Class 12 CBSE Physics Electric Charges and Field Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 Physics important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter Electric Field. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on CBSE board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 Physics syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
2017
Q1
Derive an expression for the electric field E due to a dipole of length ‘2a’ at a point distant r
from the centre of the dipole on the axial line.
Solutions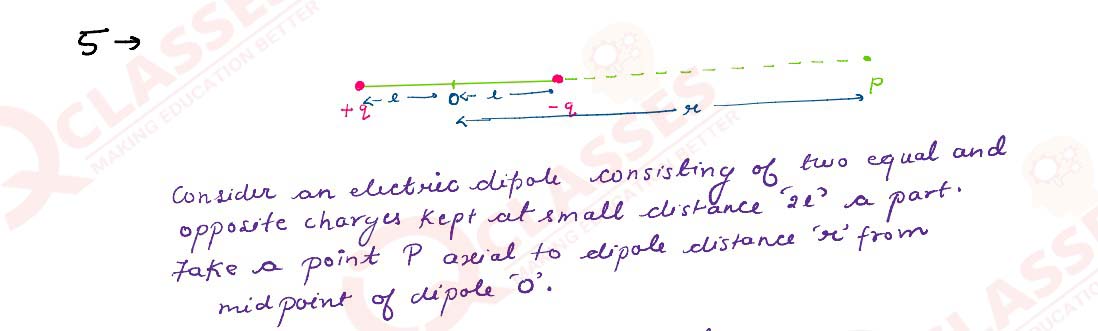
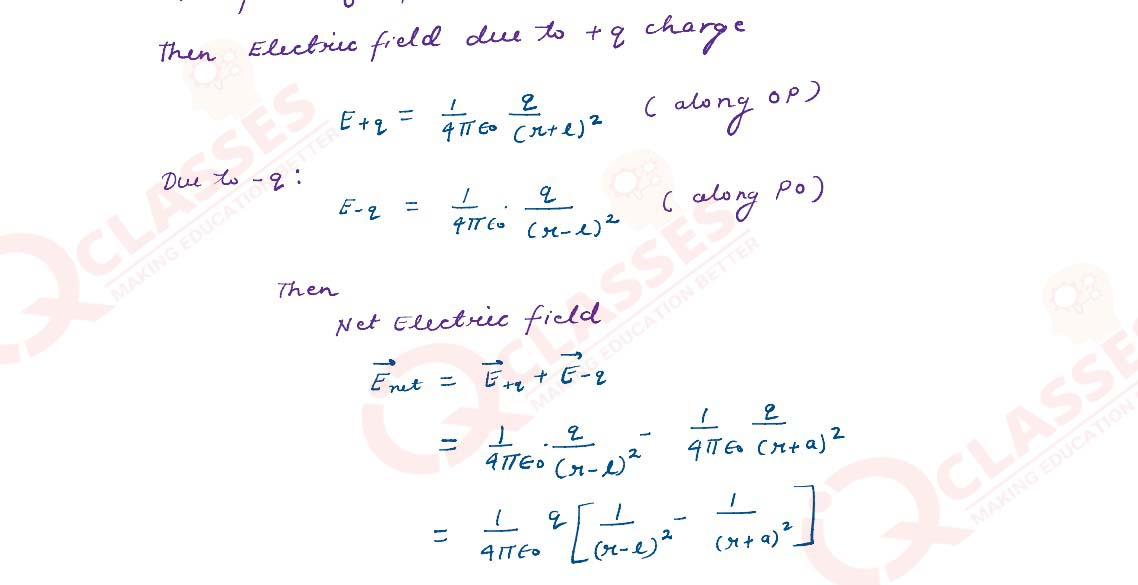
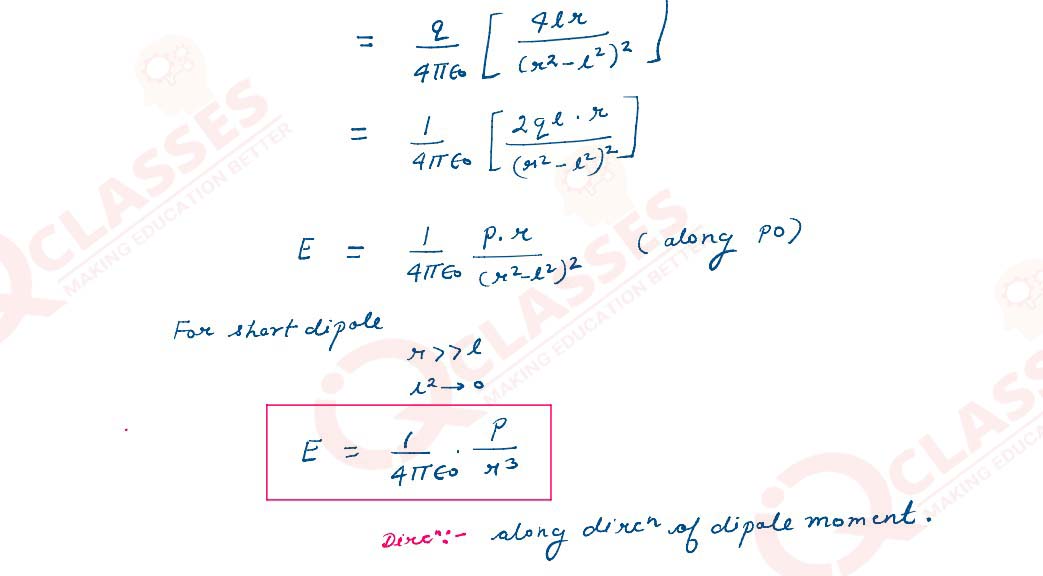
Solutions



Q2
Draw a graph of E versus r for r >> a.
Solutions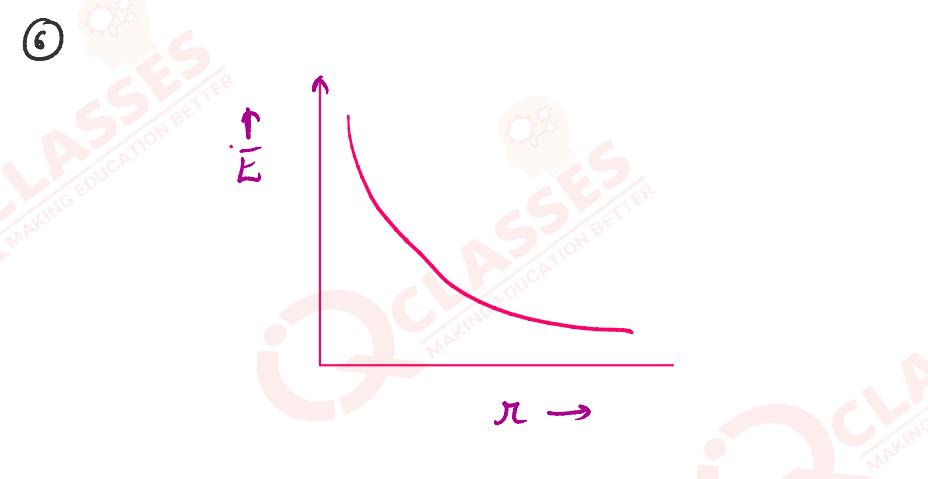
Solutions

Q3
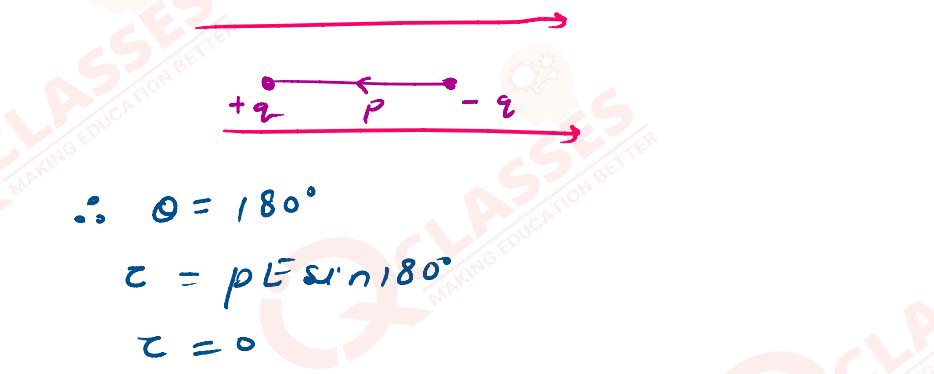
If this dipole were kept in a uniform external electric field Eo , diagrammatically
represent the
position of the dipole in stable and unstable equilibrium and write the expressions for the torque
acting on the dipole in both the cases.
Solutions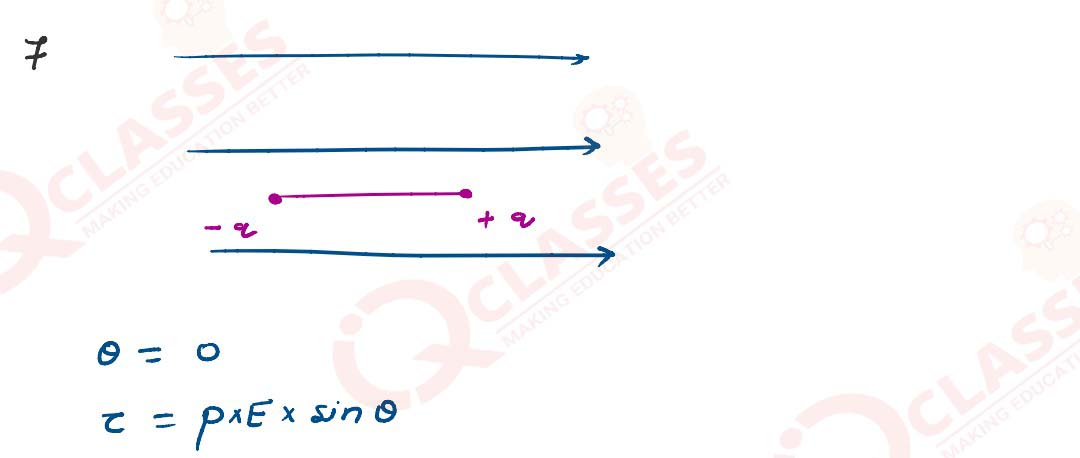

Solutions



Q4
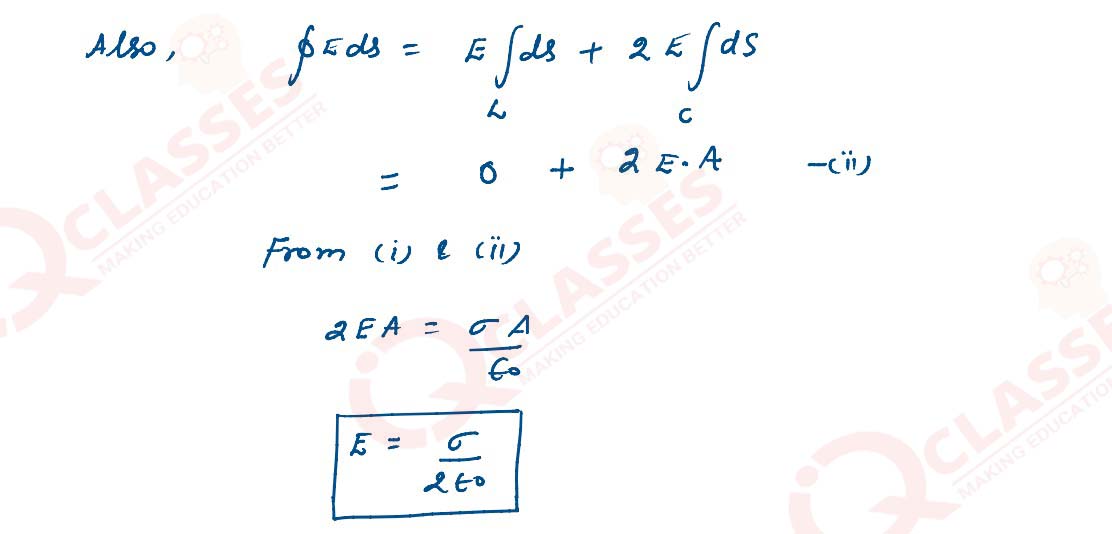
Use Gauss’s theorem to find the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinitely large plane
thin sheet with surface charge density σ
Solutions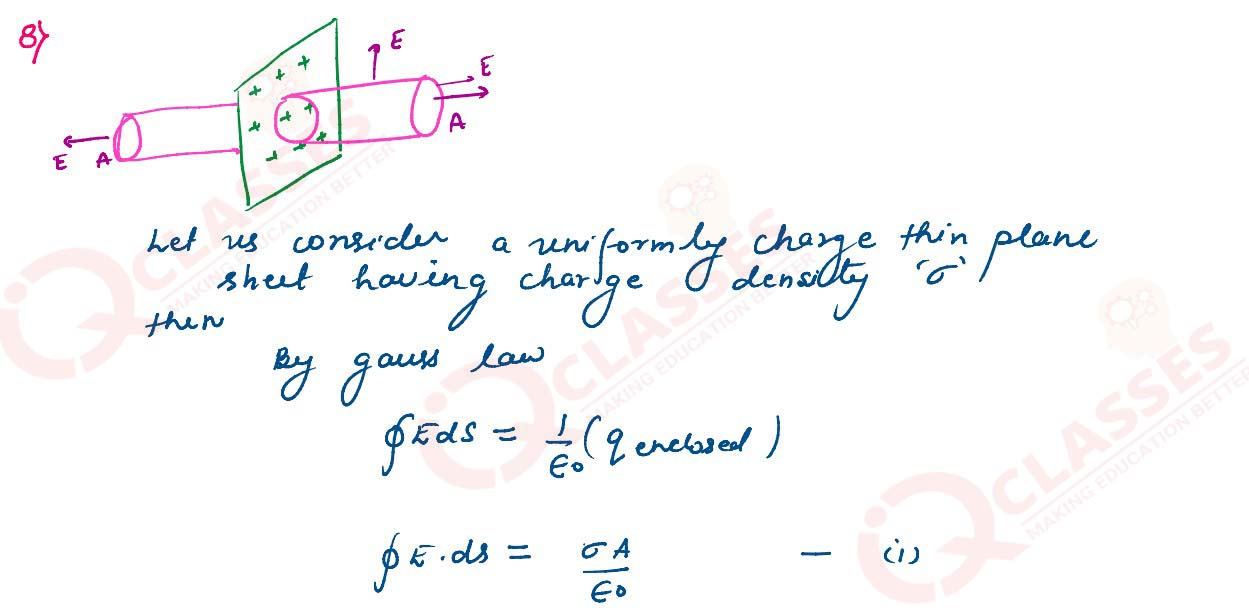
Solutions
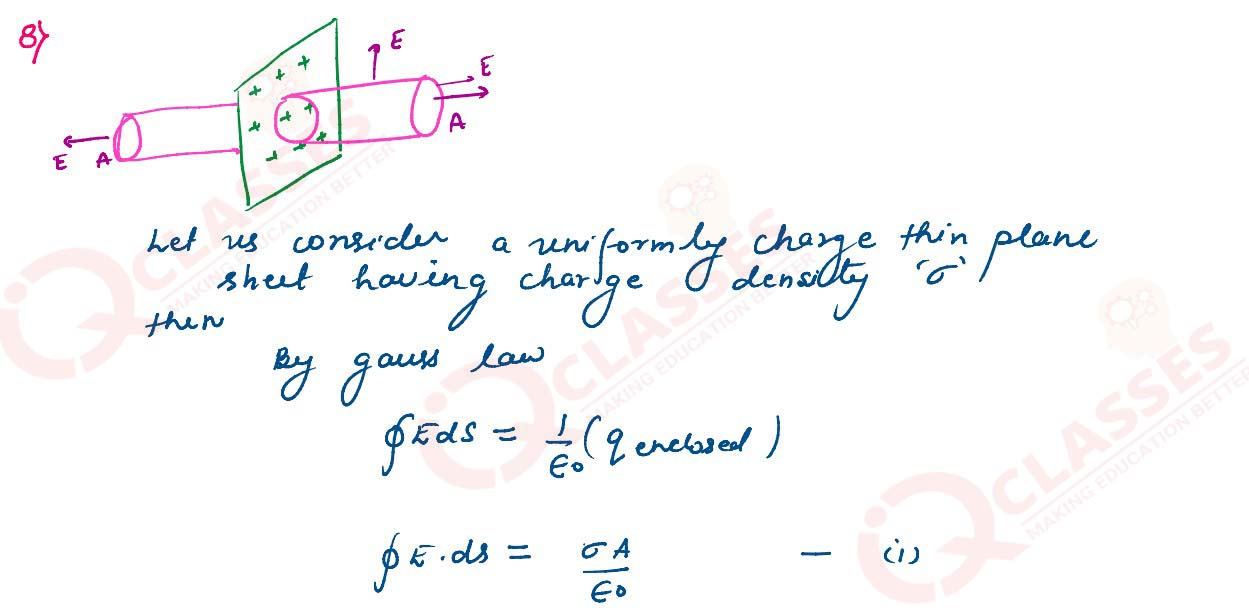

Q5
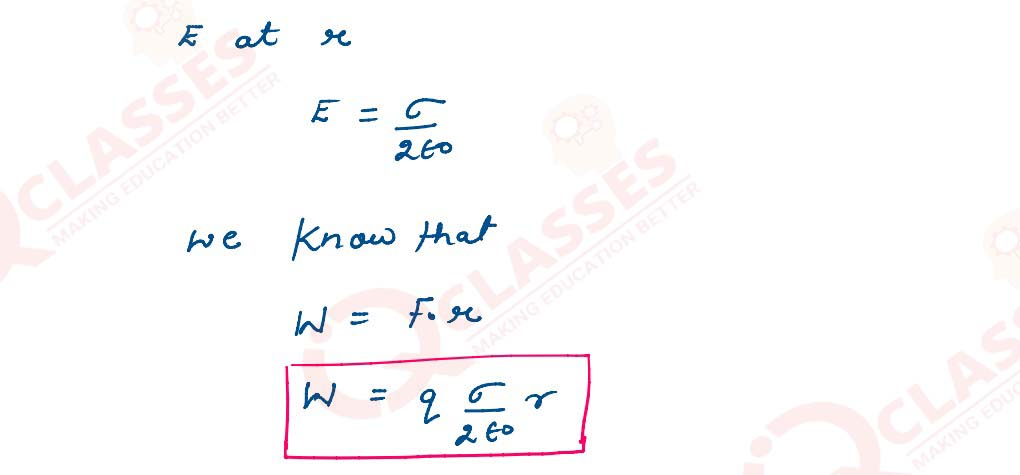
An infinitely large thin plane sheet has a uniform surface charge density +σ . Obtain the expression
for the amount of work done in bringing a point charge q from infinity to a point, distant r, in
front of the charged plane sheet.
Solutions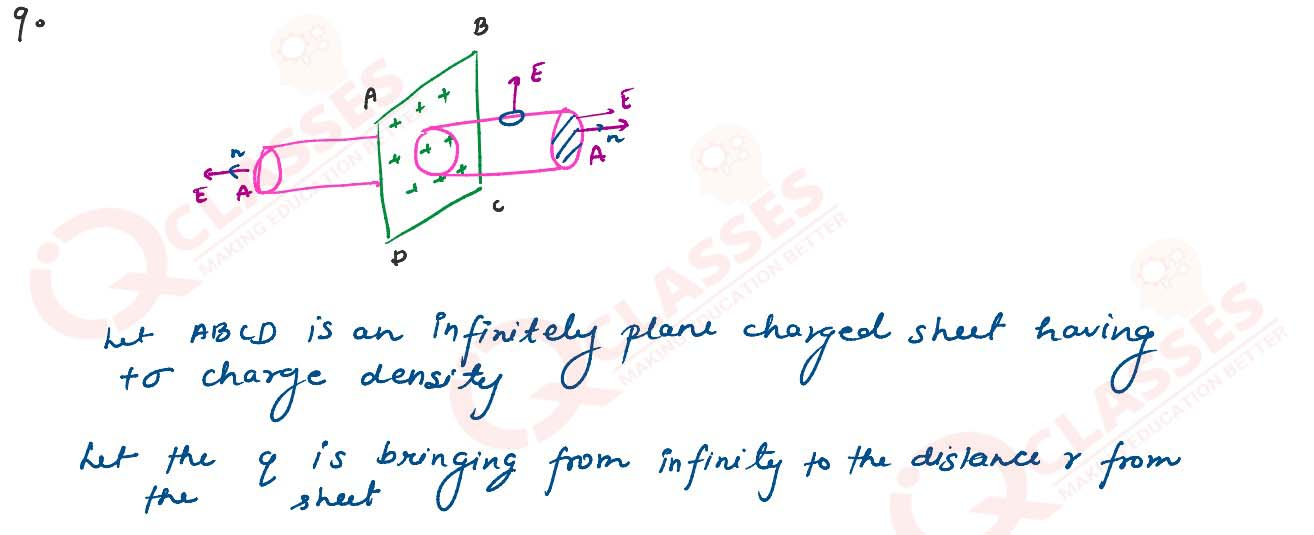
Solutions


2018
Q1
(a) Define electric flux. Is it a scalar or a vector quantity ?
A point charge q is at a distance of d/2 directly above the center of a square of side d, as shown
in the figure. Use Gauss’ law to obtain the expression for the electric flux through the square.
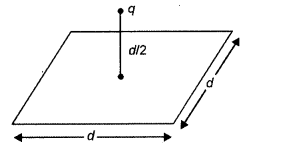
(b) If the point charge is now moved to a distance ‘d ‘ from the center of the square and the side of the square is doubled, explain how the electric flux will be affected.
OR
(a) Use Gauss’ law to derive the expression for the electric field (E) due to a straight uniformly charged infinite line of charge density λ C/m.
(b) Draw a graph to show the variation of E with perpendicular distance r from the line of charge.
(c) Find the work done in bringing a charge q from perpendicular distance r1 to r2(r2> r1)
Solutions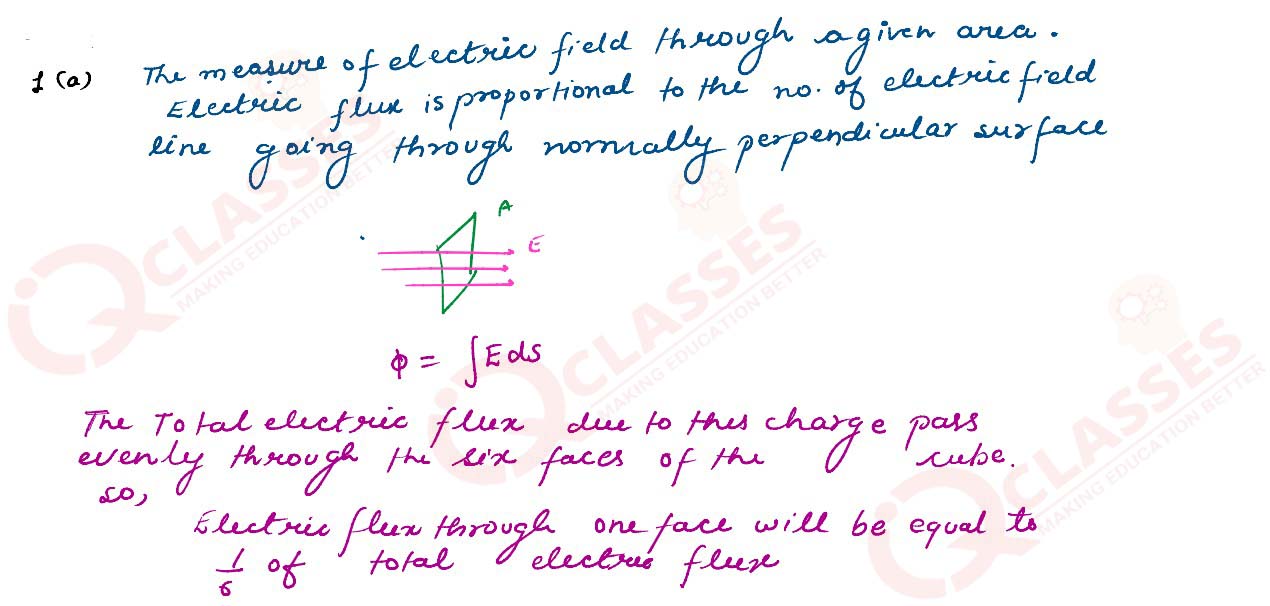

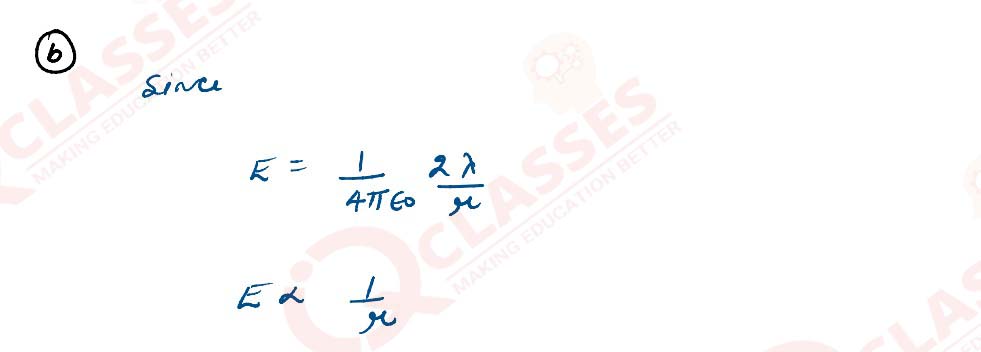


(b) If the point charge is now moved to a distance ‘d ‘ from the center of the square and the side of the square is doubled, explain how the electric flux will be affected.
OR
(a) Use Gauss’ law to derive the expression for the electric field (E) due to a straight uniformly charged infinite line of charge density λ C/m.
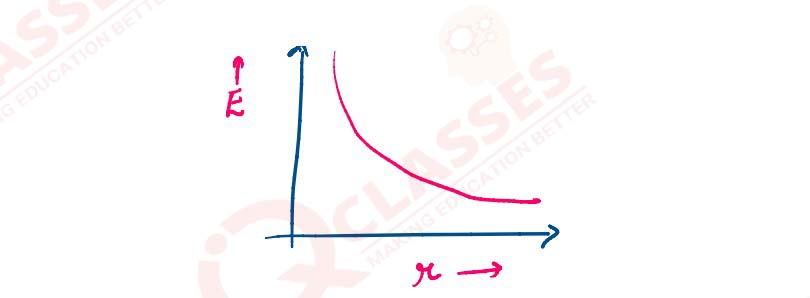
(b) Draw a graph to show the variation of E with perpendicular distance r from the line of charge.
(c) Find the work done in bringing a charge q from perpendicular distance r1 to r2(r2> r1)
Solutions


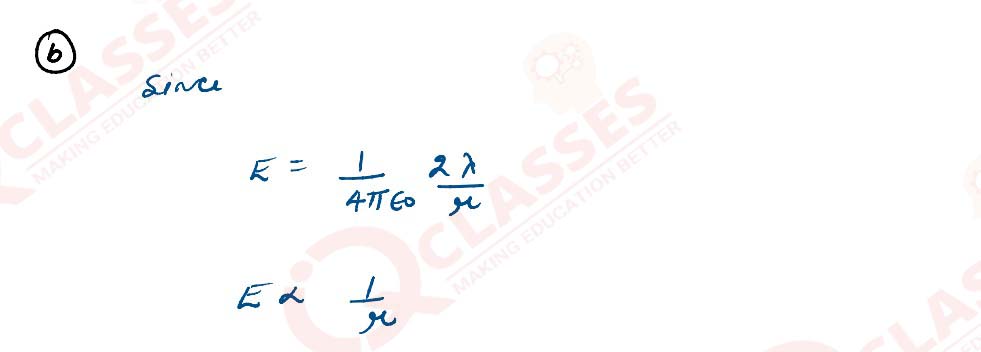


2019
Q1
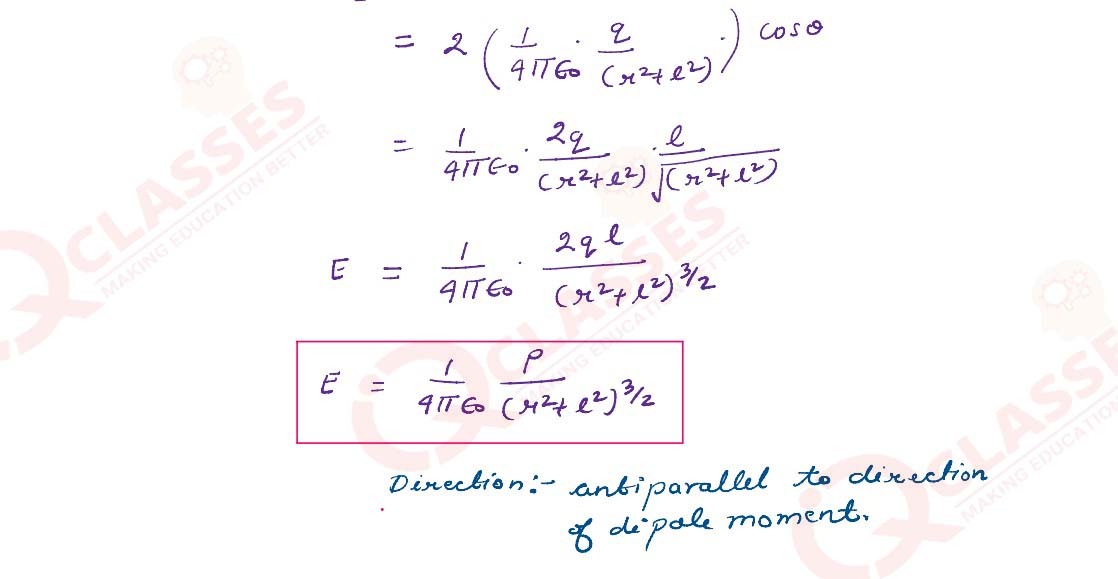
Derive an expression for the electric field at any point on the Equatorial line of an electric
dipole
Solutions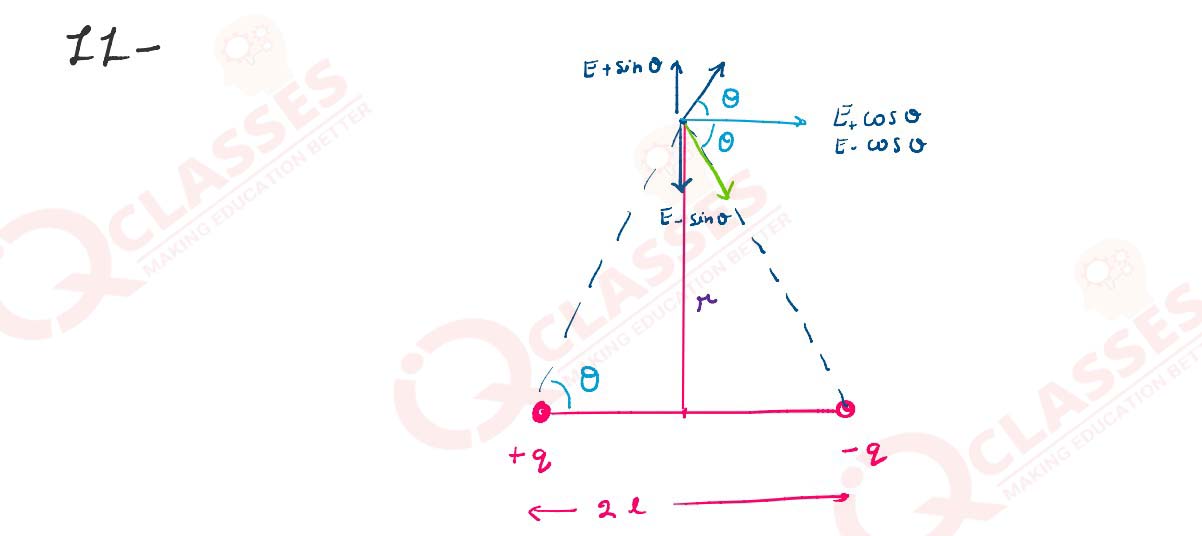
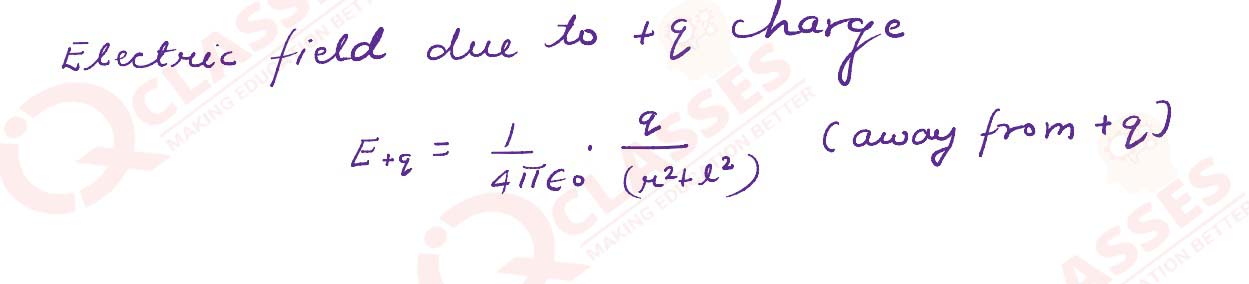

Solutions

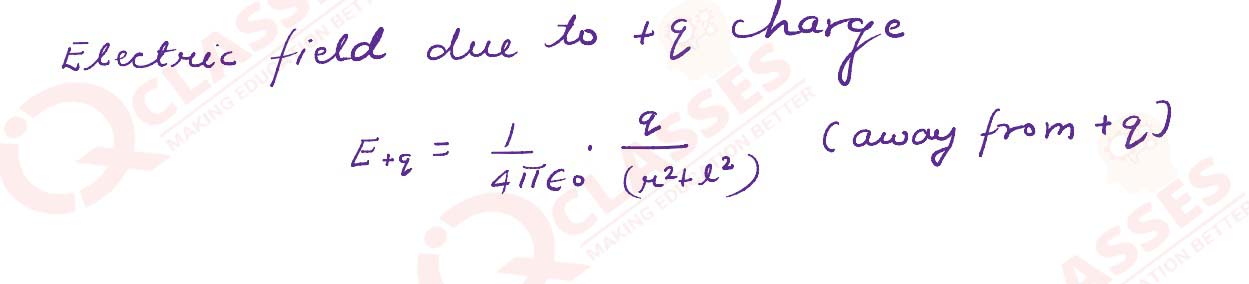


Q2
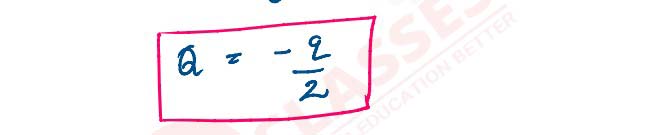
2 identical point charges q kept 2 m apart in air. A 3rd point charge Q of unknown
magnitude & sign
is placed on the line joining the charges such that the system remains in equilibrium. Find the
position and nature of the Q.
Solutions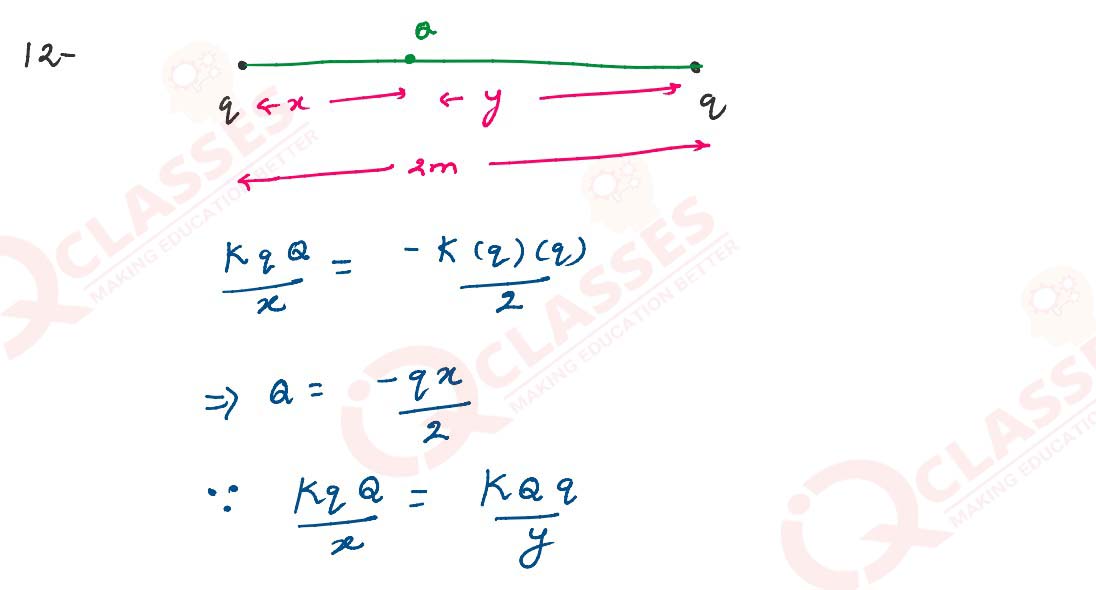
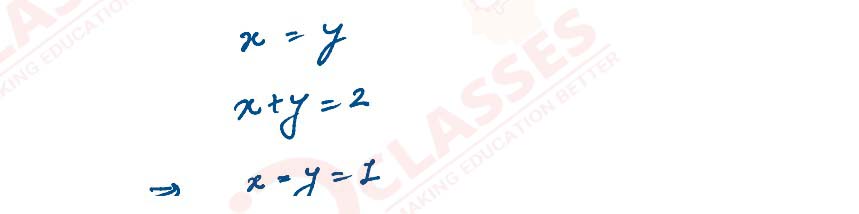
Solutions

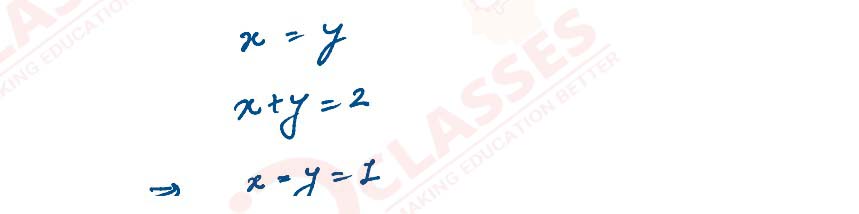

Q3
Draw the pattern for the electric field lines when a point charge Q is kept near an uncharged
conducting plate.
Solutions
Solutions
2020
Q1
If the net electric flux through a closed surface is zero, then we can infer
a) no net charge is enclosed by the surface.
b) uniform electric field exists within the surface.
c) electric potential varies from point to point inside the surface
d) charge is present inside the surface.
Solutions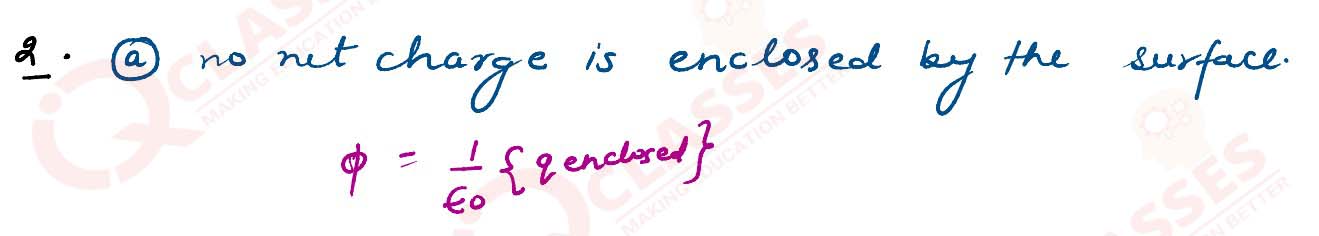
a) no net charge is enclosed by the surface.
b) uniform electric field exists within the surface.
c) electric potential varies from point to point inside the surface
d) charge is present inside the surface.
Solutions
Q2
An electric dipole consisting of charges + q and – q separated by a distance L is in stable
equilibrium in a uniform electric field E . The electrostatic potential energy of the dipole is
a) qLE
b) zero
c) – qLE
d) – 2 qEL
Solutions
a) qLE
b) zero
c) – qLE
d) – 2 qEL
Solutions

Q3
(a) Using Gauss law, derive expression for electric field due to a spherical shell of uniform
charge distribution and radius R at a point lying at a distance x from the centre of shell, such
that
i. 0 < x < R, and
ii. x> R.
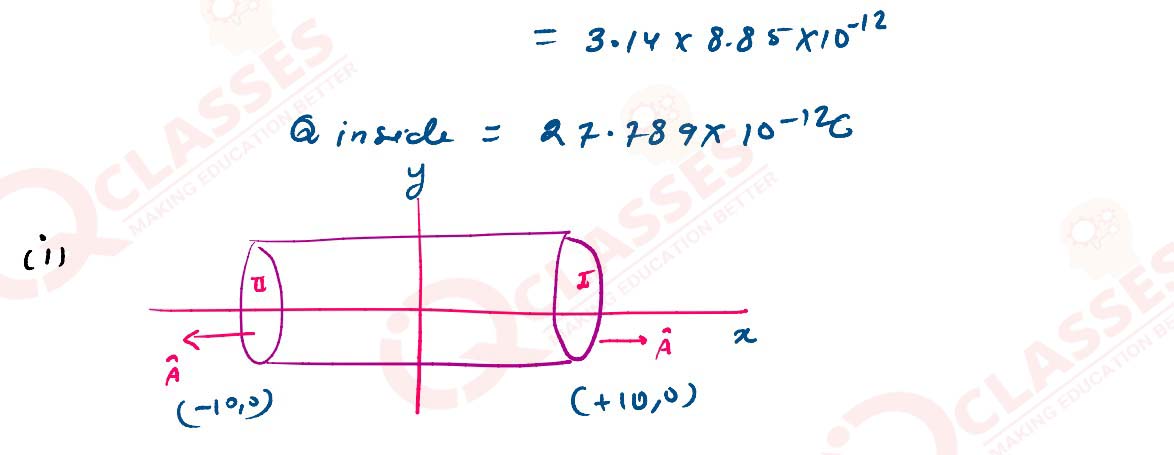
(b) An electric field is uniform and acts along + x direction in the region of positive x. It is also uniform with the same magnitude but acts in – x direction in the region of negative x. The value of the field is E = 200 N/C for x > 0 and E = – 200 N/C for x < 0. A right circular cylinder of length 20 cm and radius 5 cm has its centre at the origin and its axis along the x-axis so that one flat face is at x=+ 10 cm and the other is at x=– 10 cm.
Find :
(i) The net outward flux through the cylinder.
(ii) The net charge present inside the cylinder.
Solutions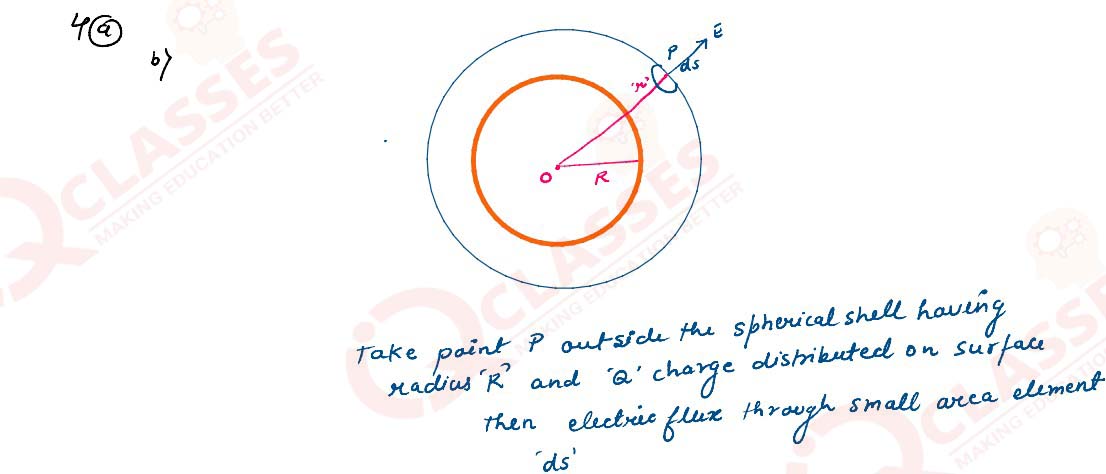
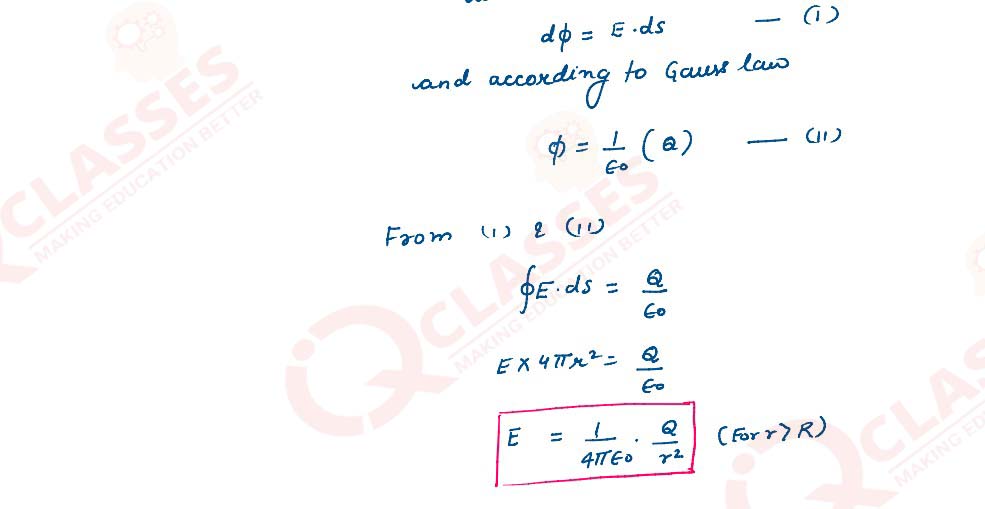
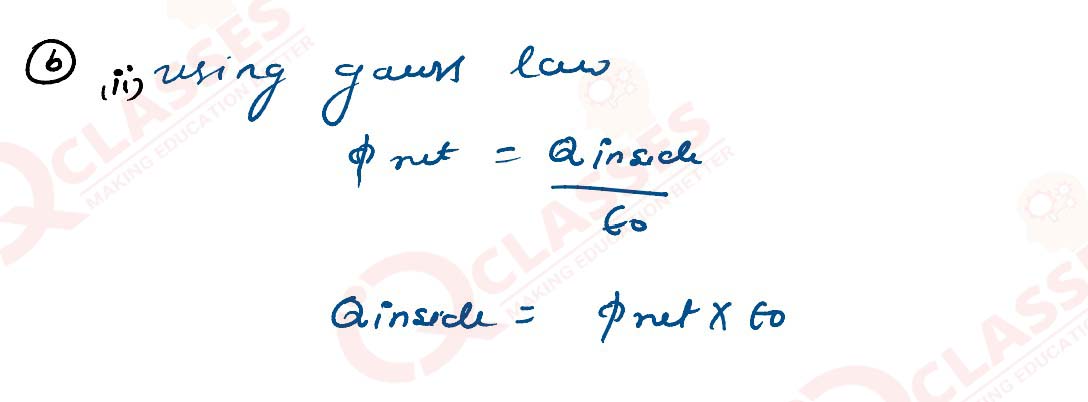

i. 0 < x < R, and
ii. x> R.
(b) An electric field is uniform and acts along + x direction in the region of positive x. It is also uniform with the same magnitude but acts in – x direction in the region of negative x. The value of the field is E = 200 N/C for x > 0 and E = – 200 N/C for x < 0. A right circular cylinder of length 20 cm and radius 5 cm has its centre at the origin and its axis along the x-axis so that one flat face is at x=+ 10 cm and the other is at x=– 10 cm.
Find :
(i) The net outward flux through the cylinder.
(ii) The net charge present inside the cylinder.
Solutions


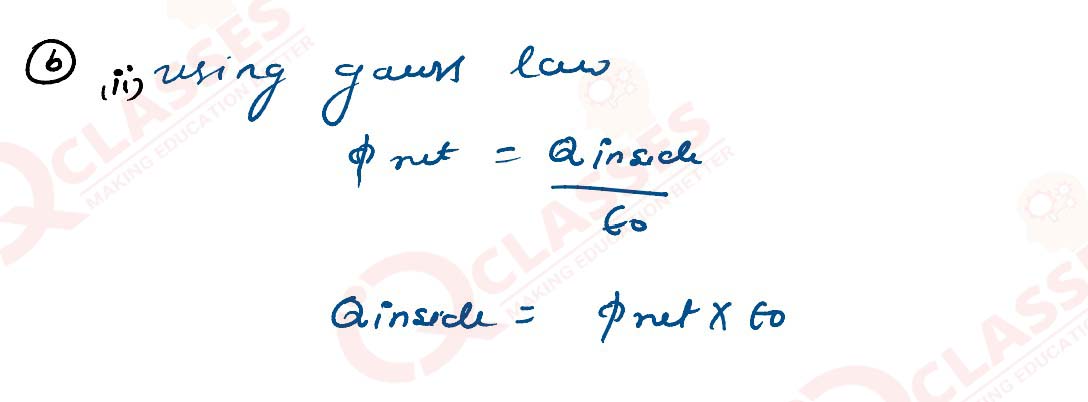




Add a comment