Class 12 ISC Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instrument Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 Physics important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on ISC board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 Physics syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
class 12 ISC Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instrument BoardQuestions
Ray Optics and Optical Instrument BoardQuestions
2017
Q1
How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is
replaced by red light ? Give reason.
solutions
solutions

Q2
Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is
1•33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
solutions
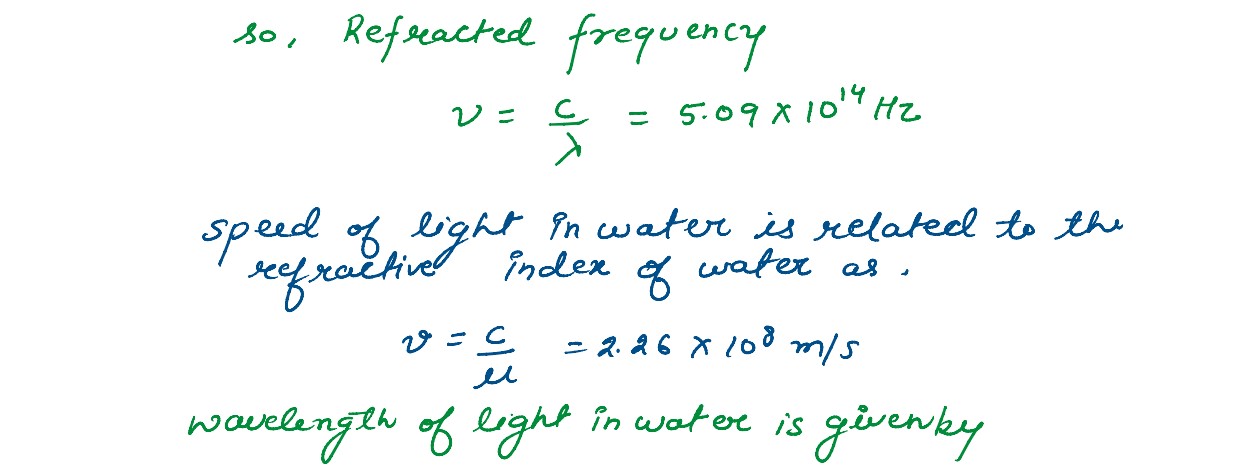
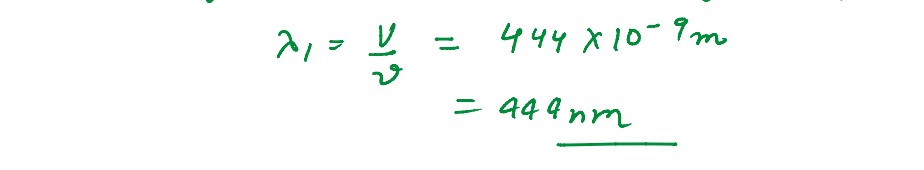
solutions

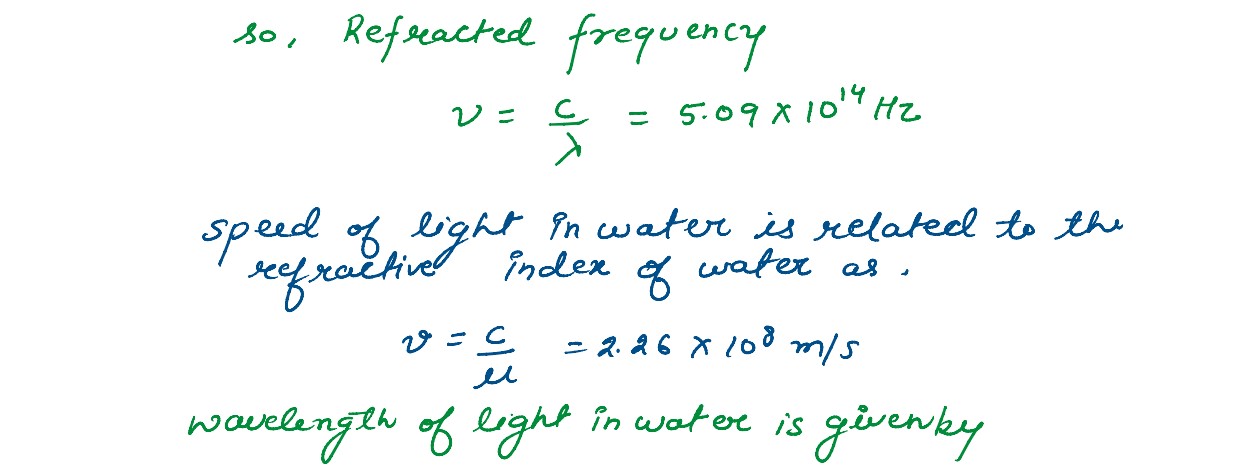
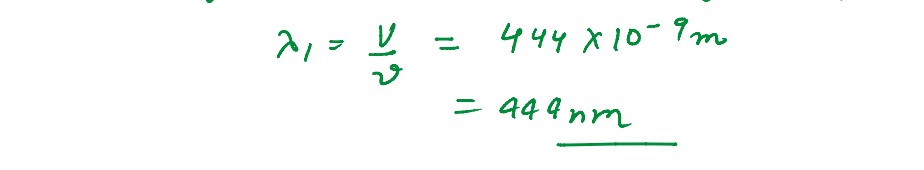
Q3
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1•55, with both faces of the same radius
of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
solutions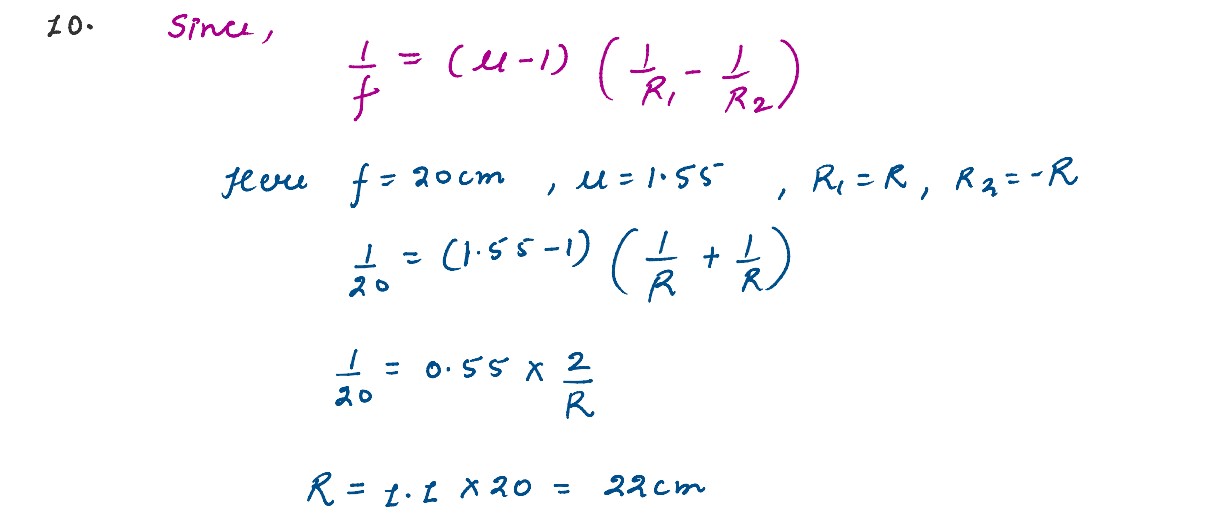
solutions
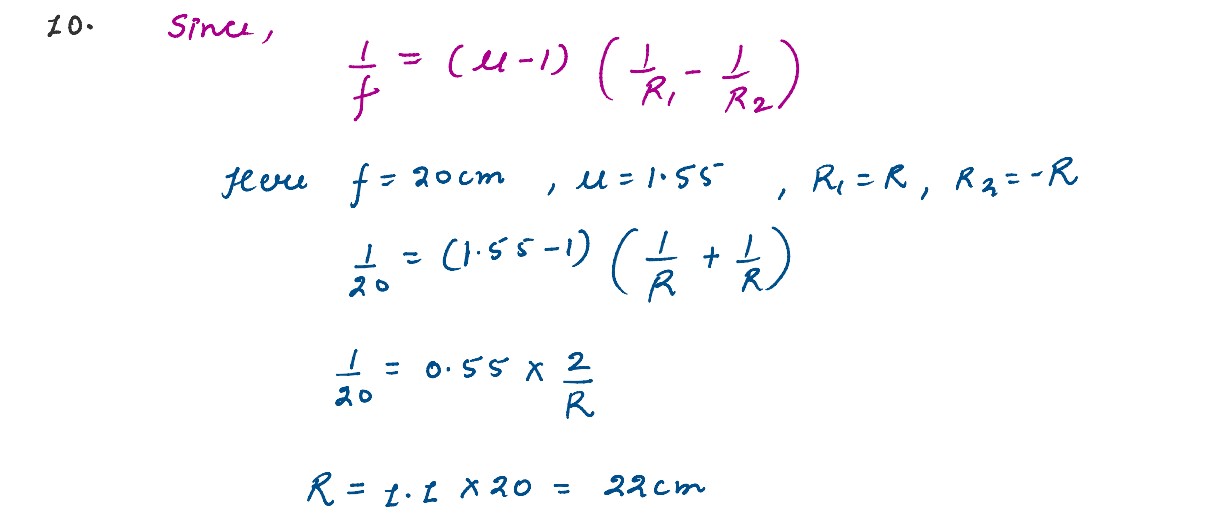
Q4
Draw a ray diagram depicting the formation of the image by an astronomical telescope in normal
adjustment.
solutions
To see the relax eye, the final image should be formed at infinity as shown in the figure.
For this, the distance between and the objective and the eye-piece is adjusted so that the image
A′B′ formed by the objective lens O.
solutions
To see the relax eye, the final image should be formed at infinity as shown in the figure.
For this, the distance between and the objective and the eye-piece is adjusted so that the image
A′B′ formed by the objective lens O.
For normal adjustment, ue=fe
The magnifying power is defined as
M=-f0/fe
where f0 is the focal length of objective lens and fe is the focal length of
eye-piece.
Q5
You are given the following three lenses. Which two lenses will you use as an eyepiece and as an
objective to construct an astronomical telescope ? Give reason.
solutions
solutions

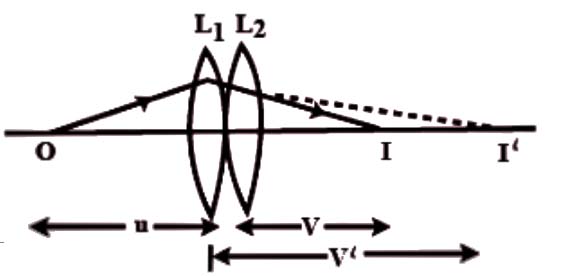
Q6
Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation by a combination of two thin convex lenses in
contact. Obtain the expression for the power of this combination in terms of the focal lengths of
the lenses.
solutions
Let us consider two thin convex lenses L1 & L2 as shown in the figure of focal lengths f1 & f2 are
placed in contact in air having a common principal axis. A point object O is placed on the principal
axis at a distance u from the first lens L1.Its image will be formed by the lens L1 alone at I′, the
image distance from the lens to the image I′ is v′.
solutions
Let us consider two thin convex lenses L1 & L2 as shown in the figure of focal lengths f1 & f2 are
placed in contact in air having a common principal axis. A point object O is placed on the principal
axis at a distance u from the first lens L1.Its image will be formed by the lens L1 alone at I′, the
image distance from the lens to the image I′ is v′.

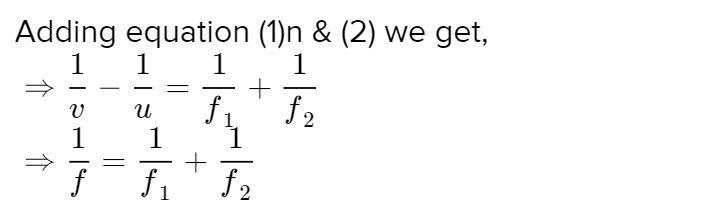
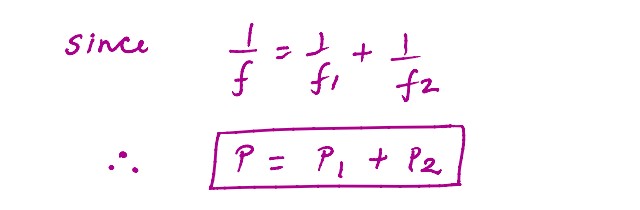
Q7
A ray of light passing from air through an equilateral glass prism undergoes minimum deviation when
the angle of incidence is ¾ th of the angle of prism. Calculate the speed of light in the prism.
solutions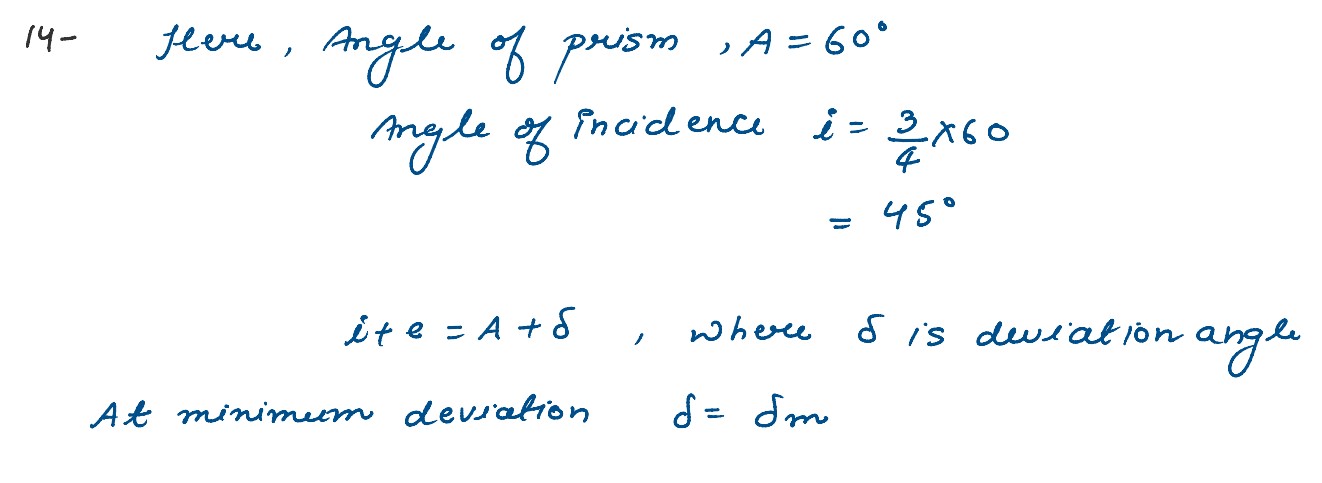
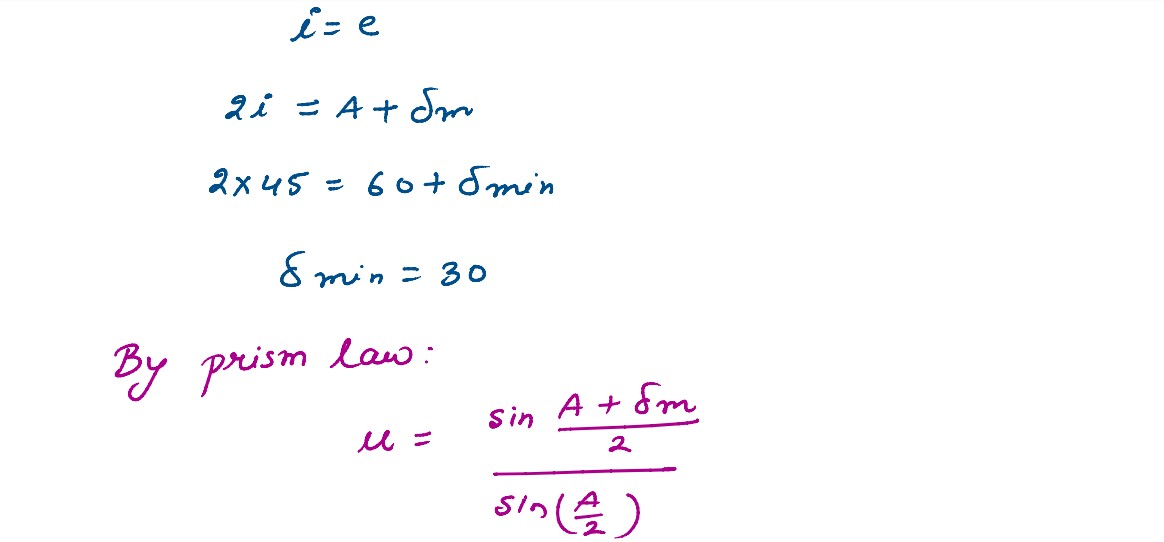
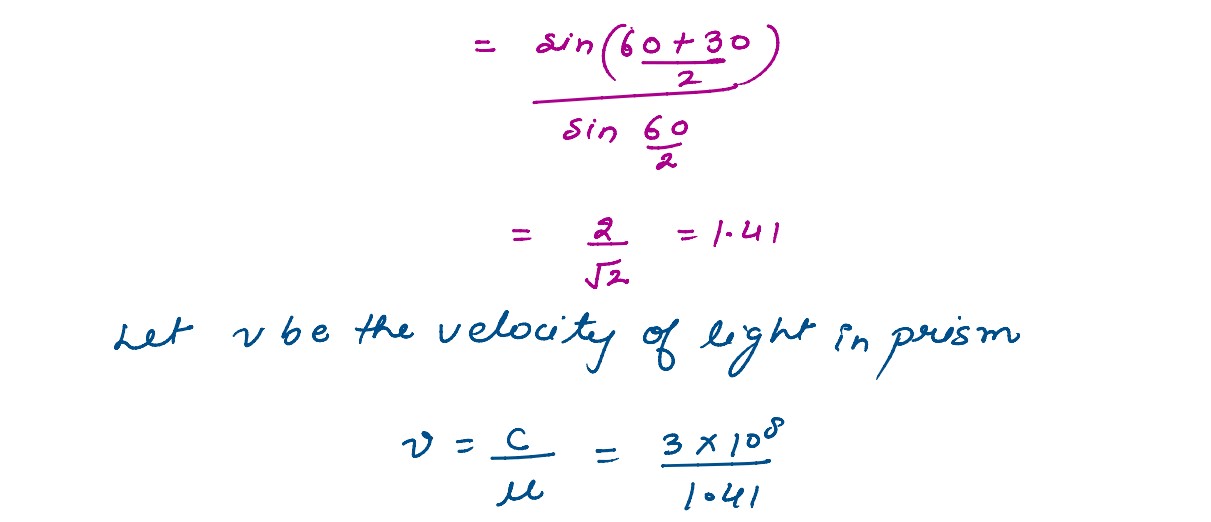
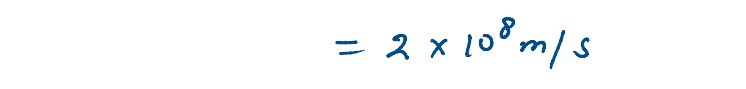
solutions
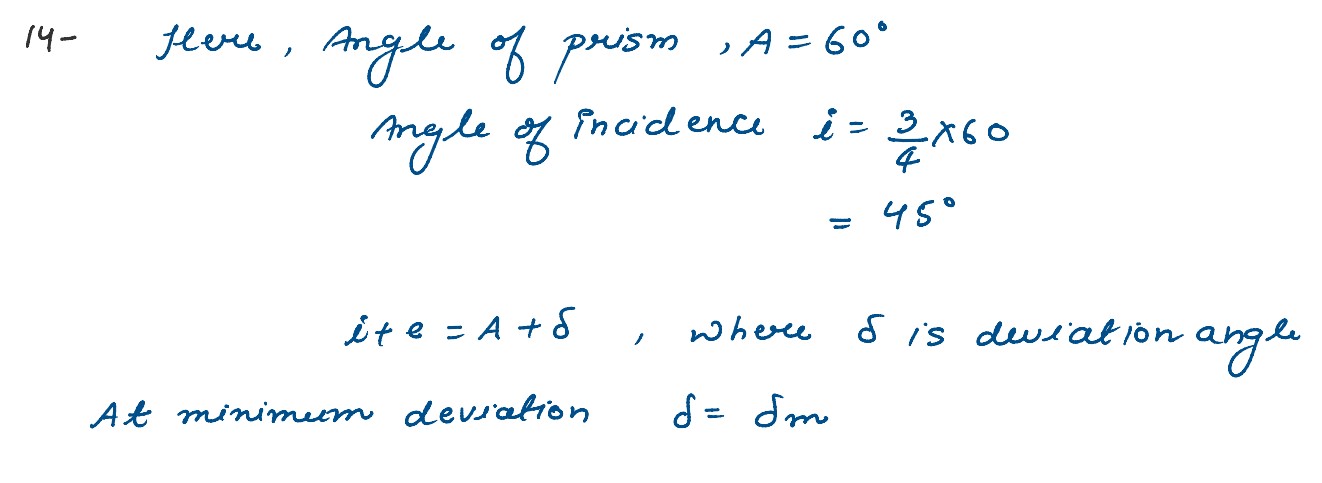
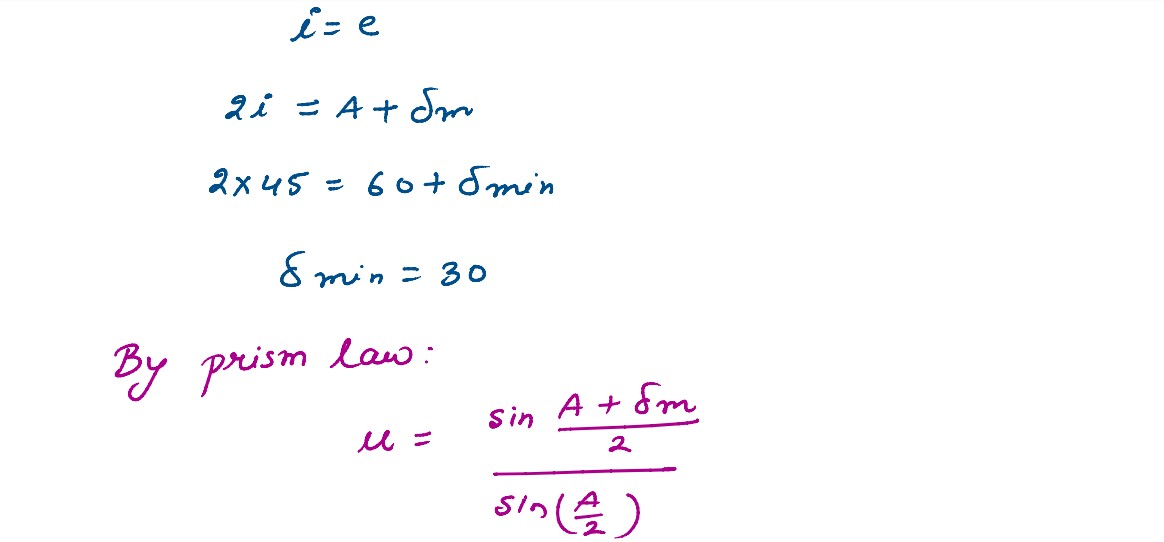
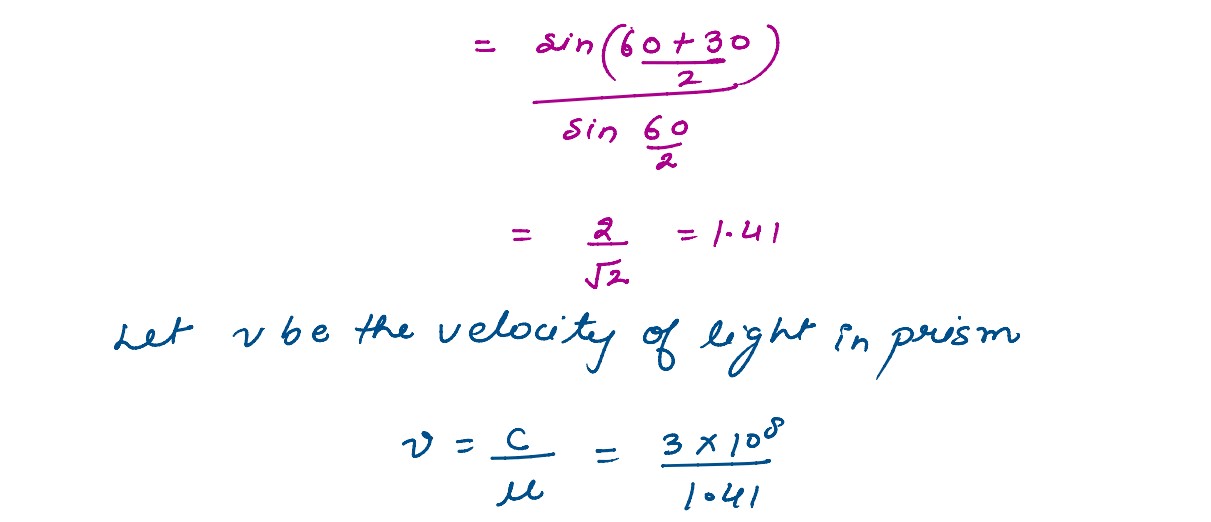
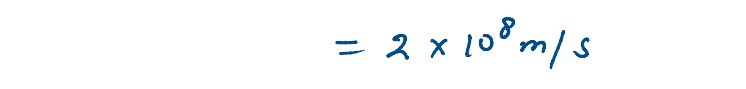
2018
Q1
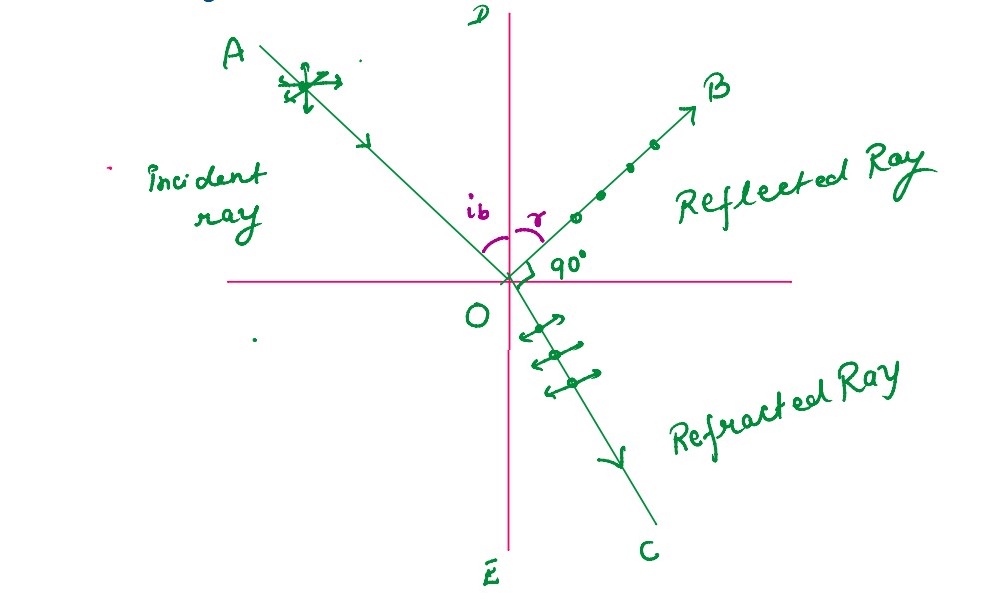
(a) Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a
transparent glass surface.
(b) The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index 3/2,placed in water of refractive index 4/3.Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC ?
solutions
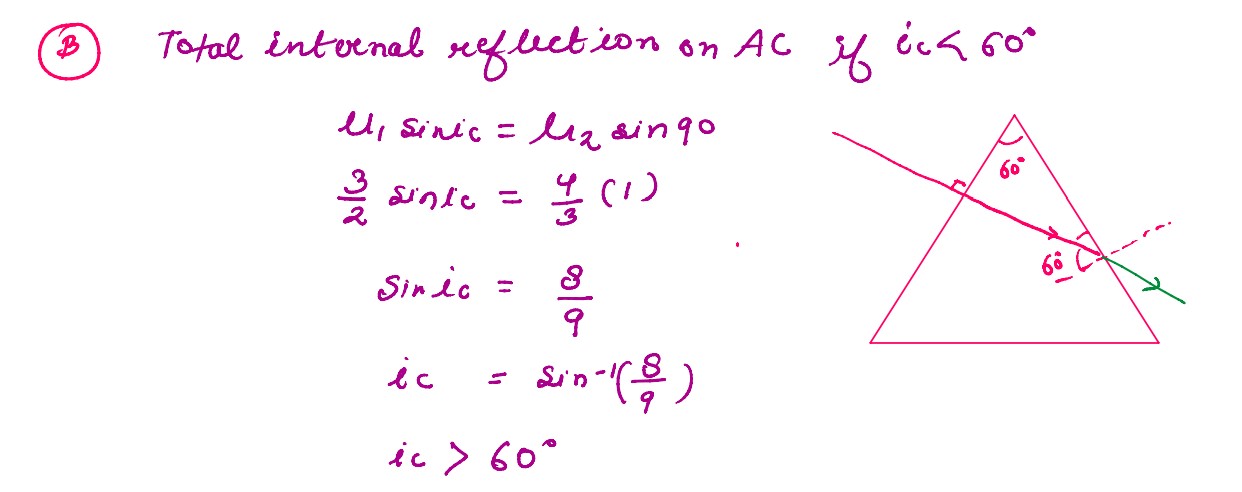
(b) The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index 3/2,placed in water of refractive index 4/3.Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC ?

solutions


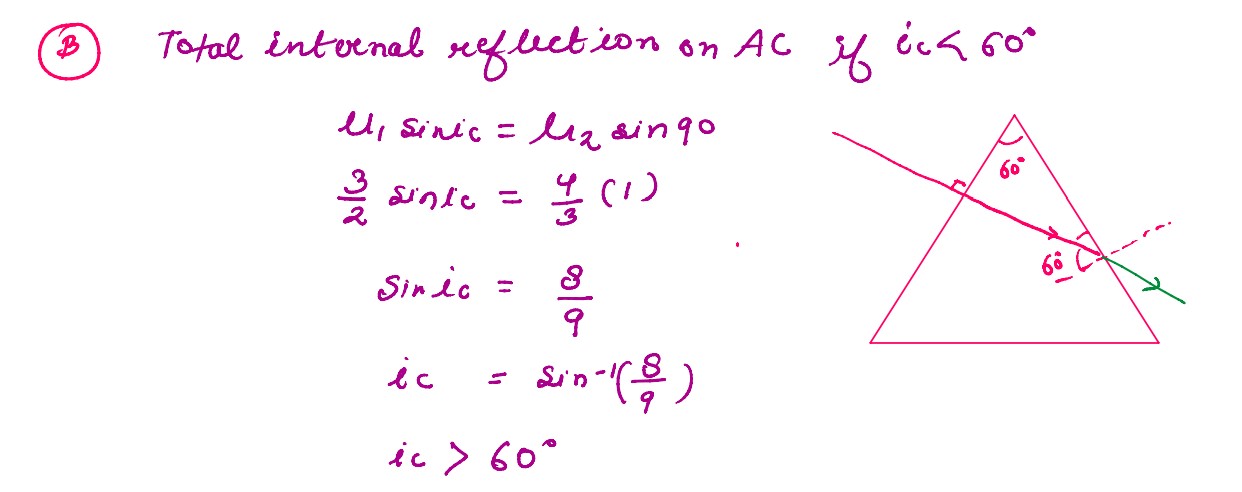
Q2
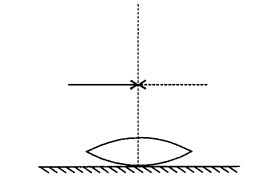
A symmetric biconvex lens of radius of curvature R and made of glass of refractive index 1.5, is
placed on a layer of liquid placed on top of a plane mirror as shown in the figure. An optical
needle with its tip on the principal axis of the lens is moved along the axis until its real,
inverted image coincides with the needle itself. The distance of the needle from the lens is
measured to be x. On removing the liquid layer and repeating the experiment, the distance is found
to be y. Obtain the expression for the refractive index of the liquid in terms of x and y.
solutions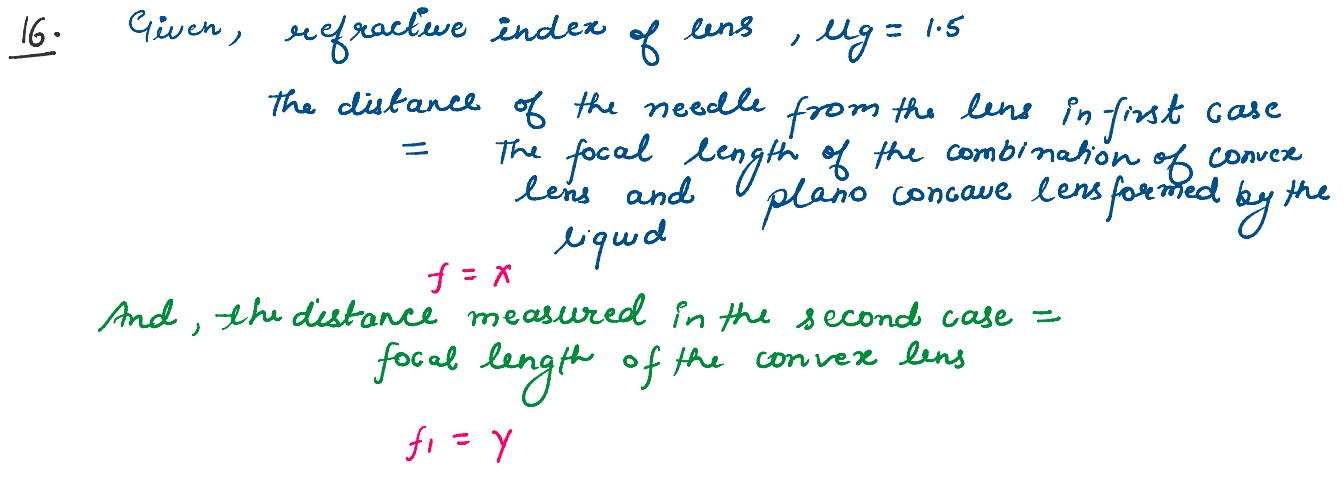
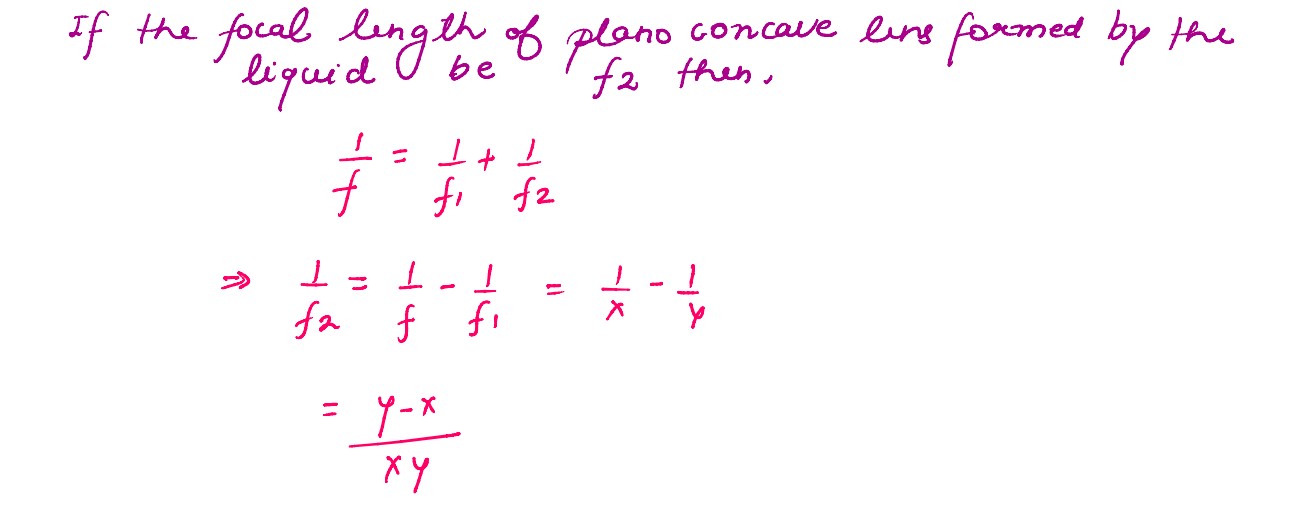
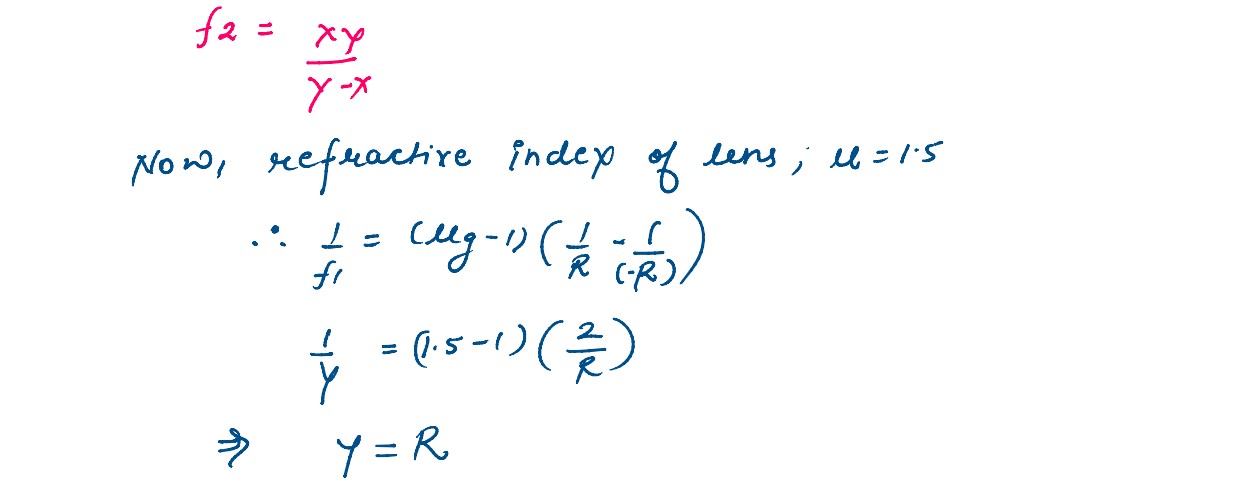
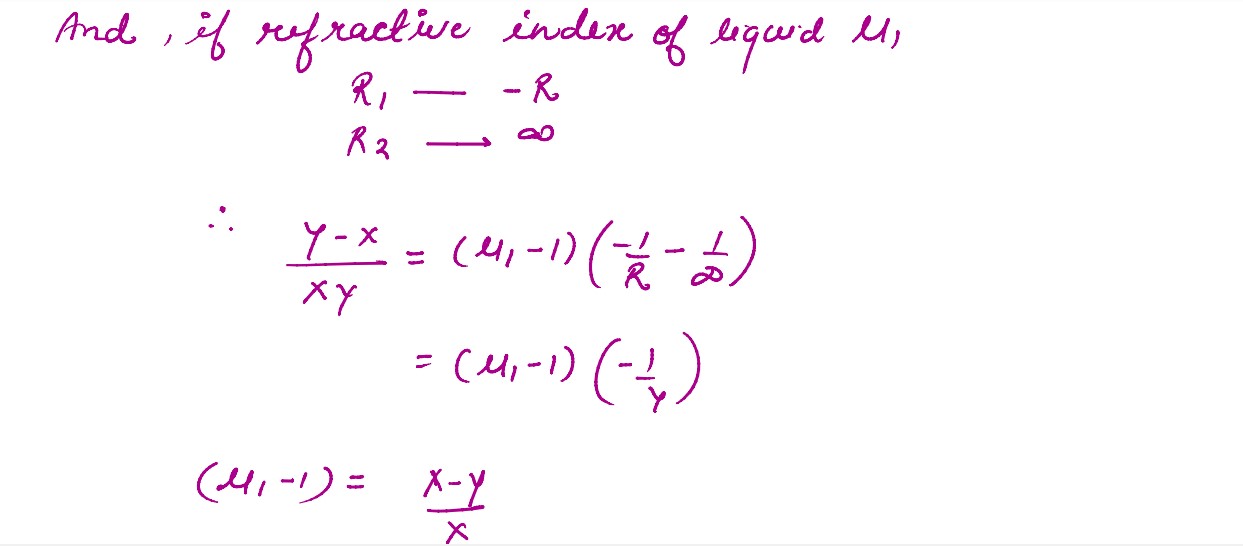
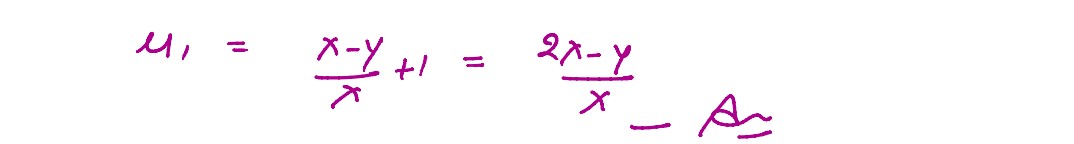

solutions
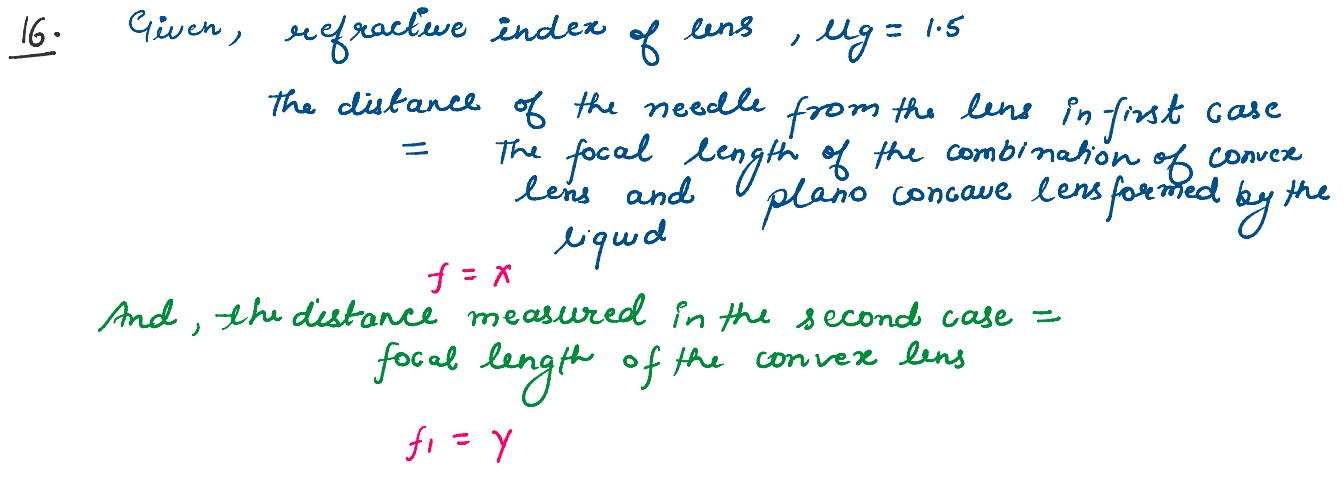
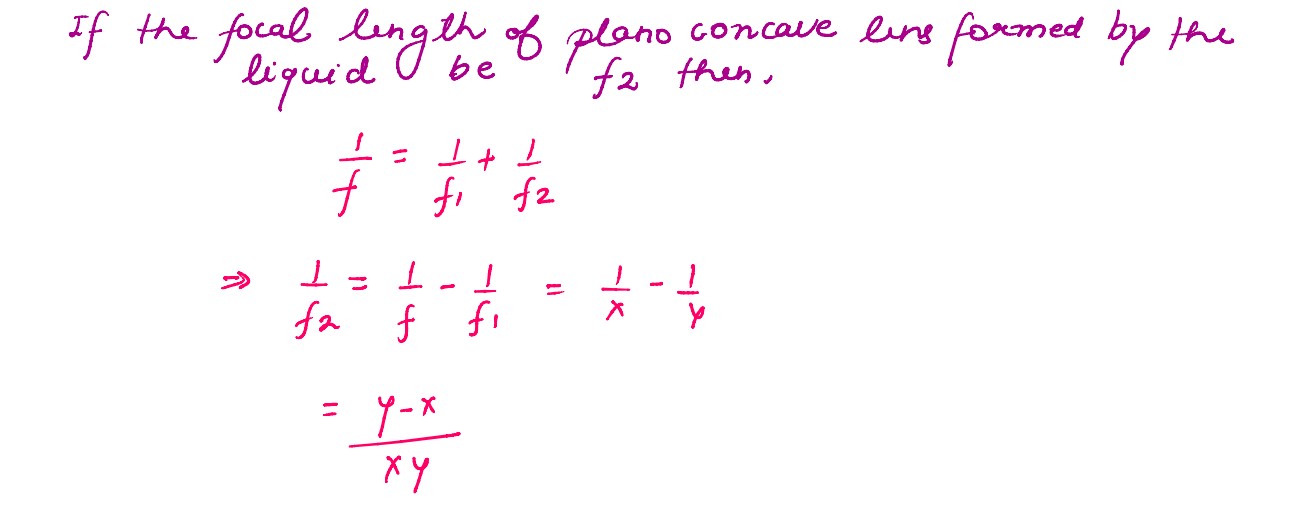
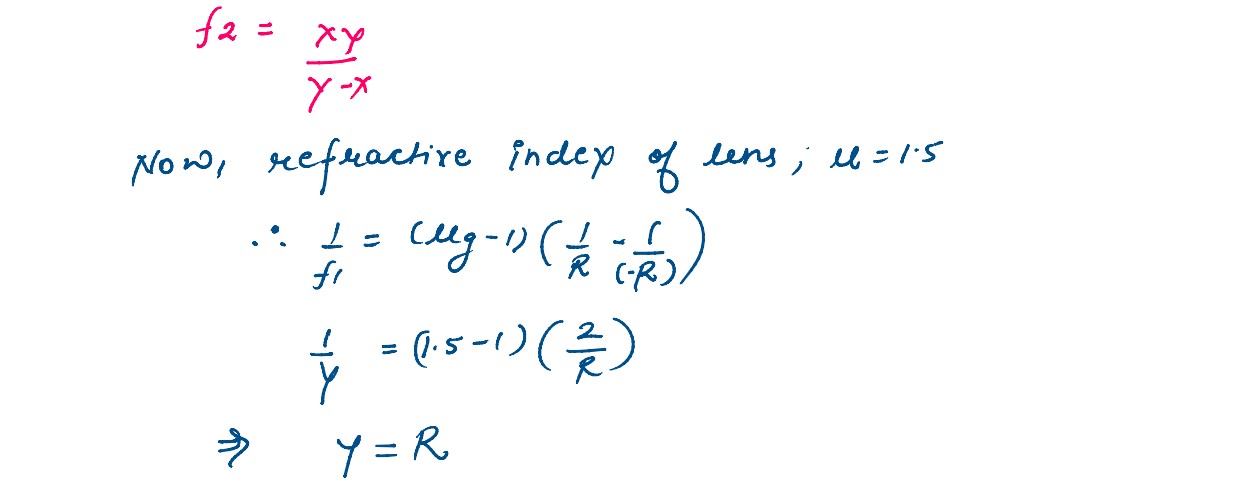
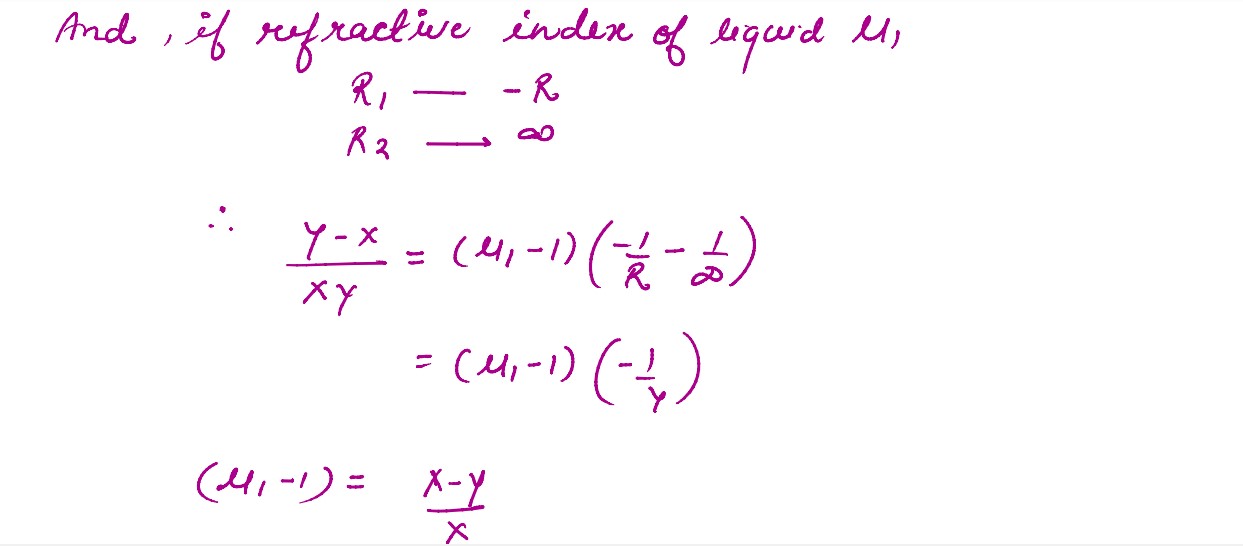
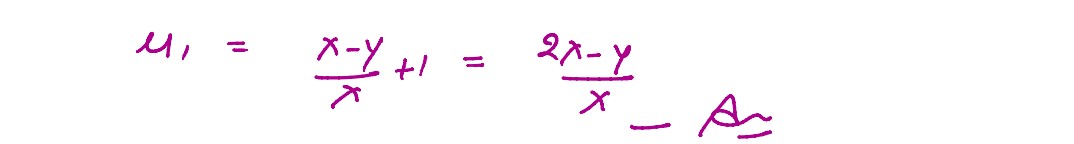
2019
Q1
What is the speed of light in a denser medium of polarising angle 30o.
solutions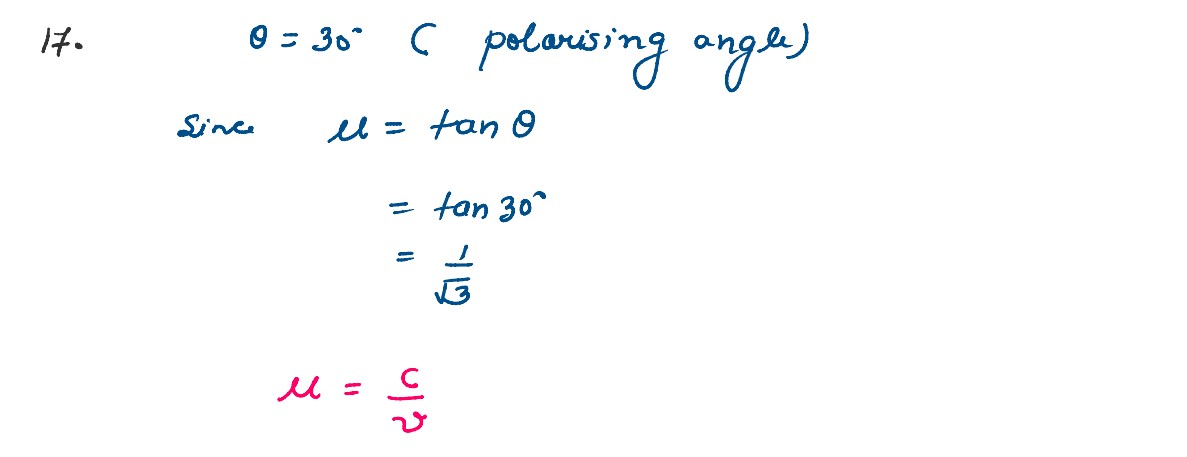
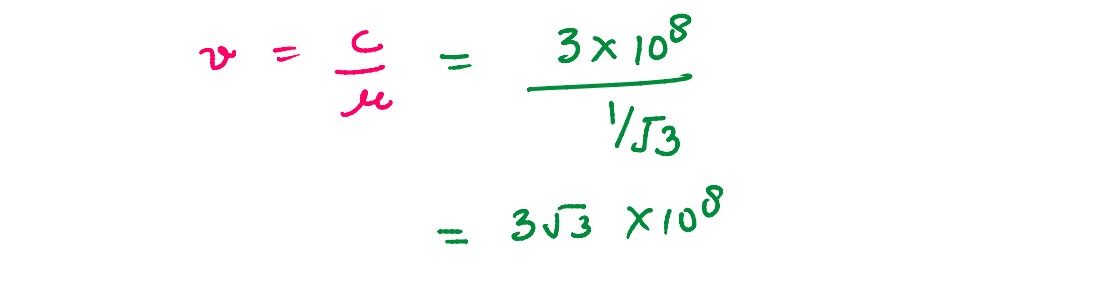
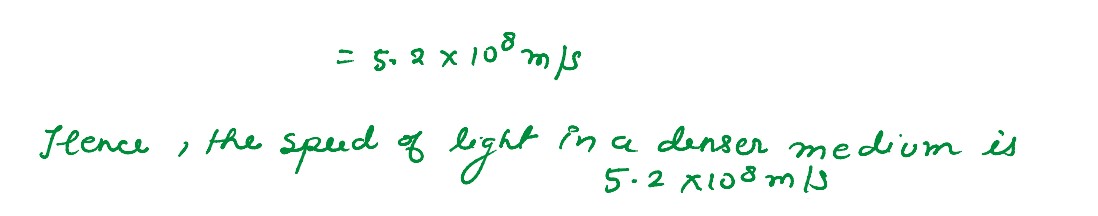
solutions
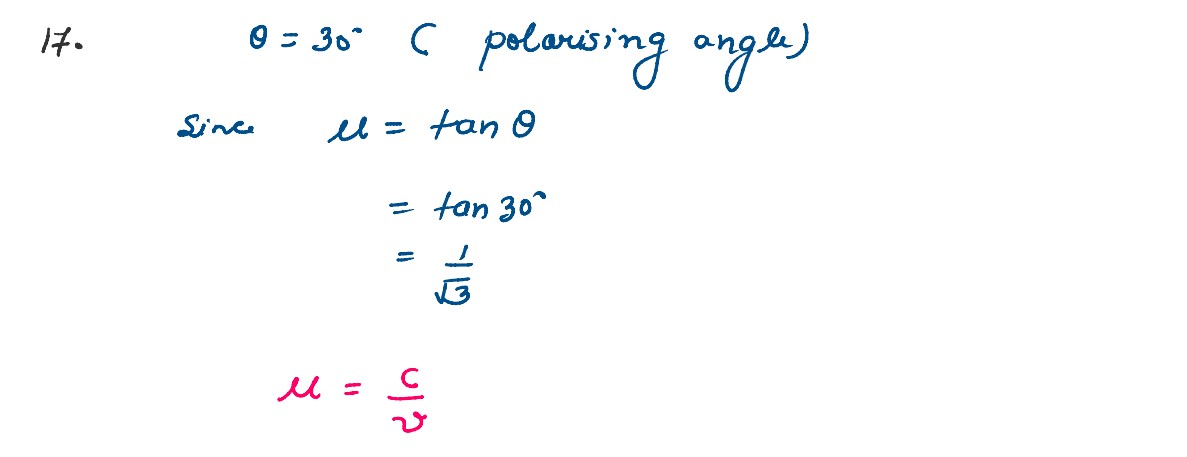
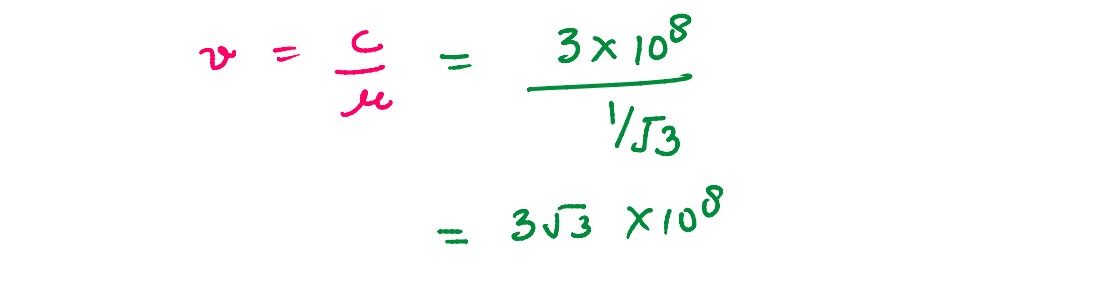
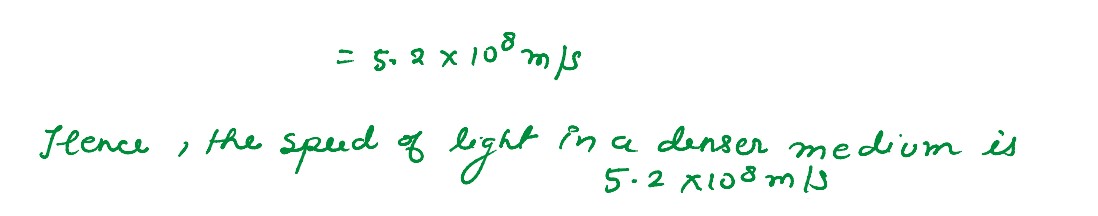
Q2
Calculate the radius of curvature of an equi concave lens of refractive index 1.5 when it is kept in
a medium refractive index 1.4 to have a power of -5 D
solutions
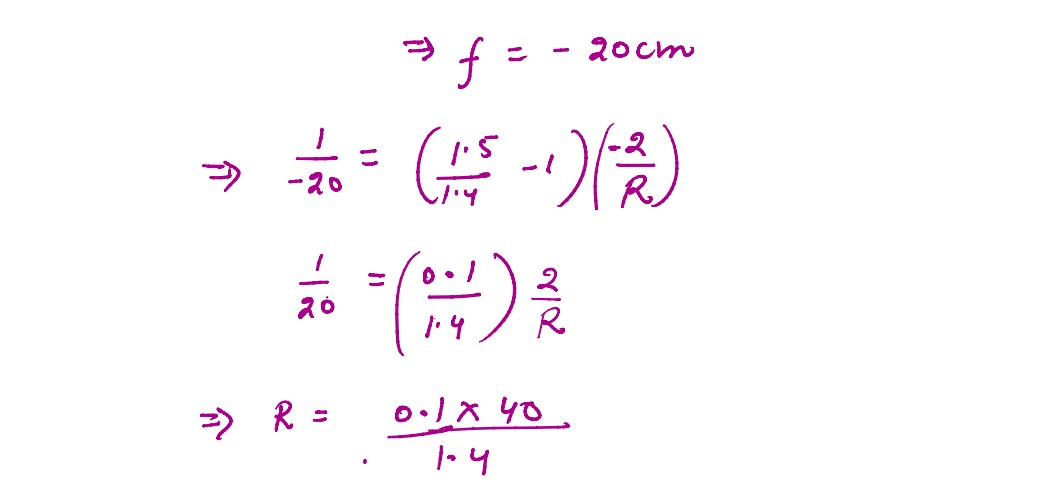
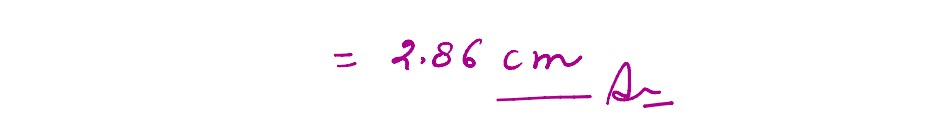
solutions

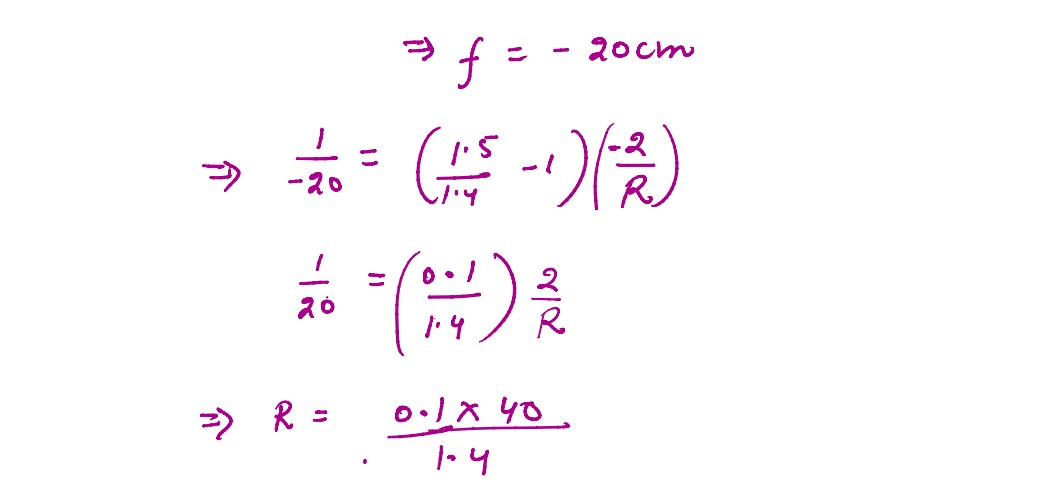
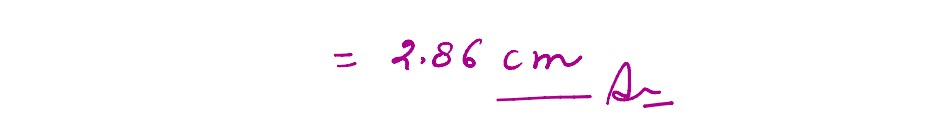
Q3
An equilateral glass prism has refractive index 1.6 in air, calculate the angle of minimum deviation
of the players when kept in a medium of refractive index 4 √2 / 5
solutions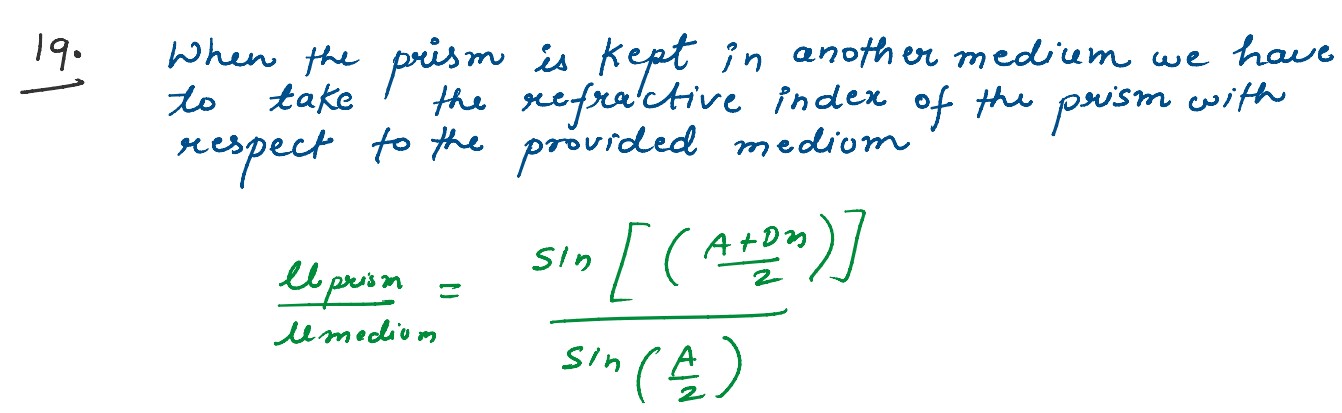
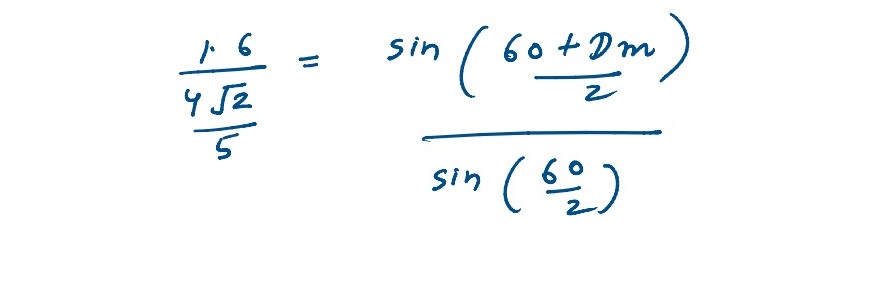
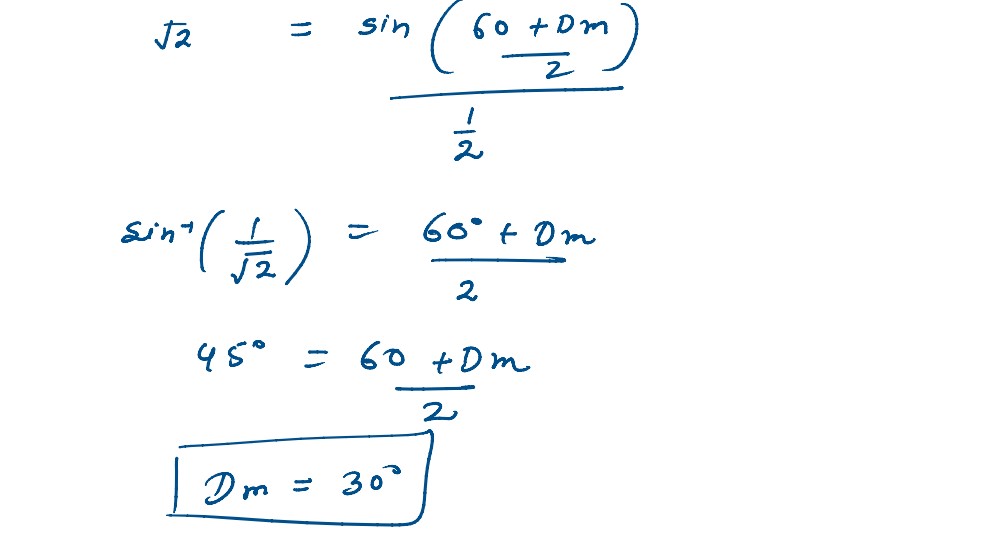
solutions
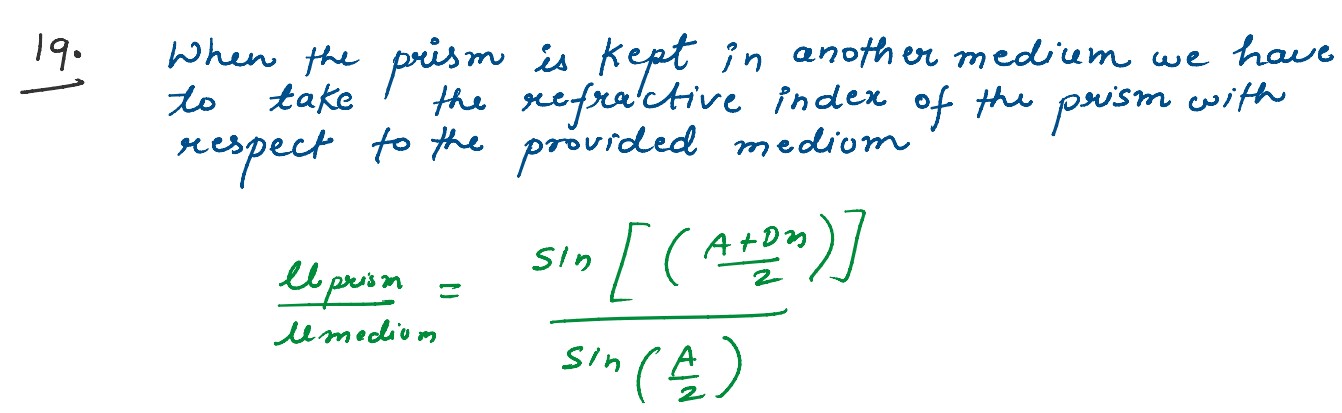
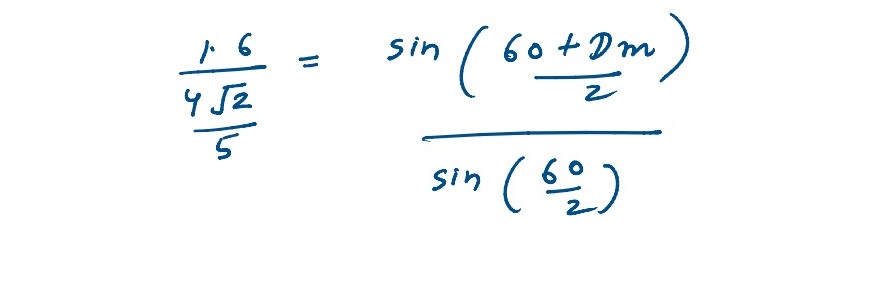
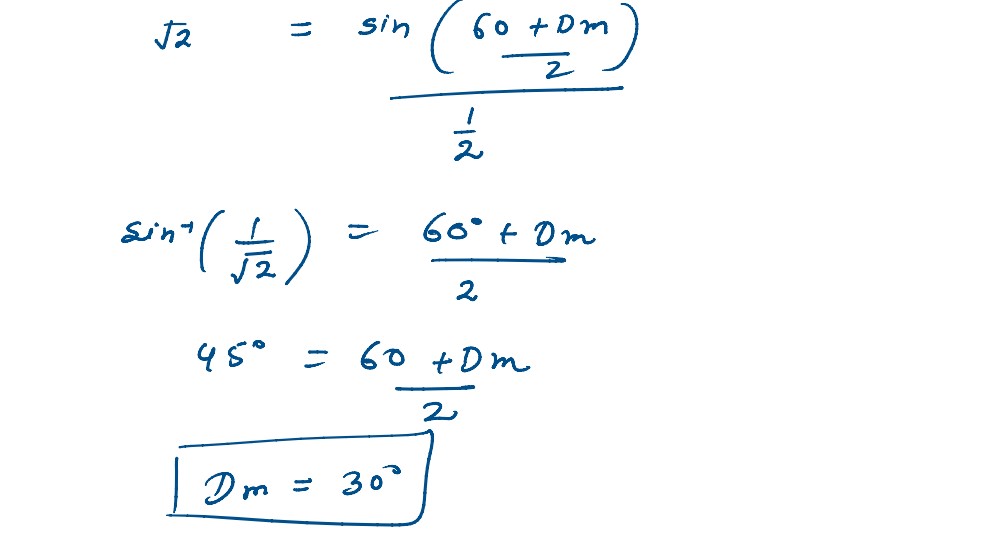
Q4
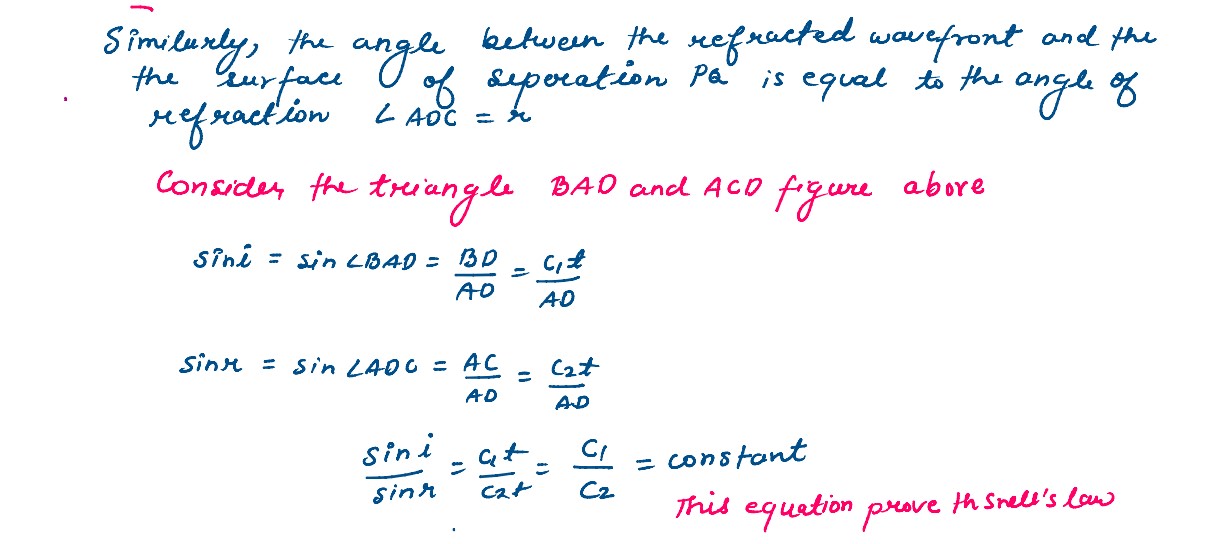
Define the term “refractive index” of a medium verified Snell’s law of refraction when plane
wavefront is propagating from a denser to rarer medium.
solutions
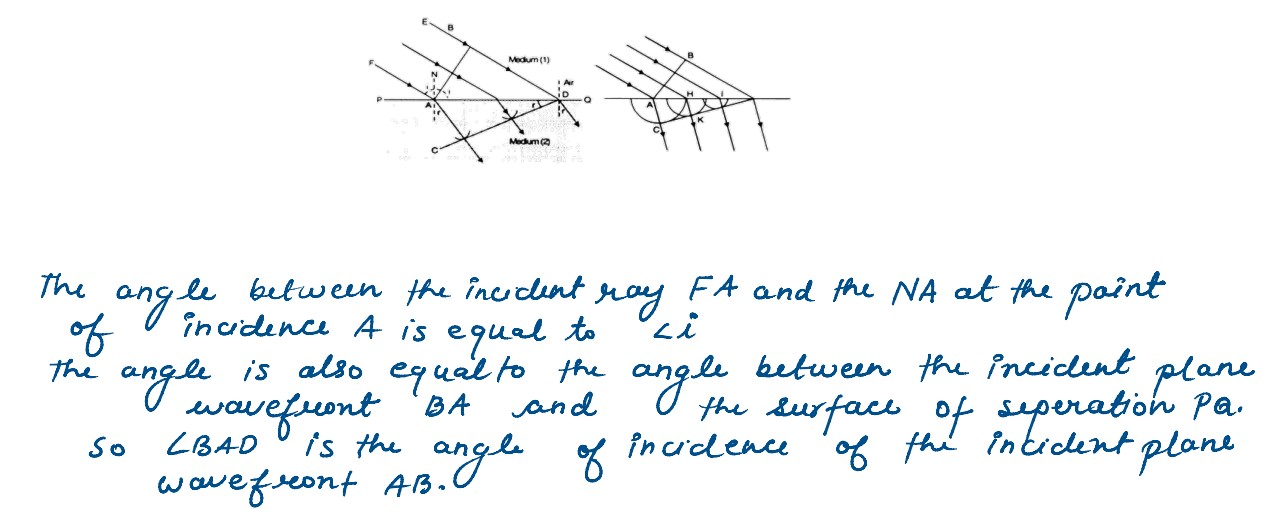
solutions



Q5
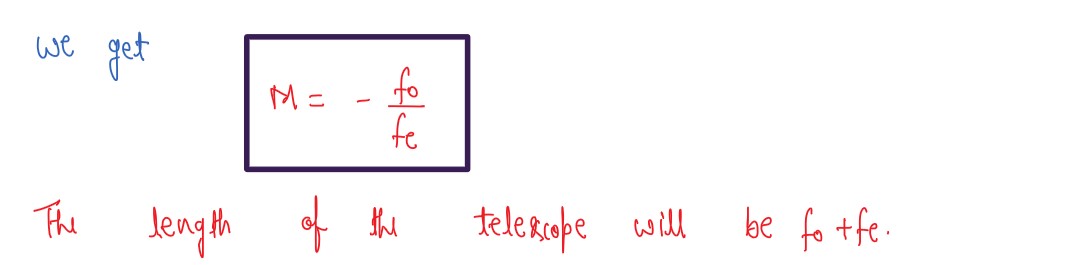
Draw a labelled ray diagram of astronomical telescope in the near point adjustment position
A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens of focal length 15 m and an eyepiece of focal length 1.0 cm. If the telescope is used to view the moon find the diameter of the image of the moon objective lens the diameter of the moon is 3.48 x 107 m in the radius of the lunar orbit is 3.8 x 108 m
solutions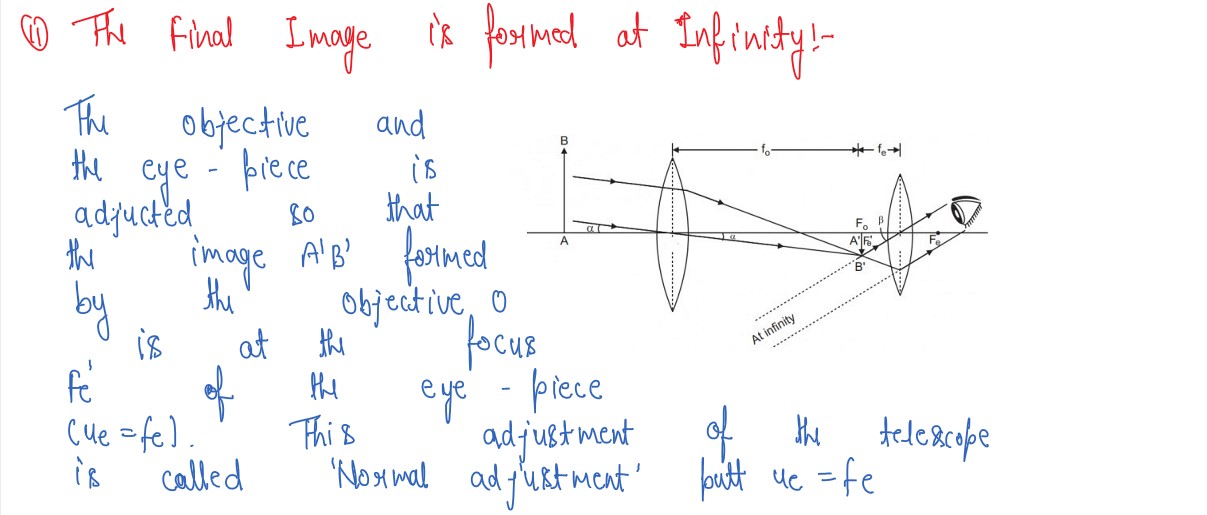

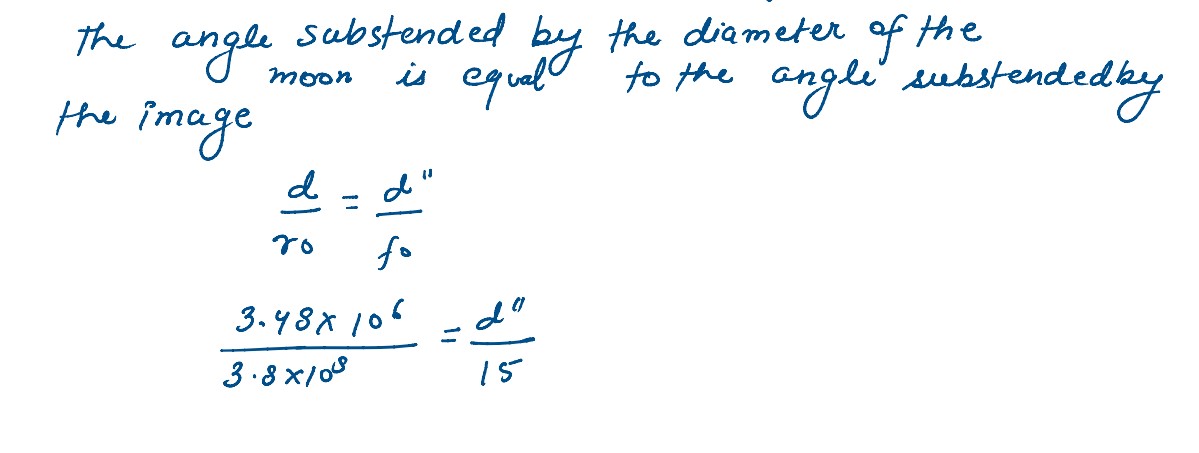
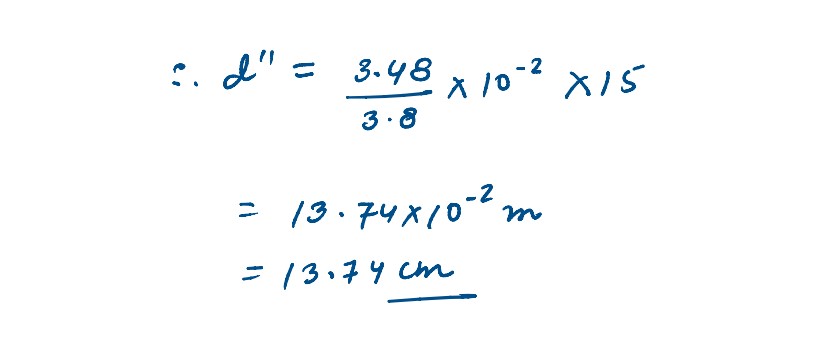
A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens of focal length 15 m and an eyepiece of focal length 1.0 cm. If the telescope is used to view the moon find the diameter of the image of the moon objective lens the diameter of the moon is 3.48 x 107 m in the radius of the lunar orbit is 3.8 x 108 m
solutions



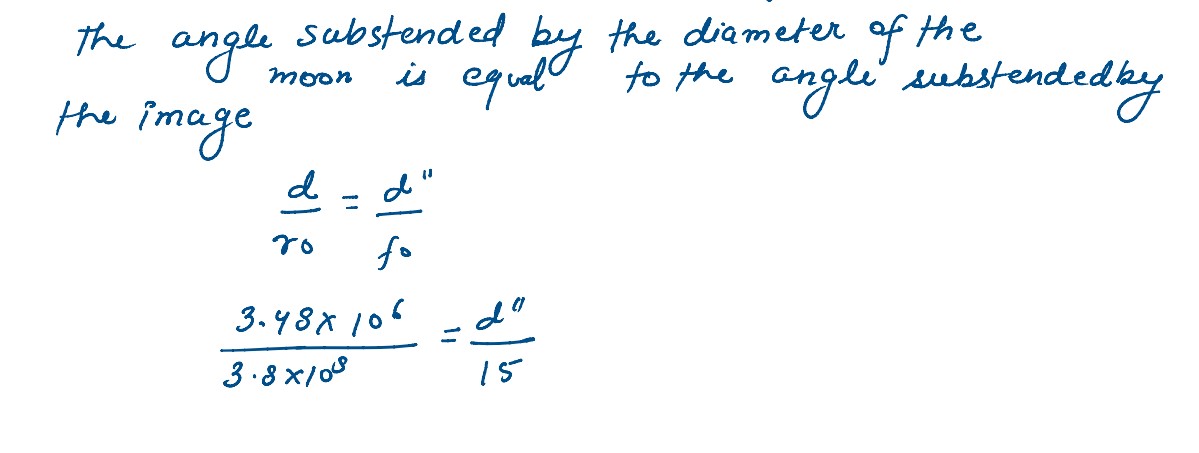
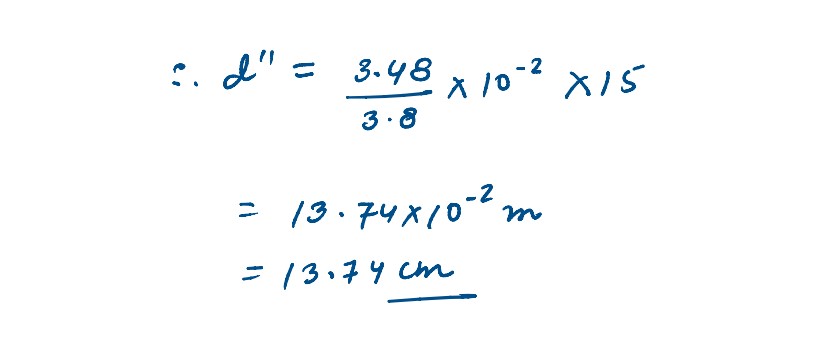
Q6
Under what condition is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed mark obtain
the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
solutions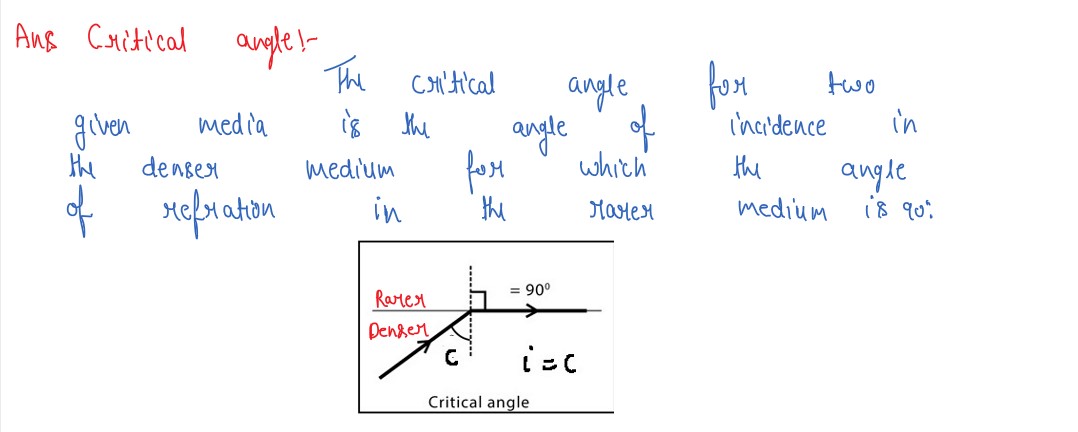
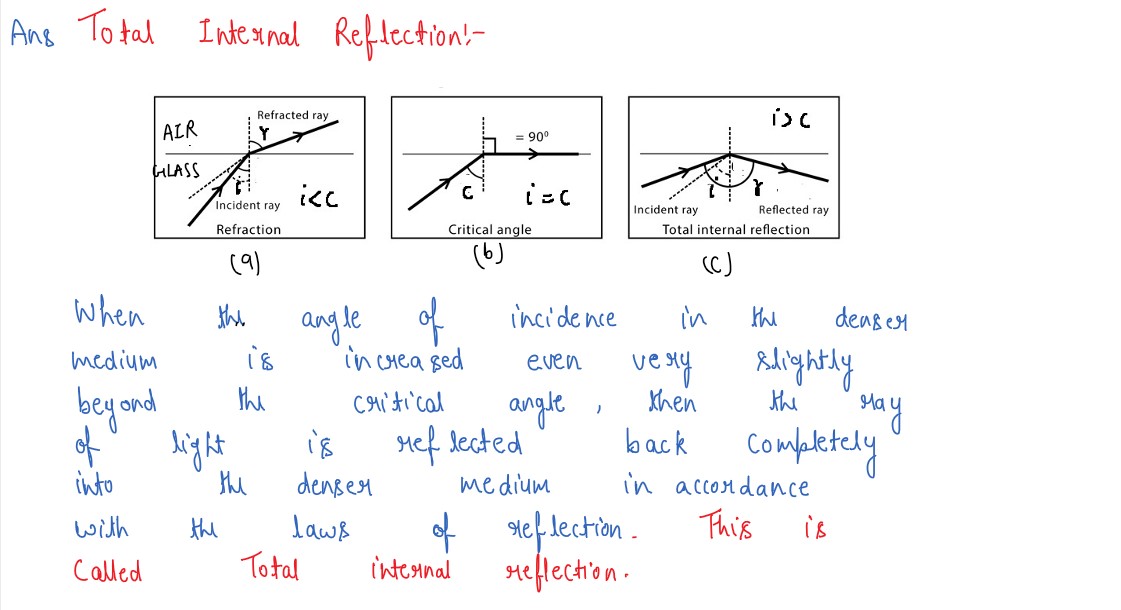
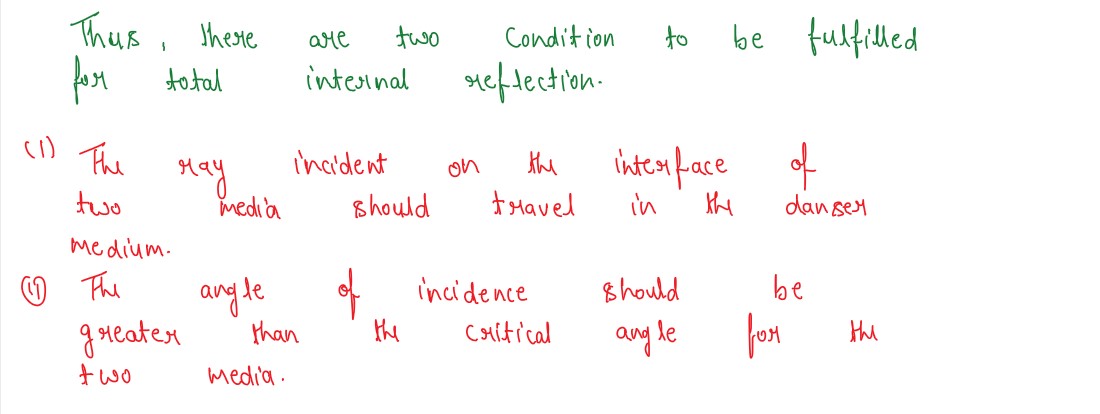
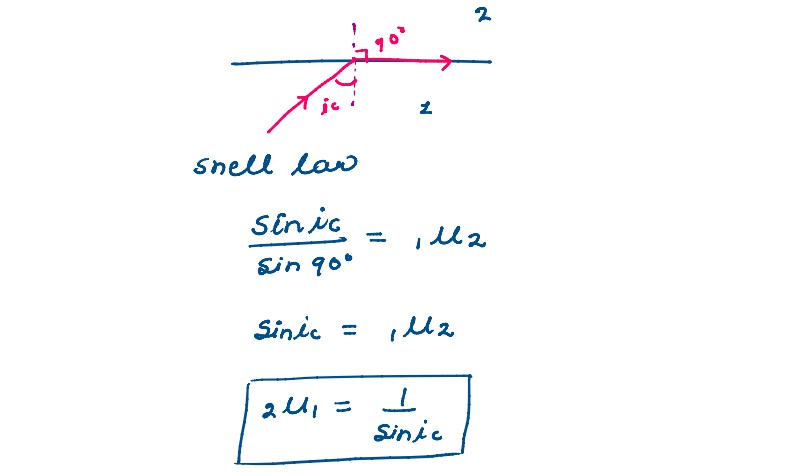
solutions



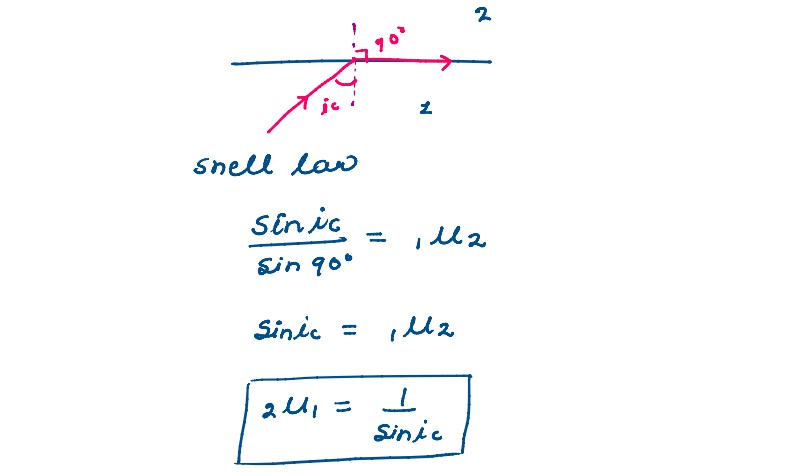
Q7
Three lens of focal lengths +10 cm, -10 cm and +30 cm arrange coaxially as in the figure given
below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.
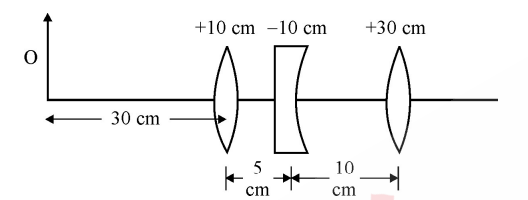
solutions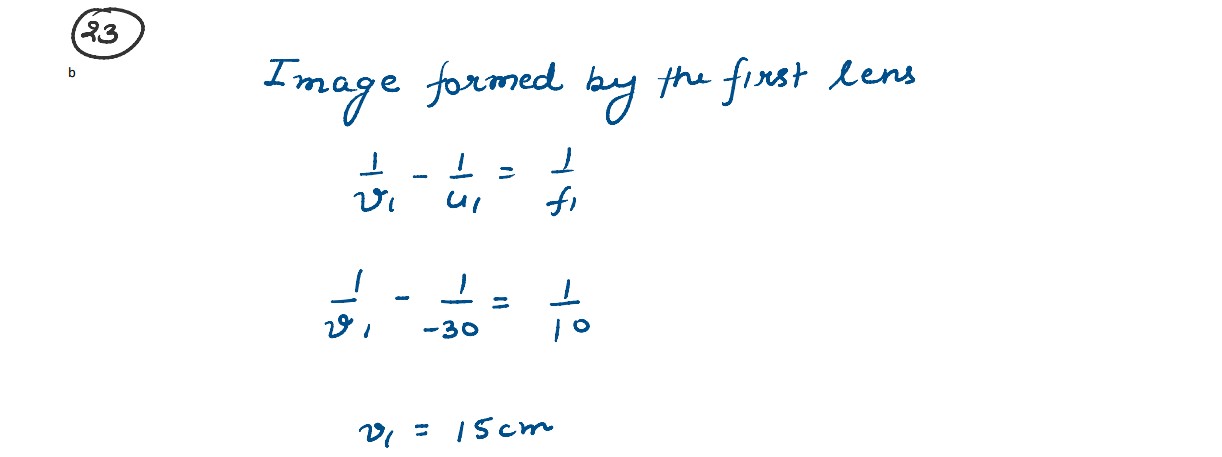
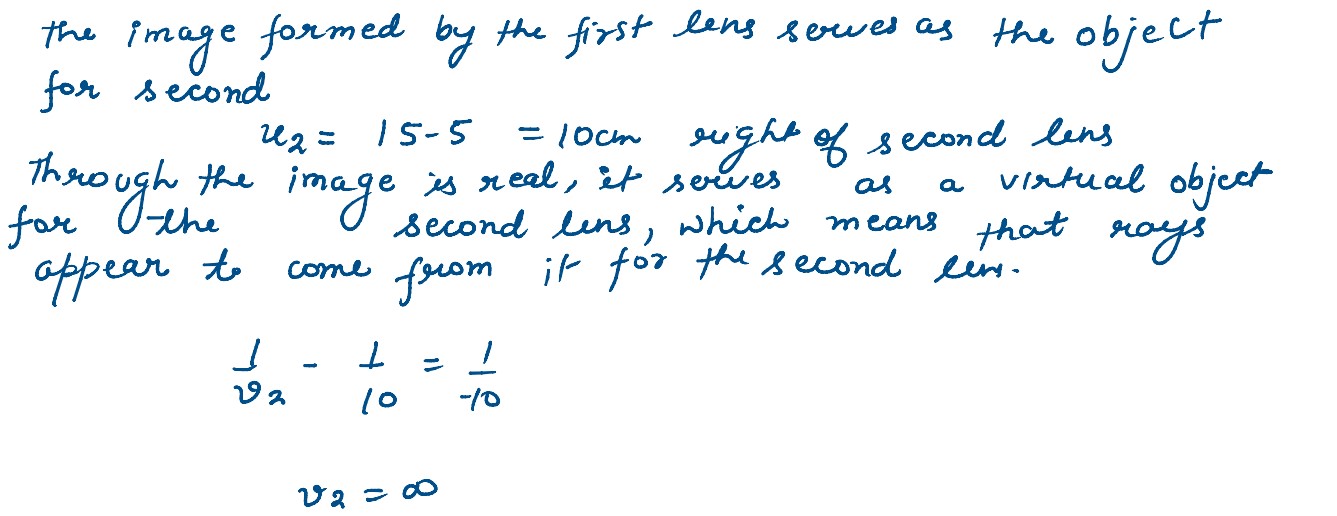


solutions
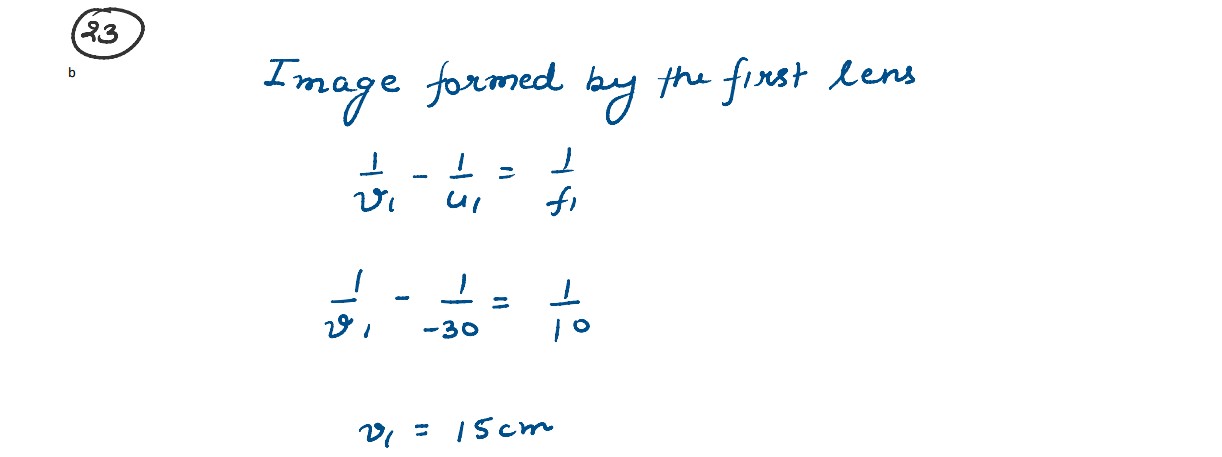
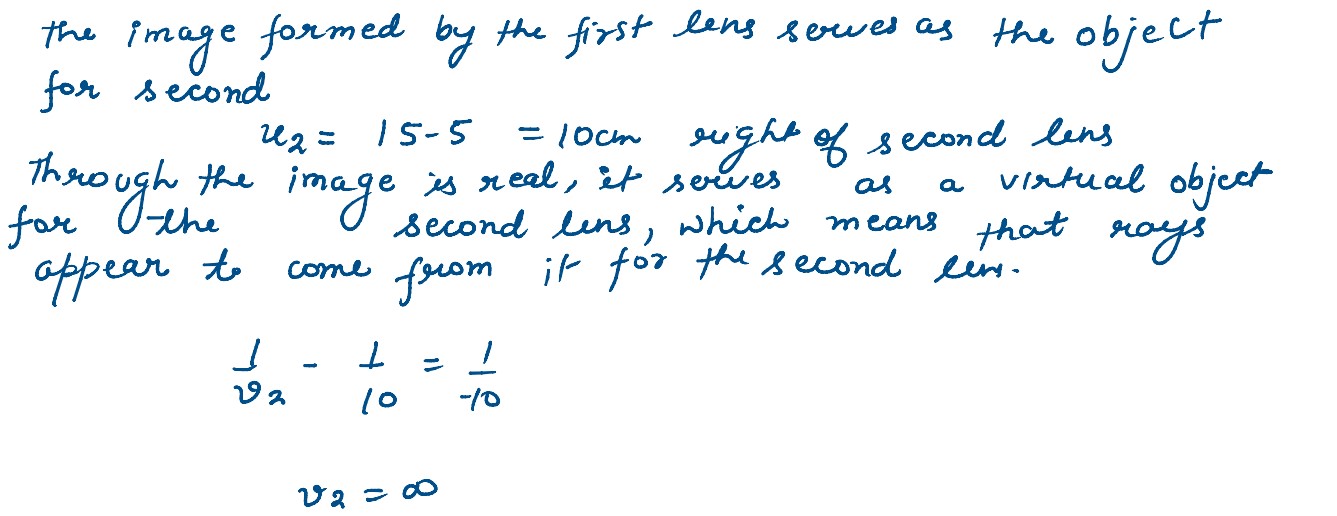

2020
Q1
Larger aperture of objective lens in an astronomical telescope
(A) increases the resolving power of telescope.
(B) decreases the brightness of the image.
(C) increases the size of the image.
(D) decreases the length of the telescope.
solutions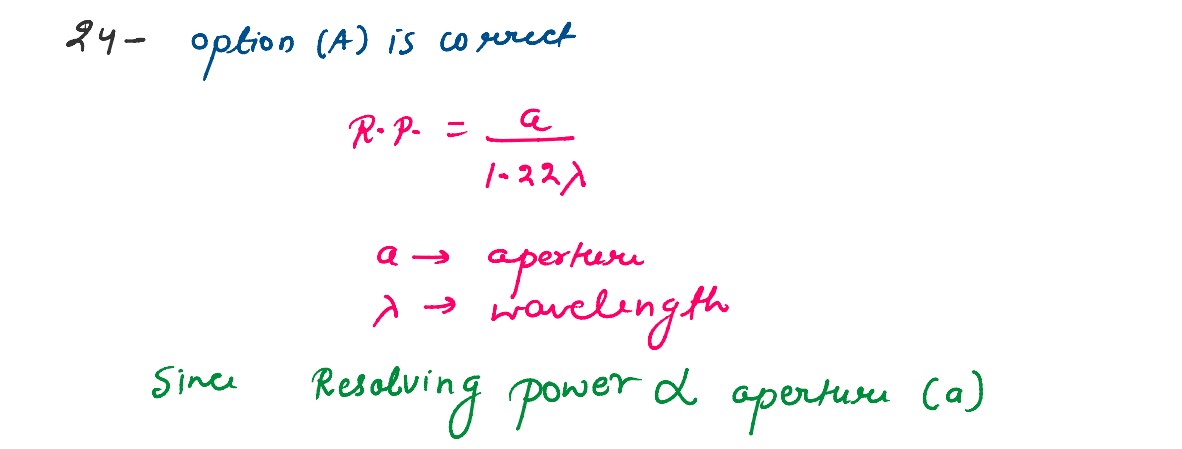
(A) increases the resolving power of telescope.
(B) decreases the brightness of the image.
(C) increases the size of the image.
(D) decreases the length of the telescope.
solutions
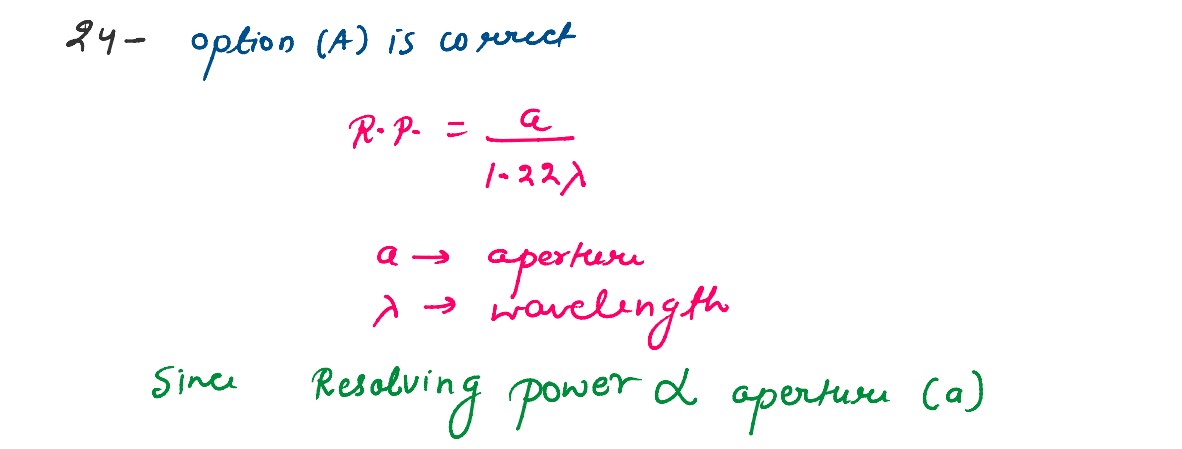
Q2
A biconvex lens of glass having refractive index 1•47 is immersed in a liquid. It becomes invisible
and behaves as a plane glass plate. The refractive index of the liquid is 1
(A) 1•47
(B) 1•62
(C) 1•33
(D) 1•51
solutions
(A) 1•47
(B) 1•62
(C) 1•33
(D) 1•51
solutions

Q3
A ray of light on passing through an equilateral glass prism, suffers a minimum deviation equal to
the angle of the prism. The value of refractive index of the material of the prism is ___________ .
solutions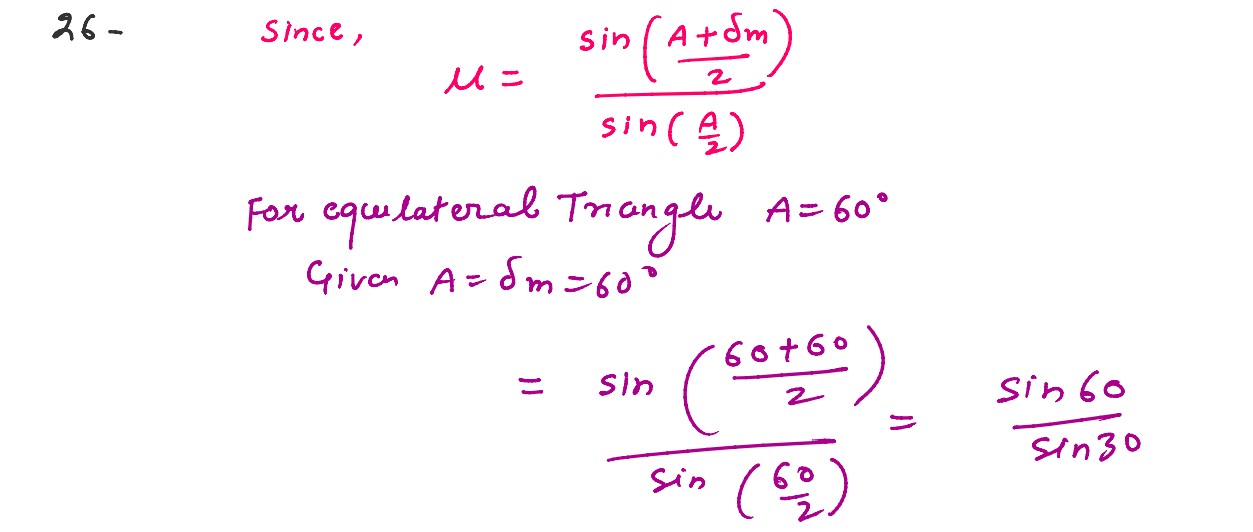
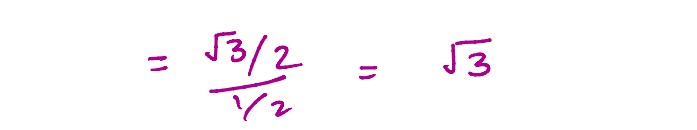
solutions
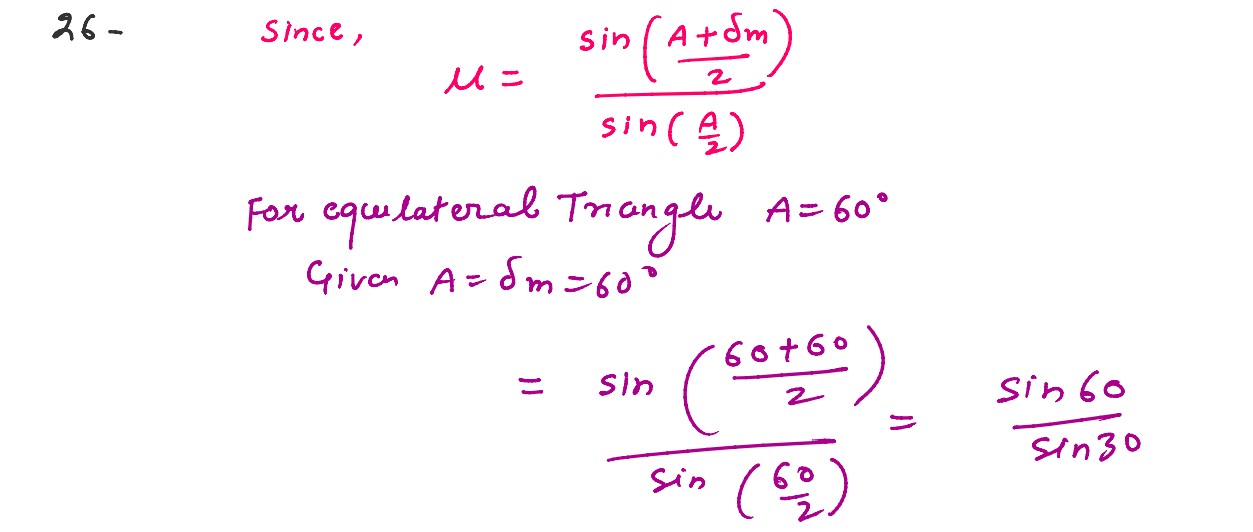
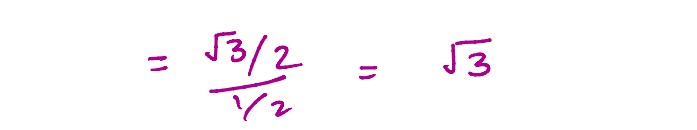
Q5
(a)Draw the ray diagram of an astronomical telescope when the final image is formed at infinity.
Write the expression for the resolving power of the telescope
(b) An astronomical telescope has an objective lens of focal length 20 m and eyepiece of focal length 1 cm.
(i) Find the angular magnification of the telescope.
(ii) If this telescope is used to view the Moon, find the diameter of the image formed by the objective lens. Given the diameter of the Moon is 3•5 x 106 m and radius of lunar orbit is 3•8 x 108 m.
solutions
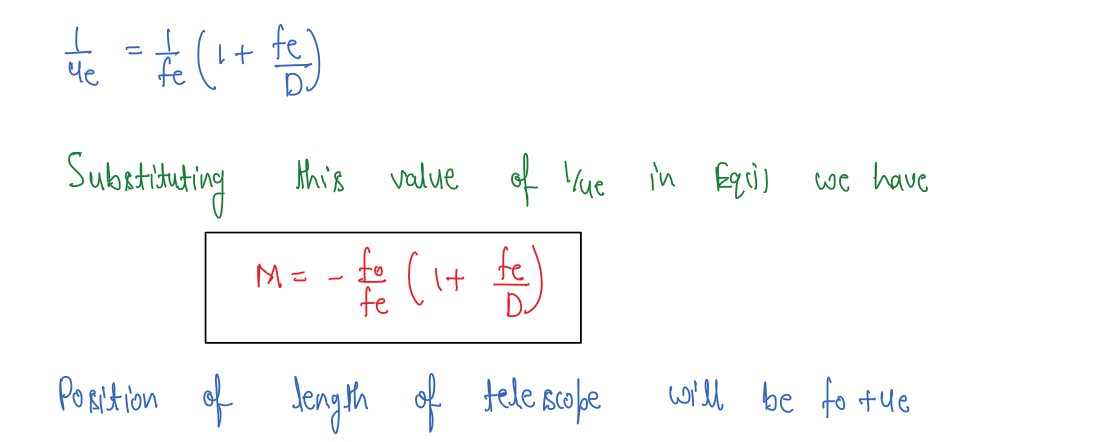
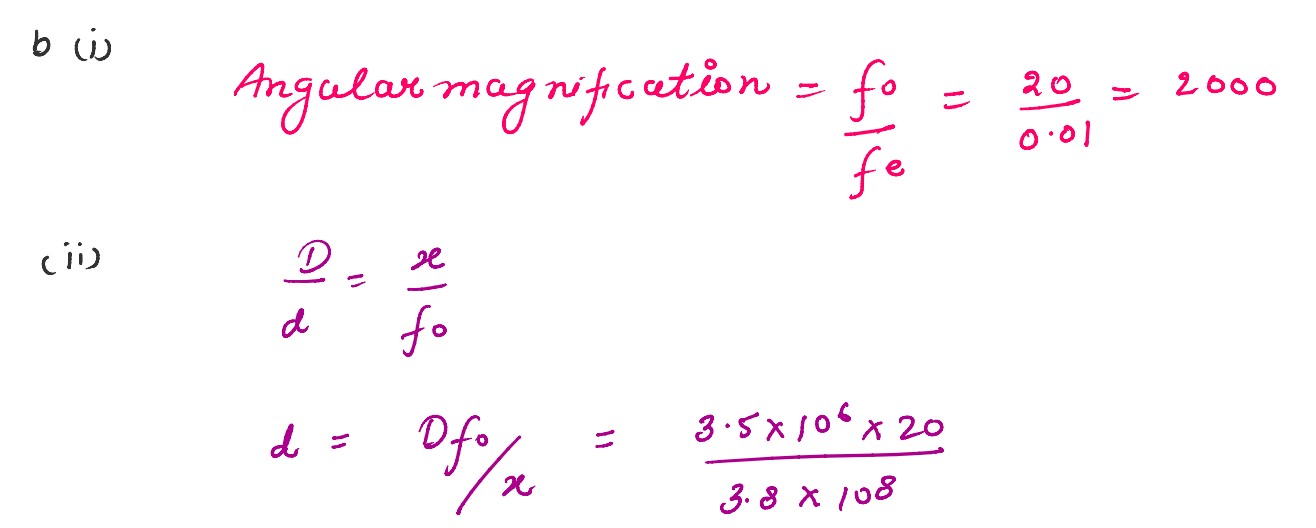

(b) An astronomical telescope has an objective lens of focal length 20 m and eyepiece of focal length 1 cm.
(i) Find the angular magnification of the telescope.
(ii) If this telescope is used to view the Moon, find the diameter of the image formed by the objective lens. Given the diameter of the Moon is 3•5 x 106 m and radius of lunar orbit is 3•8 x 108 m.
solutions


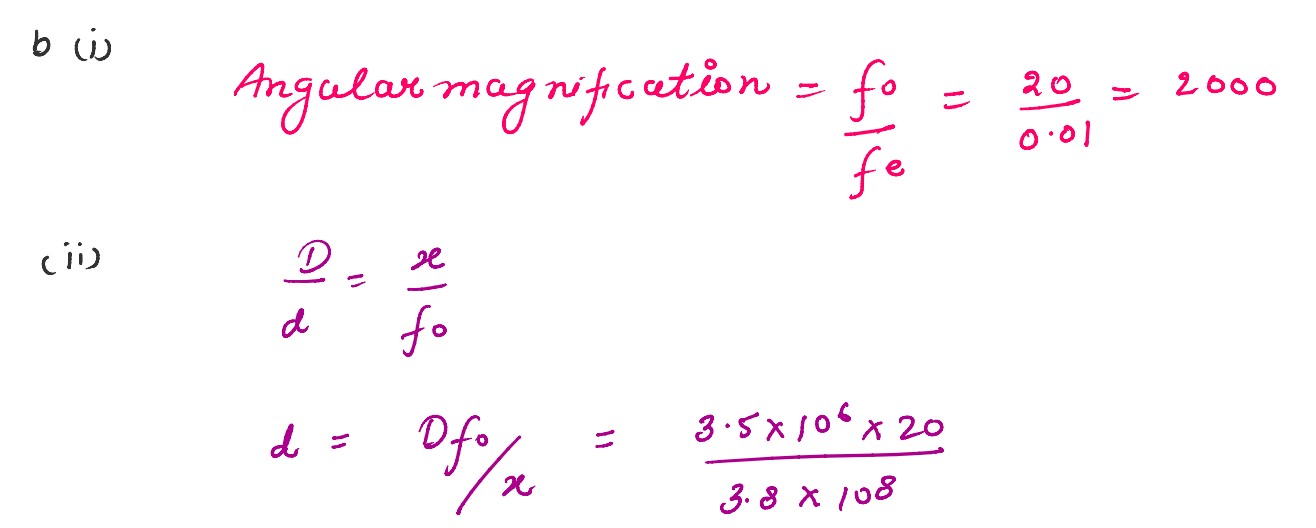

Q6
(a) An object is placed in front of a concave mirror. It is observed that a virtual image is formed.
Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation and hence derive the mirror equation 1/f=1/u+1/v
(b) An object is placed 30 cm in front of a plano-convex lens with its spherical surface of radius of curvature 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1•5, find the position and nature of the image formed.
solutions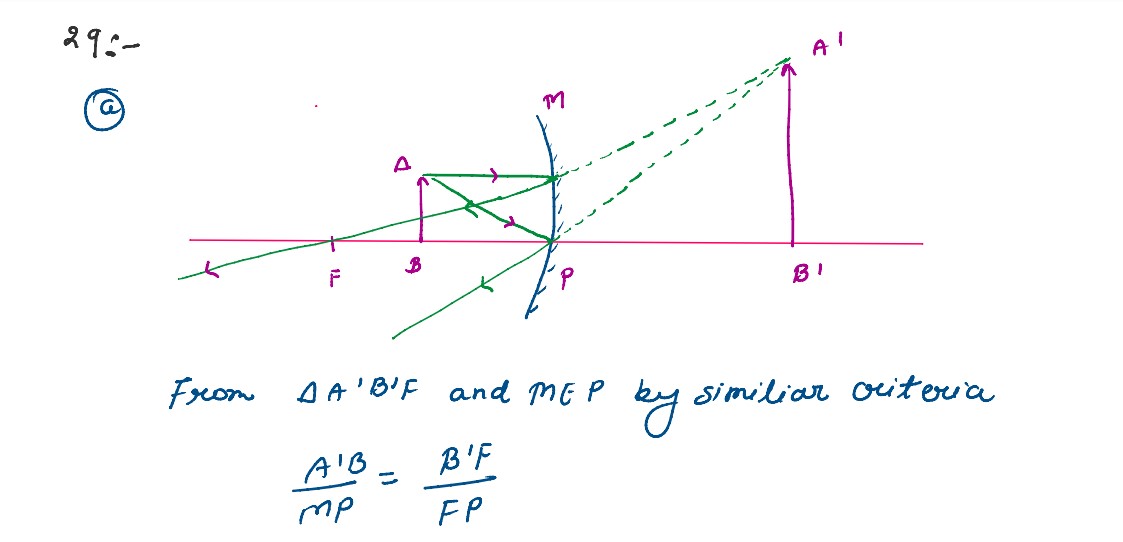
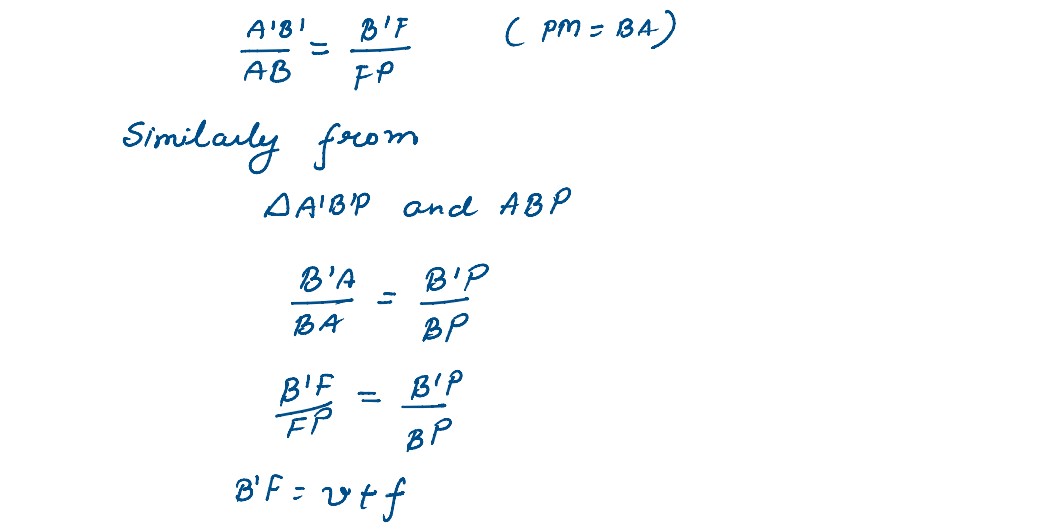
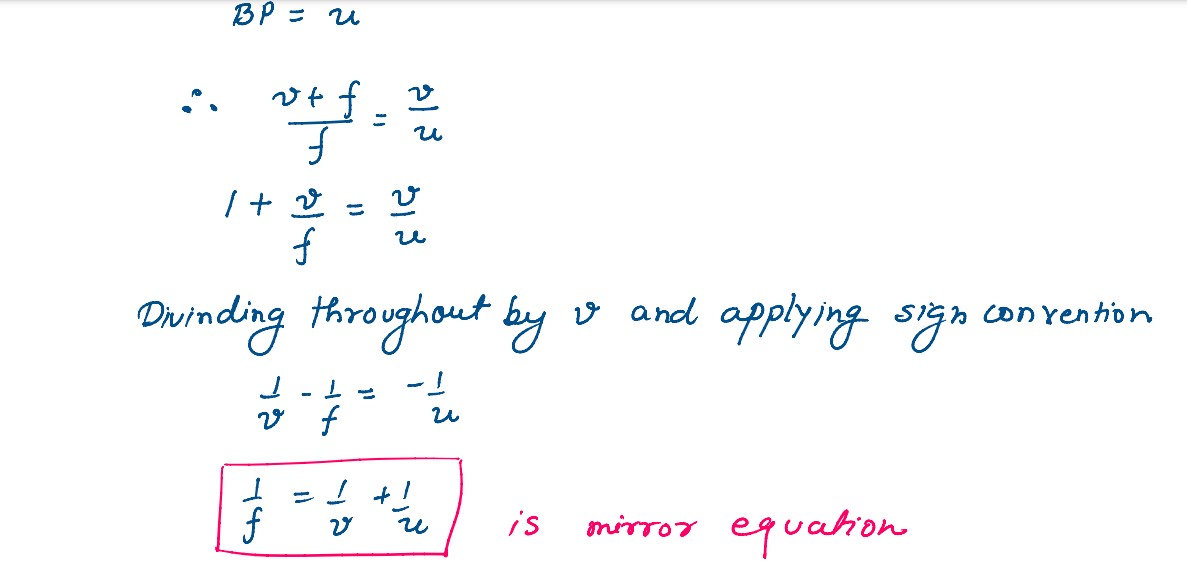
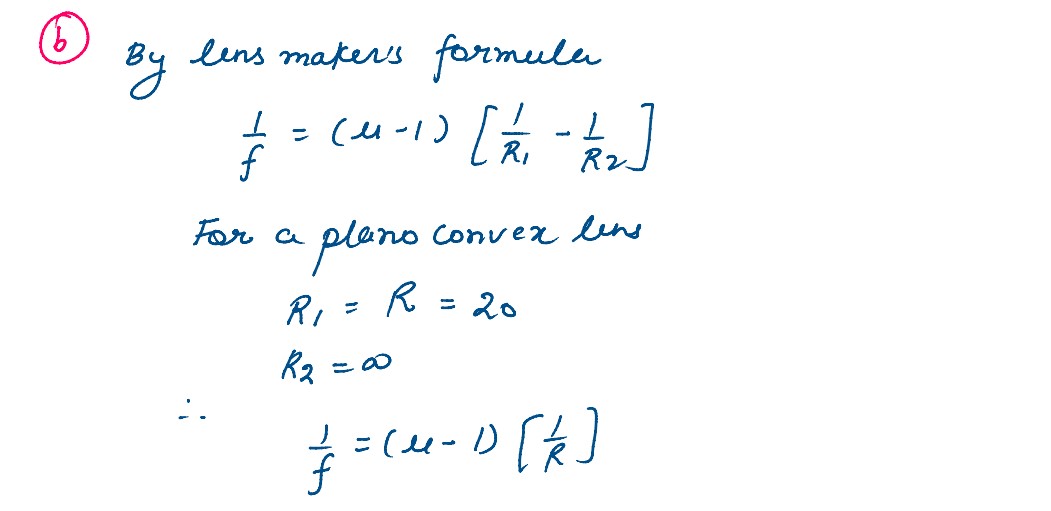
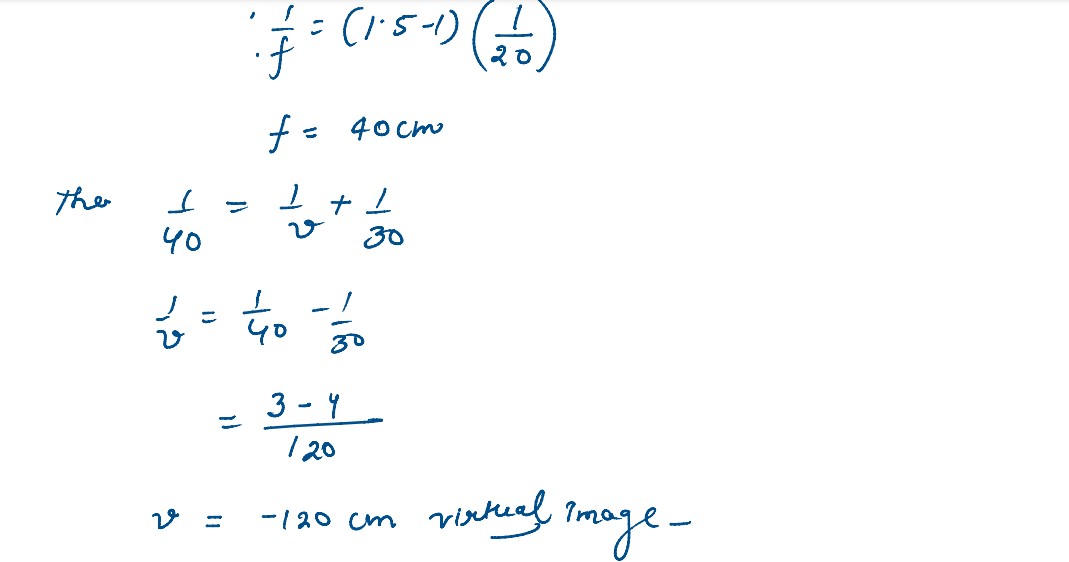
(b) An object is placed 30 cm in front of a plano-convex lens with its spherical surface of radius of curvature 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1•5, find the position and nature of the image formed.
solutions

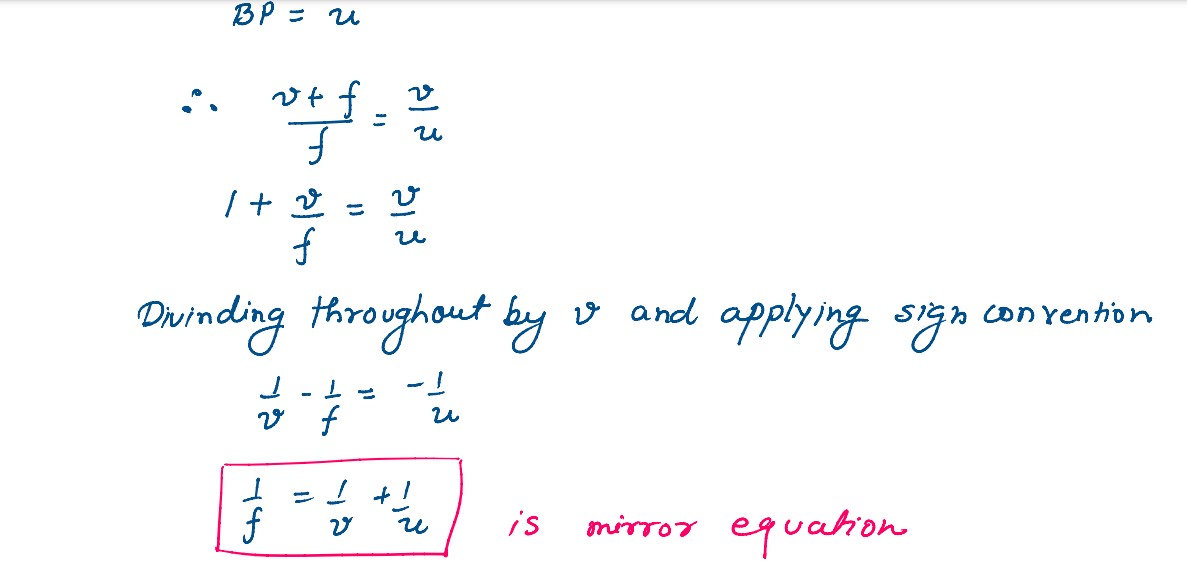
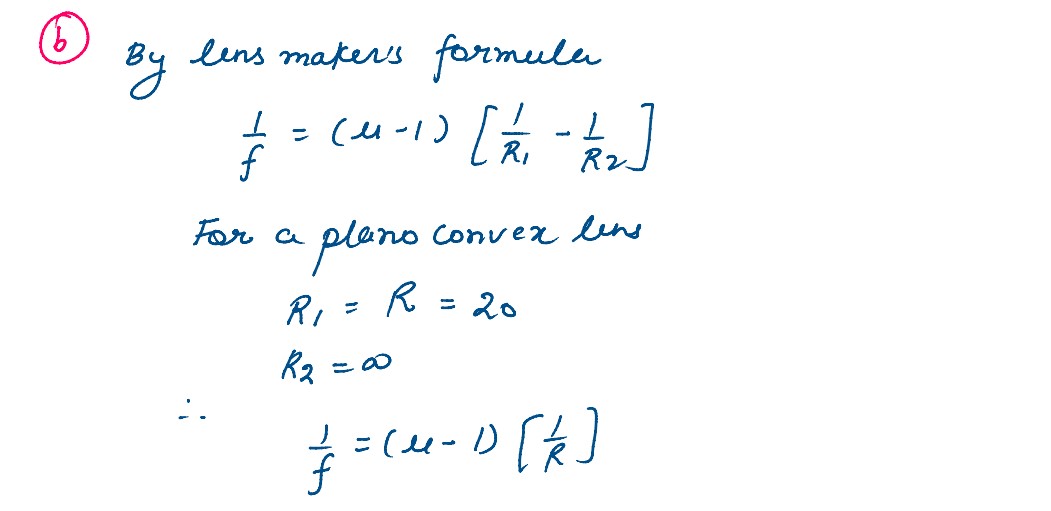
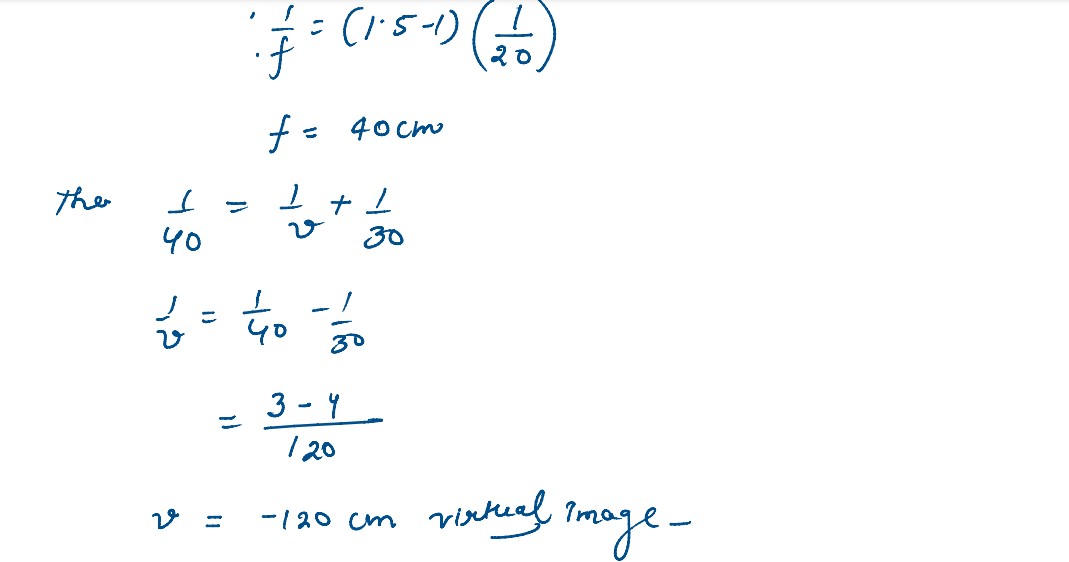


Add a comment