Class 12 ISC Physics Alternating Current Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 Physics important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter Alternating Current. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on ISC board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 Physics syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
class 12 ISC Physics Alternating Current BoardQuestions
Alternating Current BoardQuestions
Q1
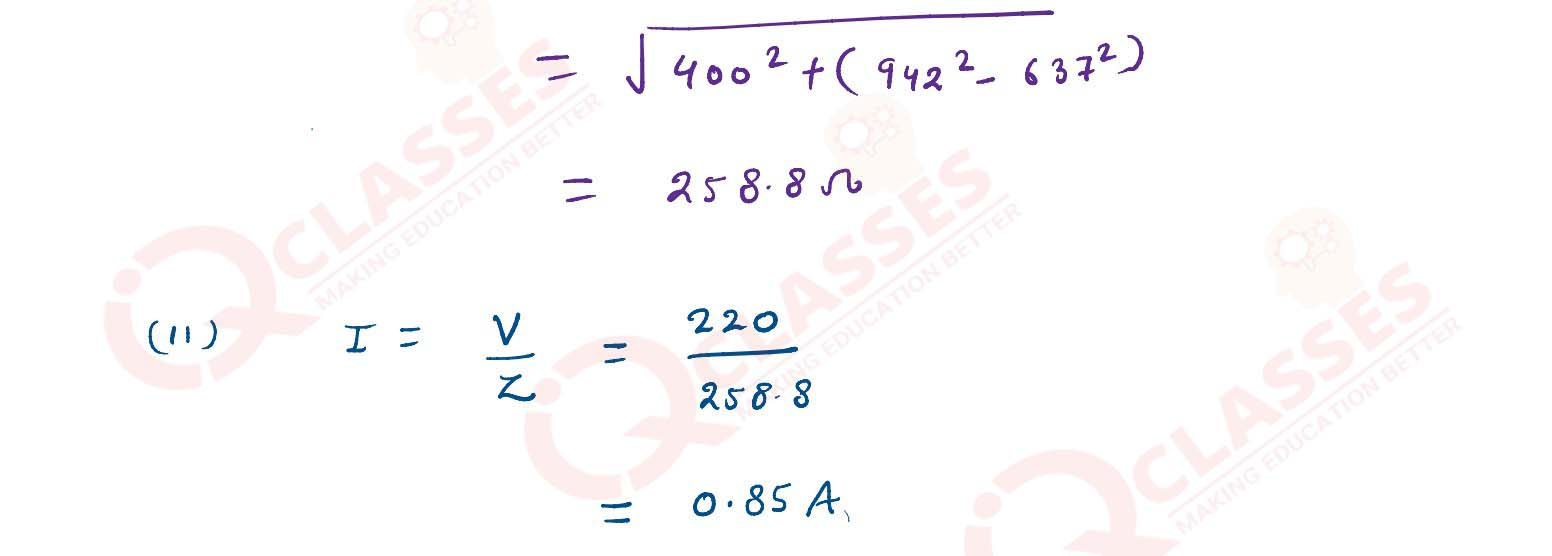
(i) A 400 Ω resistor , a 3 H inductor and a 5 μF capacitor are connected in series to a 220 V , 15
Hz ac source. Calculate the :
(1) impedance of the circuit
(2) current flowing through the circuit.
(ii) Draw a labelled graph showing the variation of impedance (Z) of a series LCR circuit versus frequency (f) of the ac supply.
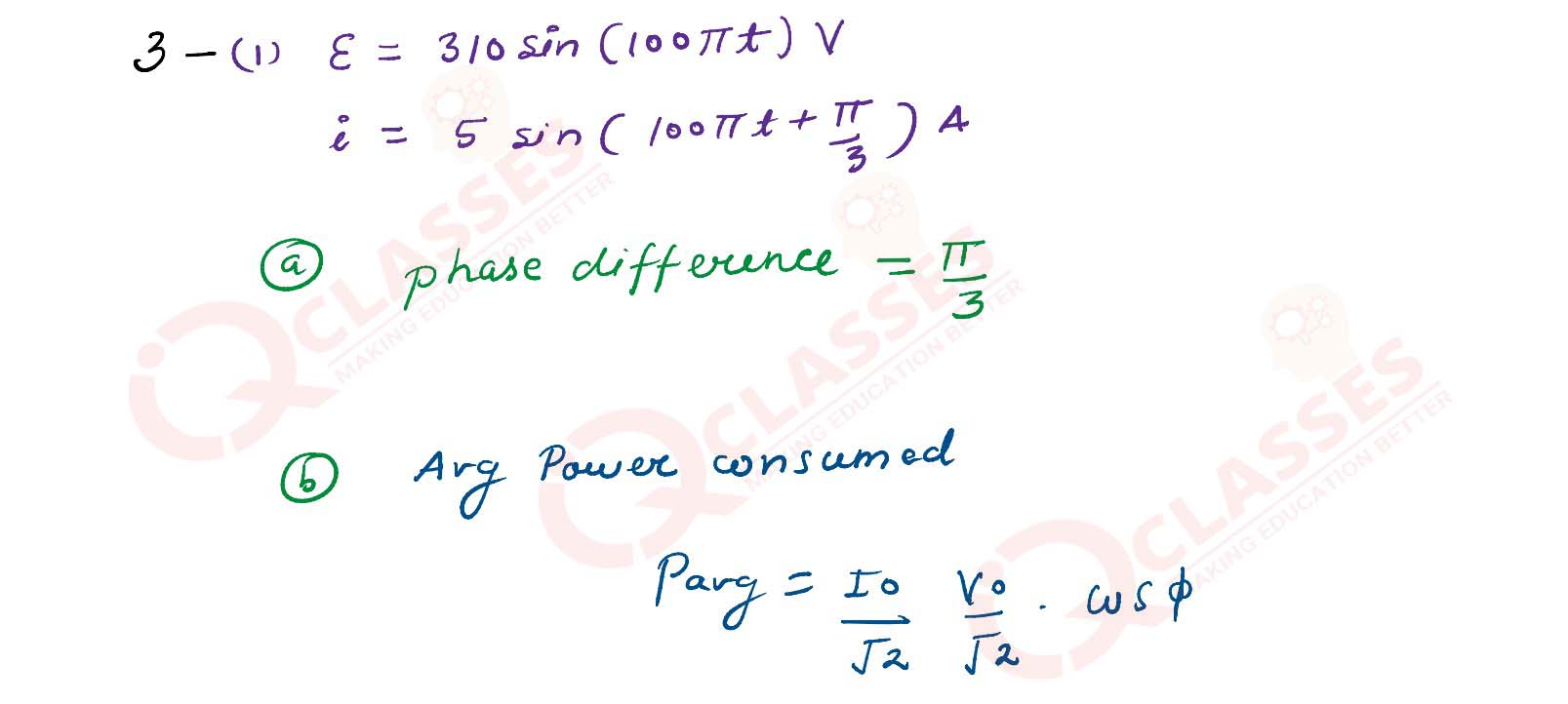
(iii) (a) when an alternating emf ε = 310 sin (100 πt)V is applied to a series LCR circuit , current flowing through it is i = 5 sin(100πt + π/3) A
(1) what is the phase difference between the current and the emf?
(2.)Calculate the average power consumed by the circuit
(b) obtain an expression for the resonant frequency (f0) of a series LCR circuit.
solutions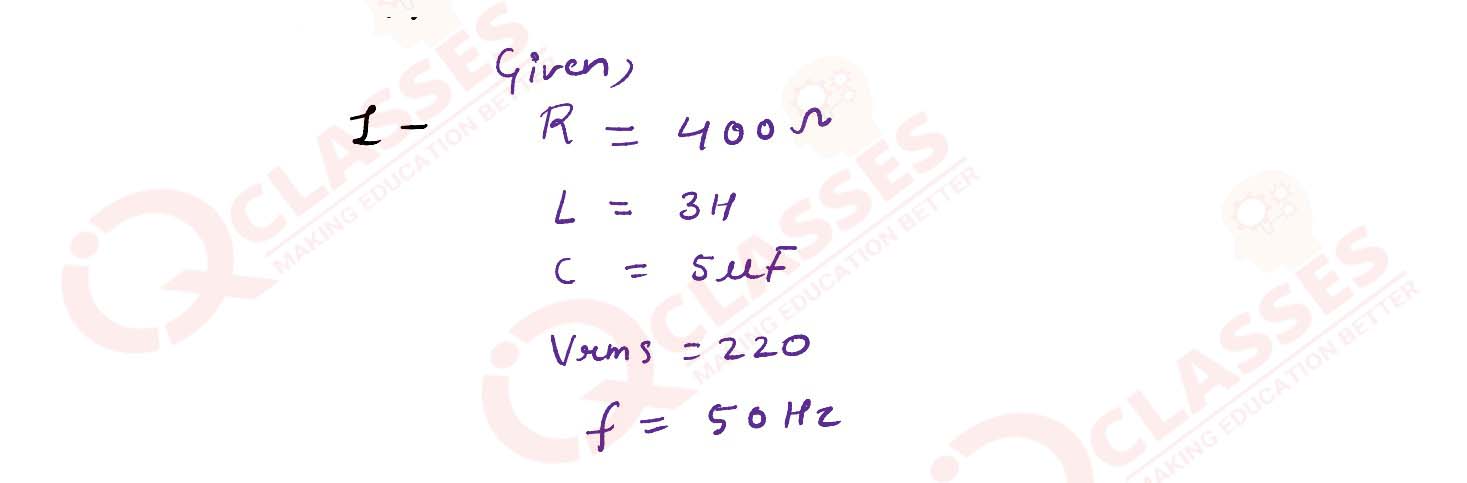
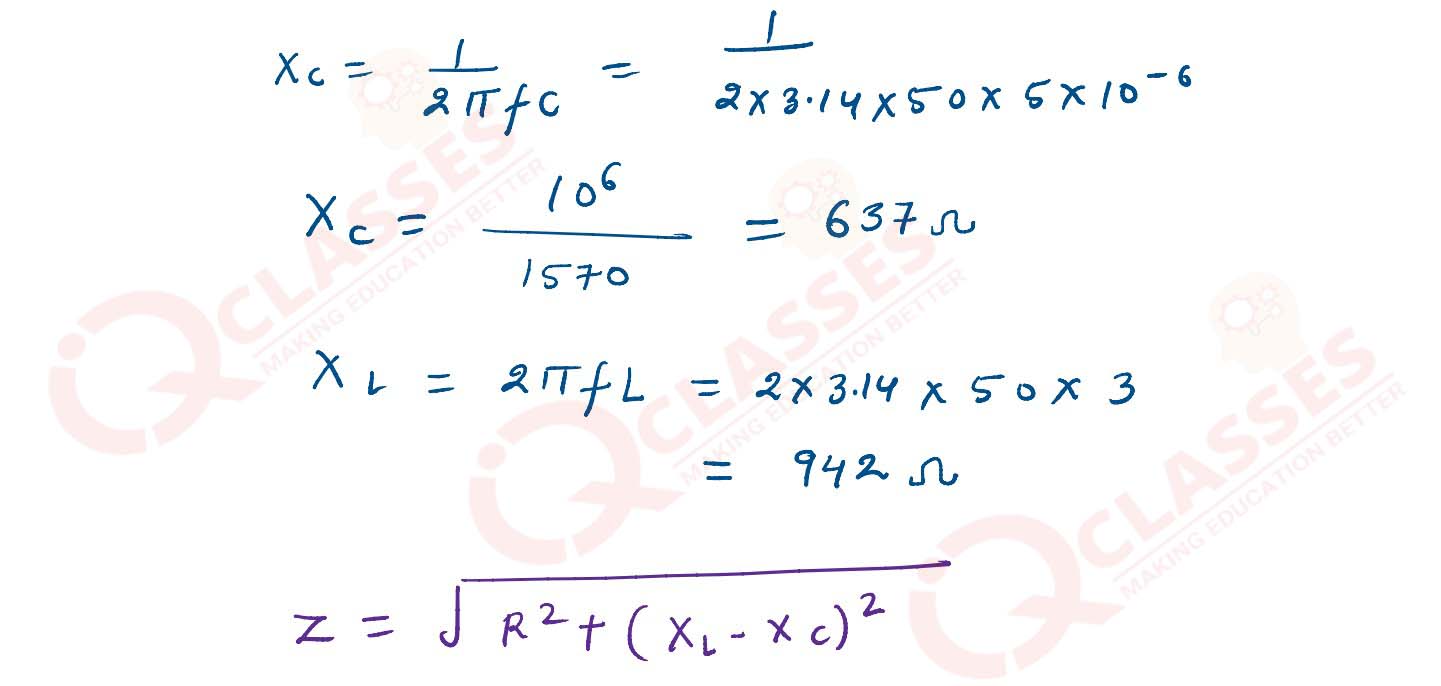
The required graph between the impedance Z and frequency f is as shown in the fig.
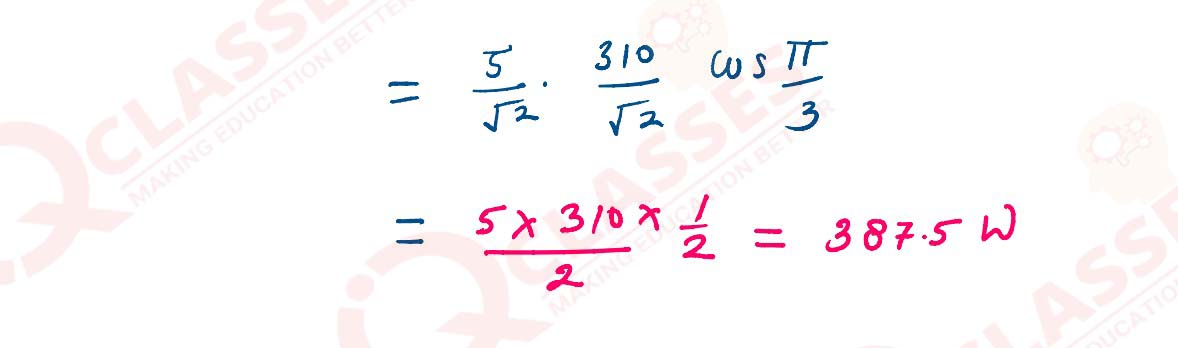

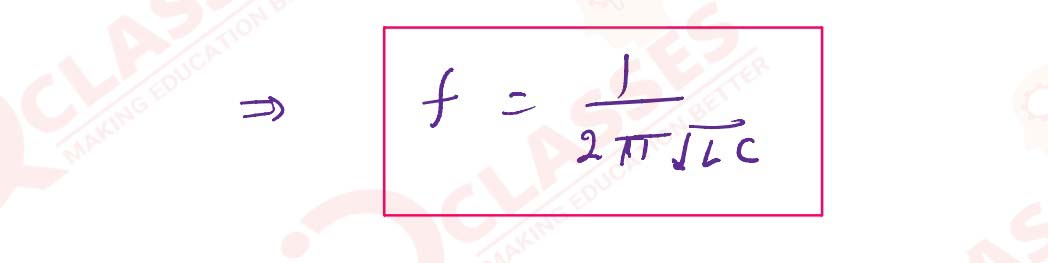
(1) impedance of the circuit
(2) current flowing through the circuit.
(ii) Draw a labelled graph showing the variation of impedance (Z) of a series LCR circuit versus frequency (f) of the ac supply.
(iii) (a) when an alternating emf ε = 310 sin (100 πt)V is applied to a series LCR circuit , current flowing through it is i = 5 sin(100πt + π/3) A
(1) what is the phase difference between the current and the emf?
(2.)Calculate the average power consumed by the circuit
(b) obtain an expression for the resonant frequency (f0) of a series LCR circuit.
solutions
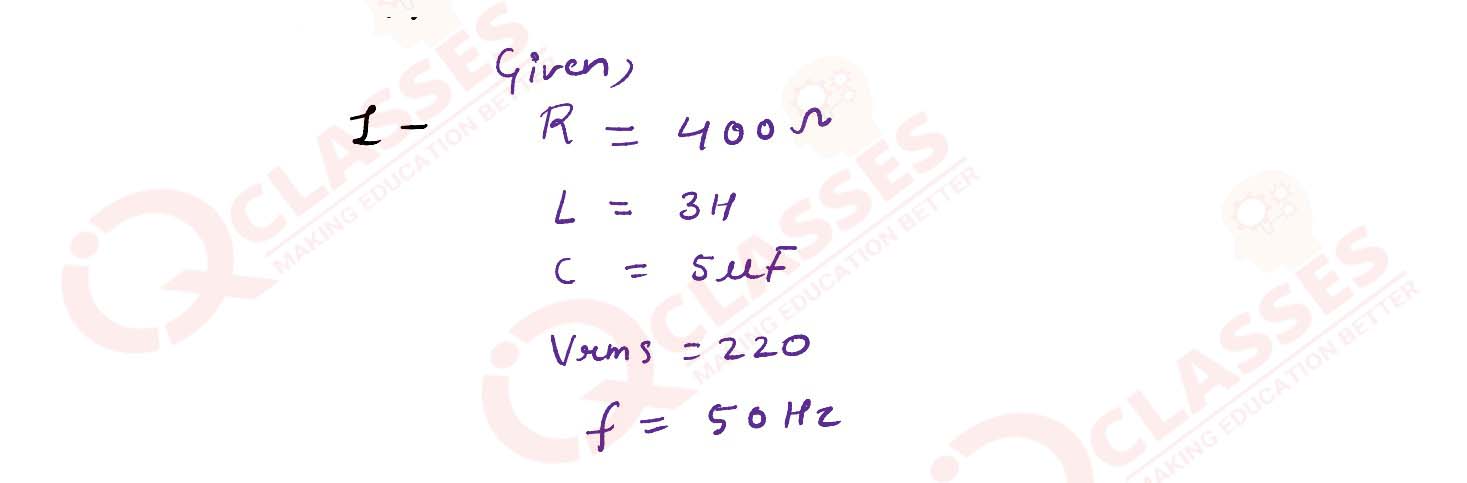
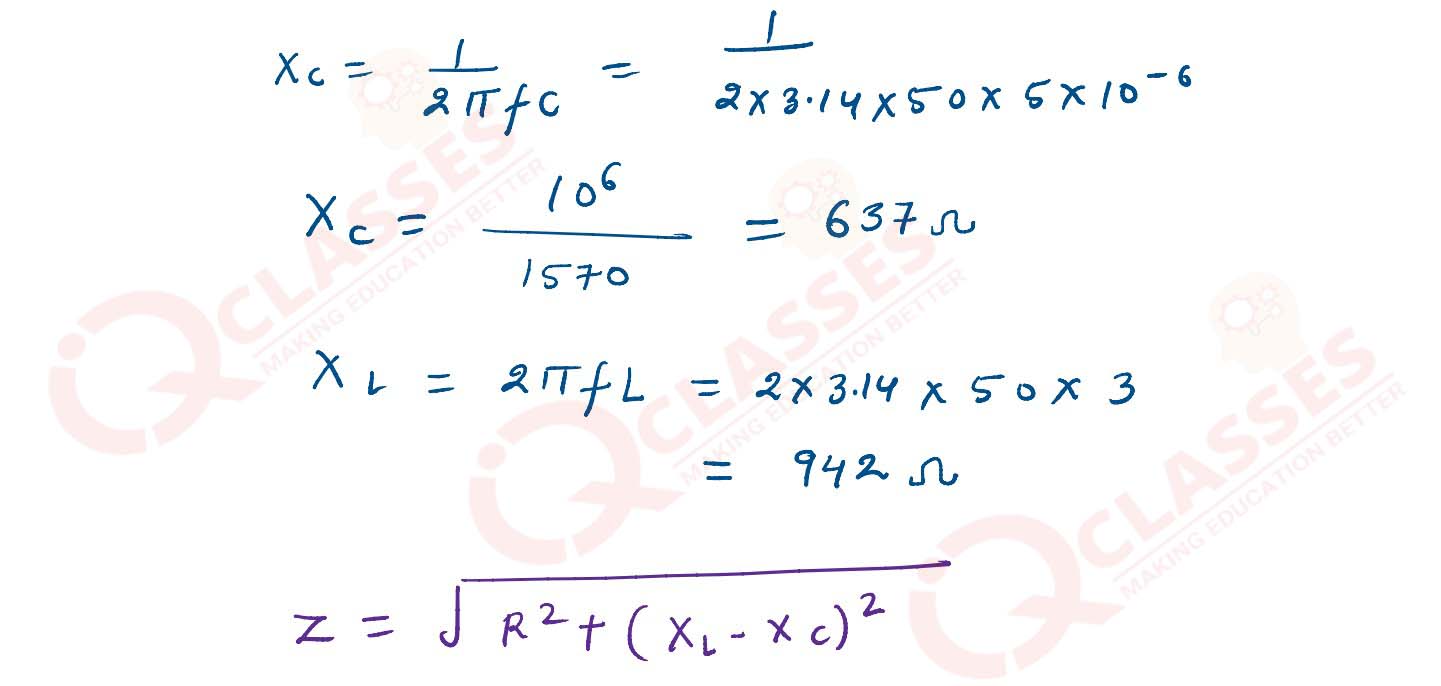

The required graph between the impedance Z and frequency f is as shown in the fig.
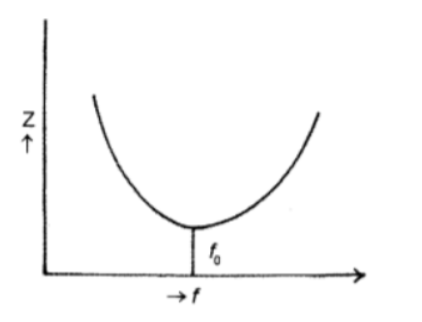
The minimum value of the impedance is R

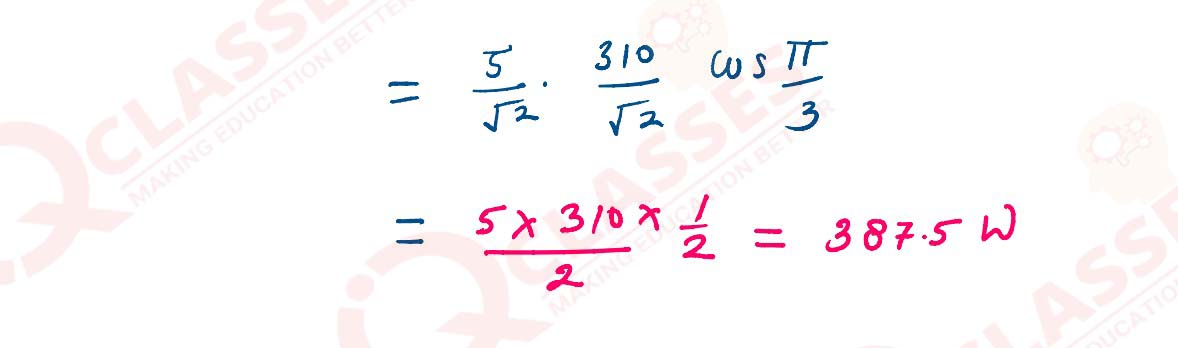

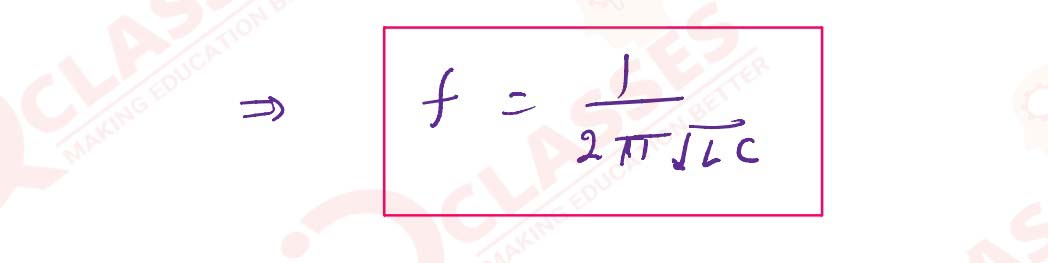
Q2
A solenoid L and a registered R are connected in series to a battery through a switch. When the
switches put on, current I flowing through it varies with a time as shown in which of the graph
given below :
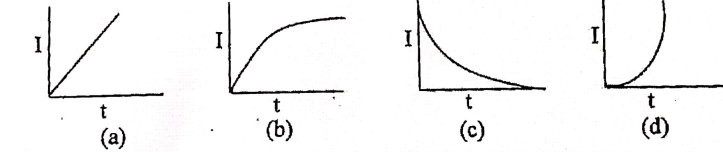
solutions
The required graph between the impedance Z and frequency f is as shown in the fig.
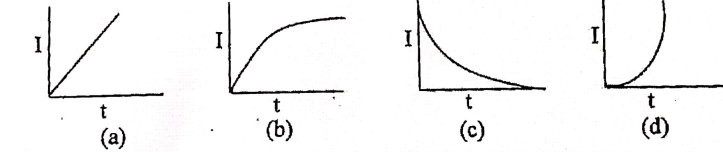
solutions
The required graph between the impedance Z and frequency f is as shown in the fig.

The minimum value of the impedance is R
Q3
What is an ideal transformer?
solutions
solutions

Q4
What is the value of power factor for a pure resistor connected to an alternating current source?
solutions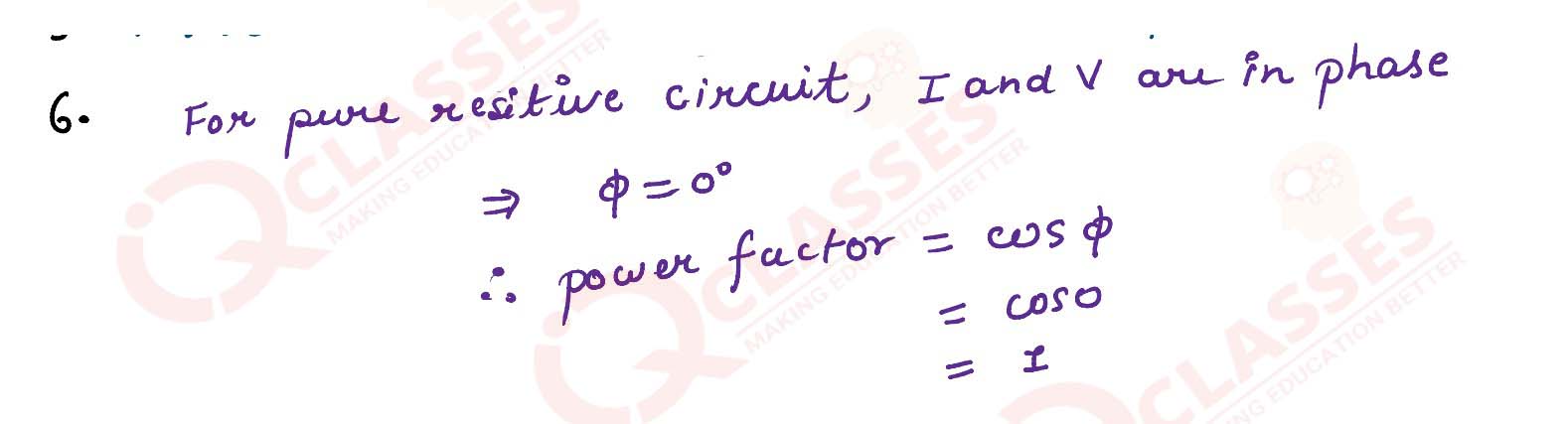
solutions
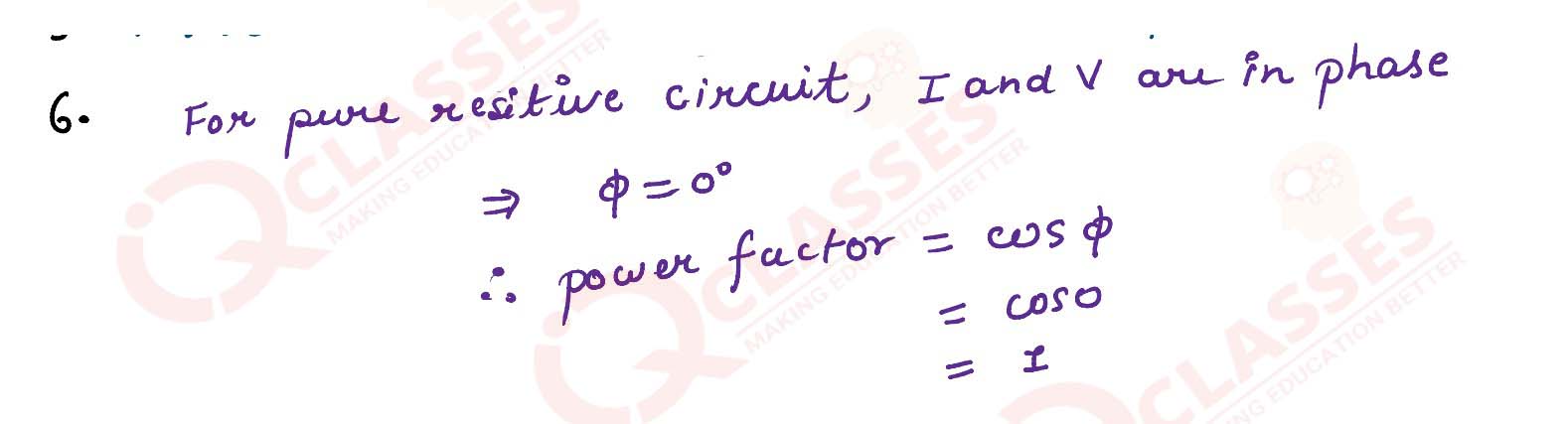
Q5
. A transformer is used to step up and alternating emf of 200 V to 440 V. If the primary coil has
1000 turns. Calculate the number of turns in the secondary coil.
solutions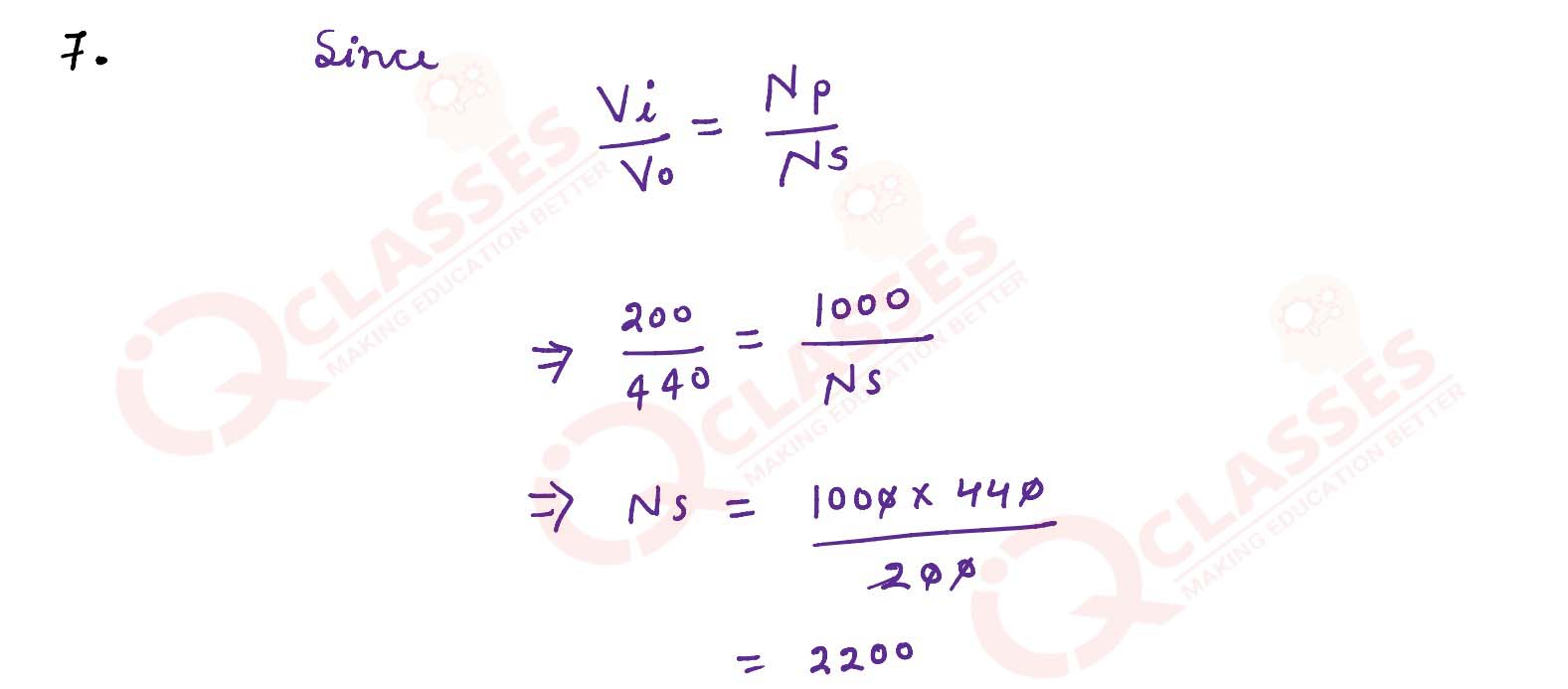
solutions

Q6
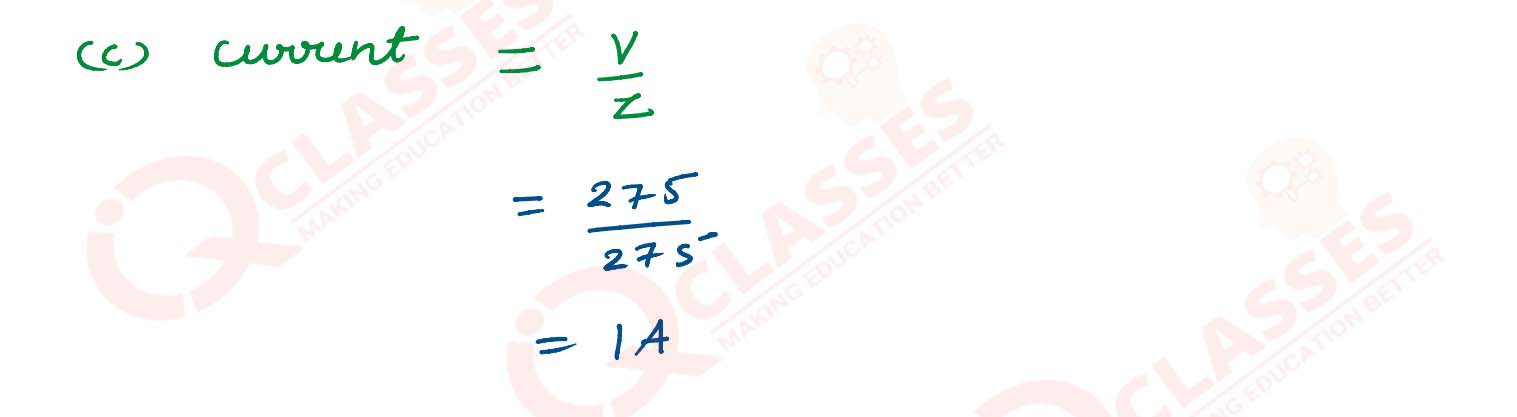
A coil having self-inductance of 0.7 H and resistance of 165 Ω is connected to an a. c. source of
275 V , 50 Hz. If π = 22/7. Calculate :
(a) Reactance of the coil.
(b) impedance of the coil.
(c) current flowing through the coil.
solutions

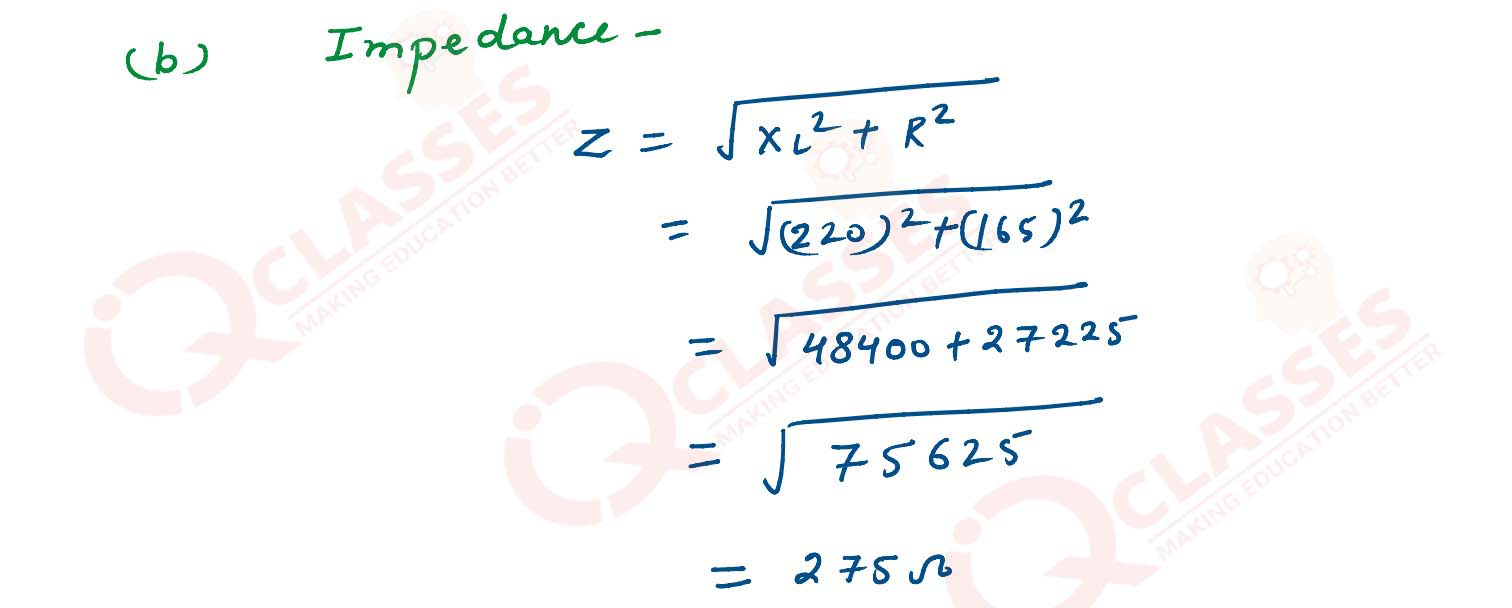
(a) Reactance of the coil.
(b) impedance of the coil.
(c) current flowing through the coil.
solutions


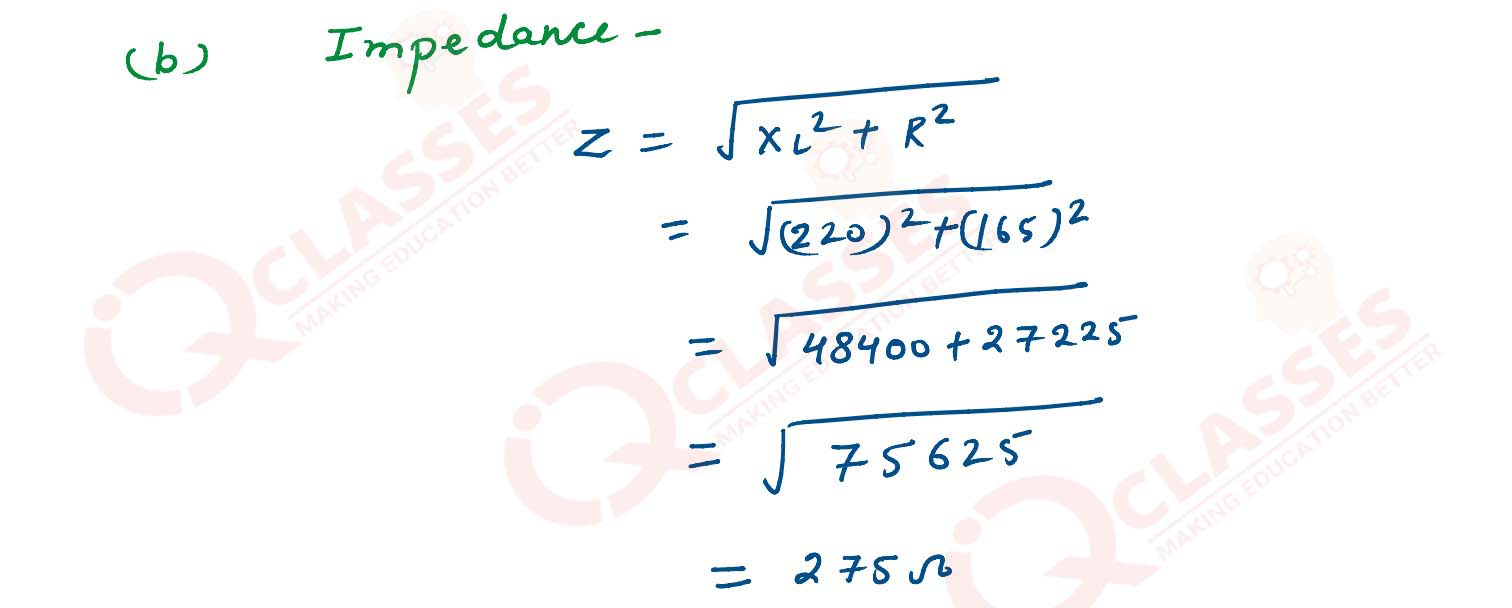

Q7
Draw a labelled graph showing variation of impedance of a series LCR circuit with frequency of the
AC supply.
solutions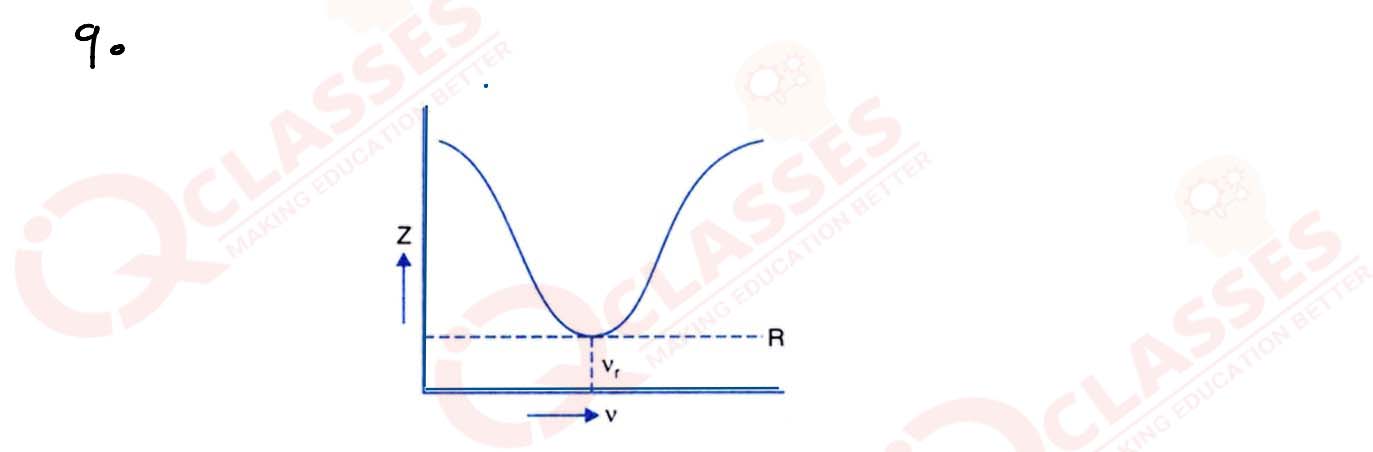
solutions

Q8
An AC generator generates an emf ‘ε' where ‘ε'= 314 Sin(50πt) volt. Calculate the frequency of the
emf ε.
solutions
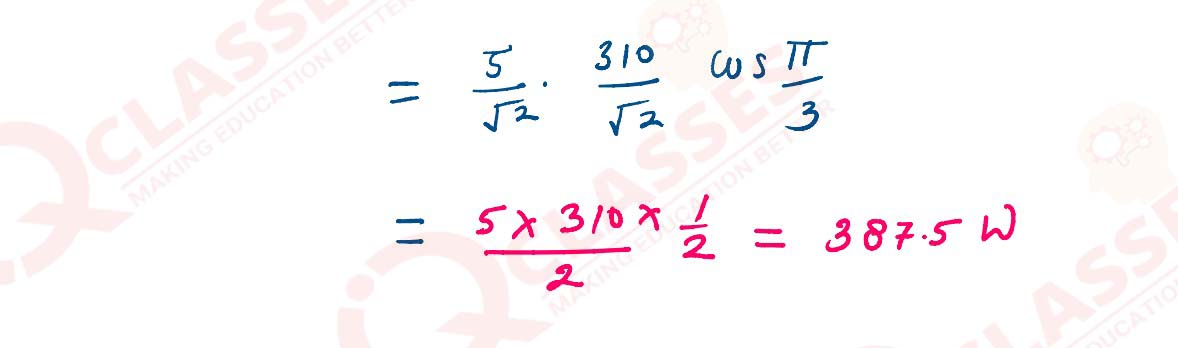

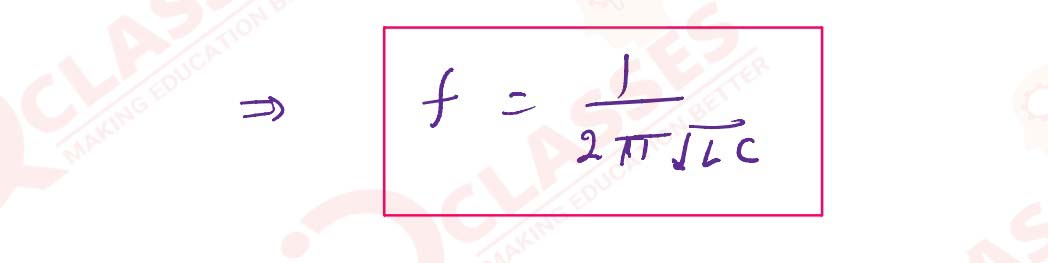
solutions

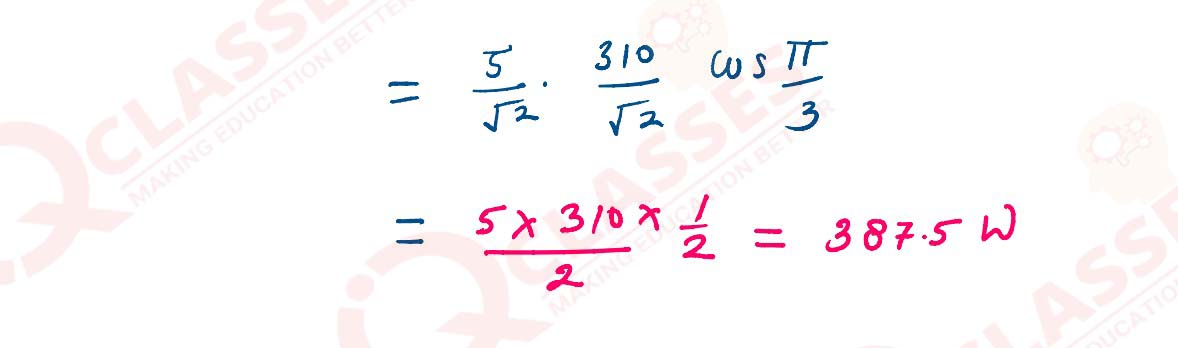

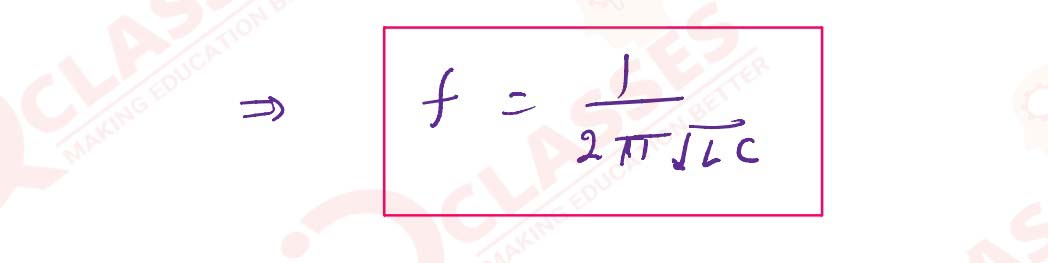
Q9
In an ideal transformer common output of 66 kV is required when input voltage of 220 V is available.
If the primary has 300 turns, how many turns, should the secondary have?
solutions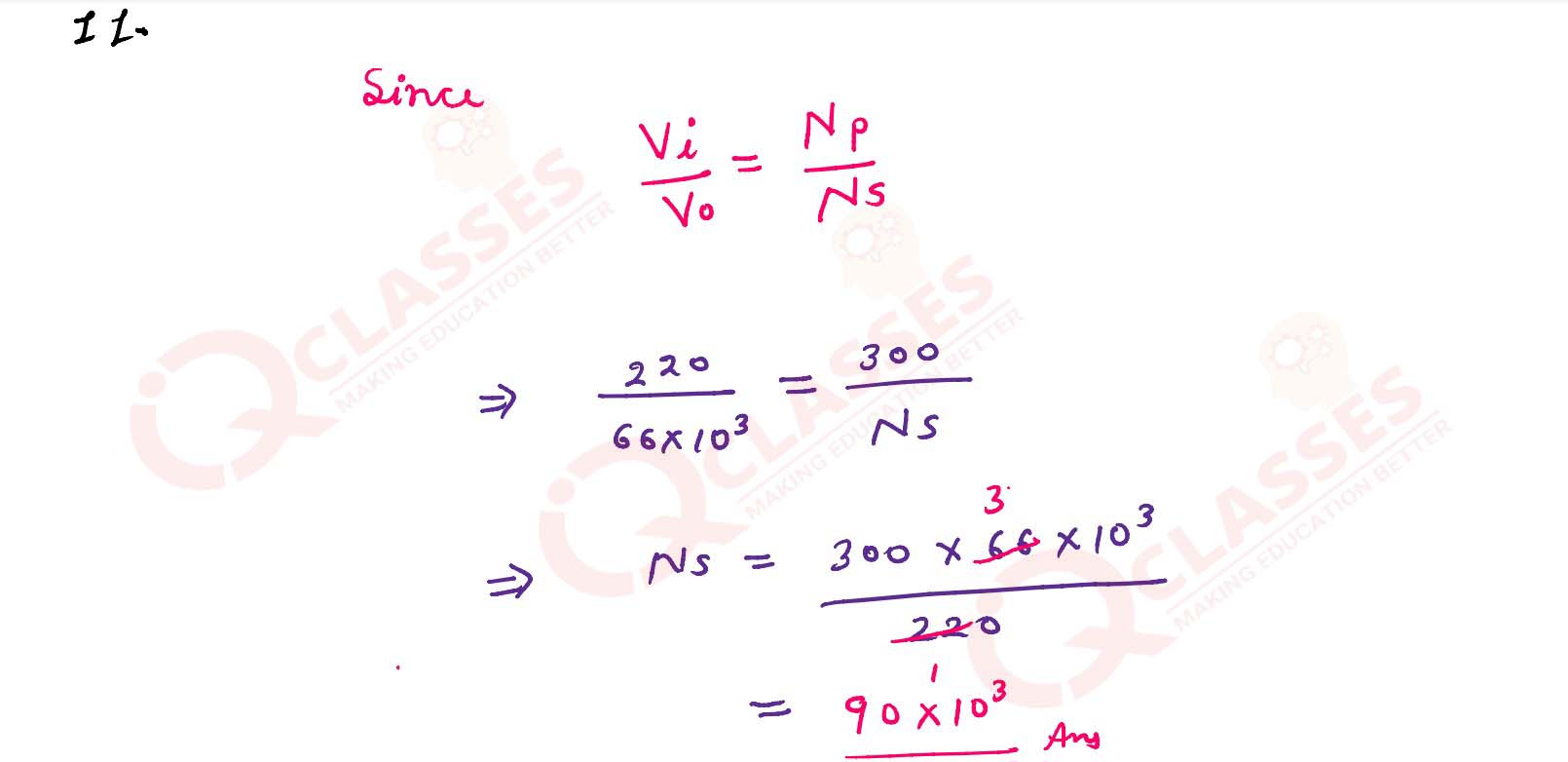
solutions

Q10
Draw labelled graph showing variation of inductive reactance (XL) versus frequency (f).
solutions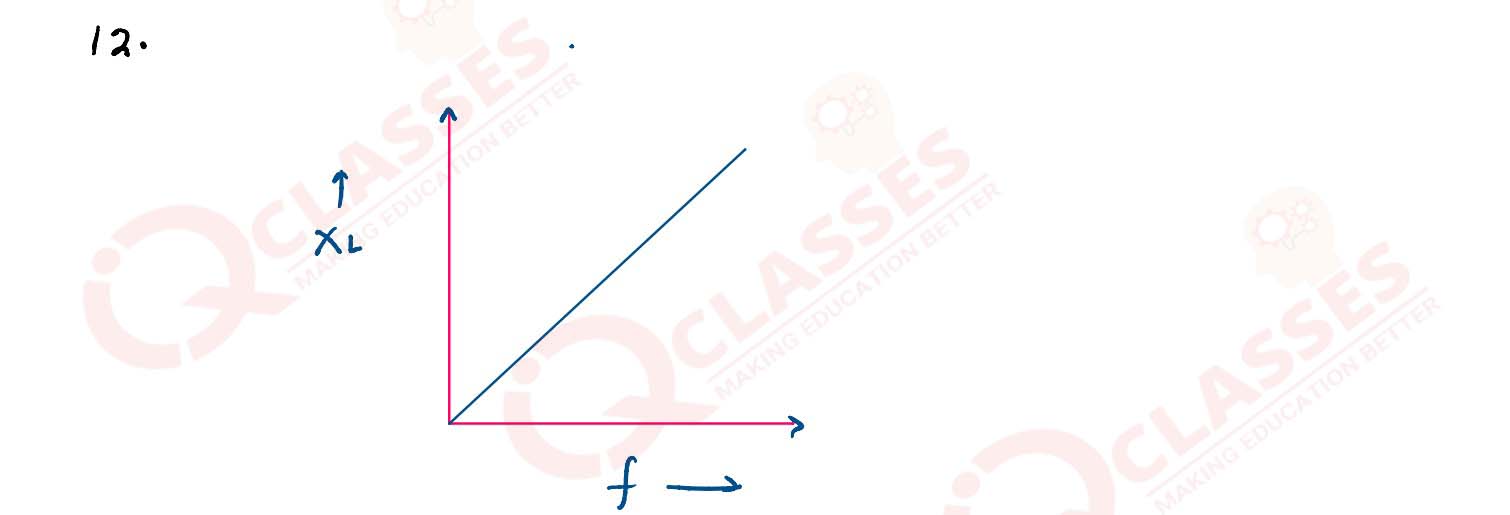
solutions

Q11
An a.c. source of emf ε = 200 sin ω is connected to register of 50 Ω. Calculate:
(1) average current (Iavg) (2) root mean square (rms) value of emf.
solutions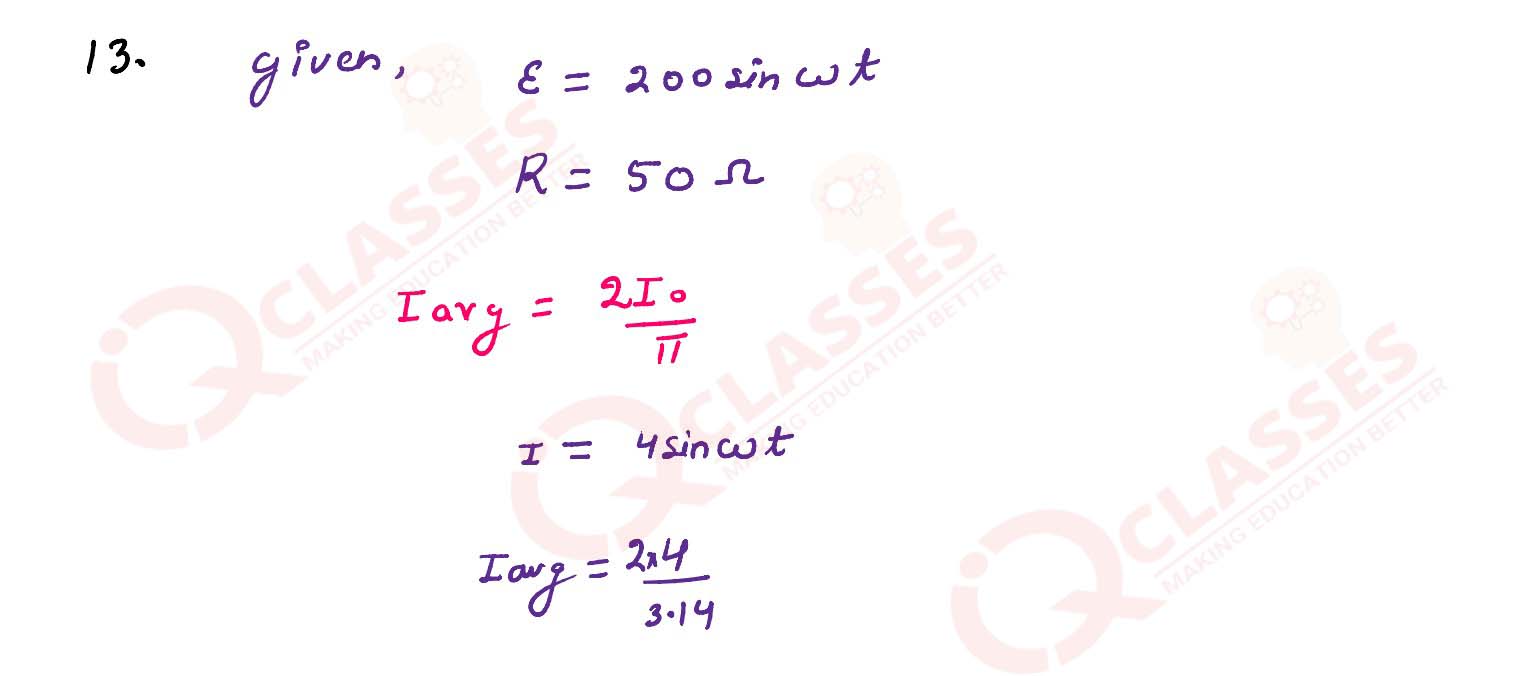
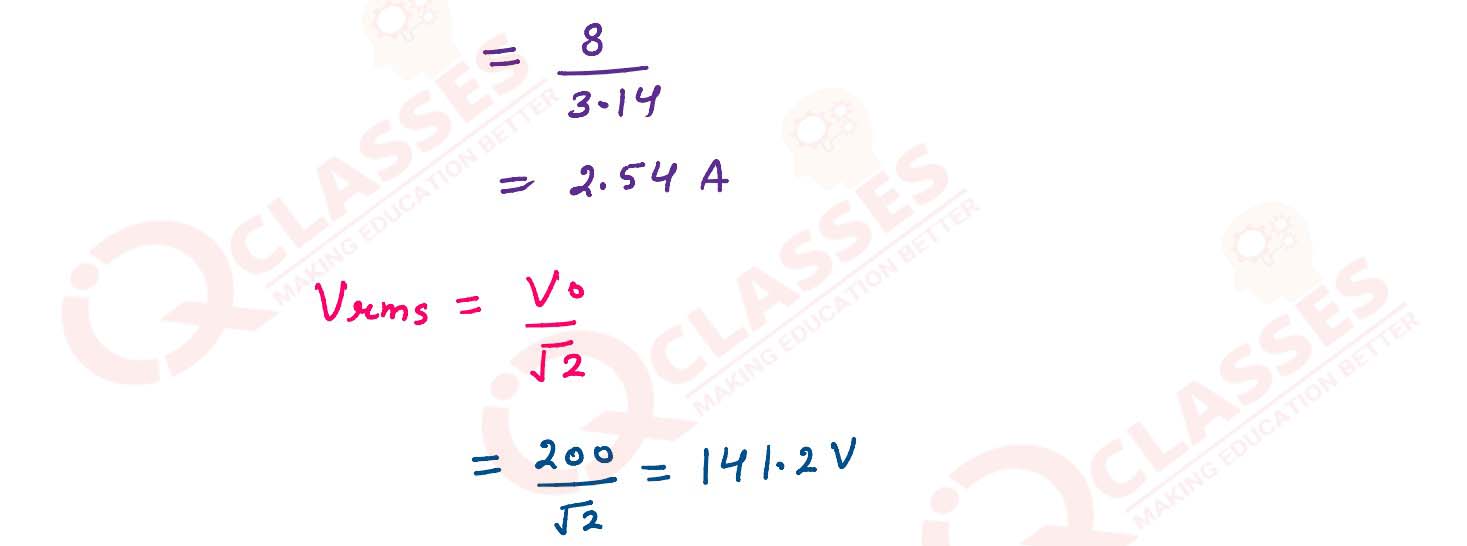
(1) average current (Iavg) (2) root mean square (rms) value of emf.
solutions
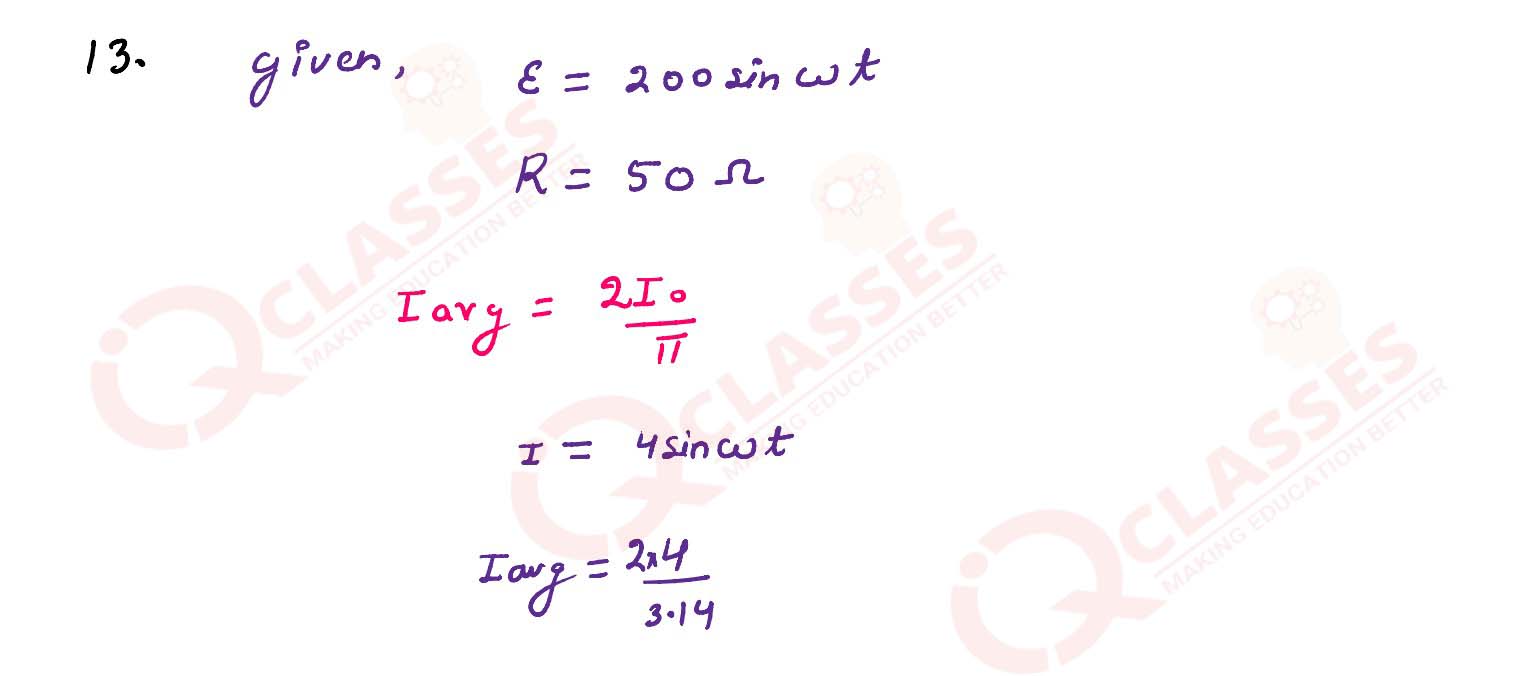
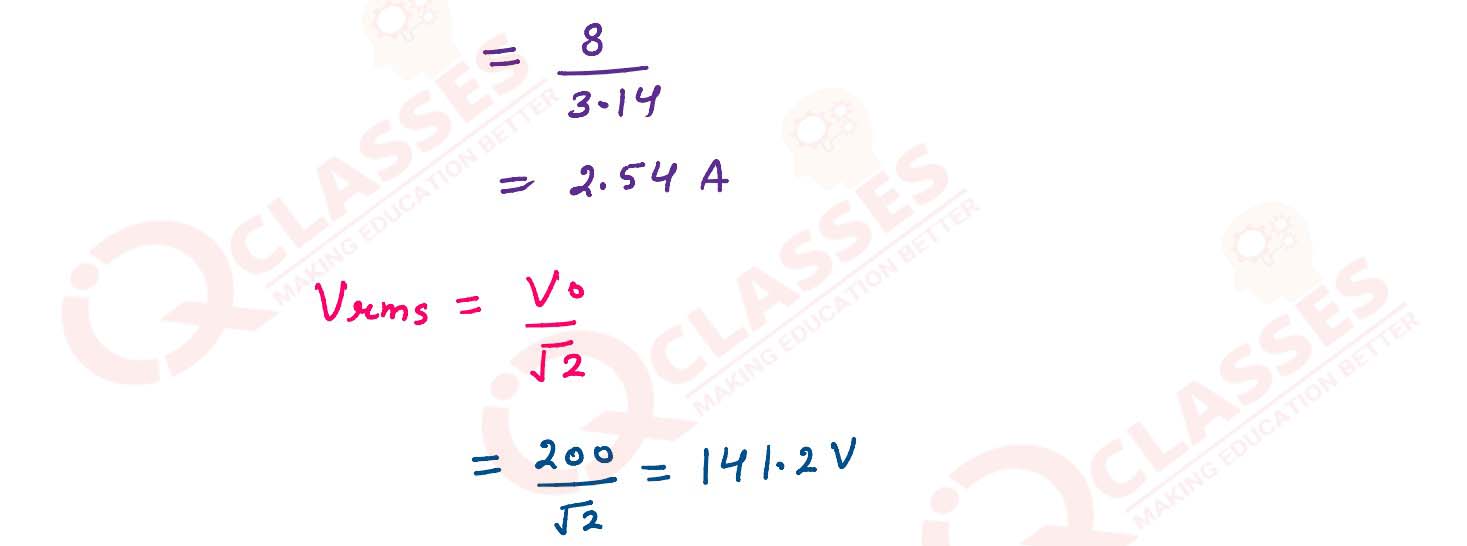
Q12
State any 2 characteristics of resonance in LCR series circuit.
solutions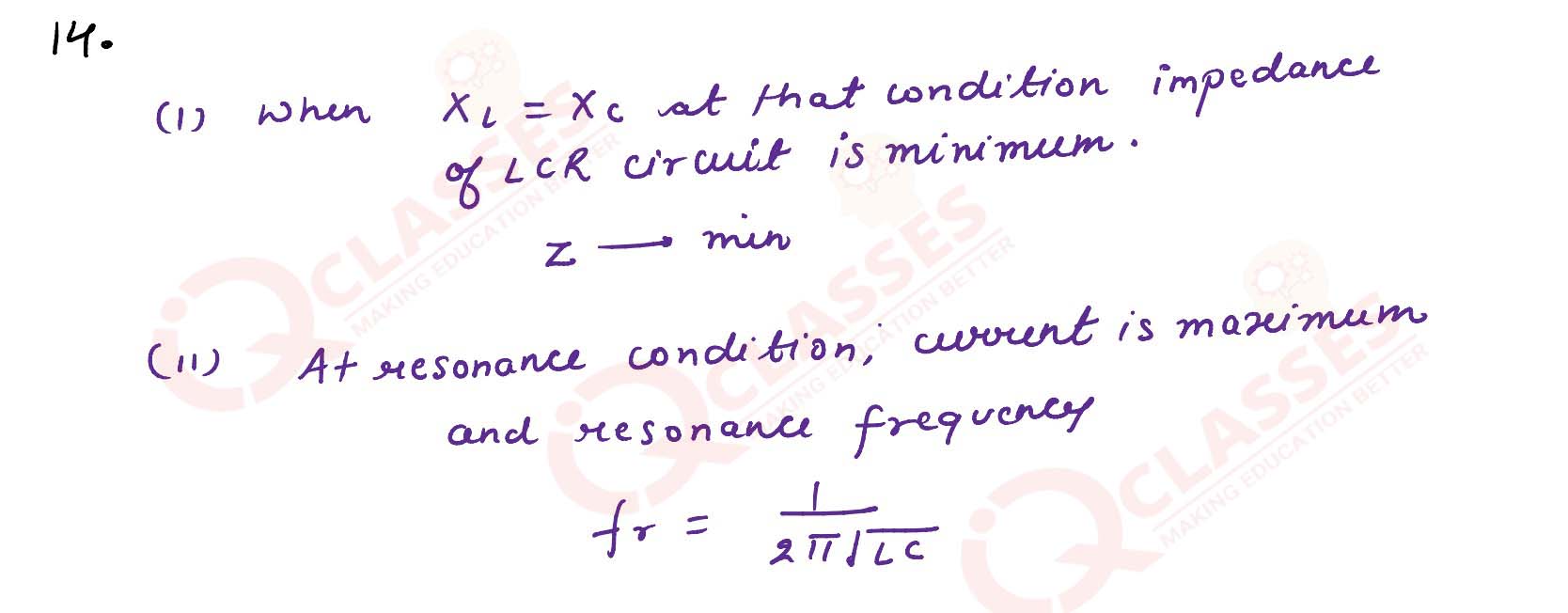
solutions

Q13
In a series LCR circuit, obtain an expression for the resonant frequency
solutions
solutions
Q14
Why is the core of a transformer laminated?
solutions
solutions

Q15
An AC generator generating an emf of ε= 300 sin(100 πt)V is connected to a series combination of 16
μF capacitor, 1 H inductor and 100 Ω resistor. Calculate :
(1) impedance of the circuit at the given frequency
(2) resonant frequency f0
(3) power factor as resonant frequency (f0)
solutions

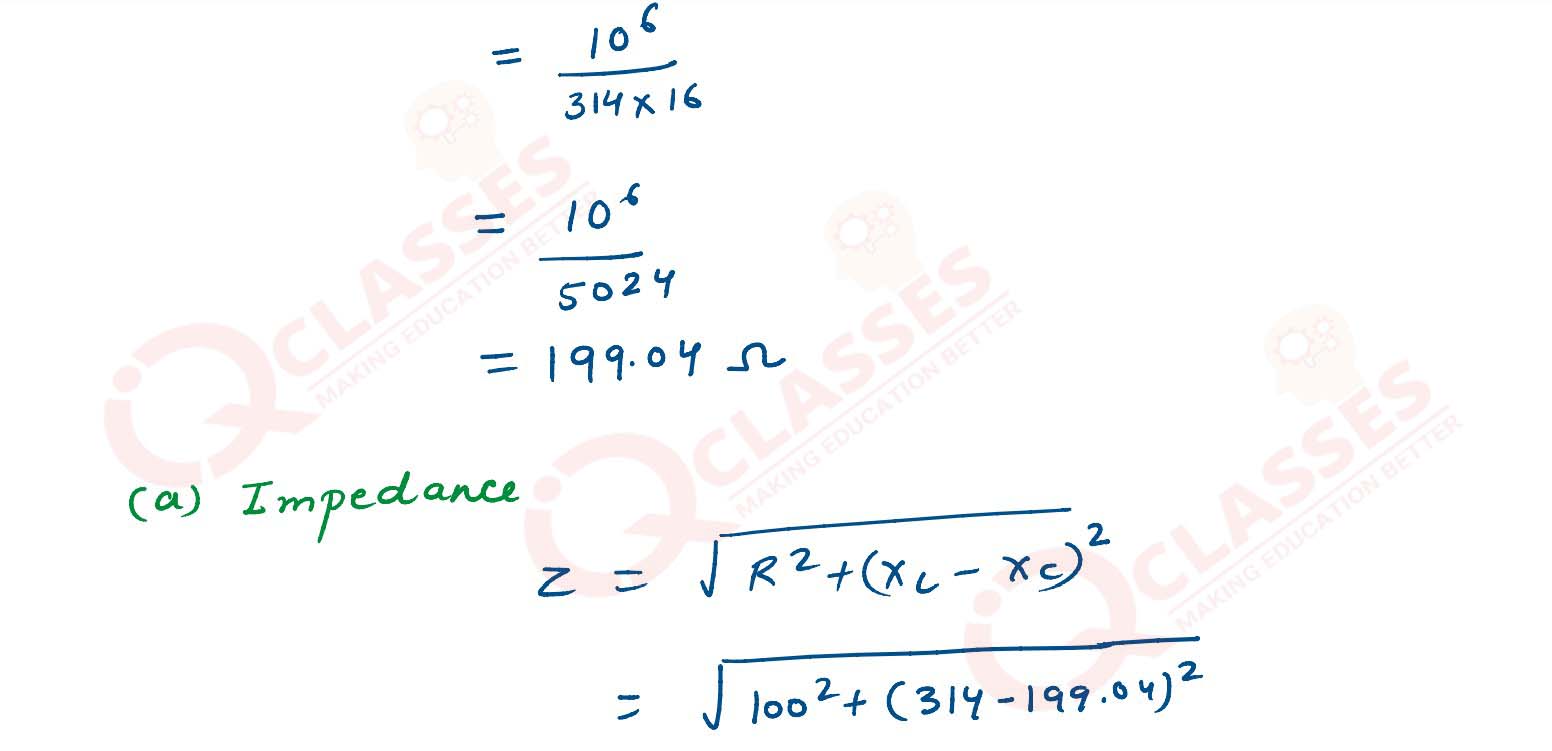
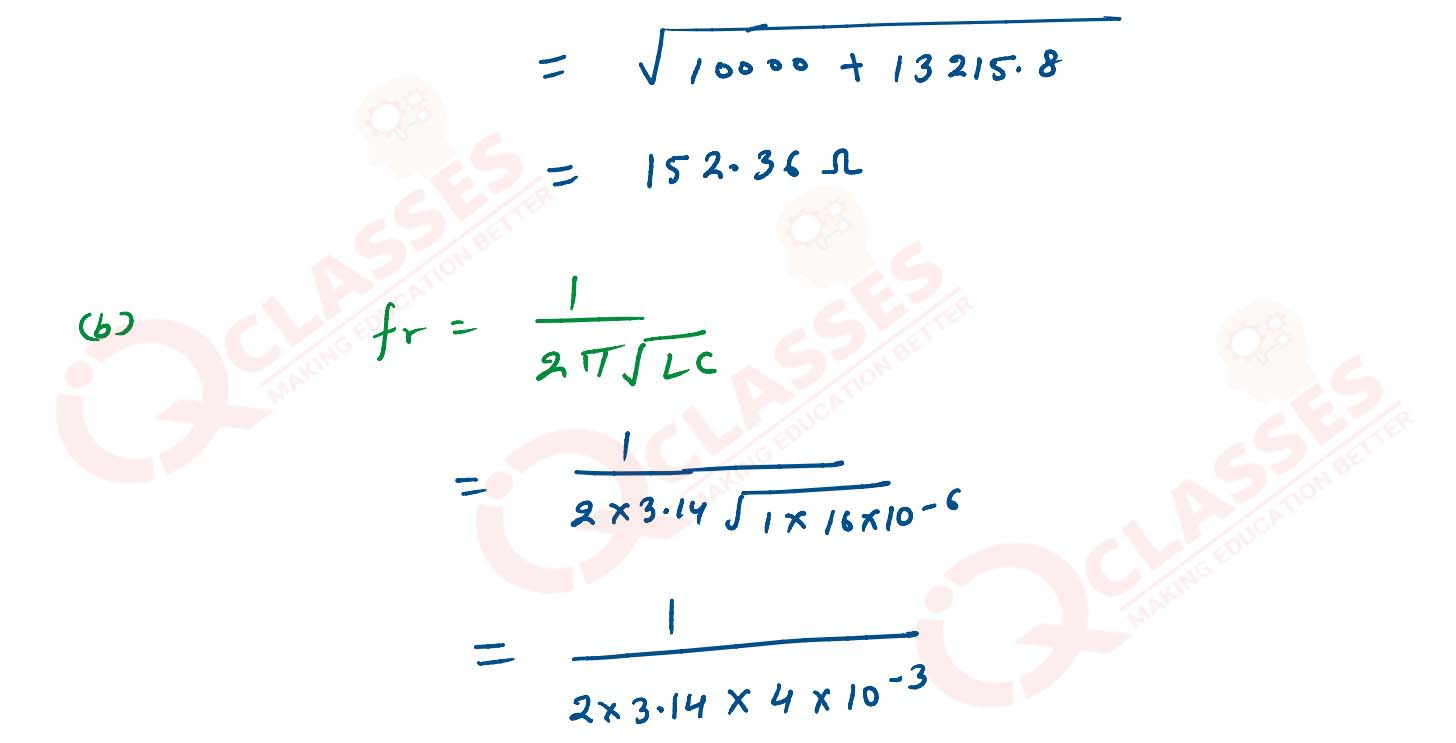
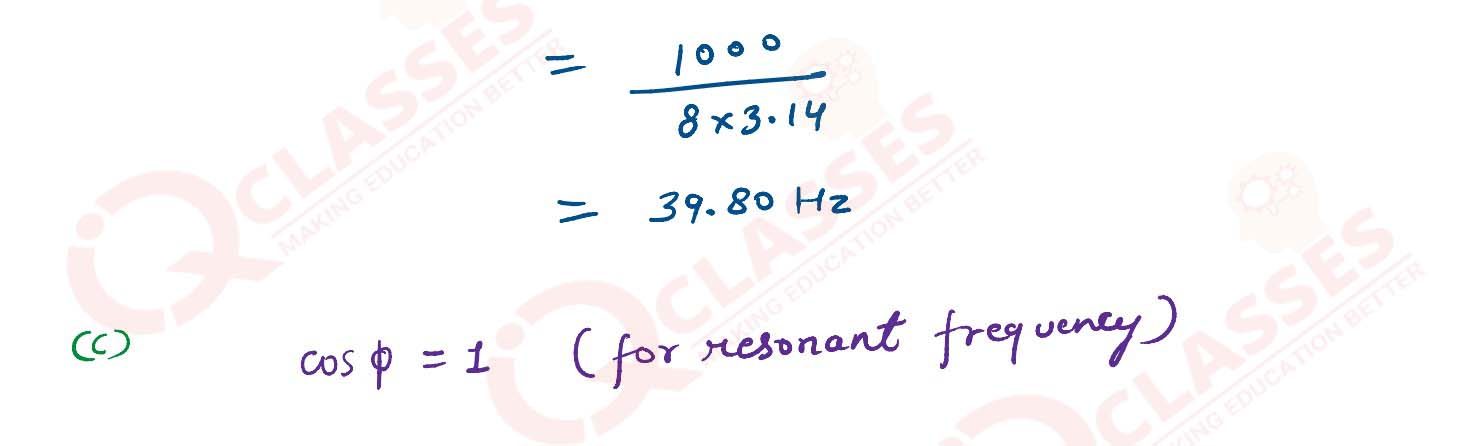
(1) impedance of the circuit at the given frequency
(2) resonant frequency f0
(3) power factor as resonant frequency (f0)
solutions


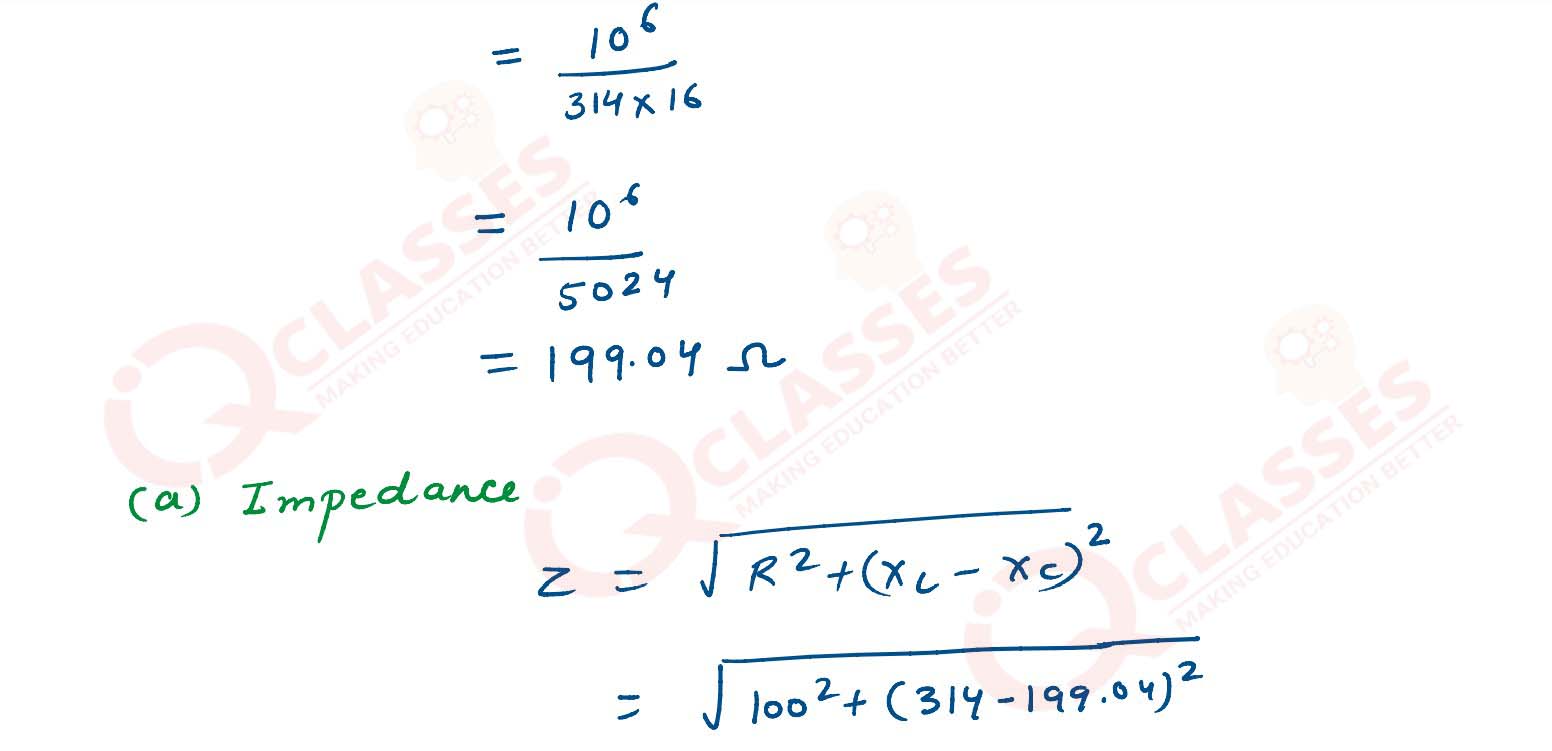
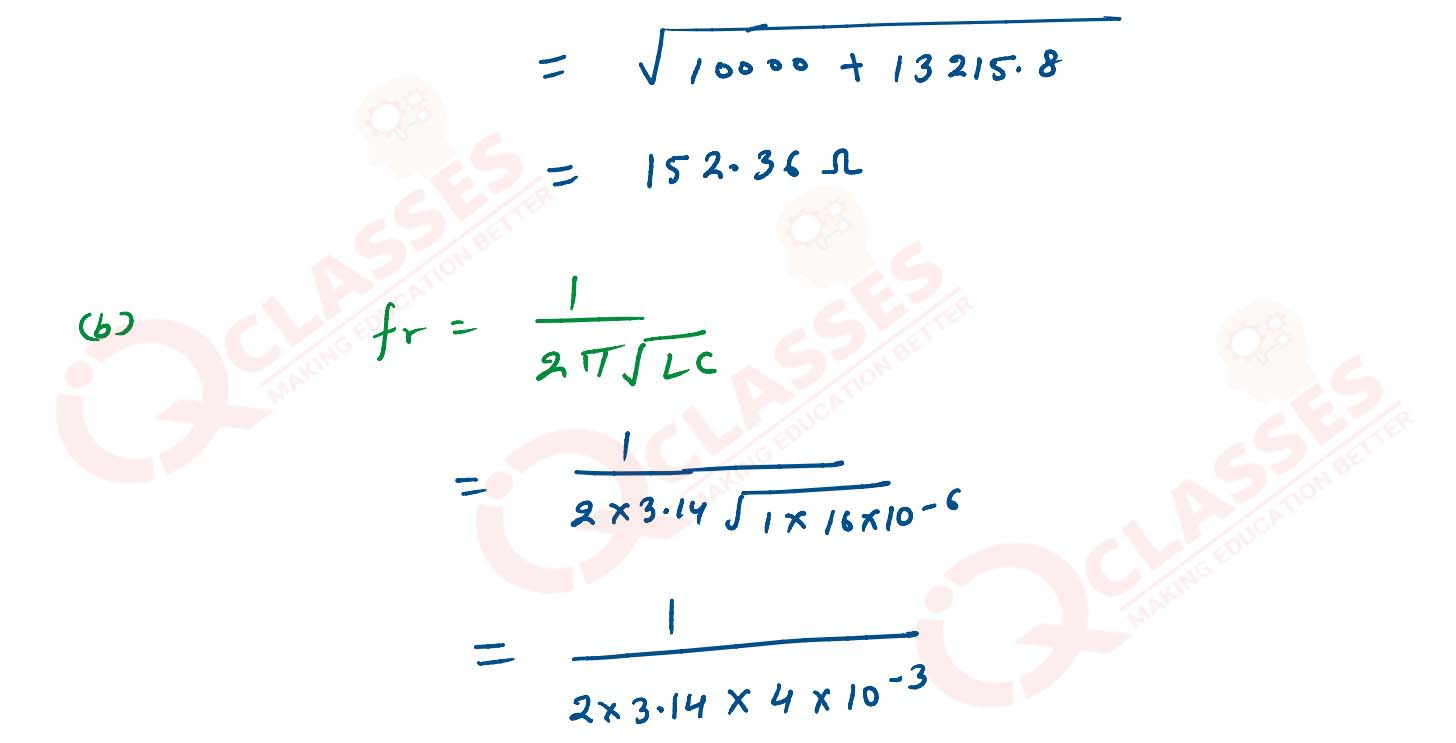
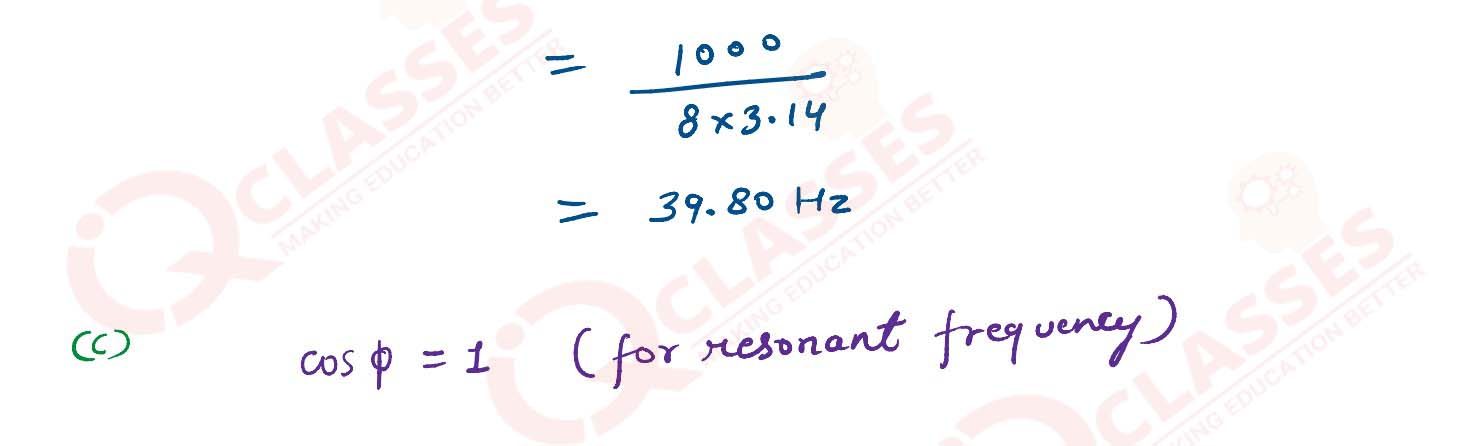
Q16
An alternating emf of 220 V is applied to a circuit containing a resistor R having resistance of 160
Ω and a capacitor ‘C’ in series. The current is found to lead the supply voltage by an angle Ɵ =
tan-1(3/4).
(i) Calculate:
(1) the capacitive reactance
(2) impedance of the circuit
(3) current flowing in the circuit
(ii) if the frequency of the applied emf is 50 Hz, what is the value of the capacitance of the capacitor C
solutions
(i) Calculate:
(1) the capacitive reactance
(2) impedance of the circuit
(3) current flowing in the circuit
(ii) if the frequency of the applied emf is 50 Hz, what is the value of the capacitance of the capacitor C
solutions


Add a comment