All questions are compulsory.
The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
Section–A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section–B has 5 questions of 2 marks each;
Section– C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section– D has 2 case-based questions of 4
marks each; and Section–E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some
questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn
Section-A
Question 1
Select the pathogen mismatched with the symptoms of disease caused by it
from the list given below:
(a) Entamoeba histolytica : Constipation, abdominal pain.
(b) Epidermophyton : Dry scaly lesions on nail.
(c)
Wuchereria bancrofti : Chronic inflammation of lymphatic vessels of
lower limb.
(d) Haemophilus influenzae: Blockage of the intestinal passage.
Solution
View Solution
Question 2
Important attributes belonging to a population but not to an individual are:
(i) Birth rate and death rate
(ii) Male and female
(iii) Birth and death
(iv) Sex-ratio
Select the correct option from the given options :
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Solution
View Solution
Question 3
Many copepods live on the body surface of marine fish. This relationship is
an example of:
(a) Commensalism
(b) Parasitism
(c) Amensalism
(d) Mutalism
Solution
View Solution
Question 4
Given below is the restriction site of a restriction endonuclease Pst-I and the
cleavage sites on a DNA molecule.

Solution
View Solution
Question 5
Given below is a sequence of bases in mRNA of a bacterial cell. Identify the
amino acid that would be incorporated at codon position 3 and codon position
5 during the process of its translation.
3' AUCAGGUUUGUGAUGGUACGA 5'
(a) Phenylalanine, Methionine
(b) Cysteine, Glycine
(c) Alanine, Proline
(d) Serine, Valine
Solution
View Solution
Question 6
Given below are structural details of a human mammary gland:
(i) The glandular tissue in the breast has 15-20 clusters of cells called
alveoli.
(ii) The milk is stored in the lumen of alveoli.
(iii) The alveoli join to form the mammary ducts.
(iv) Mammary ampulla is connected to lactiferous ducts.
Choose the option that gives the correct detail of human mammary gland.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Solution
View Solution
Question 7
Given below are the list of the commercially important products and their
source organisms. Select the option that gives the correct matches.

Solution
View Solution
Question 8
Tetanus antitoxin (Tetanus toxoid) when injected into the human body it
immediately provides :
(a) Innate immunity
(c) Auto immunity
(b) Passive immunity
(d) Active immunity
Solution
View Solution
Question 9
The primary productivity in an ecosystem is expressed as :
(a) gm-2 yr-1
(b) gm-2 yr
(c) K cal m2 yr-1
(d) K cal m-²
Solution
View Solution
Question 10
Select the option that shows the correctly identified 'U', 'X', Y and ‘Z' in a
developing dicot embryo.
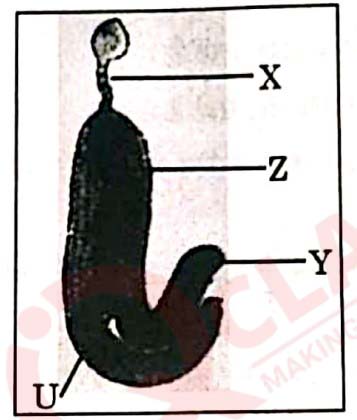
(a) X Plumule (2n), Y Suspensor (n), Z - Cotyledon (2n), U- Radicle
(2n).
(b)
X-Plumule (2n), Y- Suspensor (2n), Z - Radicle (2n), U - Cotyledon
(2n).
(c) X Suspensor (2n), Y- Cotyledon (2n), Z - Radicle (2n), U- Plumule
(2n).
(d) X-Cotyledon (2n), Y - Radicle (n), Z - Plumule (n), U- Suspensor (n).
Solution
View Solution
Question 11
The sixth extinction in progress currently is different from all previous
extinctions on earth as it is :
(a) 10-100 times faster
(c) 100-10000 times faster
(b) 100-1000 times faster
(d) 1000-10000 times faster
Solution
View Solution
Question 12
At which stage during evolution did human use hides to protect their bodies
and buried their dend?
(n) Homo habilis
(b) Neanderthal man
(c) Java man
(d) Homo erectus
Solution
View Solution
Question Nos. 13 to 16 consists of two statements Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 13
Assertion (A): Decomposition process is slower if detritus is rich in lignin
and cutin.
Reason (R): Decomposition is largely an oxygen requiring process.
Solution
View Solution
Question 14
Assertion (A): Determining the sex of an unborn child followed by MTP is
an illegal practice.
Reason (R): Amniocentesis is a practice to test the presence of genetic
disorders also.
Solution
View Solution
Question 15
Assertion (A): In Thalassemia an abnormal myoglobin chain is synthesized
due to a gene defect.
Reason (R): α-Thalassemia is controlled by genes HBA1 and HBA2 on
chromosome 16
Solution
View Solution
Question 16
Assertion (A): Synthetic oligonucleotide polymers are used during
Annealing in a PCR.
Reason (R): The primers bind to the double stranded DNA at their
complementary regions.
Solution
View Solution
SECTION-B
Question 17
(a) Name (i) a GM cereal crop having enhanced nutritional value, (ii) the
nutrient it is rich in.
(b)
State any two benefits of Genetically modified crops.
Solution
View Solution
Question 18
By using Punnett square depict the genotypes and phenotypes of test crosses
(where green pod colour (G) is dominant over yellow pod colour (g)) in Garden
pea with unknown genotype.
Solution
View Solution
Question 19
(a)
Certain specific bacterial spores are mixed in water and sprayed over
Brassica crop to control butterfly catterpillars.
Name this bacterium and its mode of action on the butterfly catterpillars.
OR
(b) Immunotherapy these days is one of the most efficient way of treatment
of cancer. The therapy involved activates the immune system and
destroys the tumour.
Primordial follicles/ovary
(i) Write an example of one such biological response modifier used in
immunotherapy.
(ii)
Why do patients need such substances if immune system is already
working in body?
(iii) State what is 'Contact inhibition'.
Solution
View Solution
Question 20
The graph given below shows the number of primordial follicles per ovary in
women at different ages. Study the graph and answer the questions that
follow.
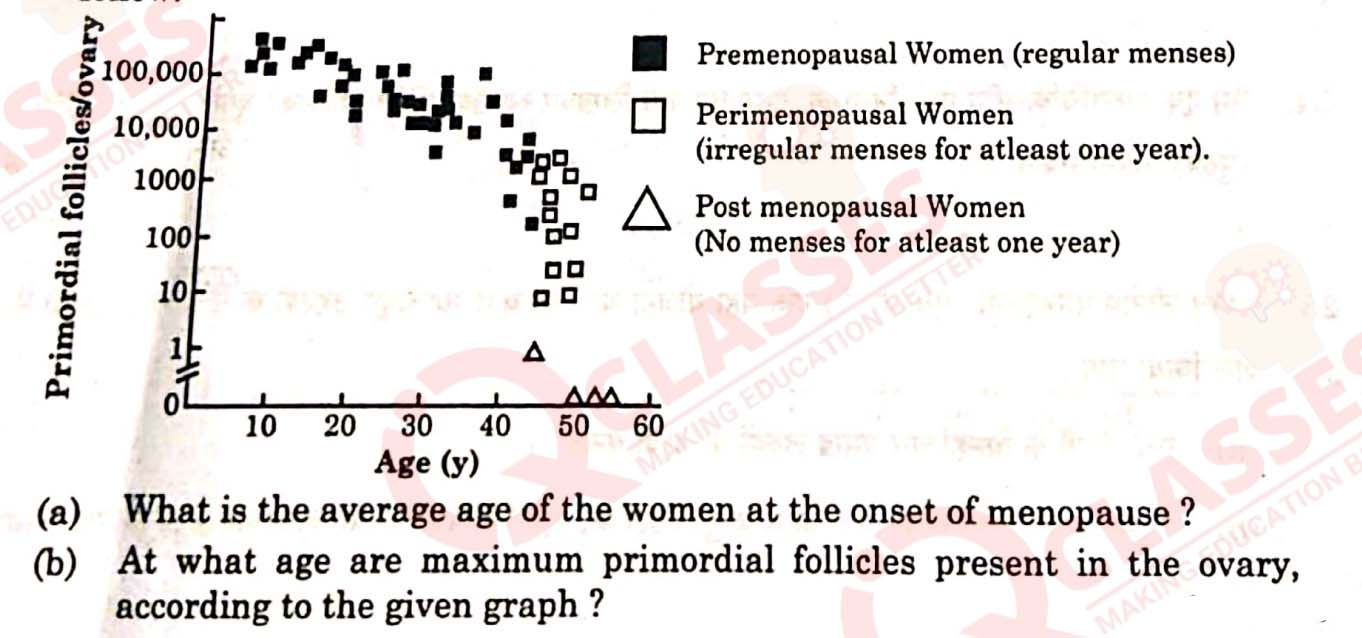
Solution
View Solution
Question 21
"Some species of insects and frogs have evolved with various specific features
that help them from being detected."
(a) Justify the statement giving reasons.
(b)
Mention any two such features.
Solution
View Solution
SECTION-C
Question 22
(a) "Plasmodium protozoan needs both a mosquito and a human host for its
continuity." Explain.
OR
(b) We all must work towards maintaining good health because 'health is
wealth'. Enlist any six ways of achieving good health.
Solution
View Solution
Question 23
"Biodiversity plays a major role in many ecosystem services that nature
provides."
(a) Describe any two broadly utilatarian arguments to justify the given
statement.
(b) State one ethical reason of conserving biodiversity.
Solution
View Solution
Question 24
Name and explain a surgical contraceptive method that can be adopted by
the male partner of a couple.
Solution
View Solution
Question 25
Human Genome Project (HGP) was a mega project launched in the year 1990
with some important goals.
(a) Enlist any four prime goals of HGP.
(b) Name any one common non-human animal model organism which has
also been sequenced thereafter.
Solution
View Solution
Question 26
One of the major approaches of crop improvement programme is Artificial
Hybridisation. Explain the steps involved in making sure that only the
desired pollen grain pollinate the stigma of a bisexual flower by a plant
breeder.
Solution
View Solution
Question 27
Mention Darwin's observations made on finches during his visit to Galapagos
Islands. Write the explanation given by Darwin on his observations.
Solution
View Solution
Question 28
"RNA interference has been used to produce transgenic tobacco plants to
protect them from the infestation by specific nematodes." Explain the novel
strategy exploited by the biotechnologists.
Solution
View Solution
SECTION-D
Question 29
When a microorganism invades a host, a definite sequence of events usually
occur leading to infection and disease, causing suffering to the host. This
process is called pathogenesis. Once a microorganism overcomes the defense
system of the host, development of the disease follows a certain sequence of
events as shown in the graph. Study the graph given below for the sequence
of events leading to appearance of a disease and answer the questions that
follow:
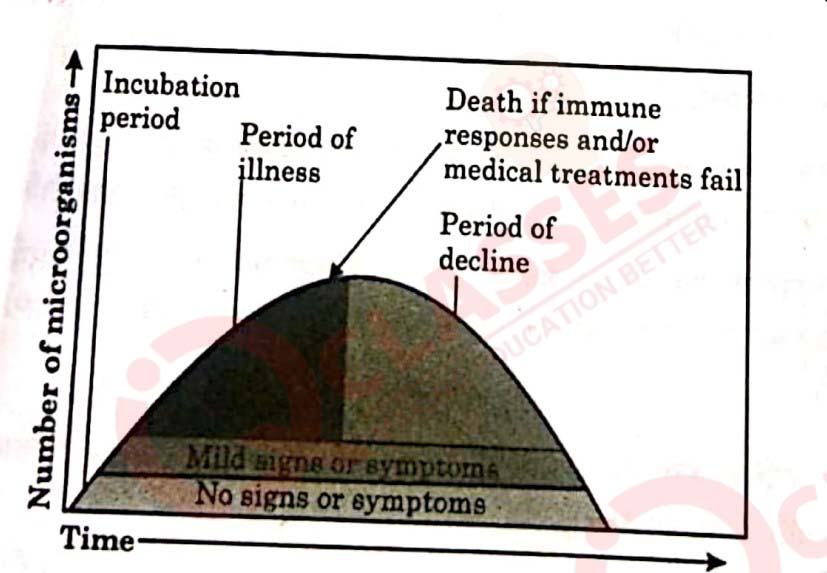
(a) In which period, according to the graph there are maximum chances of a
person transmitting a disease / infection and why?
(b)
Study the graph and write what is an incubation period. Name a
sexually transmitted disease that can be easily transmitted during this
period. Name the specific type of lymphocytes that are attacked by the
pathogen of this disease.
OR
(b) Draw a schematic labelled diagram of an antibody.
(c)
In which period, the number of immune cells forming antibodies will be
the highest in a person suffering from pneumonia ?
Name the immune cells that produce antibodies.
Solution
View Solution
Question 30
The chromosome number is fixed for all normal organisms leading to
species specification whereas any abnormality in the chromosome number of
an organism results into abnormal individuals. For example, in humans 46 is
the fixed number of chromosomes both in male and female. In male it is '44 +
XY and in female it is '44 + XX'. Thus the human male is heterogametic, in
other words produces two different types of gametes one with '22 + X
chromosomes and the other with '22+ Y' chromosomes respectively. Human
female, on the other hand is homogametic i.e. produces only one type of
gamete with '22 + X' chromosomes only.
Sometimes an error may occur during meiosis of cell cycle, where the
sister chromatids fail to segregate called nondisjunction, leading to the
production of abnormal gametes with altered chromosome number. On
fertilisation such gametes develop into abnormal individuals.
(a) State what is aneuploidy.
(b) If during spermatogenesis, the chromatids of sex chromosomes fail to
segregate during meiosis, write only the different types of gametes with
altered chromosome number that could possibly be produced.
(c) A normal human sperm (22+ Y) fertilises an ovum with karyotype '22 +
XX'. Name the disorder the offspring thus produced would suffer from
and write any two symptoms of the disorder.
OR
(c) Name a best known and most common autosomal aneuploid
abnormality in human and write any two symptoms.
Solution
View Solution
SECTION-E
Question 31
How and why is charging of tRNA essential in the process of
translation ?
(ii)
State the function of ribosome as a catalyst in bacteria during the
process of translation.
(iii) Explain the process of binding of ribosomal units to mRNA during
protein synthesis.
OR
(b) Describe the dihybrid cross upto F₂ generation as conducted by Gregor
Mendel using pure lines of Garden Pea for characters seed shape and
seed colour.
Solution
View Solution
Question 32
(a) Bioreactors are the containment vehicles of any biotechnology-based
production process. For large scale production and for economic reasons
the final success of biotechnological process depends on the efficiency of
the bioreactor.
Answer the following questions w.r.t. the given paragraph:
(i) List the operational guidelines that must be adhered to so as to
achieve optimisation of the bioreactor system. Enlist any four.
(ii) Mention the phase of the growth we refer to in the statement
"Optimisation of growth and metabolic activity of the cells".
(iii) Is the biological product formed in the bioreactor suitable for the
intended use immediate ? Give reason in support of your answer.
OR
(b) (i) 'EcoRI' has played very significant role in r-DNA technology.
(I) Explain the convention for naming EcoRI.
(II) Write the recognition site and the cleavage sites of this
restriction endonuclease.
(ii) What are the protruding and hanging stretches of DNA produced
by these restriction enzymes called ? Describe their role in
formation of r-DNA
Solution
View Solution
Question 33
(a) (i) Explain the monosporic development of embryo sac in the ovule of
an angiosperm.
(ii)
Draw a diagram of the mature embryo sac of an angiospermic
ovule and label any four parts in it.
OR
(b) (i) Explain the formation of placenta after the implantation in a
human female.
(ii)
Draw a diagram showing human foetus within the uterus and label
any four parts in it.
Solution
View Solution




