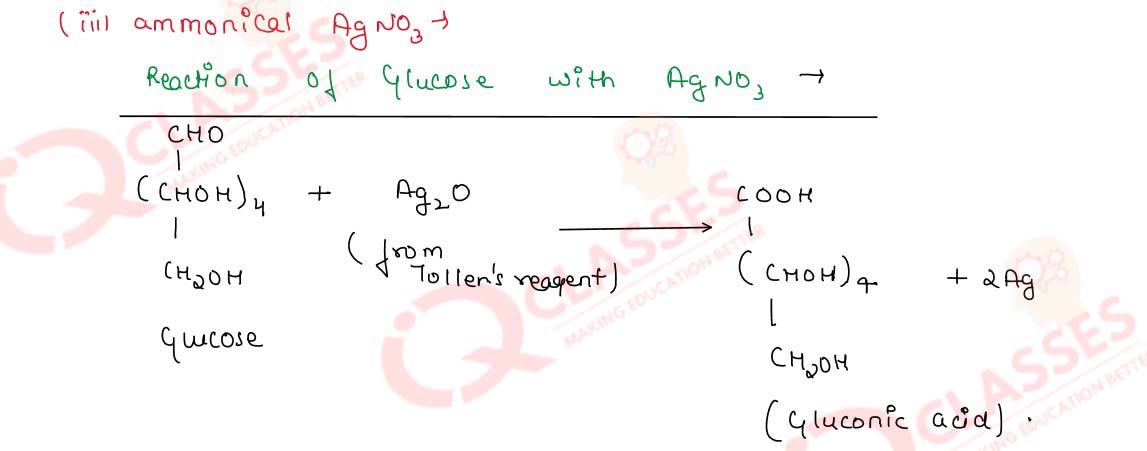Q14.1
What are biomolecules ? Give some examples.
Solution
Biomolecules are macromolecules because they are polymers made of hundreds or even thousand of
smaller molecules Called monomers
Examples- Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
Q14.2
What are carbohydrates and how are they classified ?
Solution
Carbohydrates→
It as a group of organic Compounds occurring on living tissues and foods in the form of starch ,
cellulose , sugars .
The ratio of Carbon and Hydrogen in Carbohydrates is the same as in water 2:1. It typically breaks
down in the animal body
to release energy.
Types of Carbohydrates-
- Monosaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Polysaccharides
Q14.3
Discuss the role of glucose as energy source in living
organisms
Solution
Through the process of Cellular respiration, the energy in food is converted,into energy that can be
used by the body's cells.
During Cellular respiration,glucose and oxygen are converted into CO2 and
H2O,and the energy is transferred to ATP.
Q14.4
What are polysaccharides ? Give one example.
Solution
A polysaccharide is a Large molecules made of many Smaller monosaccharides . Monosaccharides are
simple sugars,like glucose.
A polysaccharides is also called a glycan.A polysaccharides can be homopolysaccharides, in which all
the monosaccharides are the same.
Eg-> cellulose and chitin
Glycogen and starch
Q14.5
What is the source of pectin? What is its use ?
Solution
-
Pectin, a multifunctional constituent of Cell wall is
a high value functional food ingredients widely used as
getting agent and as stabilizers .
-
It is produced commercially in form of white to Light brown powder,mainly extracted from
citrus fruits and used in food as a gelling agent particularly in jams and jellies.
Q14.6
Distinguish between α-glucose and β-glucose
Solution

- -OH group lies below the ring on carbon
- α-glucose folds up into a helix

- -OH group lies above the ring on carbon
- β;-glucose folds up into a plated sheet
Q14.7
Name two carbohydrates which are used as bio-fuels
Solution
Starch and glycogen
Q14.8
Mention two structural differences between amylopectin and cellulose
Solution
| Amylopectin |
Cellulose |
| It has a branched chain structure |
It has a linear polymer |
| It is made of α-glucose units |
It is made of β-glucose units |
Q14.9
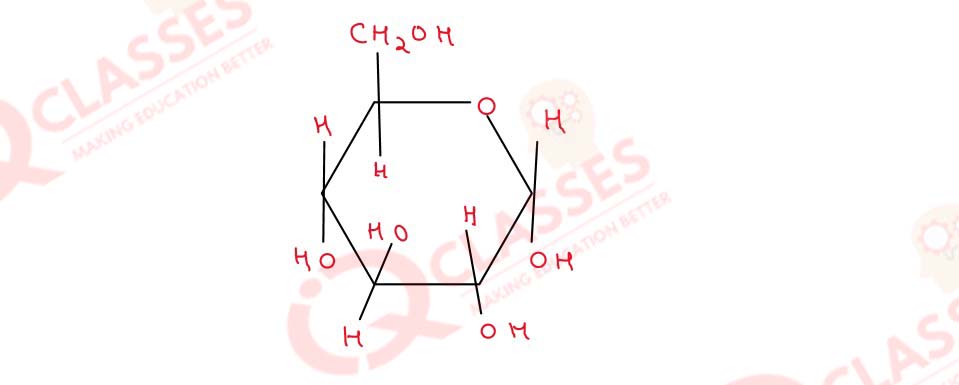
Write the structural formula of anomeric form of α-glucose
Solution
structural formulae of anomeric form α-glucose -
α-Glucose is a form of glucose that is in a ring shape.
Glucose structure occur when the hydroxy I-OH group on the C-6 atom reacts with the -CHO group on
the C-1 atom
Q14.10
Write the hydrolysis products of lactose and starch.
Solution
-
Lactose→
The hydrolysis of lactose gives B-D-galactose and B-D glucose

-
Starch→
Lactose on hydrolysis gives glucose and fructose

Q14.11
Mention two main functions of carbohydrates in plants
Solution
Carbohydrates are the source of energy in plants.
Their too main function are growth and metabolism.
Q14.12
What is the basic difference between starch and cellulose?
Solution
| Cellulose |
Starch |
| 1 type of β-Glucose |
2 types of β-Glucose |
| Cellulose has β-1,4 linkage |
Cellulose has α;-1,4 linkage |
| not dissolve in water |
dissolves in warm water |
| cannot be consumed by humans |
can be consumed by humans |
Q14.13
Why are carbohydrates generally optically active ?
Solution
carbohydrates are generally optically active because they have one or more chiral carbon atoms in
their molecules.
Eg→ Glucose has 4-chiral Carbon and it is optically active.

Q14.14
What are polysaccharides ? Name two such substances of
immense use to us and state their usefulness.
Solution
A polysaccharide is a Large molecules made of many Smaller monosaccharides . Monosaccharides are
simple sugars,like glucose.
A polysaccharides is also called a glycan.A polysaccharides can be homopolysaccharides, in which all
the monosaccharides are the same.
Eg-> cellulose and chitin
Glycogen and starch
Q14.15
Describe the reaction for release of energy from carbohydrates
in human body
Solution
1 mole of Glucose gives CO2 and H2O and gives 38 moles of ATP which is
converted into ADP producing energy. this energy is used for maintaining body temperature and for
doing work.
Q14.16
State two main functions of carbohydratees.
Solution
Two functions of carbohydrates :-
-
Carbohydrates act as biofuel to provide energy for functioning of causing organisms
-
They act as constituents of cell walls.
Q14.17
What are chemotrophs ? Where from do they get energy for their cellular activities?
Solution
Chemotrophs- are organisms that obtain energy by the oxidations of
e- donar in their environment.
These molecules organic or inorganic.
Chematrophs are organisms that obtain their energy from a chemical reaction but their source of
carbon is the most oxidised form of Carbon,CO2.
Q14.18
What is meant by inversion of sugar ?
Solution
sucrose is dextro but on hydrolysis it gives an equimolar mixture of D (+) glucose
and D-(-) fructose which is levororatatory.
This changes of specific rotation from dextrorotation to laevorotation is known as inversion of
sugar.
Q14.19
How do cells derive their need of ATP ?
Solution
Beginning with energy sources obtained from their environment in the form of sunlight and organic
food molecules, eukaryotic Cells make energy rich molecules Like ATP and NADH including
photosynthesis
Q14.21
What is mutarotation ? Explain occurrence of mutarotation in D-glucose
Solution
The spontaneous change in the specific rotation of an optically active compound with time is called
mutarotation.
The accepted mechanism of mutarotation of D-glucose involves a simultaneous attack by an acid and a
base to yield the open-chain aldehyde form

Q14.22
Write the major classes in which the carbohydrates are
divided depending upon
whether these undergo hydrolysis,
and if so, on the number of products formed.
Solution
The carbohydrates are divided into 3major classes
- Monosaccharides
- oligosaccharides
- polysaccharide
(i) Monosaccharides→
they are polyhydroxy aldehydes
or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to gives simpler carbohydrates

(ii) oligosaccharides→
carbohydrates which yield a definite number of mono (2-19) molecules
on hydrolysis.
They include-Disaccharides, Trisaccharides and tetrasaccharides.
(iii) Polysaccharides→
These are carbohydrates of high molecular wt. which yield many monosaccharides molecules on
hydrolysis.

Q14.23
The concept of coupling reactions is useful in making the
occurrence of a non-spontaneous
reaction possible. Explain
giving one suitable example.
Solution
The non- spontaneous reaction proceed with an increase in free energy (▵G>0). Such reaction
are not feasible.
Such reaction can be made to proceed in the
desired direction by coupling with a reaction having large negative ▵G value to that the
overall change in free energy becomes (-ve)

Q14.24
-
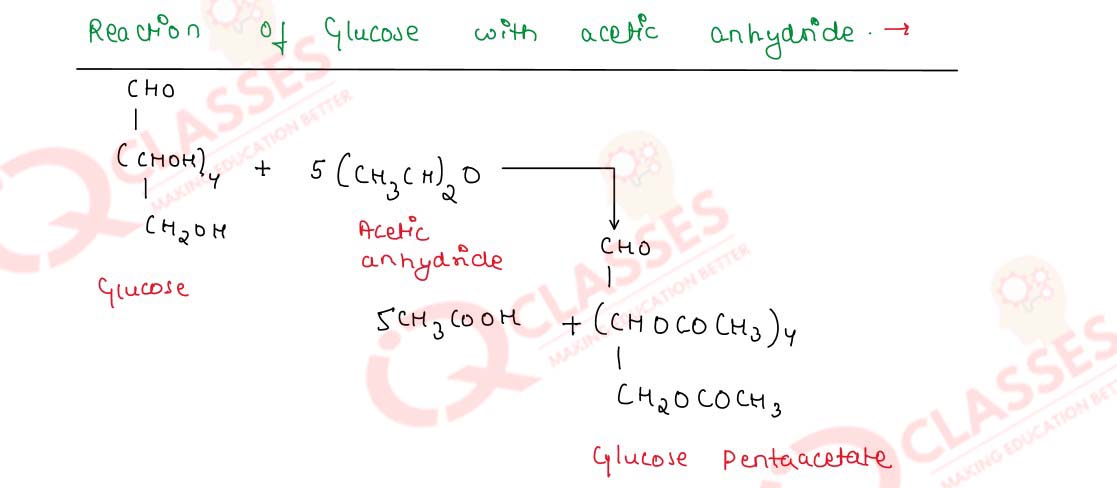
Write chemical equations for the reactions of glucose with
- acetic anhydride and
- ammonical silver nitrate solution
-
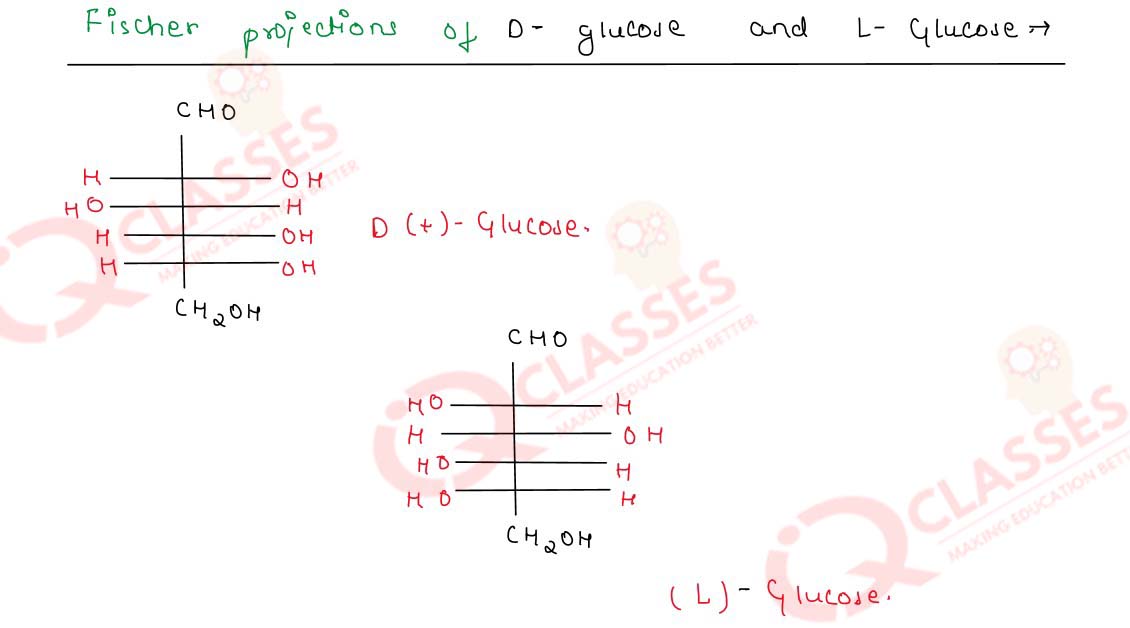
Draw simple Fischer projections of D-glucose and
L-glucose. Can these be called enantiomers
Solution

Q14.25
Write reactions to show how glucose separately reacts with
- NH20H
- HNO3
- ammonical AgNO3
Solution

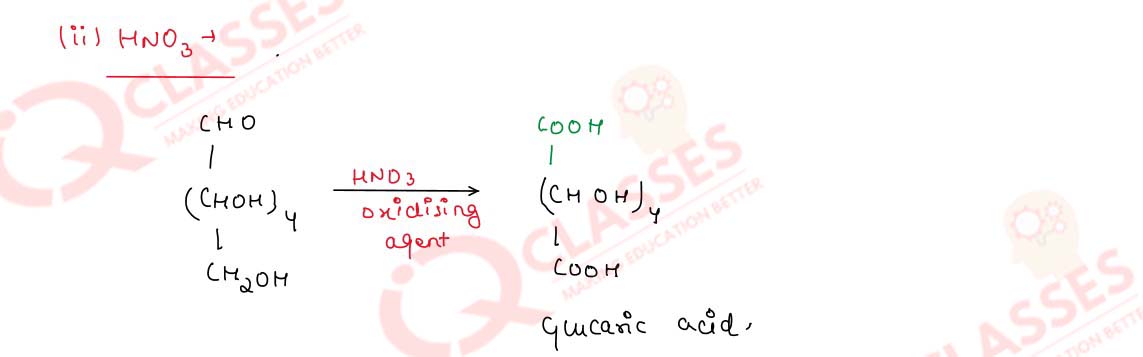
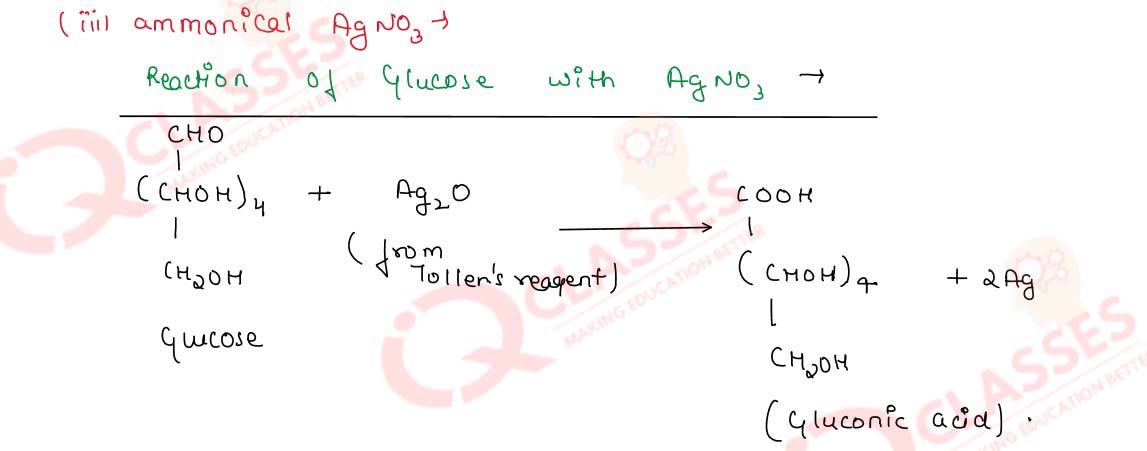
Q14.26
What are reducing sugars ? Give two examples
Solution
All those carbohydrates which contain a free,-CHO or ketonic group and reduce fenling's solution and
Tollen's reagent are referred as a reducing sugar
Eg-> galactose, glucose, fructose etc.
Q14.27
Name the three major classes of carbohydrates and give an example of each of these classes.
Solution
The carbohydrates are divided into 3major classes
- Monosaccharides
- oligosaccharides
- polysaccharide
(i) Monosaccharides→
they are polyhydroxy aldehydes
or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to gives simpler carbohydrates

(ii) oligosaccharides→
carbohydrates which yield a definite number of mono (2-19) molecules
on hydrolysis.
They include-Disaccharides, Trisaccharides and tetrasaccharides.
(iii) Polysaccharides→
These are carbohydrates of high molecular wt. which yield many monosaccharides molecules on
hydrolysis.

Q14.28
What is a peptide bond? Explain the primary structure of proteins
Solution
The carbohydrates are divided into 3major classes
- Monosaccharides
- oligosaccharides
- polysaccharide
(i) Monosaccharides→
they are polyhydroxy aldehydes
or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to gives simpler carbohydrates

(ii) oligosaccharides→
carbohydrates which yield a definite number of mono (2-19) molecules
on hydrolysis.
They include-Disaccharides, Trisaccharides and tetrasaccharides.
(iii) Polysaccharides→
These are carbohydrates of high molecular wt. which yield many monosaccharides molecules on
hydrolysis.