Class 12 ISC Physics Atoms Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 Physics important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter Atoms. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on ISC board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 Physics syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
Q1
Total energy state of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. Its total energy, when hydrogen atom is in the
first excited state is:
(a) + 13.6 eV
(b) + 3.4 eV
(c) – 3.4 eV
(d) – 54.4 eV
solutions
(a) + 13.6 eV
(b) + 3.4 eV
(c) – 3.4 eV
(d) – 54.4 eV
solutions

Q2
Calculate angular momentum of an electron in the 3rd Bohr orbit of hydrogen atom.
solutions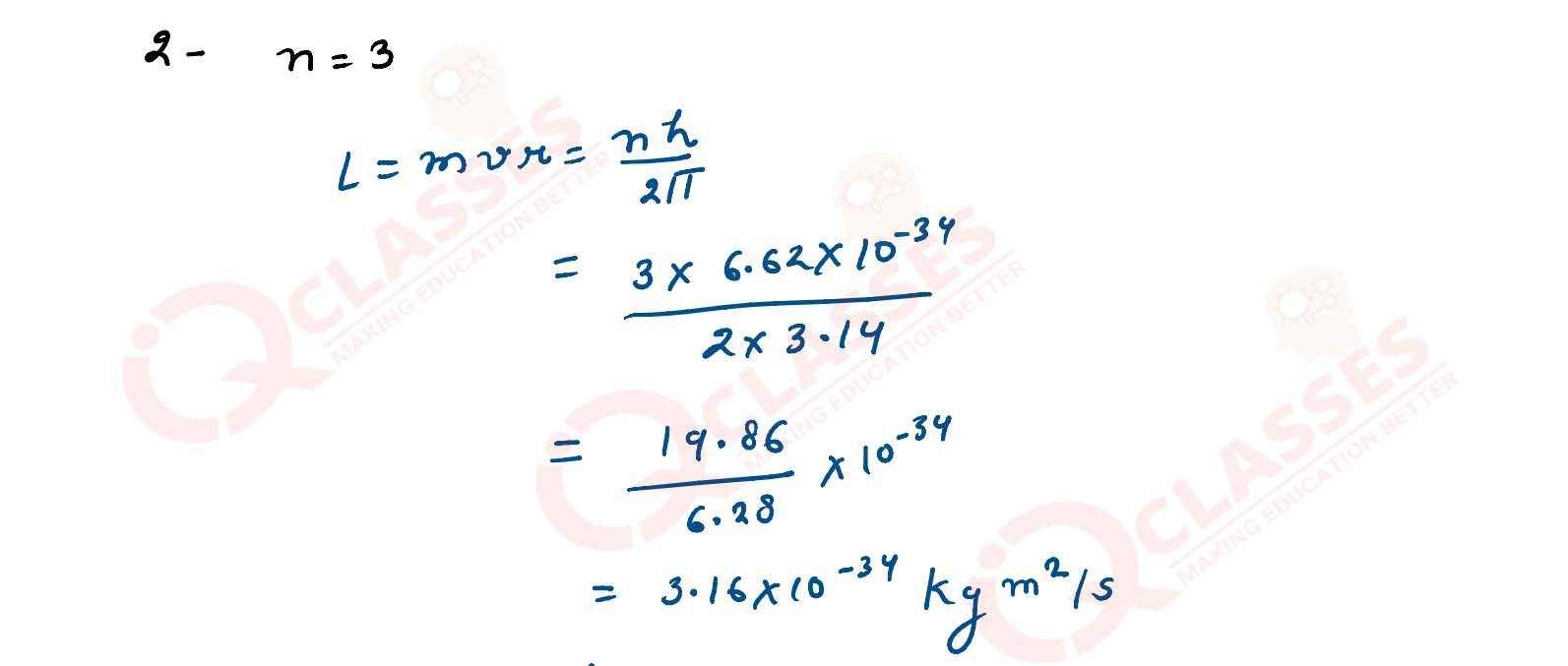
solutions
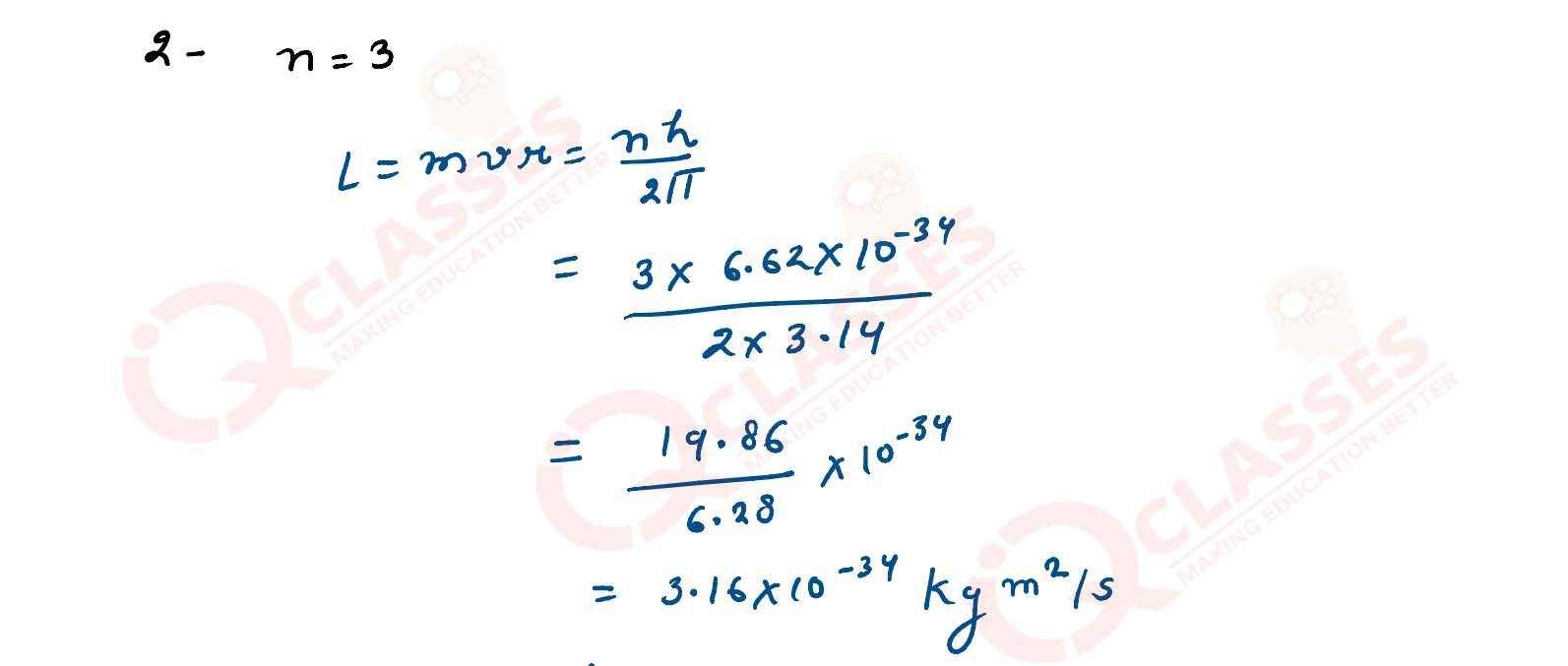
Q3
(i) How are various lines of Lyman series formed? Explain on the basis of Bohr’s theory.
(ii) Calculate the shortest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation present in Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum.
solutions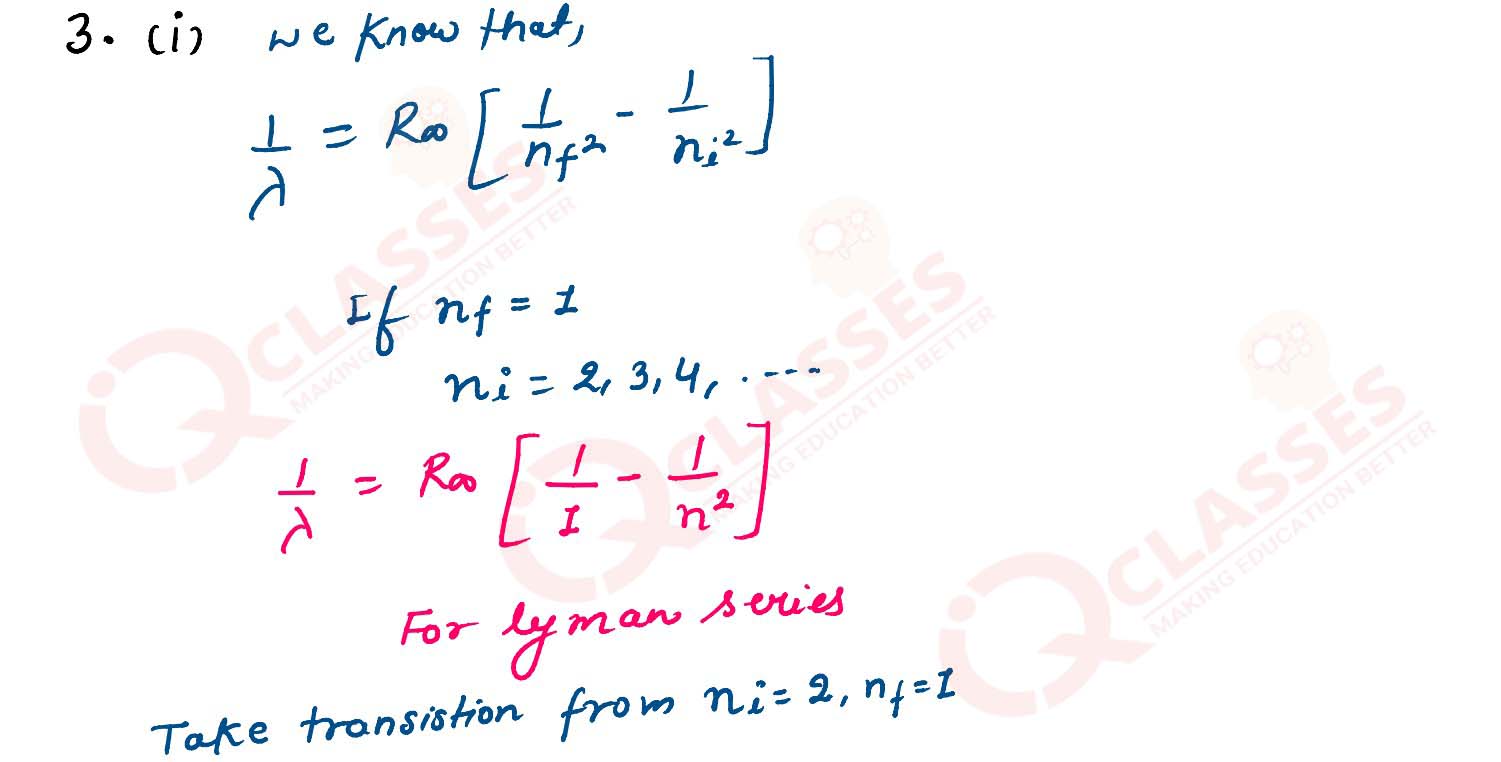
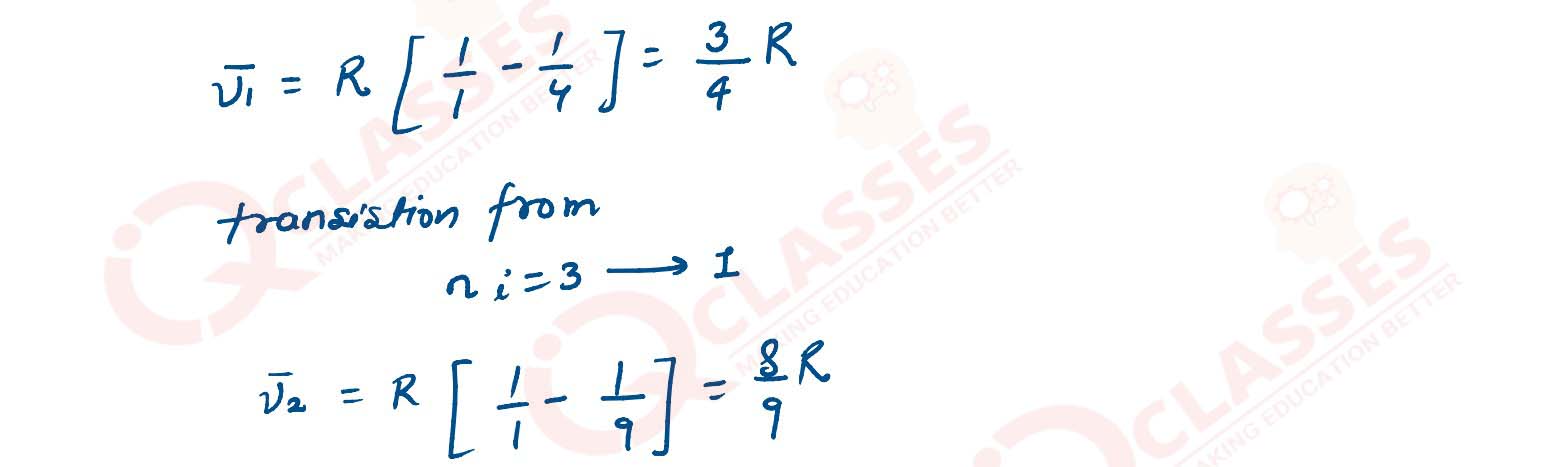
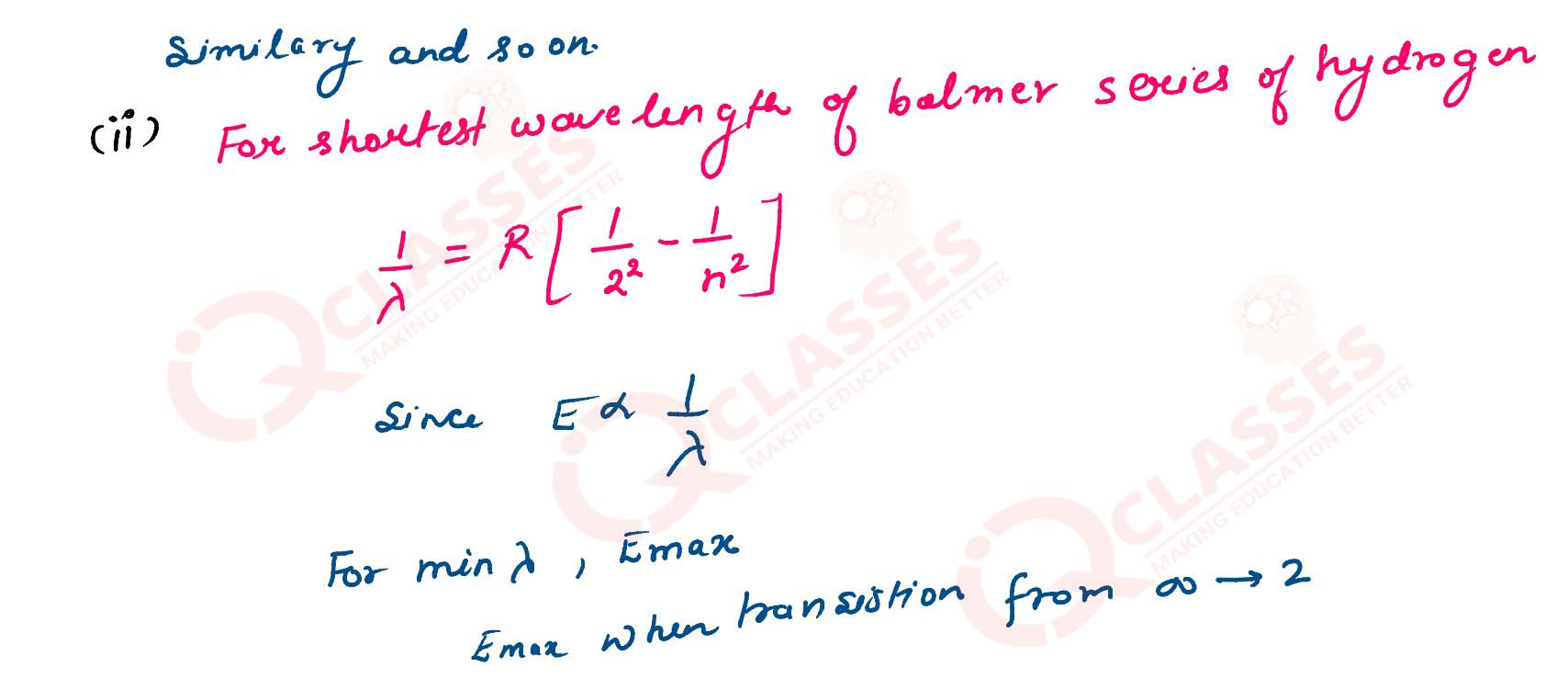
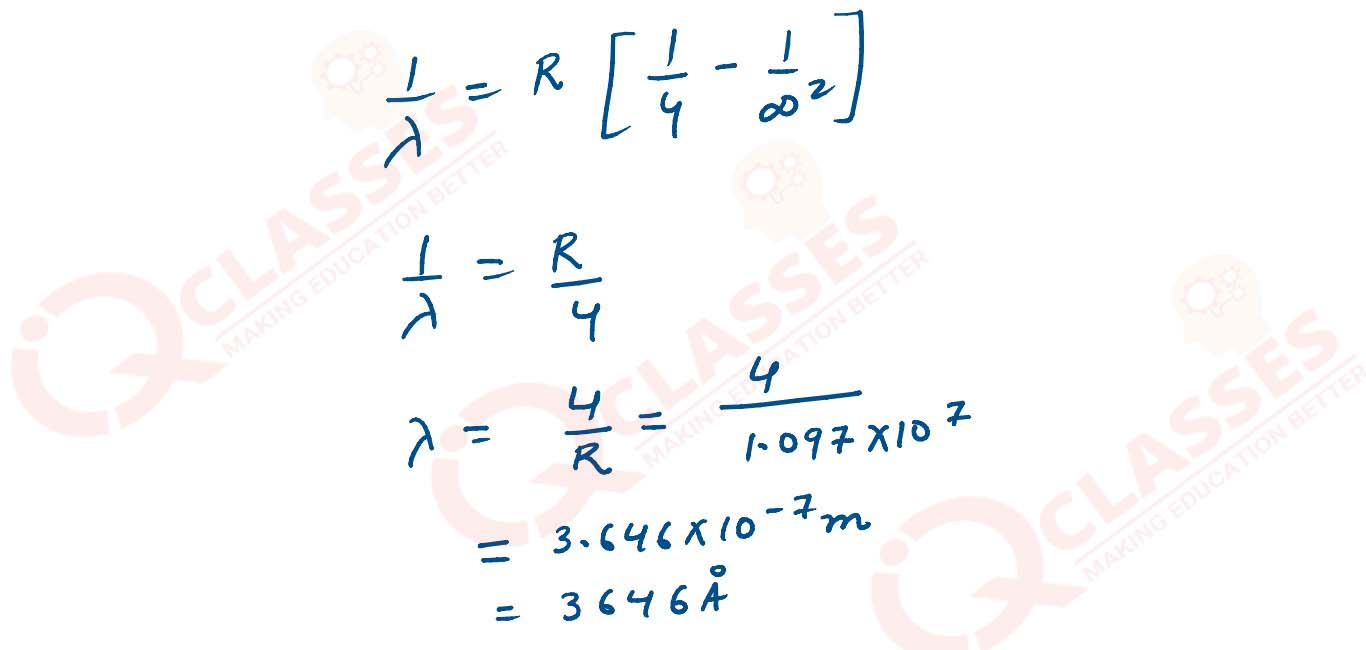
(ii) Calculate the shortest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation present in Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum.
solutions

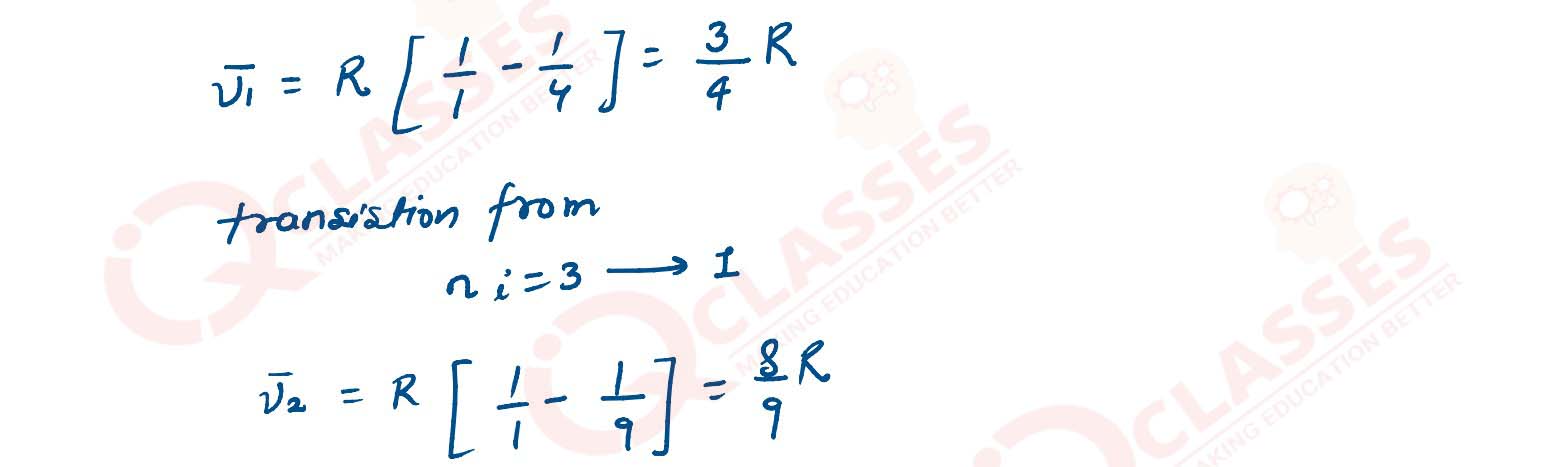

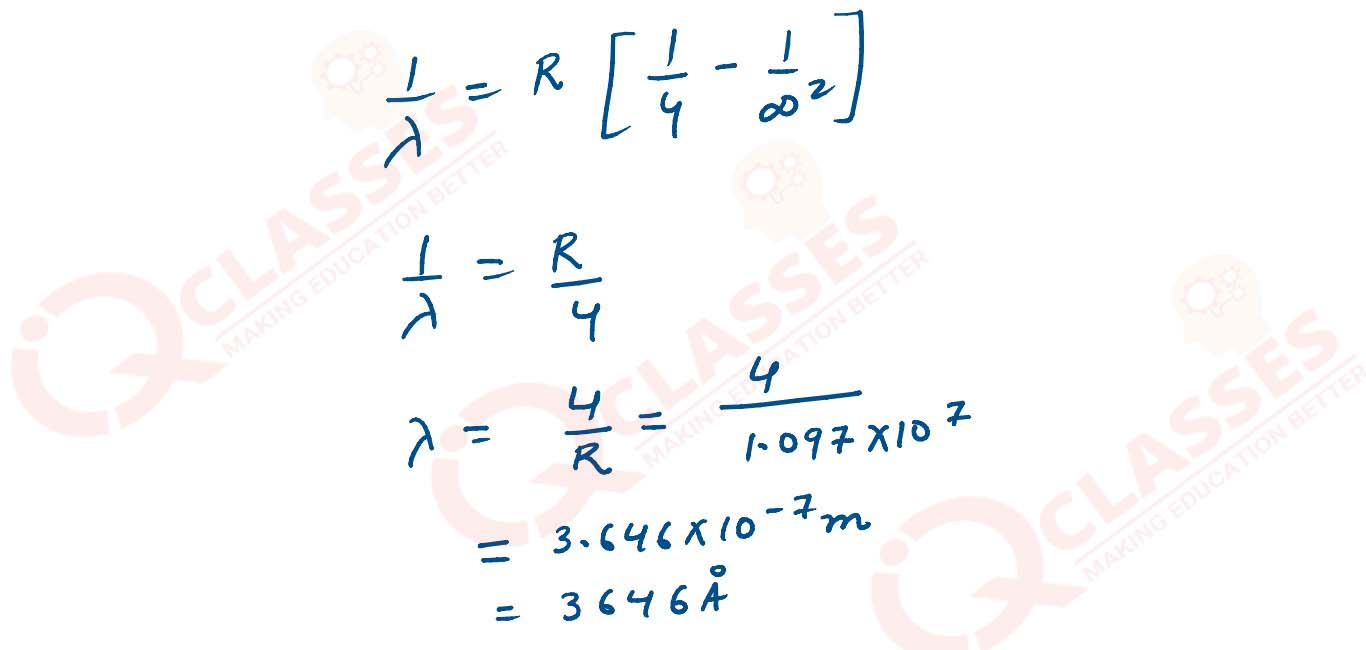
Q4
Calculate the minimum wavelength of the spectral line present in balmer series of hydrogen.
solutions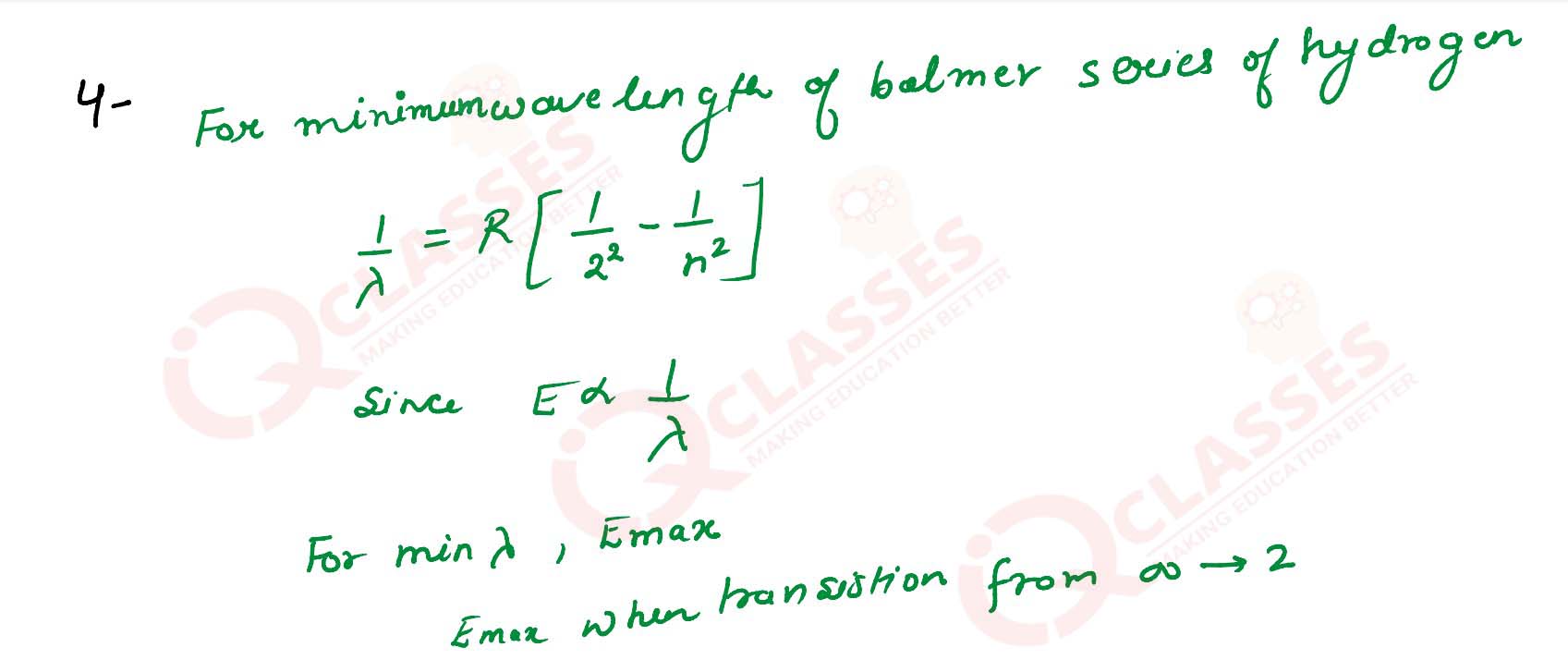
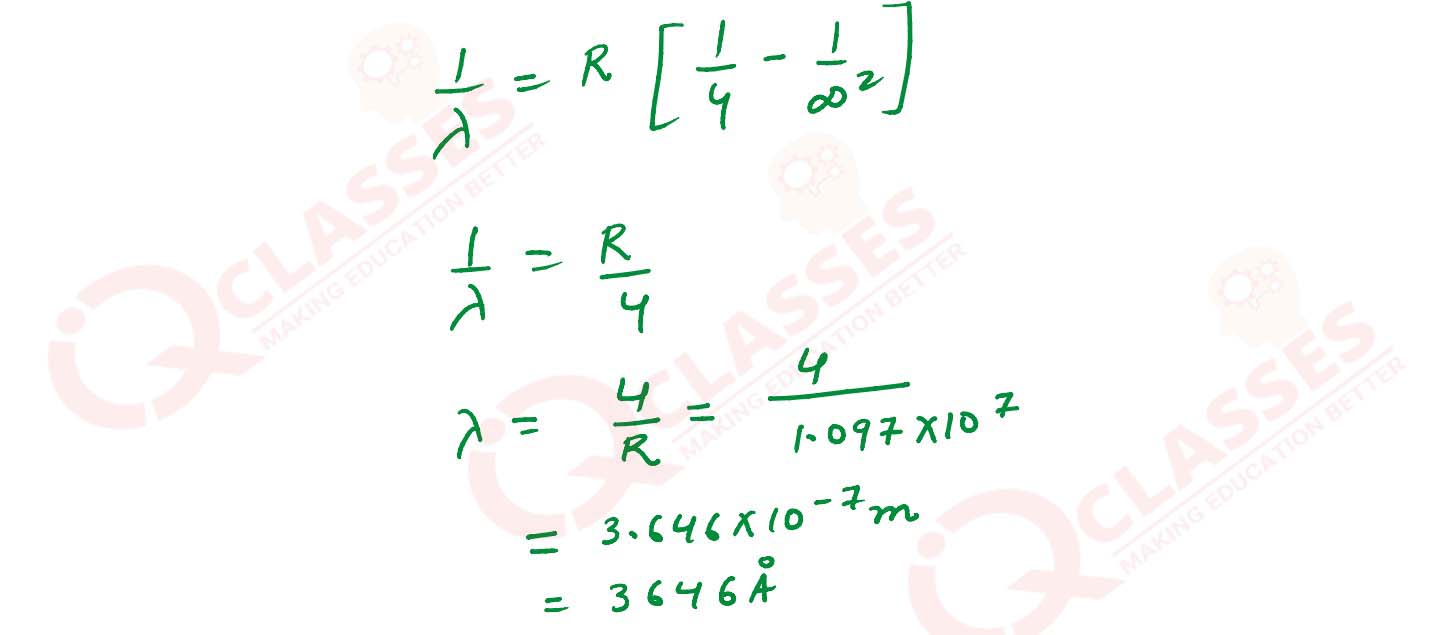
solutions

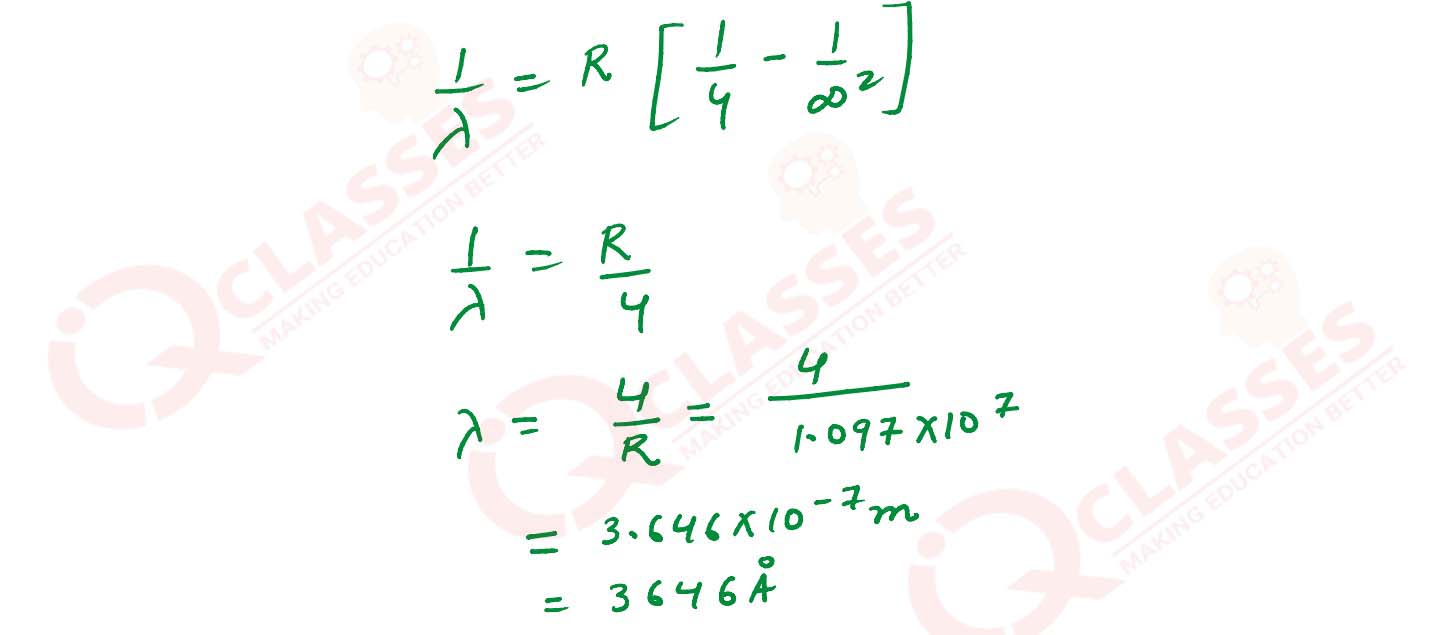
Q5
State any 2 Bohr’s postulates and write the energy value of the ground state of the hydrogen atom.
solutions
According to Bohr’s theory angular momentum of electron moving around the nucleus in orbit is
quantized in nature. According to his theory, electrons can move only in those orbits in which
angular momentum of an electron is an integral multiple of h/2.
Bohr proposed this theory as the particle nature of electron. Bohr assumed that standing waves will
be formed in the string only when the total distance travelled by a wave will be an integral number
of wavelengths. Hence if electron is moving in nth circular orbit of radius r, the total distance
covered by electron will be equal to the circumference of the orbit, 2πr.
solutions
According to Bohr’s theory angular momentum of electron moving around the nucleus in orbit is
quantized in nature. According to his theory, electrons can move only in those orbits in which
angular momentum of an electron is an integral multiple of h/2.
Bohr proposed this theory as the particle nature of electron. Bohr assumed that standing waves will
be formed in the string only when the total distance travelled by a wave will be an integral number
of wavelengths. Hence if electron is moving in nth circular orbit of radius r, the total distance
covered by electron will be equal to the circumference of the orbit, 2πr.
Bohr's third postulate (emission of photon):
When the atom receives energy from outside, then one(or more) of its outer electrons leaves its
orbit and goes to some higher orbit. This state is called 'excited state'. The electron in the
higher orbit stays only for 10-8
second and returns back to a lower orbit. While returning back, the electron radiates energy in the
form of photons.
If the energy of the electron in higher orbit is E2
and that in the lower orbit is E1
, then the frequency of the radiated wave is given by
hv=E2-E1
v= E2-E1/h
Q6
According to Bohr, ‘Angular momentum of an orbiting electron is quantised’ what is meant by this
statement?
solutions
solutions

Q7
What conclusion is drawn from rutherford’s scattering experiment of α-particles ?
solutions
solutions

Q8
Draw energy level diagram for hydrogen atom showing first for energy levels corresponding to n = 1,
2, 3 and 4. Show transition responsible for:
(i) absorption spectrum of Lyman series.
(ii) Emission spectrum of Balmer series
solutions
(i) In Absorption spectrum of Lyman series the transition occur to n>1 from the first orbit that is
n=1. It lies in UV region.
(i) absorption spectrum of Lyman series.
(ii) Emission spectrum of Balmer series
solutions
(i) In Absorption spectrum of Lyman series the transition occur to n>1 from the first orbit that is
n=1. It lies in UV region.
(ii) In Emission spectrum of Balmer series the transition occur from n>2to the second orbit that is
n=2. It lies in Visible region.
Q9
Name the series in the atomic Spectra of the hydrogen atom that falls in the ultraviolet region.
solutions
solutions
Lymann Series
Q10
In Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom radius of the first orbit of an electron is ro then radius of the
3rd orbit is :
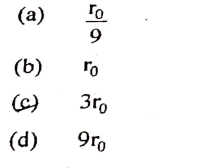
solutions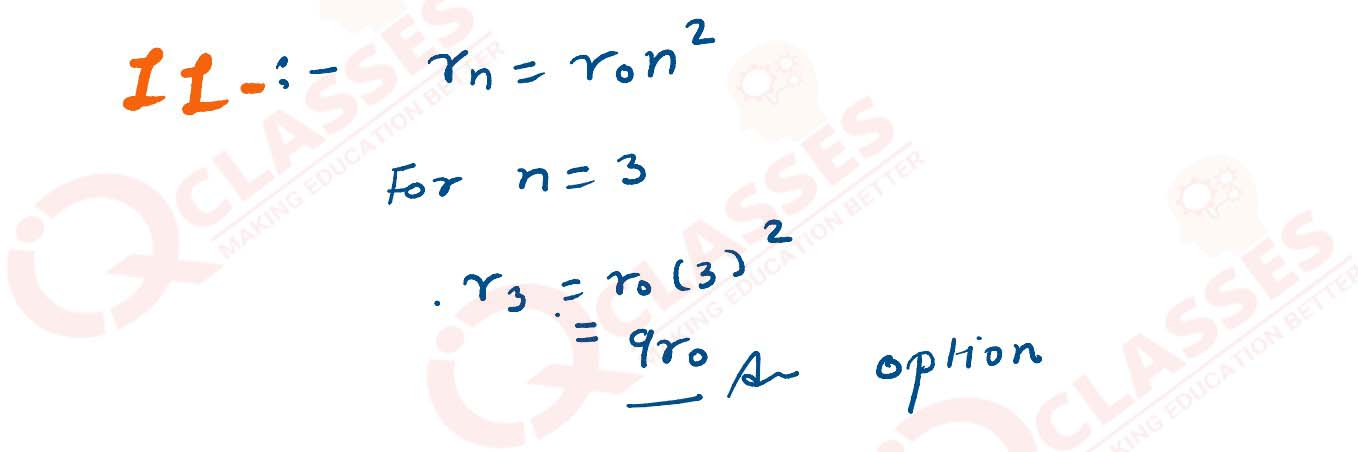
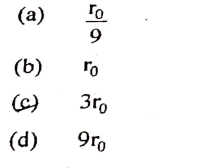
solutions


Add a comment