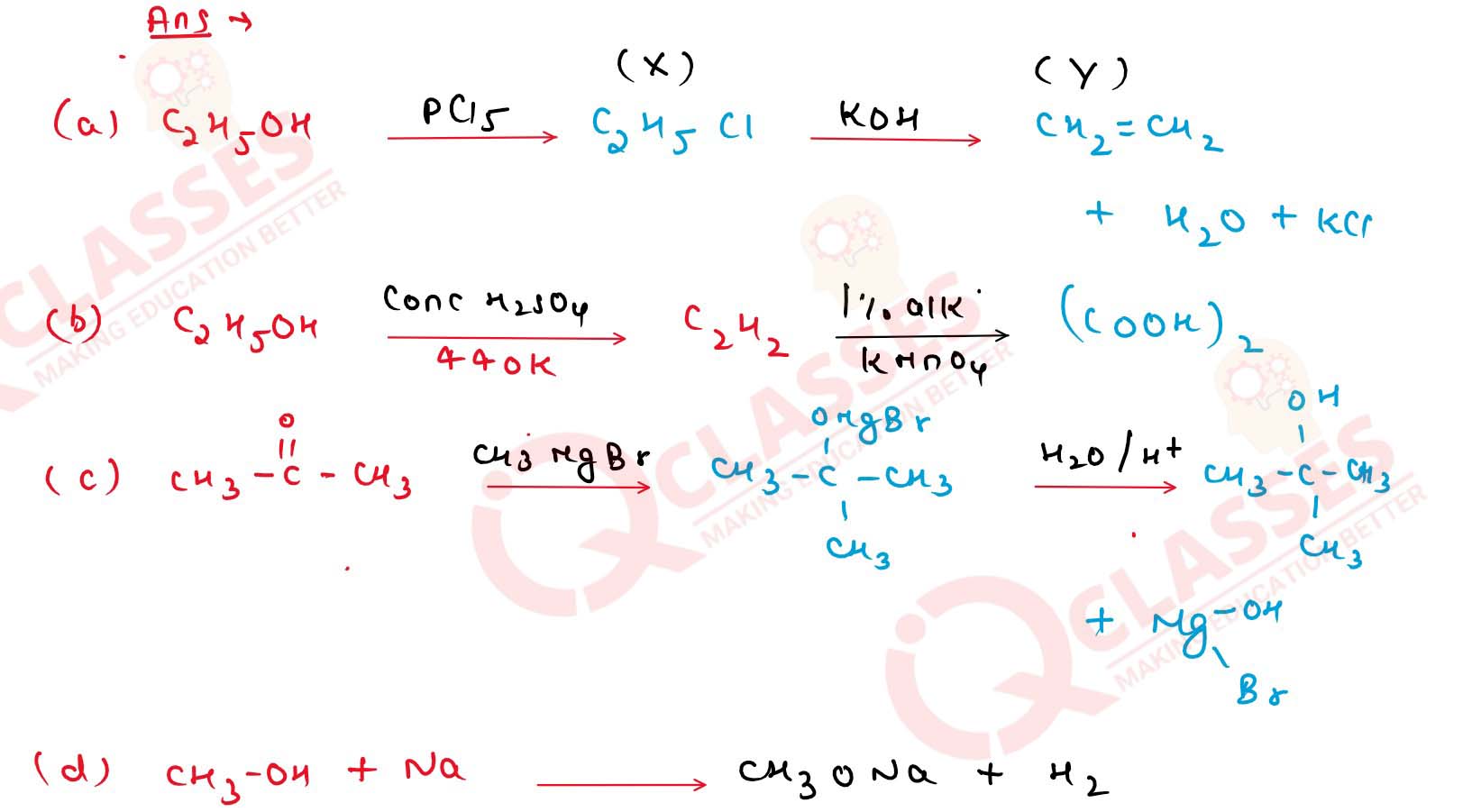
 Solution
Solution

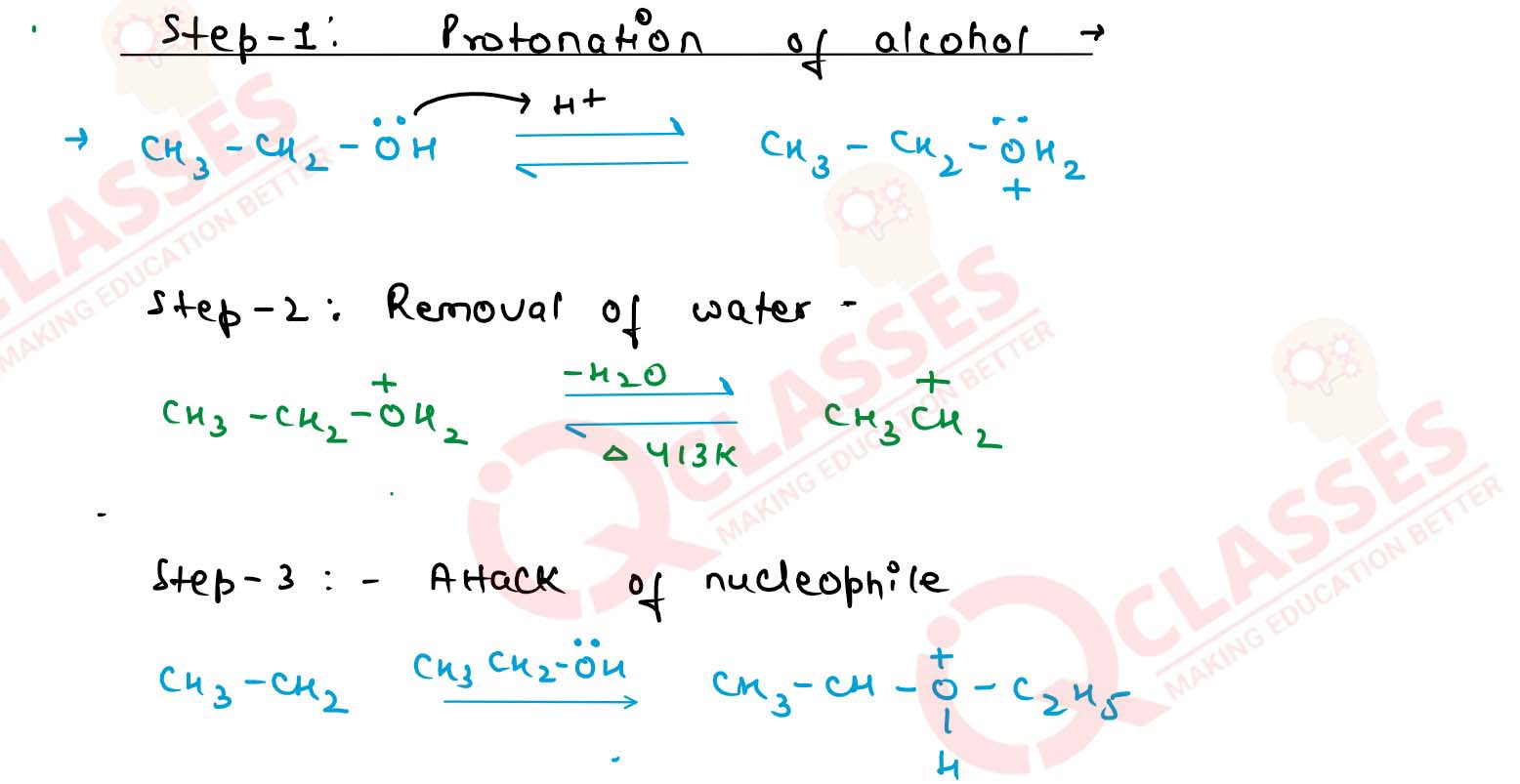
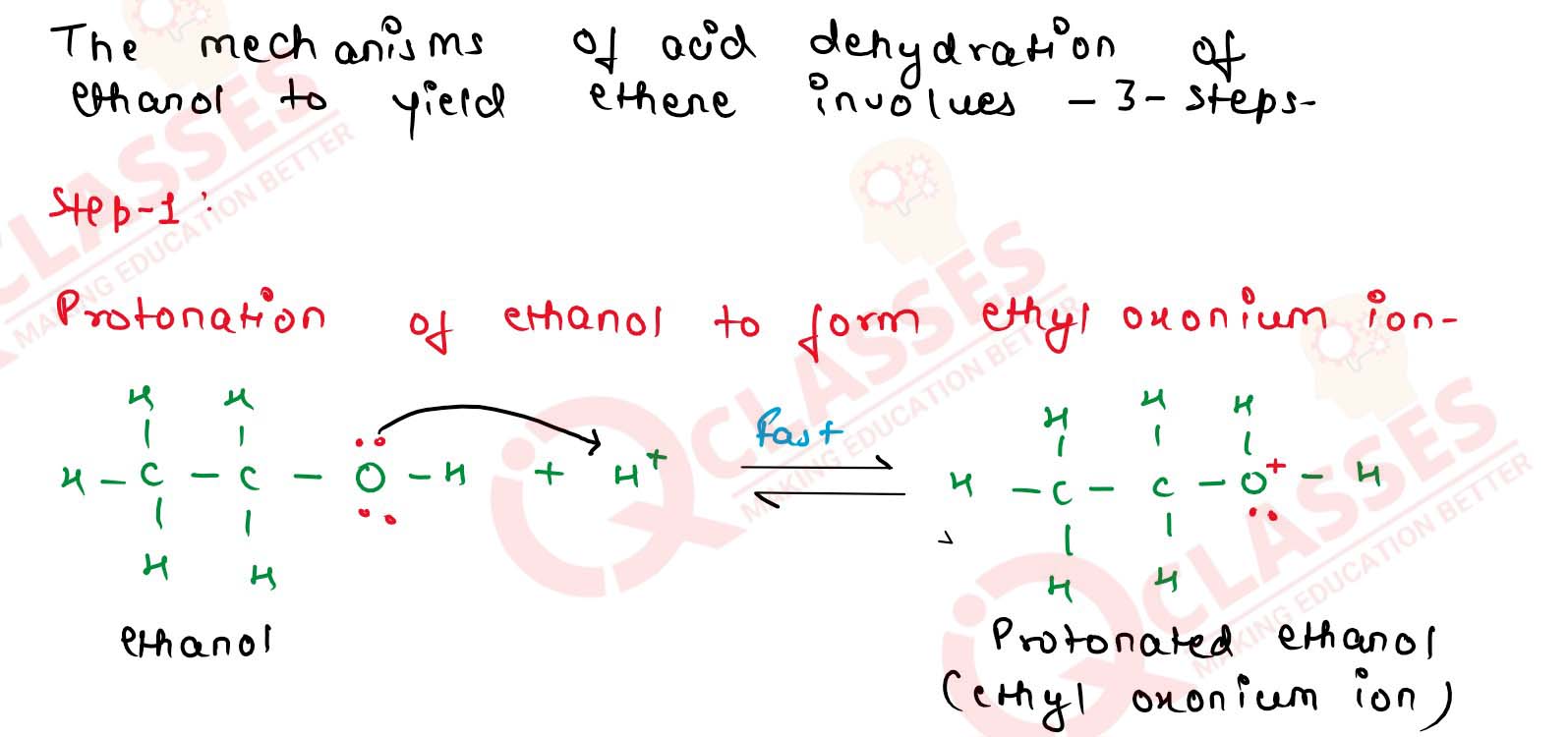
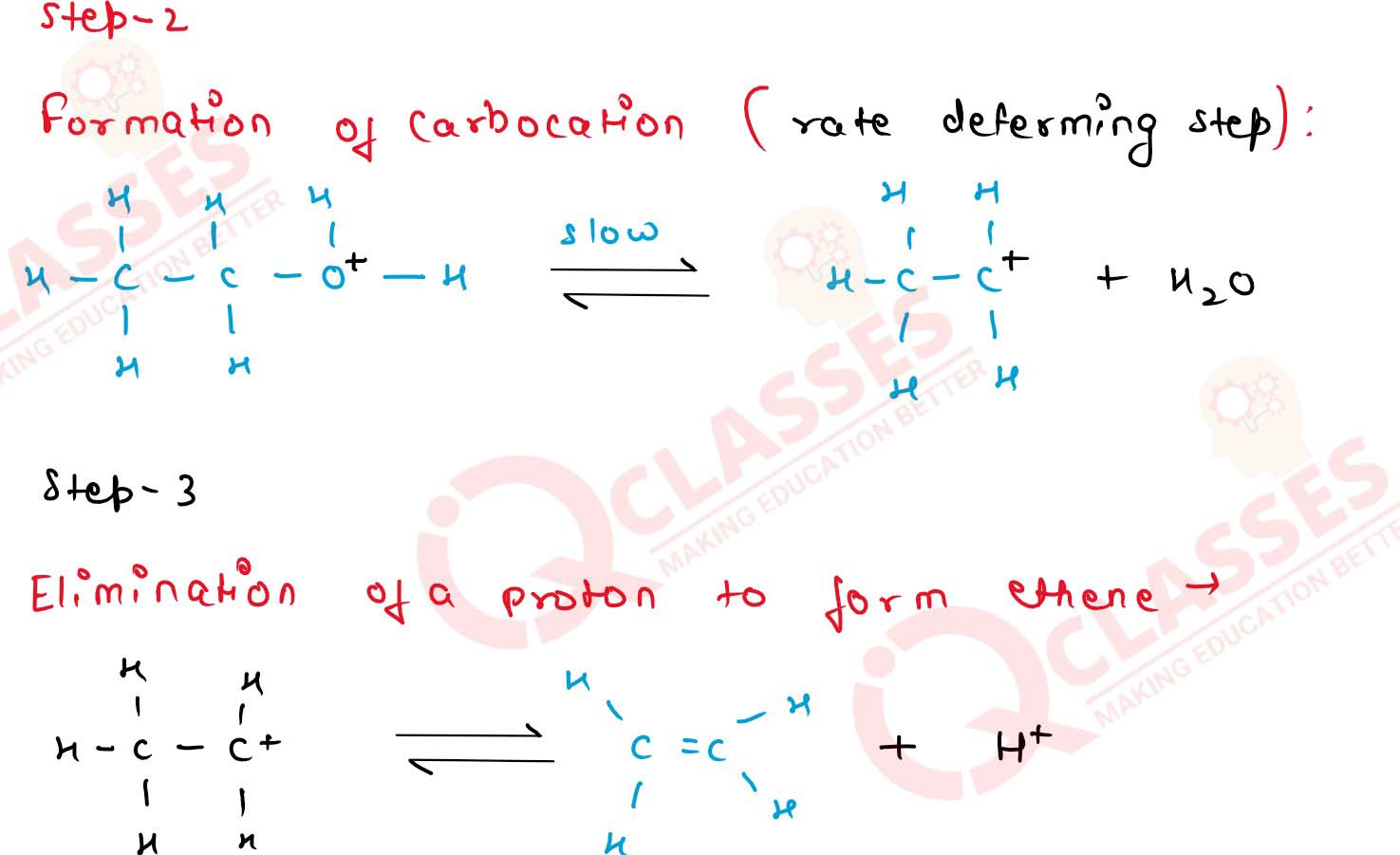
11-24
Explain the mechanism of. acid catalysed dehydration of
ethanol at high temperatures
Solution


11-25
Describe a test to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary
alcohols.
Solution


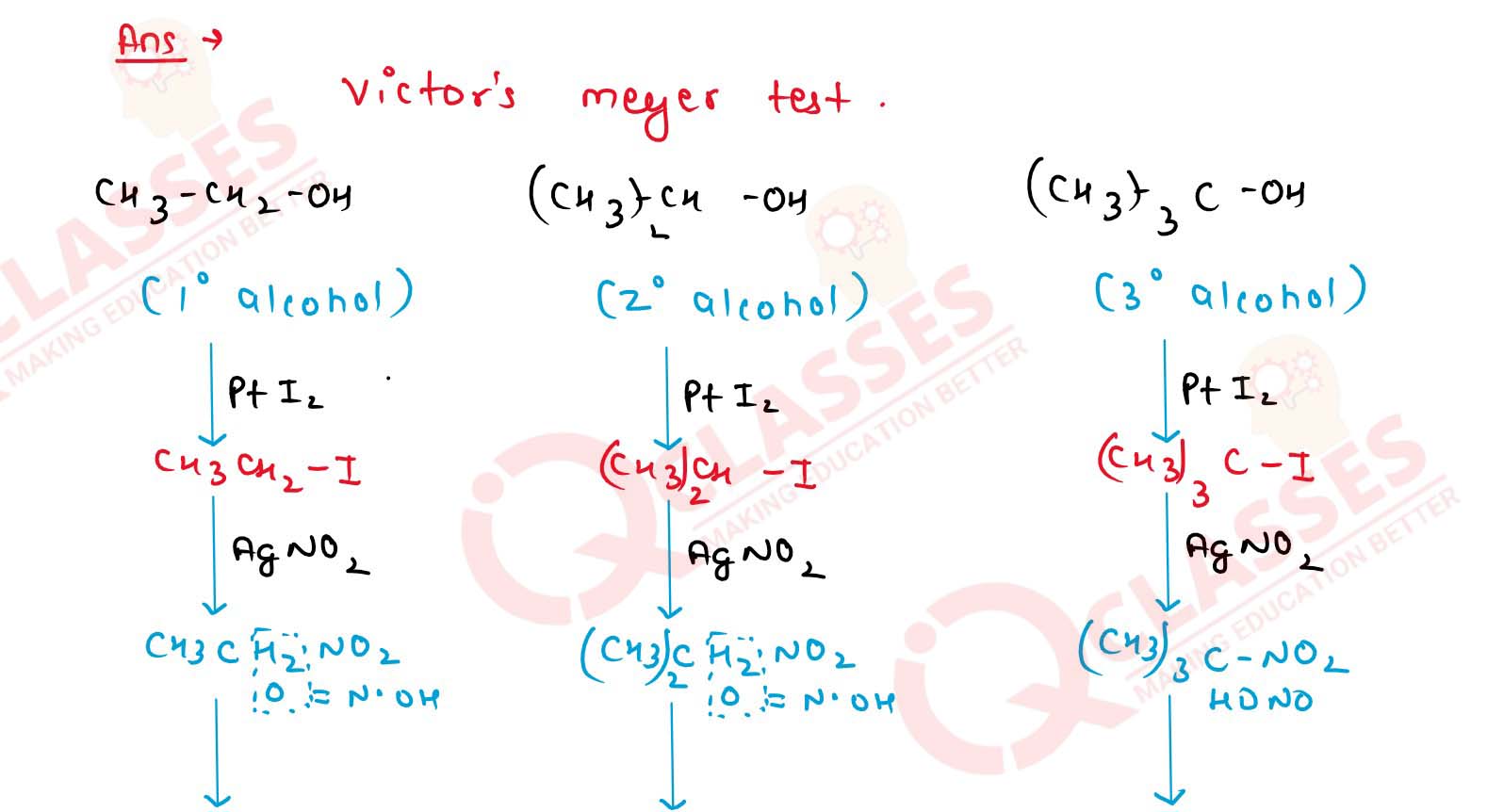
11-26
How will you distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary
alcohols by Victor Meyer’s Test? Give chemical reactions also.
Solution
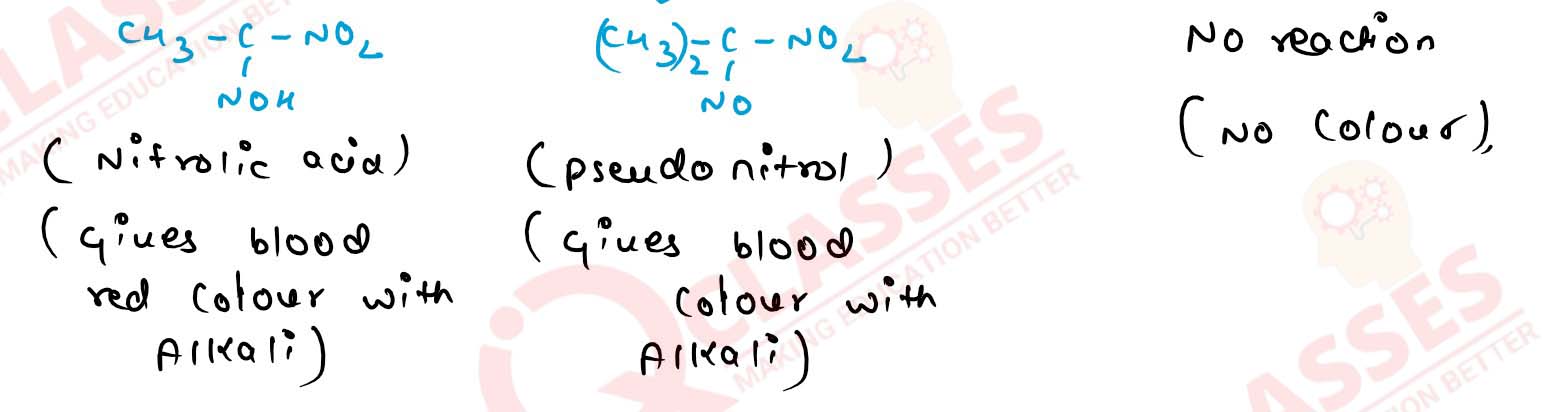

11-27
How will you distinguish primary and secondary alcohols?
Solution

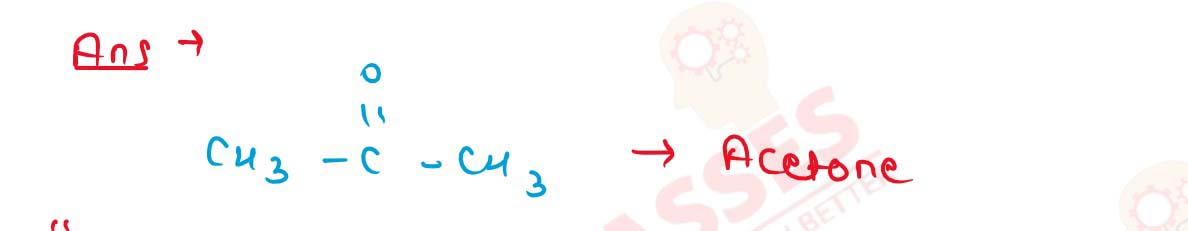
11-28
What is the main product obtained when vapours of isopropyl
alcohol are passed over copper at 573K?
Solution

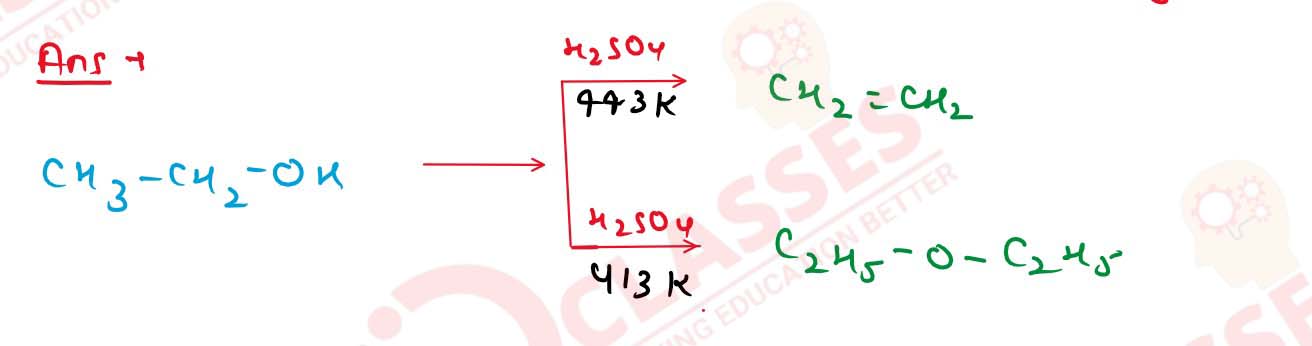
11-29
“Formation of products by the reaction of ethanol and
sulphuric acid depends on experimental conditions.” Justify
the statement.
Solution

11-30
How will you distinguish between the following pairs? Write
chemical reactions.
(i) CH30H and C2H5OH .
(ii) Propan-1-o] and propan-2-ol
(iii) Propan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iv) Ethanol and propan-1-ol Solution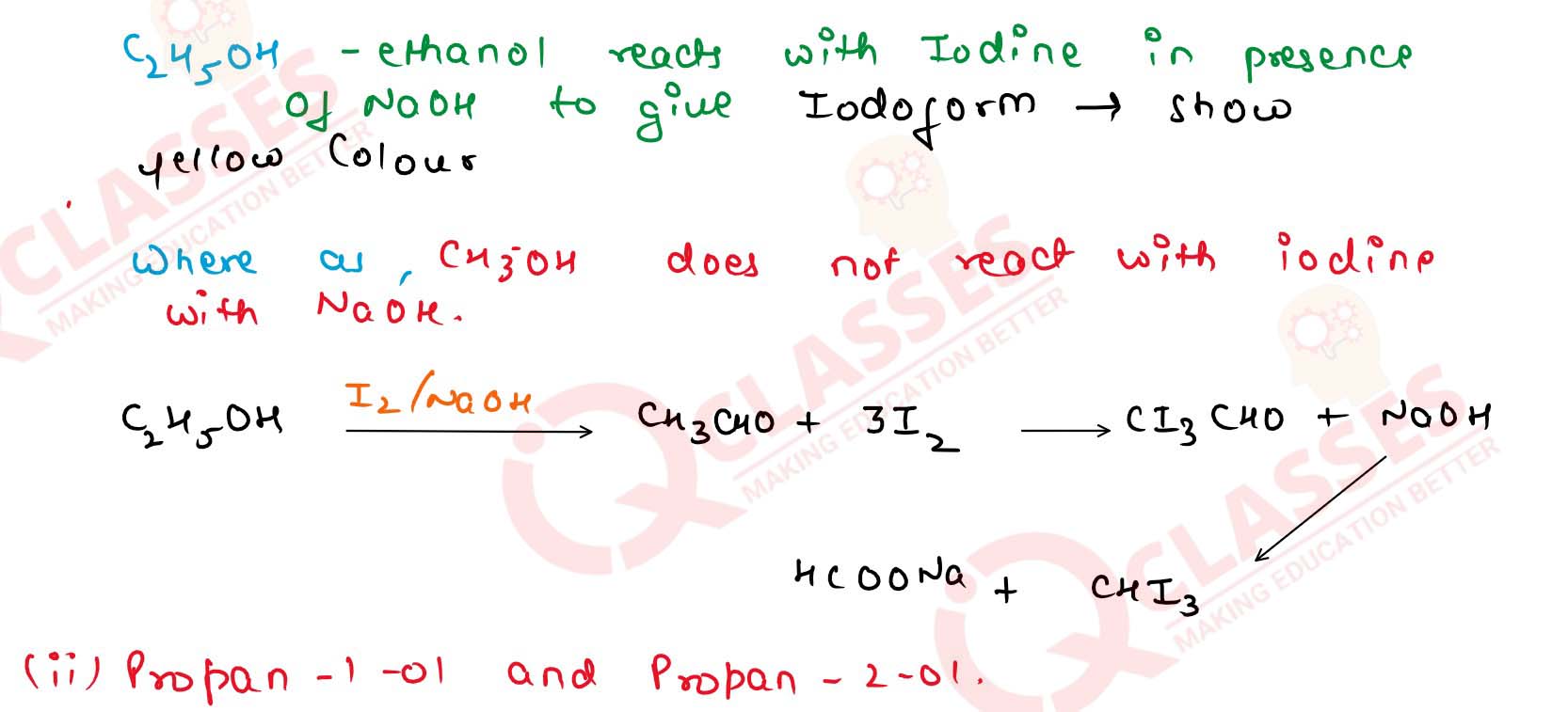


(i) CH30H and C2H5OH .
(ii) Propan-1-o] and propan-2-ol
(iii) Propan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iv) Ethanol and propan-1-ol Solution



11-31
Write the reactions involved in the preparation of
(i) iodoform from propan-2-ol, and
(ii) ethane-1-2-diol from ethene. Solution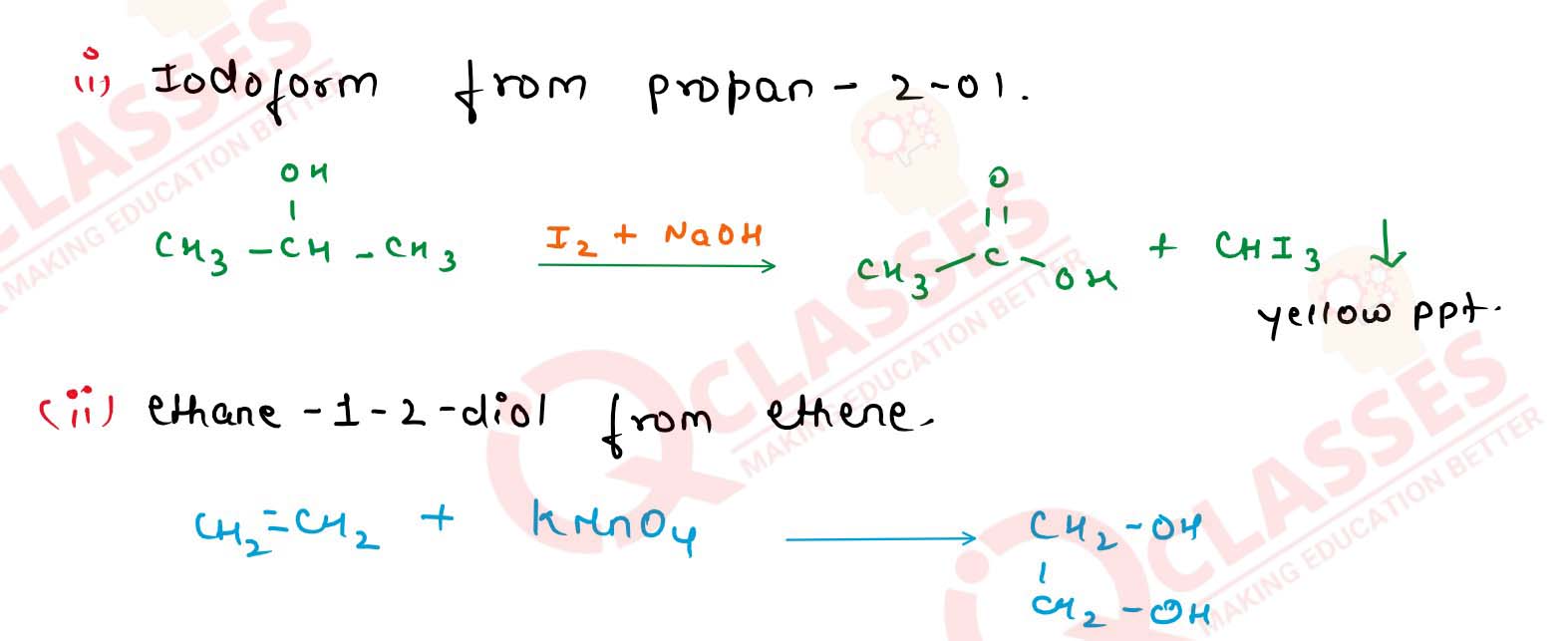
(i) iodoform from propan-2-ol, and
(ii) ethane-1-2-diol from ethene. Solution

11-32
Write chemical equations for what happens when
(i) 2-methylpropan-2-ol vapours are passed over heated copper;
(ii) a glyceride is treated with sodium hydroxide solution. Solution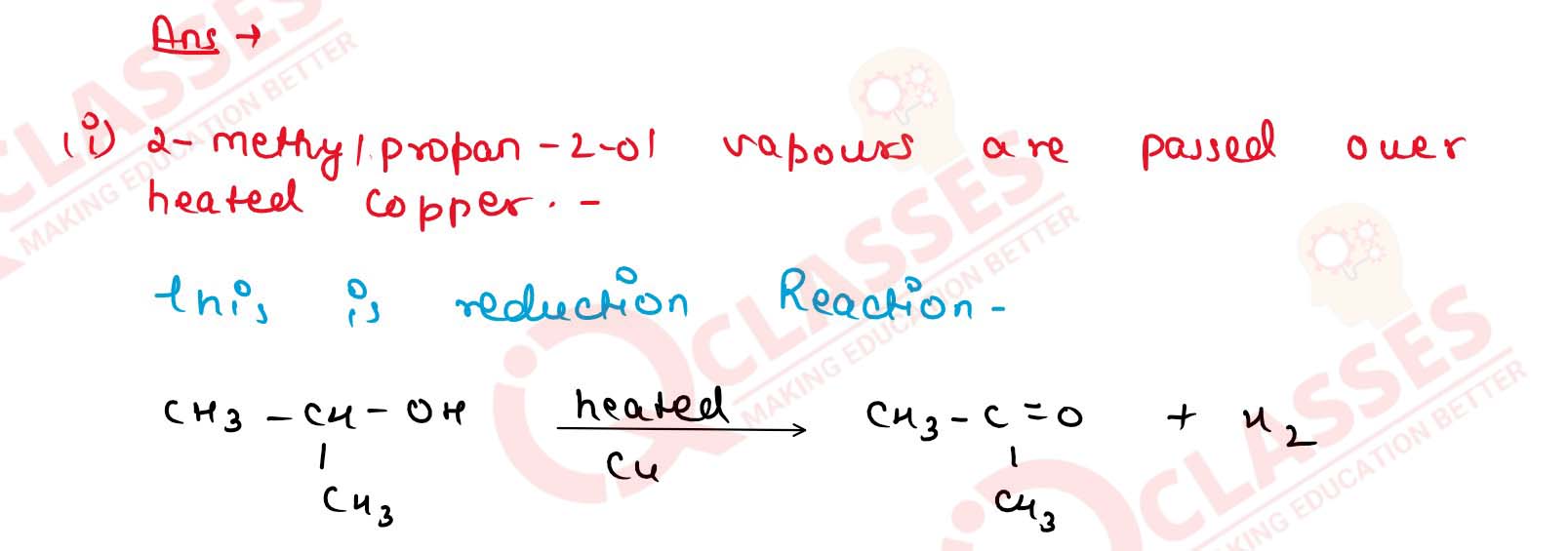

(i) 2-methylpropan-2-ol vapours are passed over heated copper;
(ii) a glyceride is treated with sodium hydroxide solution. Solution


11-33
Write one distinction test for ethyl alcohol and propan-2-ol.
Solution
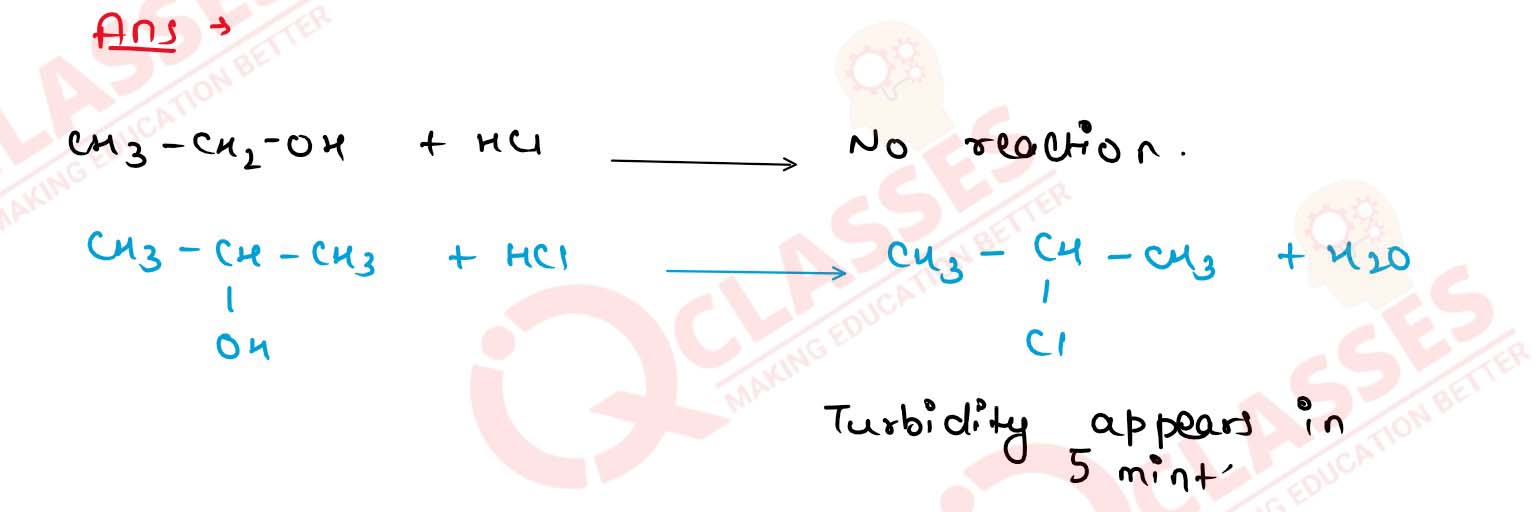

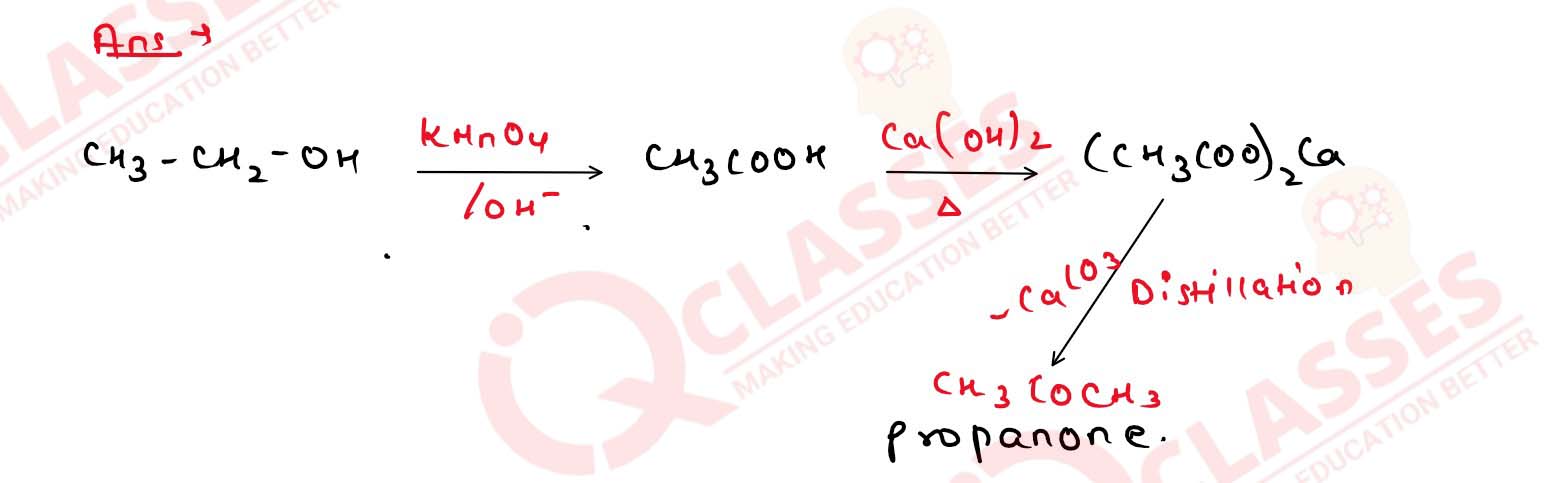
11-34
Write the series of reactions which would convert ethanol
into propanone.
Solution

11-35
Write chemical reactions for getting propan-2-ol from ethanol.
Solution
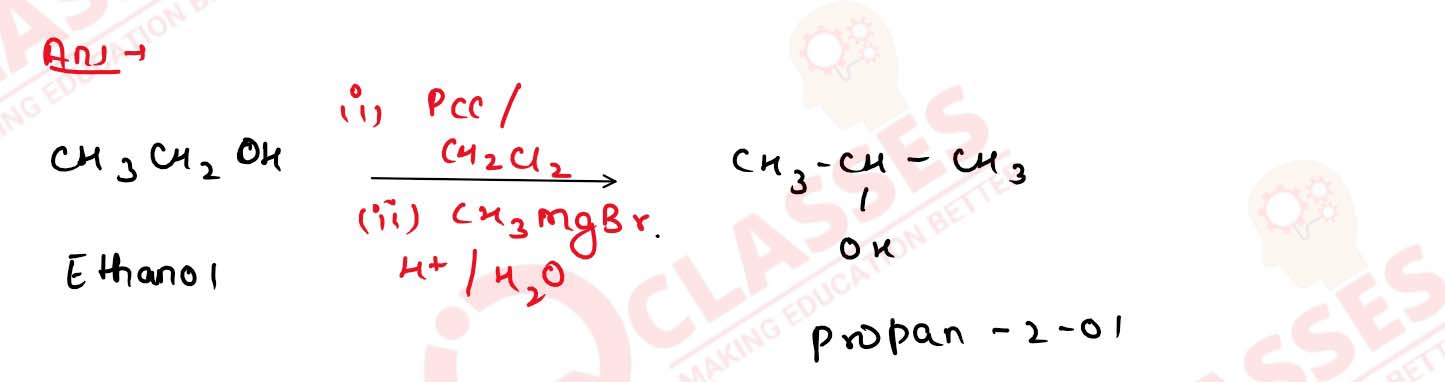
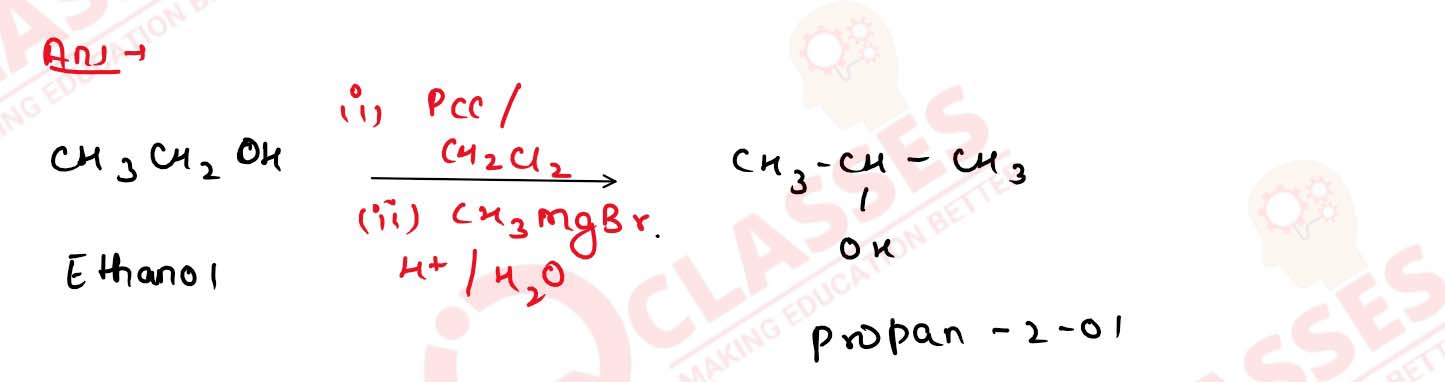
11-36
Of ethanol and n-propanol, which one gives the iodoform test
and why does the other one not do so?
Solution


11-37
Write reaction equation for what happens when tertiary butyl
alcohol is heated with reduced copper at 573 K.
Solution
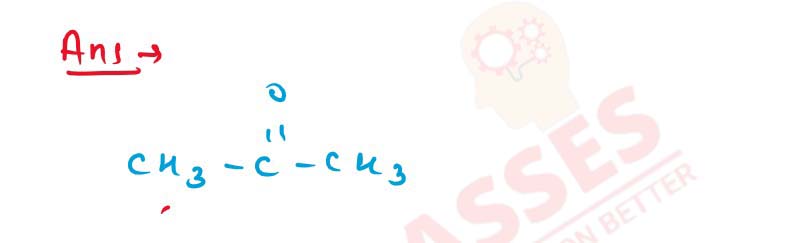
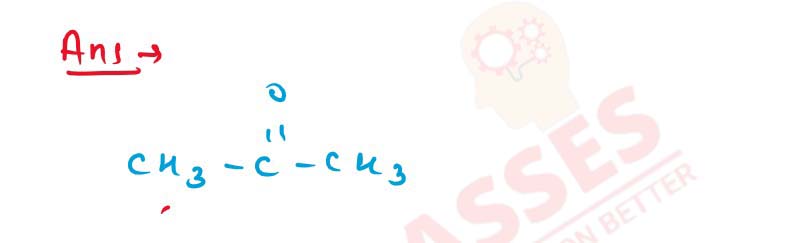
11-38
Complete the following reactions :
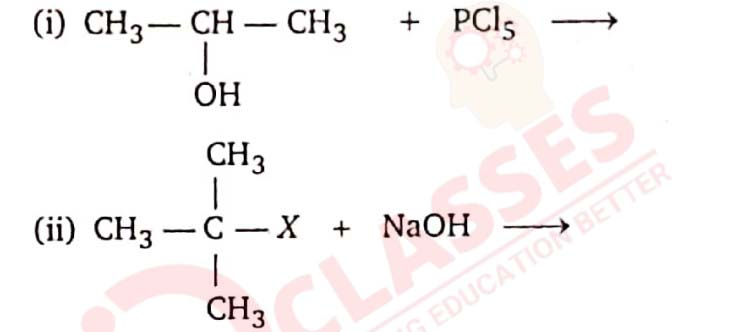 Solution
Solution
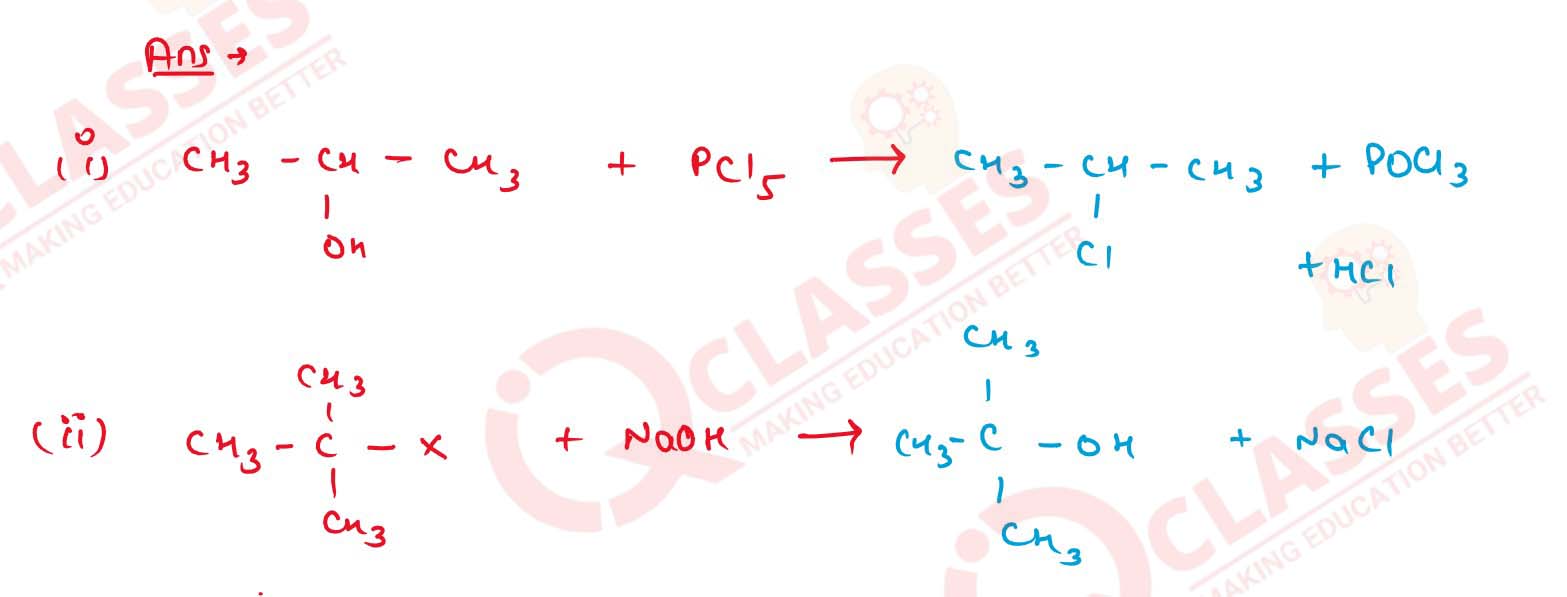
 Solution
Solution

11-39
How will you obtain 2-methylpentan-2-ol from 2-methylpent1-ene?
Solution
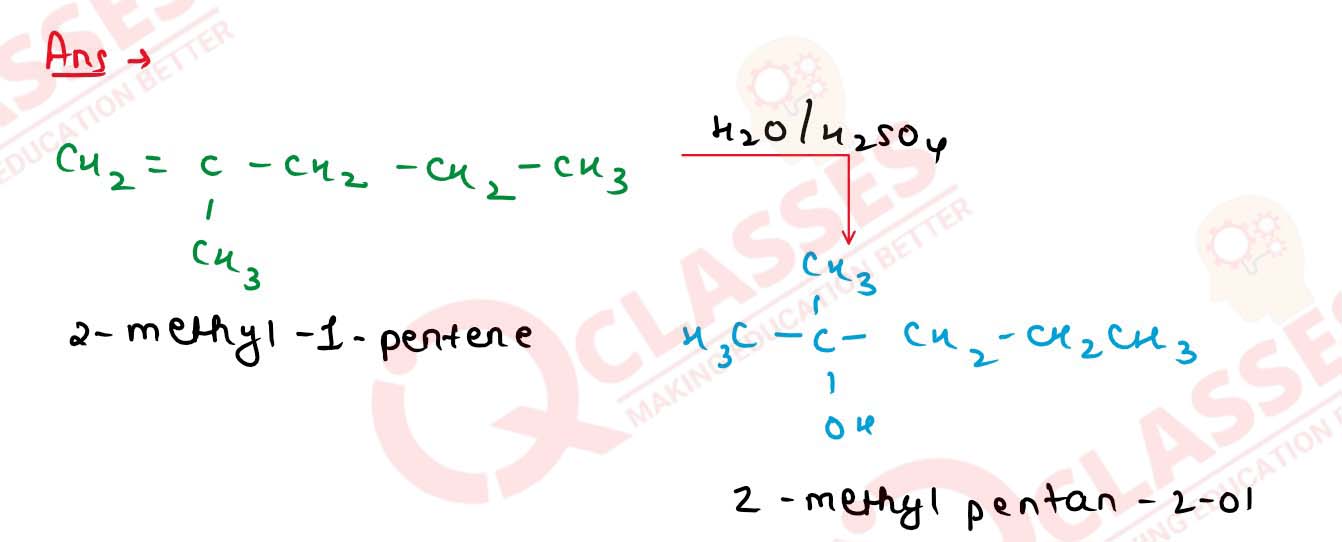

11-40
What happens when ethanol is heated with conc. sulphuric
acid at 453 K? Explain the mechanism of this reaction.
Solution
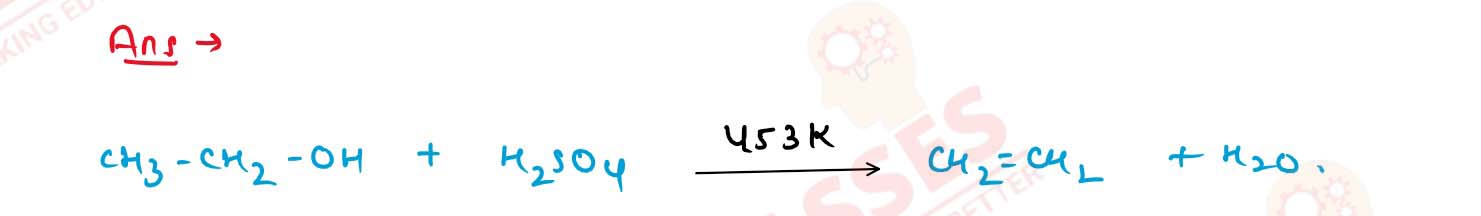
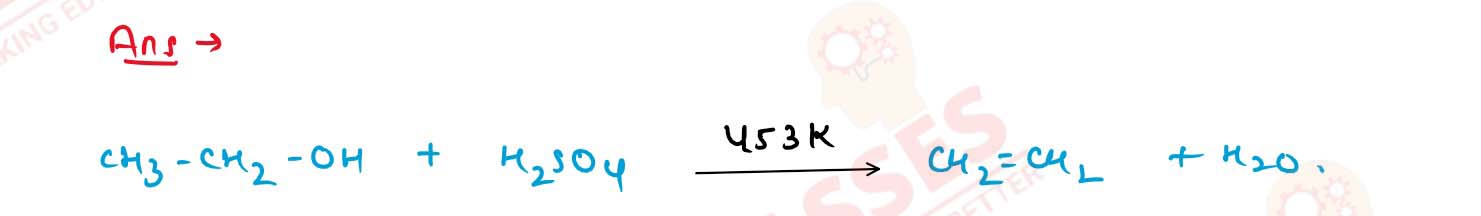
11-41
Write the reactions with conditions for the following
conversions :
(i) Methanol to propan-1-ol
(ii) Benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid. Solution Solution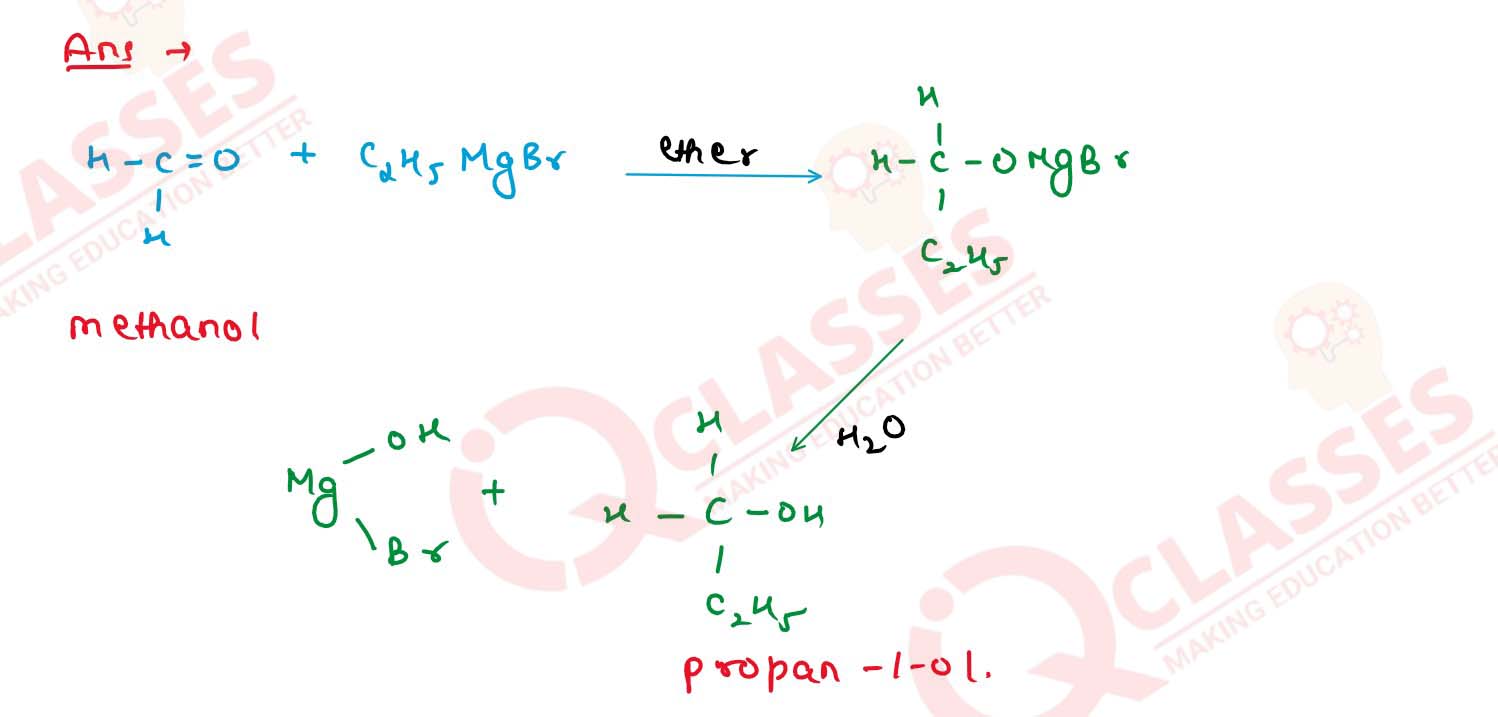
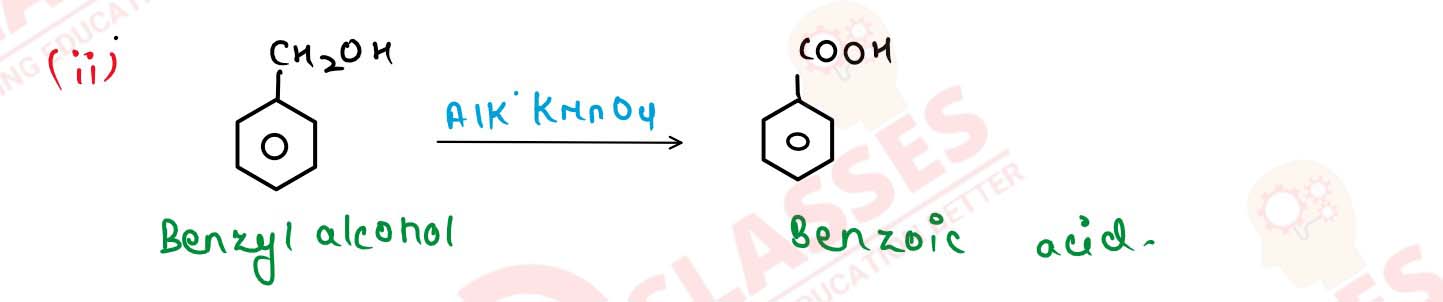
(i) Methanol to propan-1-ol
(ii) Benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid. Solution Solution


11-42
Write the IUPAC name of :
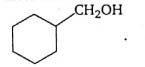 Solution
Solution

 Solution
Solution

11-43
How is that alcohol and water are miscible in all proportions?
Solution

