Q1
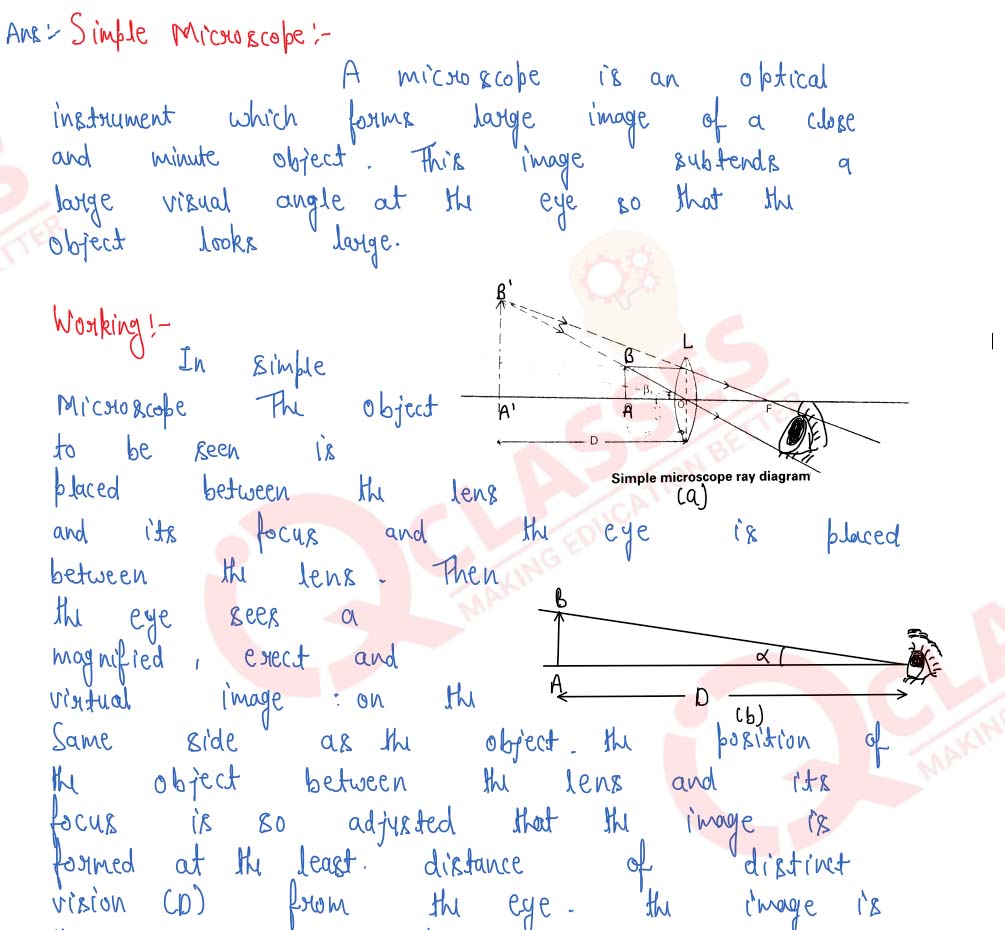
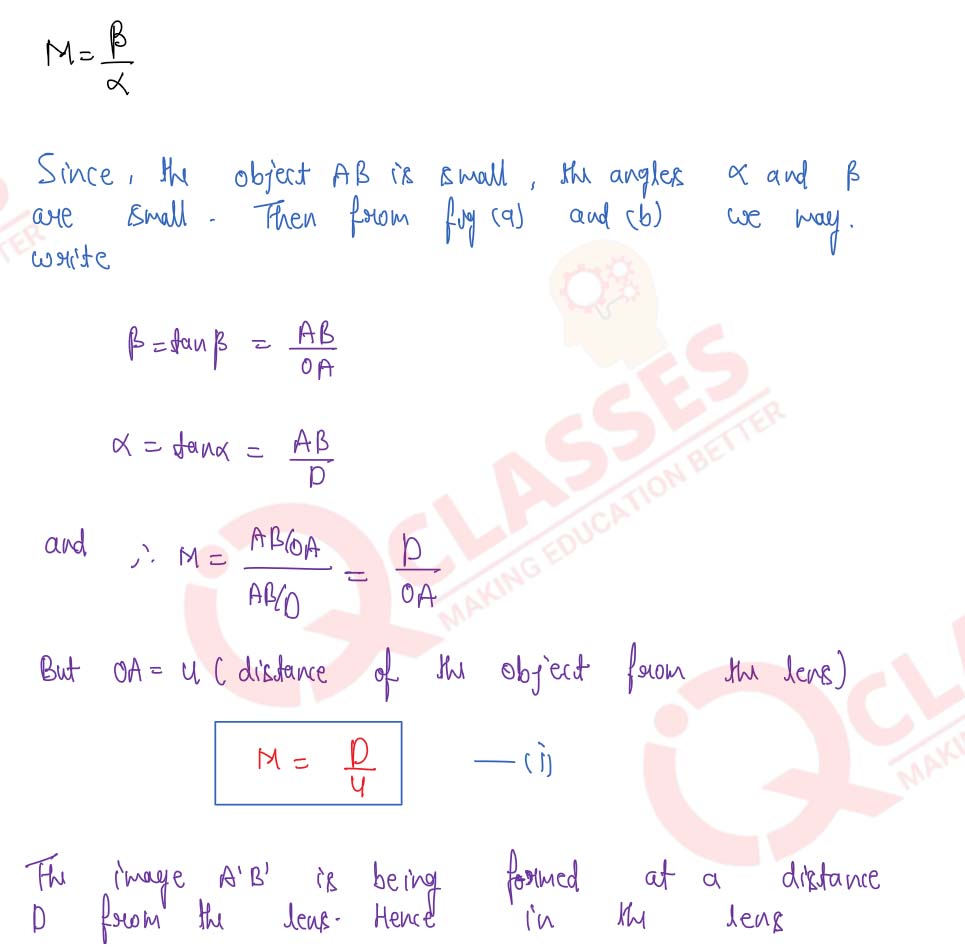
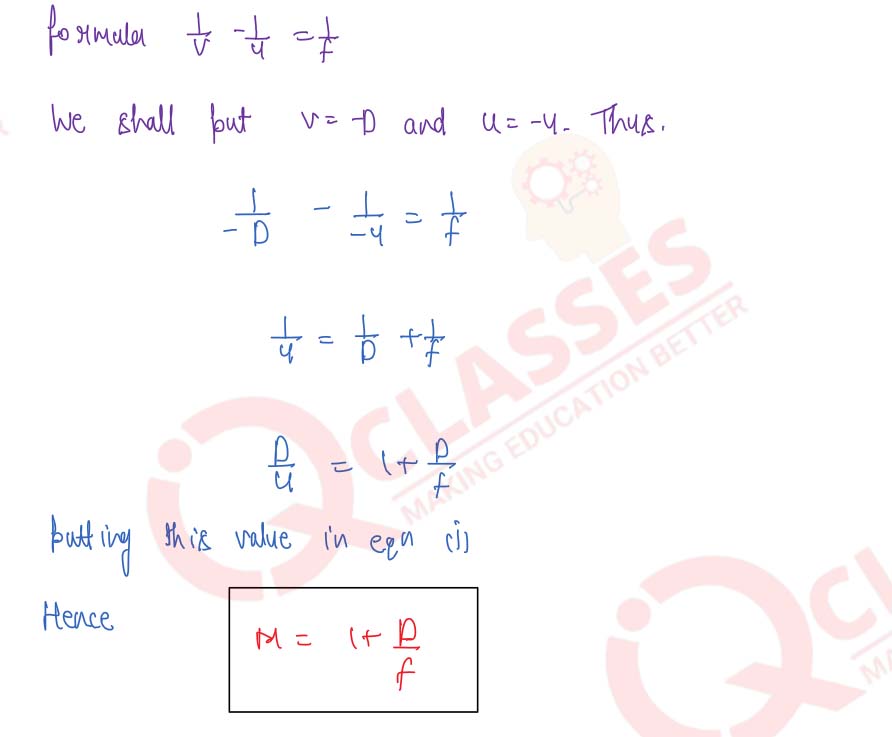
Explain the working of a simple microscope and show that its angular magnification is given by (м= 1+ (D/f), where D is the least distance of distinct vision.
Solution





Q2
Draw a labelled ray-diagram for a simple microscope (magnifying glass) and deduce an expression for its angular magnification in normal use.
Solution








Q3
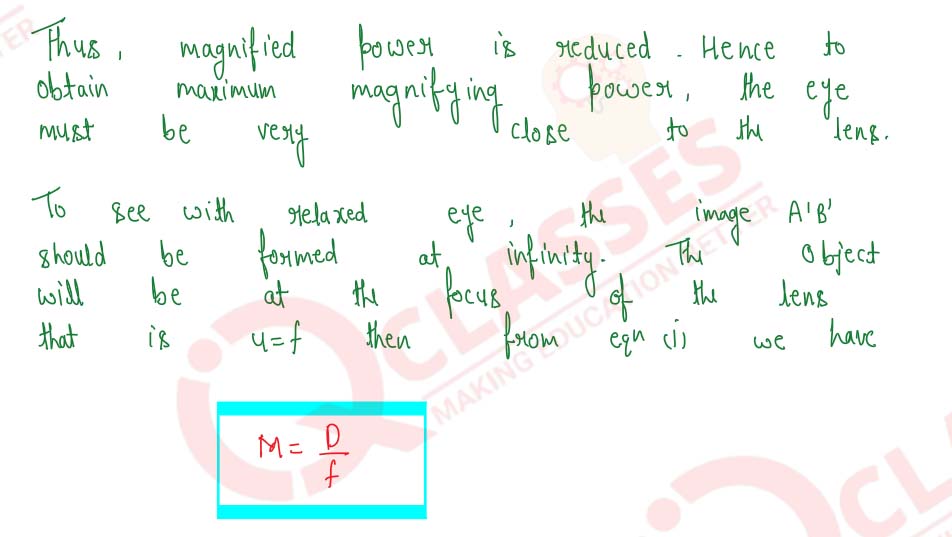
Draw a neat labelled ray diagram showing the formation of an image at the least distance of distinct vision D by a simple microscope. When the final image is at D, derive an expression for its magnifying power at D.
Solution









Q4
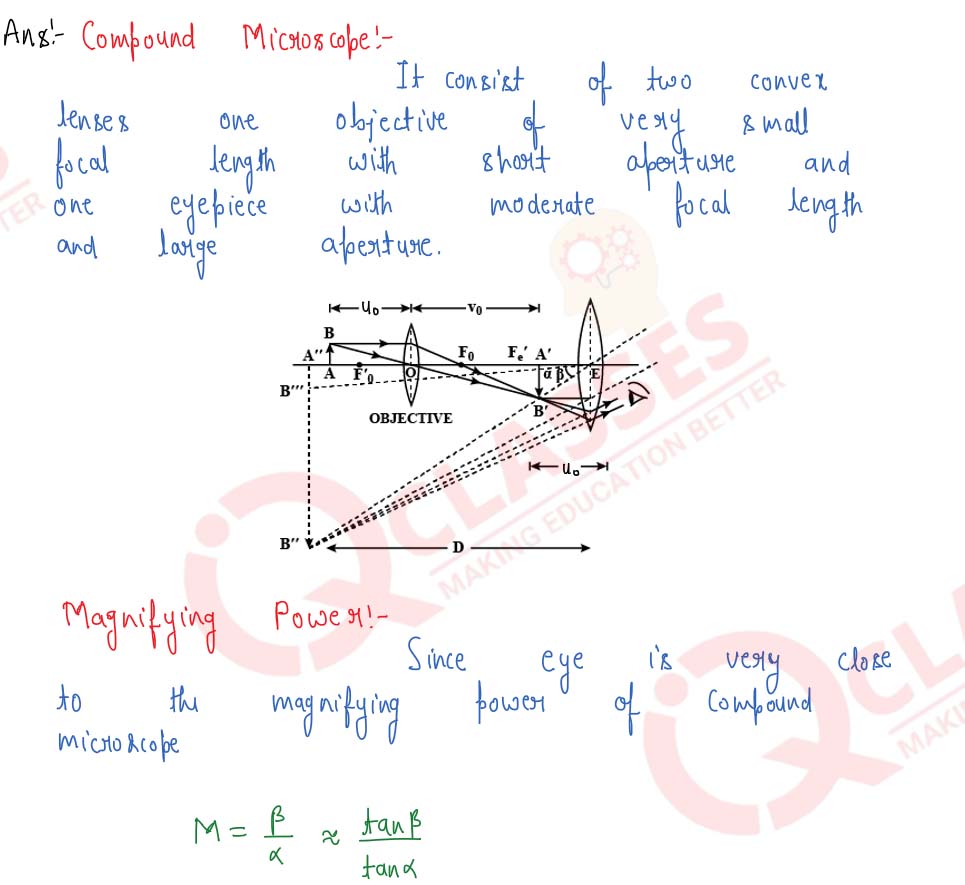
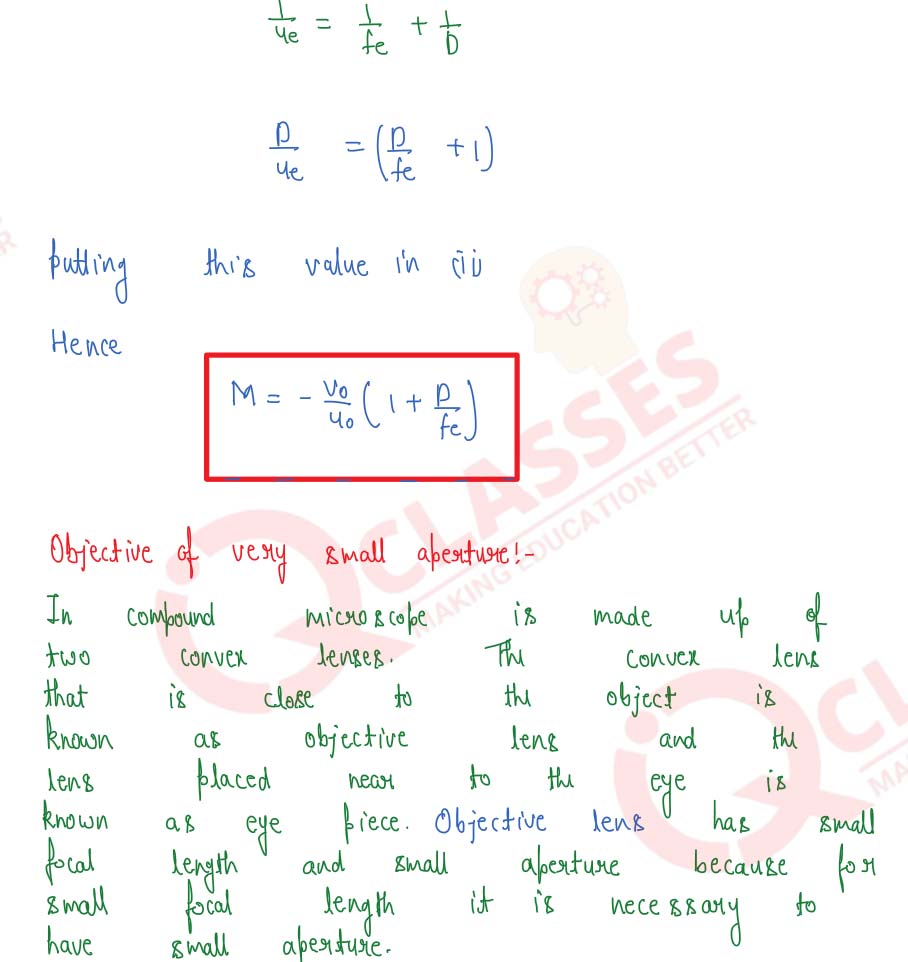
Draw a labelled ray-diagram of an image formed by a compound microscope when the final image lies at least distance of distinct vision. Write any one expression for its magnifying power. Why is its objective of a very small aperture?
Solution




Q5
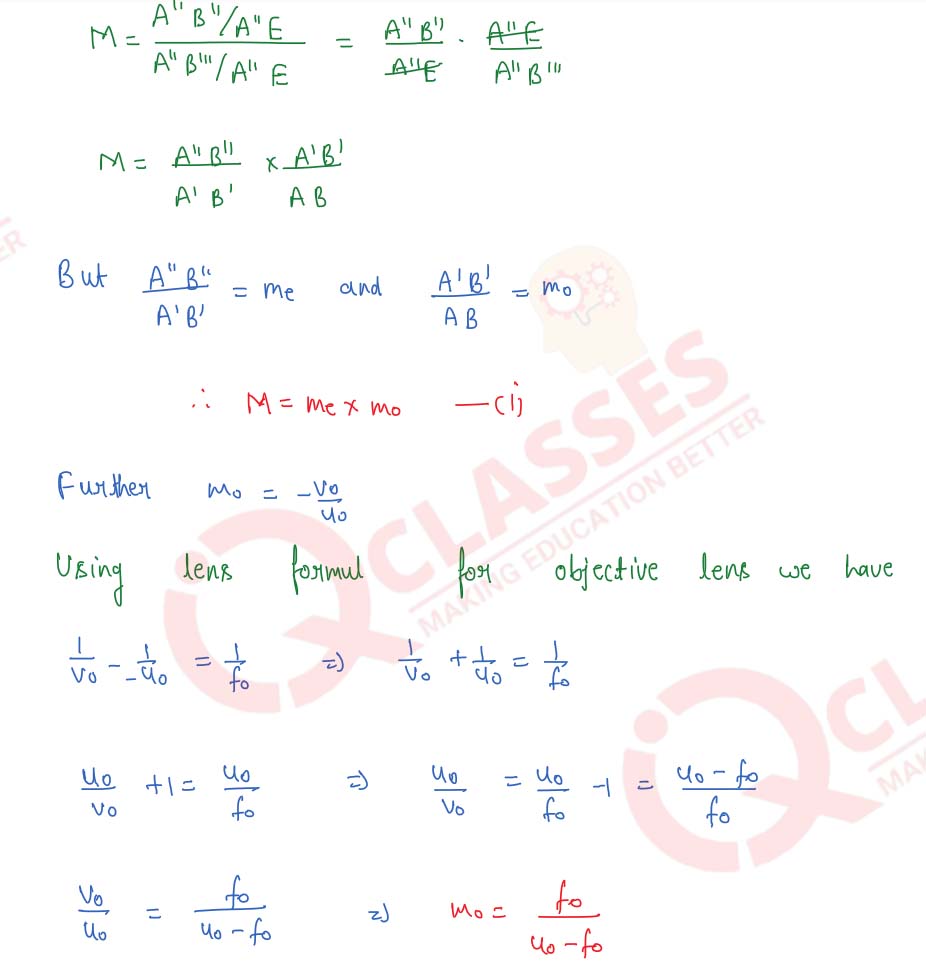
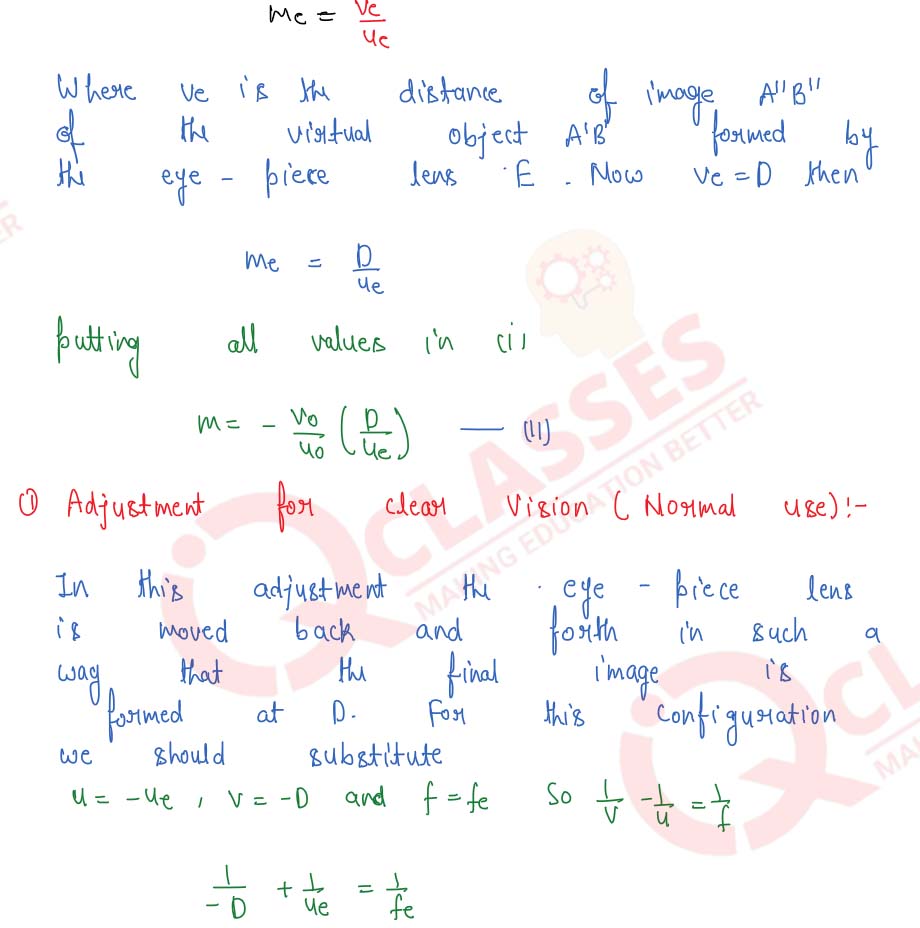
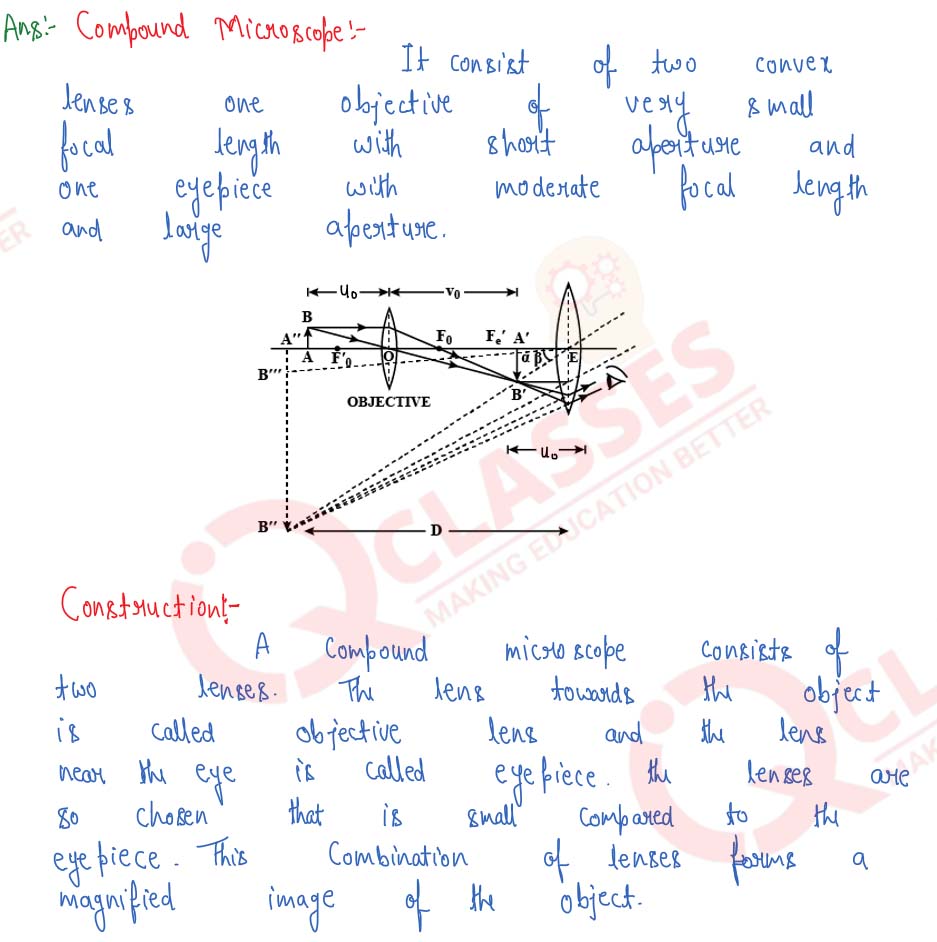
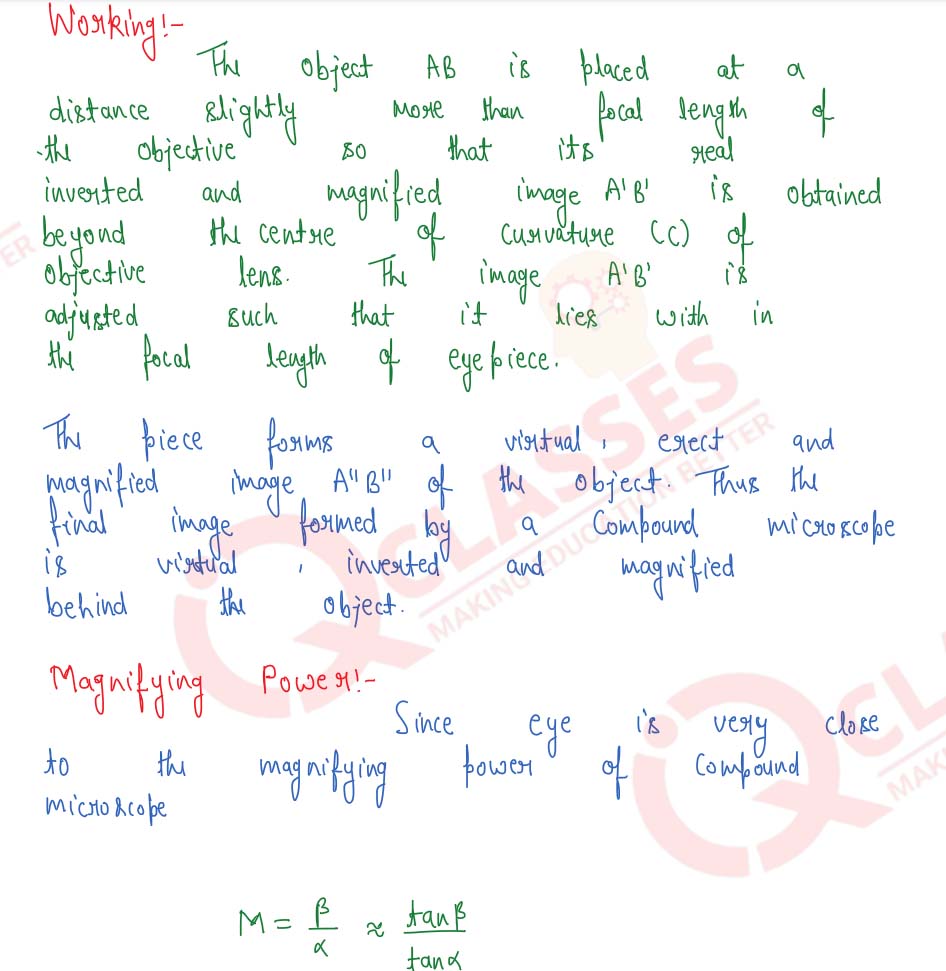
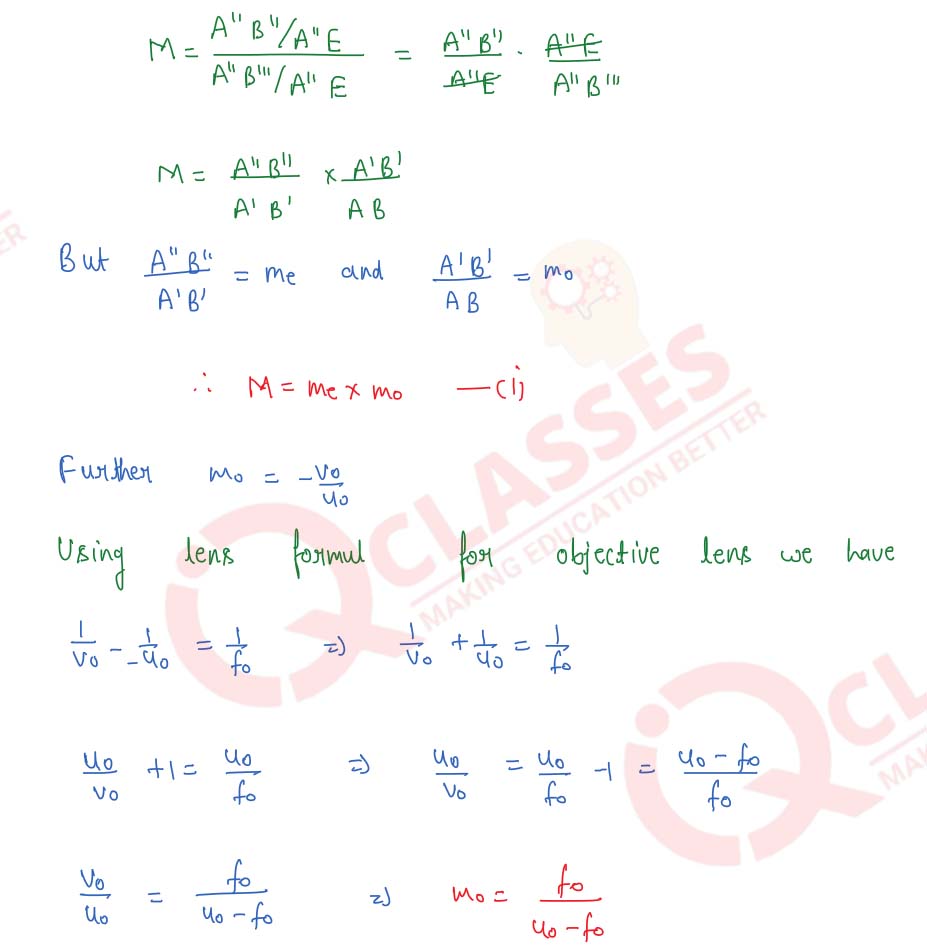
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain the construction and working of a compound microscope. Derive an expression for its magnifying power. How can the magnifying power be increased?
Solution
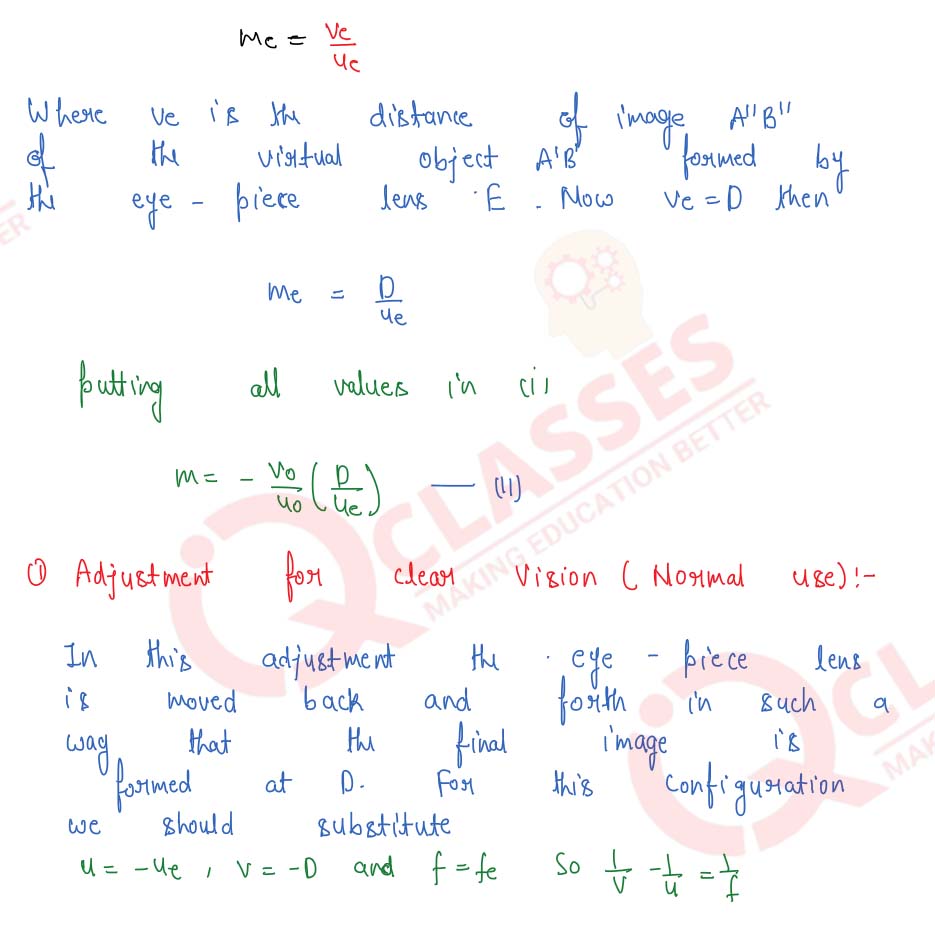








Q6
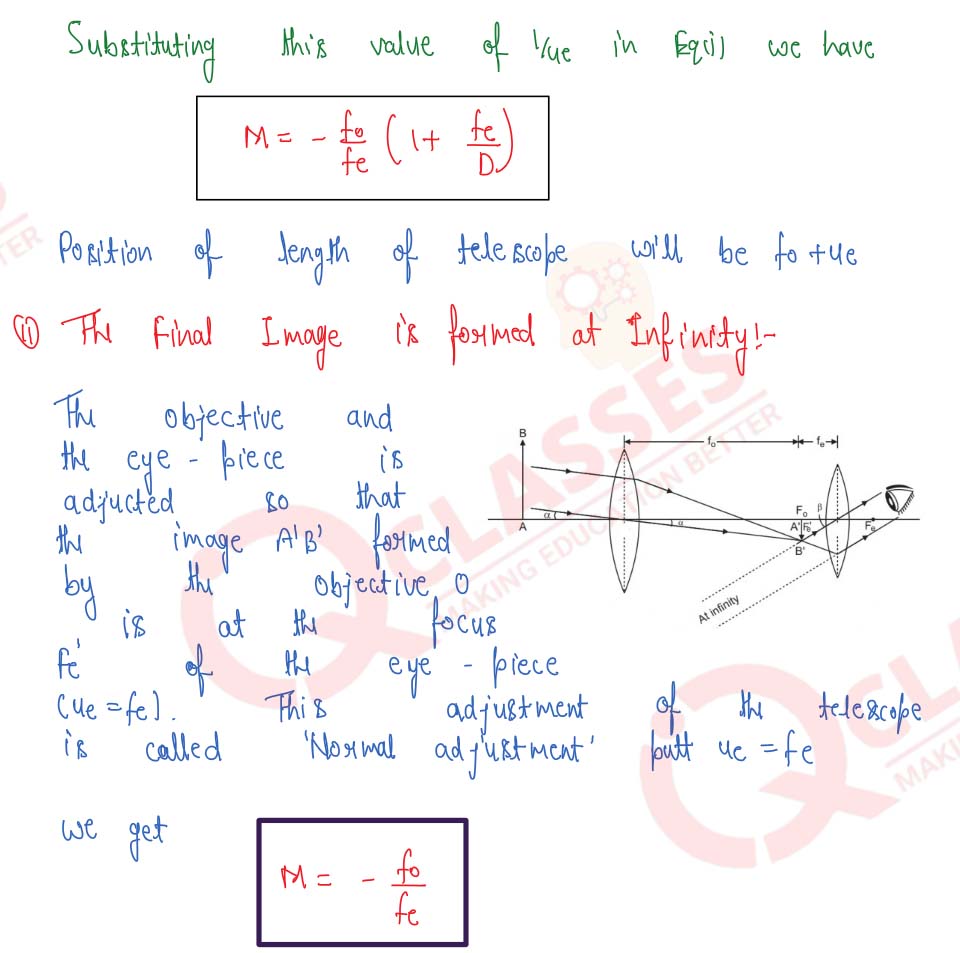
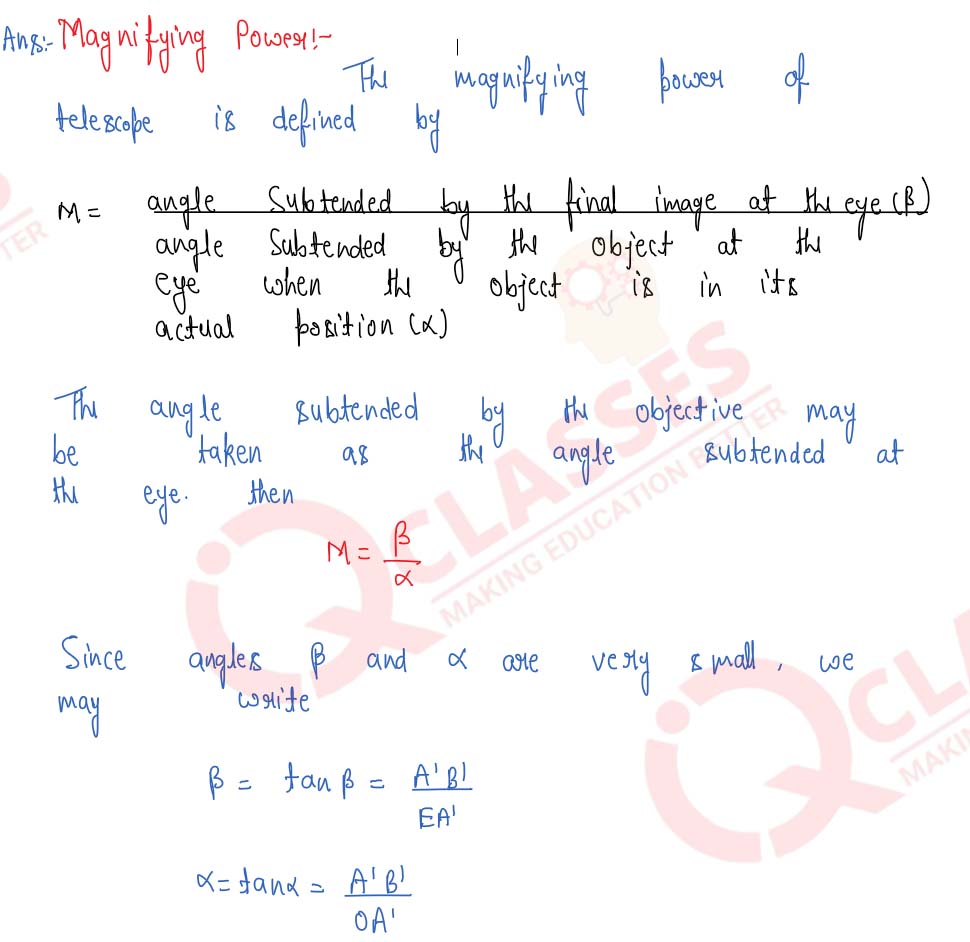
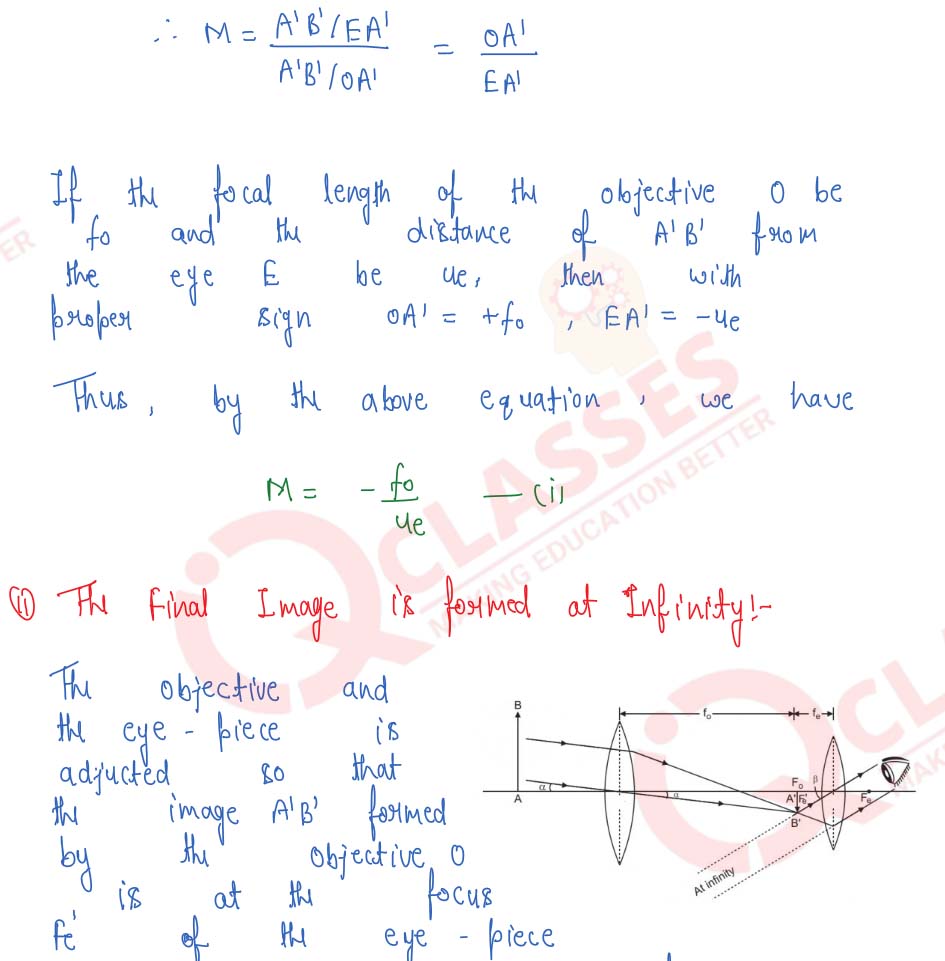
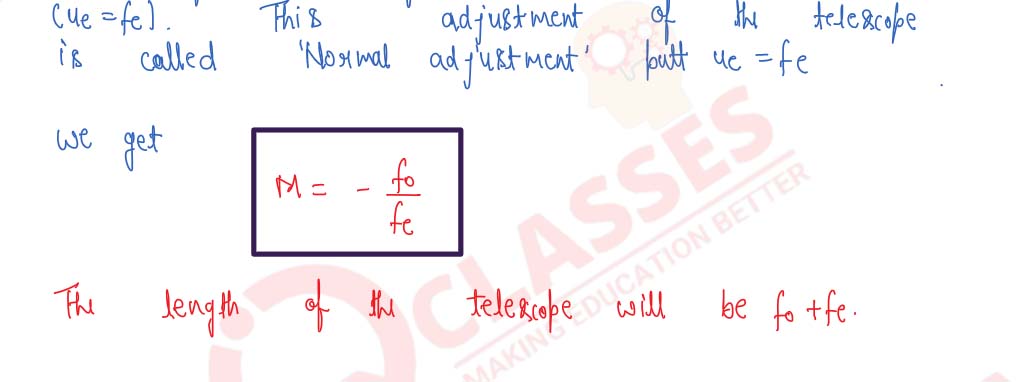
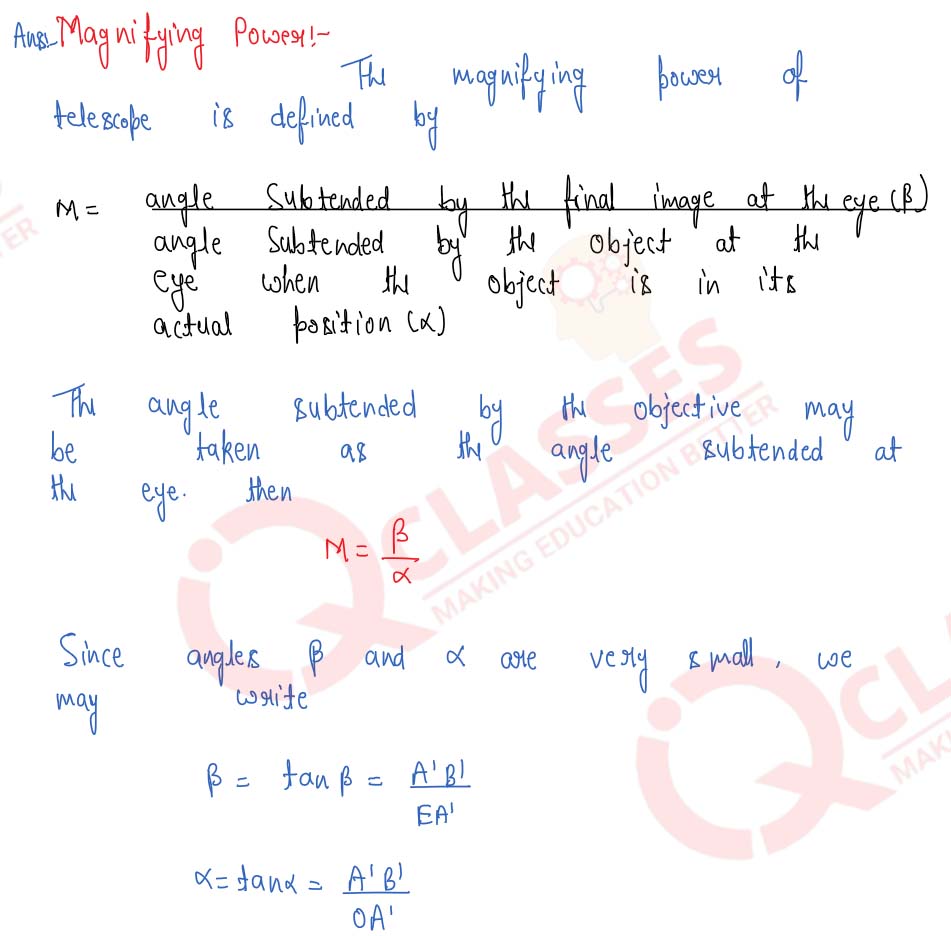
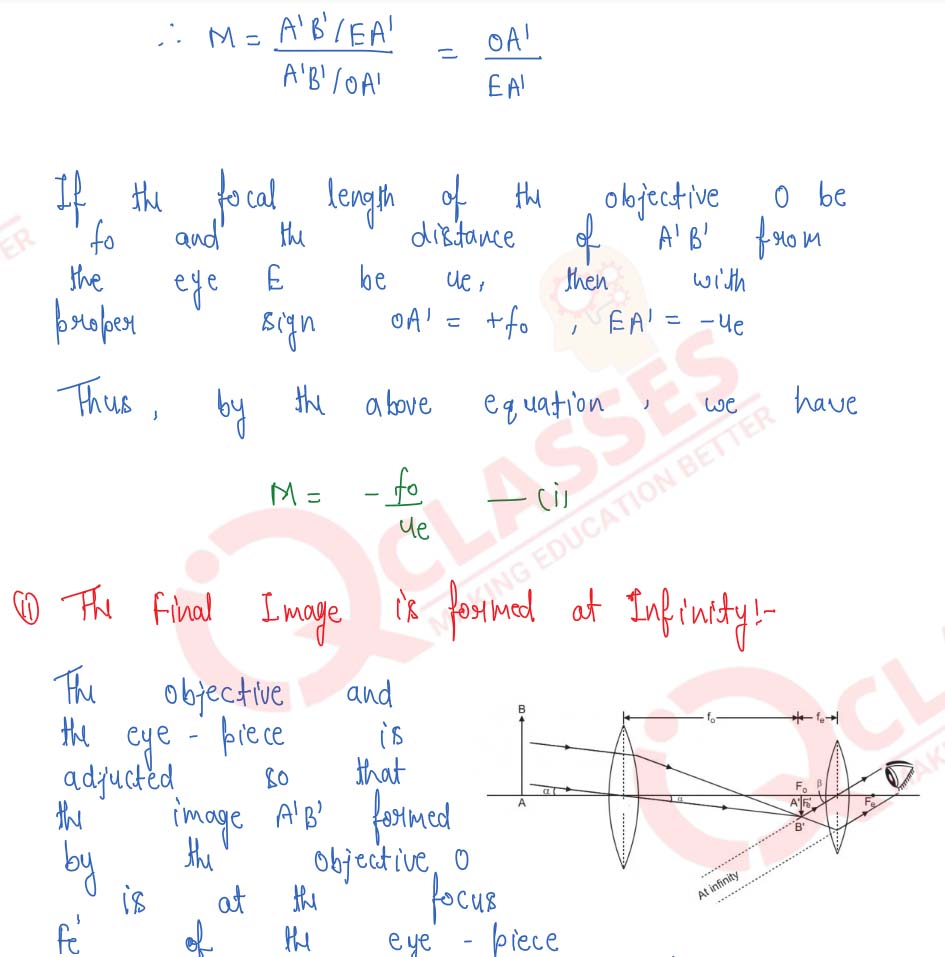
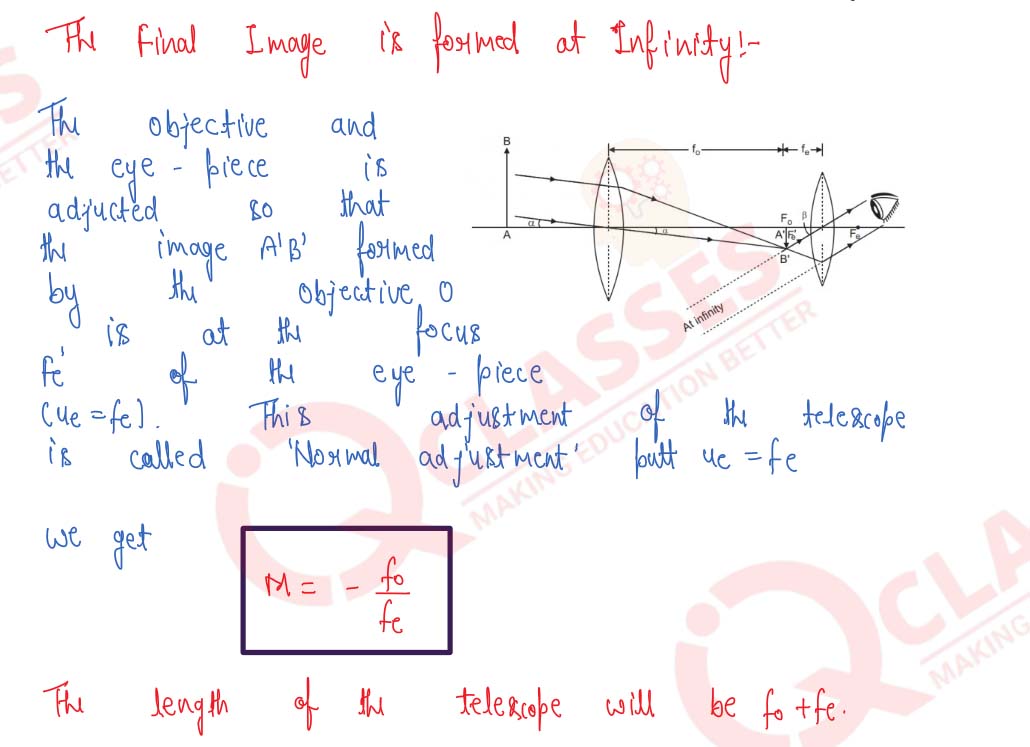
Draw a ray-diagram of an astronomical telescope and derive an expression for its magnifying power when : (i) the image is formed at infinity, (ii) the image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
Solution
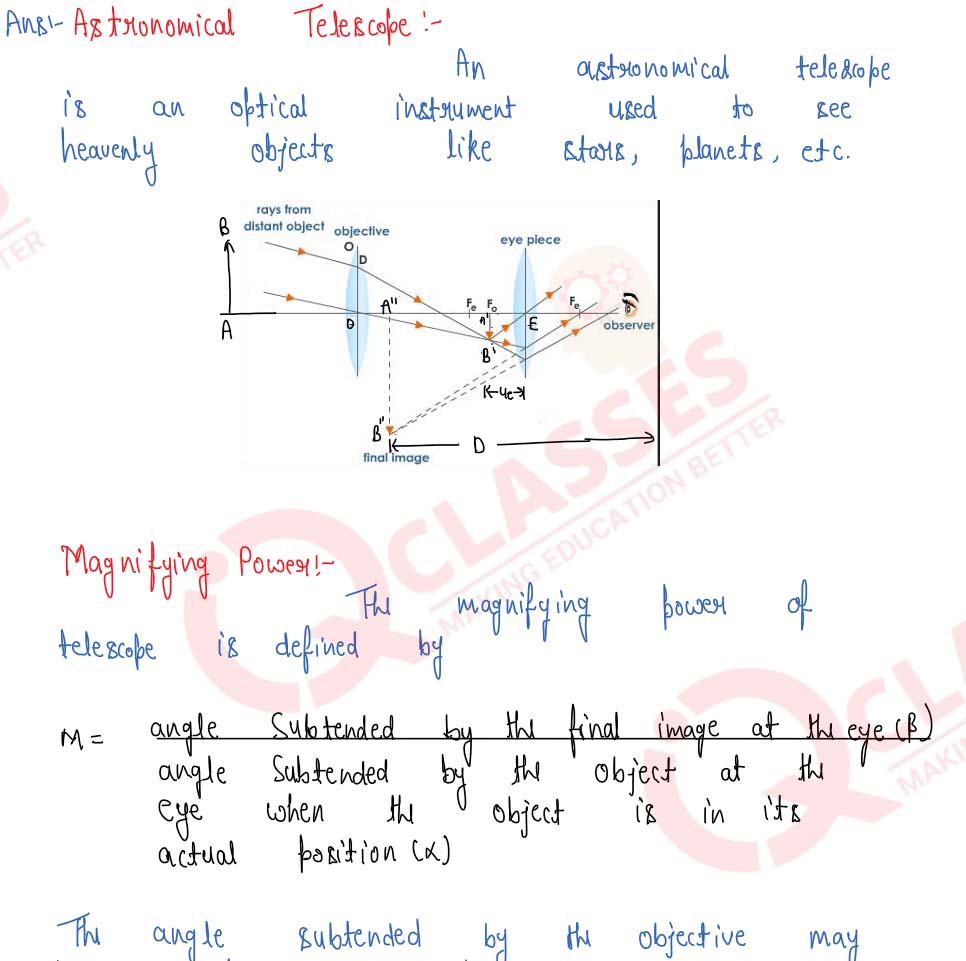
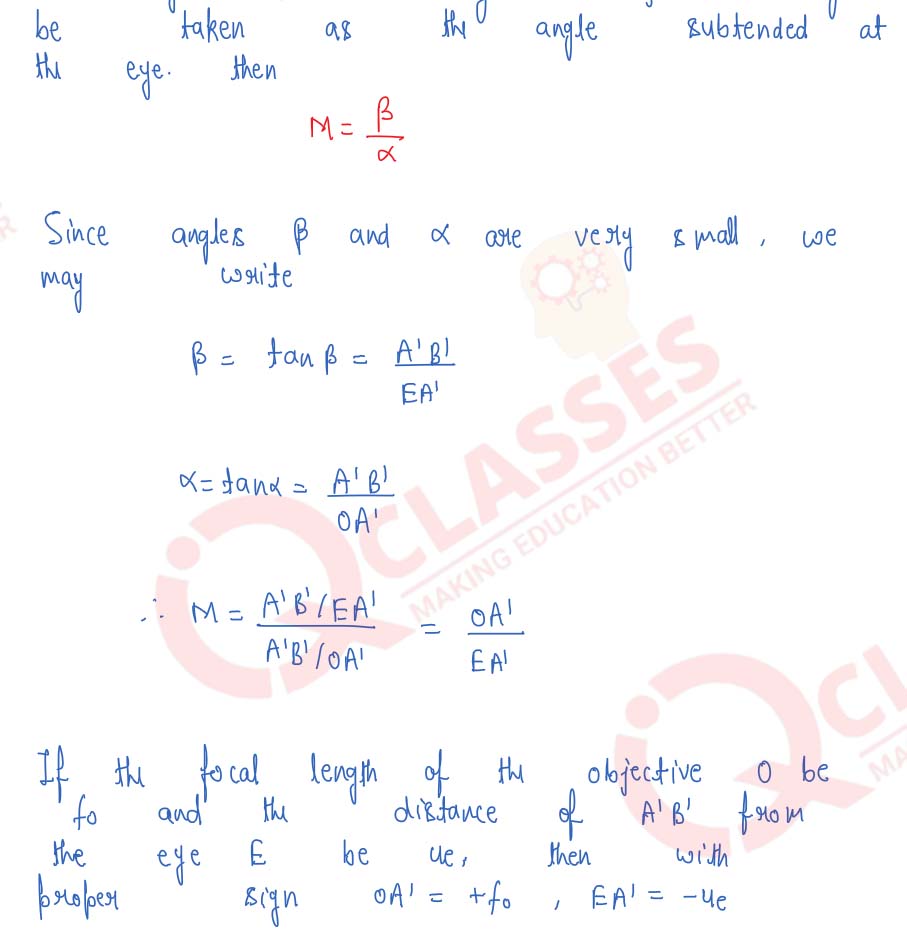
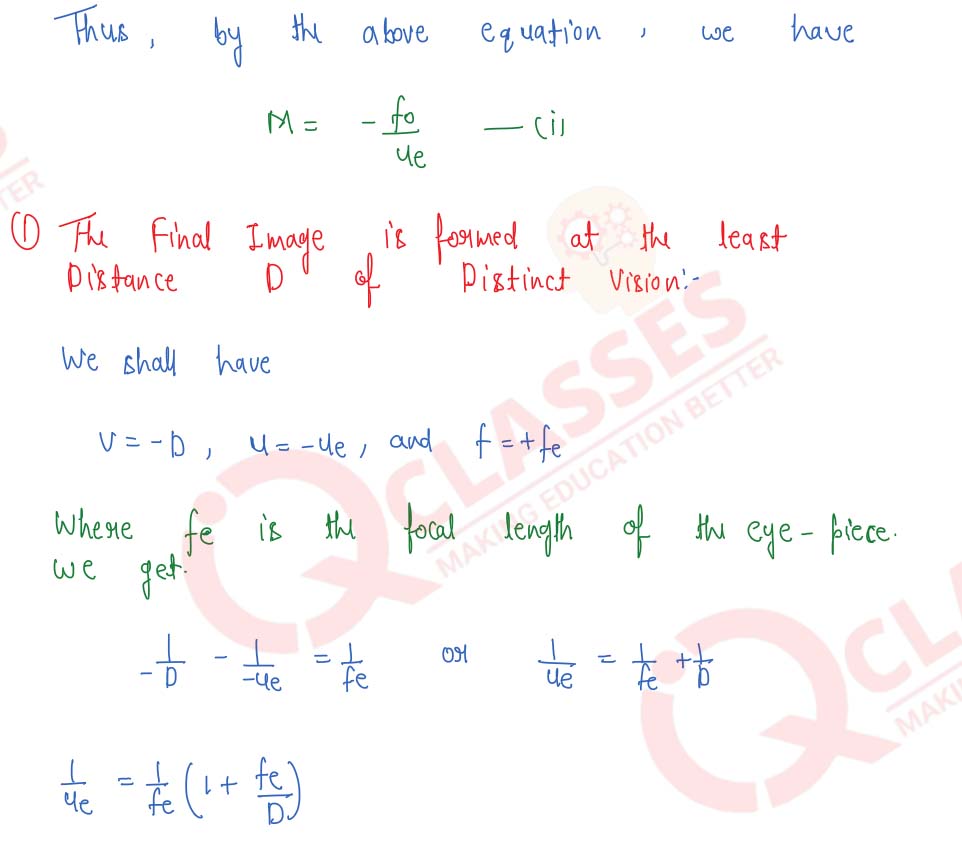






Q7
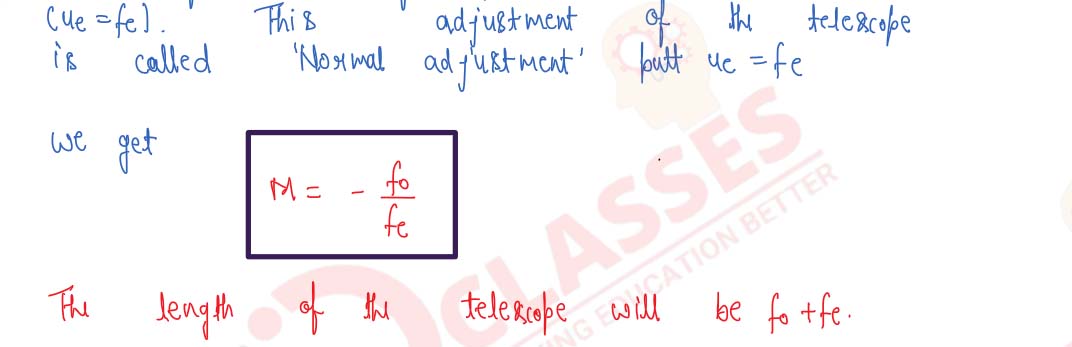
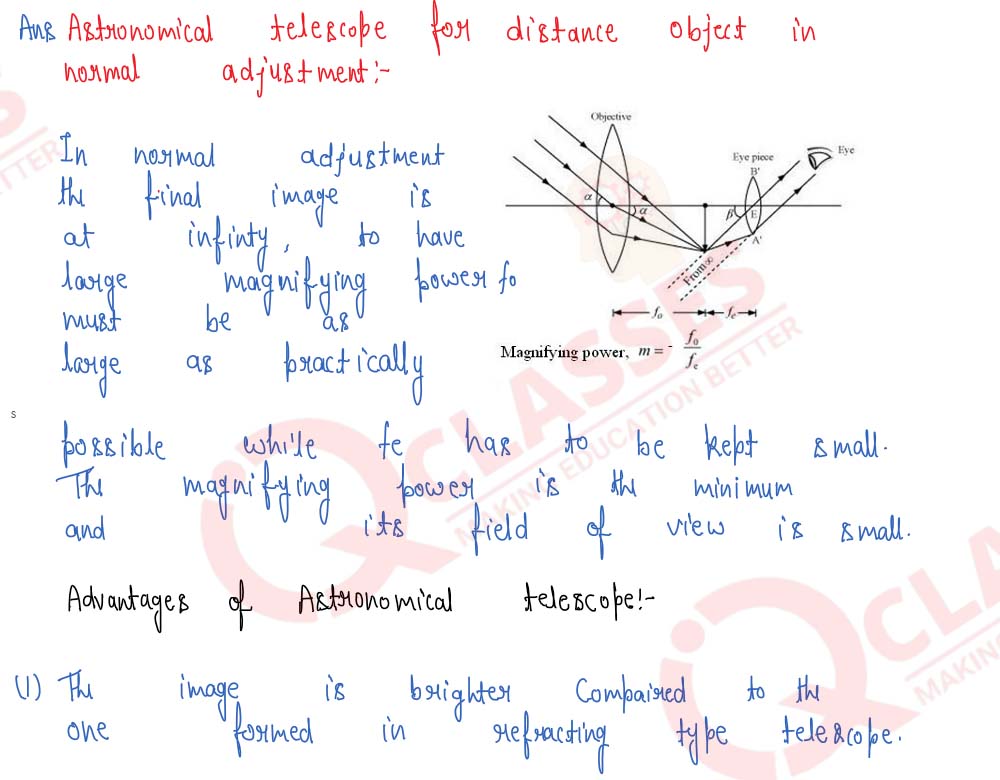
Draw a labelled ray diagram of an image formed by a refracting telescope with final image formed at infinity. Derive an expression for its magnifying power with the final image at infinity.
Solution



Q8
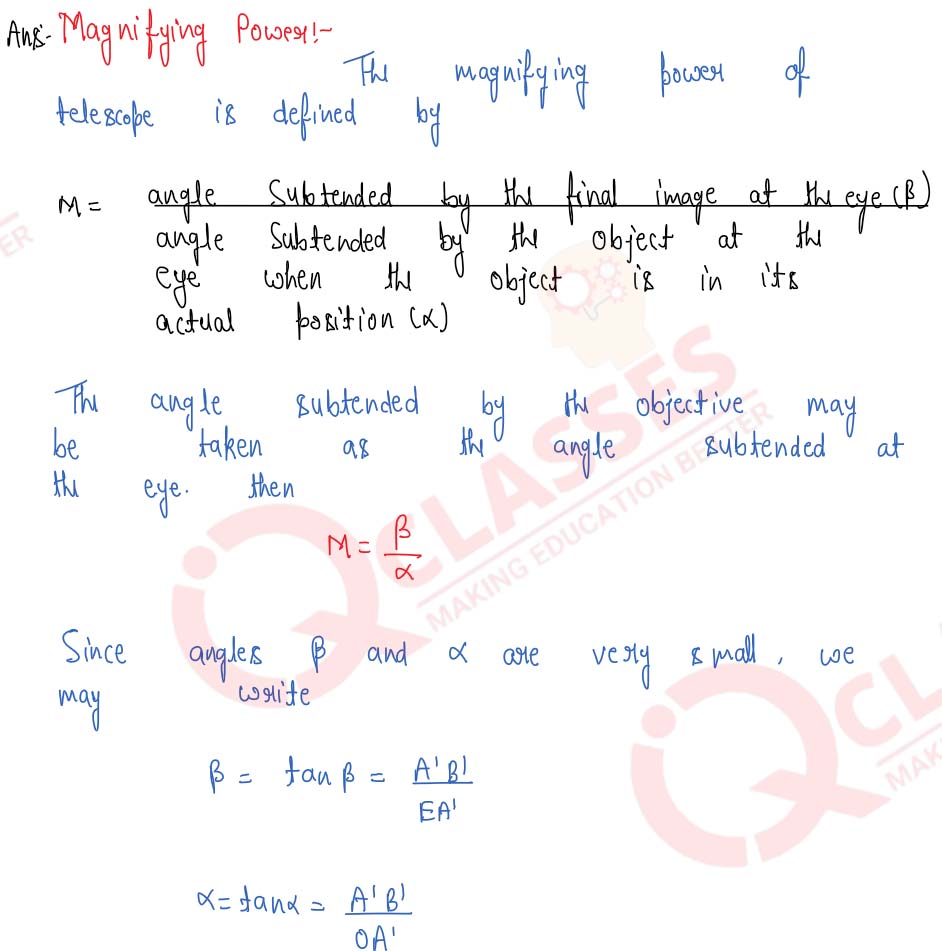
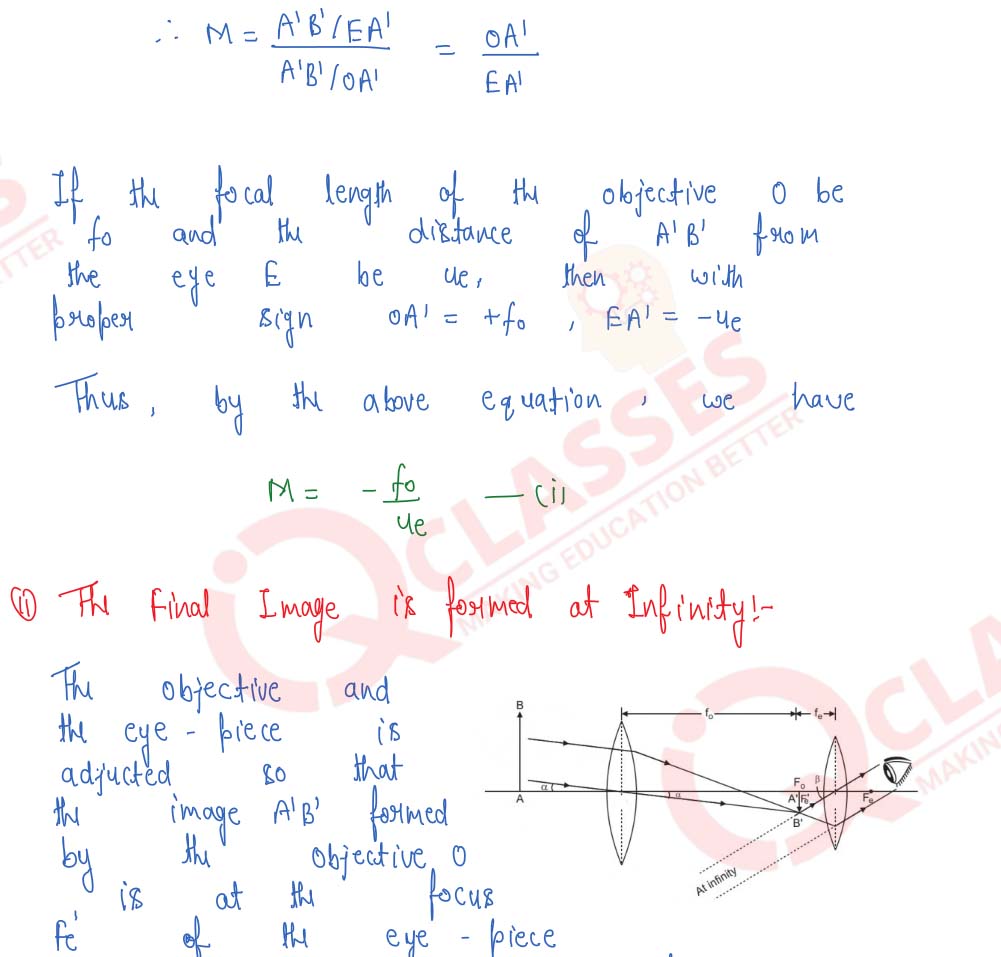
Draw the ray-diagram for the formation of image by a refracting telescope having the final image formed at infinity. Define the angular magnification and derive the formula for the same for image formed at infinity.
Solution



Q9
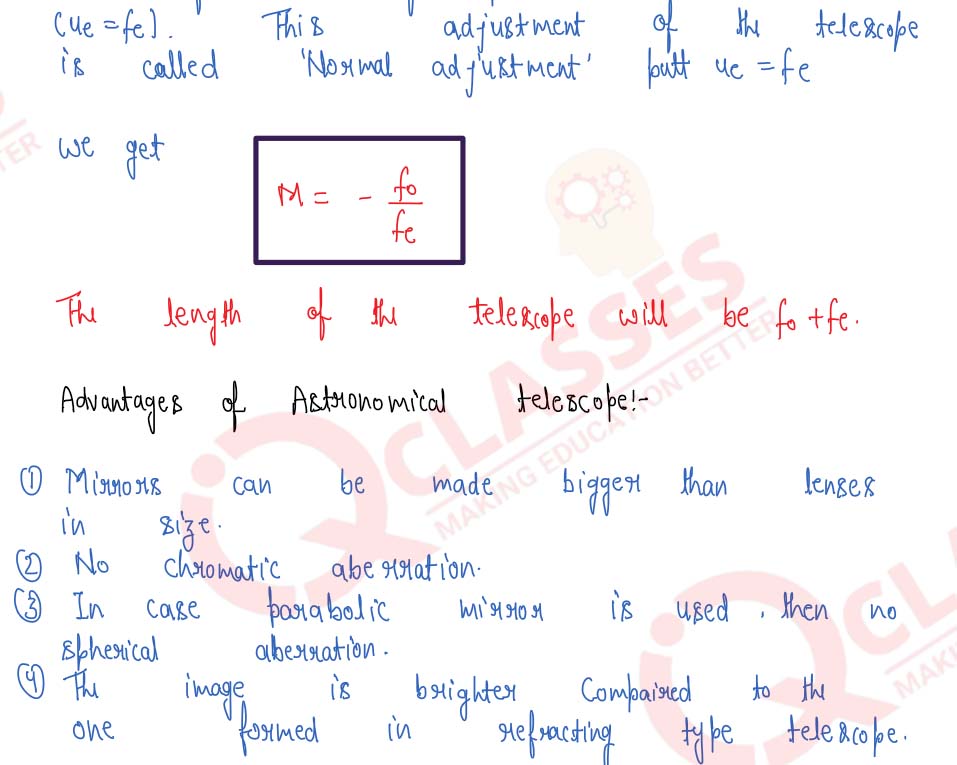
Derive the general relation for the magnifying power of an astronomical telescope when image is formed at infinity. State any one advantage of an astronomical telescope of the reflecting type over a refracting type.
Solution



Q10
Draw a ray-diagram to show how the image of a distant object is formed by a reflecting astronomical telescope when in normal use. State one advantage over a refracting-type telescope.
Solution

Q11
Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the formation of an image by a refracting telescope when the final image lies at infinity.
Solution

Q12
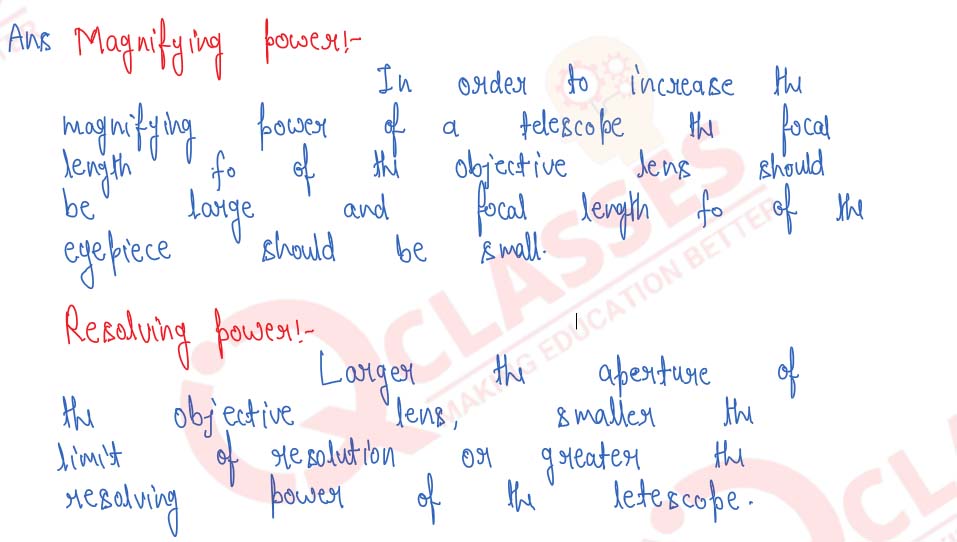
What do you mean by the resolving power of a telescope? How does the resolving power of a telescope depend upon the wavelength of the light and the aperture of the objective lens?
Solution




Q13
(i) Define resolving power of a simple astronomical telescope.
(ii) State one advantage of a reflecting telescope over refracting telescope.
Solution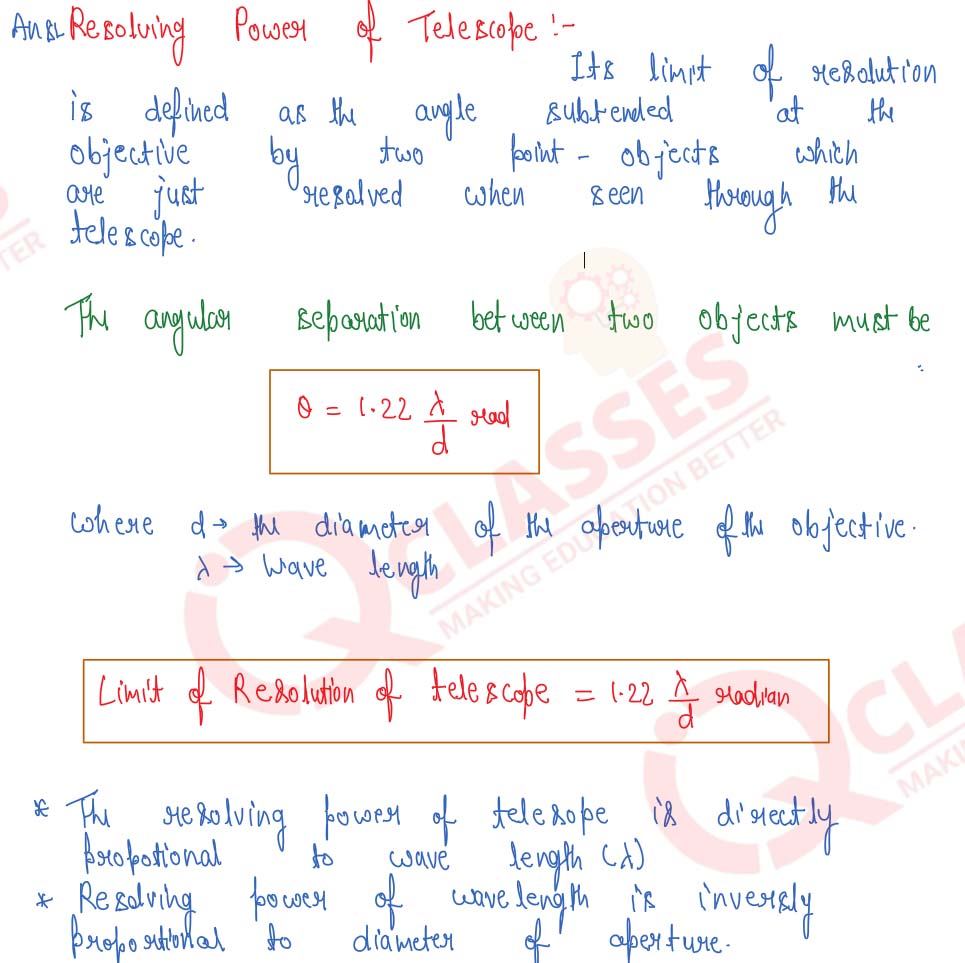

(ii) State one advantage of a reflecting telescope over refracting telescope.
Solution


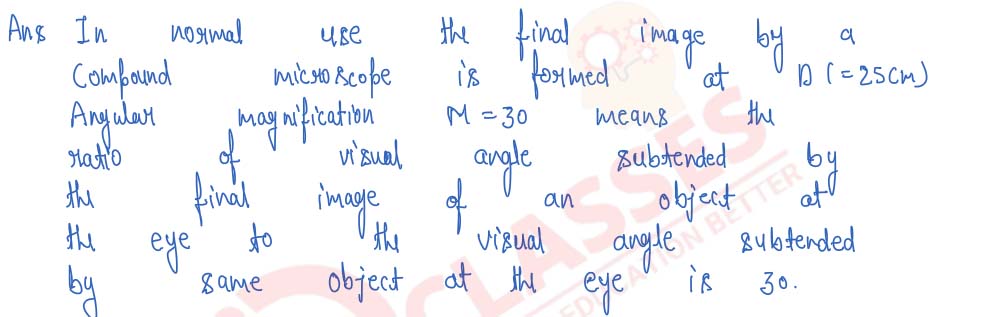
Q14
Explain the statement; "Angular magnification of a compound microscope in normal use is 30".
Solution

Q15
With regard to an astronomical telescope of refracting type, state how will you increase its : (i) magenta
Solution