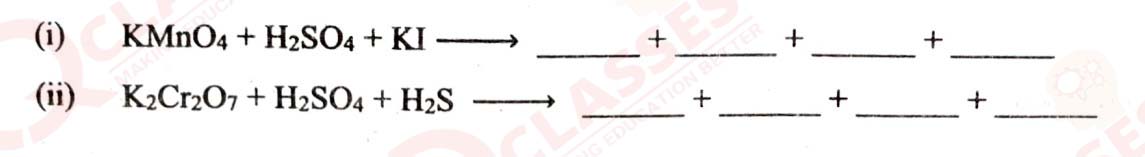
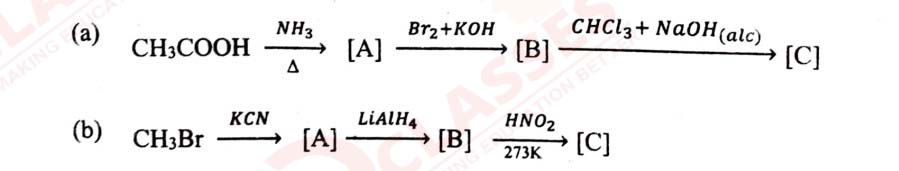
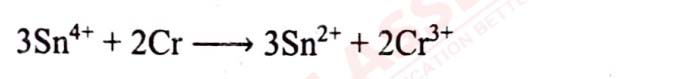Class 12 ISC Chemistry Question Paper 2023
Maximum Marks: 70
Time Allowed: Three hours
(Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper.
They must NOT start writing during this time).
This paper is divided into four sections – A, B, C and D.
Answer all questions.
Section A consists of one question having sub-parts of one mark each.
Section B consists of seven questions of two marks each.
Section C consists of nine questions of three marks each, and
Section D consists of three questions of five marks each
.
Internal choices have been provided in two questions each in Section B,
Section C and Section D.
The intended marks for questions are given in brackets [ ].
All working, including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as and
adjacent to the rest of the answer.
Answers to sub parts of the same question must be given in one place only.
A list of useful physical constants is given at the end of this paper.
A simple scientific calculator without a programmable memory may be used for
calculations.