Class 12 Chemistry ISC Solutions Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 chemistry important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter solutions. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on ISC board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 chemistry syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
2020
Q1
(i) The elevation in boiling paint when 0.30 g of acetic acid is dissolved in 100 g of benzene is
0.0633oC. Calculate the molecular weight, of acetic acid from this data. What conclusion
can you draw about the molecular state of the solute in the solution? (Given Kb for
benzene= 2.53 K kg mol-1), at. wt. of C=12, H=1 , O=16
(ii) Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.025 g of K2SO4 in 2 litres of water at 25oC, assuming that K2SO4 is completely dissociated
(R=0.0821 Lit atm K-1 mol-1 , mol.wt. of K2SO4=174 g mol-1)
solutions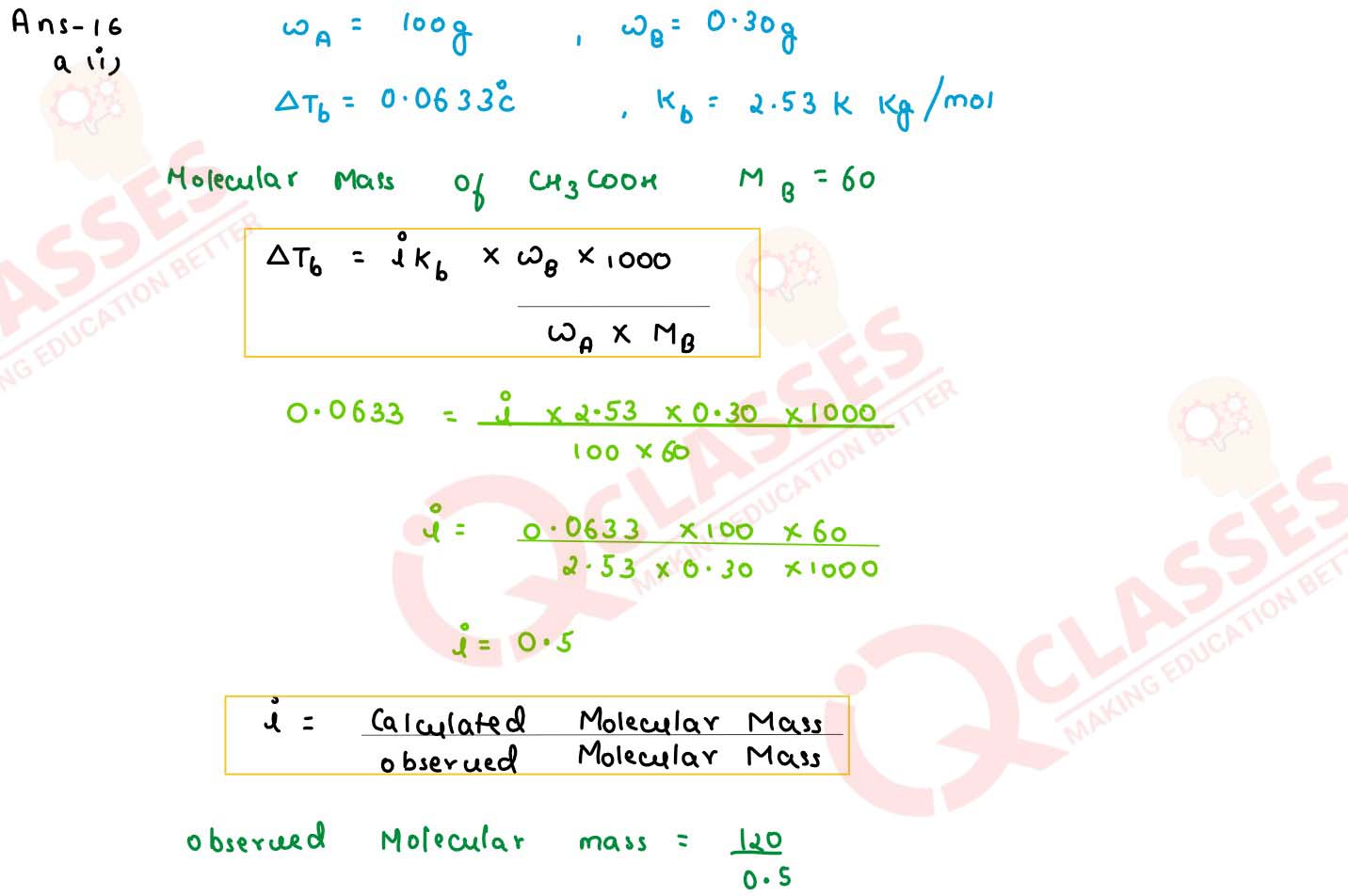
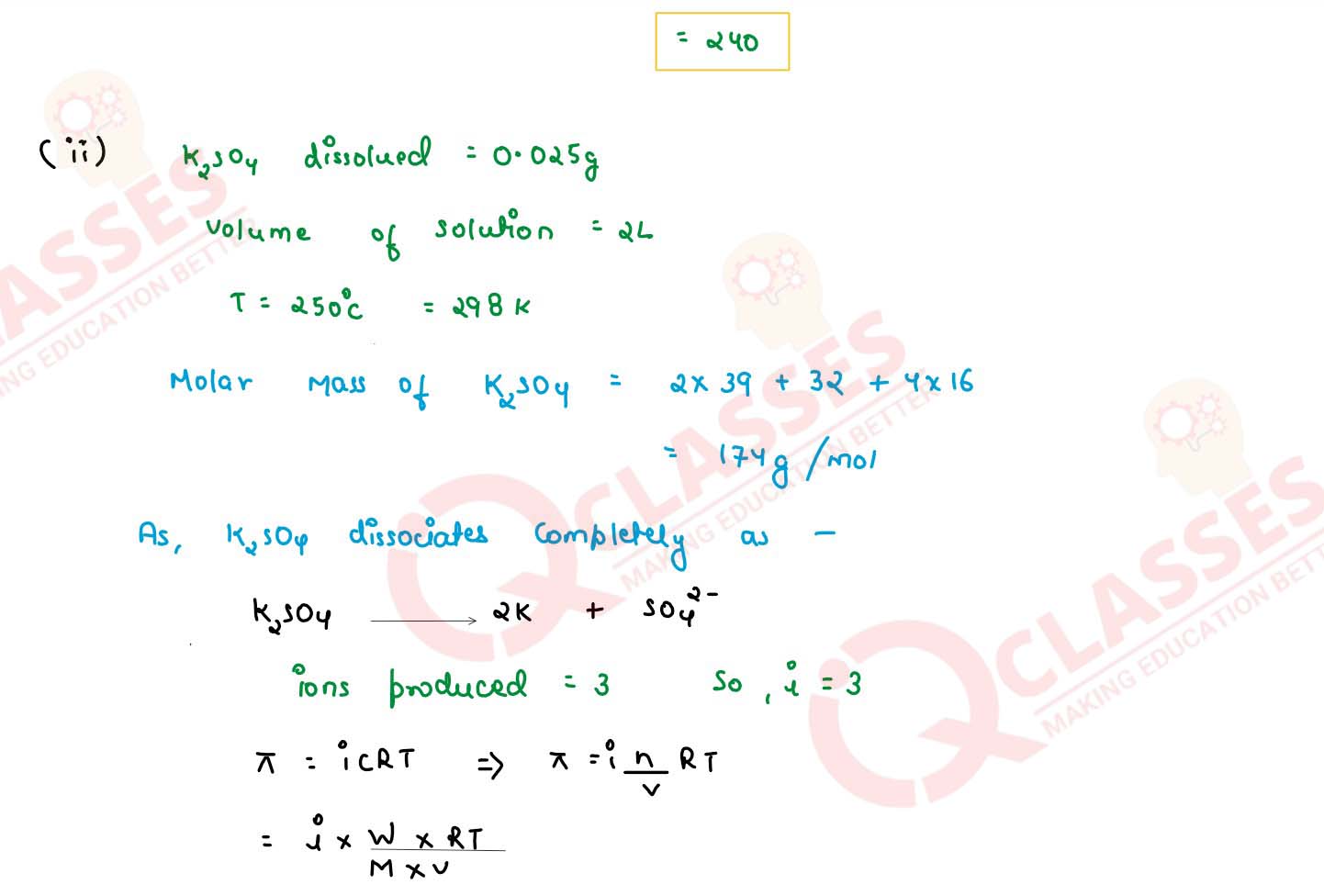
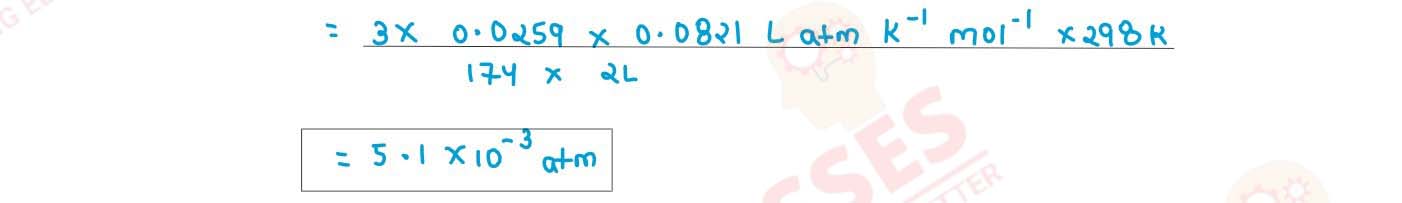
(ii) Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.025 g of K2SO4 in 2 litres of water at 25oC, assuming that K2SO4 is completely dissociated
(R=0.0821 Lit atm K-1 mol-1 , mol.wt. of K2SO4=174 g mol-1)
solutions



OR
Q2
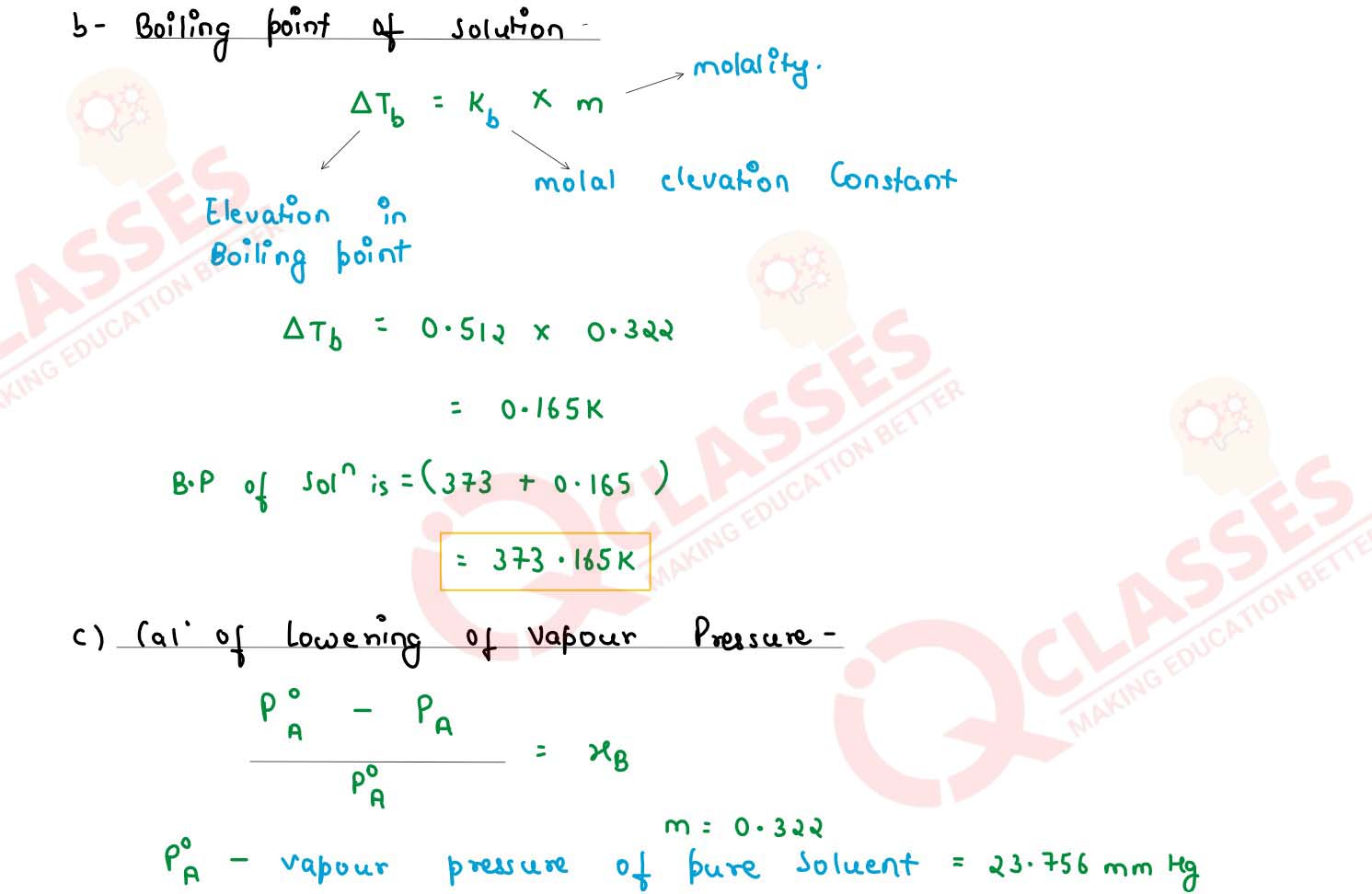
(i) An aqueous solution of a non volatile solute freezes at 272.4 K while pure water freezes at
273.0 K. Determine the following:
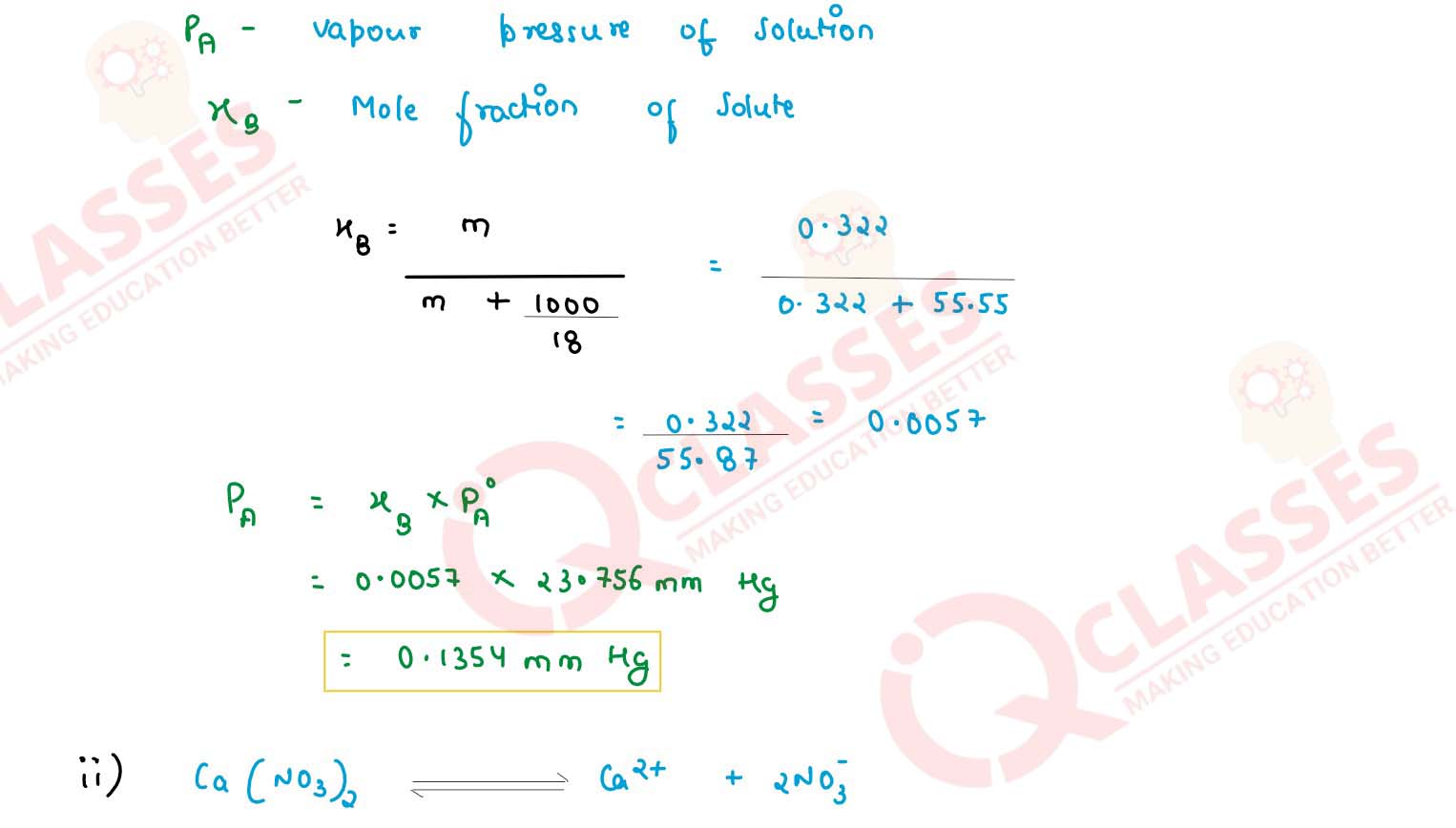
(Given Kf = 1.86 K kg mol-1 , Kb = 0.512 K kg mol-1 and vapour pressure of water at 298 K= 23.756 mm Hg)
(1)the molality of the solution
(2)boiling point of the solution
(3) the lowering of vapour pressure of water at 298 K
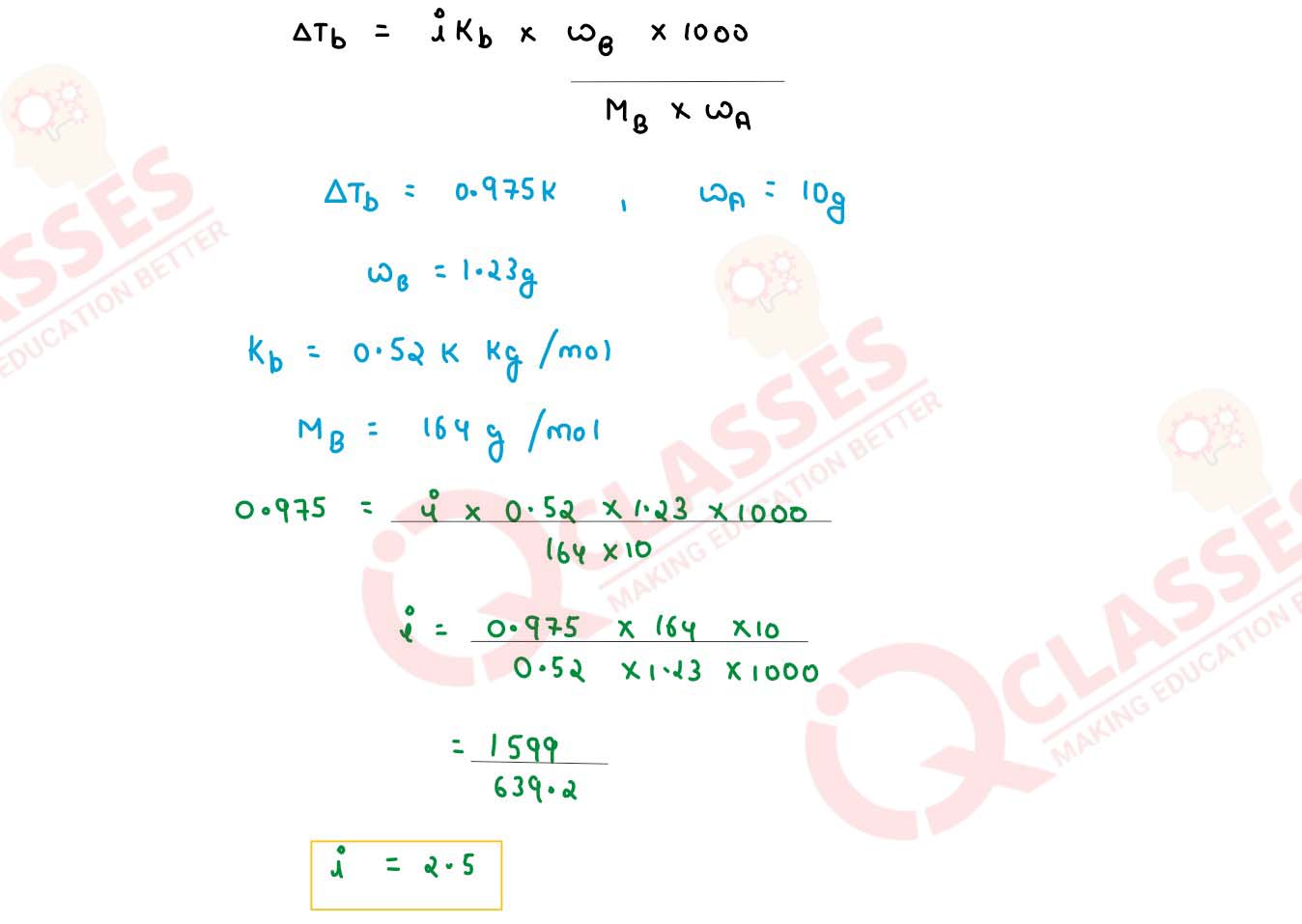
(ii) A solution containing 1.23 g of calcium nitrate in 10 g of water, boils at 100.975o C at 760 mm of Hg. Calculate the Van't half factor for the salt at this concentration.
(Given Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol-1 , mol. wt. pf calcium nitrate = 164 g mol-1)
solutions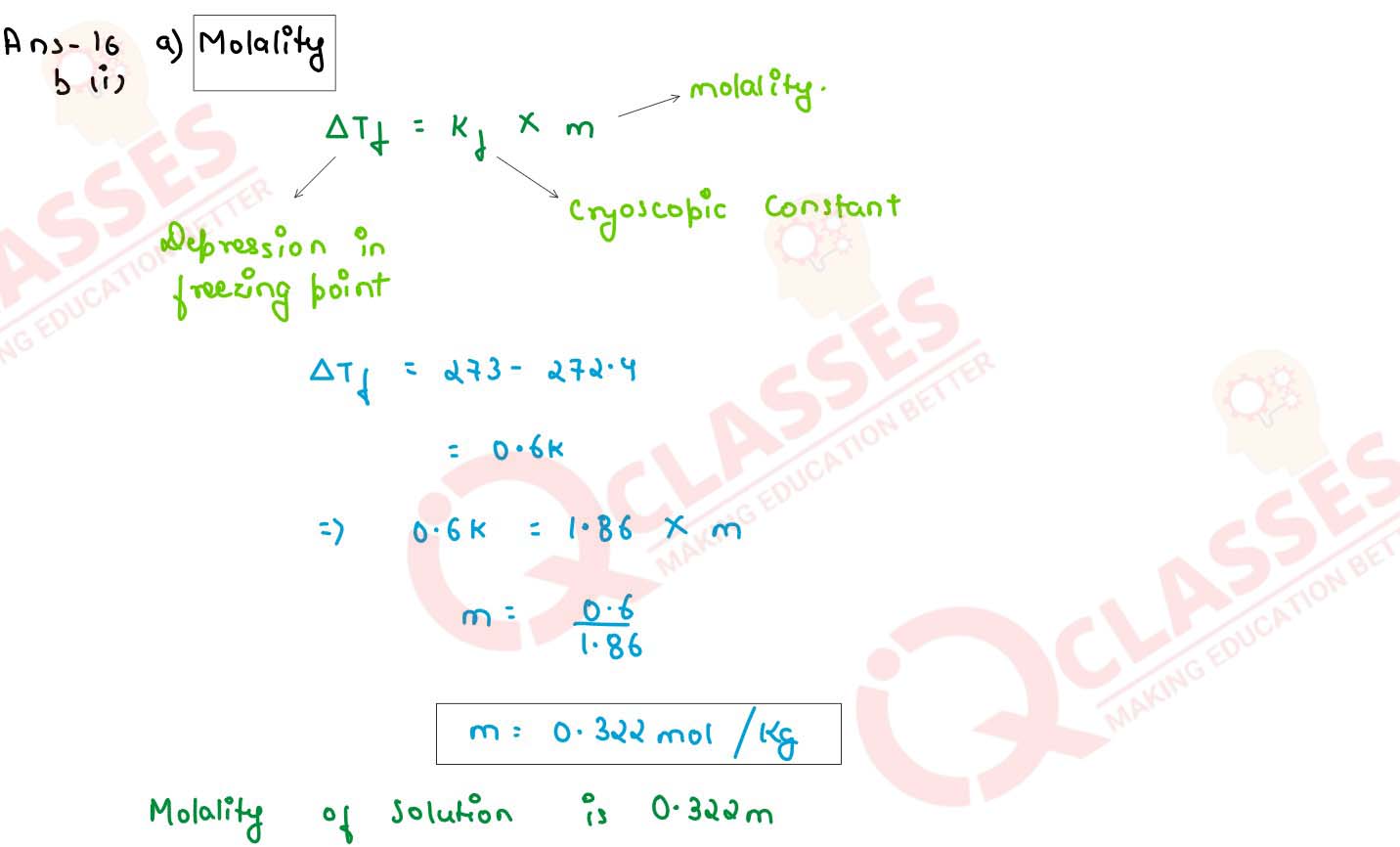
(Given Kf = 1.86 K kg mol-1 , Kb = 0.512 K kg mol-1 and vapour pressure of water at 298 K= 23.756 mm Hg)
(1)the molality of the solution
(2)boiling point of the solution
(3) the lowering of vapour pressure of water at 298 K
(ii) A solution containing 1.23 g of calcium nitrate in 10 g of water, boils at 100.975o C at 760 mm of Hg. Calculate the Van't half factor for the salt at this concentration.
(Given Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol-1 , mol. wt. pf calcium nitrate = 164 g mol-1)
solutions




2019
Q3
Calculate the boiling point of urea solution when 6 g of urea is dissolved in 200 g of water.
(Kb for water = 0 52 K kg mol-1, boiling point of pure water = 273 K, mol. wt.
of urea= 60)
solutions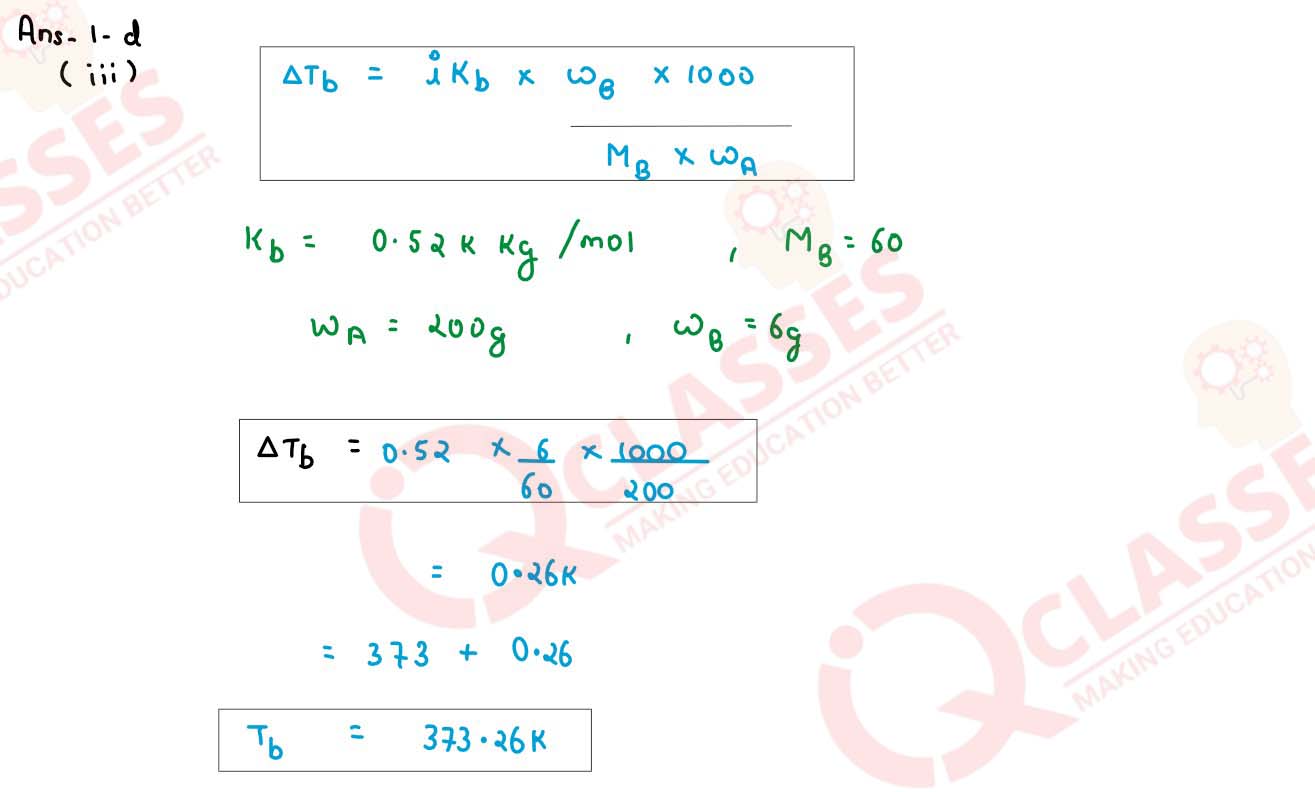
solutions

Q4
When 0.4g of acetic acid is dissolved in 40g of benzene, the freezing point of the solution is
lowered by 0.45K. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid. Acetic acid forms dimer when
dissolved in benzene. (Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H =
1, O = 16)
solutions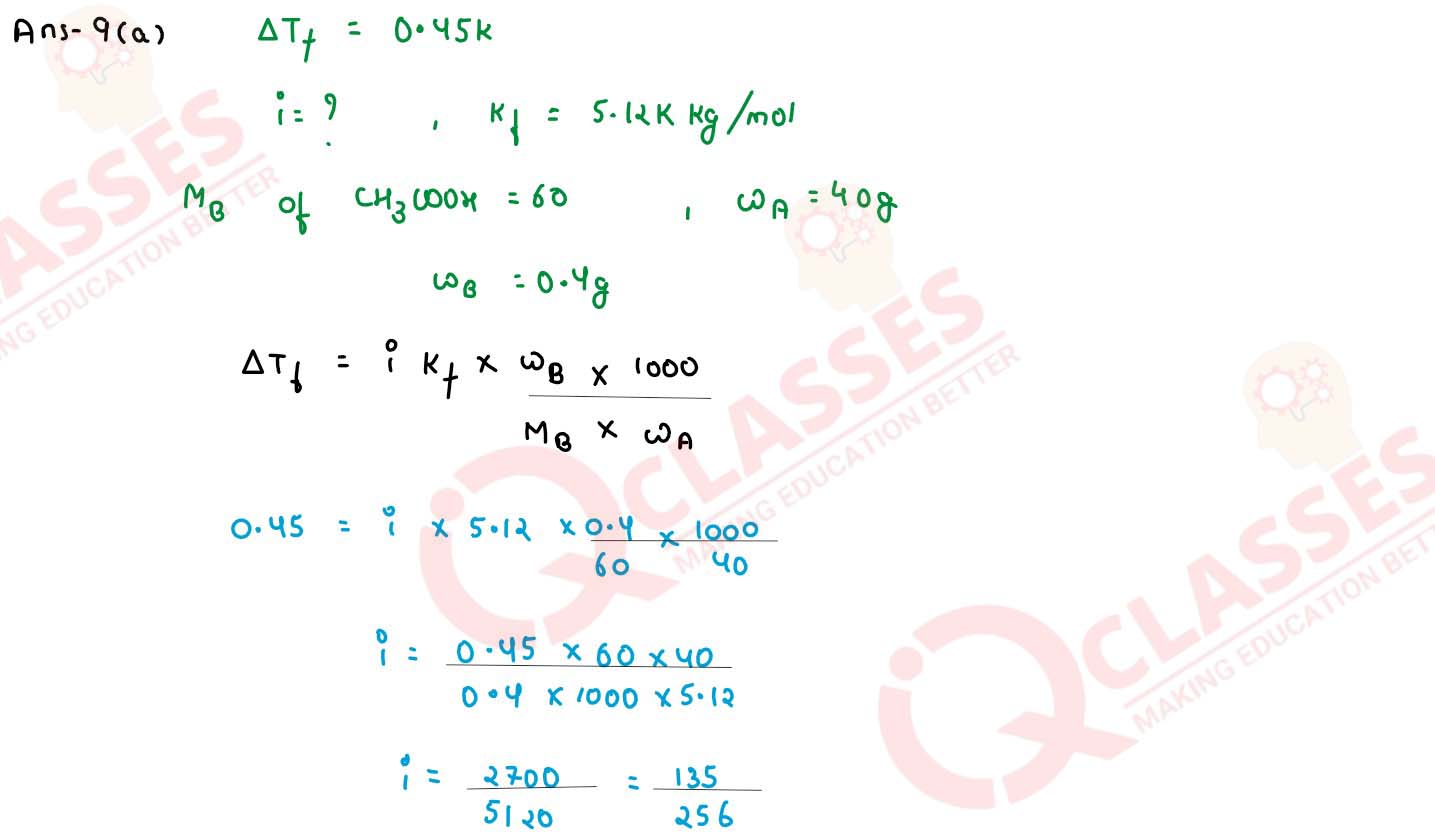
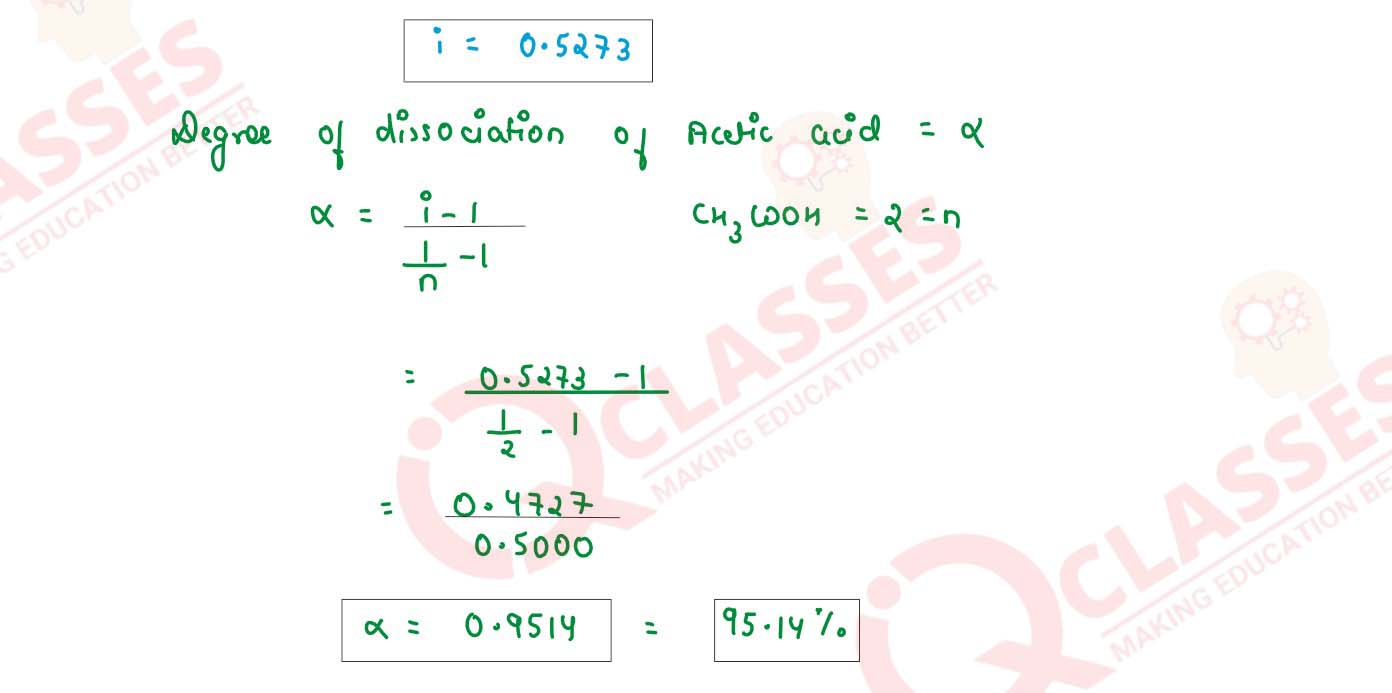
solutions


OR
Q5
A solution is prepared by dissolving 9.25g of non-volatile solute in 450 ml of water. It has an
osmotic pressure of 350 mm of Hg at 27°C. Assuming the solute is non-electrolyte, determine its
molecular mass. (R — 0.0821 lit atm K-1 mol-1)
solutions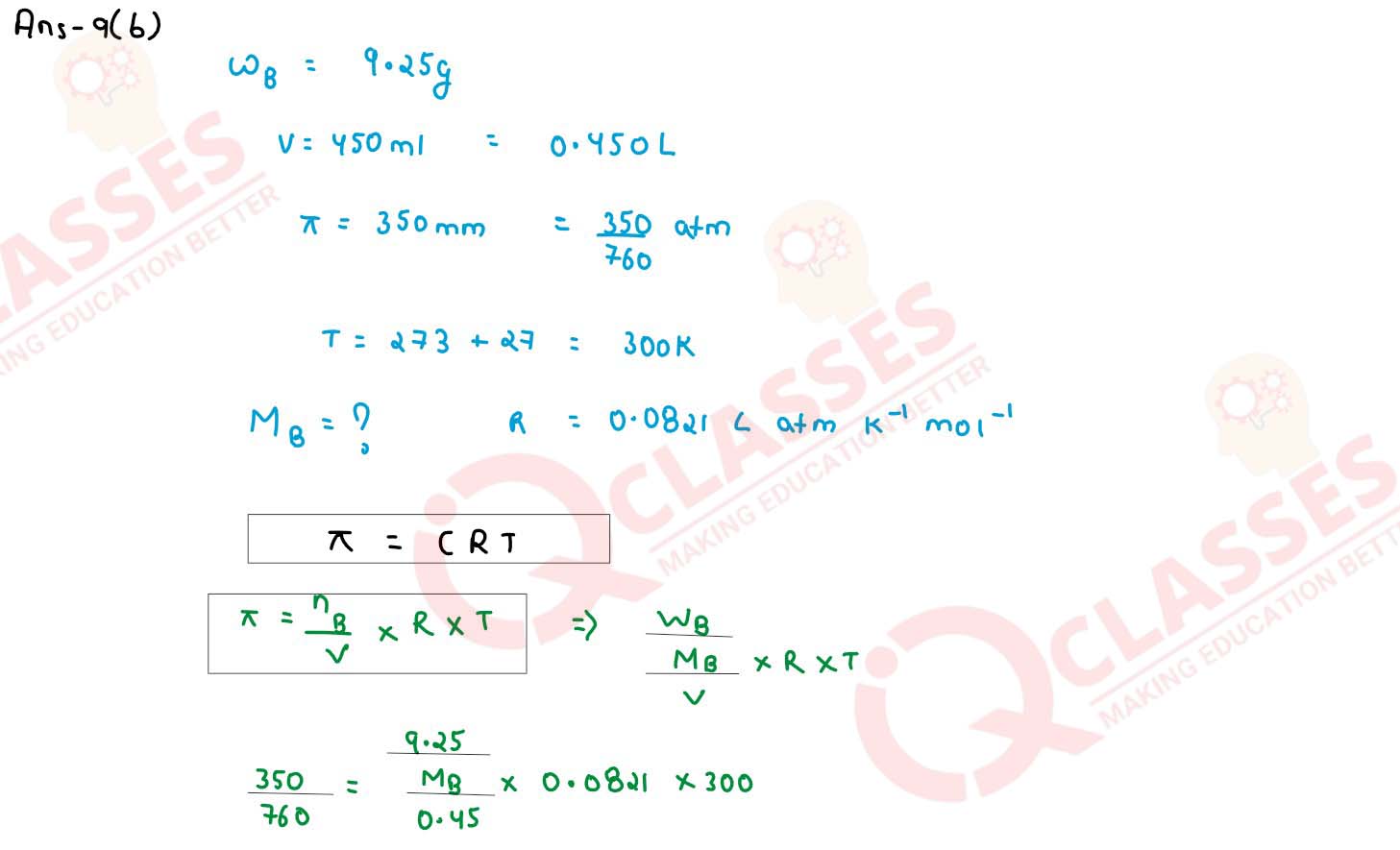

solutions


2018
Q6
Calculate the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 0 025g of
K2SO4 in 2.0 litres of water at 25°C assuming that K2SO4
is completely dissociated. (mot. wt. of K2SO4 = 174 g mol-1)
solutions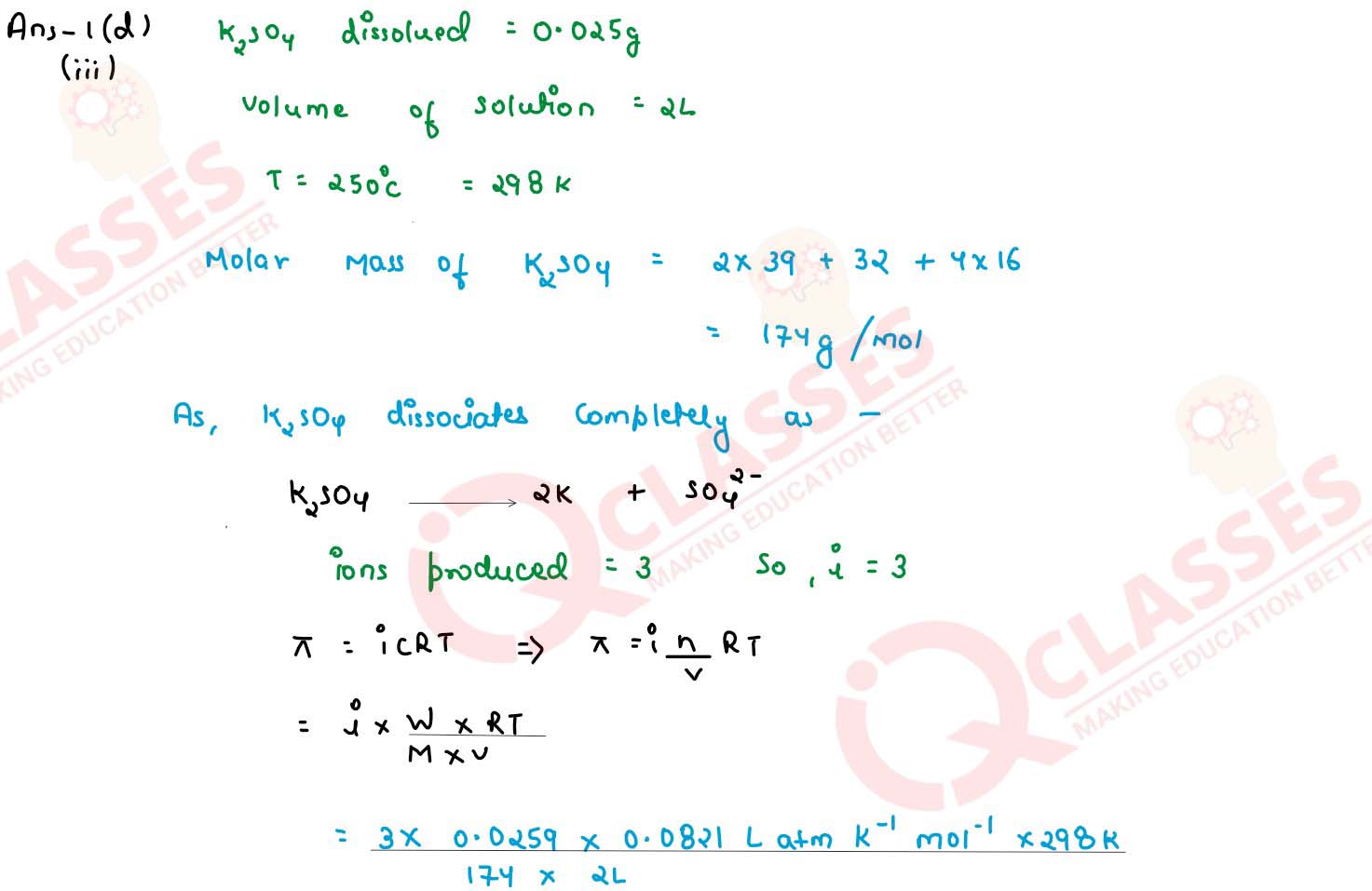

solutions


Q7
The freezing point of a solution containing 5.85g of NaCl in 100g of water is -3348°C. Calculate
van't Hoff factor 'i' for this solution. What will be the experimental molecular weight of NaCl?
(Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1, at. wt. Na = 23, Cl = 35.5)
solutions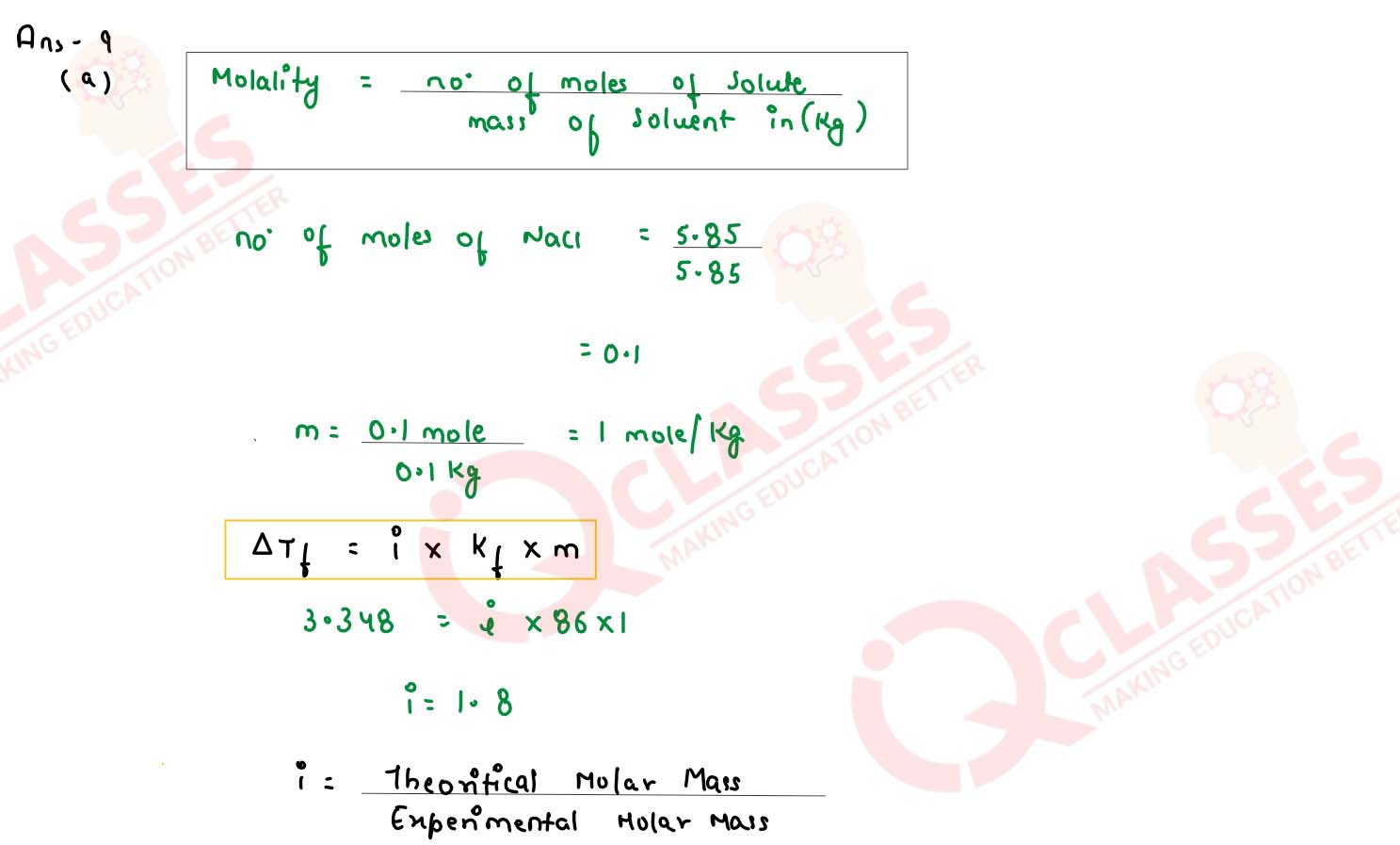

solutions


OR
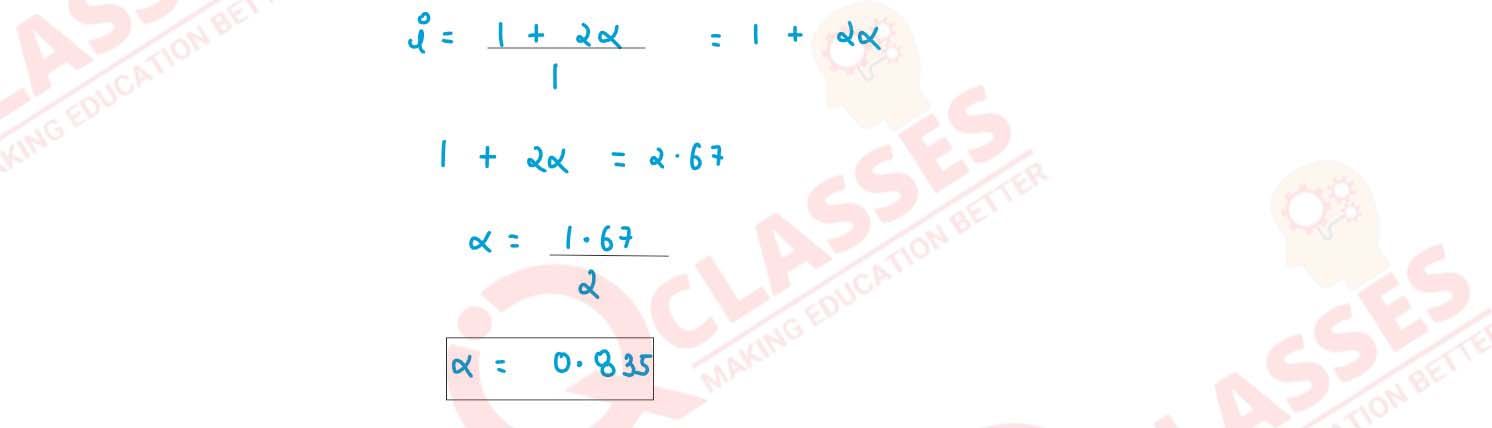
Q8
An aqueous solution containing 12.48g of barium chloride (BaCl2) in 1000g of water, boils
at 1000832°C. Calculate the degree of dissociation of barium chloride. (Kb for water =
0.52 K kg mol-1 , at. wt. Ba = 137, Cl = 35.5)
solutions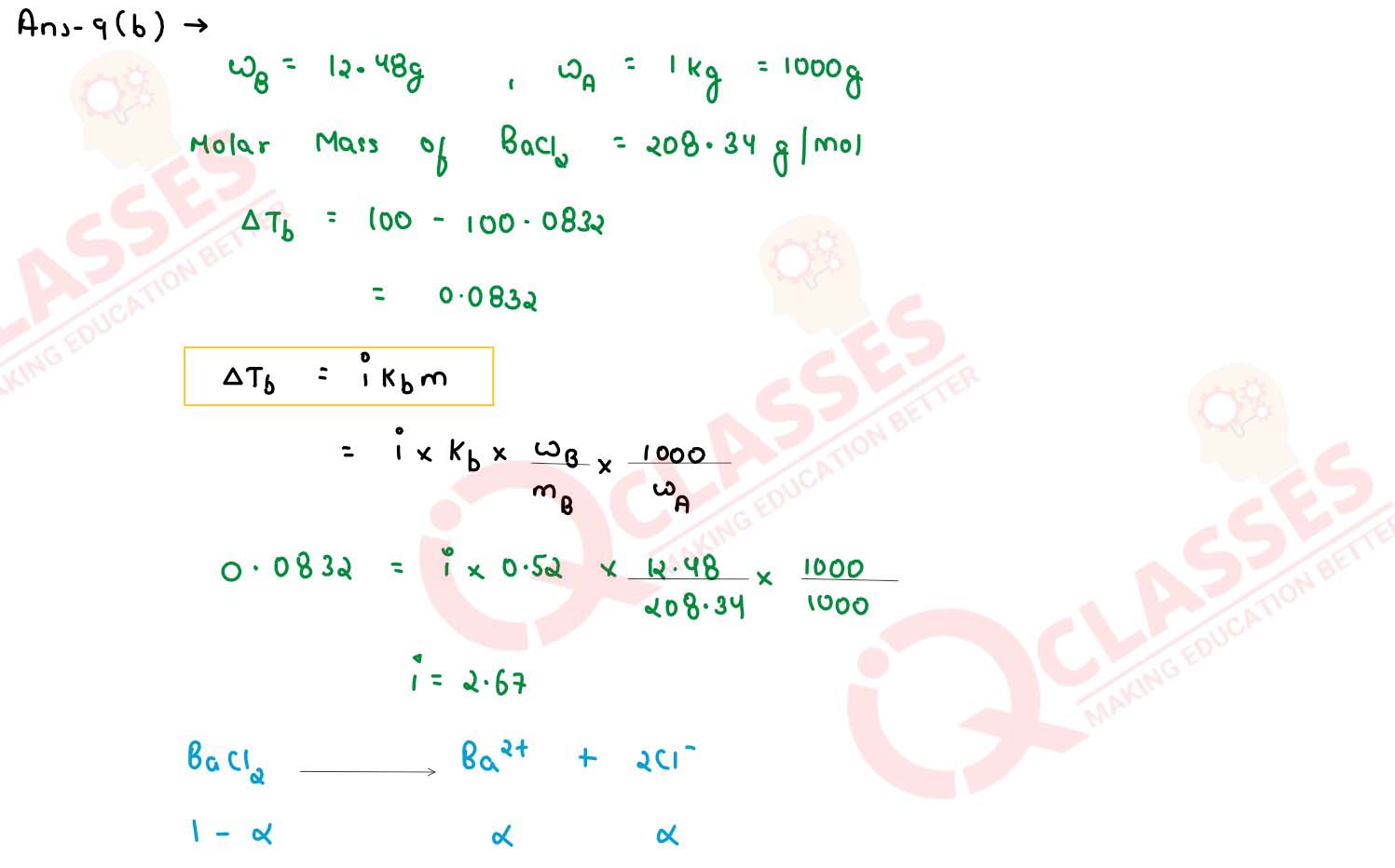
solutions


2017
Q9
Why the freezing point depression ( △Tf) of 0.4M NaCI solution is nearly twice than
that of 0.4M glucose solution?
solutions
solutions

Q10
Determine the freezing point of a solution containing 0.625 g of glucose
(C6H12O6) dissolved in 102.8 g of water. (Freezing point of water =
273 K, Kf for water = 1.87K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H=1,O=16)
solutions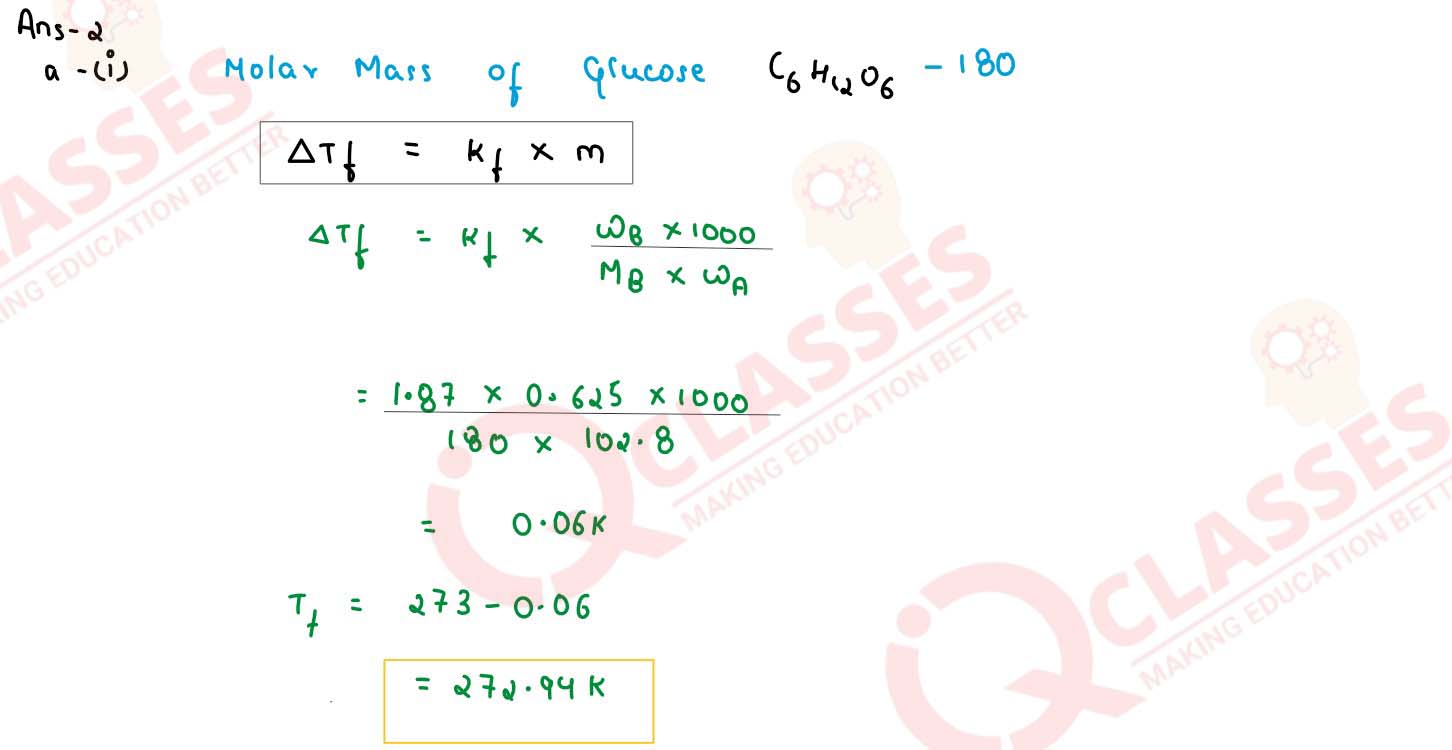
solutions

Q11
A 0.15 M aqueous solution of KCl exerts an osmotic pressure of 6.8 atm at 310 K. Calculate the
degree of dissociation of KCl. (R = 0.0821 Lit atm K-1 mol-1).
solutions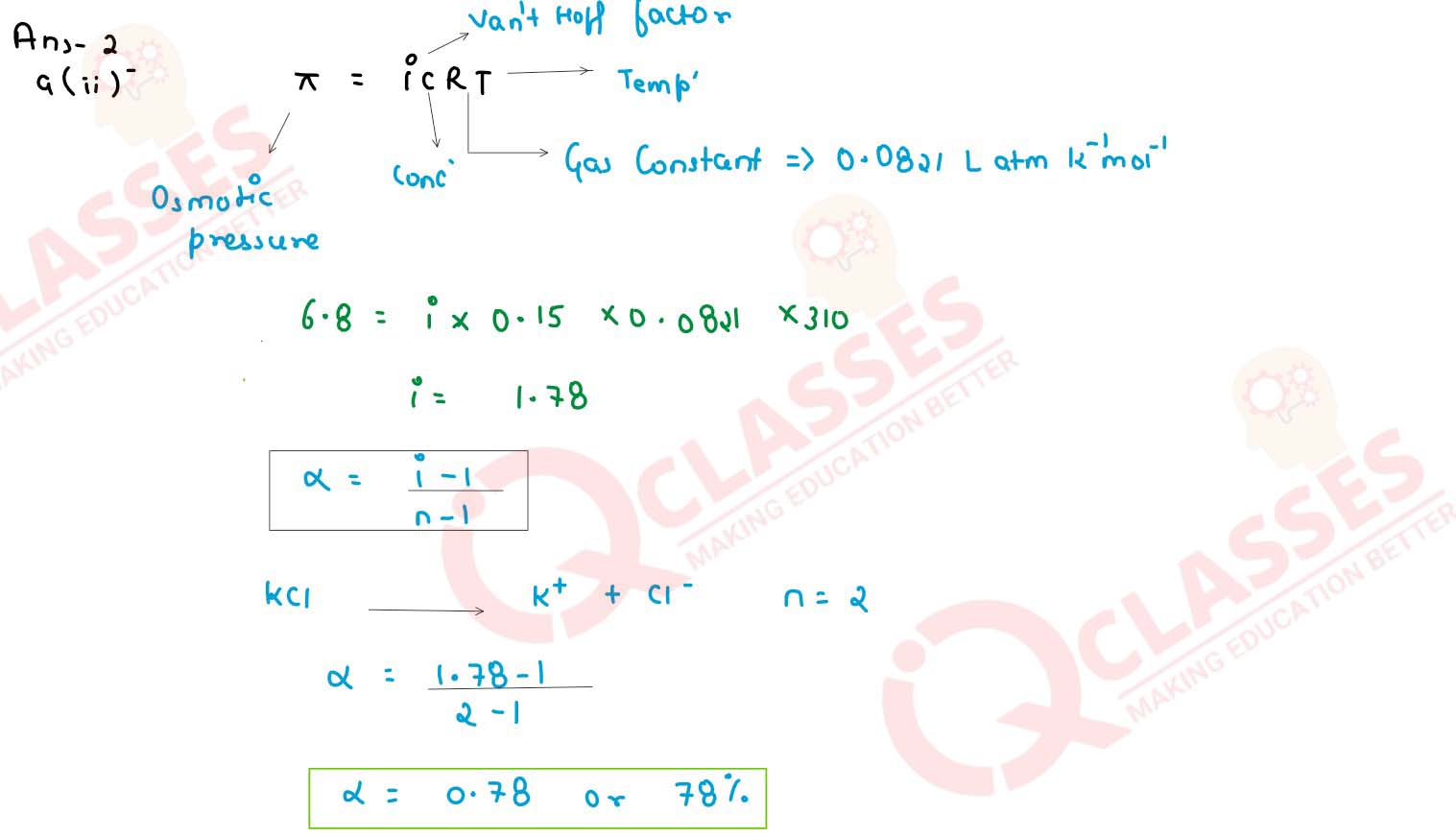
solutions

Q12
A solution containing 8.44 g of sucrose in 100 g of water has a vapour pressure 4.56 mm of Hg at
273K. If the vapour pressure of pure water is 4.58 mm of Hg at the same temperature, calculate the
molecular weight of sucrose.
solutions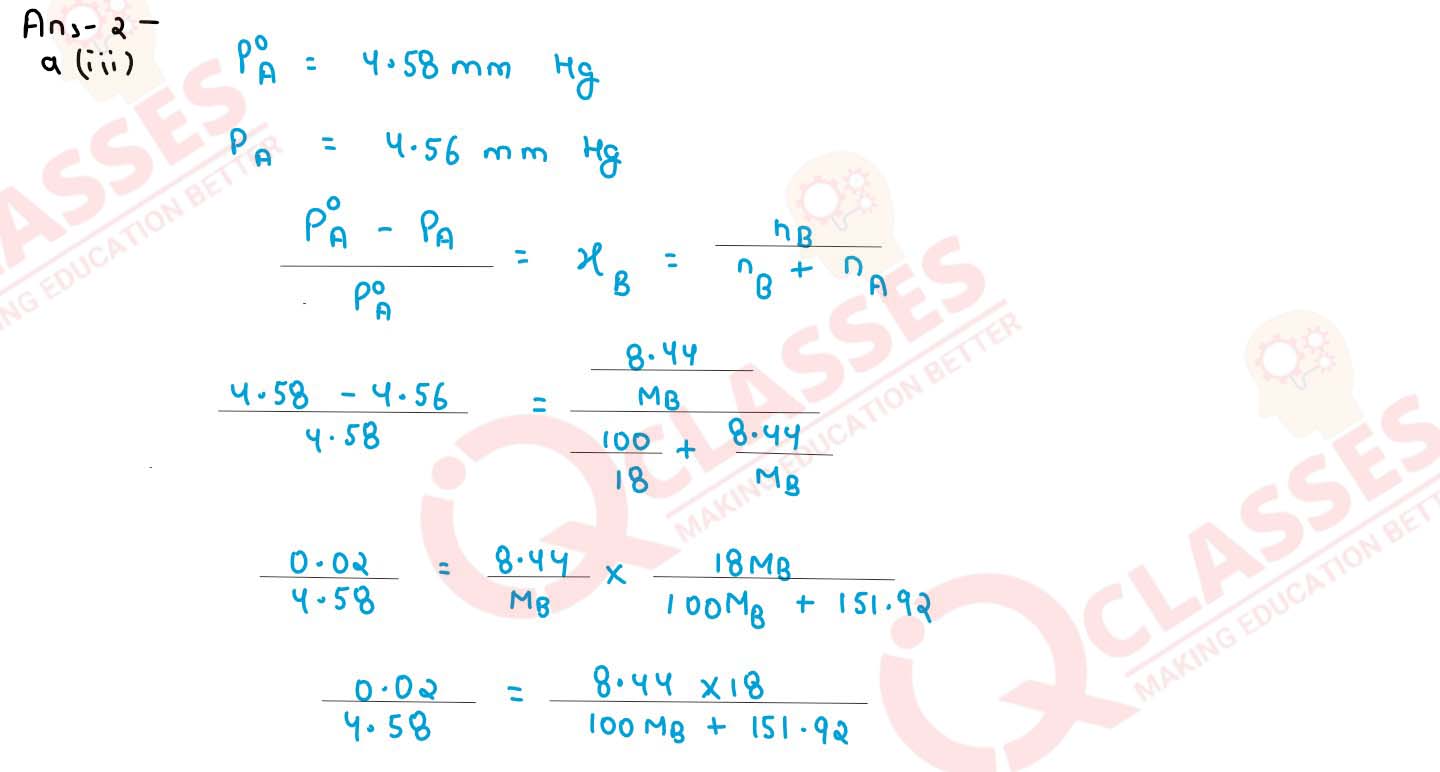

solutions




Add a comment