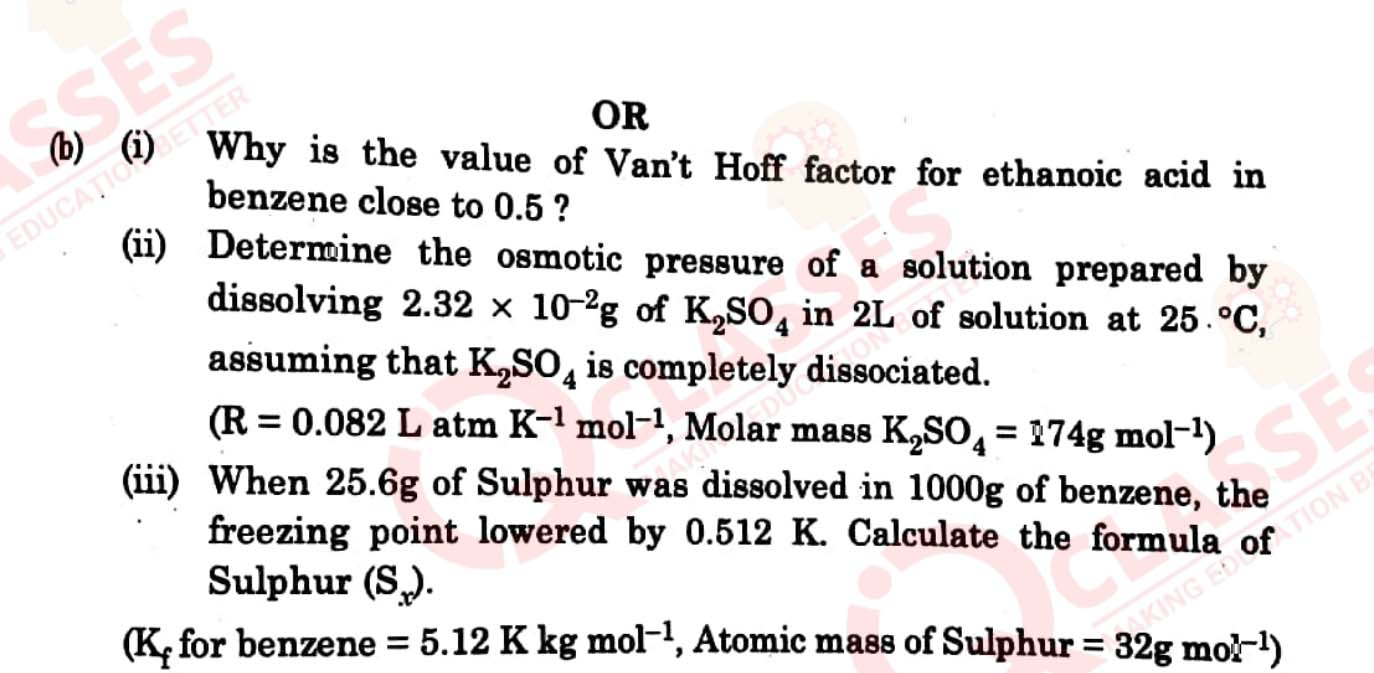
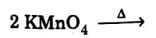There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
SECTION A consists of 18 multiple-choice questions carrying 1 mark each.
SECTION B consists of 7 very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
SECTION C consists of 5 short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
SECTION D consists of 2 case- based questions carrying 4 marks each.
SECTION E consists of 3 long answer questions carrying 5 marks each.
All questions are compulsory.
Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed
Section-A
Question
1
Which one of the following has lowest pK, value ?
(a) CH3-COOH (b) O2N- CH2-COOH
(c) Cl-CH2-COOH. (d) HCOOH
View
Solution
Question 2
Which of the following cell was used in Apollo space programme ?
(a) Mercury cell
(b) Daniel cell
(c) H2—O2 Fuel cell
(d) Dry cell
View
Solution
Question
3
Question
4
Question
5
The magnetic moment of [NiCl4]2-?
(a) 1.82 BM
(b) 2.82 BM
(c) 4.42 BM
(d) 5.46BM
[Atomic number : Ni = 28]
View
Solution
Question 6
Which of the following ions has the electronic configuration 3d6 ?
(Atomic
number : Mn = 25, Co = 27, Ni= 28) :
(a) Ni3+
(b) Co+
(c) Mn2+
(d) Mn3+
View
Solution
Question
7
Which of the following aqueous solution will have highest boiling point ?
(a) 1.0M KCl
(b) 1.0M K2SO4
(c) 2.0M KCl
(d) 2.0M K2SO4
View
Solution
Question
8
A voltaic cell is made by connecting two half cells represented by half
equations below :
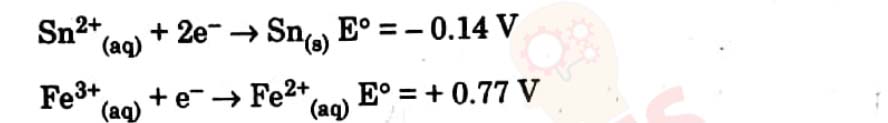
Which statement is correct about this voltaic cell ?
(a) Fe2+ is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is -0.91 V.
(b) Sn is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.91 V.
(c) Fe2+ is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.91 V.
(d) Sn is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.63 V.
View
Solution
Question
9
Amides can be converted into amines by the reaction named
(a) Hoffmann degradation
(b) Ammonolysis
(c) Carbylamine
(d) Diazotisation
View
Solution
Question
10
Which of the following statements is not true about glucose ?
(a) It is an aldohexose.
(b) On heating with HI it forms n-hexane
(c) It is present in pyranose form
(d) it gives 2, 4 DNP test
View
Solution
Question
11
Which of the following alcohols will not undergo oxidation ?
(a) Butanol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
(d) 3-Methylbutan-2-ol
View
Solution
Question
12
Question
13
Which property of transition metals enables them to behave as catalysts ?
(a) High melting point
(b) High ionisation enthalpy
(c) Alloy formation
(d) Variable oxidation states
View
Solution
Question
14
Which of the following would not be a good choice for reducing
nitrobenzene to aniline ?
(a) LiAlH4
(b) H2/Ni
(c) Fe and HCl
(d) Sn and HCl
View
Solution
Question
15
Given below are two Statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of
(A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Assertion (A) : Vitamin C cannot be stored in our body.
Reason (R) : Vitamin C is fat soluble and is excreted from the body in
urine,
View
Solution
Question
16
Assertion (A) : The half life of & reaction is the time in which the
concentration of the reactant is reduced to one half of its initial
concentration.
Reason (R) : In first order kinetics when concentration of reactant is
doubled, its half life is doubled.
View
Solution
Question
17
Assertion (A) : Bromination of benzoic acid gives m-bromobenzoic acid.
Reason (R) : Carboxyl group increases the electron density at the meta
position.
View
Solution
Question
18
Assertion (A) : EDTA is a hexadentate ligand.
Reason (R) : EDTA has 2 nitrogen and 4 oxygen donor atoms.
View
Solution
SECTION-B
Question
19
(a) Which of the following species cannot act as a ligand ? Give reason.
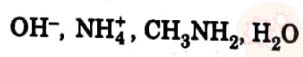
(b) The complex 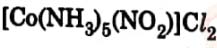 is red in colour. Give
IUPAC name
of its linkage isomer.
is red in colour. Give
IUPAC name
of its linkage isomer.
View
Solution
Question
20
For the pair phenol and cyclohexanol, answer the following :
(a) Why is phenol more acidic than cyclohexanol ?
(b) Give one chemical test to distinguish between the two.
View
Solution
Question
21
(a) (i) Draw the zwitter ion structure for sulphanilic acid.
(ii) How can the activating effect of -NH2 group in aniline be
controlled ?

View
Solution
Question
22
Write equations for the following :
(a) Oxidation of chloroform by air and light
(b) Reaction of chlorobenzene with CH3Cl / anhyd. AlCl3
View
Solution
Question
23
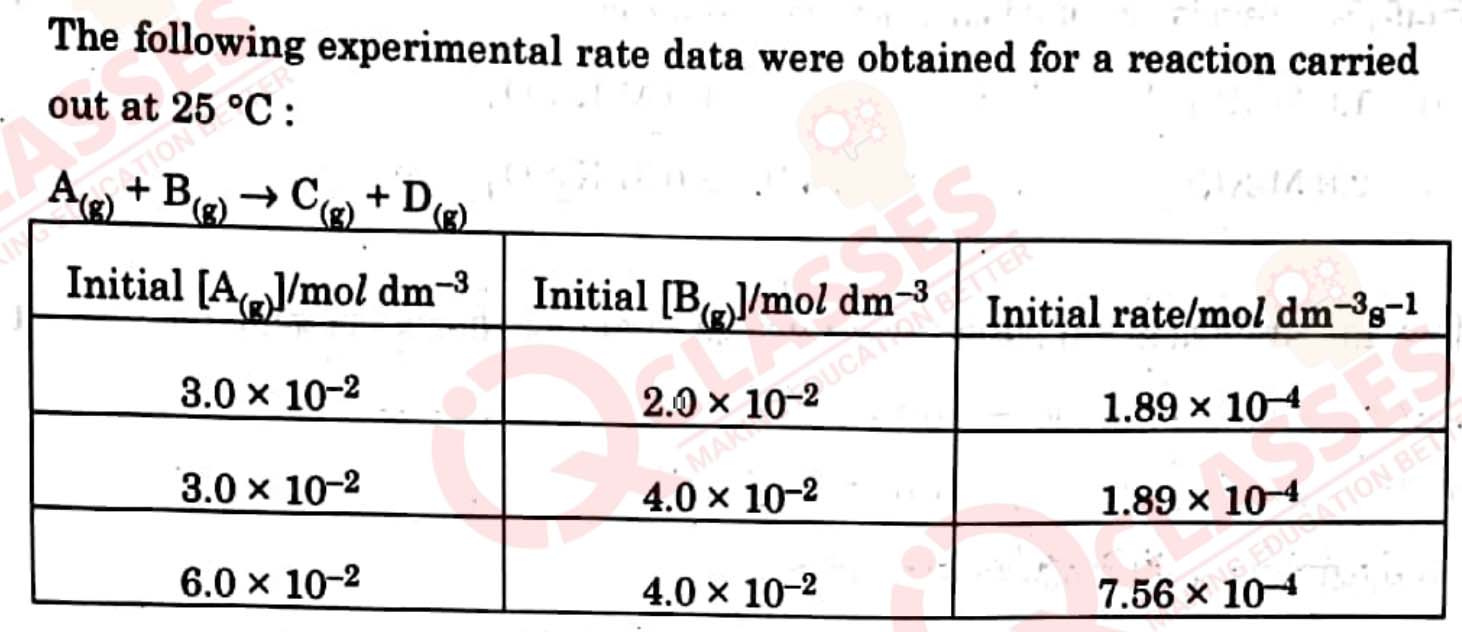
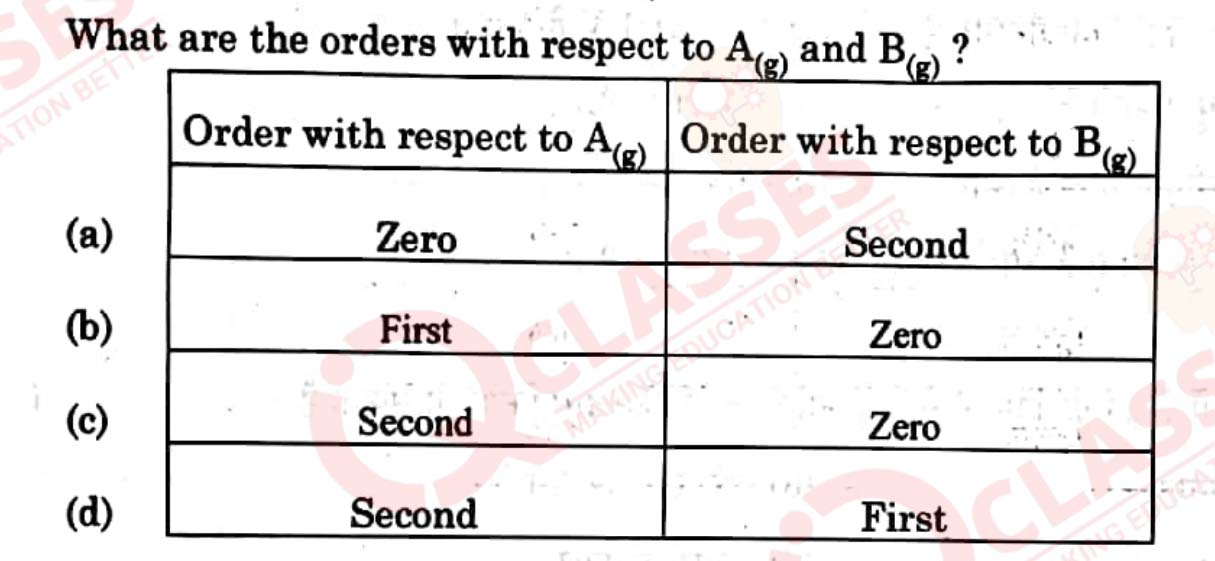
What happens to the rate constant k and activation energy Ea as the
temperature of a chemical reaction is increased ? Justify.
View
Solution
Question
24
(a) (i) What should be the signs (positive/negative) for E°cell and △G°
for a spontaneous redox reaction occurring under standard conditions ?
(ii) State Faraday’s first law of electrolysis.
OR

View
Solution
Question
25
Give the reaction of glucose with acetic anhydride. Presence of which
group is confirmed by this reaction ?
View
Solution
SECTION-C
Question
26
(a) (i) Why is the C-O bond length in phenols less than that in methanol ?
(ii) Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling point : Ethoxyethane, Butanal, Butanol,
n-butane
(iii) How can phenol be prepared from anisole ? Give reaction.

View
Solution
Question
27
(a) On the basis of crystal field theory write the electronic configuration
for d® ion with a weak ligand for which △o
< P.
(b) Explain [Fe(CN)6]3- is an inner orbital complex whereas
[FeF6]3- is an outer orbital complex.
[Atomic number : Fe = 26]
View
Solution
Question
28
Give reasons for any 8 of the following observations :
(a) Penta-acetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
(b) Amino acids behave like salts.
(c) Water soluble vitamins must be taken regularly in diet.
(d) The two strands in DNA are complimentary to each other.
View
Solution
Question
29
Question
30
(a) Illustrate Sandmeyer’s reaction with an equation.
(b) Explain, why (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in
aqueous
solution.
View
Solution
SECTION-D
Question
31
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage
carefully and answer the questions that follow :
Rahul set-up an experiment to find resistance of aqueous KCl solution for
different concentrations at 298 K using a conductivity cell connected to a
Wheatstone bridge. He fed the Wheatstone bridge with a.c. power in the
audio frequency range 550 to 5000 cycles per second. Once the resistance
was calculated from null point he also calculated the conductivity K
and molar conductivity ^m and recorded his readings in tabular form.
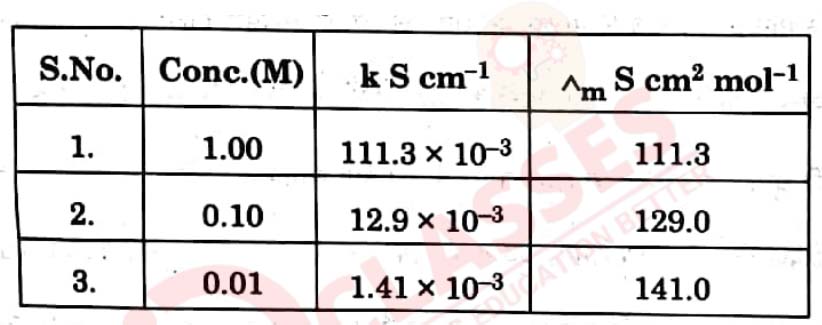

View
Solution
Question
32
Nucleophilic Substitution reaction of haloalkane can be conducted
according to both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. SN1 is a two step reaction
while SN2 is a single step reaction. For any haloalkane which mechanism
is followed depends on factors such as structure of haloalkane, properties
of leaving group, nucleophilic reagent and solvent.
Influences of solvent polarity : In SN1 reaction, the polarity of the system
increases from the reactant to the transition state, because a polar solvent
has a greater effect on the transition state than the reactant, thereby
reducing activation energy and accelerating the reaction. In SN2 reaction, -
the polarity of the system generally does not change from the reactant to
the transition state and only charge dispersion occurs. At this time, polar
solvent has a great stabilizing effect on Nu than the transition state,
thereby increasing activation energy and slow down the reaction rate. For
example, the decomposition rate (SN1) of tertiary chlorobutane at 25 °C in
water (dielectric constant 79) is 300000 times faster than in ethanol
(dielectric constant 24). The reaction rate (SN2) of 2-Bromopropane and
NaOH in ethanol containing 40% water is twice slower than in absolute
ethanol. Hence the level of solvent polarity has influence on both N,1 and
SN2 reaction, but with different results. Generally speaking weak polar
solvent is favourable for SN2 reaction, while strong polar solvent is
favourable for SN1. Generally speaking the substitution reaction of
tertiary haloalkane is based on SN1 mechanism in solvents with a strong
polarity (for example ethanol containing water).
Answer the following questions :
(a) Why racemisation occurs in SN1?
(b) Why is ethanol less polar than water ?
(c) Which one of the following in each pair is more reactive towards SN2
reaction ?
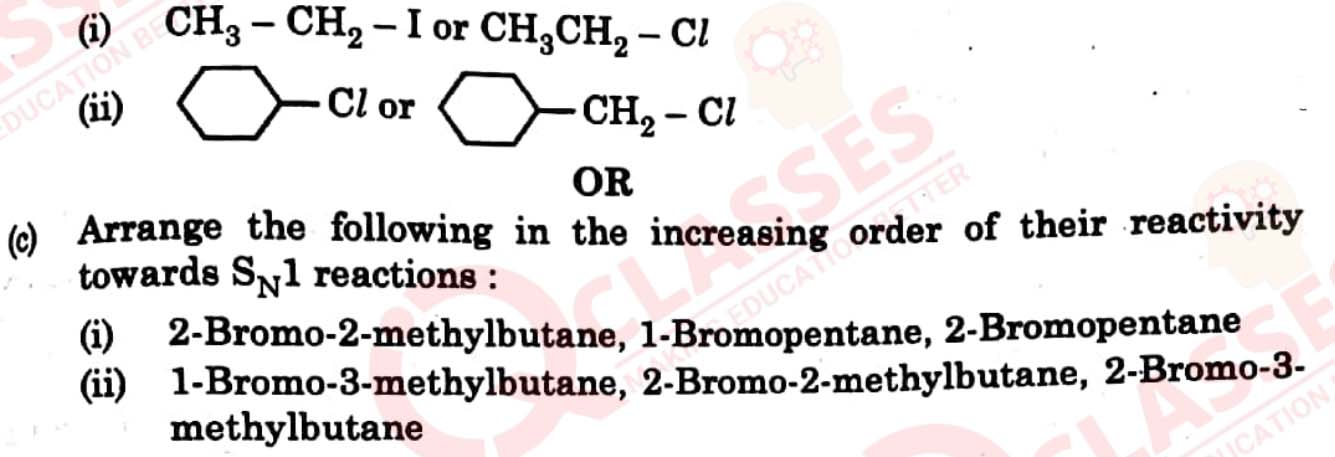
View
Solution
SECTION-E
Question
33
(a) (i)Write the reaction involved in Cannizaro’s reaction.
(ii) Why are the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones lower than
that of corresponding carboxylic acids ?
(iii) An organic compound 'A' with molecular formula C5H8O2 is
reduced to n-pentane with hydrazine followed by heating with
NaOH and Glycol. ‘a’ forms a dioxime with hydroxylamine and
gives a positive Iodoform and Tollen’s test. Identify ‘A’ and give
its reaction for Iodoform and Tollen’s test.
OR

View
Solution
Question
34
Question
35
(a) A transition element X has electronic configuration [Ar] 4s2
3d3.
Predict its likely oxidation states.
(b) Complete the reaction mentioning all the products formed :
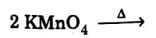
(c) Account for the following :
(i) In the 3d transition series, zinc has the lowest enthalpy of
atomisation.
(ii) Cu+ ion 1s unstable in aqueous solution.
(iii) Actinoids show more number of oxidation states than
lanthanoids.
View
Solution

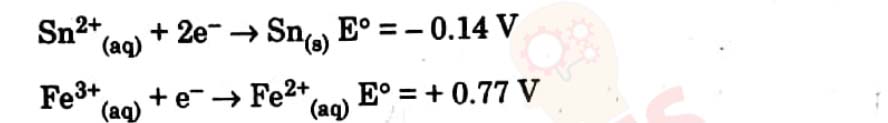

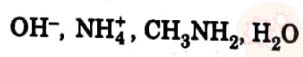
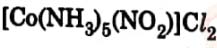 is red in colour. Give
IUPAC name
of its linkage isomer.
is red in colour. Give
IUPAC name
of its linkage isomer.