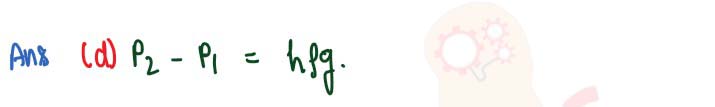Q1
Define the term thrust. State its S.I. unit.
solutions
solutions

Q2
What is meant by pressure? State its S.I. unit.
solutions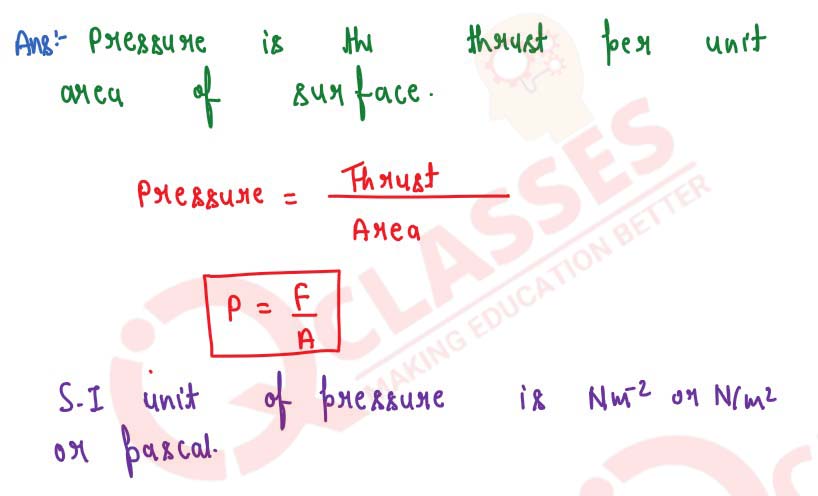
solutions

Q3
(a) What physical quantity is measured in bar?
(b) How is the unit bar related to the S.I. unit pascal?
solutions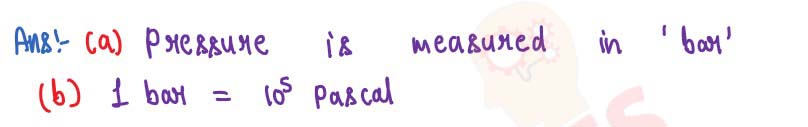
(b) How is the unit bar related to the S.I. unit pascal?
solutions
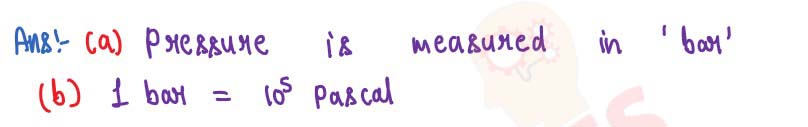
Q4
Define one pascal (Pa), the S.I. unit of pressure.
solutions
solutions

Q5
State whether thrust is a scalar or vector?
solutions
solutions

Q6
State whether pressure is a scalar or vector?
solutions
solutions

Q7
Differentiate between thrust and pressure.
solutions
solutions

Q8
How does the pressure exerted by a thrust depend on the area of surface on which it acts?
Explain with a suitable example.
solutions
solutions

Q9
Why is the tip of an allpin made sharp?
solutions
solutions

Q10
Explain the following:
(a) It is easier to cut with a sharp knife than with a blunt one.
(b) Sleepers are laid below the rails
solutions
(a) It is easier to cut with a sharp knife than with a blunt one.
(b) Sleepers are laid below the rails
solutions

Q11
What is a fluid?
solutions
solutions

Q12
What do you mean by the term fluid pressure?
solutions
solutions

Q13
How does the pressure exerted by a solid and a fluid differ?
solutions
solutions

Q14
Describe a simple experiment to demonstrate that a liquid enclosed in a vessel exerts pressure
in all directions
solutions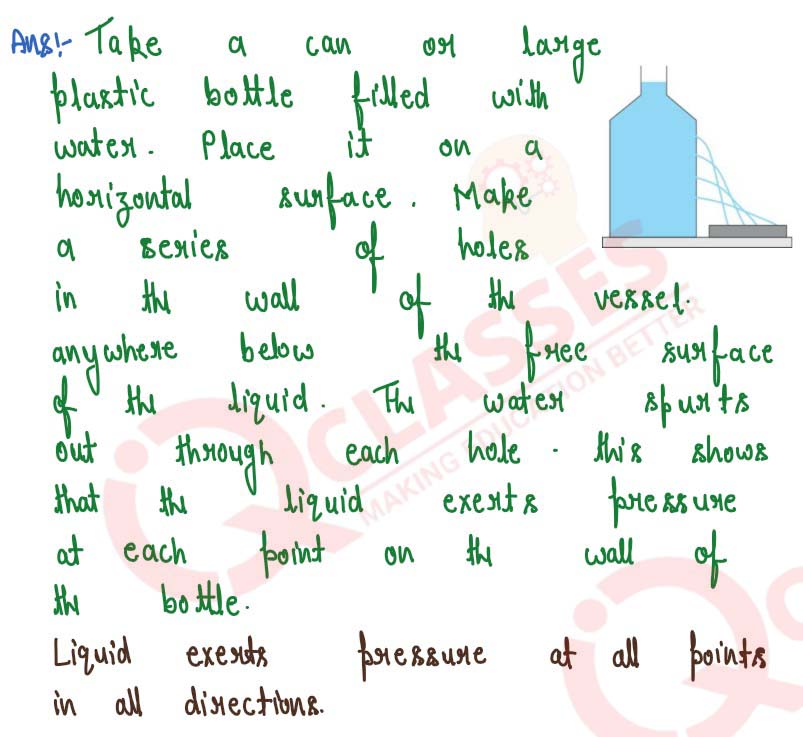
solutions

Q15
State three factors on which the pressure at a point in a liquid depends.
solutions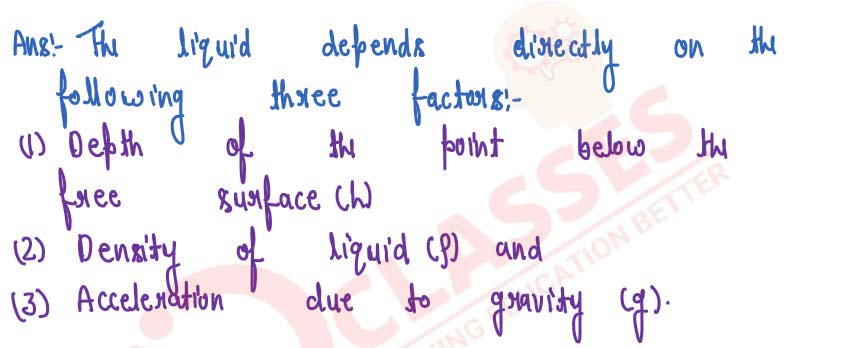
solutions

Q16
Write an expression for the pressure at a point inside a liquid. Explain the meaning of the
symbols used.
solutions
solutions

Q17
Deduce an expression for the pressure at a depth inside a liquid.
solutions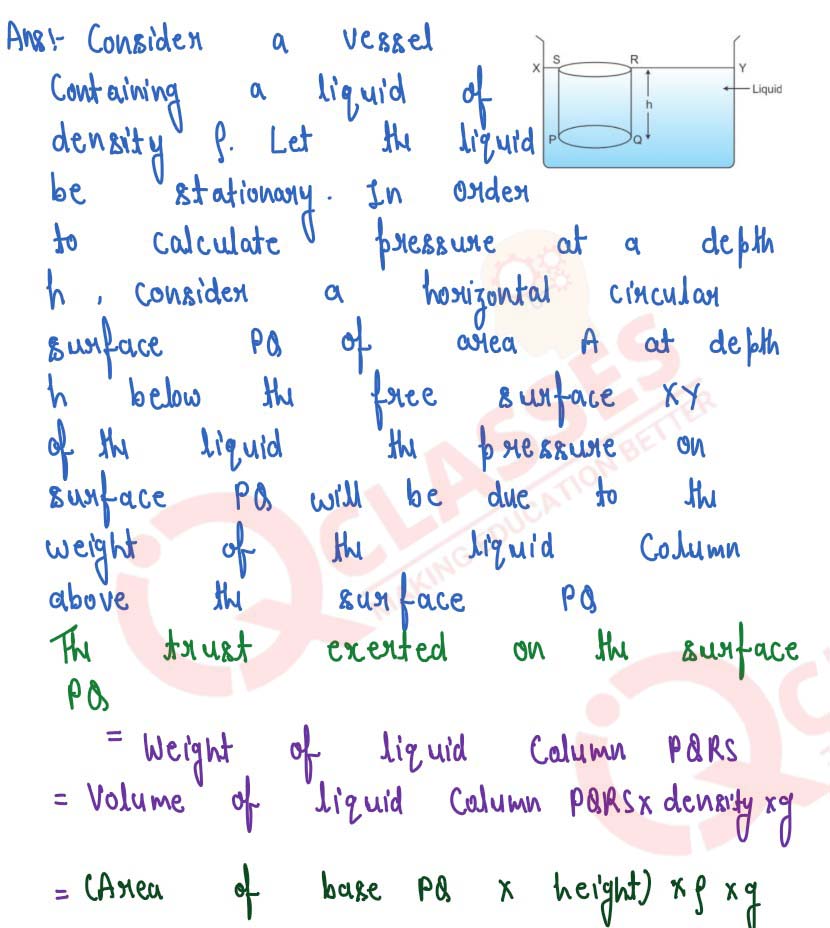
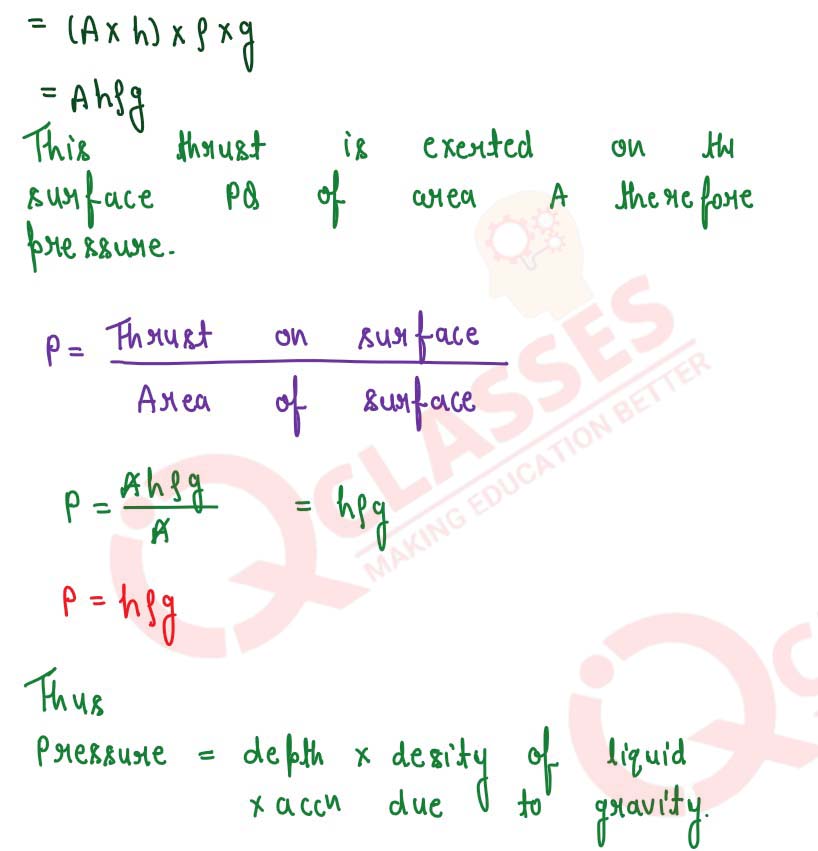
solutions


Q18
How does the pressure at a certain depth in sea water differ from that at the same depth in
river water? Explain your answer.
solutions
solutions

Q19
Pressure at free surface of a water lake is P1, while at a point at depth h below its free surface
is P2. (a) How are P1 and P2 related? (b) Which is more P1 or P2?
solutions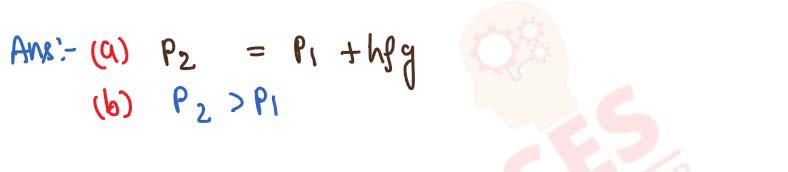
solutions
Q20
Explain why a gas bubble released at the bottom of a lake grows in size as it rises to the surface
of lake.
solutions
solutions

Q21
A dam has broader walls at the bottom than at the top. Explain.
solutions
solutions

Q22
Why do sea divers need special protective suit?
solutions
solutions

Q23
State the laws of liquid pressure.
solutions
solutions

Q24
A tall vertical cylinder filled with water is kept on a horizontal table top. Two small holes A
and B are made on the wall of the cylinder, A near the middle and B just below the free
surface of water. State and explain your observation.
solutions
solutions

Q25
How does the liquid pressure on a diver change if:
(i) The diver moves to the greater depth, and
(ii) The diver moves horizontally?
solutions
(i) The diver moves to the greater depth, and
(ii) The diver moves horizontally?
solutions

Q26
State Pascal’s law of transmission of pressure.
solutions
solutions

Q27
Name two applications of Pascal’s law.
solutions
solutions

Q28
Explain the principle of a hydraulic machine. Name two devices which work on this principle.
solutions
solutions

Q29
Name and state the principle on which a hydraulic press works. Write one use of the hydraulic
press.
solutions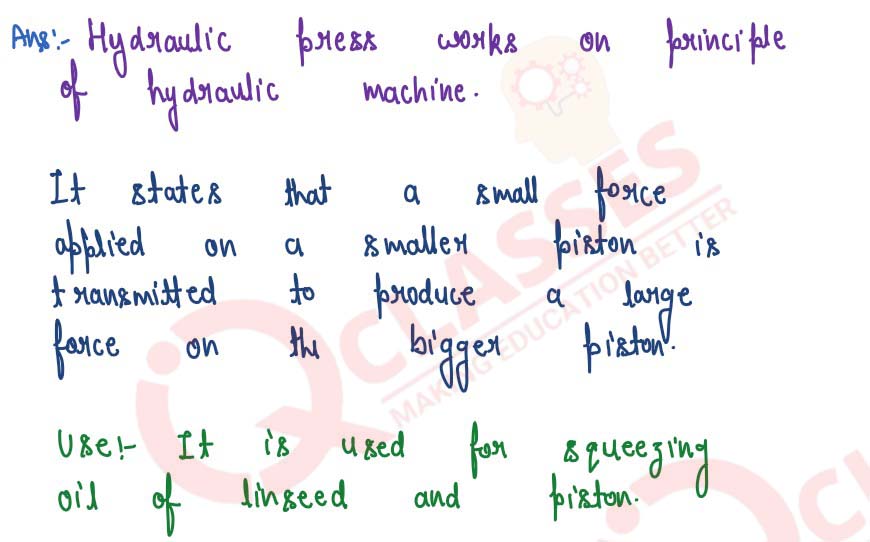
solutions

Q30
The diagram in figure shows a device which makes use of the principle of transmission of
pressure.
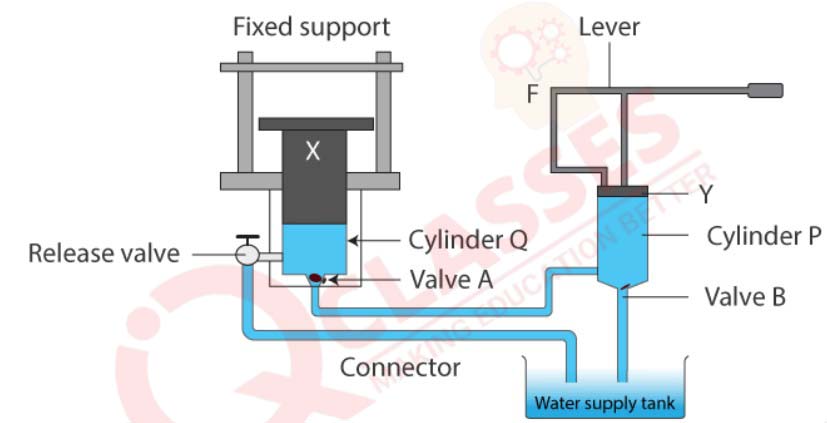
(i) Name the parts labelled by the letters X and Y.
(ii) Describe what happens to the valves A and B and to the quantity of water in the two cylinders when the lever arm is moved down.
(iii) Give reasons for what happens to the valves A and B in part (ii).
(iv) What happens when the release valve is opened?
(v) What happens to the valve B in cylinder P when the lever arm is moved up?
(vi) Give a reason for your answer in part (v)
(vii) State one use of the above device.
solutions


(i) Name the parts labelled by the letters X and Y.
(ii) Describe what happens to the valves A and B and to the quantity of water in the two cylinders when the lever arm is moved down.
(iii) Give reasons for what happens to the valves A and B in part (ii).
(iv) What happens when the release valve is opened?
(v) What happens to the valve B in cylinder P when the lever arm is moved up?
(vi) Give a reason for your answer in part (v)
(vii) State one use of the above device.
solutions


Q31
Draw a simple diagram of a hydraulic jack and explain its working.
solutions

solutions


Q32
Explain the working of a hydraulic brake with a simple labelled diagram.
solutions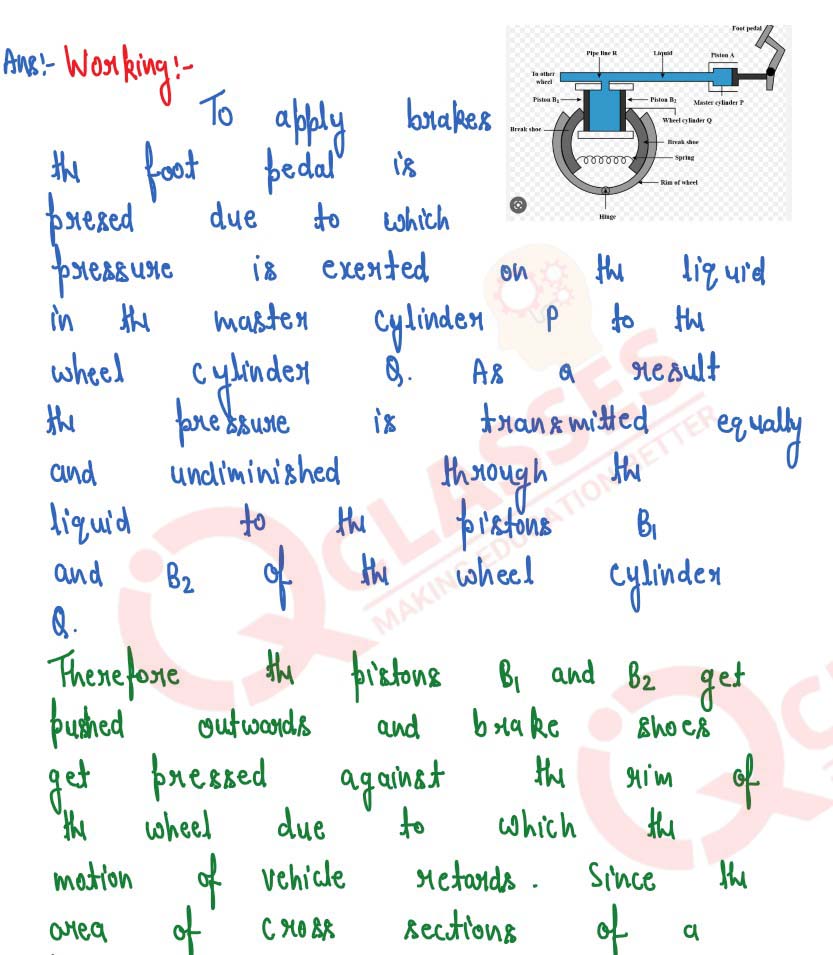

solutions


Q33
Complete the following sentences:
(a) Pressure at a depth h in a liquid of density ρ is ___________
(b) Pressure is ________ in all directions about a point in a liquid
(c) Pressure at all points at the same depth is _________
(d) Pressure at a point inside a liquid is __________ to its depth.
(e) Pressure of a liquid at a given depth is _______ to the density of liquid.
solutions
(a) Pressure at a depth h in a liquid of density ρ is ___________
(b) Pressure is ________ in all directions about a point in a liquid
(c) Pressure at all points at the same depth is _________
(d) Pressure at a point inside a liquid is __________ to its depth.
(e) Pressure of a liquid at a given depth is _______ to the density of liquid.
solutions

Multiple Choice type Questions
:
Q1
The S.I. unit of pressure is:
(a) N cm-2
(b) Pa
(c) N
(d) N m2
solutions
(a) N cm-2
(b) Pa
(c) N
(d) N m2
solutions

Q2
The pressure inside a liquid of density ρ at a depth h is:
(a) h ρ g
(b) h/ ρ g
(c) h ρ/ g
(d) h ρ
solutions
(a) h ρ g
(b) h/ ρ g
(c) h ρ/ g
(d) h ρ
solutions

Q3
The pressure P1 at a certain depth in river water and P2 at the same depth in sea water are
related as:
(a) P1 > P2
(b) P1 = P2
(c) P1 < P2
(d) P1 - P2 = atmospheric pressure
solutions
(a) P1 > P2
(b) P1 = P2
(c) P1 < P2
(d) P1 - P2 = atmospheric pressure
solutions

Q4
The pressure P1 at the top of a dam and P2 at a depth h from the top inside water
(density ρ) are related as:
(a) P1 > P2
(b) P1 = P2
(c) P1 - P2 = h ρ g
(d) P2 – P1 = h ρ g
solutions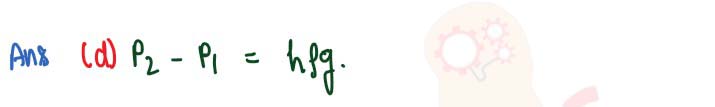
(a) P1 > P2
(b) P1 = P2
(c) P1 - P2 = h ρ g
(d) P2 – P1 = h ρ g
solutions