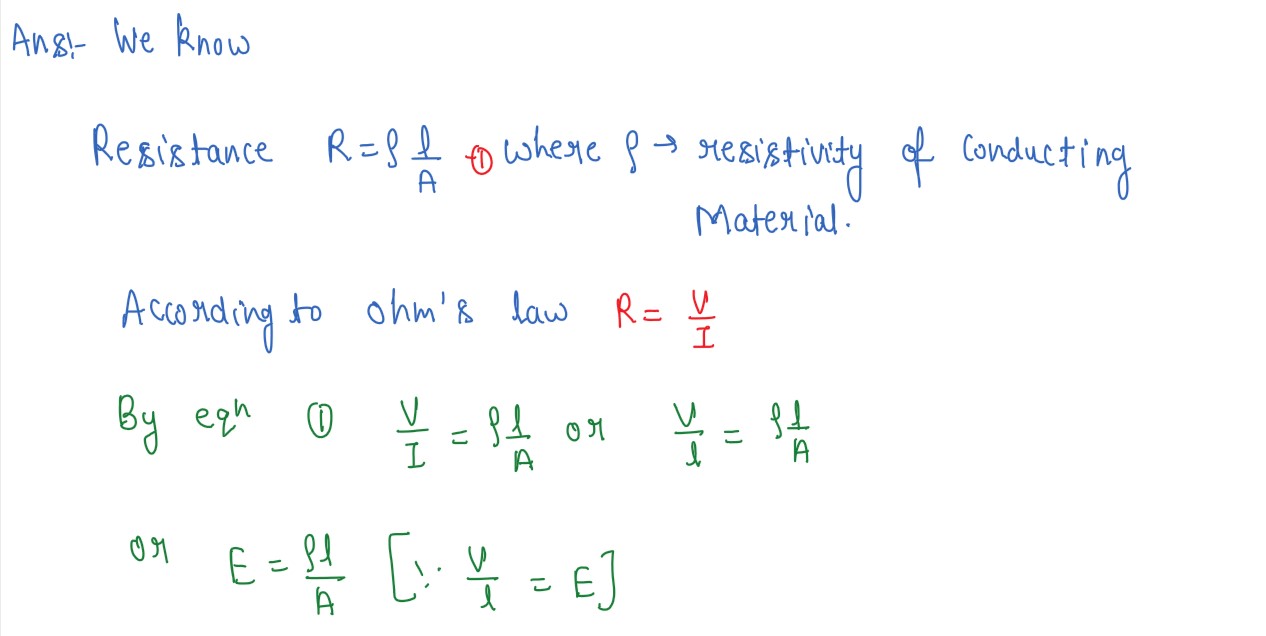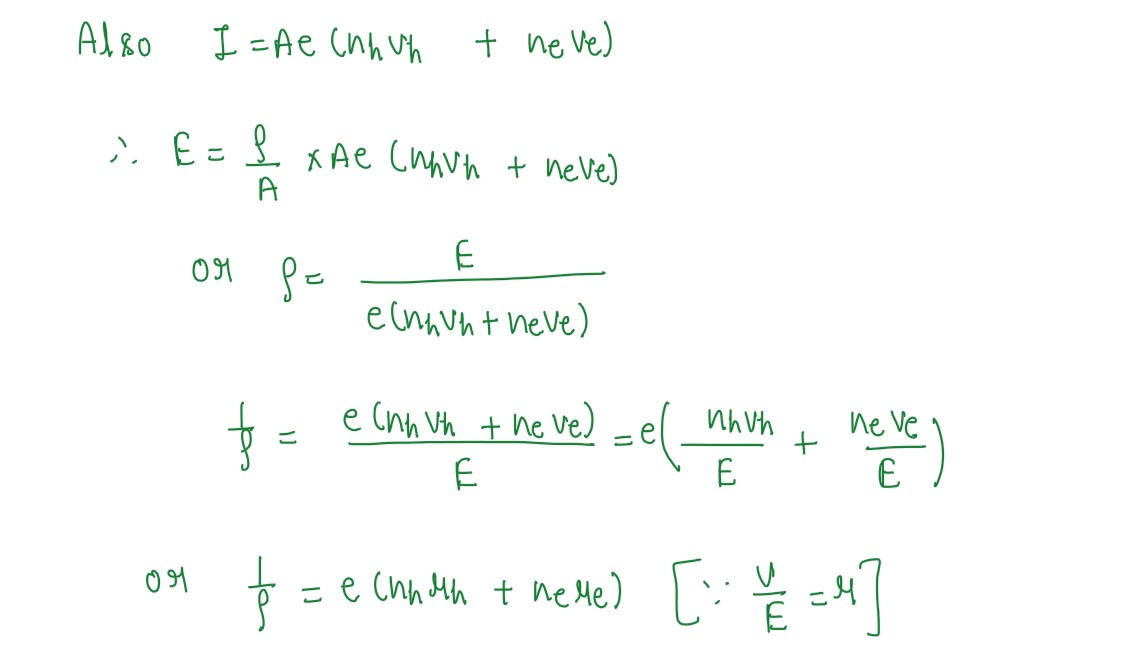Q1
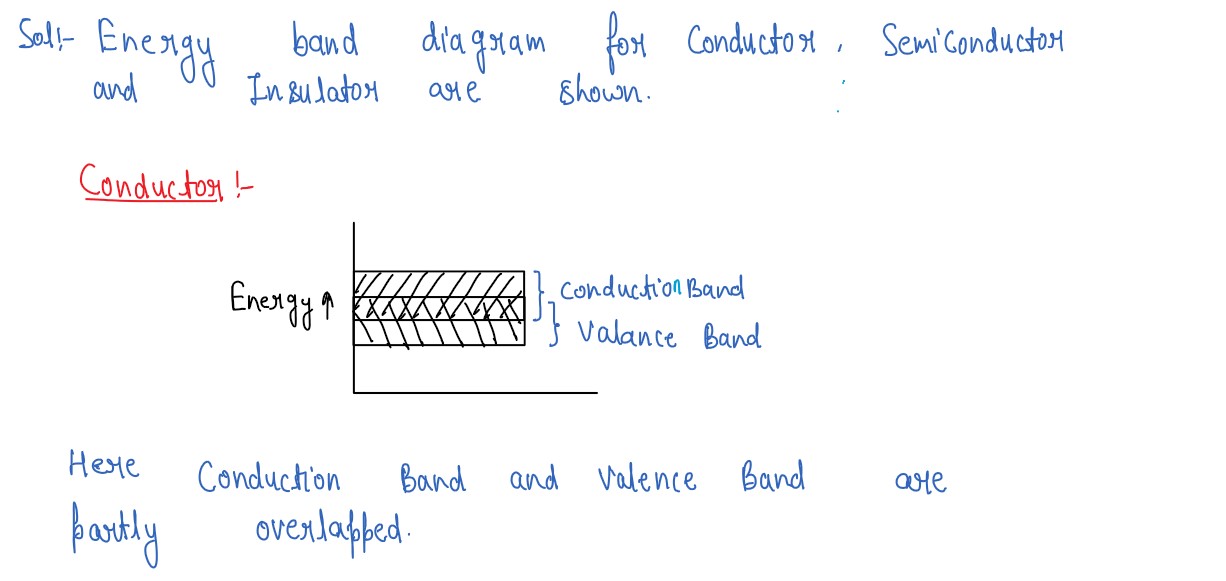
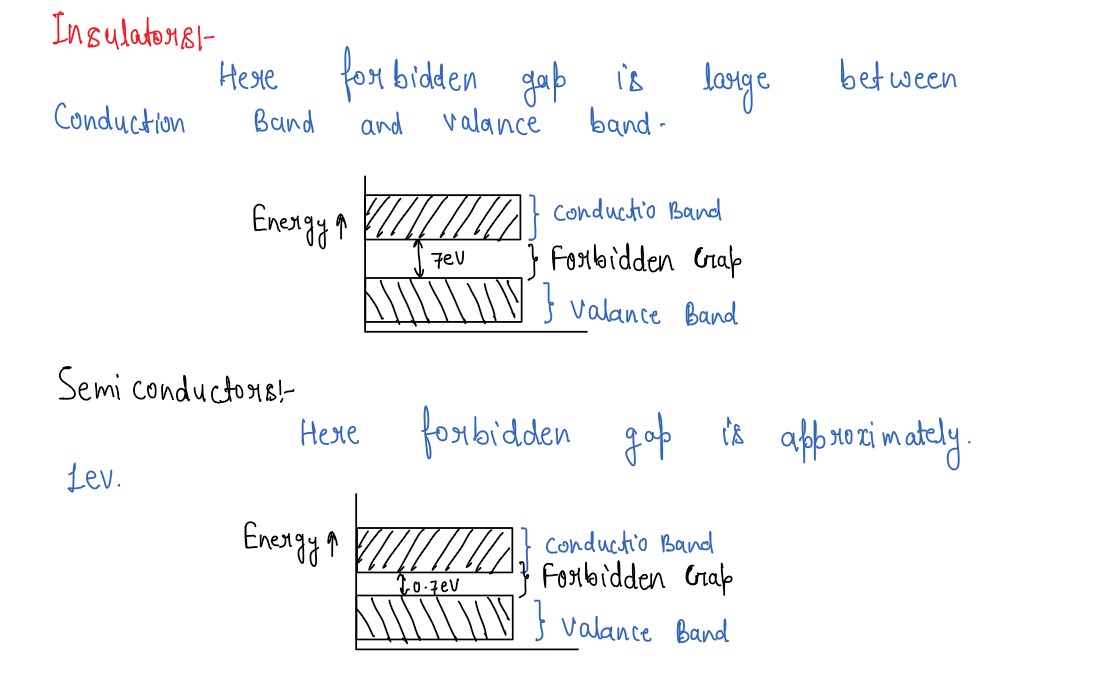
Draw separate energy-level bands for conductors, semiconductors and insulators and label each of them to
illustrate the behaviour of (i) a conductor, (ii) a pure semiconductor and (iii) an insulator.
Solution
Q2
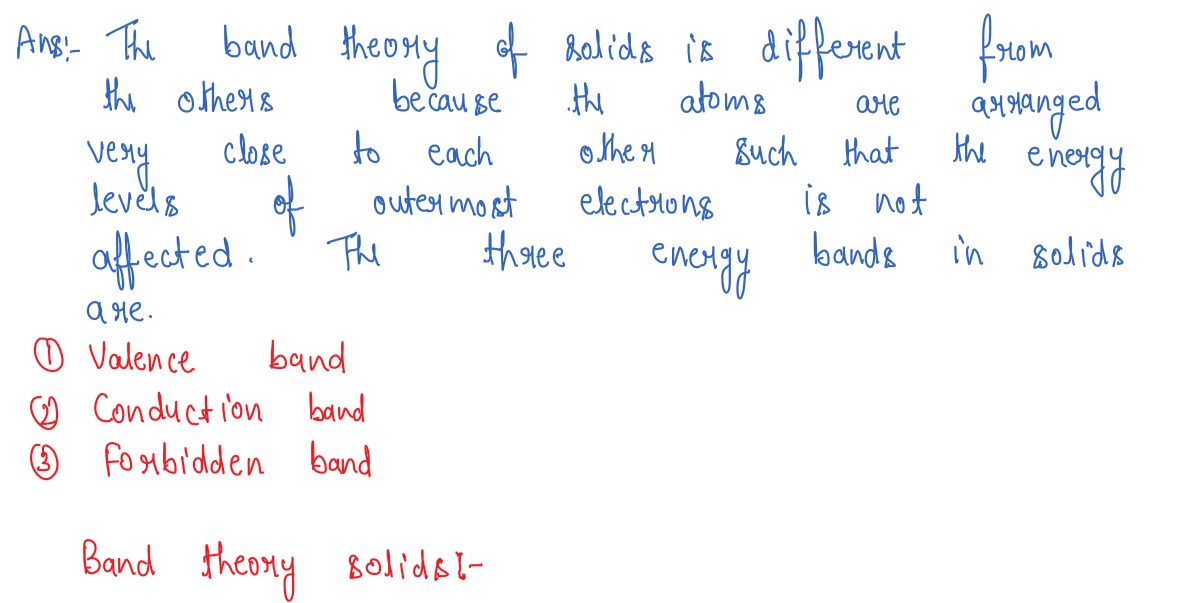
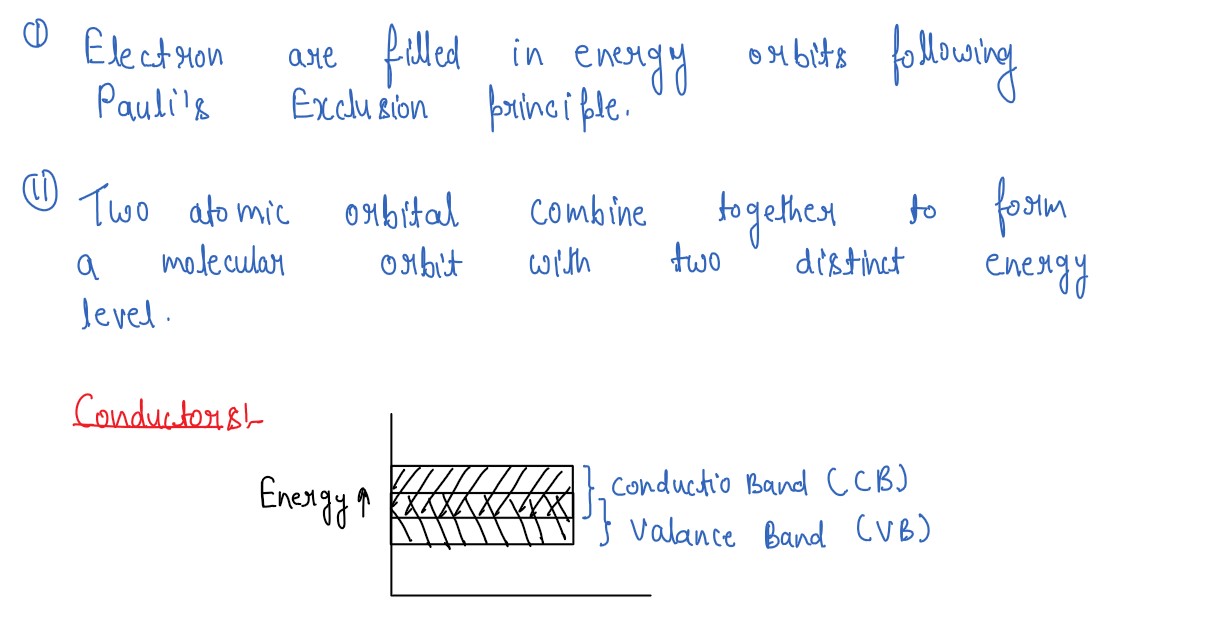
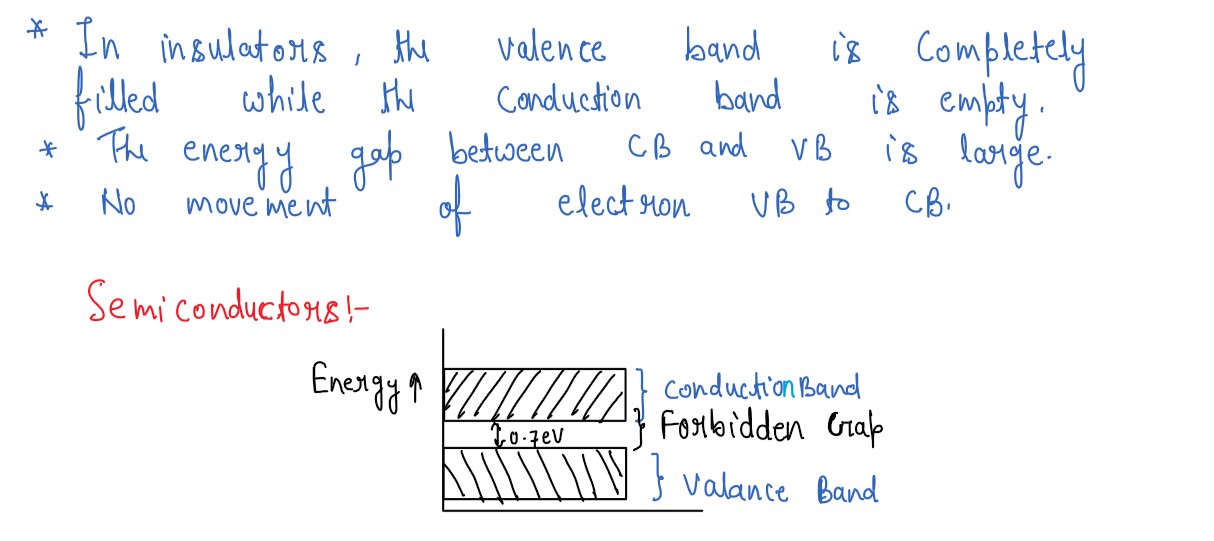
Explain formation of energy bands in solids. Distinguish between conductors (metals), insulators and
semiconductors on the basis of their energy band diagrams.
Solution

Q3
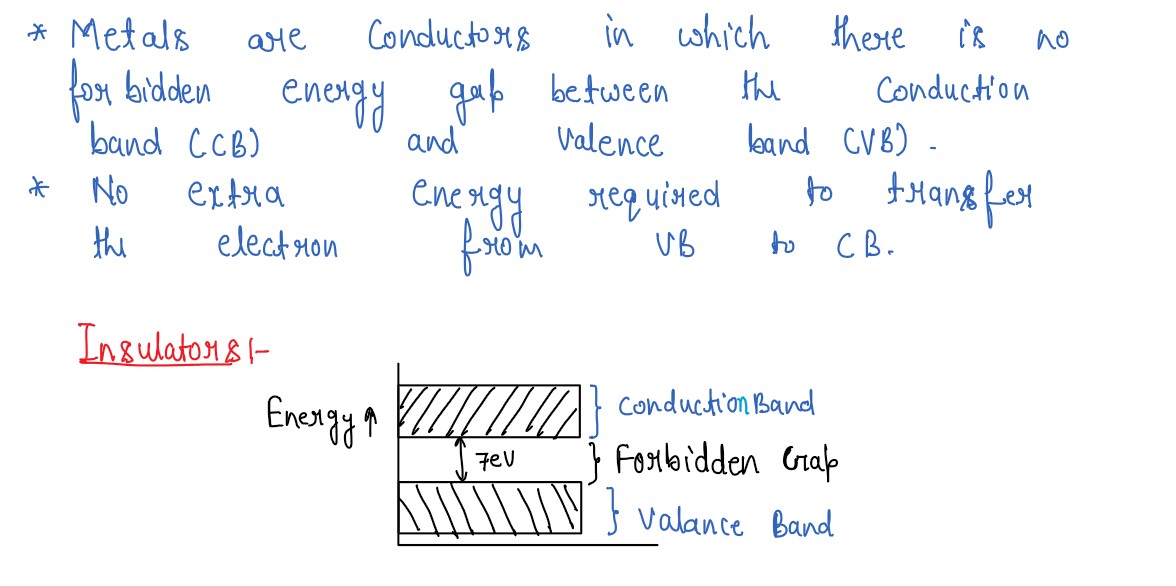
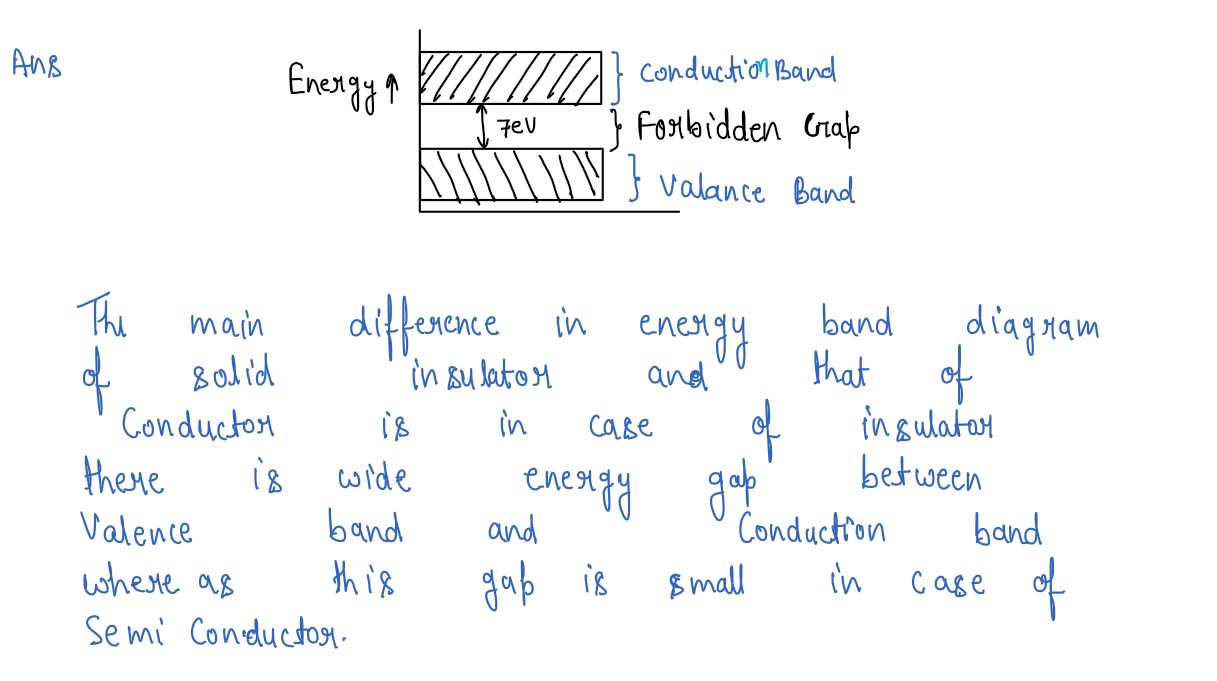
Draw a labelled energy band diagram for a solid which is an insulator. What is the main difference
between this diagram and that of a semiconductor?
Solution
Q4
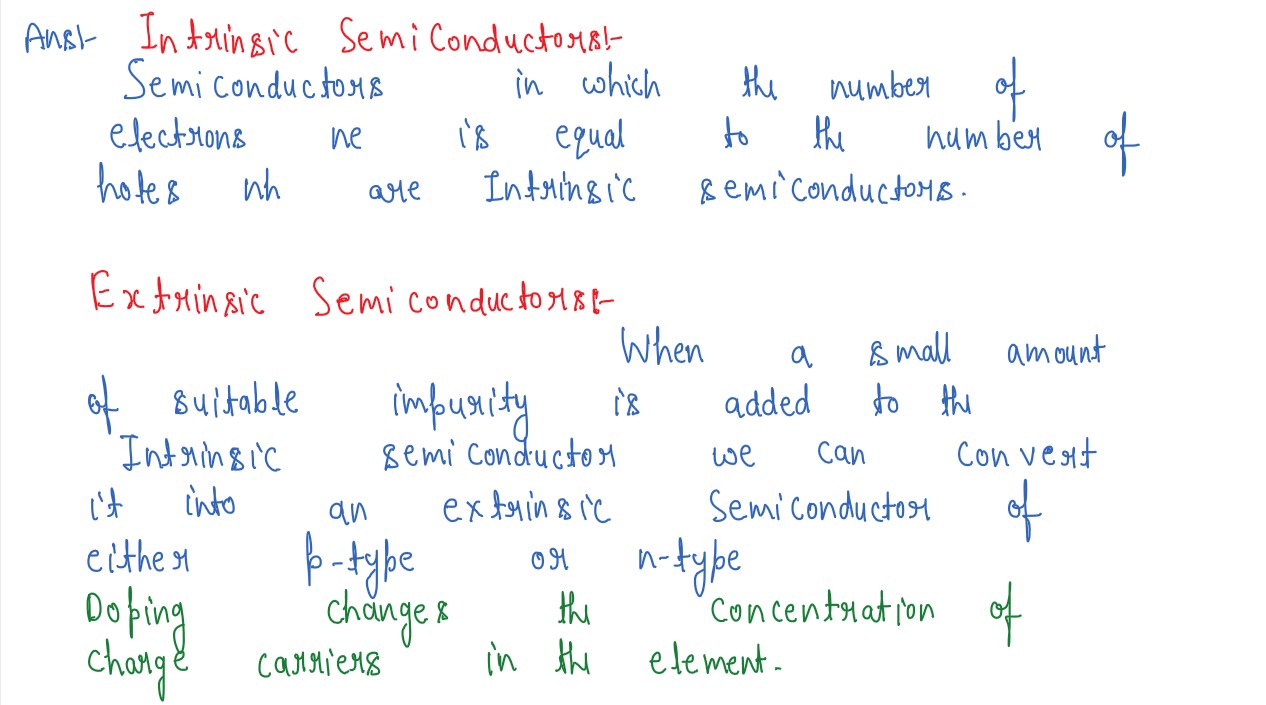
What is meant by doping in semiconductors? What
are p-type semiconductors?
Solution

Q5
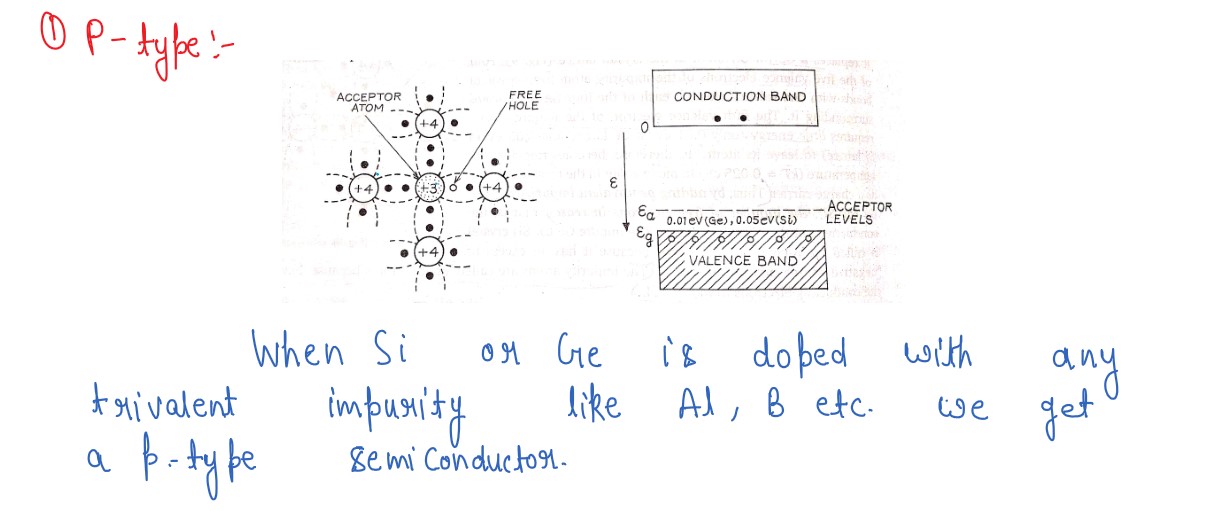
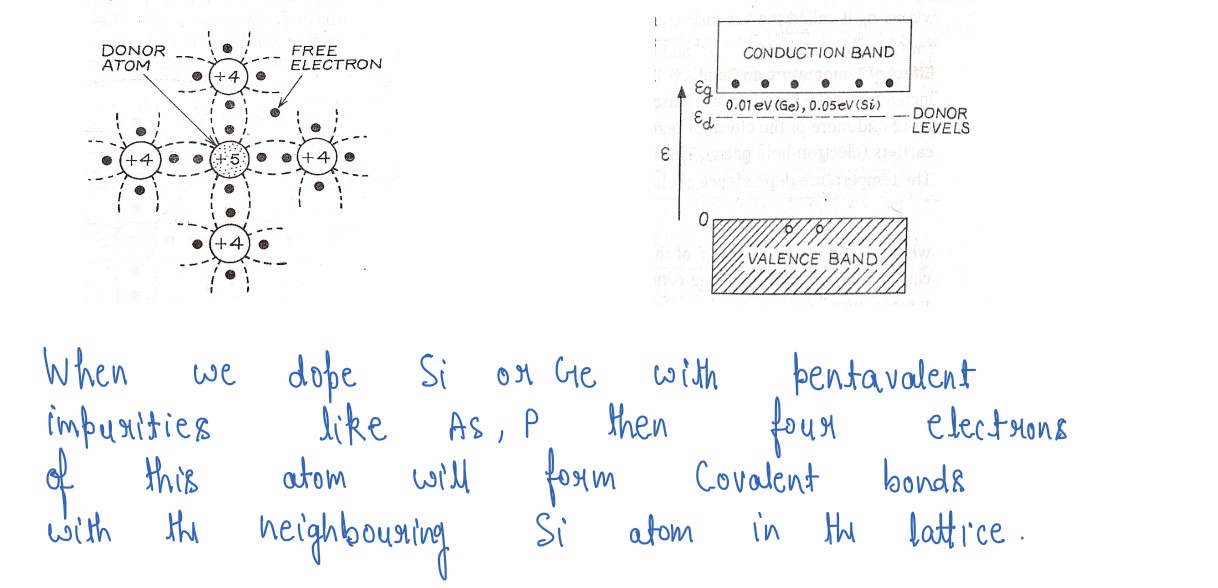
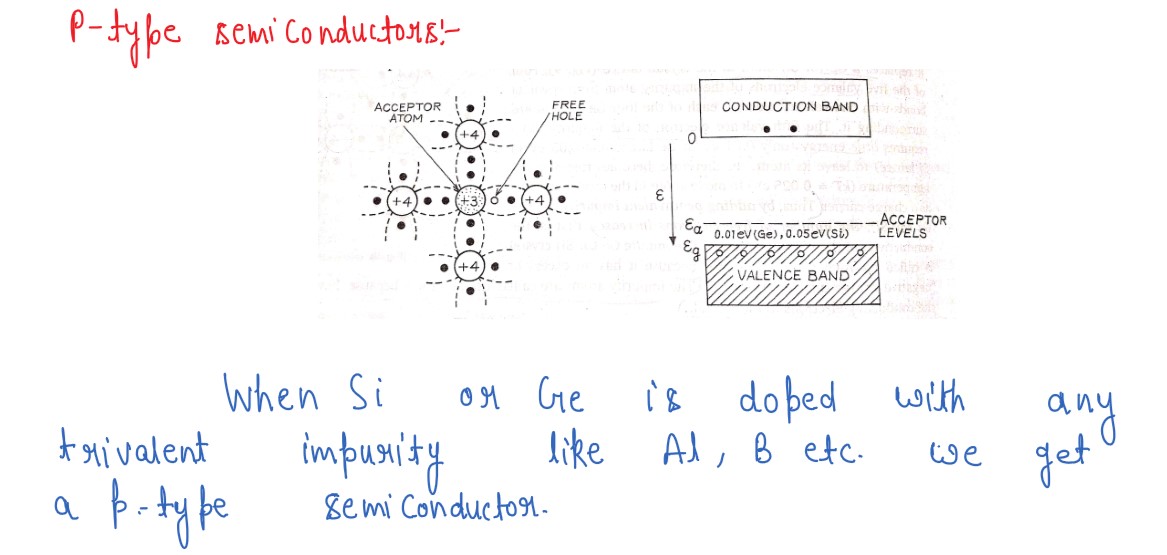
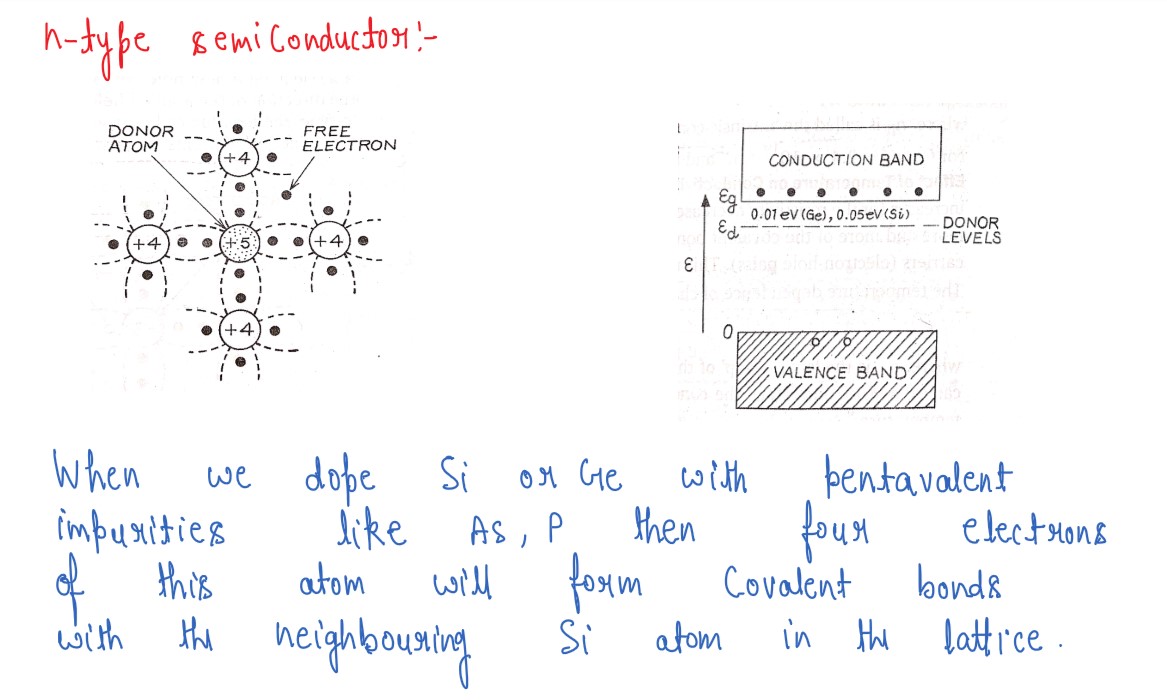
Explain, how an intrinsic semiconductor can be converted into (i) n-type, (ii)
p-type semiconductor.Given one example of each and draw their energy
band diagrams.
Solution

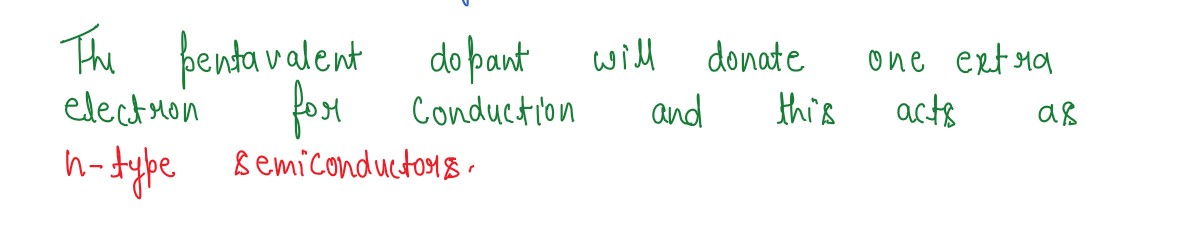
Q6
What do semiconductors? Distinguish between them on the basis of energy band diagram.
Solution
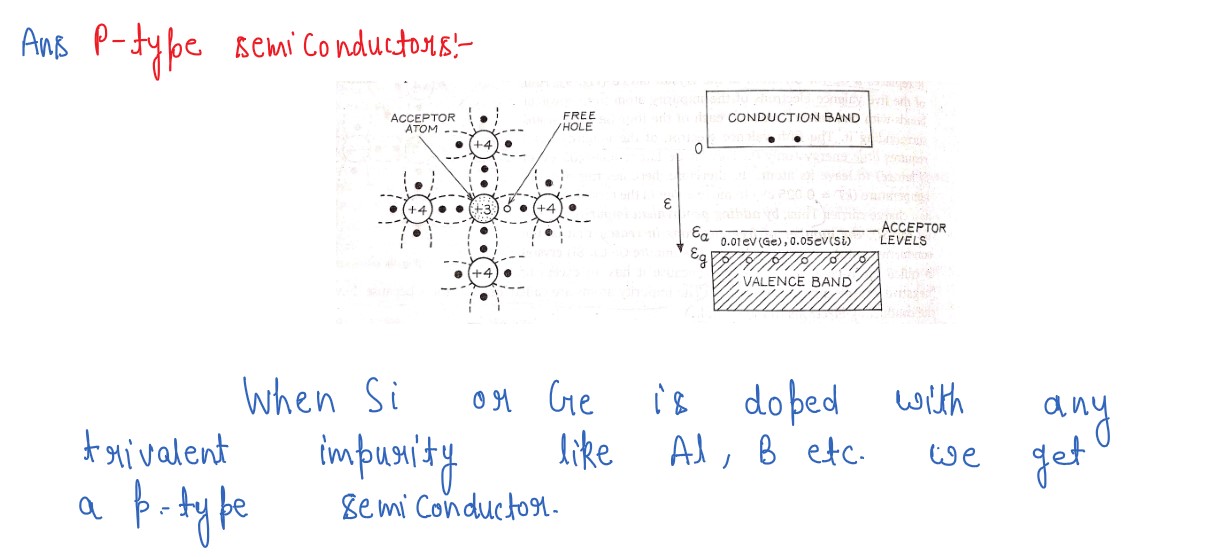
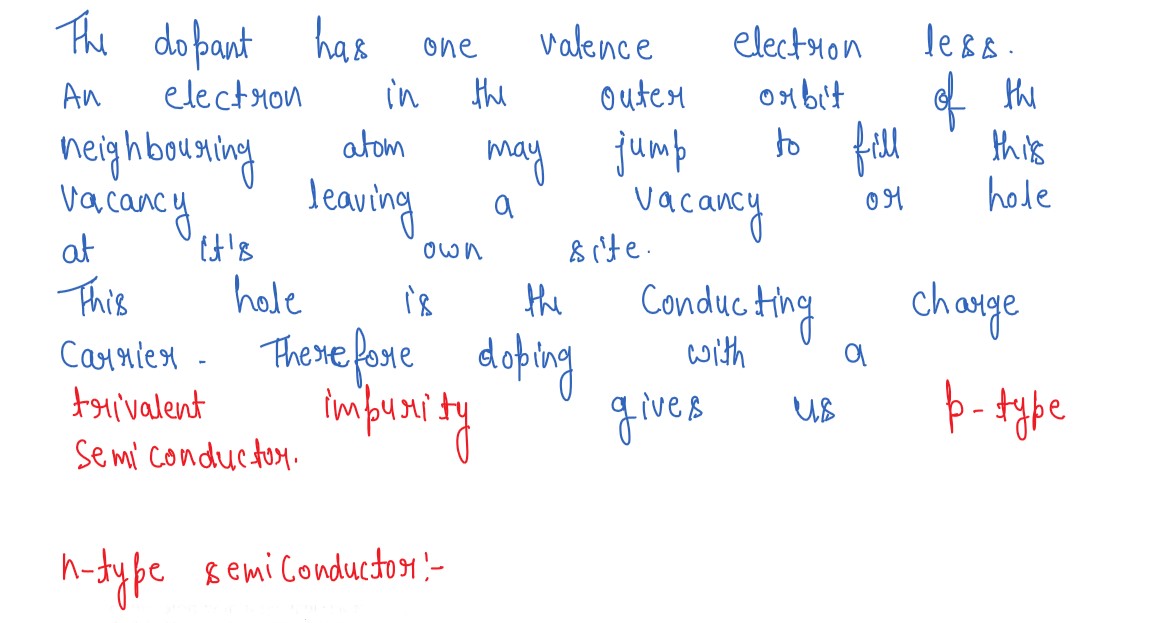
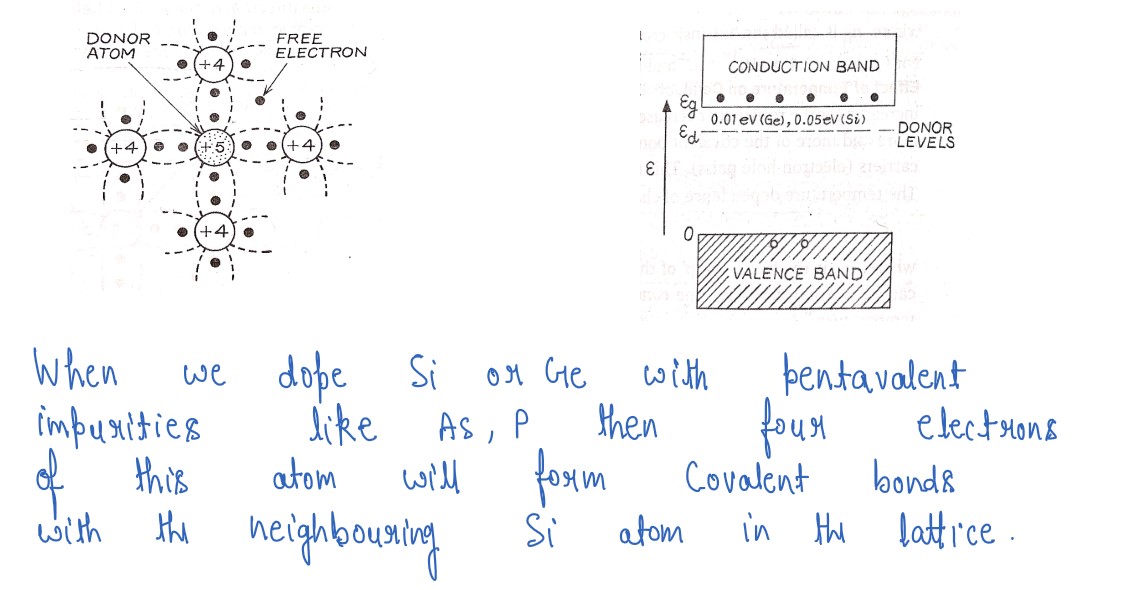
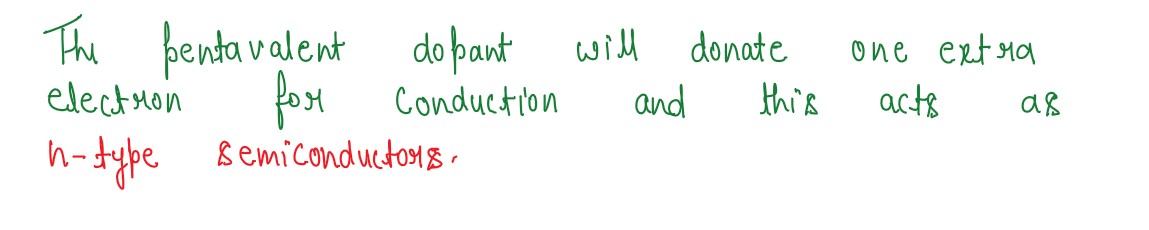
Q7
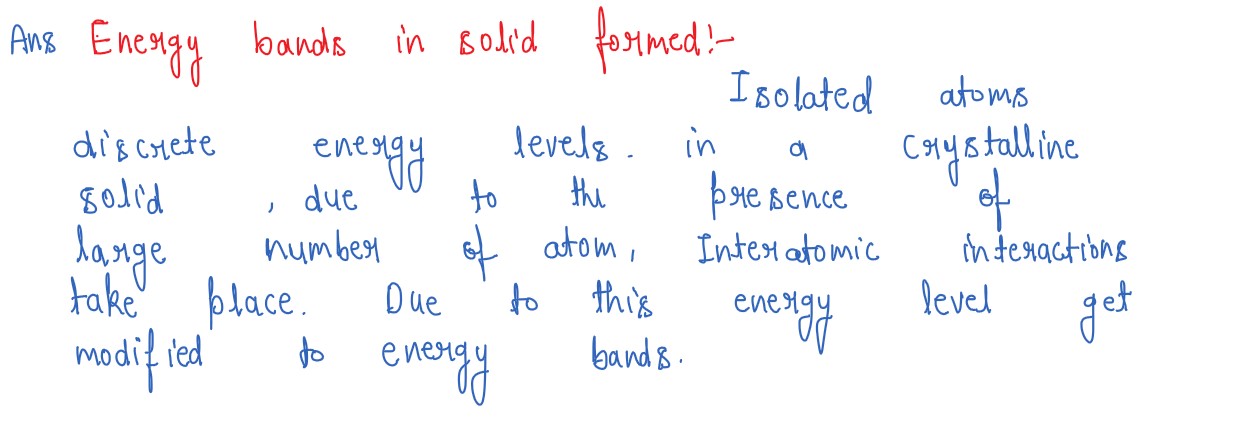
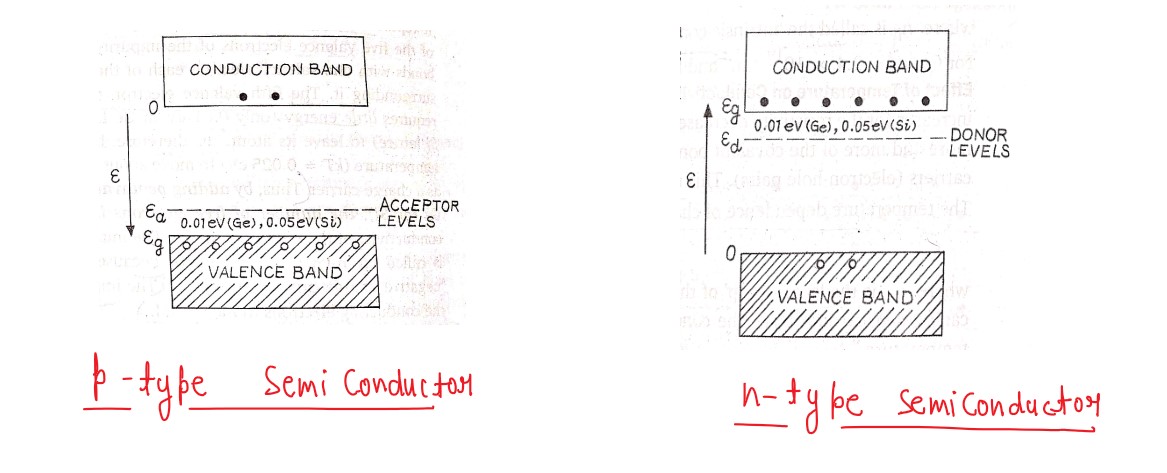
How are energy bands in solids formed? Explain, by drawing energy band diagrams, conduction in n-type
and p-type semiconductors.
Solution
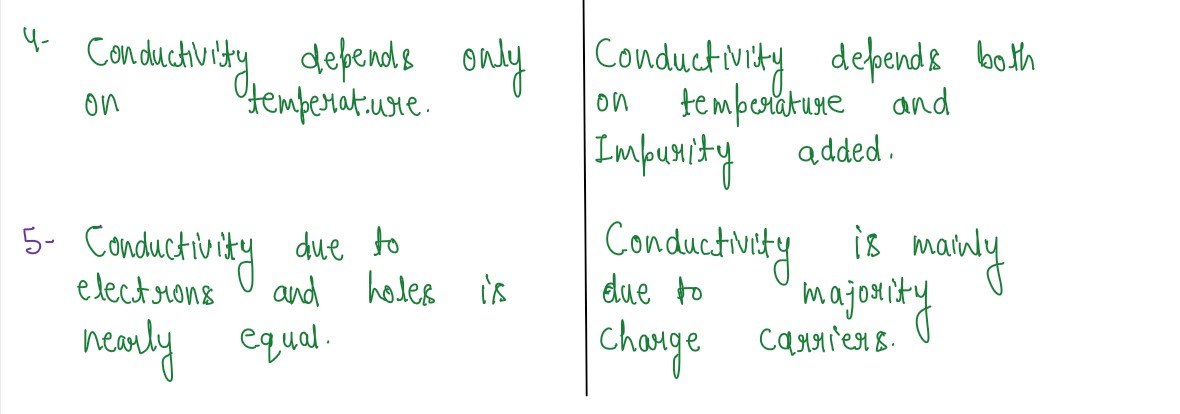
Q8
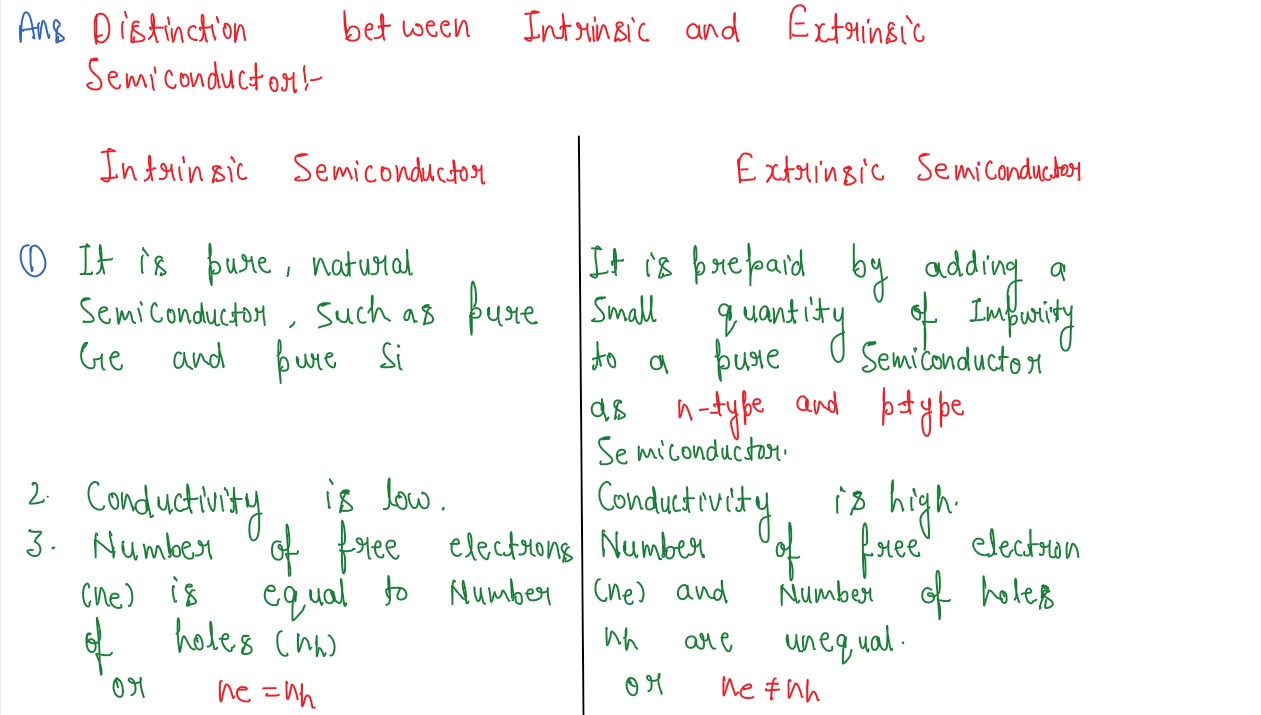
Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
Solution
Q9
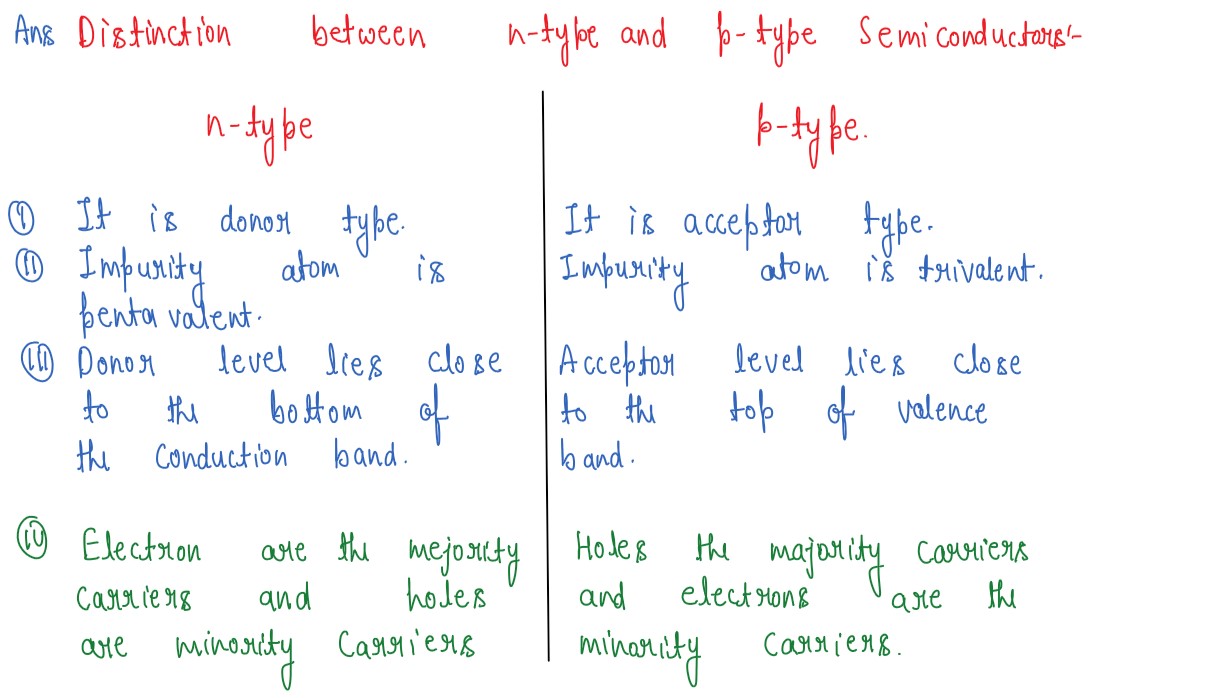
Distinguish between p-type and n-type semiconductors.
Solution
Q10
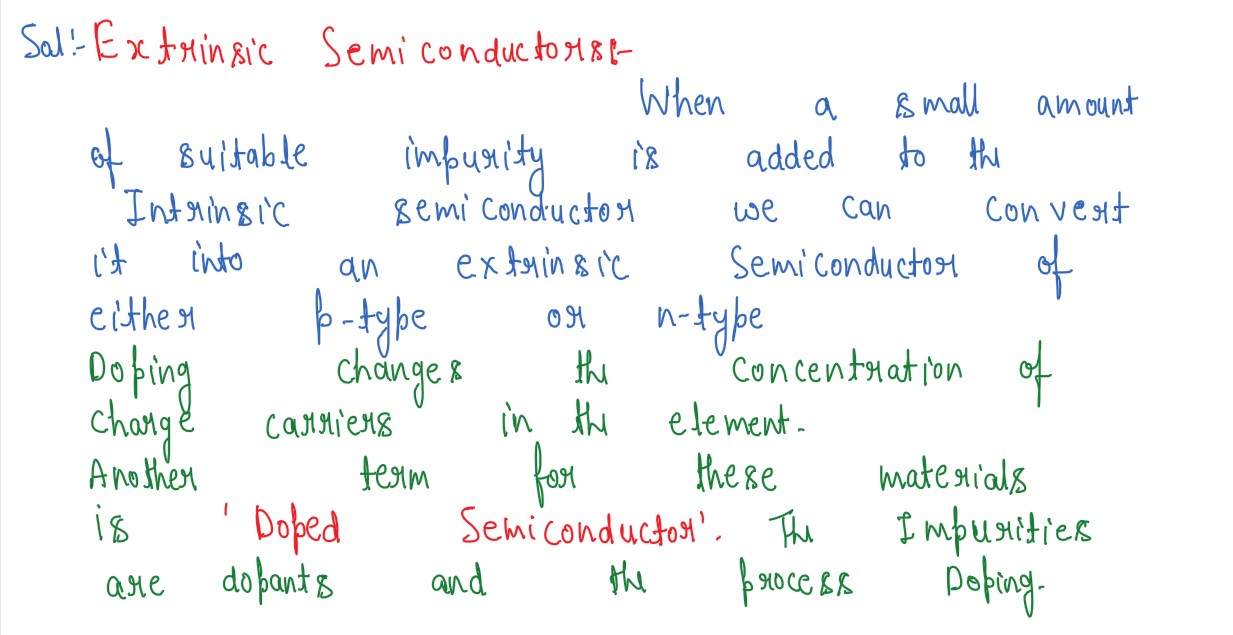
Explain briefly what what is meant by extrinsic semiconductors, including the terms donor and acceptor
impurities as well as p-type and n-type semiconductors.
Solution
Q11
Using the concept of electron and hole currents, derive expression for the conductivity of
a semiconductor.
Solution