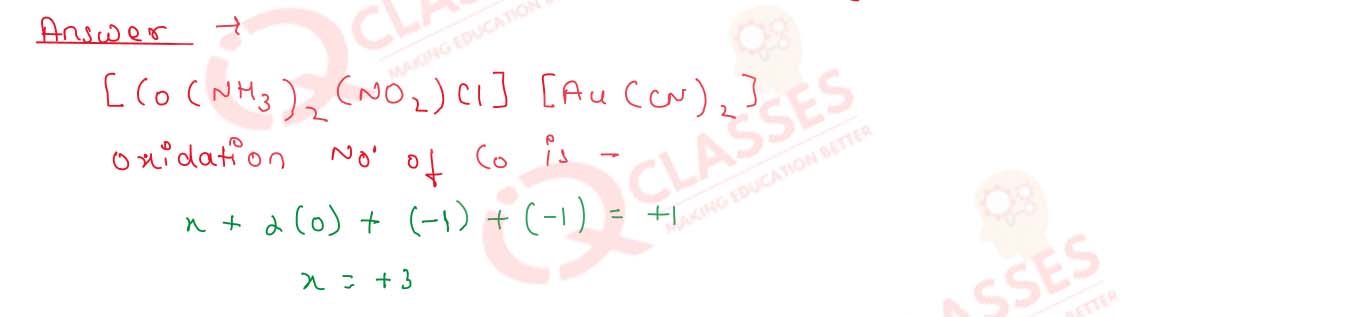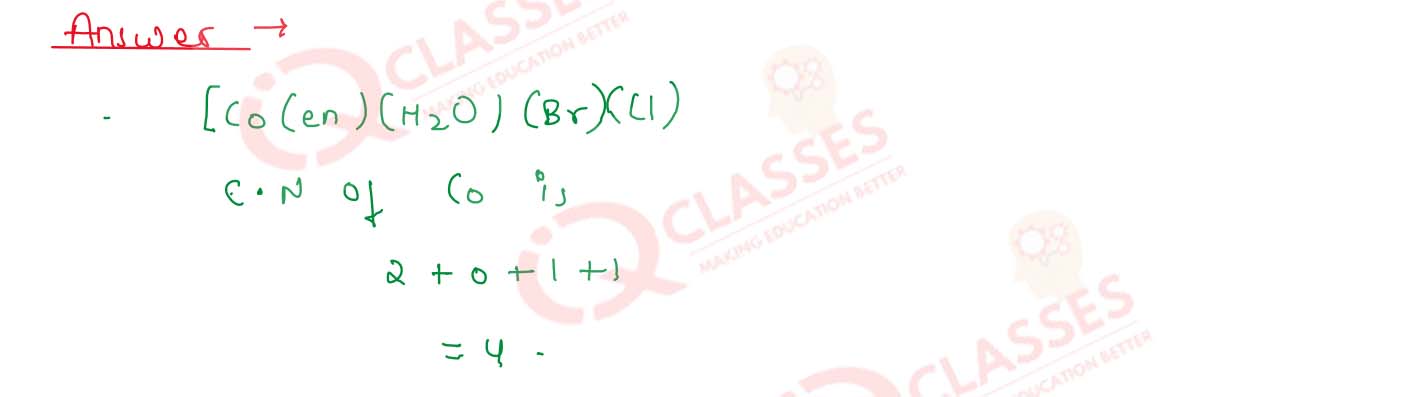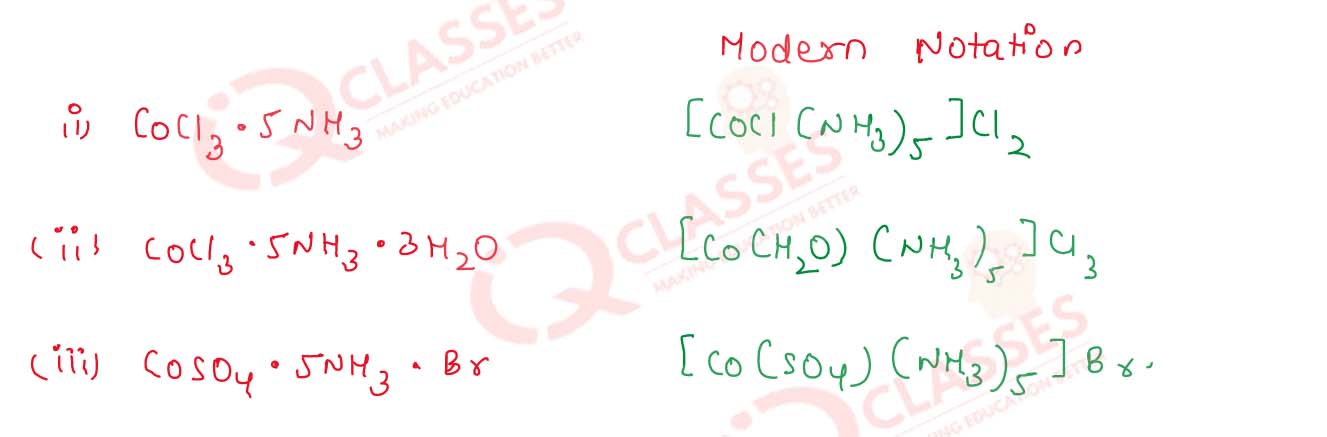9.1
What are coordination compounds and how do they differ from double salts? Explain with examples.
Solution
Double salts are those molecular or edition compounds which exists in a solid state but dissolve in constituent
ions when dissolved in water
Eg : Mohr salt FeSO4(NH4)SO4 . 6H2O
Coordination compound are
those molecular or edition compound which retain their identity in aqueous solution and shows property entirely
different from their constituents ions
Eg : K4[Fe(CN6)]
9.2
Explain the following terms with respect to coordination
compounds :
(i) Ligands
(ii) Coordination sphere
(iii) Coordination number
Solution
(i) Ligands=> the molecular or ionic species which gets directly attached to
the central metal atom or ion during the formation of a complex is called ligand
Eg :
K4[Fe(CN6-)] CN-=> ligand
(ii)
coordination sphere=> the coordination sphere consists of the central atom oblique iron and the
legend attached to it the ionizable group called counter ion are written outside the bracket
Eg :
K4[Fe(CN6)] [Fe(CN6)]4- is the coordination sphere
(iii) coordination number=> the maximum number of ligands which can be
coordinated to a central metal atom or ion is known as coordination number.
Eg : K4[Fe(CN6)] -> 6 - CN- is a coordination number.
9.3
What is the oxidation state of Ni in Ni(CO)4?
Solution

9.4
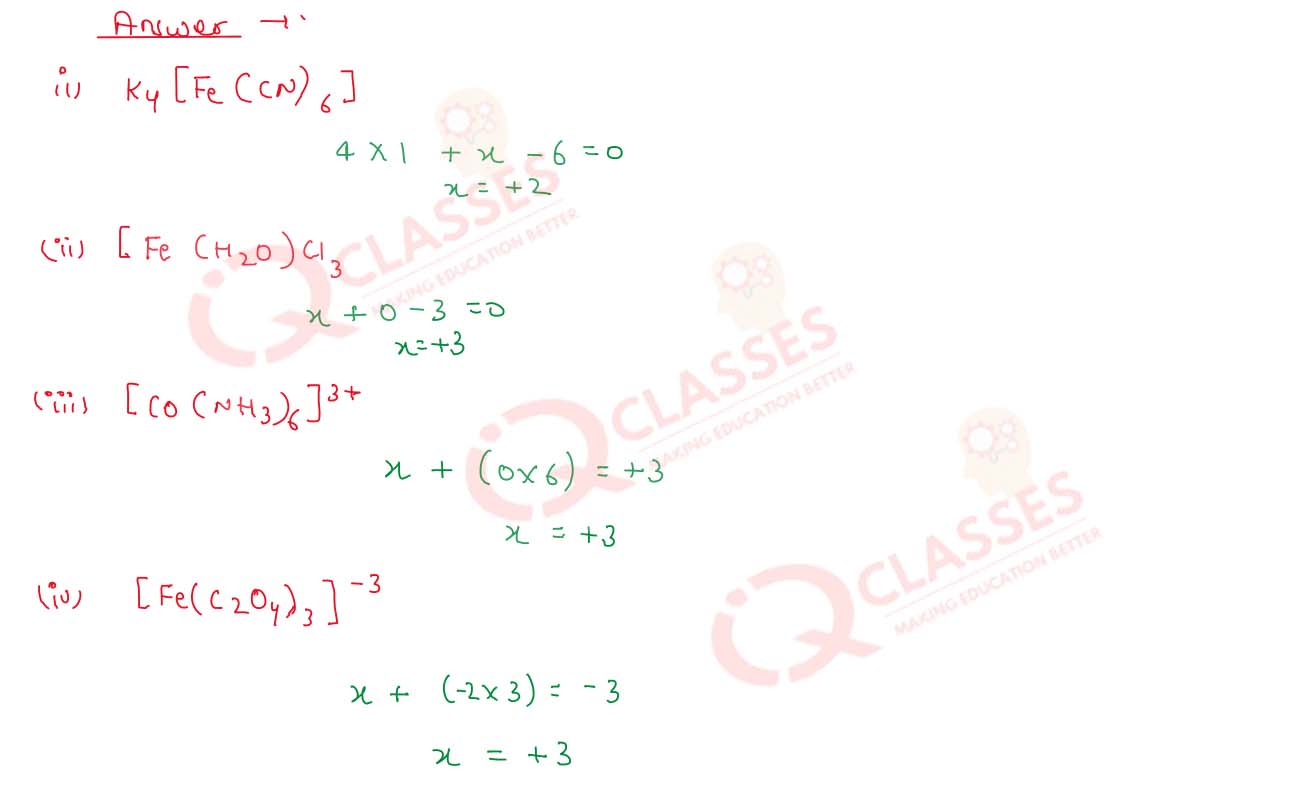
Calculate the oxidation number of the central metal atom (underlined) in each of the following complex species
:
(i) K4[Fe(CN)6]
(ii) [Fe(H2O)6)Cl,
(iii)
[Co(NH3)6]3+
(iv)
[Fe(C2O4)3]3-
Solution
9.5
In the complex ion [Co(NH3)3 (H2O)2 Cl]+
(a) identify the ligands formulae and charge on each of them
(b) write the geometry of the complex ion.
Solution
(i) [Co(NH3)3 (H2 O)2 Cl]+
NH3 - 0 , H2 O - 0 , Cl- = -1
(ii) octahedral
9.6
Define coordination number. Find the coordination number
of the central metal atom in each of the following:
(i) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
(ii) K4[FeCl4]
Solution
coordination number=> the maximum number of ligands which can be coordinated
to a central metal atom or ion is known as coordination number.
Eg : K4[Fe(CN6)] -> 6 - CN- is a coordination number.
(i) [Co(NH3)5 Cl]Cl2
(ii) K2[FeCl4]
9.7
What is the oxidation state of Co in the complex [Co(NH3)2
(NO2)Cl] [Au(CN)2] ?
Solution
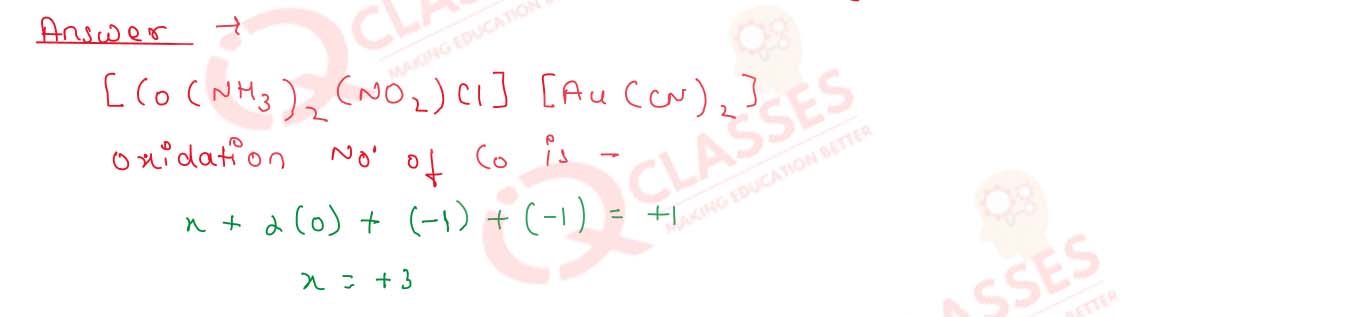
9.8
What is the oxidation state of platinum in the complex
[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]Cl2?
Solution

9.9
What is the oxidation state of cobalt in the complex
[Co(NH3)4(H2O)Br] (NO3)2?
Solution

9.10
What is the coordination number of Fe in the complex
K3[Fe(C2O4)3] ?
Solution
K3[Fe(C2O4)3]
C.N -> Fe is 6
9.11
What is the coordination number of cobalt in [Co(en )(H2O)
(Br)Cl] ?
Solution
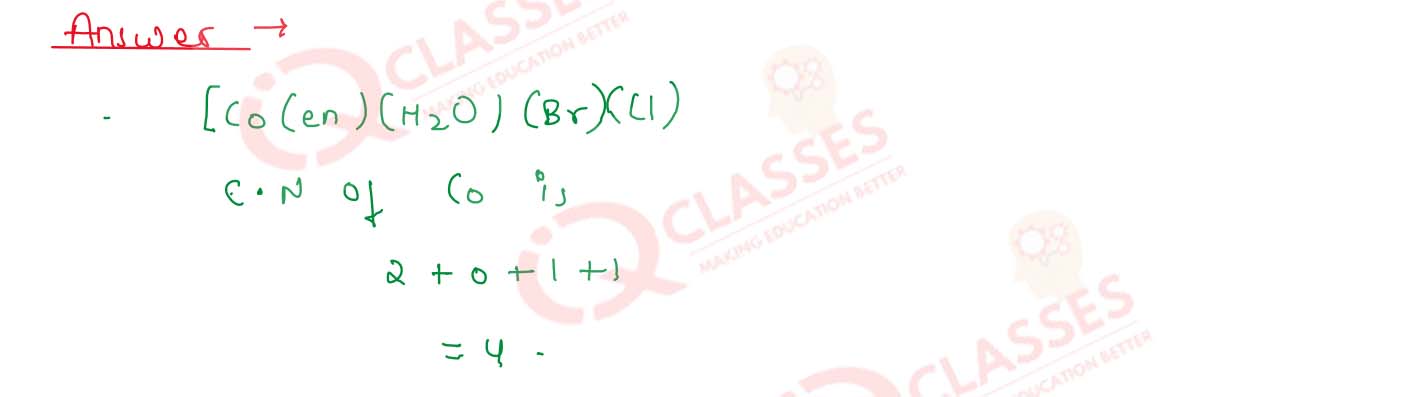
9.12
What is meant by a hexadentate ligand? Give an example.
Solution
Hexadentate ligand => The legand which contains 6 donor atoms are called as
hexa dentate ligand. Example : EDTA (Ethylene diamine Tetra acetato)
9.13
What do you understand by chelating ligands and what are
chelates ? Give one example each.
Solution
Chelating Ligands =>
The ligands containing 2 or more donor atoms are usually referred to as to polydentate ligands
These ligands
may contain donor atoms positioned in such a way that they may form a 5 or 6 membered ring with a metal ion and
thus the ring called as Chelates.
9.14
Give one example of each of the following :
(i) a neutral ligand
(ii) an anionic ligand
(iii) a cationic complex ion
(iv) an anionic complex.
Solution

9.15
Calculate the charge number of the following complex ions :
(i) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
(ii)
[Pt(NH3)2Cl2].
Solution
(i) [Co(NH3)2Cl2]+
charge is + 1
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
charge is 0
9.16
Describe the main postulates of Werner's theory.
Solution
The main postulates of Werner's theory of C.N are -:
=> In C.N metals show 2 types of linkage (valences)
primary and secondary
=> The primary valencies are normally ionizable and are satisfied by negative ions
=> The secondary valencies are non ionizable these are satisfied by neutral molecules or negative ions
9.17
According to Werner's theory, what is the main difference
between primary and secondary valencies of the central metal
atom in a complex?
Solution
Primary Valencies :
=>Primary valency is the oxidation state of the central
metal atom of a coordination complex
=> the number of ligands that we need to satisfy the charge on the
metal ions
=> Eg : Fe in K4[Fe(CN)6] is +2
Secondary
Valency :
=> Secondary valencies is the coordination number of the central metal atom in
coordination complex
=> the number of ligands attached to the central metal atom
=> Eg : Fe in
K4[Fe(CN)6] is 6.
9.18
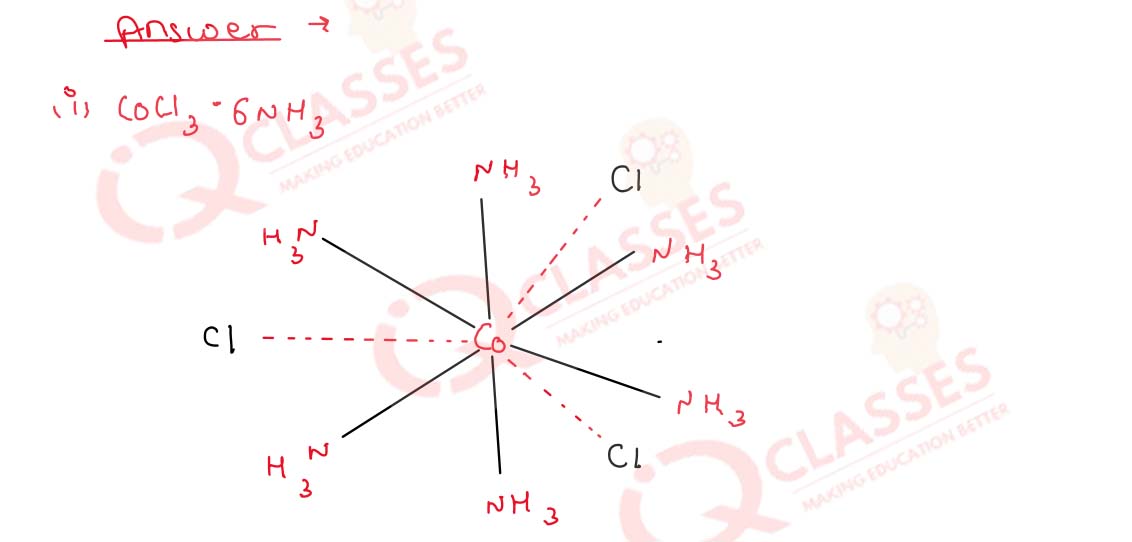
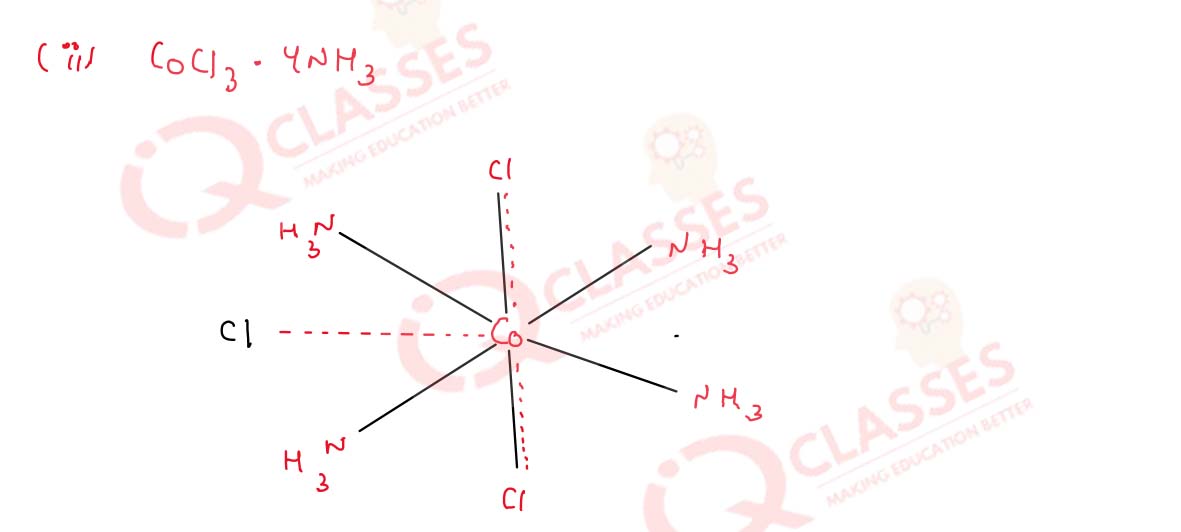
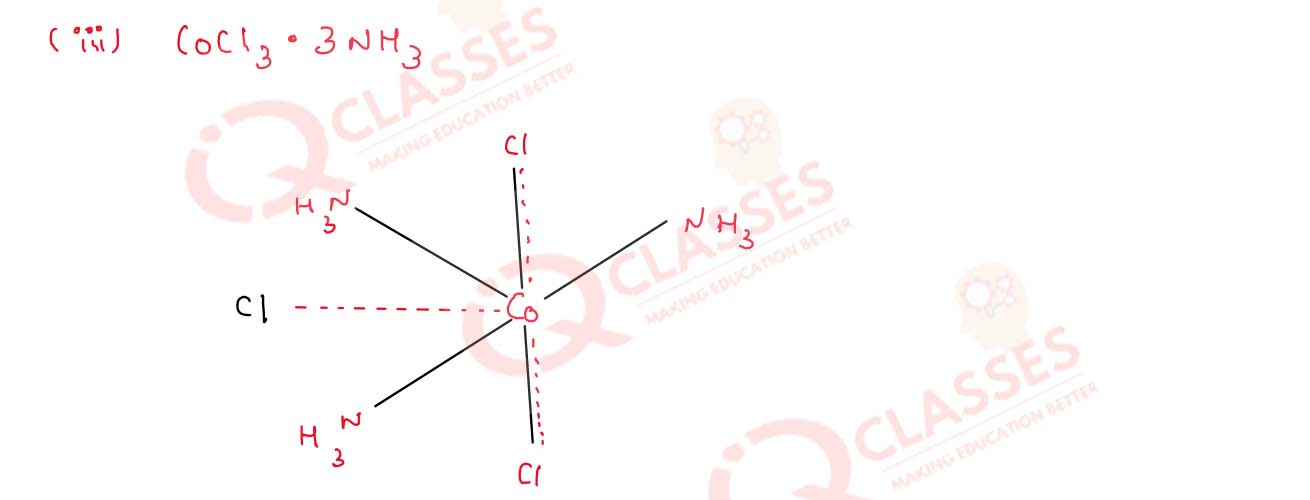
Write the structures of the following complexes on the basis
of Werner’s theory :
(i) CoCl3.6NH3
(ii) CoCl2.4NH3
(iii) CoCl2.3NH3
Solution
9.19
Give the modern notations of the following complexes :
(i) CoCl2.5NH3
(ii) CoCl3.5NH3.H2O
(iii) CoSO4.5NH3.Br
Solution
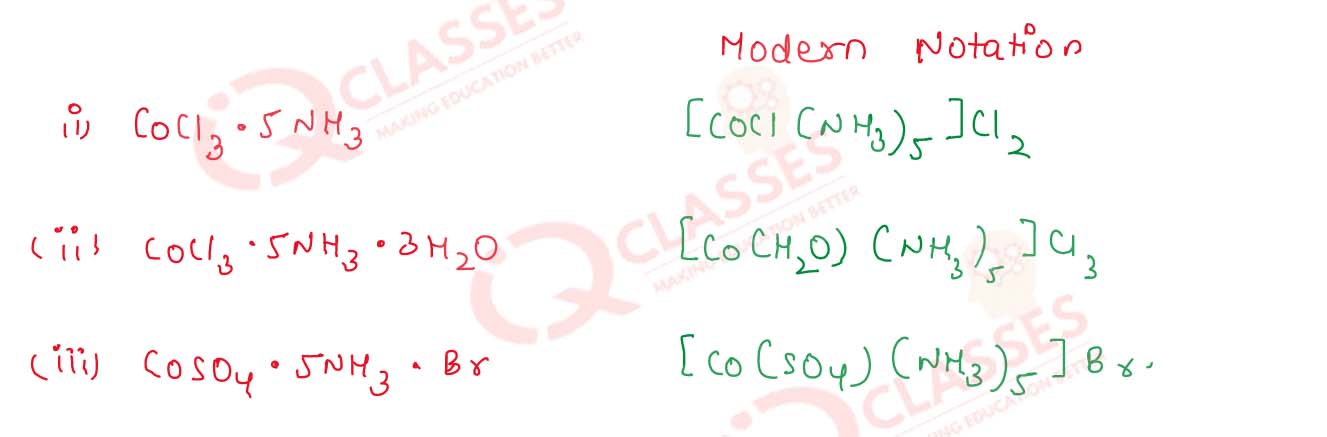
9.20
What is the coordination number of central metal ion in
[Fe(C2O4)3]3- ?
Solution
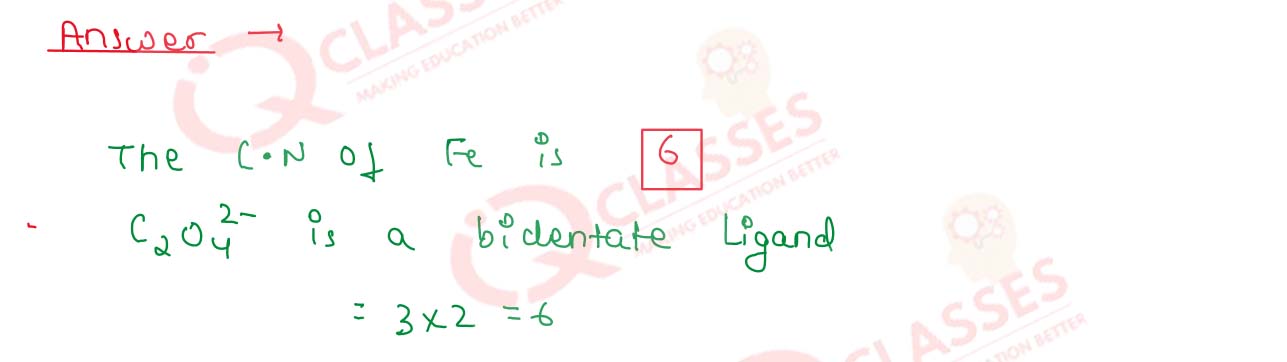
9.21
Give an example of chelate complexes.
Solution
Examples of chelate complexes are en(ethylenediamine) , ox(oxalato) , EDTA, etc
9.22
How is ammonia molecule a good ligand ?
Solution
Due to the presence of lone pair electrons on N-atoms NH3 act as a good legend (NH3)aq.
forms complex ion with several metal ions such as Cu2+, Ag2+ etc.
9.23
Name a ligand which is bidentate and give an example of the
complex formed by this ligand.
Solution
Etylene diamine (en) is a bidentate ligand [Co(en)3]+3
IUPAC name : tri(ethylenediamine) Co(III) ions