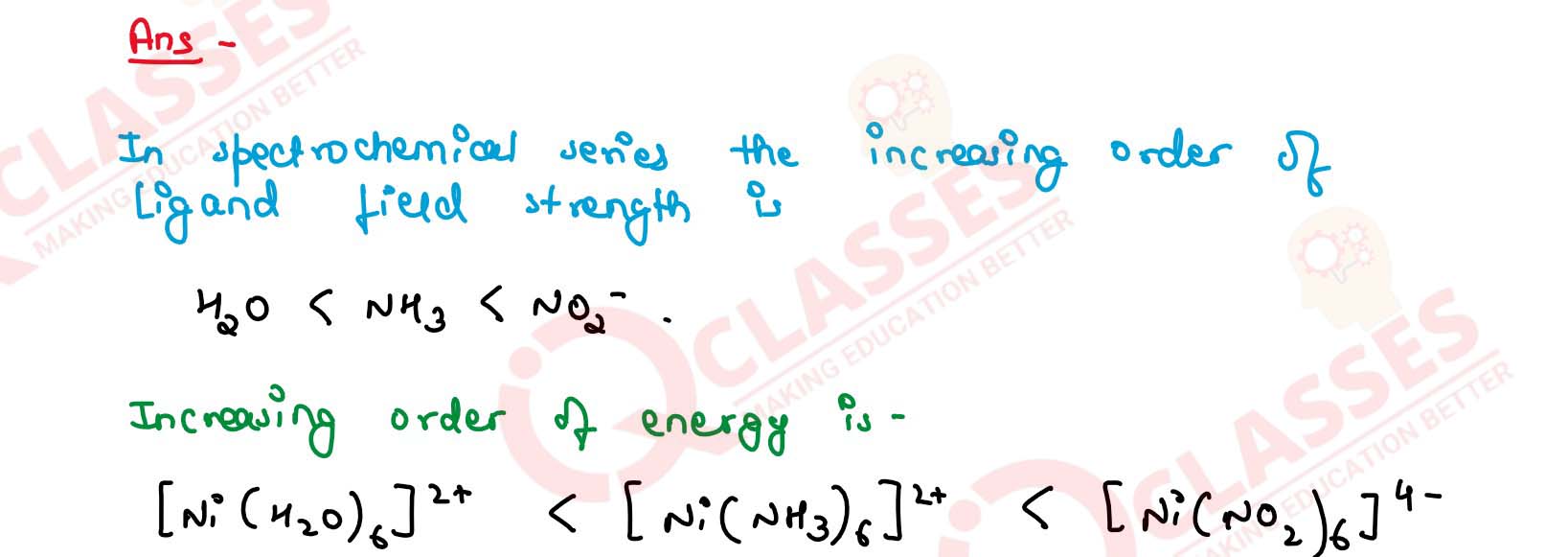Q2.1
Explain the bonding in coordination compounds in terms of Werner’s postulates
Solution


Q2.2
FeSO4 solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4 solution in 1:1 molar
ratio gives the
test of Fe2+ ion but CuSO4 solution mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1:4
molar ratio does not give the test of Cu2+ ion. Explain why?
Solution


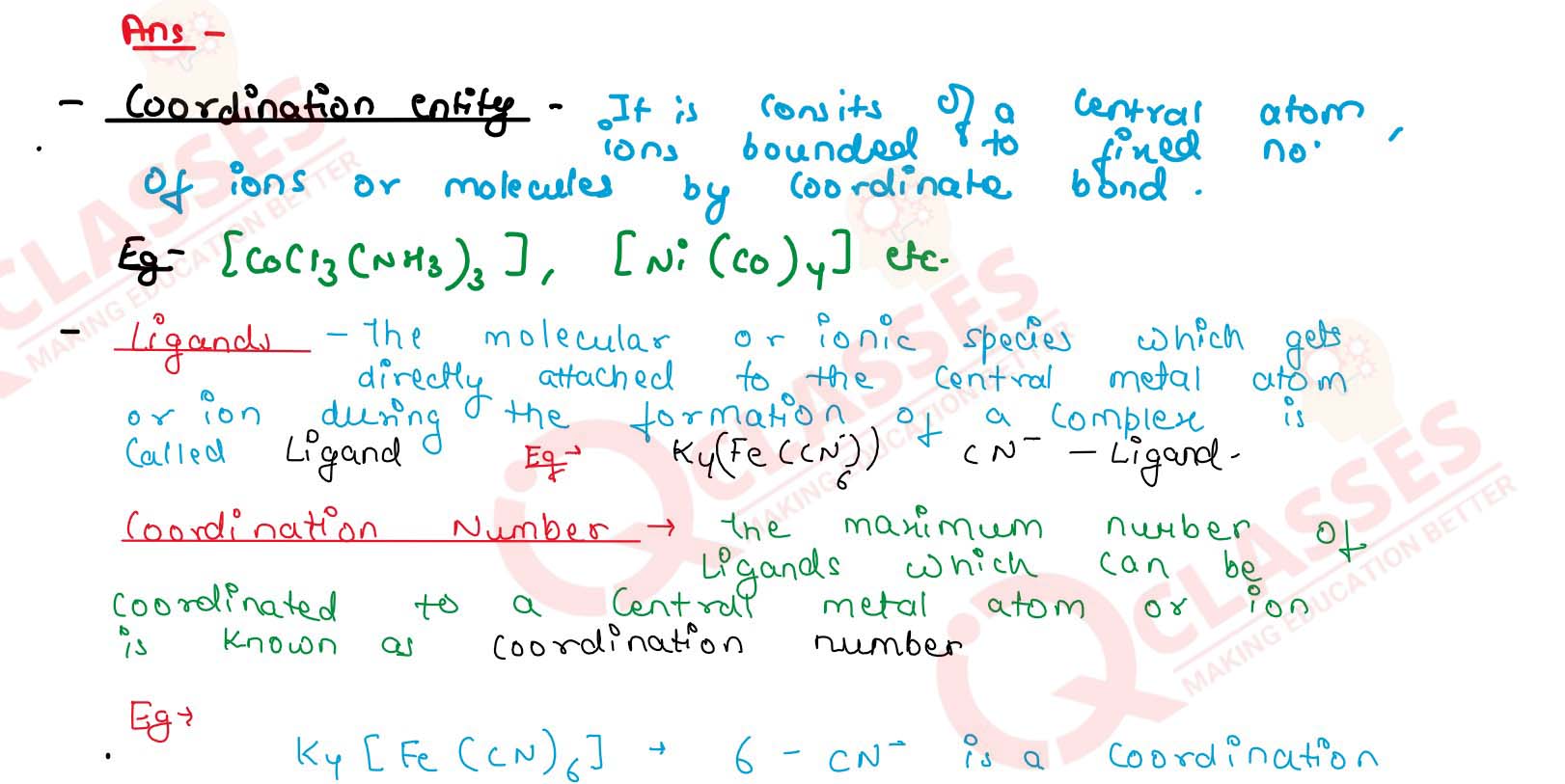
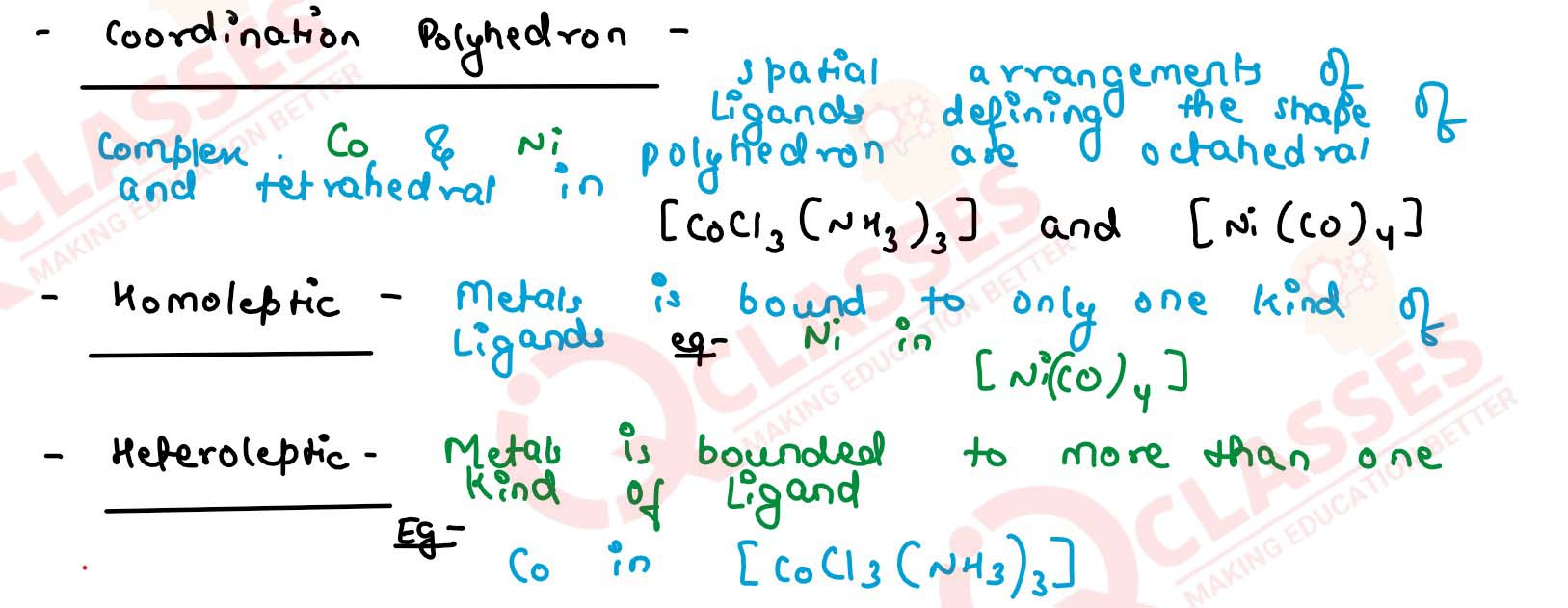
Q2.3
Explain with two examples each of the following: coordination entity, ligand,
coordination number, coordination polyhedron, homoleptic and heteroleptic.
Solution


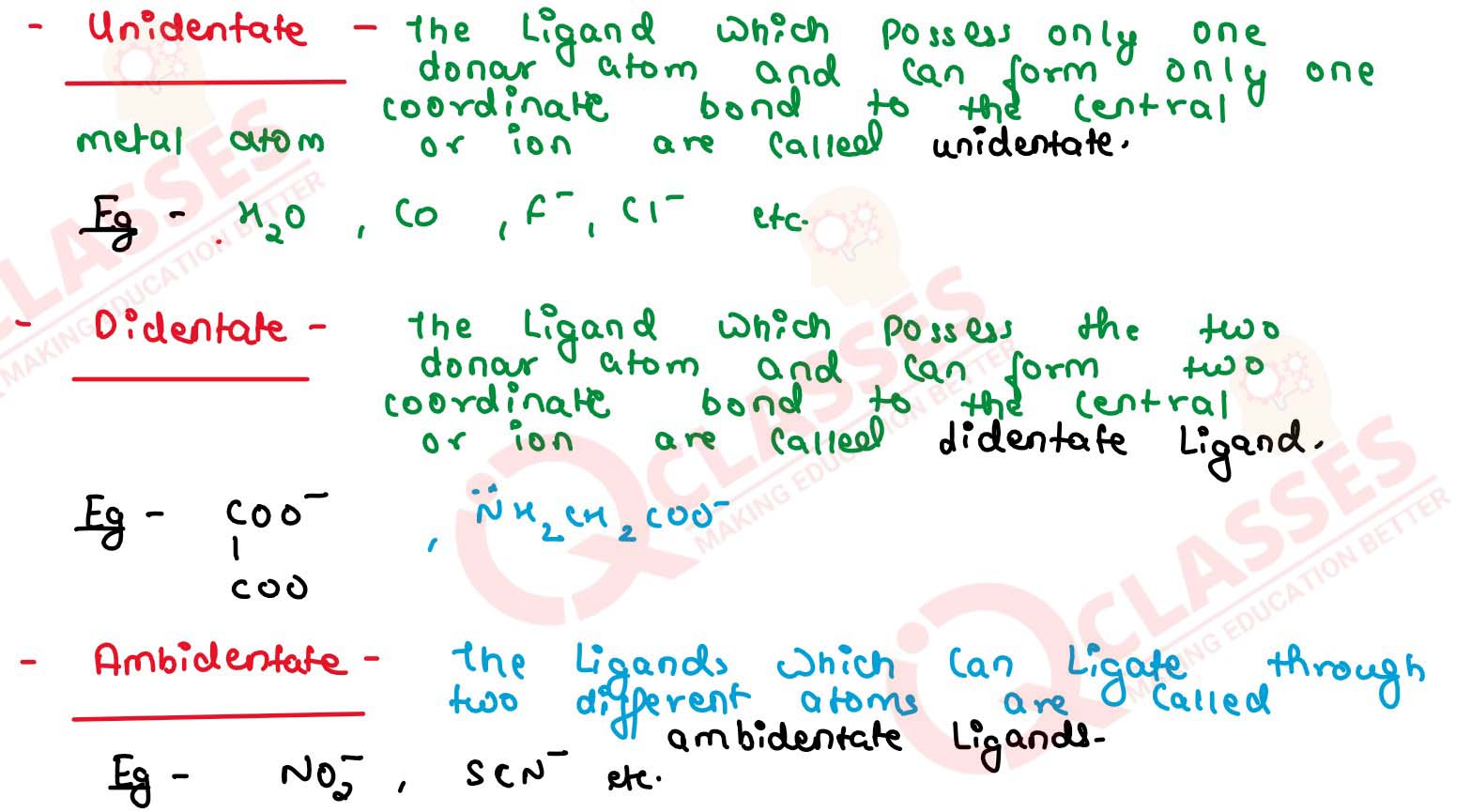
Q2.4
What is meant by unidentate, didentate and ambidentate ligands? Give two
examples for each.
Solution

Q2.5
Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordination entities:
(i) [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2]2+
(ii) [CoBr2(en)2]+
(iii) [PtCl4 ]4-
(iv) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(v) [Cr(NH3)3Cl3] Solution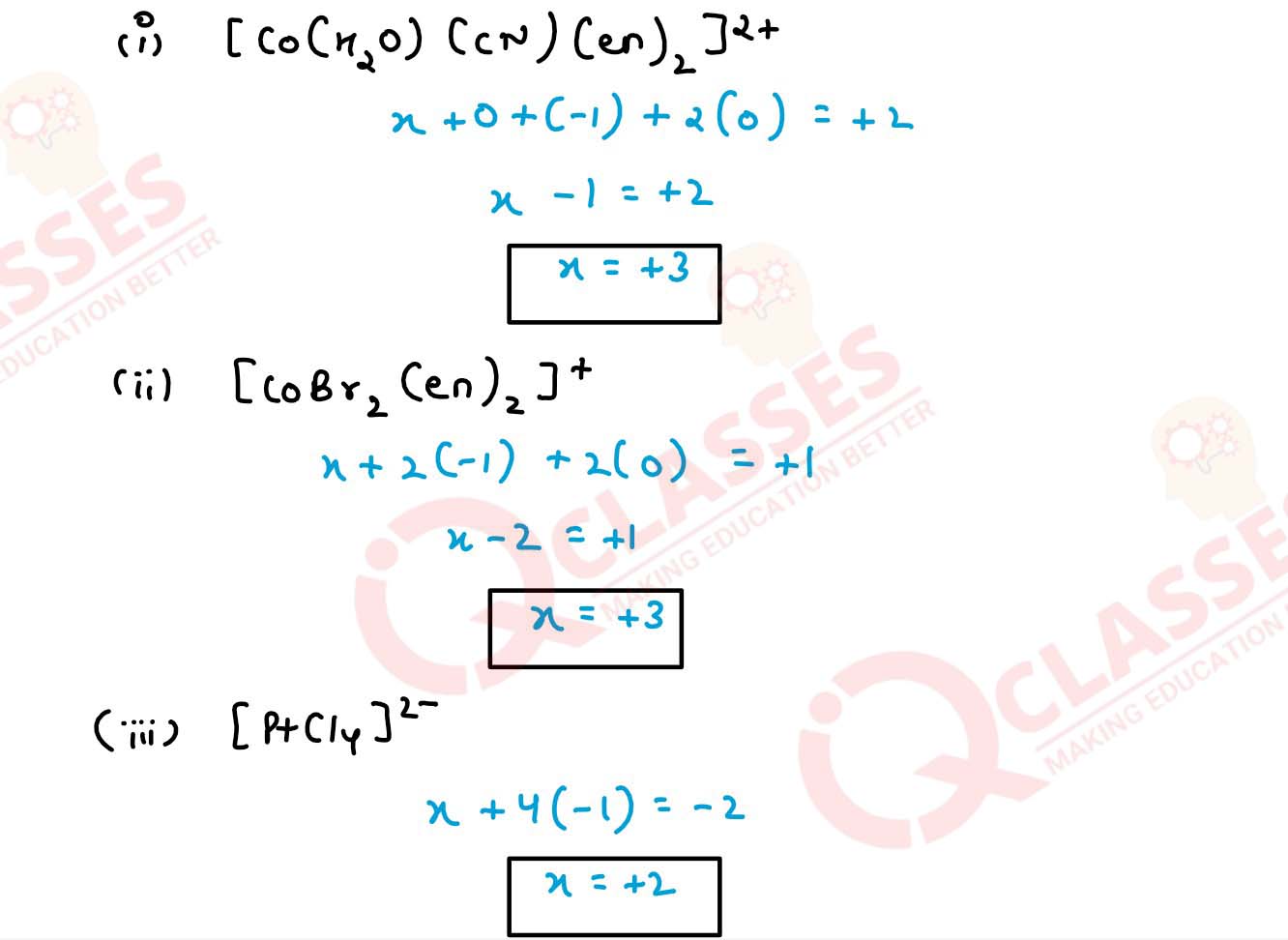
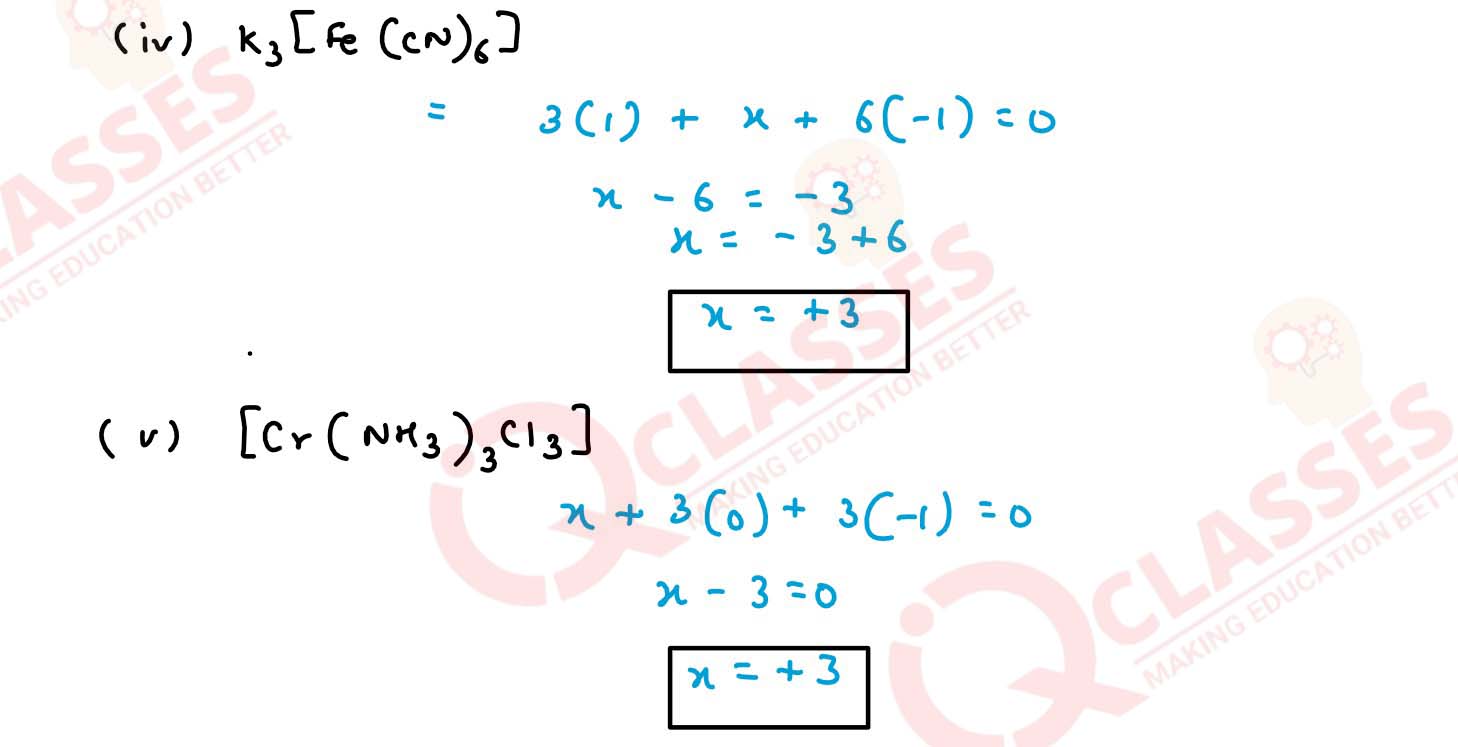
(i) [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2]2+
(ii) [CoBr2(en)2]+
(iii) [PtCl
(iv) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(v) [Cr(NH3)3Cl3] Solution

Q2.6
Using IUPAC norms write the formulas for the following:
(i) Tetrahydroxidozincate(II)
(ii) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II)
(iii) Diamminedichloridoplatinum(II)
(iv) Potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II)
(v) Pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt(III)
(vi) Hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate
(vii) Potassium tri(oxalato)chromate(III)
(viii) Hexaammineplatinum(IV)
(ix) Tetrabromidocuprate(II)
(x) Pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(III)
Solution

(i) Tetrahydroxidozincate(II)
(ii) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II)
(iii) Diamminedichloridoplatinum(II)
(iv) Potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II)
(v) Pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt(III)
(vi) Hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate
(vii) Potassium tri(oxalato)chromate(III)
(viii) Hexaammineplatinum(IV)
(ix) Tetrabromidocuprate(II)
(x) Pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(III)
Solution


Q2.7
Using IUPAC norms write the systematic names of the following:
(i) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 (iv) [Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]Cl (vii) [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NH2CH3)]Cl (v) [Mn(H2O)6]2+ (viii) [Co(en)3]3+
(iii) [Ti(H2O)6]3+ (vi) [NiCl4]2- (ix) [Ni(CO)4]
Solution
(i) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 (iv) [Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]Cl (vii) [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NH2CH3)]Cl (v) [Mn(H2O)6]2+ (viii) [Co(en)3]3+
(iii) [Ti(H2O)6]3+ (vi) [NiCl4]2- (ix) [Ni(CO)4]
Solution

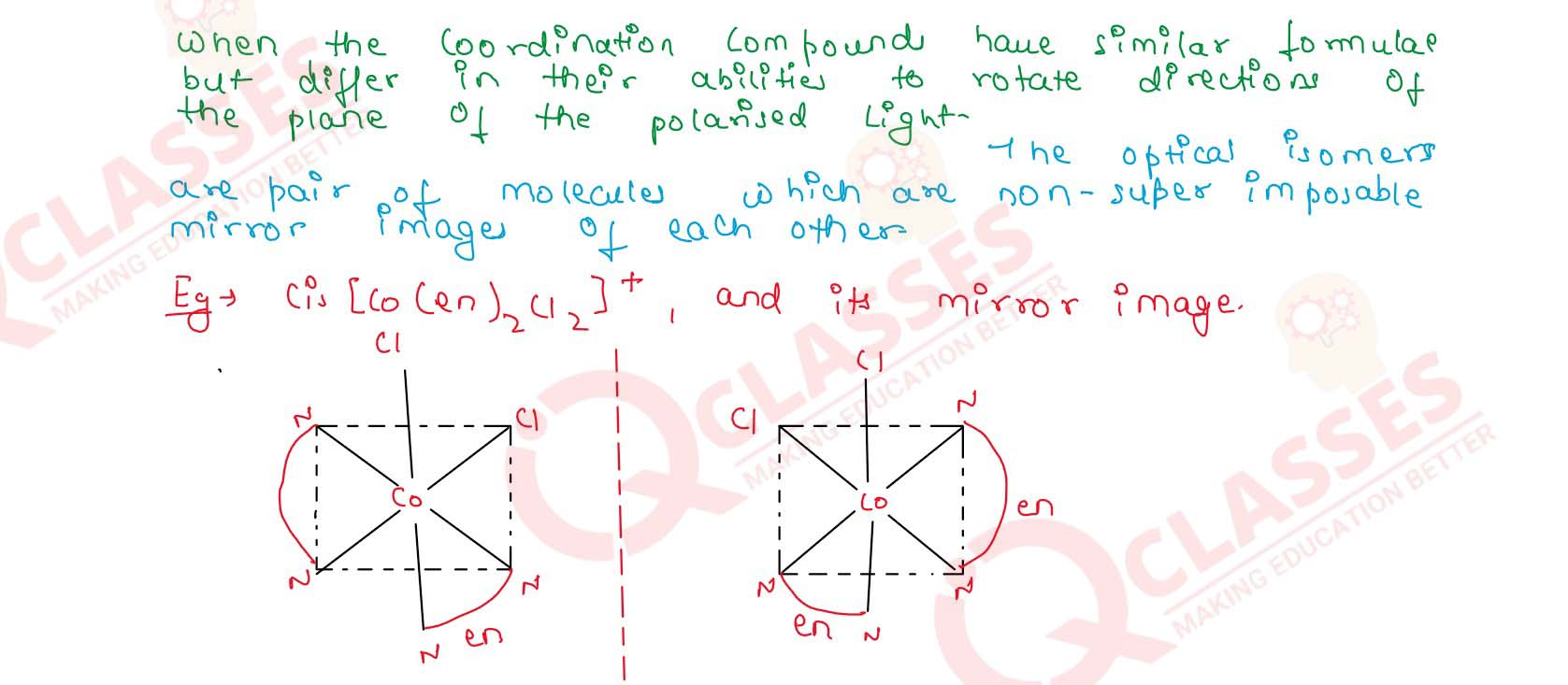
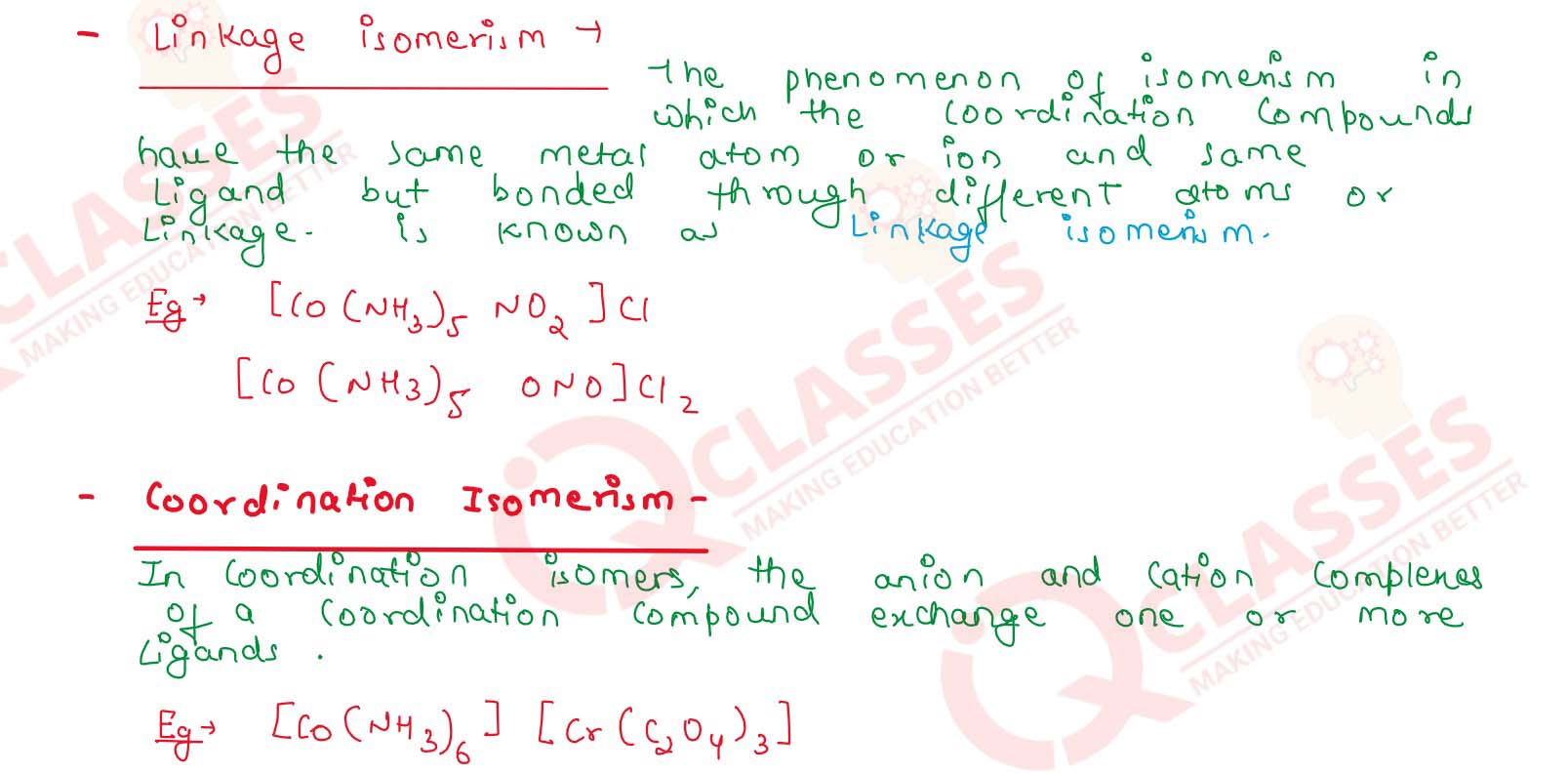
Q2.8
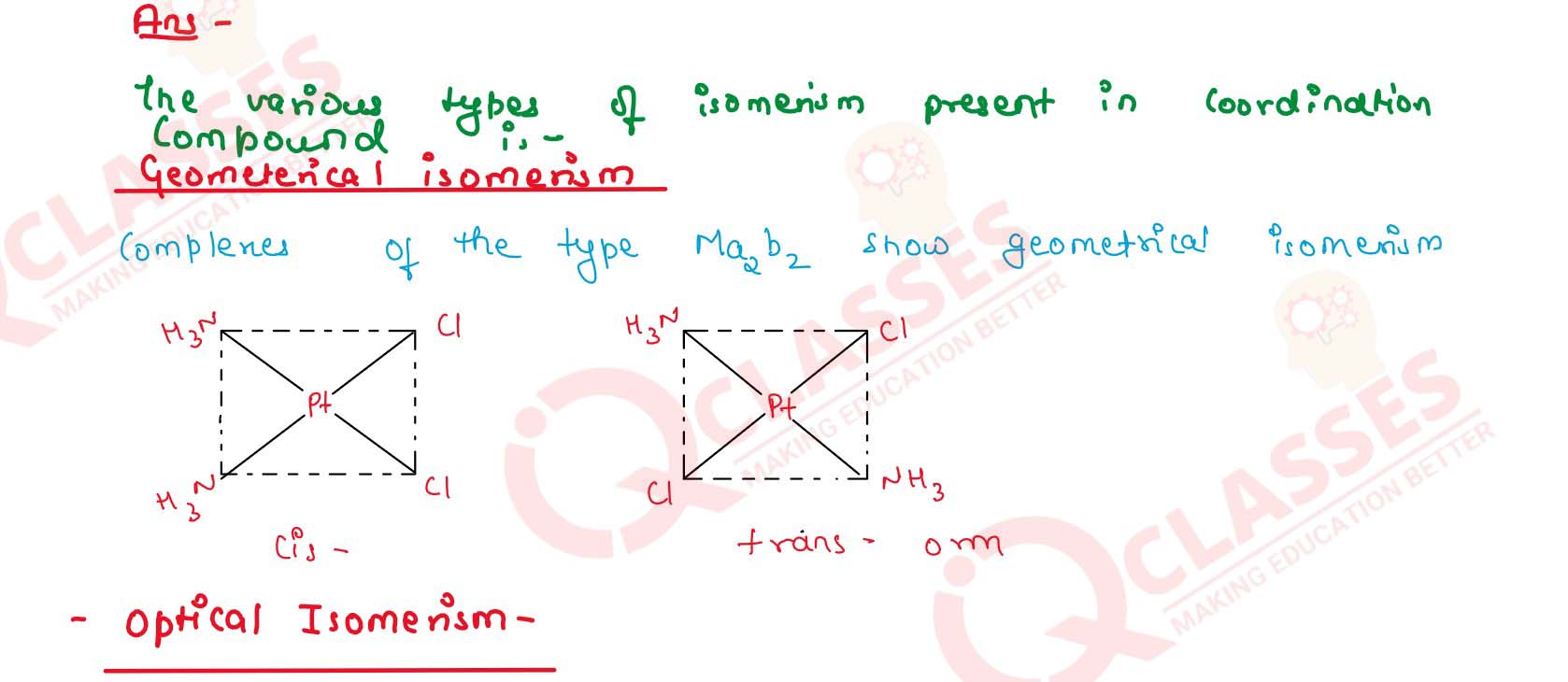
List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, giving
an example of each.
Solution



Q2.9
How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities?
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3-
(ii) [Co(NH3)3Cl3] Solution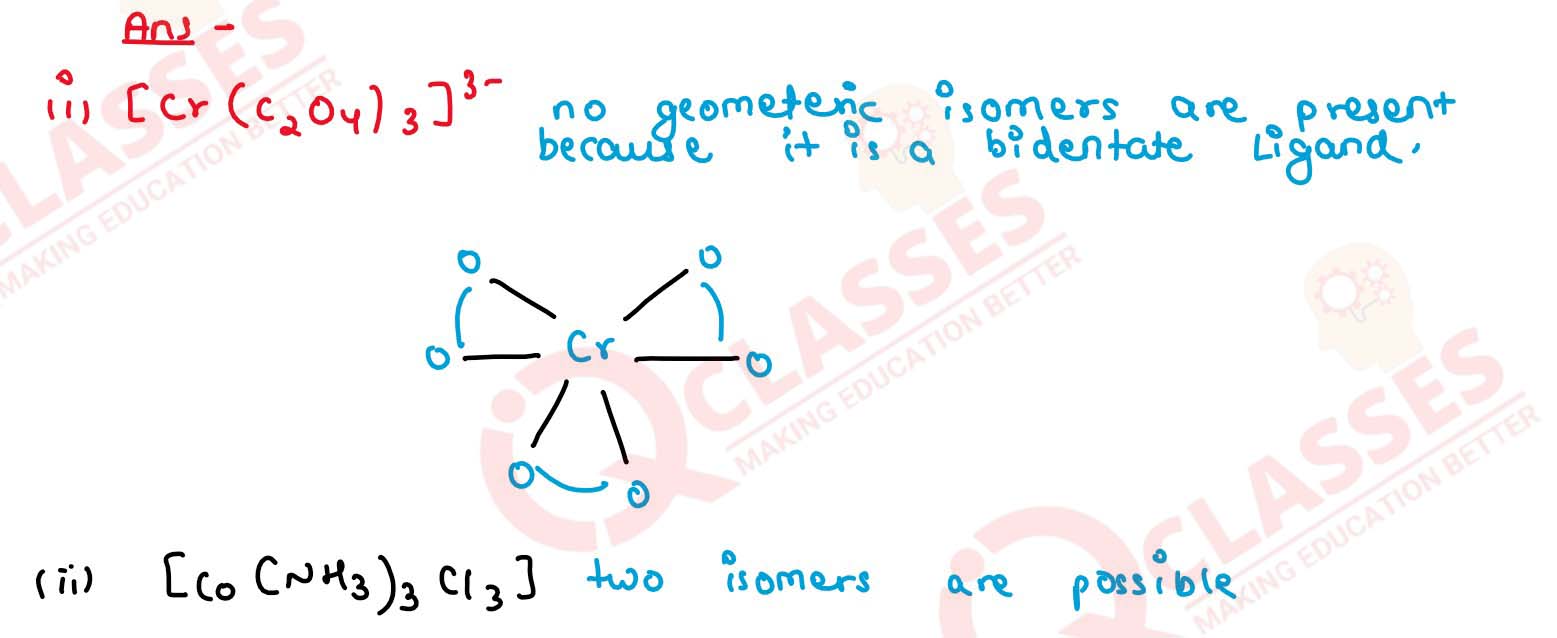
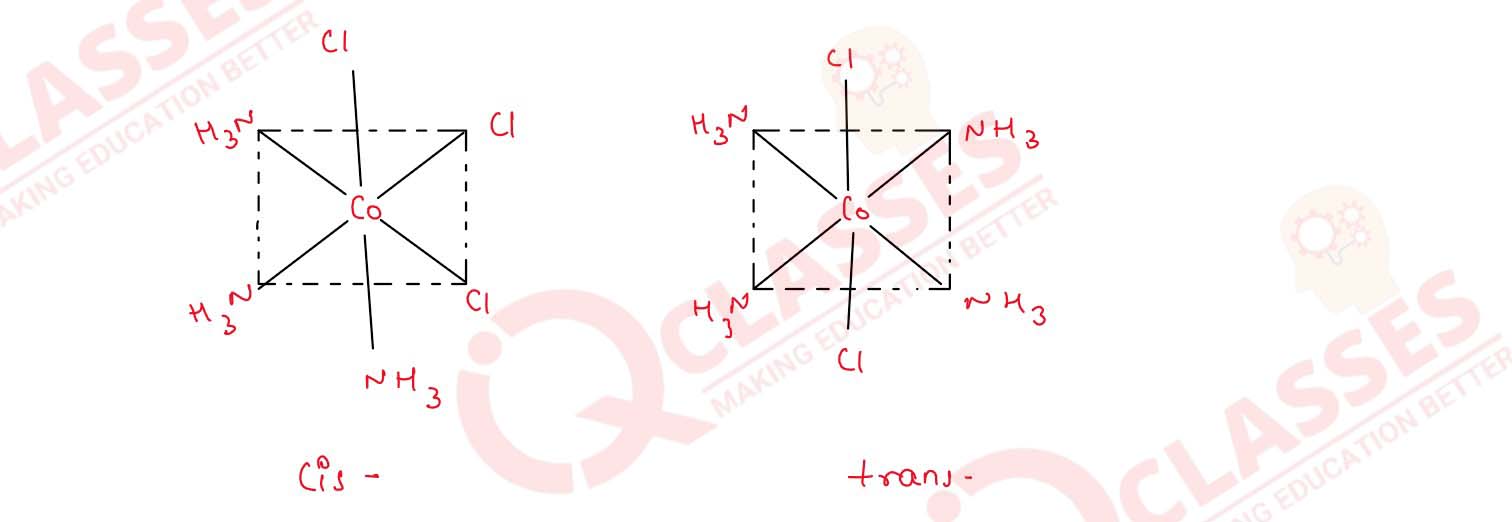
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3-
(ii) [Co(NH3)3Cl3] Solution


Q2.10
Draw the structures of optical isomers of:
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3-
(ii) [PtCl2(en)2]2+
(iii) [Cr(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+ Solution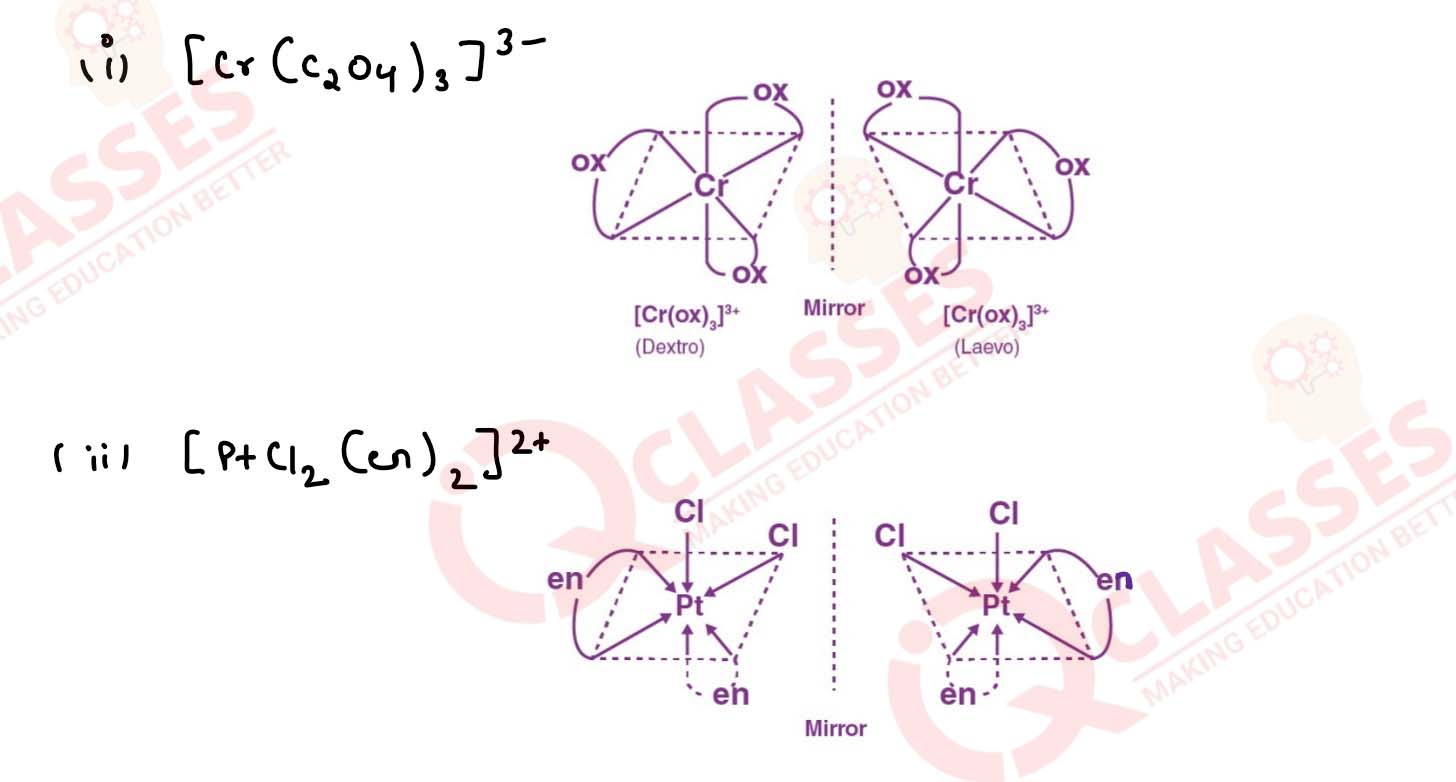
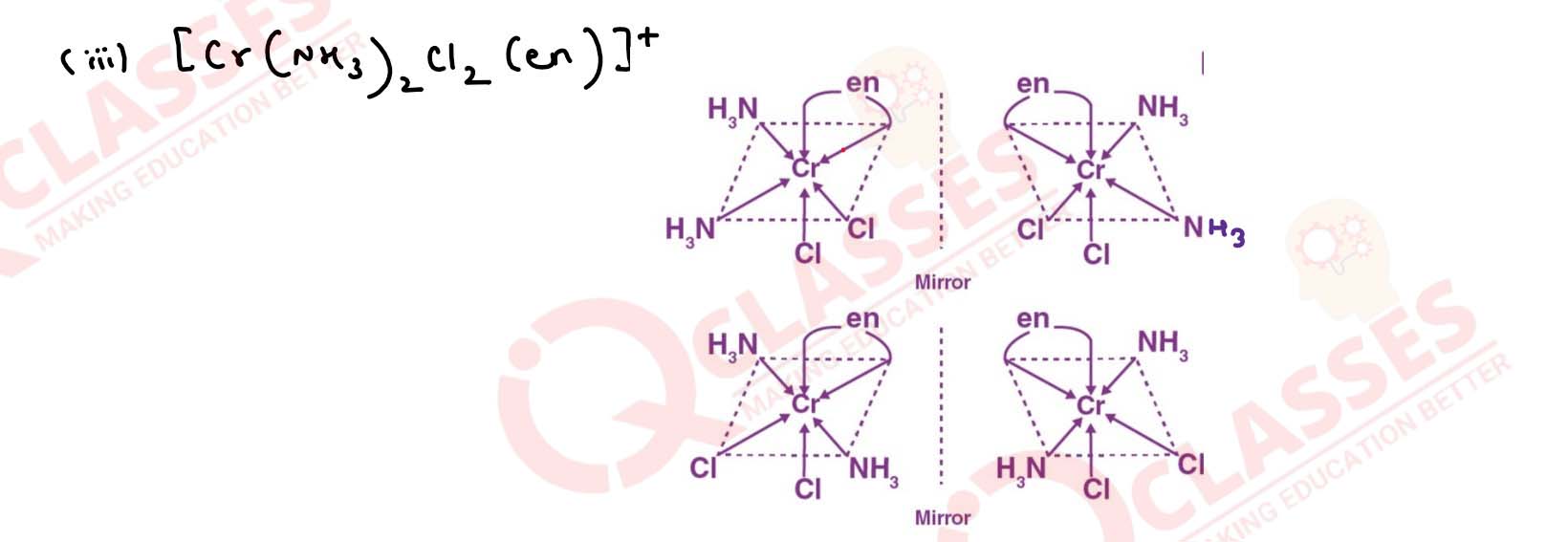
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3-
(ii) [PtCl2(en)2]2+
(iii) [Cr(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+ Solution


Q2.11
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of:
(i) [CoCl2(en)2]+
(ii) [Co(NH3)Cl(en)2]3+
(iii) [Co(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+ Solution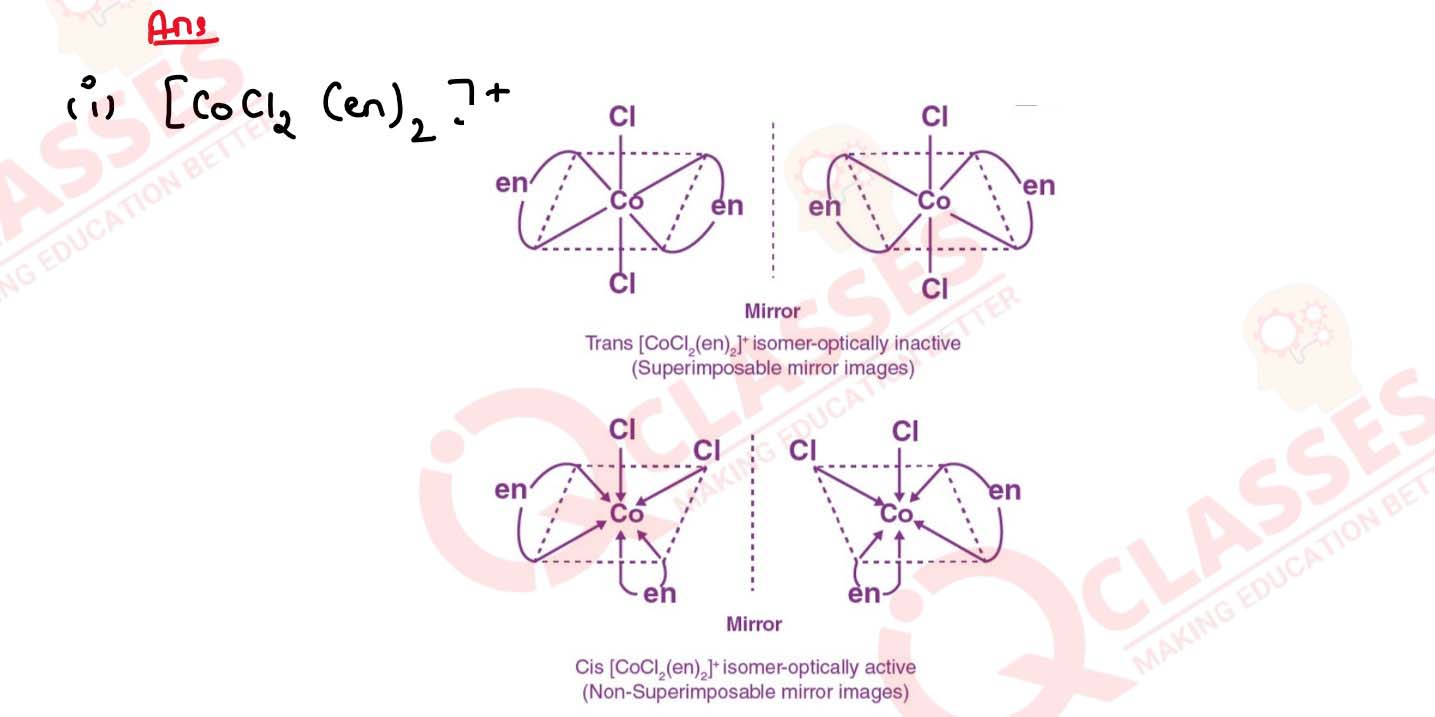
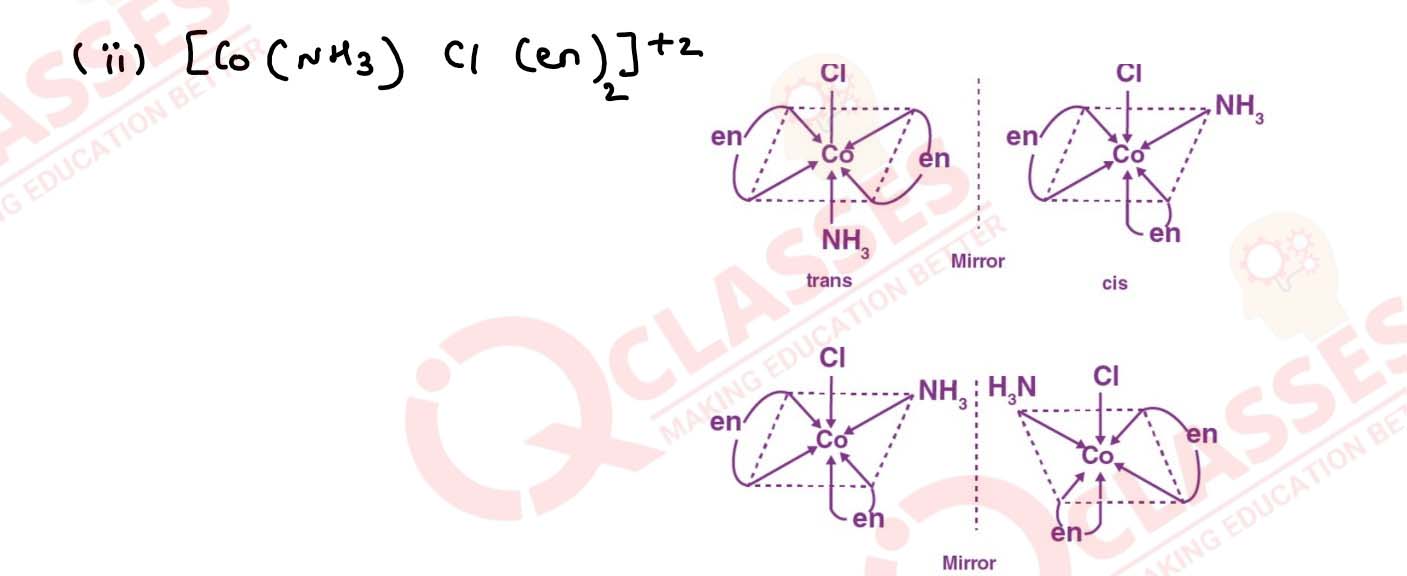
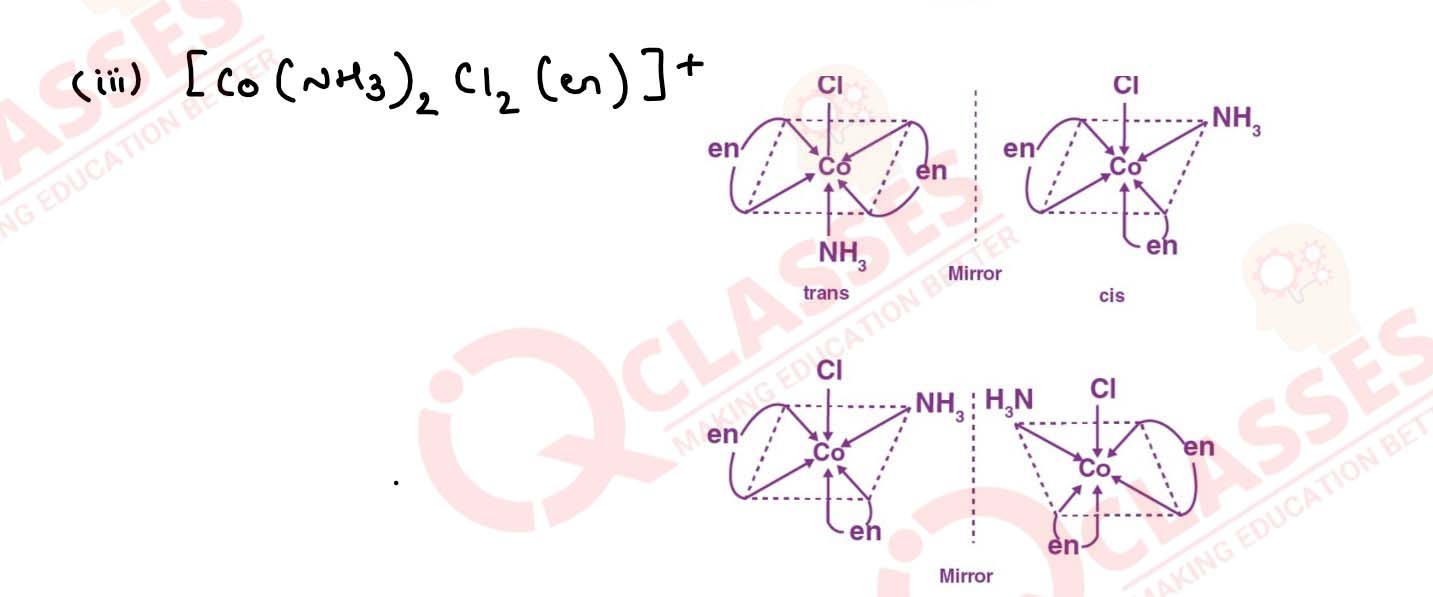
(i) [CoCl2(en)2]+
(ii) [Co(NH3)Cl(en)2]3+
(iii) [Co(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+ Solution



Q2.12
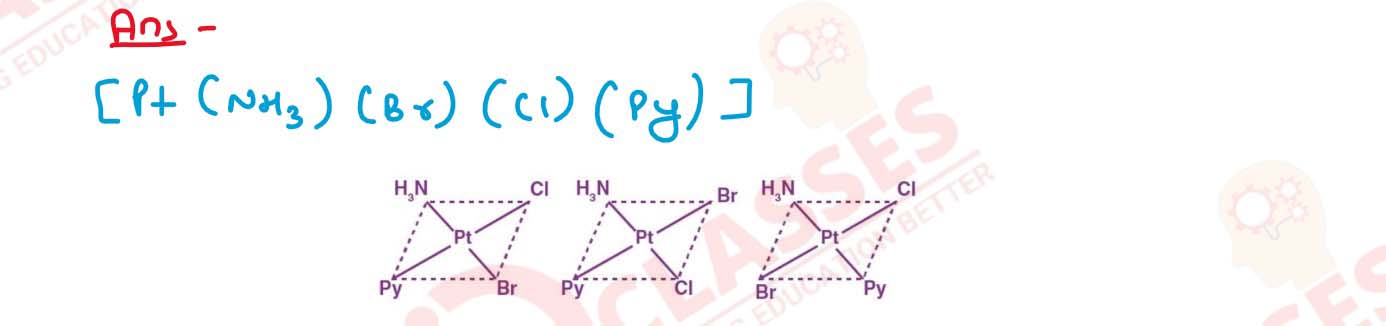
Write all the geometrical isomers of [Pt(NH3)(Br)(Cl)(py)] and how many of these
will exhibit optical isomers?
Solution

Q2.13
Aqueous copper sulphate solution (blue in colour) gives:
(i) a green precipitate with aqueous potassium fluoride and
(ii) a bright green solution with aqueous potassium chloride. Explain these experimental results
Solution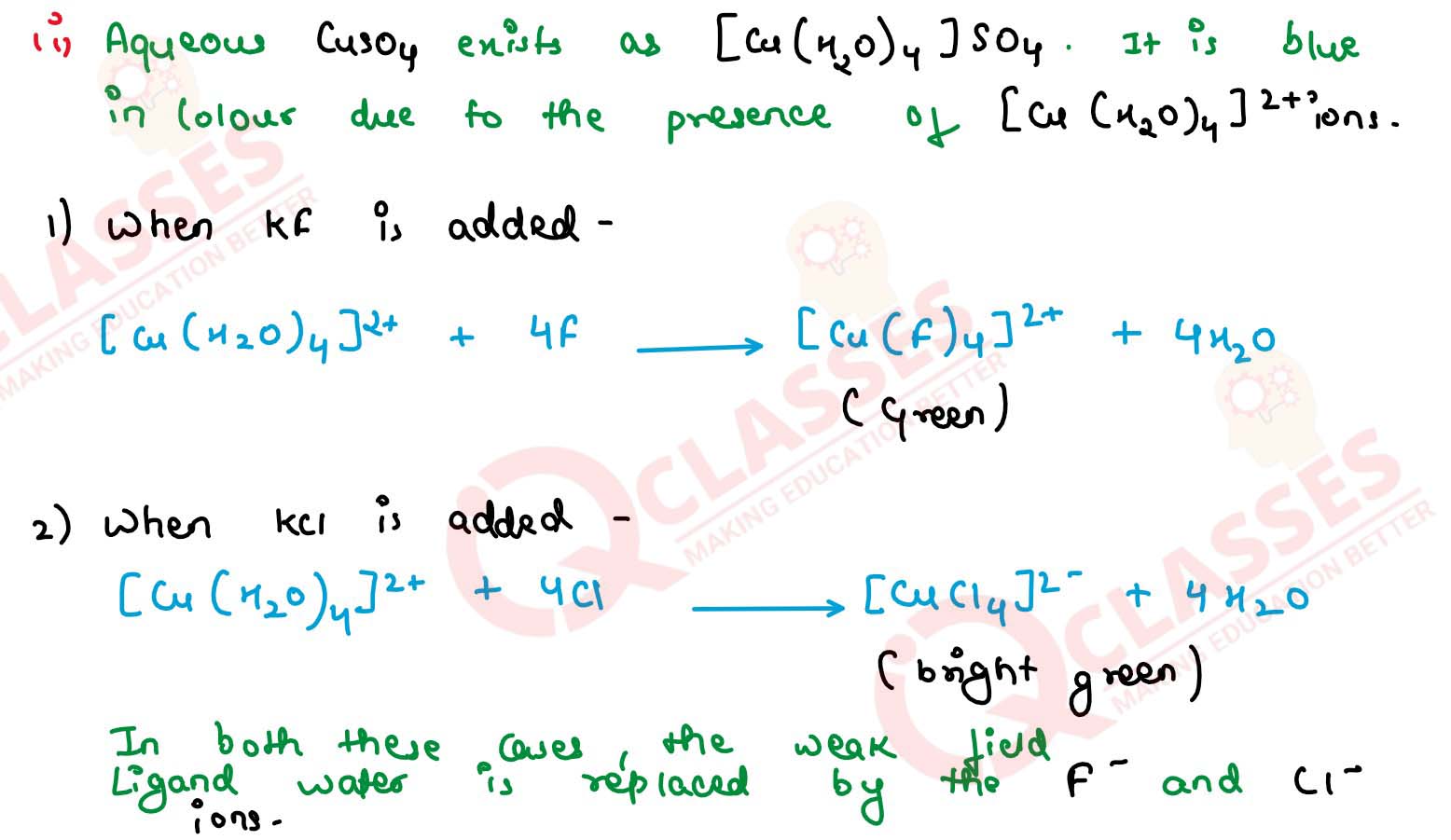
(i) a green precipitate with aqueous potassium fluoride and
(ii) a bright green solution with aqueous potassium chloride. Explain these experimental results
Solution

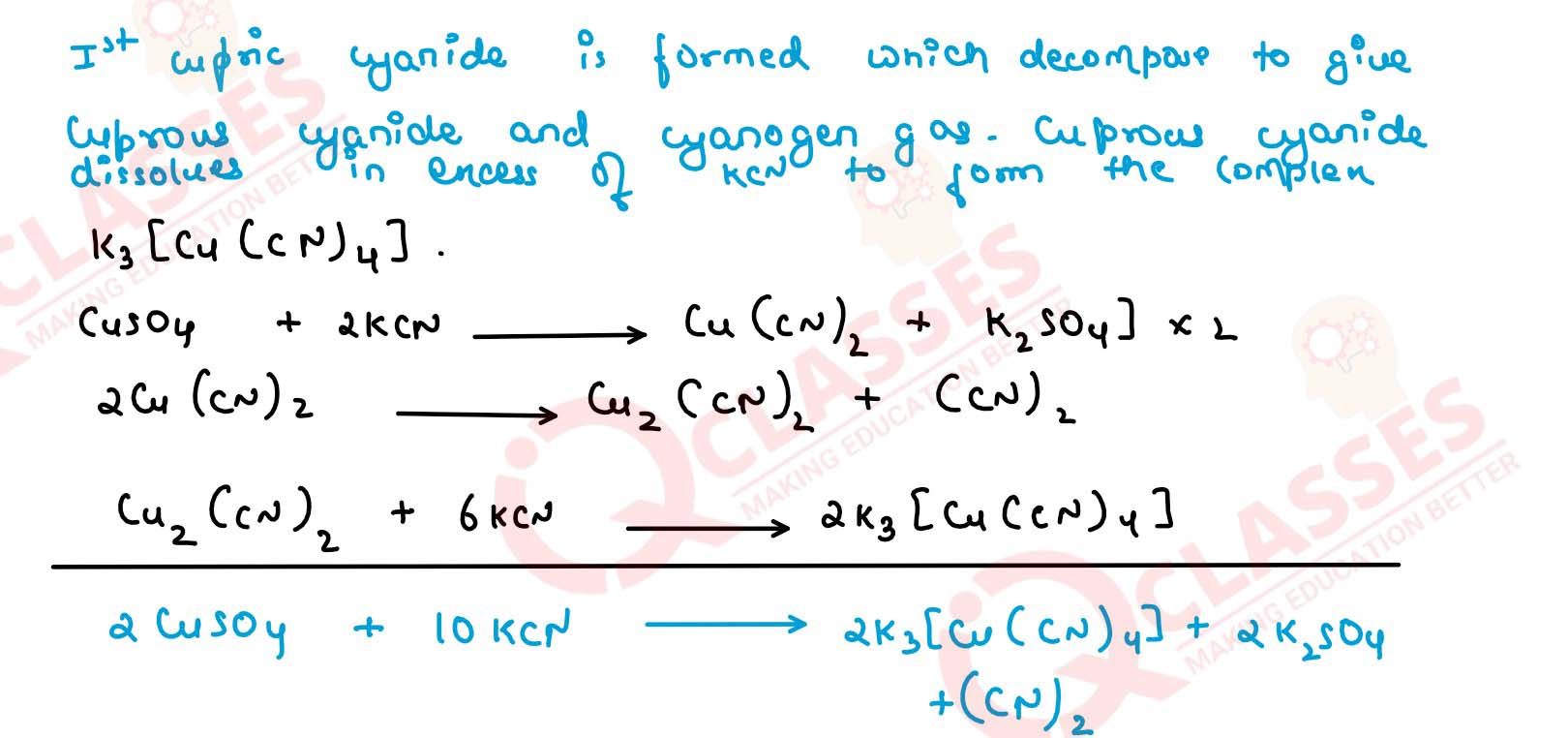
Q2.14
What is the coordination entity formed when excess of aqueous KCN is
added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate? Why is it that no precipitate
of copper sulphide is obtained when H2S(g) is passed through this solution?
Solution



Q2.15
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the
basis of valence bond theory:
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4-
(ii) [FeF6]3-
(iii) [Co(C2O4)3]3-
(iv) [CoF6]3- Solution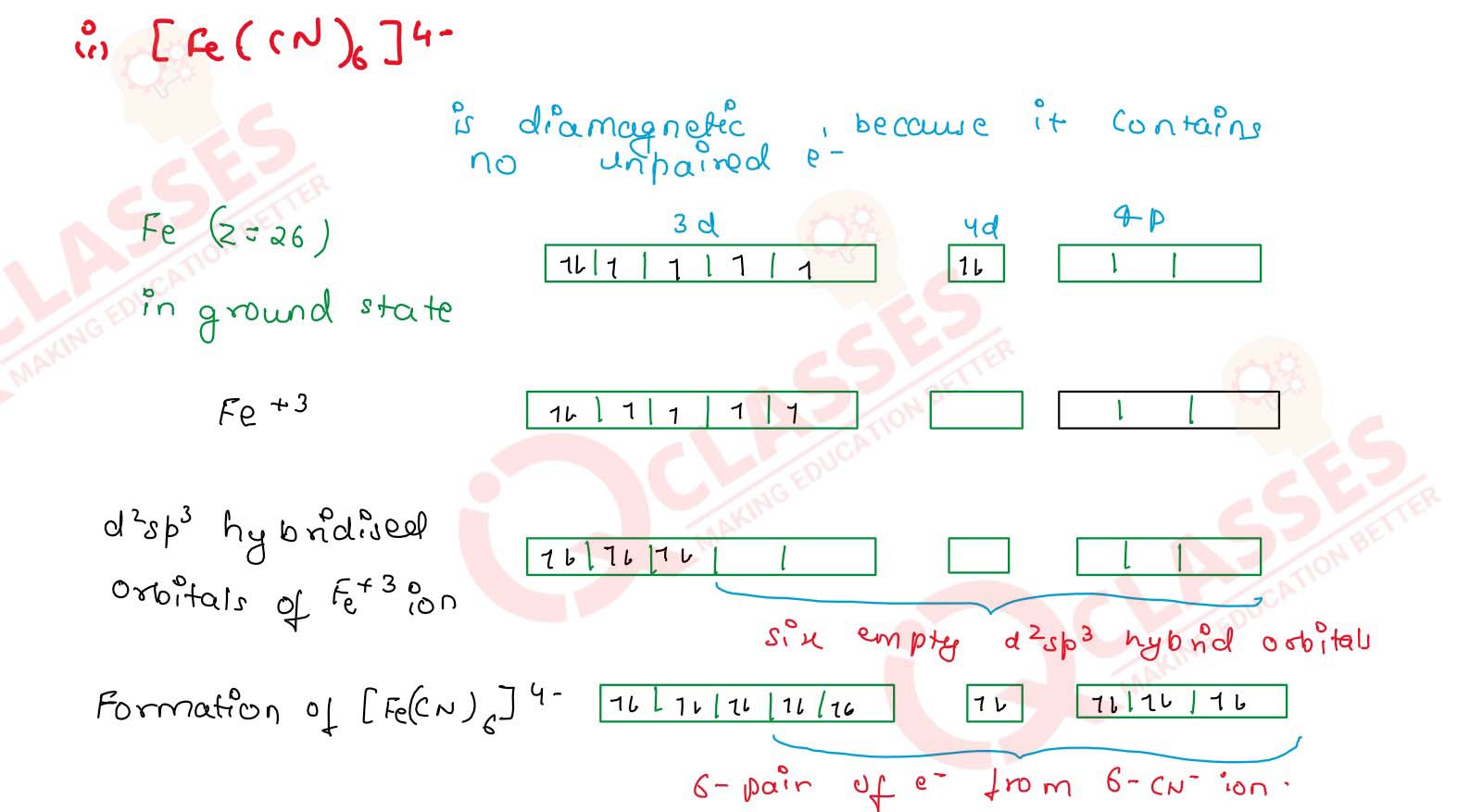
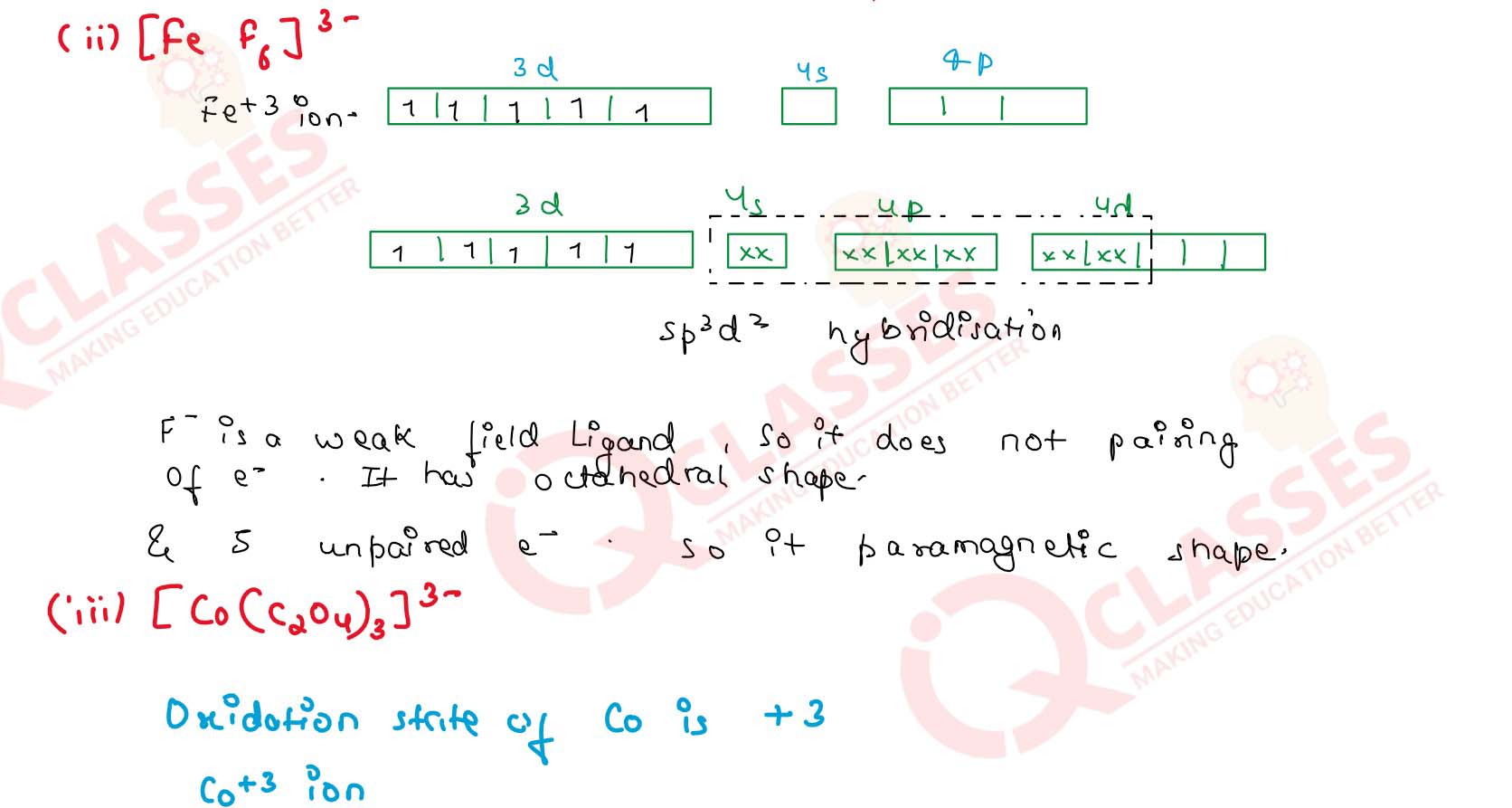
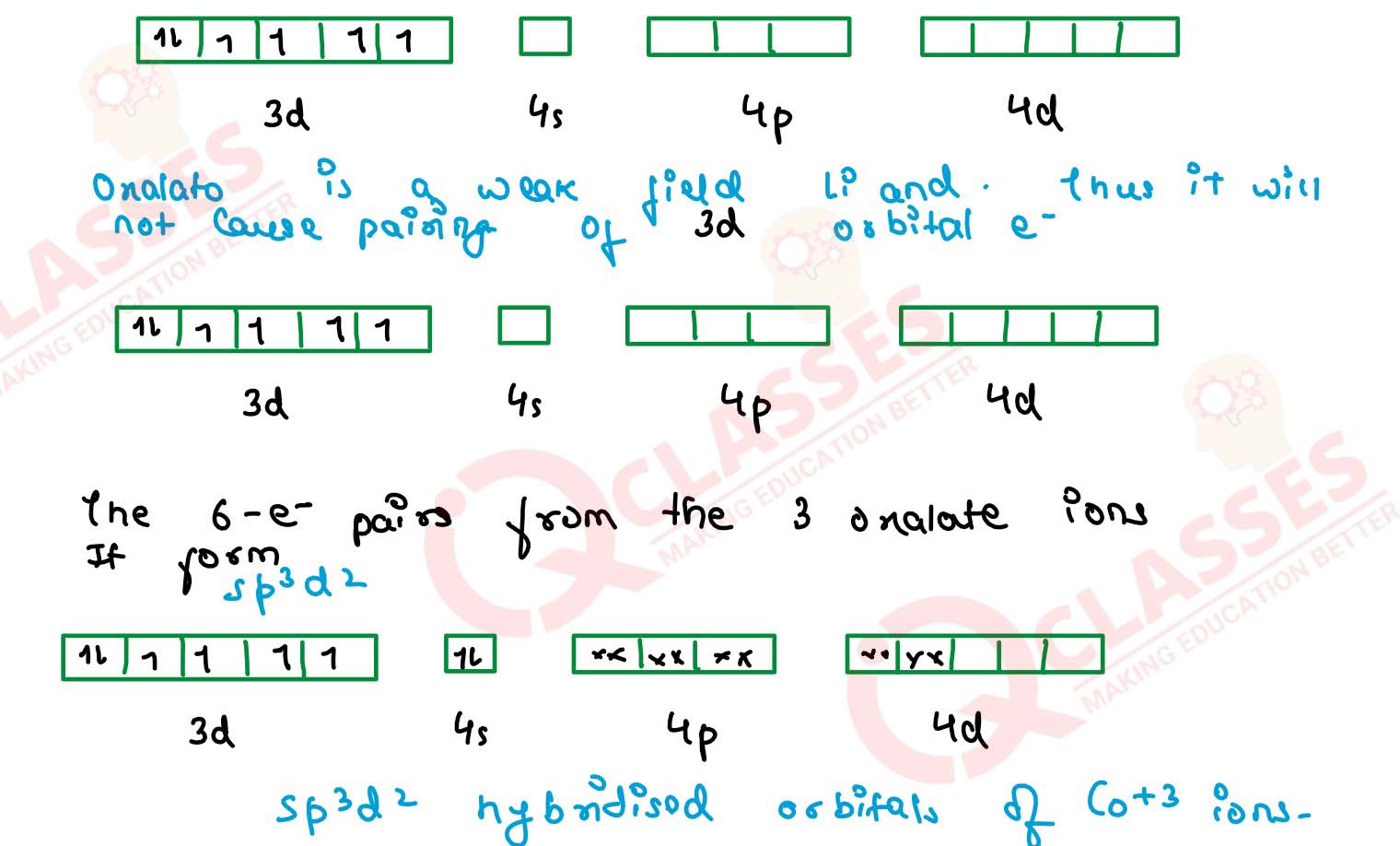
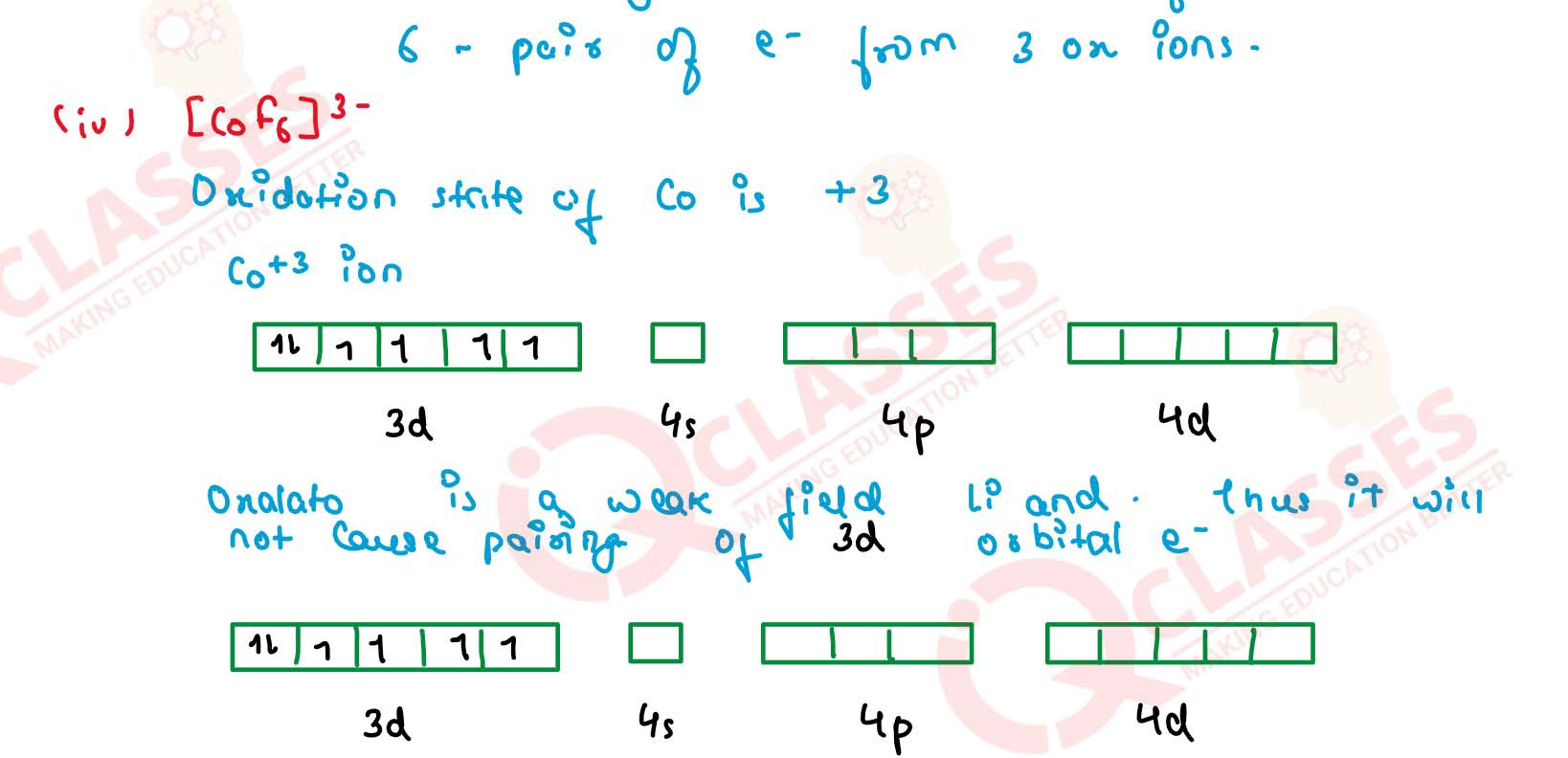
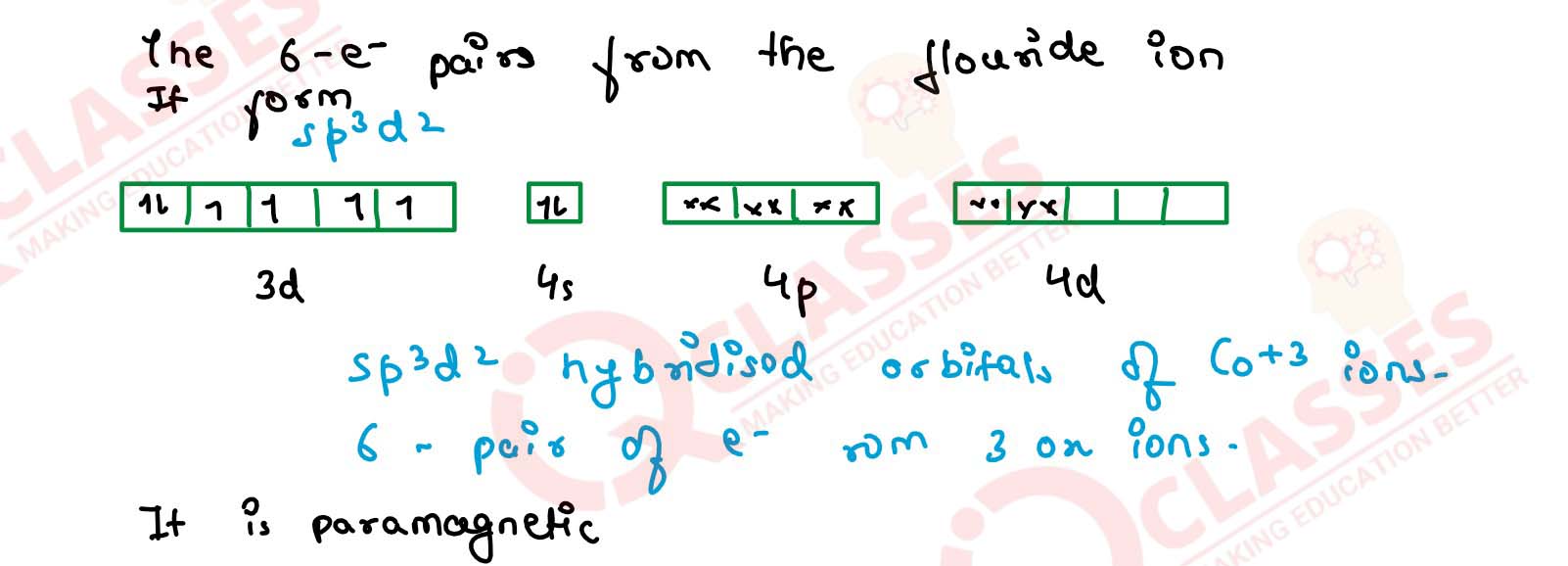
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4-
(ii) [FeF6]3-
(iii) [Co(C2O4)3]3-
(iv) [CoF6]3- Solution





Q2.16
Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field
Solution
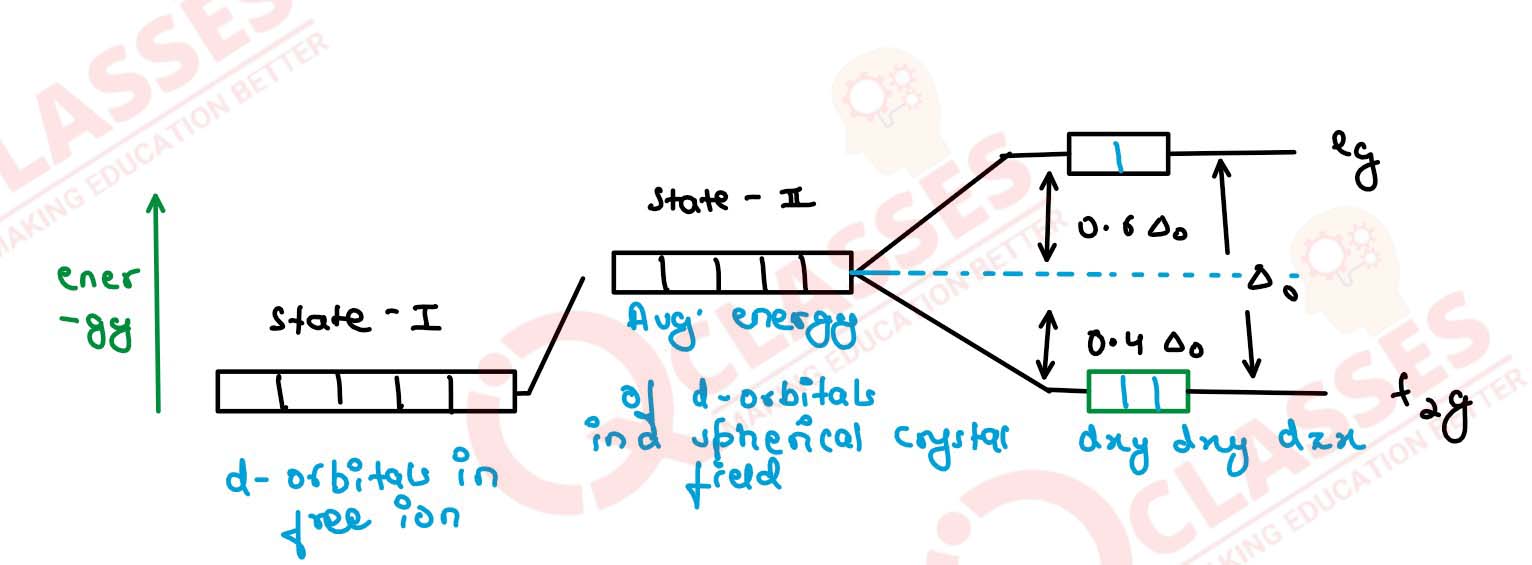

Q2.17
What is spectrochemical series? Explain the difference between a weak
field ligand and a strong field ligand
Solution


Q2.18
What is crystal field splitting energy? How does the magnitude of ∆odecide
the actual configuration of d orbitals in a coordination entity?
Solution


Q2.19
[Cr(NH3)6]3+ is paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2- is
diamagnetic. Explain why?
Solution
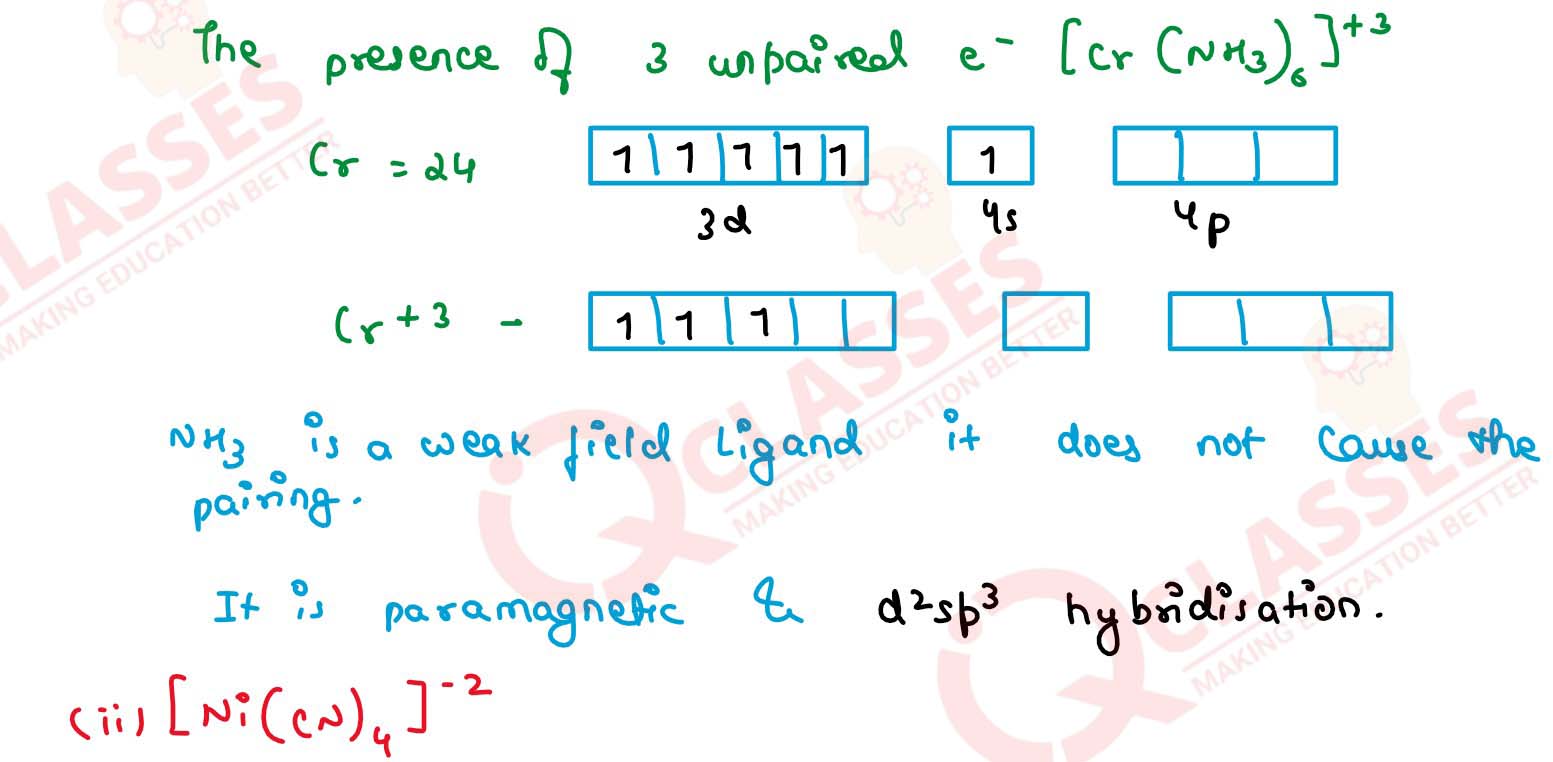
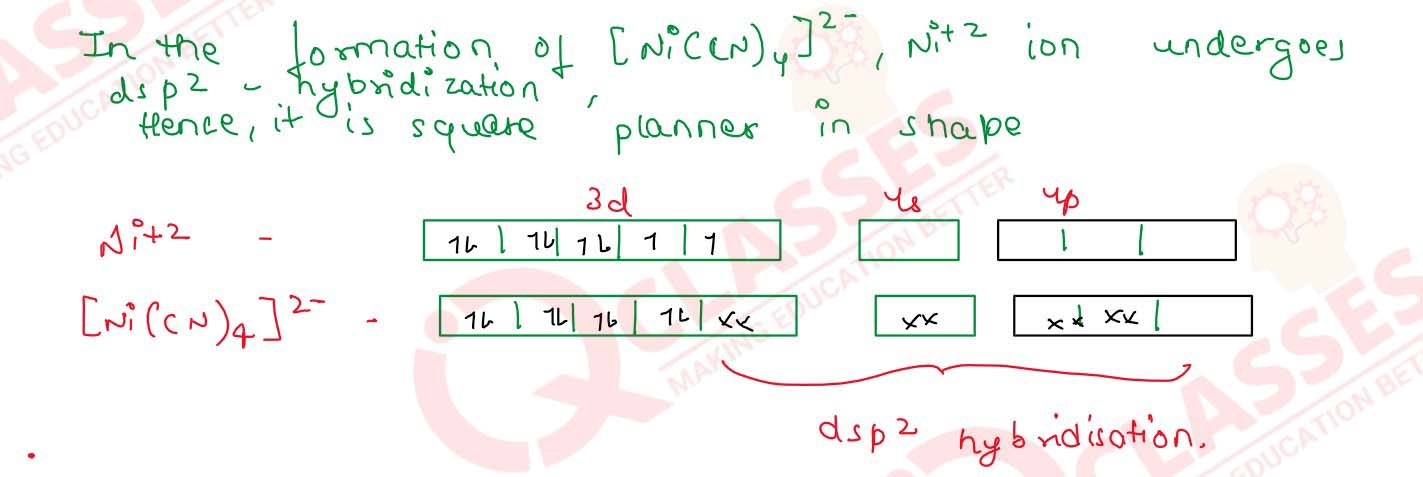


Q2.20
A solution of [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is green but a solution of
[Ni(CN)4]2-is colourless.
Explain
Solution


Q2.21
[Fe(CN)6]4- and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ are of different
colours in dilute solutions. Why?
Solution


Q2.22
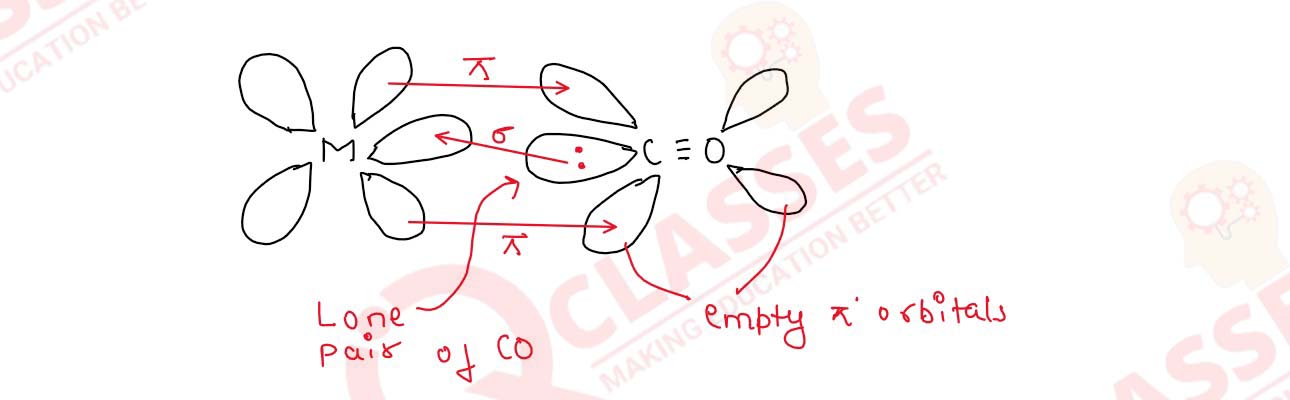
Discuss the nature of bonding in metal carbonyls.
Solution



Q2.23
Give the oxidation state, d orbital occupation and coordination number of
the central metal ion in the following complexes:
(i) K3[Co(C2O4)3]
(ii) cis-[CrCl2(en)2]Cl
(iii) (NH4)2[CoF4]
(iv) [Mn(H2O)6]SO4 Solution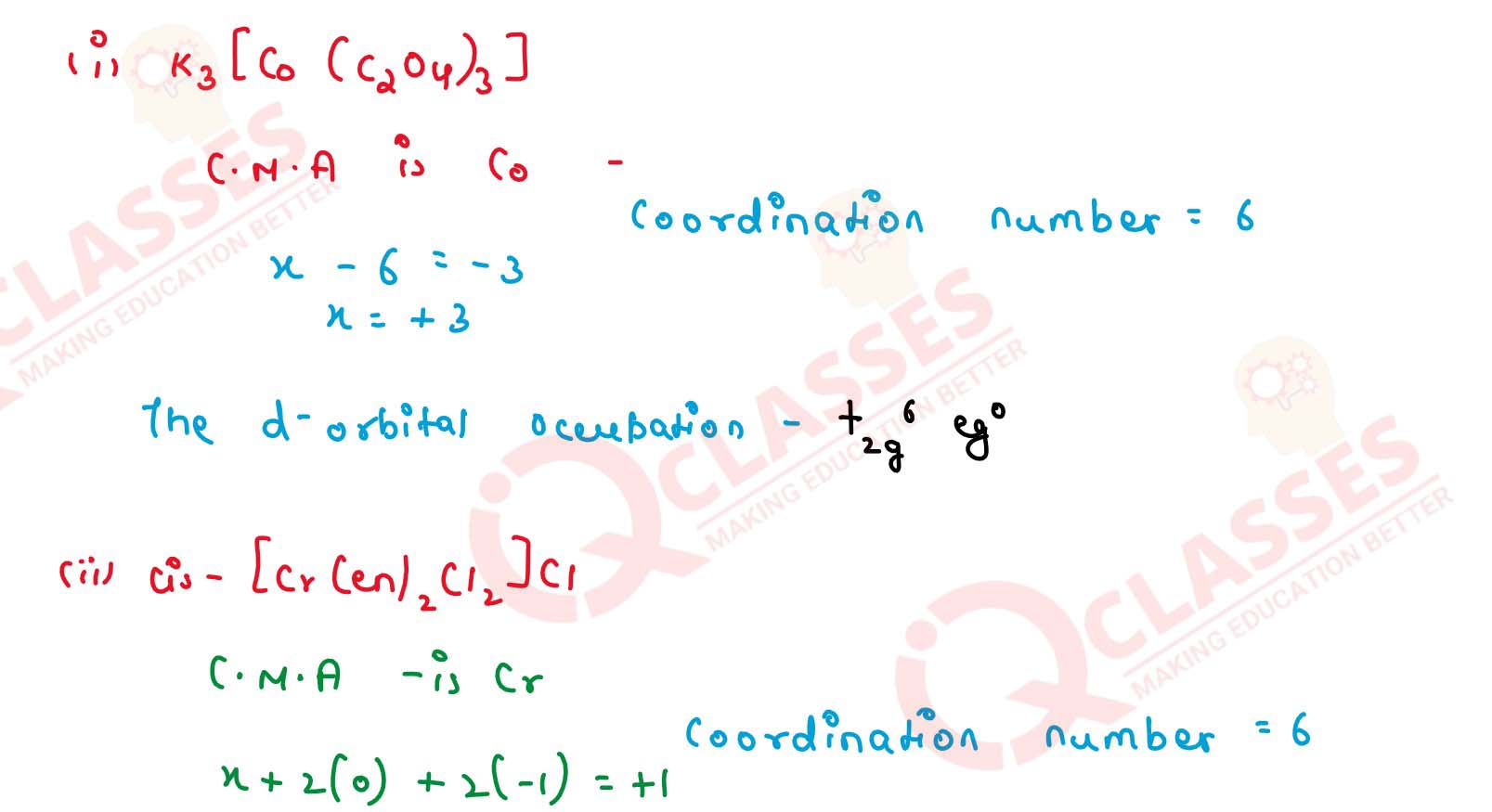
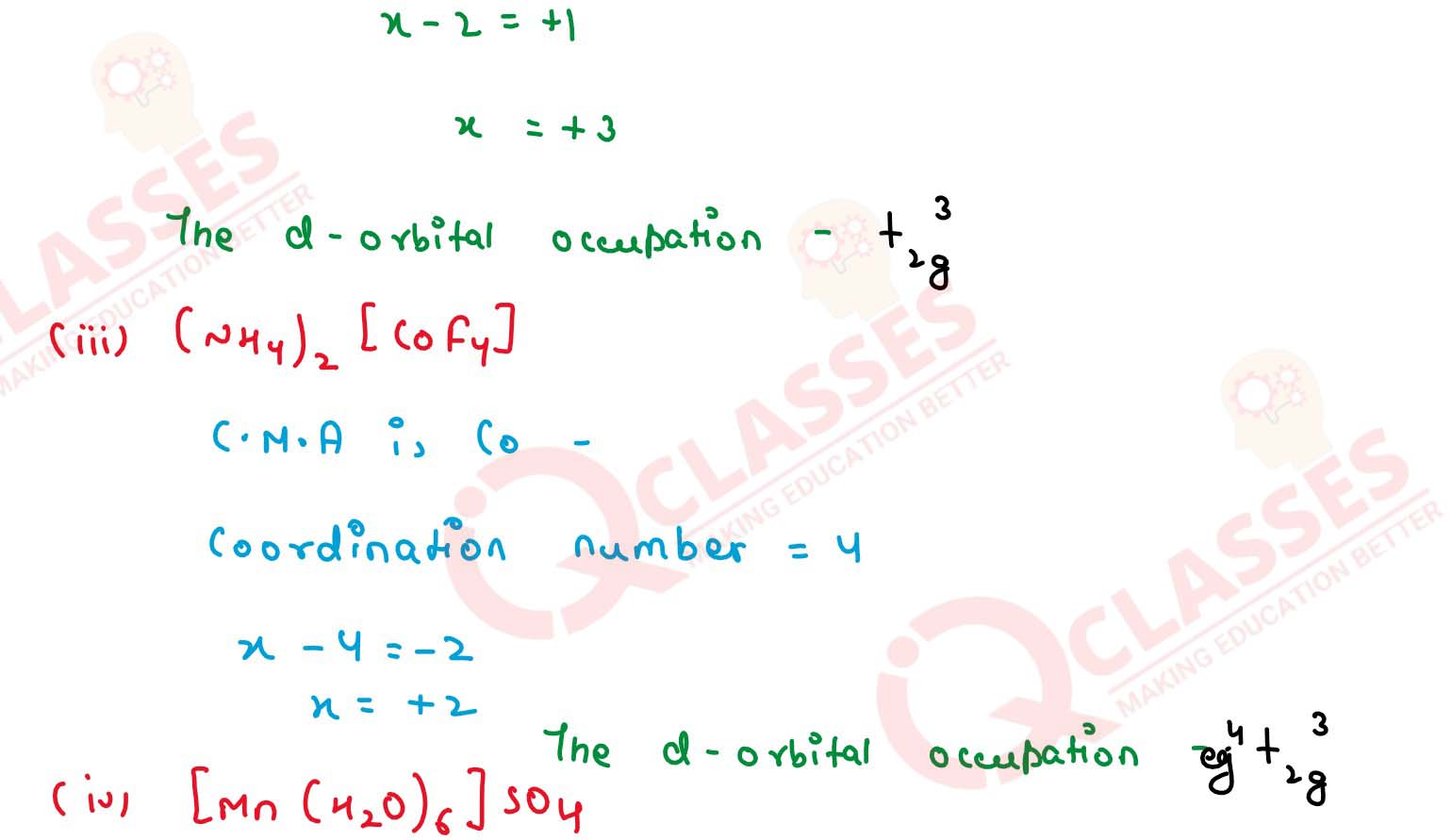

(i) K3[Co(C2O4)3]
(ii) cis-[CrCl2(en)2]Cl
(iii) (NH4)2[CoF4]
(iv) [Mn(H2O)6]SO4 Solution



Q2.24
Write down the IUPAC name for each of the following complexes and indicate
the oxidation state, electronic configuration and coordination number. Also
give stereochemistry and magnetic moment of the complex:
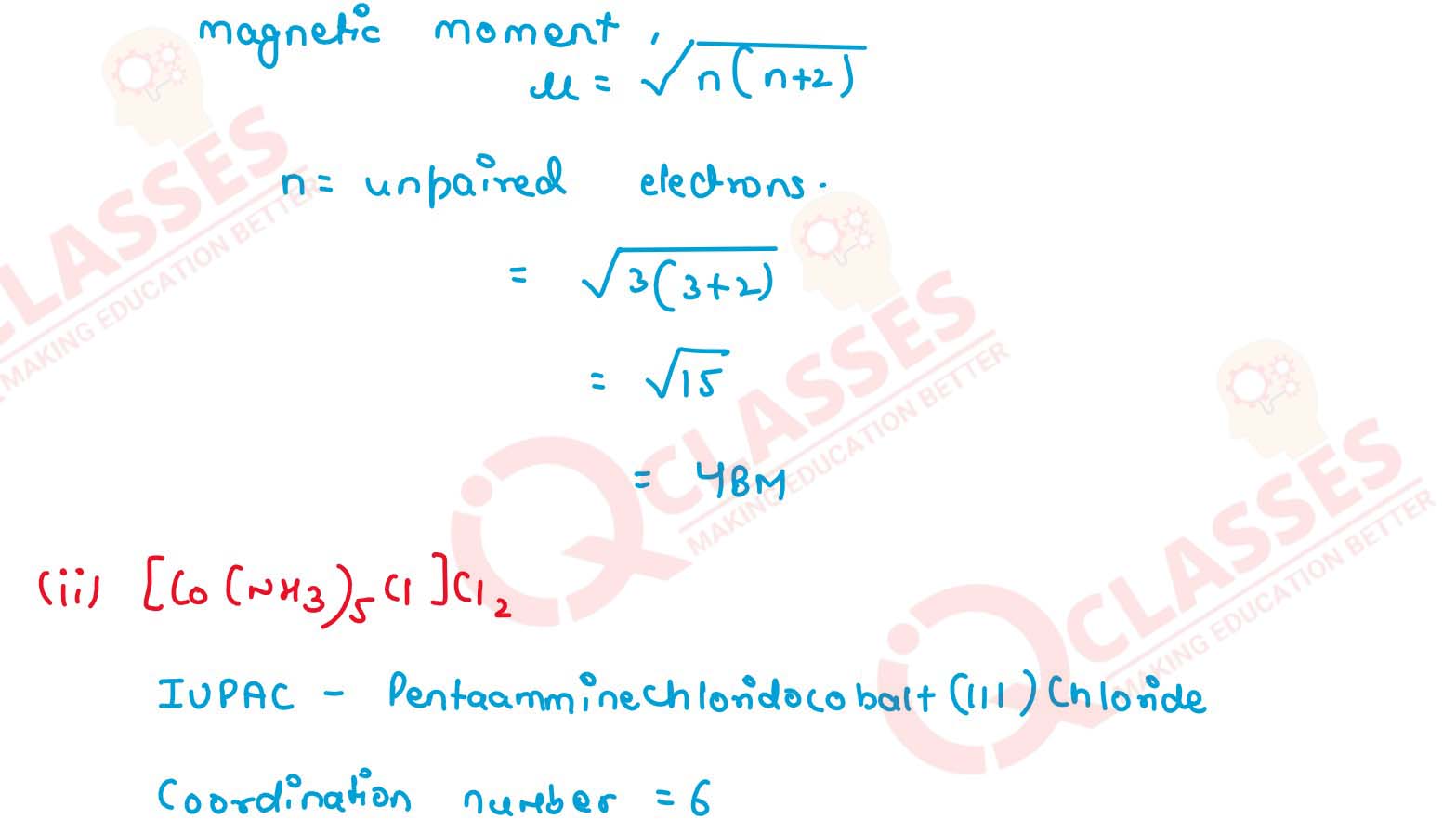
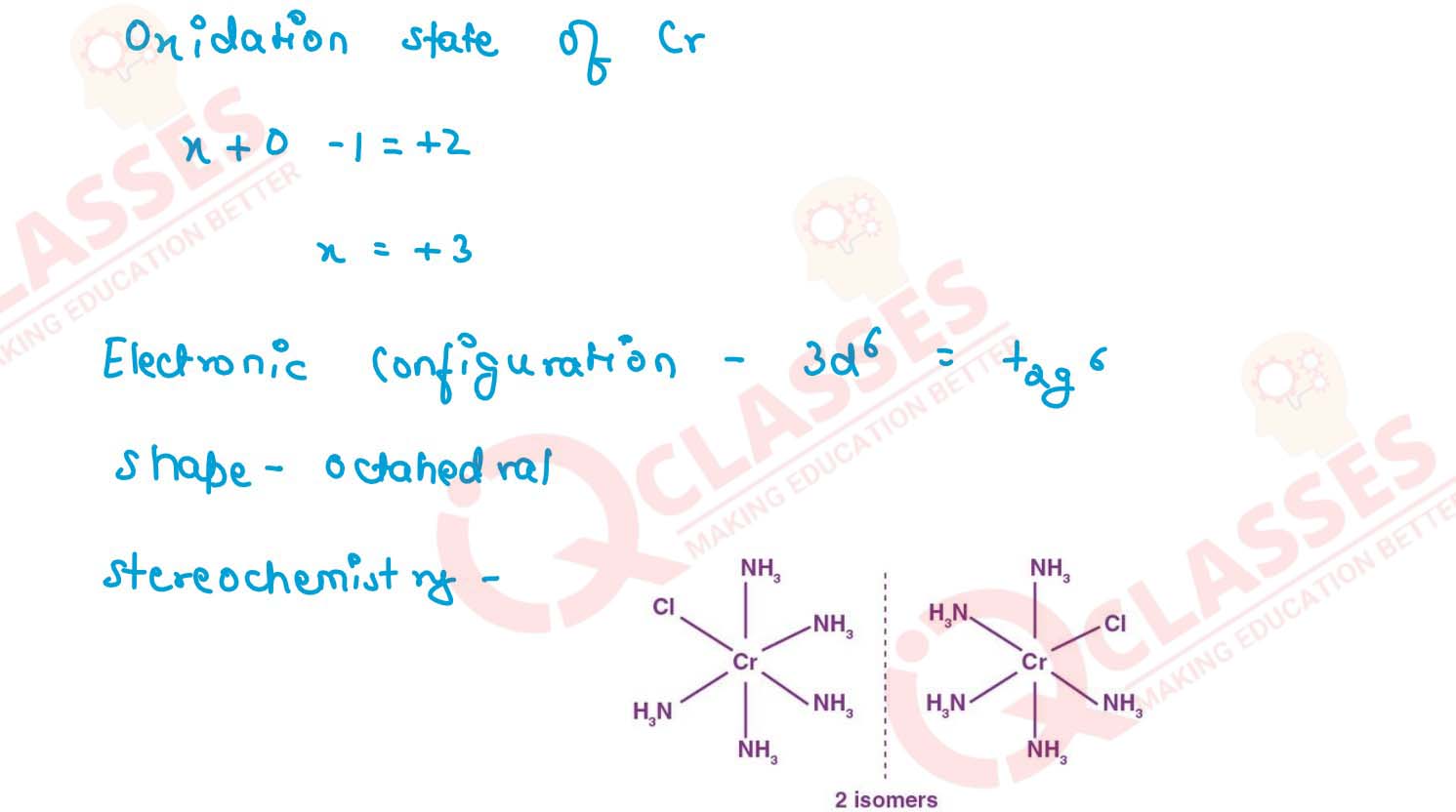
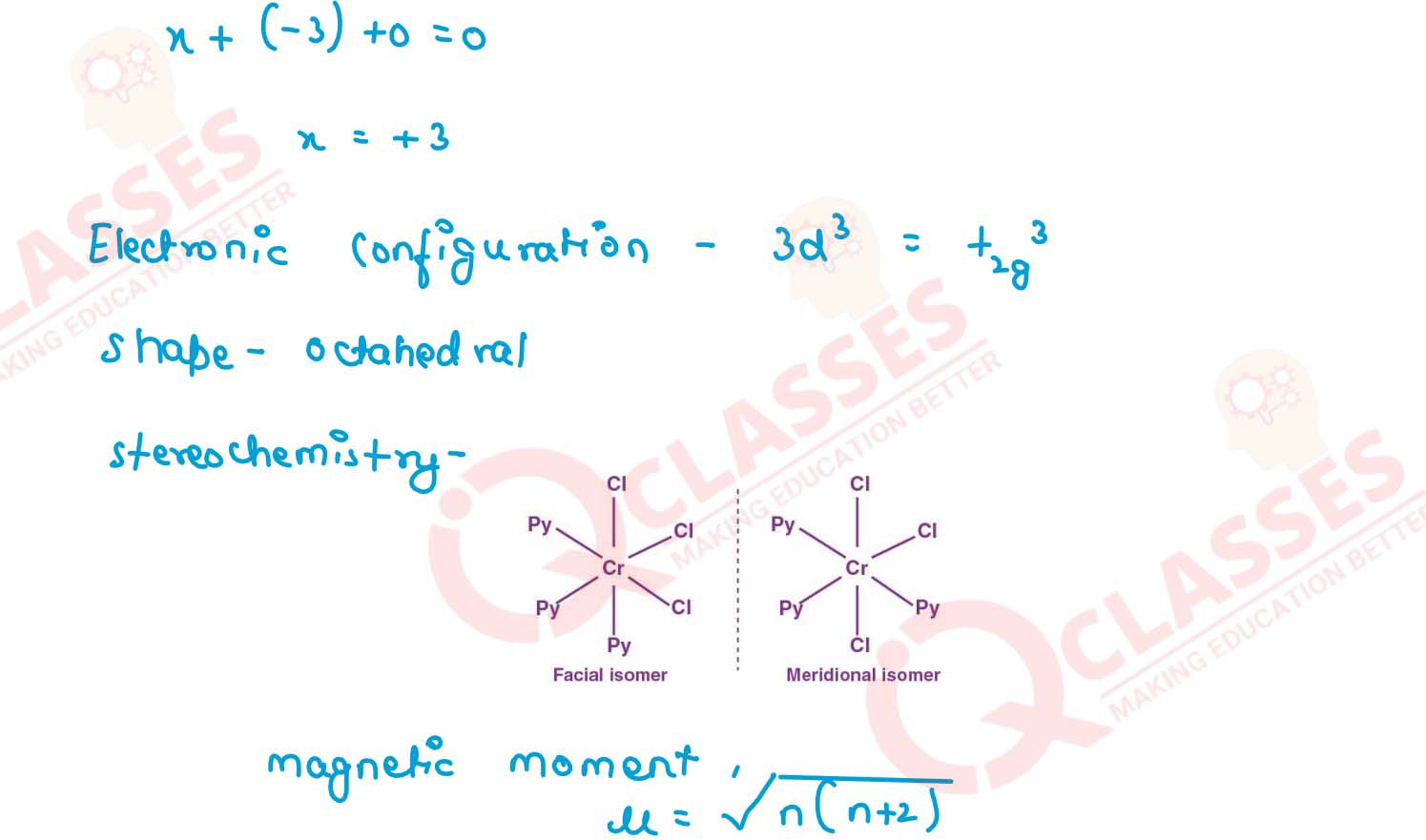
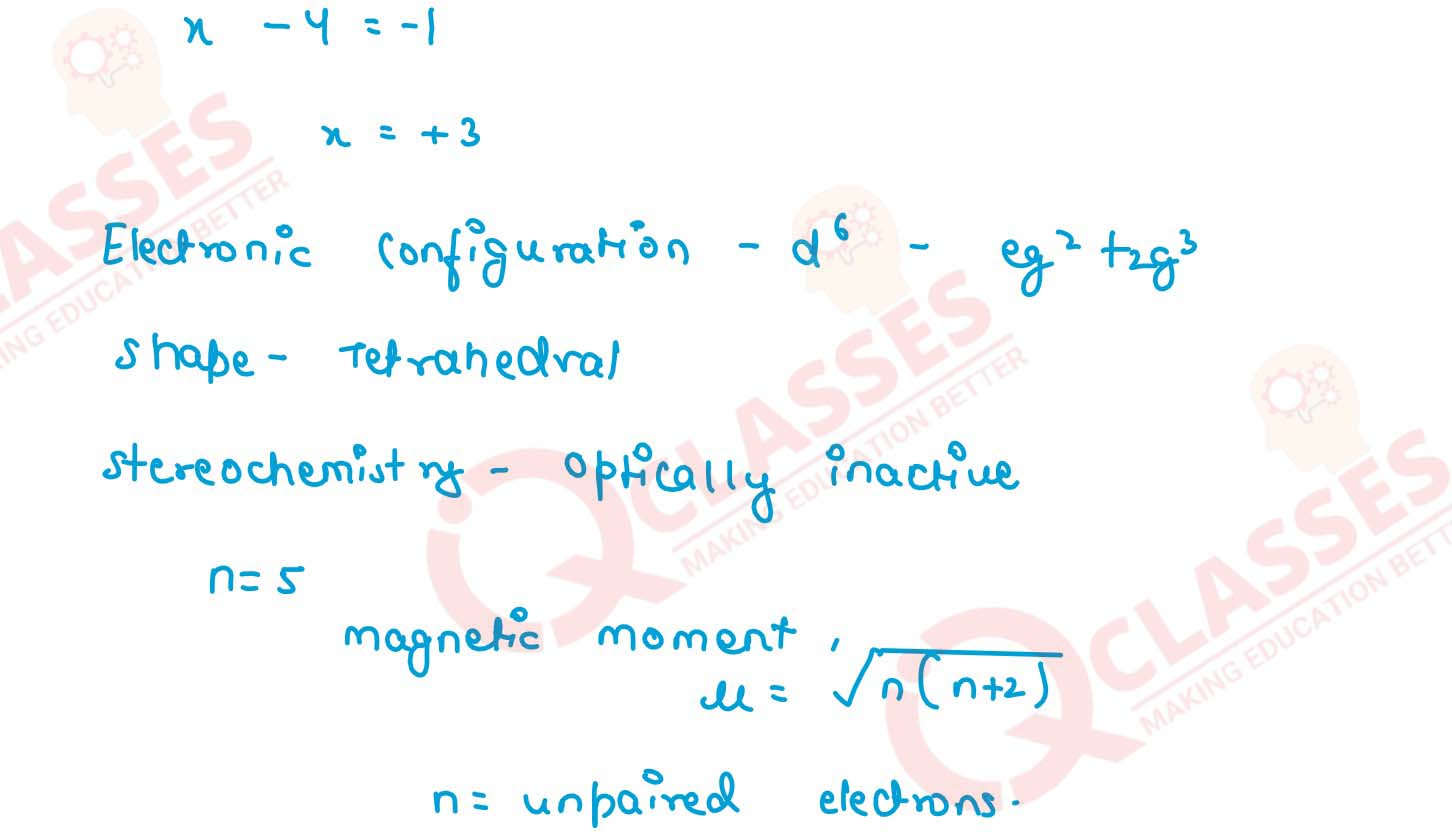
(i) K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2].3H2O (ii) [Co(NH3)5Cl-]Cl2
(iii) [CrCl3(py)3]
(iv) Cs[FeCl4]
(v) K4[Mn(CN)6] Solution
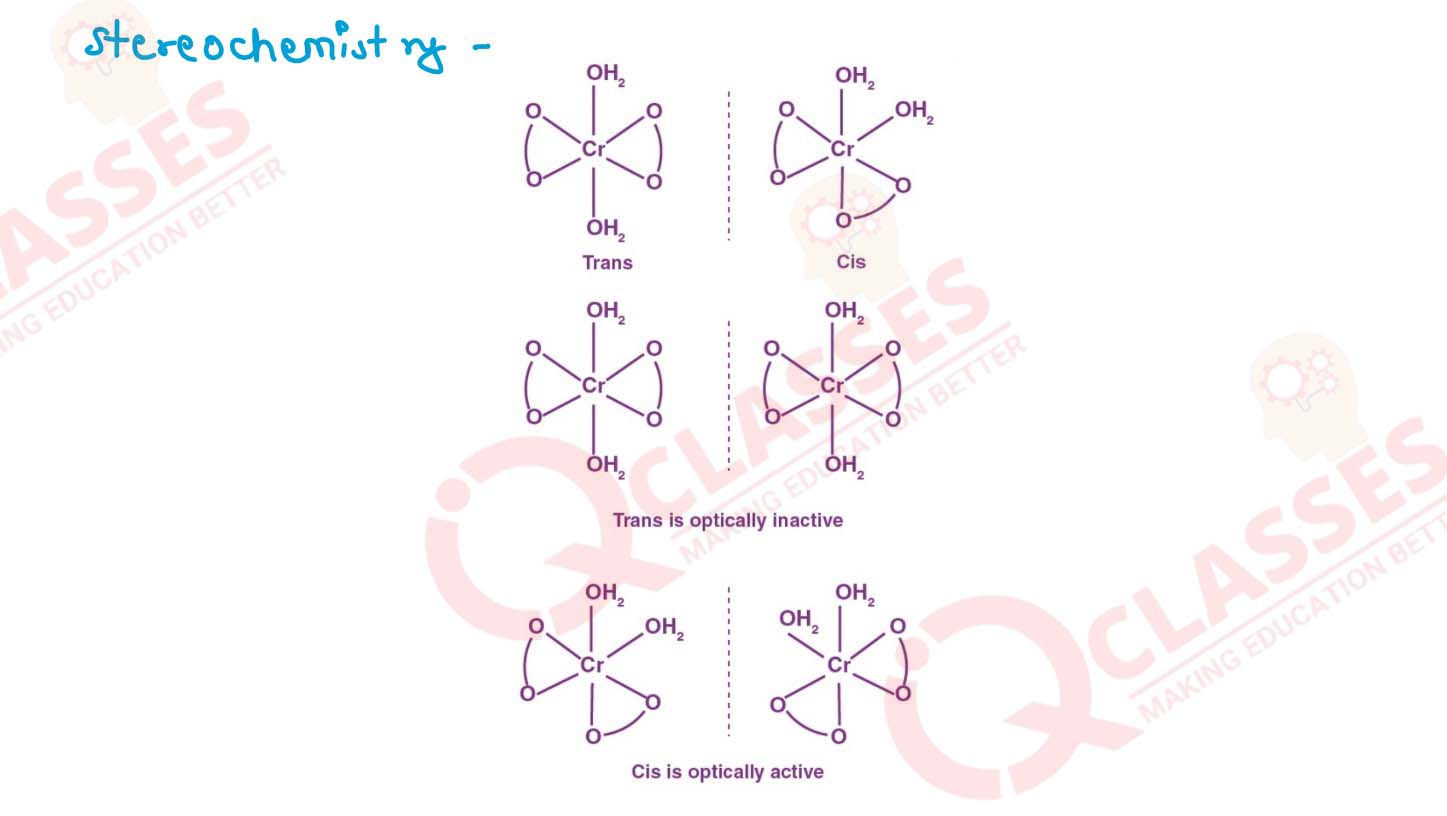




 v
v
(i) K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2].3H2O (ii) [Co(NH3)5Cl-]Cl2
(iii) [CrCl3(py)3]
(iv) Cs[FeCl4]
(v) K4[Mn(CN)6] Solution










 v
v
Q2.25
Explain the violet colour of the complex [Ti(H2O)6]3+ on the basis of
crystal
field theory.
Solution


Q2.26
What is meant by the chelate effect? Give an example.
Solution


Q2.27
Discuss briefly giving an example in each case the role of coordination
compounds in:
(i) biological systems
(ii) medicinal chemistry and
(iii) analytical chemistry
(iv) extraction/metallurgy of metals
Solution

(i) biological systems
(ii) medicinal chemistry and
(iii) analytical chemistry
(iv) extraction/metallurgy of metals
Solution


Q2.28
How many ions are produced from the complex Co(NH3)6Cl2
in solution?
(i) 6 (ii) 4 (iii) 3 (iv) 2 Solution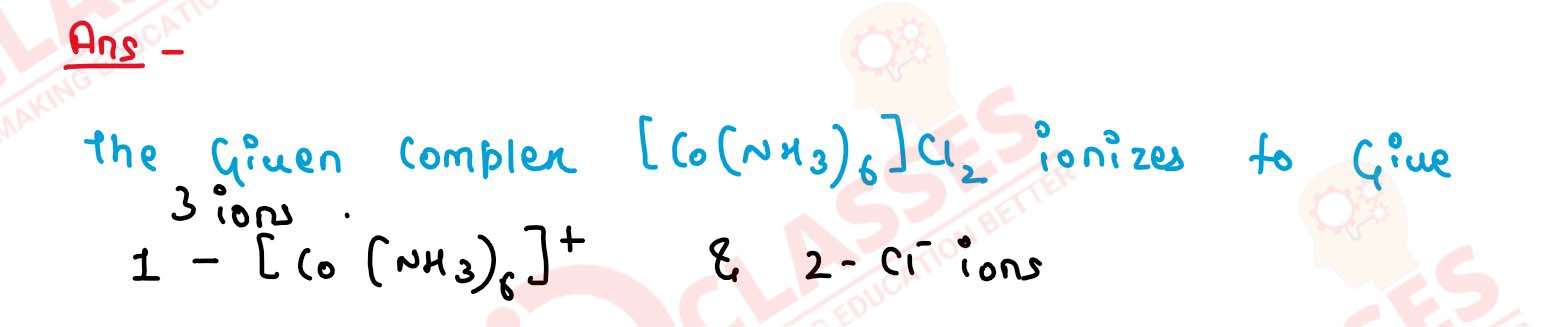
(i) 6 (ii) 4 (iii) 3 (iv) 2 Solution
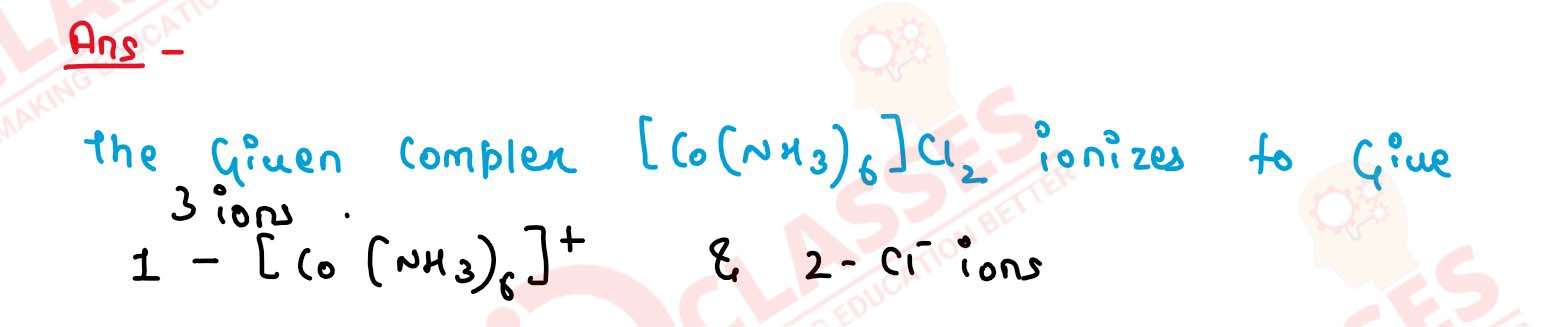
Q2.29
Amongst the following ions which one has the highest magnetic moment value?
(i) [Cr(H2O)6]3+
(ii) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
(iii) [Zn(H2O)6]2+ Solution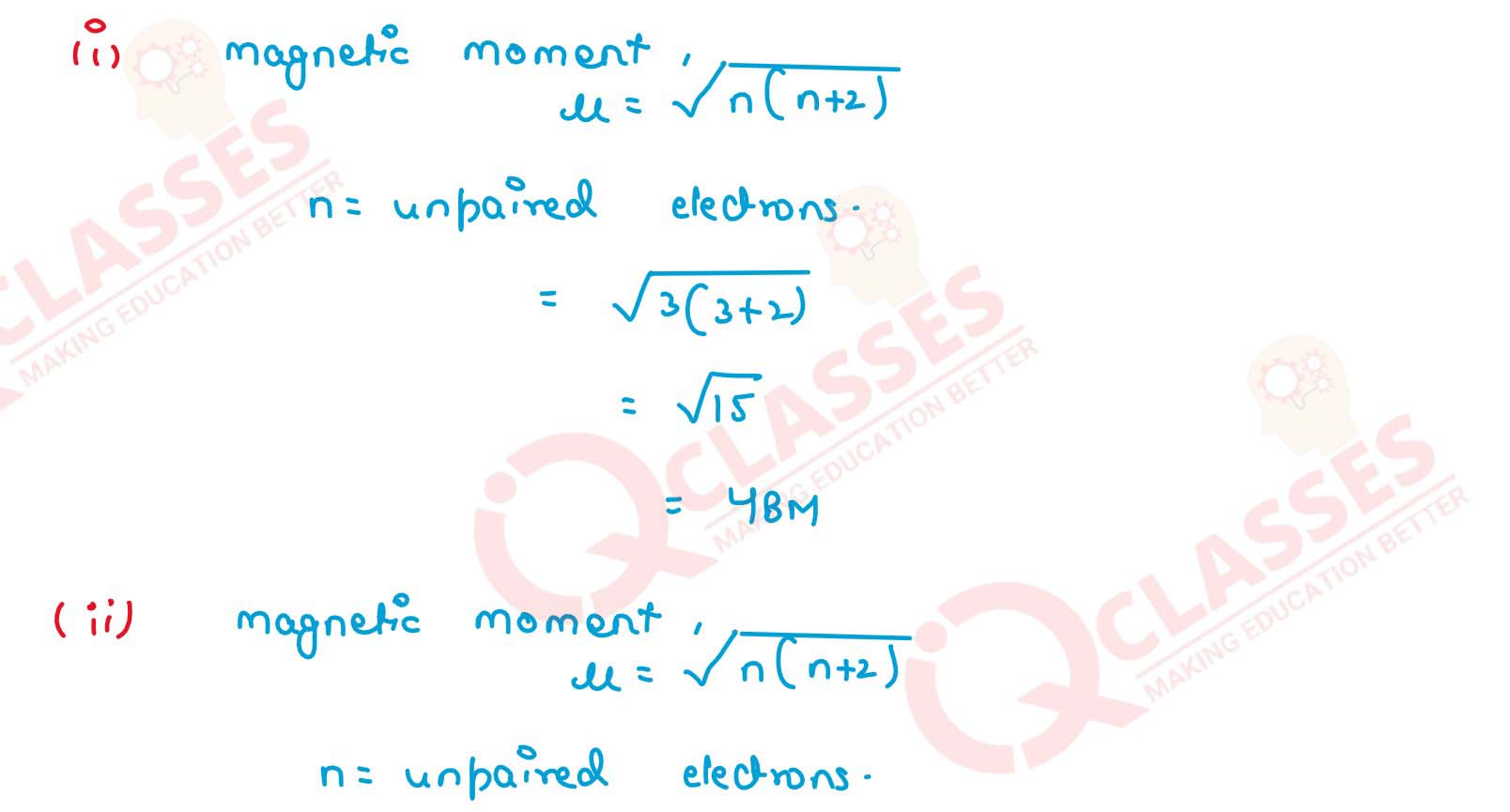
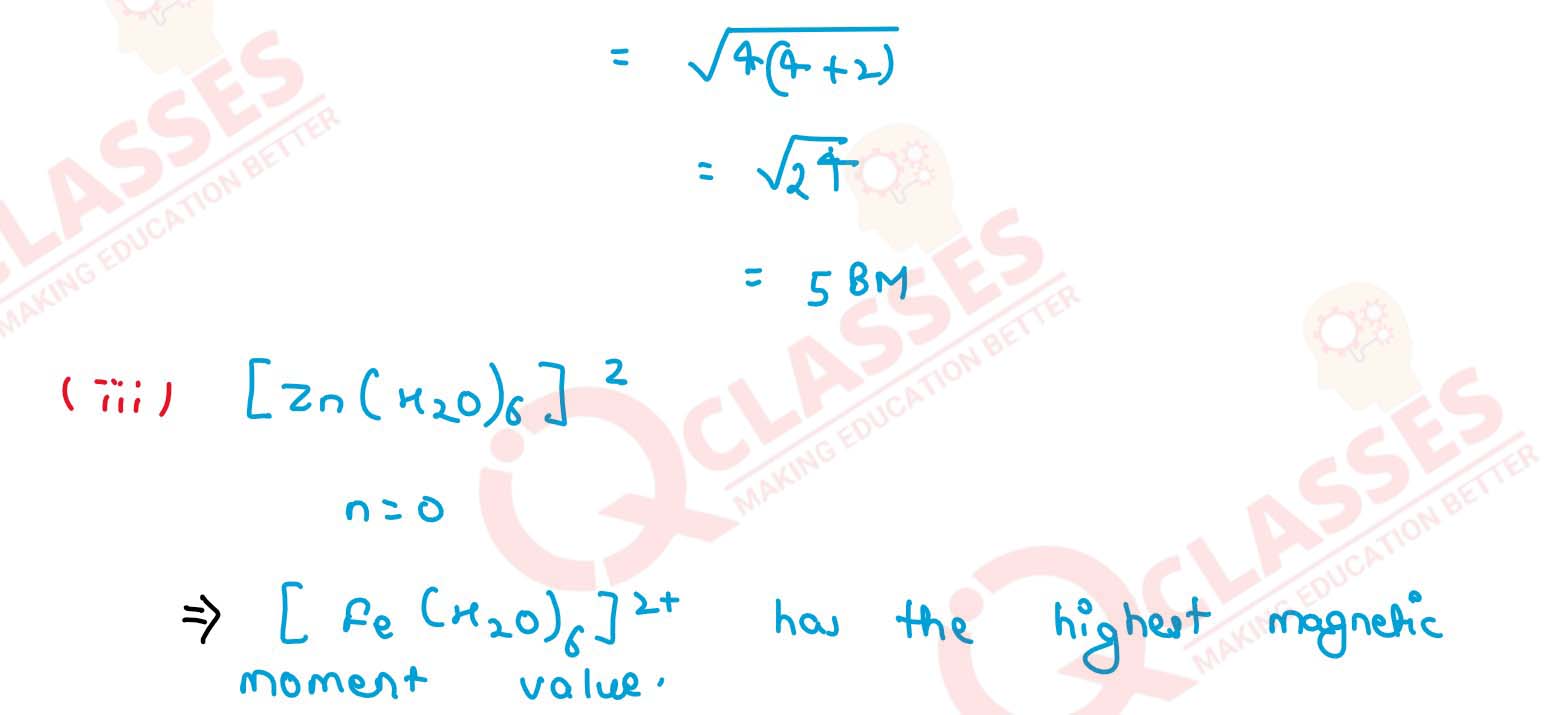
(i) [Cr(H2O)6]3+
(ii) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
(iii) [Zn(H2O)6]2+ Solution


Q2.30
Solution


Q2.31
Amongst the following, the most stable complex is
(i) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
(ii) [Fe(NH3)6]3+
(iii) [Fe(C2O4)3]3-
(iv) [FeCl6]3- Solution
(i) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
(ii) [Fe(NH3)6]3+
(iii) [Fe(C2O4)3]3-
(iv) [FeCl6]3- Solution
Q2.32
What will be the correct order for the wavelengths of absorption in the visible
region for the following:
[Ni(NO2)6]4-, [Ni(NH3)6]2+, [Ni(H2O)6]2+ ? Solution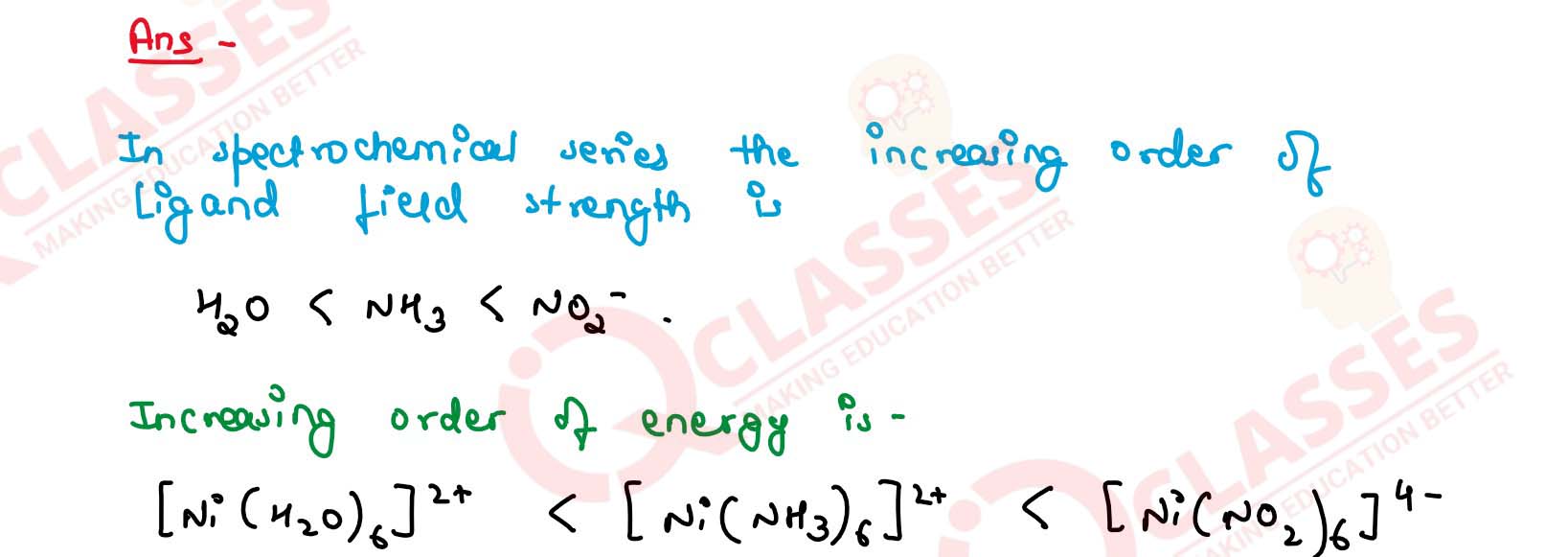
[Ni(NO2)6]4-, [Ni(NH3)6]2+, [Ni(H2O)6]2+ ? Solution