Class 12 Chemistry CBSE Solutions Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 chemistry important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter solutions. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on CBSE board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 chemistry syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
2020
Q1
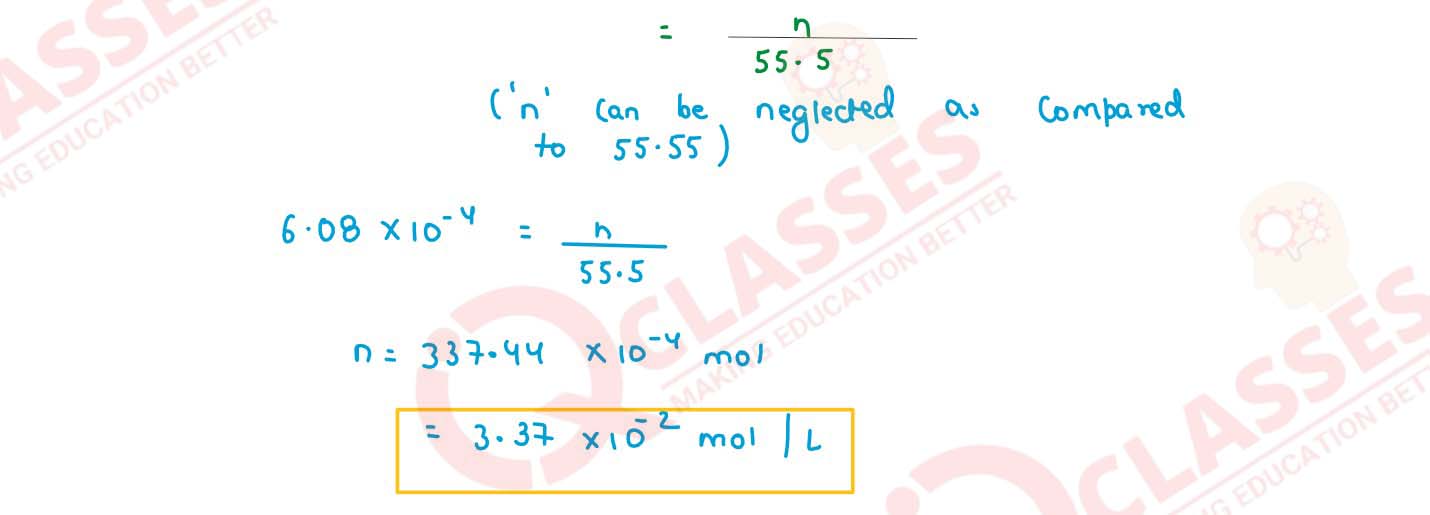
The freezing point of a solution containing 5g of benzoic acid (M = 122 g mol-1) in 35g
of benzene is depressed by 2.94 K. What is the percentage association of benzoic acid if it forms a
dimer in solution ? (Kf for benzene = 4.9 K kg mol-1)
solutions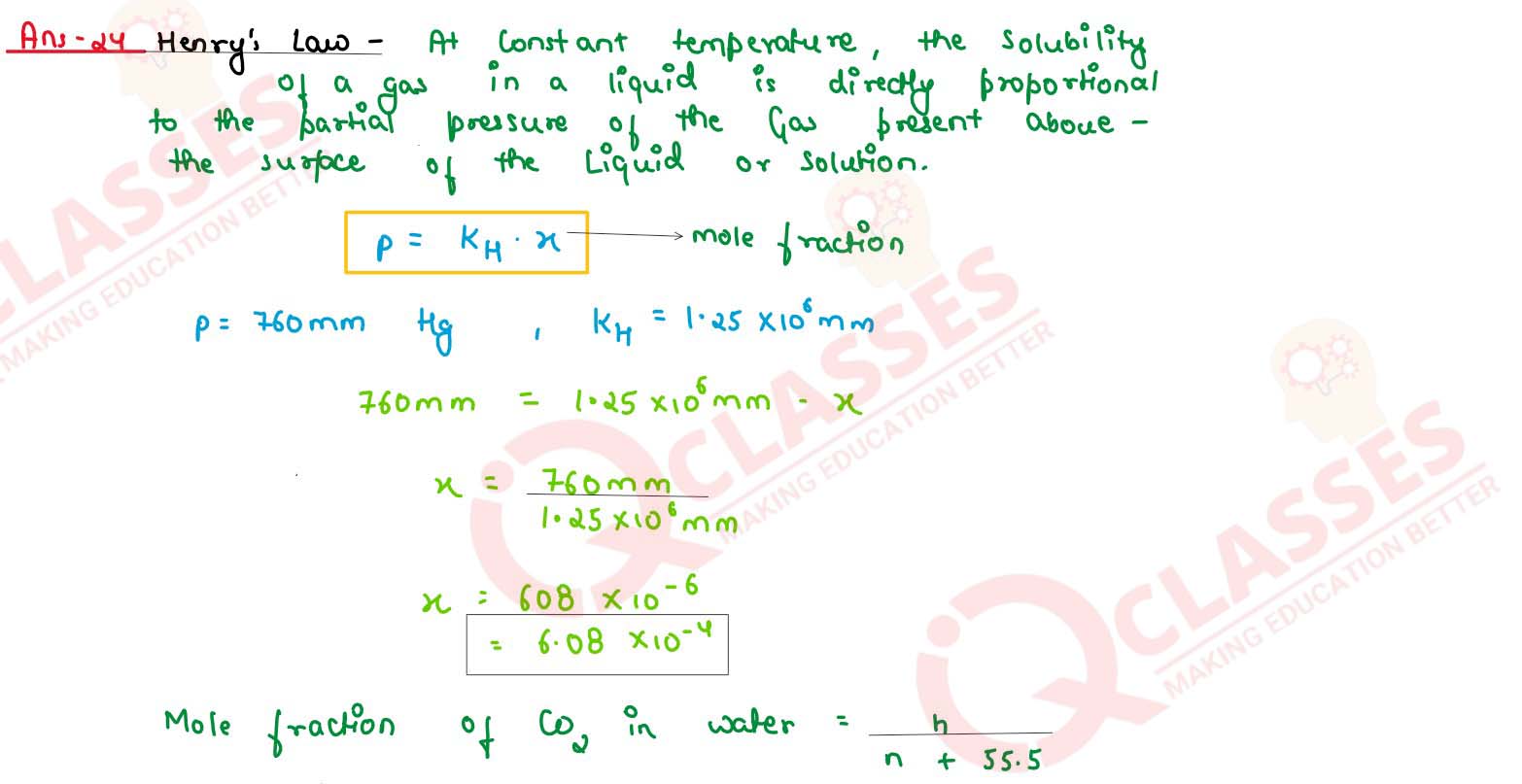
solutions


Q2
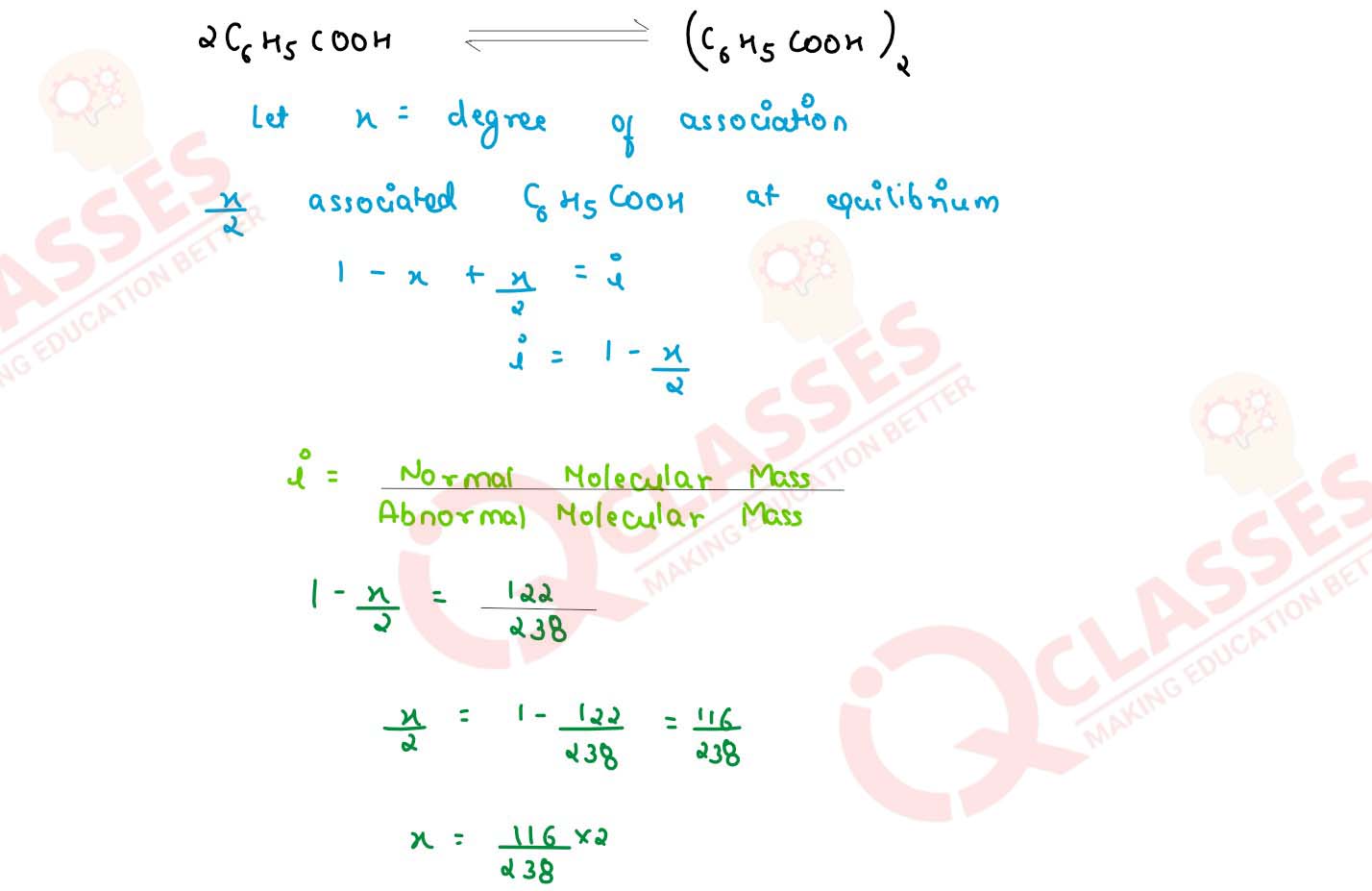
State Henry's law. Calculate the solubility of CO2 in water at 298 K under 760 mm Hg.
(KH for CO2 in water at 298 K is 1.25 x 106 mm Hg)
solutions

solutions



2019
Q3
A 4% solution(w/w) of sucrose (M = 342 g mol-1) in water has a freezing point of 271.15
K. Calculate the freezing point of 5% glucose (M = 180 g mol-1) in water. (Given :
Freezing point of pure water = 273.15 K)
solutions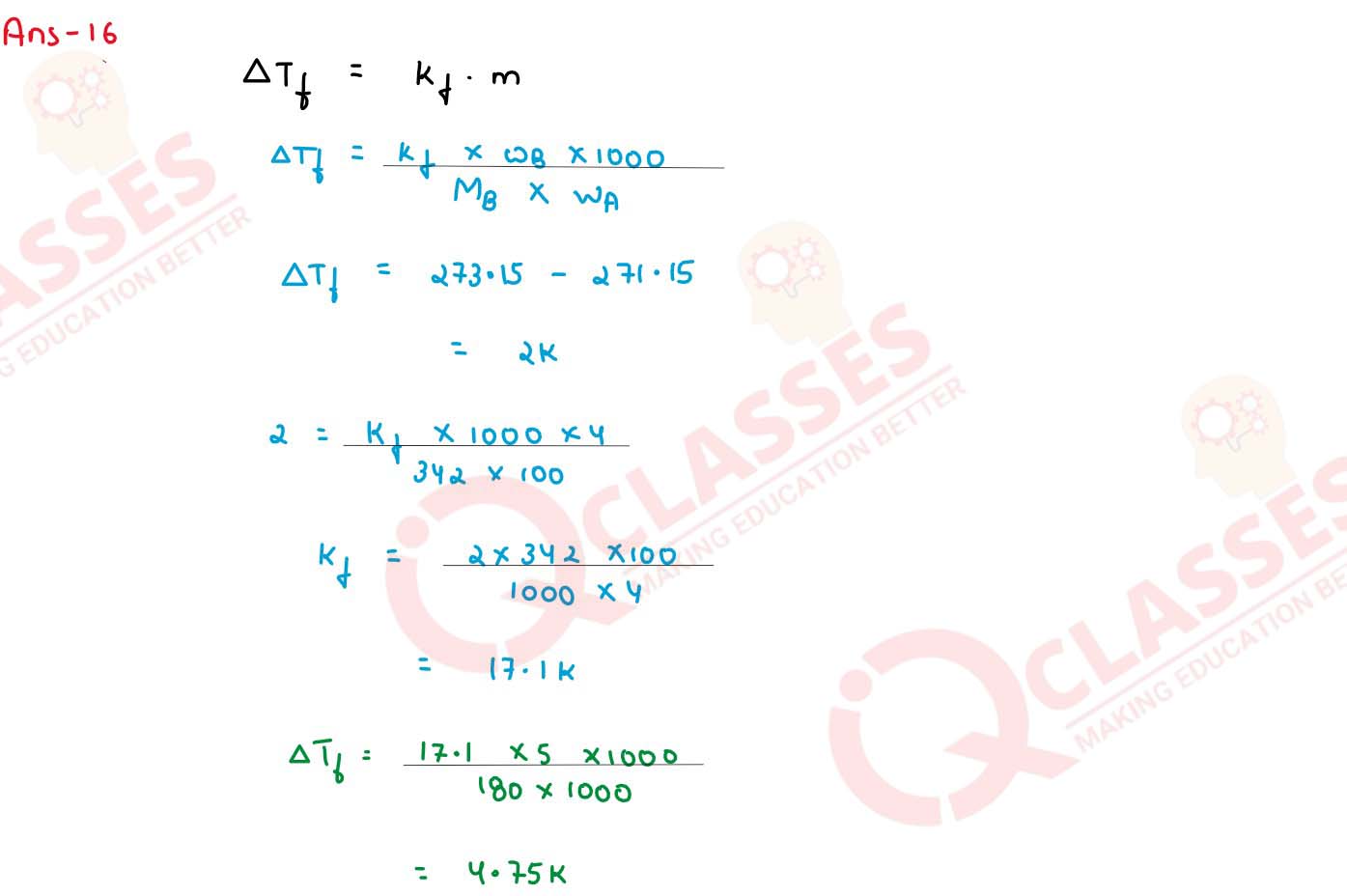

solutions


2018
Q4
Calculate the freezing point of a solution containing 60 g of glucose (Molar mass = 180 g
mol-1) in 250 g of water. (Kf of water = 1.86 K kg mol-1)
solutions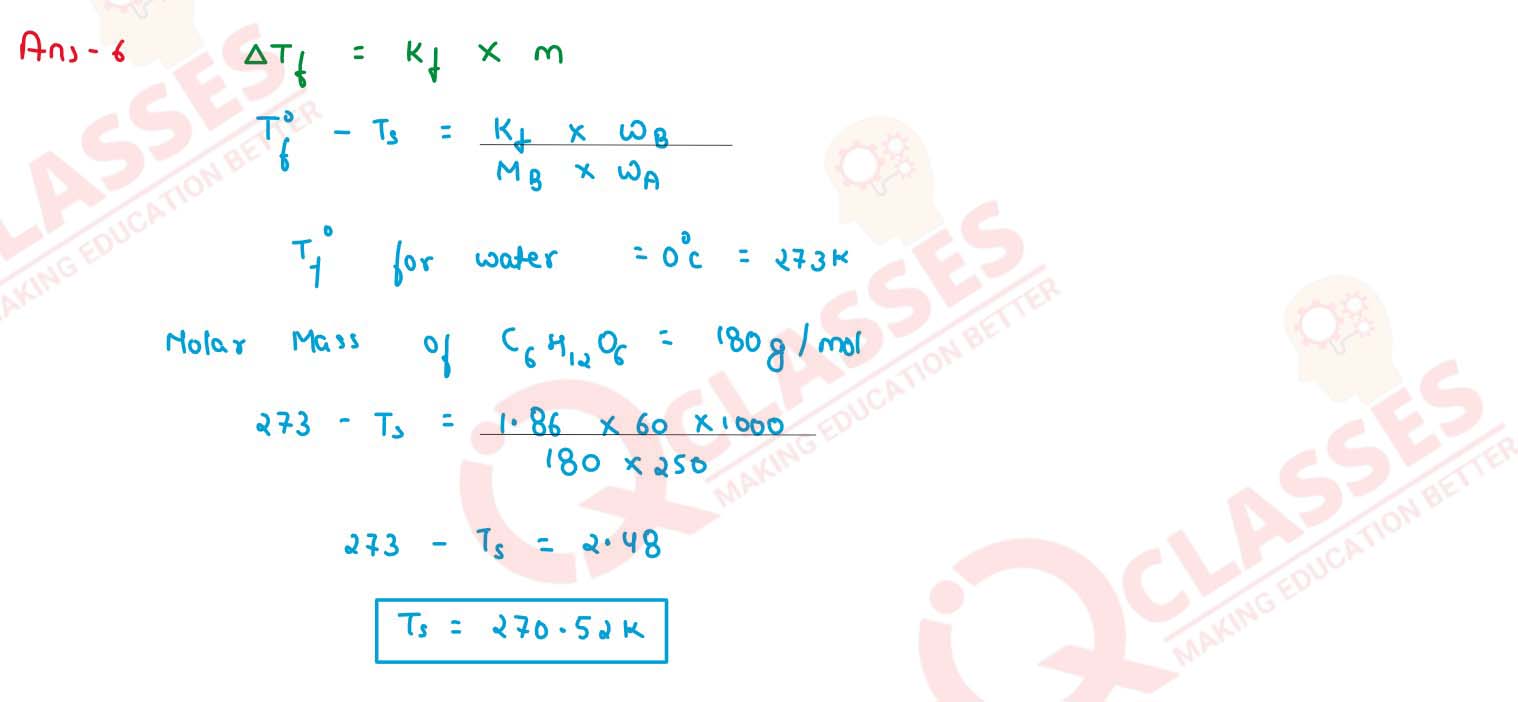
solutions

2017
Q5
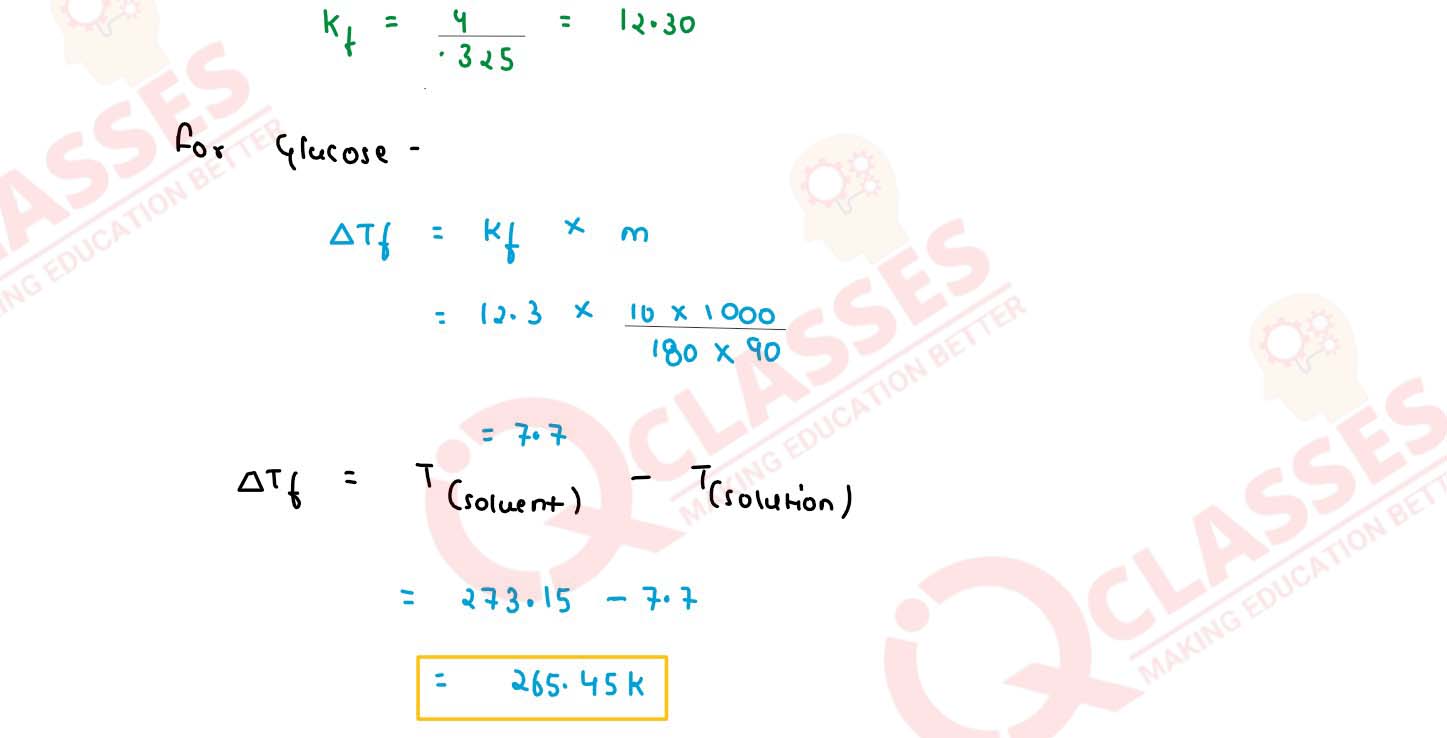
(a) A 10% solution (by mass) of sucrose in water has a freezing point of 269.15 K. Calculate the
freezing point of 10% glucose in water if the freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K. Given :
(Molar mass of sucrose = 342 g mol-1) (Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mo1-1)
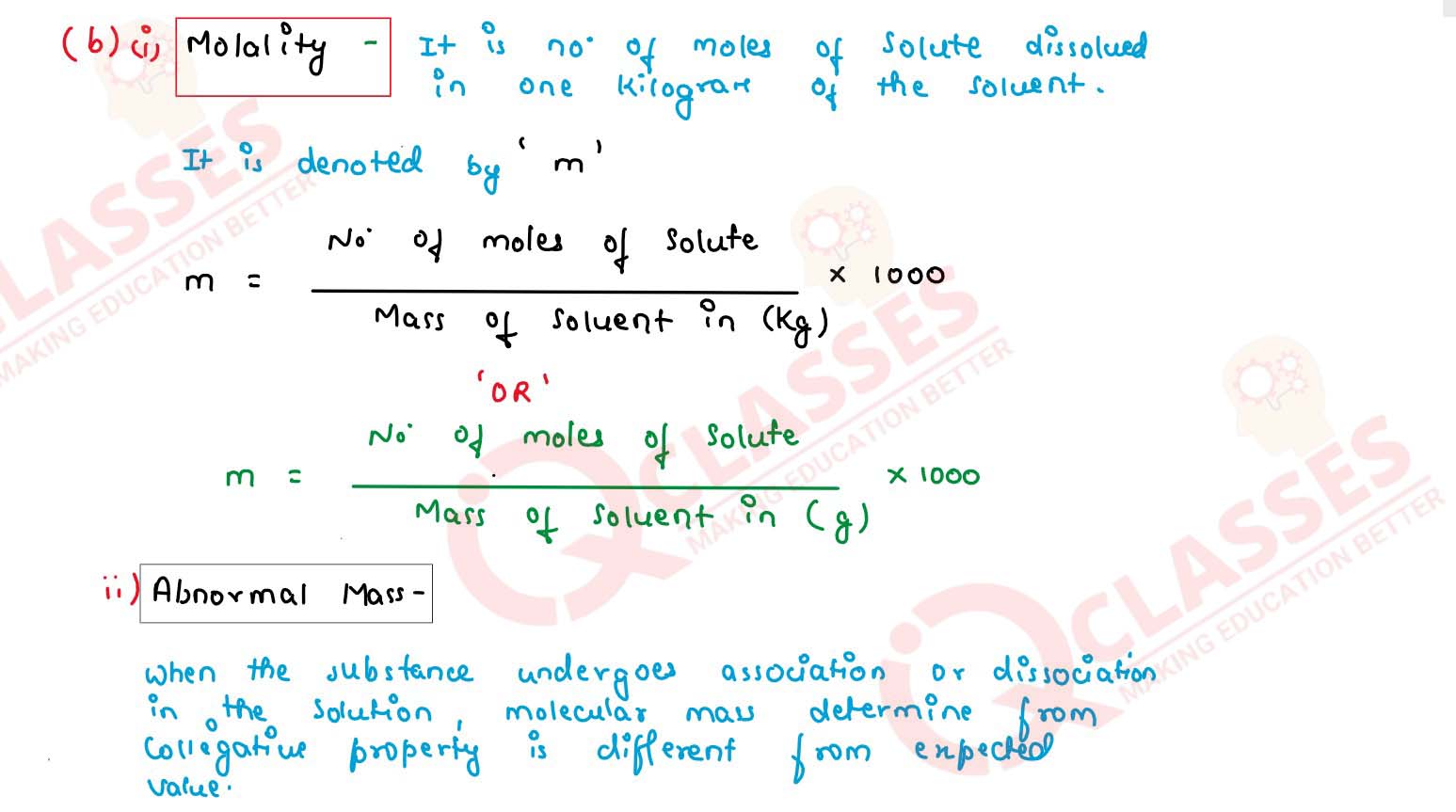
(b) Define the following terms :
(i) Molality (m)
(ii) Abnormal molar mass
solutions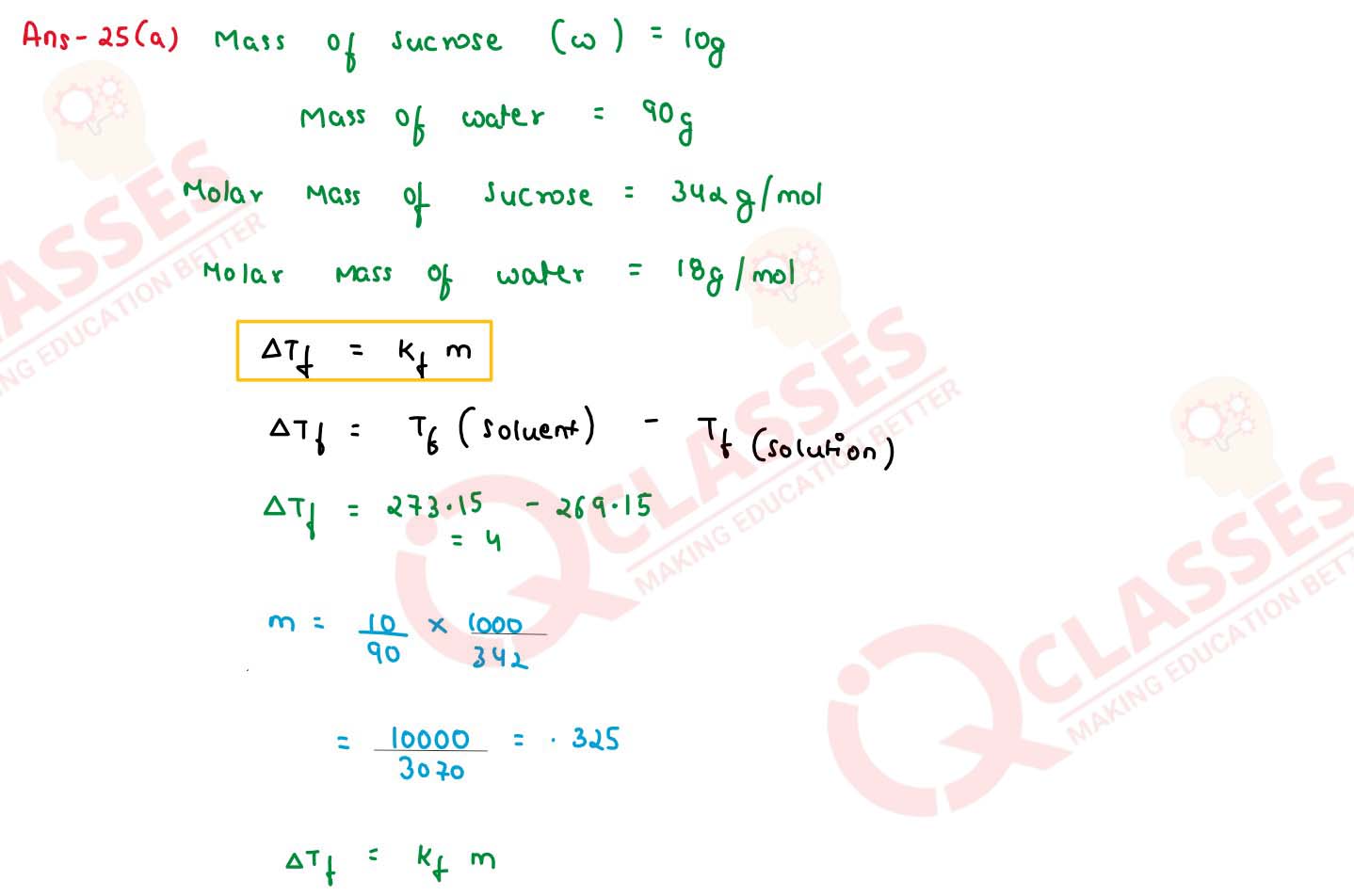
(b) Define the following terms :
(i) Molality (m)
(ii) Abnormal molar mass
solutions



Q6
(a) 30 g of urea (M = 60 g mol-1) is dissolved in 846 g of water. Calculate the vapour
pressure of water for this solution if vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg.
(b) Write two differences between ideal solutions and non-ideal solutions.
solutions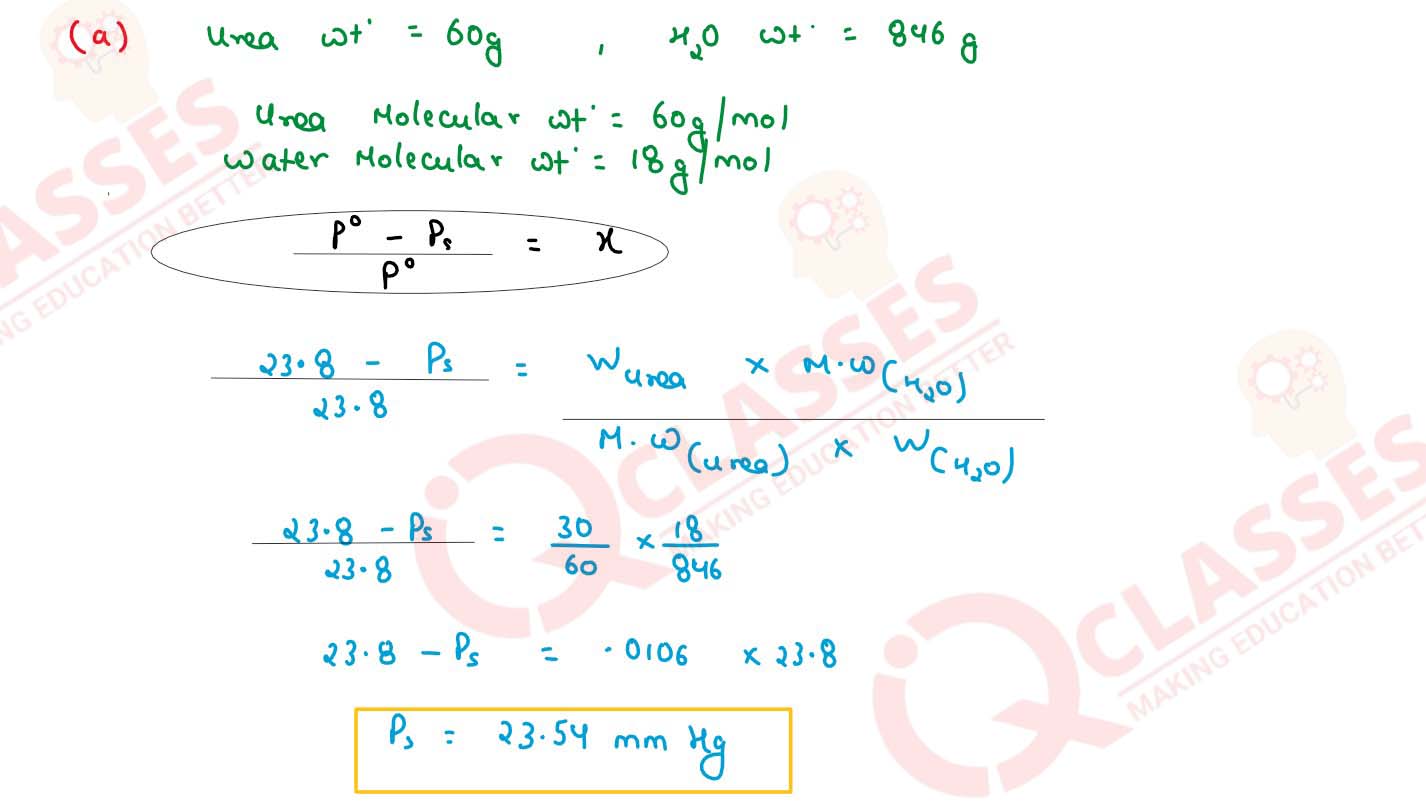

(b) Write two differences between ideal solutions and non-ideal solutions.
solutions


2016
Q7
Calculate the boiling point of solution when 4 g of MgSO4 (M=120 g mol-1) was
dissolved in 100 g of water, assuming MgSO4 undergoes complete ionization.
(Kb for water = 0.52 K kg mol-1)
solutions

solutions




Add a comment