Class 12 Chemistry ISC Electrochemistry Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 chemistry important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter Electrochemistry. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on ISC board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 chemistry syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
2020
Q1
The molar conductivity of NaCl, CH3COONa and HCl at infinite dilution is 126.45, 91.0 and
426.16 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 respectively. Calculate the molar
conductivity (λ∞m ) for CH3COOH at infinite dilution.
solutions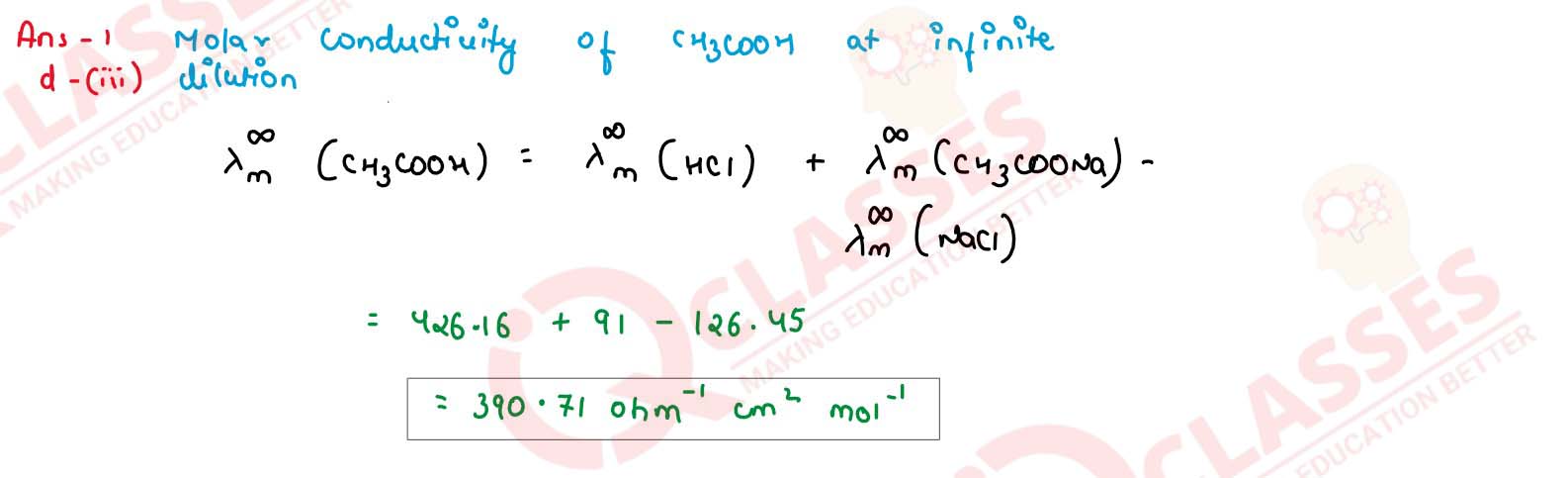
solutions

Q2
Calculate the emf and △G for the given cell at 25°C: Cr(s)/Cr3+ (0.1 M)
// Fe2+ (0.01 M)/ Fe(s) Given: E0Cr3+/Cr =
0.74V , E0Fe2+/Fe = - 0.44 V (1 F = 96500 C, R = 8.314 J
K-1 mol-1)
40.95 S cm2 mot
solutions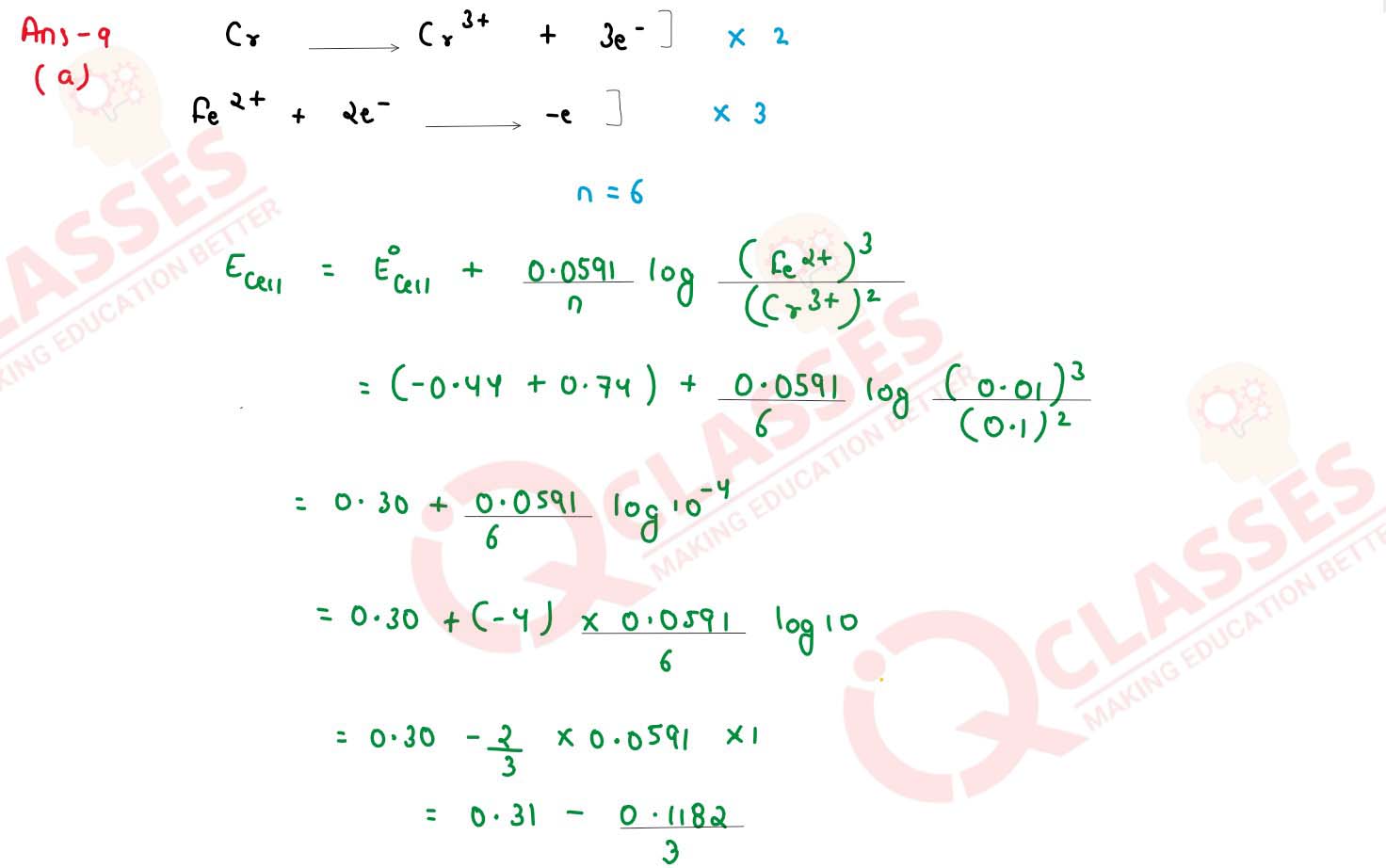

solutions


OR
Q3
Calculate the degree of dissociation (∞) of acetic acid, if its molar conductivity
(λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol -1 Given
(λ0H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol-1 and
(λ0CH3COO-) = 40.95 S cm2
mol-1
solutions
solutions

2019
Q4
Calculate the mass of silver deposited at cathode when a current of 2 amperes is passed through a
solution of a AgNO3 for 15 minutes (atomic weight of Ag = 108, 1 F = 96,500 C)
solutions
solutions

Q5
Calculate the emf and △G0 for the cell reaction at 298 K
Mg(s) | Mg2+(0.1M) || Cu2+(0.01 M) |Cu(s)
Given E0cell = 2.71 V
1 F = 96,500 C
solutions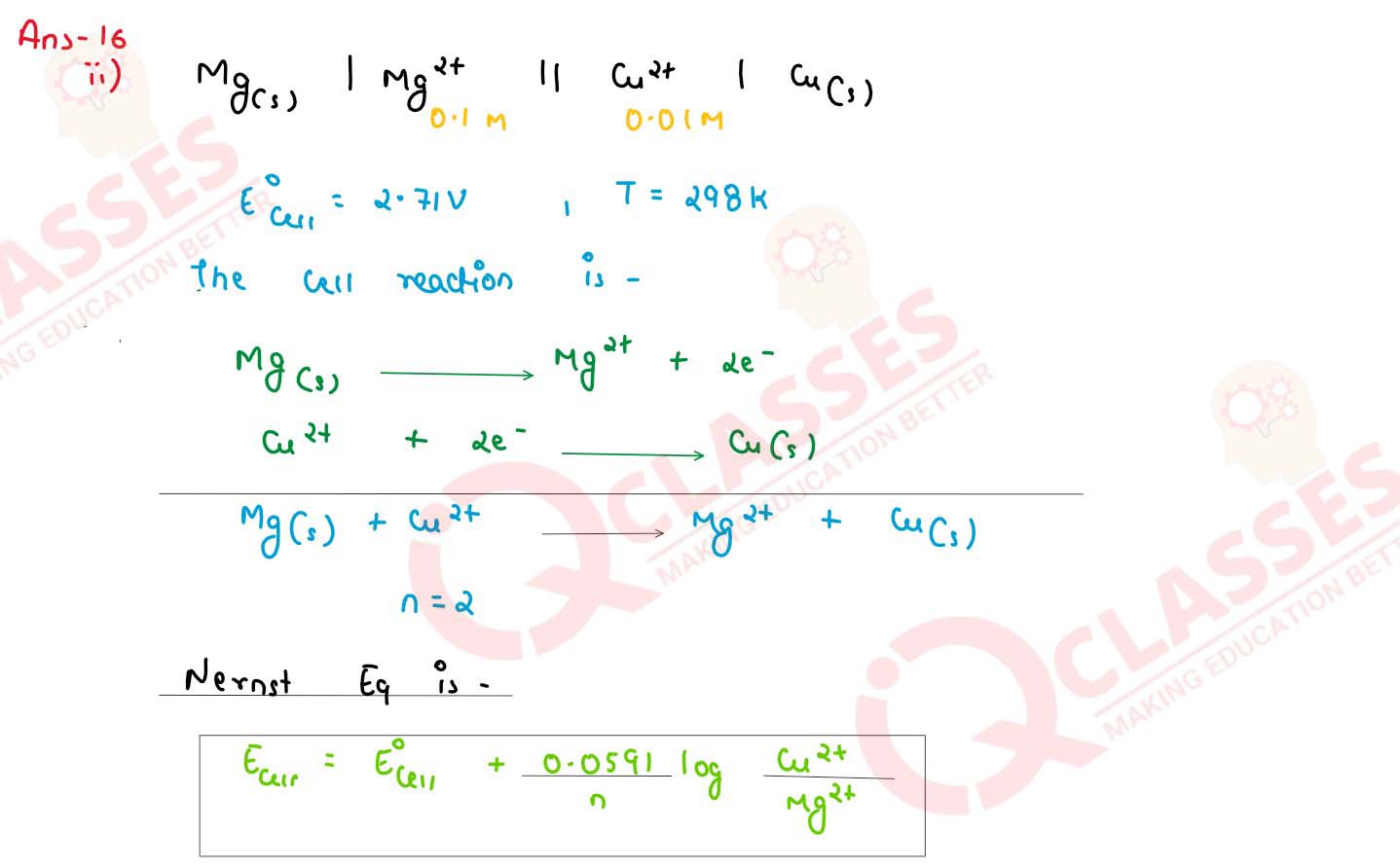

Mg(s) | Mg2+(0.1M) || Cu2+(0.01 M) |Cu(s)
Given E0cell = 2.71 V
1 F = 96,500 C
solutions


OR
Q6
(i) Define the following terms :
(1) specific conductance
(2) Kohlrausch's law
solutions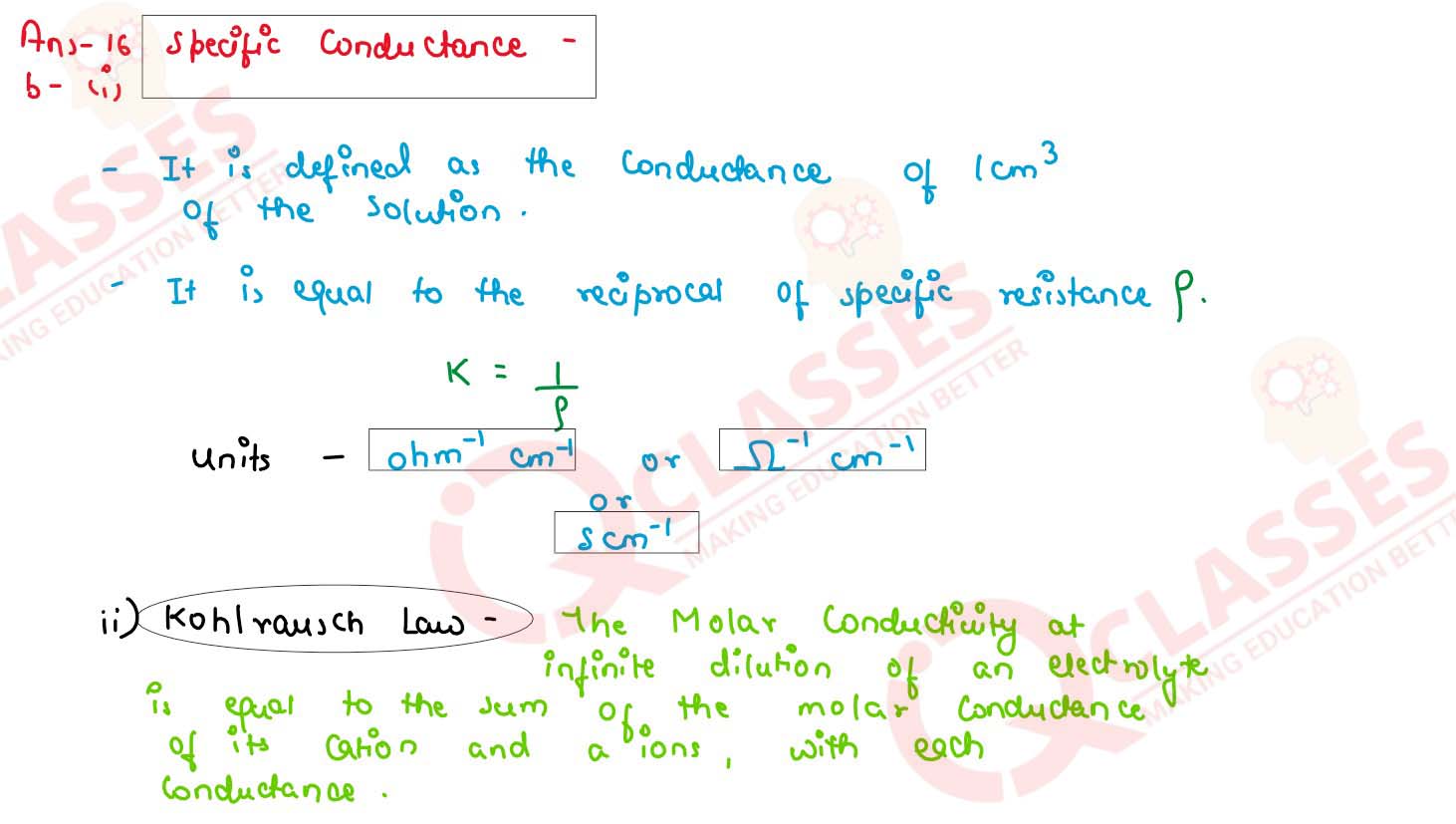
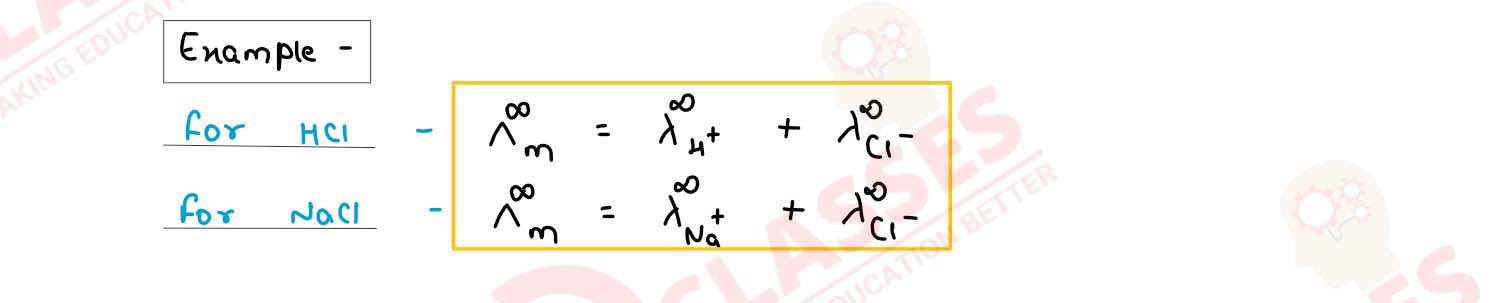
(1) specific conductance
(2) Kohlrausch's law
solutions


Q7
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.01 M KCl solution of 298 K is 1500 ohm. What is
the cell constant and molar conductivity of 0.01 M KCl solution , if the conductivity of this
solution is 0.146 x 10-3 ohm-1 cm-1 at 298 K ?
solutions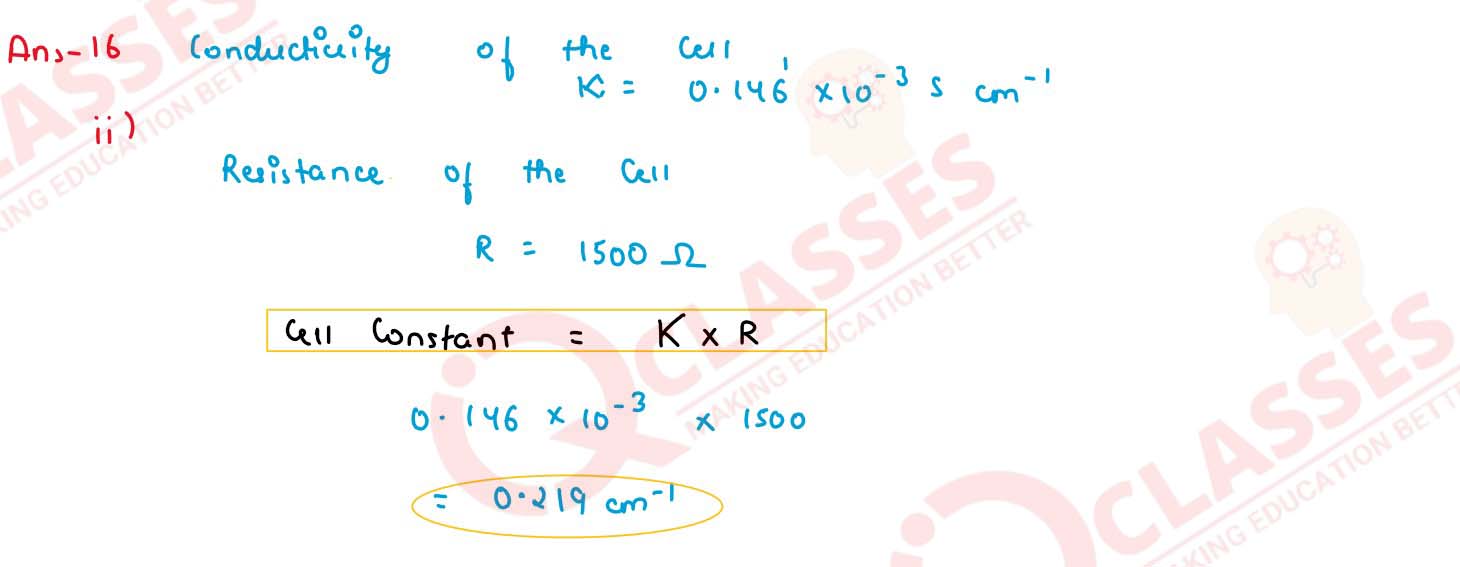
solutions

2018
Q8
(i) Calculate the emf and △G0 for the cell reaction at 25oC :
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) (0.1 M) || Cd2+(aq) | Cd(s)(0.01 M)
Given E0Zn2+/ Zn = -0.763 and E0Cd2+/ Cd = -0.403 V
1 F = 96,500 C
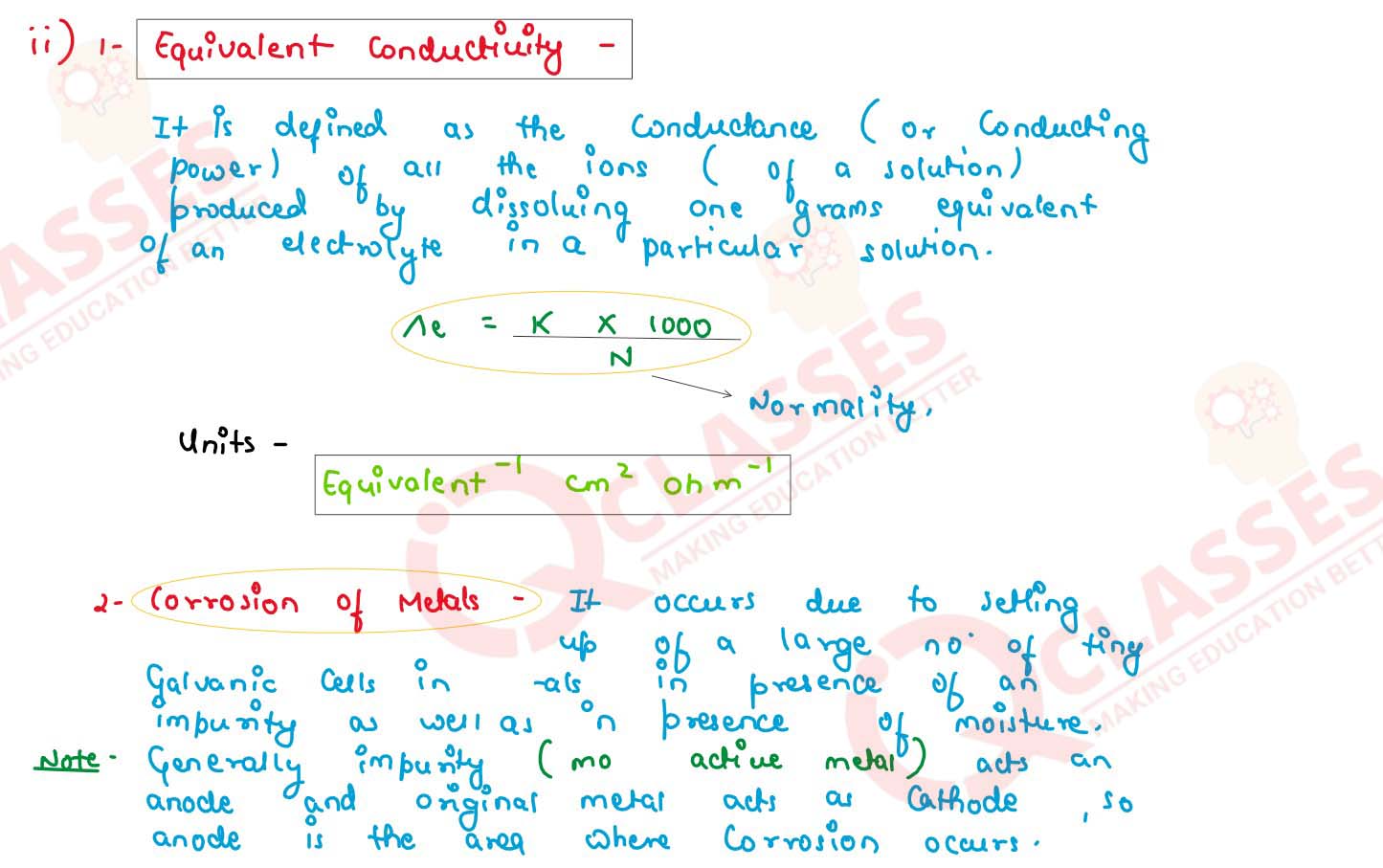
(ii) Define the following terms :
(1) equivalent conductivity
(2) corrosion of metals
solutions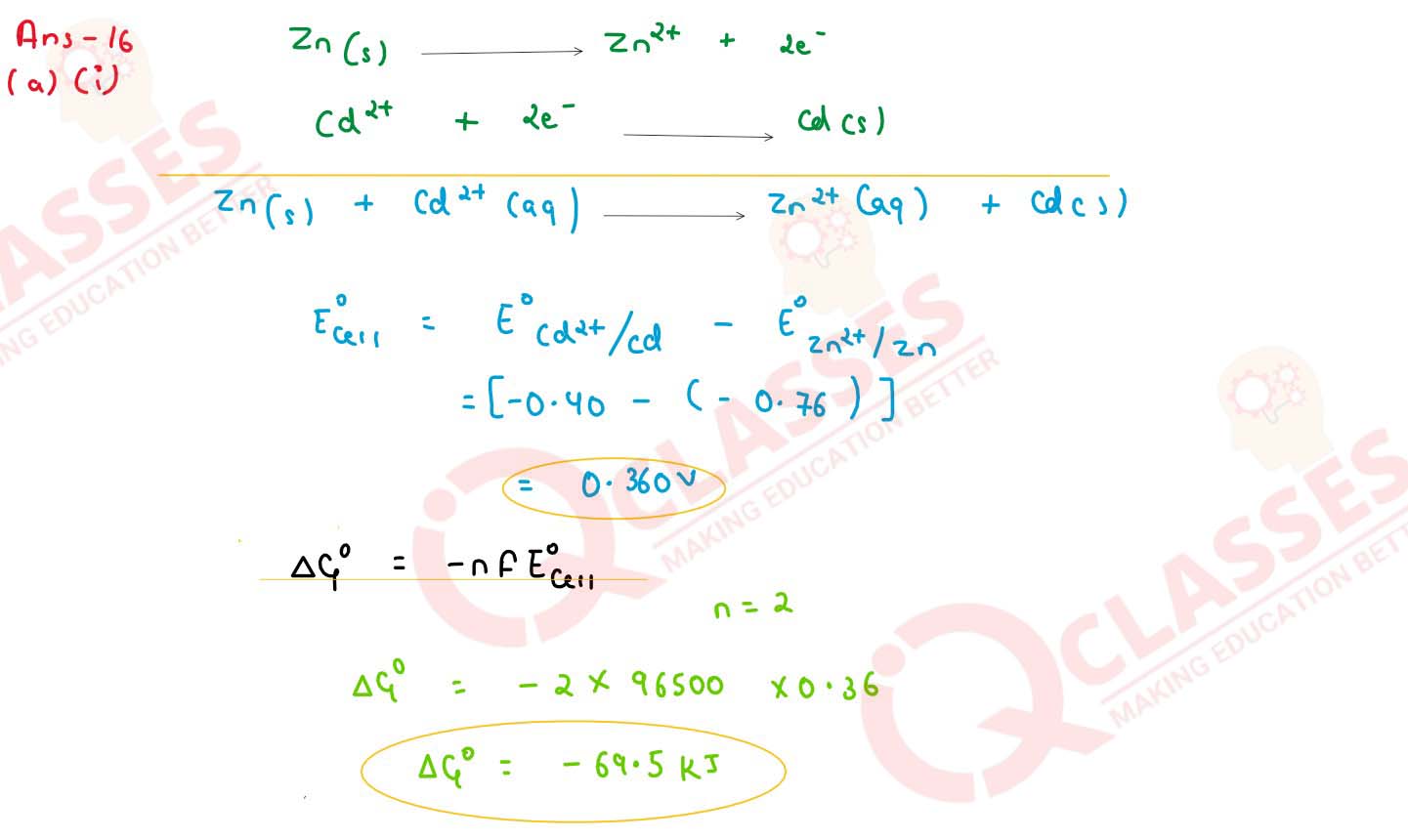
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) (0.1 M) || Cd2+(aq) | Cd(s)(0.01 M)
Given E0Zn2+/ Zn = -0.763 and E0Cd2+/ Cd = -0.403 V
1 F = 96,500 C
(ii) Define the following terms :
(1) equivalent conductivity
(2) corrosion of metals
solutions


OR
Q9
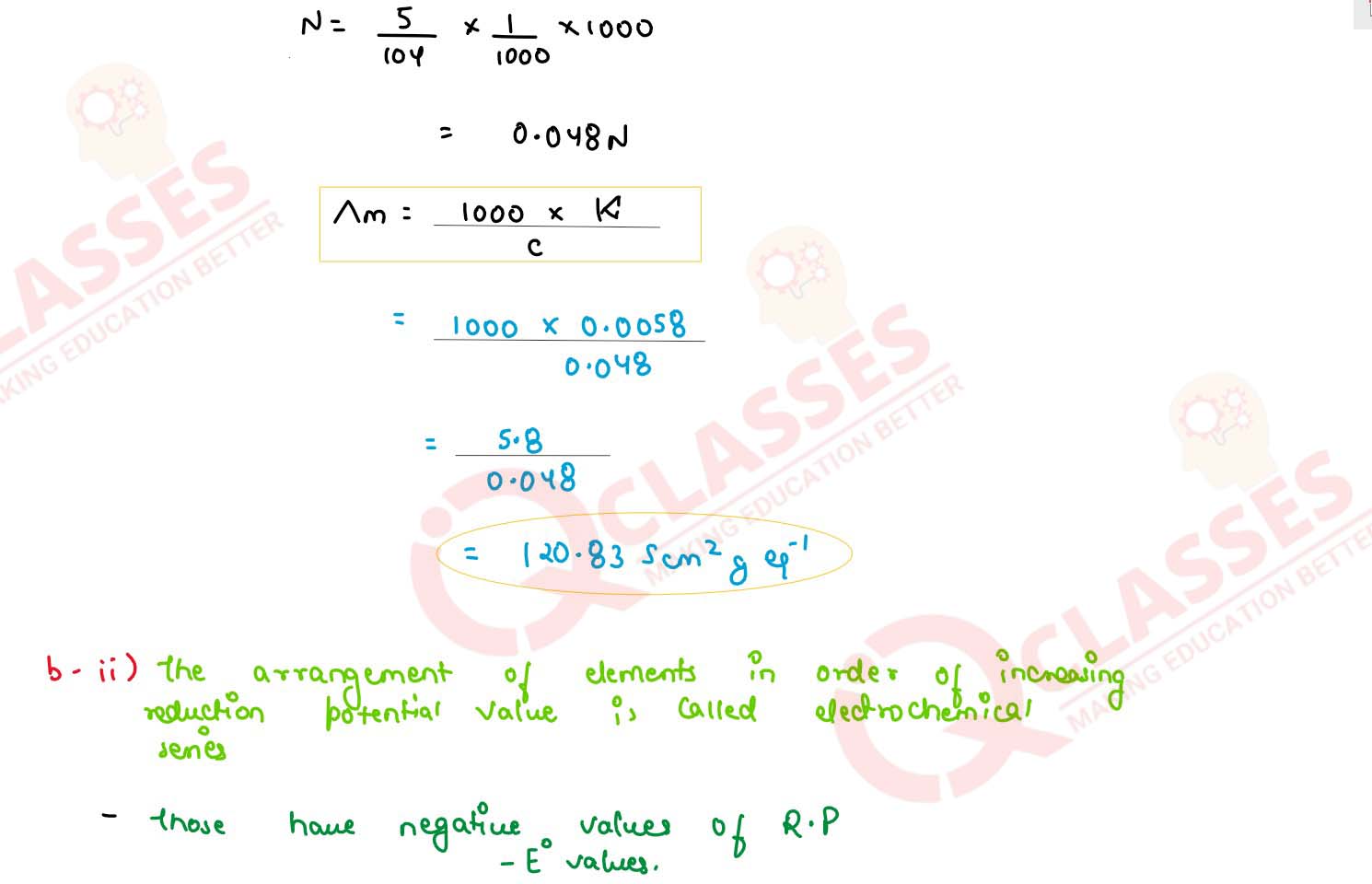
(i) The specific conductivity of a solution containing 5 g of anhydrous BaCl2 (molar
weight = 208) in 1000 cm3 of a solution is found to be 0.0058 ohm-1
cm-1 calculate the molar and equivalent conductivity of the solution.
(ii) What is electrochemical series? How it is useful in predicting whether metal can liberate hydrogen from acid or not ?
solutions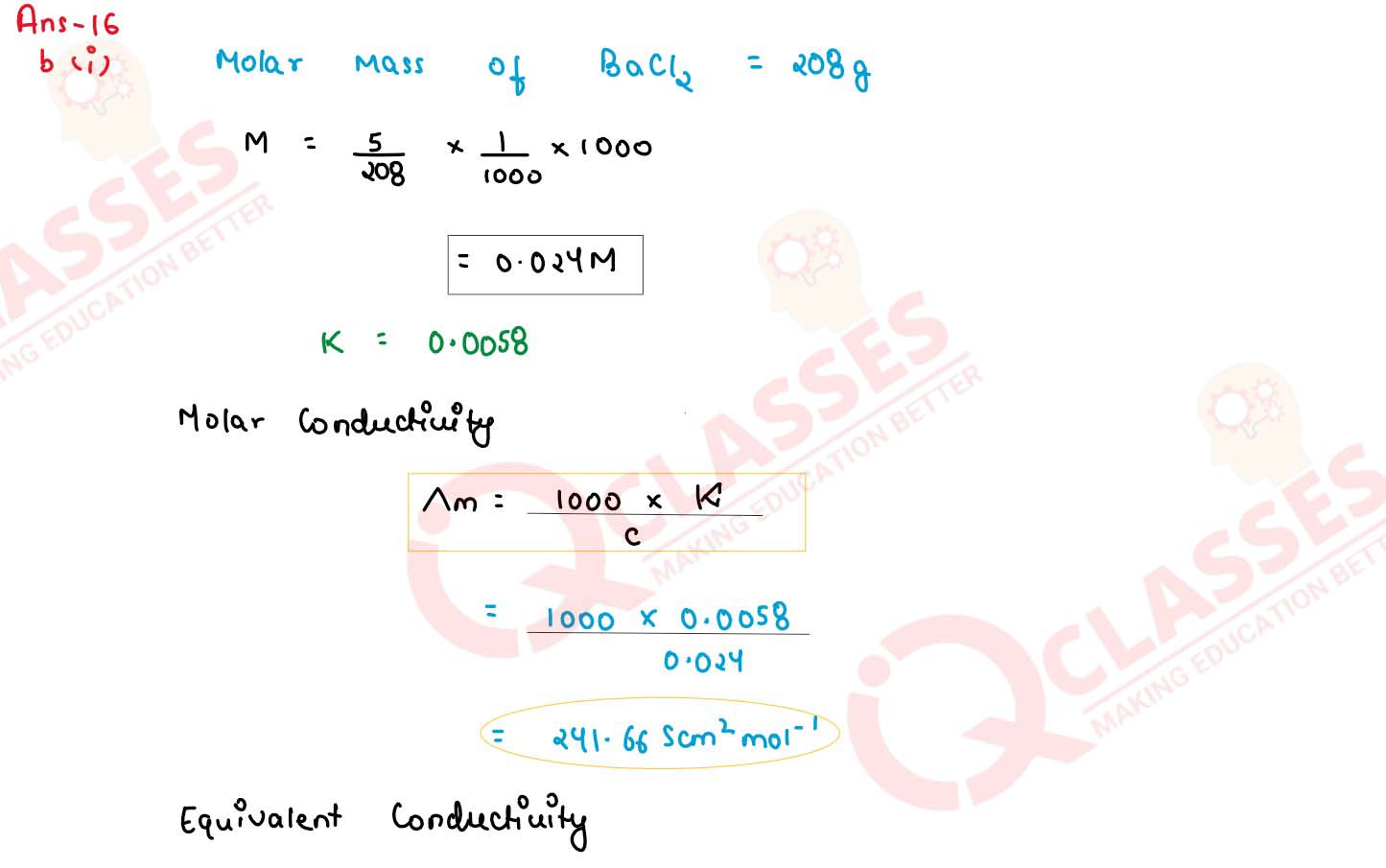
(ii) What is electrochemical series? How it is useful in predicting whether metal can liberate hydrogen from acid or not ?
solutions


2017
Q10
Specific conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 8298 K is 0.025. Calculate its molar
conductivity.
solutions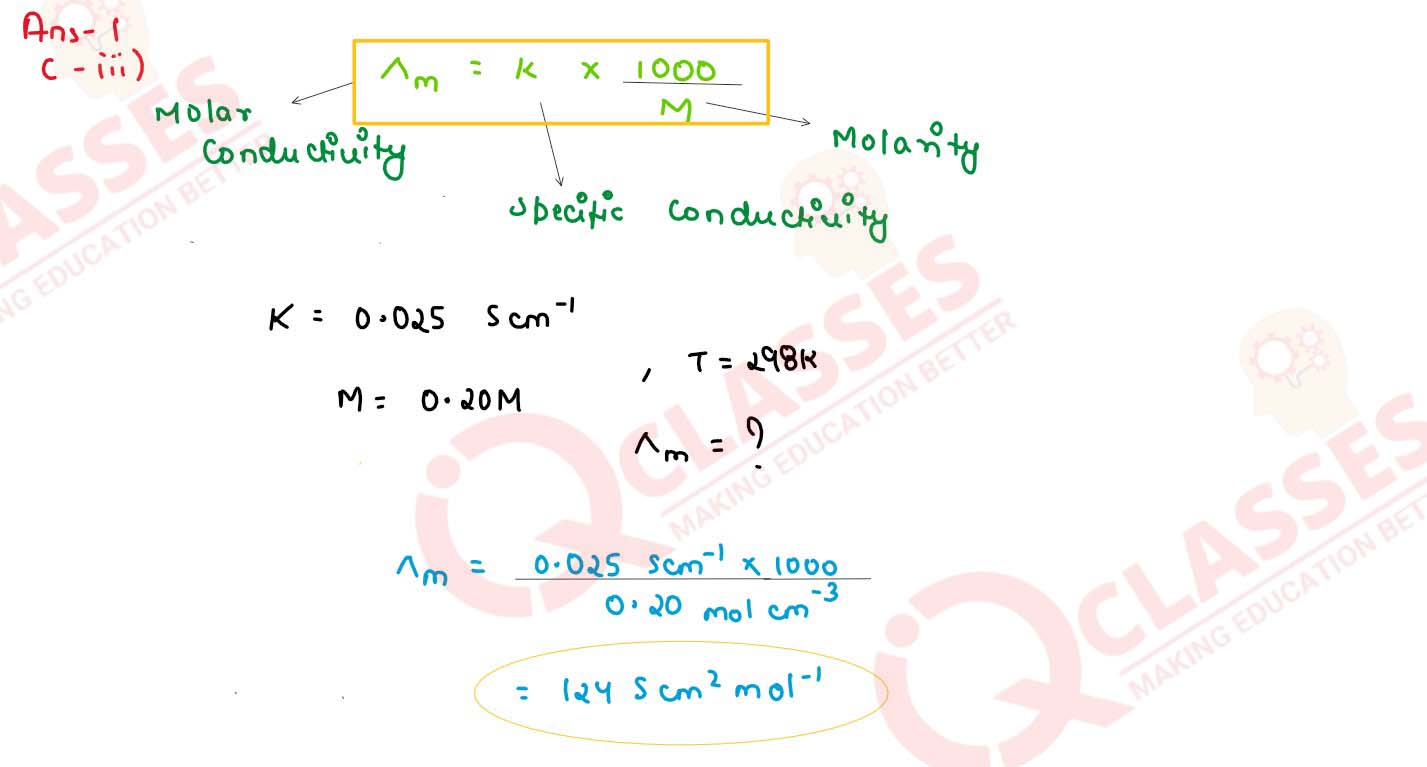
solutions

2016
Q11
Consider the following cell reaction at 298 K :
the standard reduction potentials (Eo) for Ag+/ Ag and Cd2+/Cd are 0.80 V and -0.40 V respectively
(1) Write the cell representation
(2) What will the emf of the cell if the concentration of Cd2+ 0.1 M and that of Ag2+ is 0.2 M
(3) Will the cell work spontaneously for the condition given in (2) above.
solutions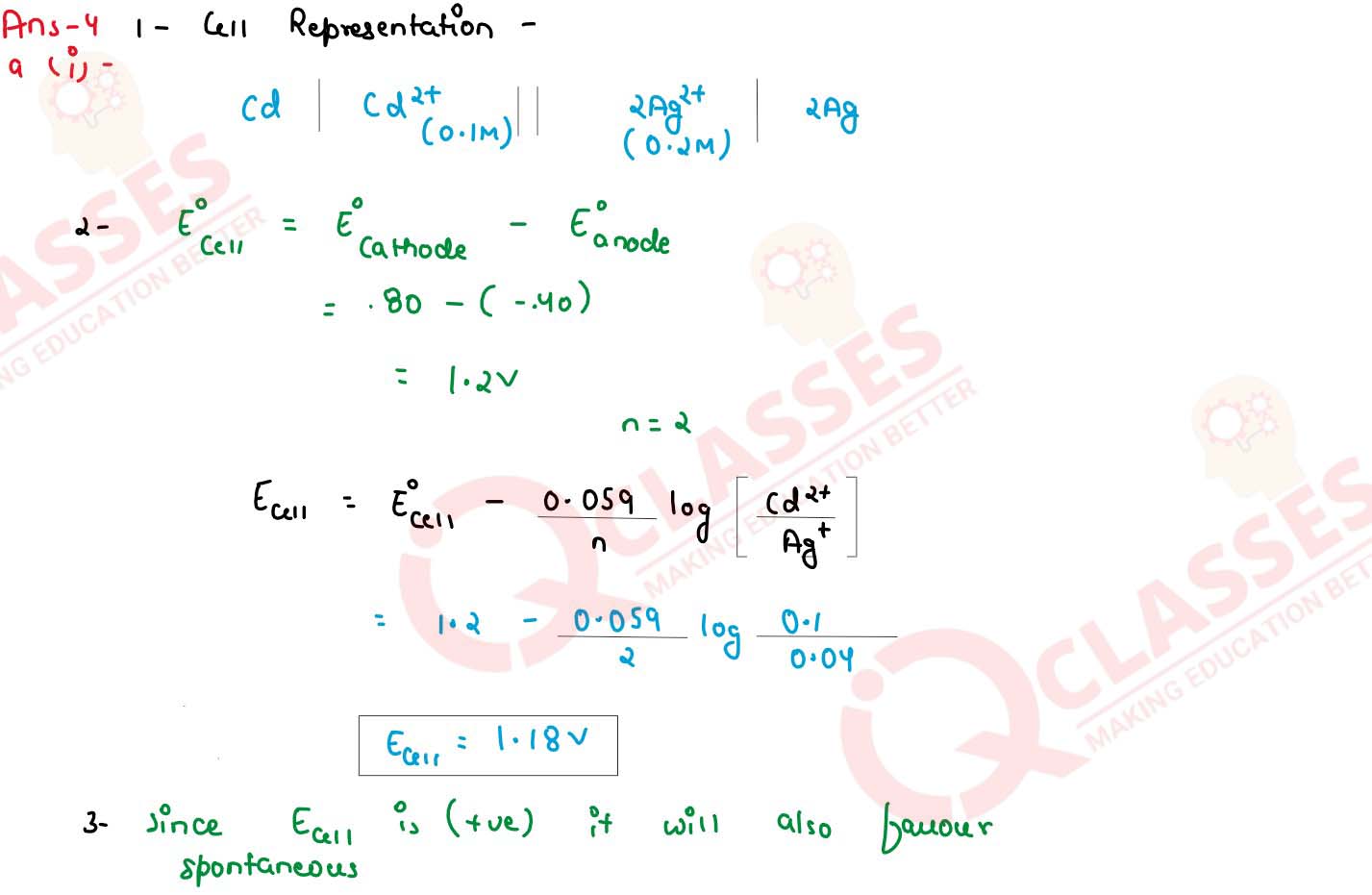
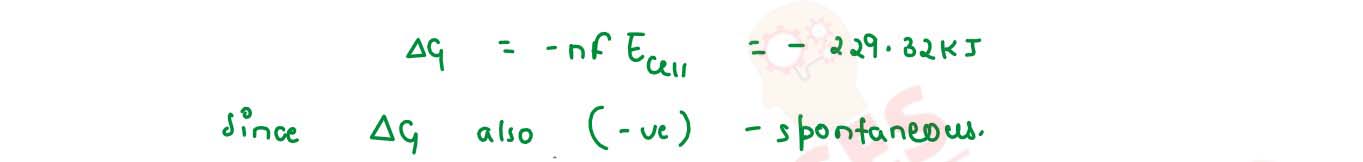
the standard reduction potentials (Eo) for Ag+/ Ag and Cd2+/Cd are 0.80 V and -0.40 V respectively
(1) Write the cell representation
(2) What will the emf of the cell if the concentration of Cd2+ 0.1 M and that of Ag2+ is 0.2 M
(3) Will the cell work spontaneously for the condition given in (2) above.
solutions

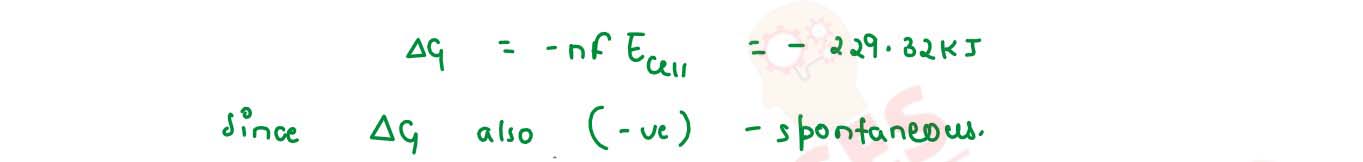
Q12
What is a buffer solution? How it is prepared? Explain the buffer action of a basic buffer with a
suitable example.
solutions
solutions

Q13
Explain the following :
(i) When NaCl is added to AgNO3 solution of white precipitate is formed
(ii) An aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is acidic in nature
solutions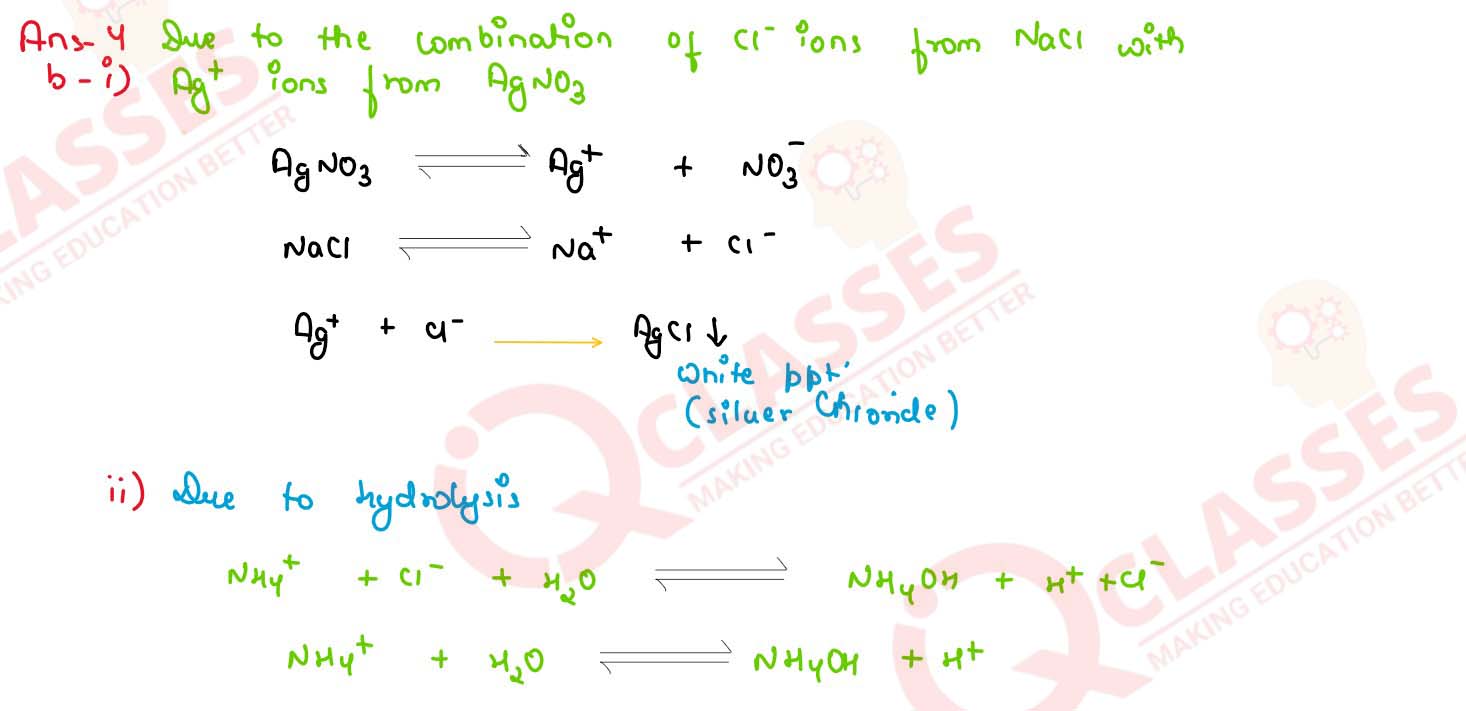
(i) When NaCl is added to AgNO3 solution of white precipitate is formed
(ii) An aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is acidic in nature
solutions


Reach Us
SERVICES
- ACADEMIC
- ON-LINE PREPARATION
- FOUNDATION & CRASH COURSES
CONTACT
B-54, Krishna Bhawan, Parag Narain Road,
Near Butler Palace Colony Lucknow
Contact:+918081967119

Add a comment