Class 12 ISC Physics Mass Energy Equivalence Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 Physics important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter Mass Energy Equivalence. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on ISC board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 Physics syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
class 12 ISC Physics Mass Energy Equivalence BoardQuestions
Mass Energy Equivalence BoardQuestions
Q1
What is pair production?
solutions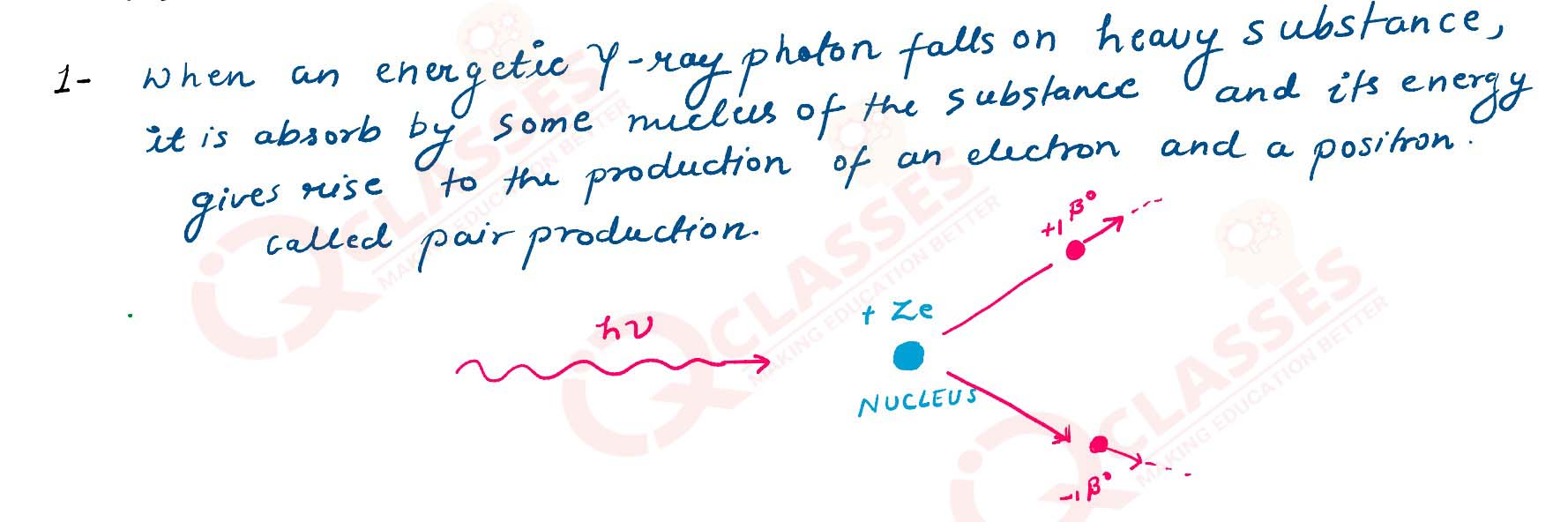
solutions

Q2
What is meant by mass defect?
solutions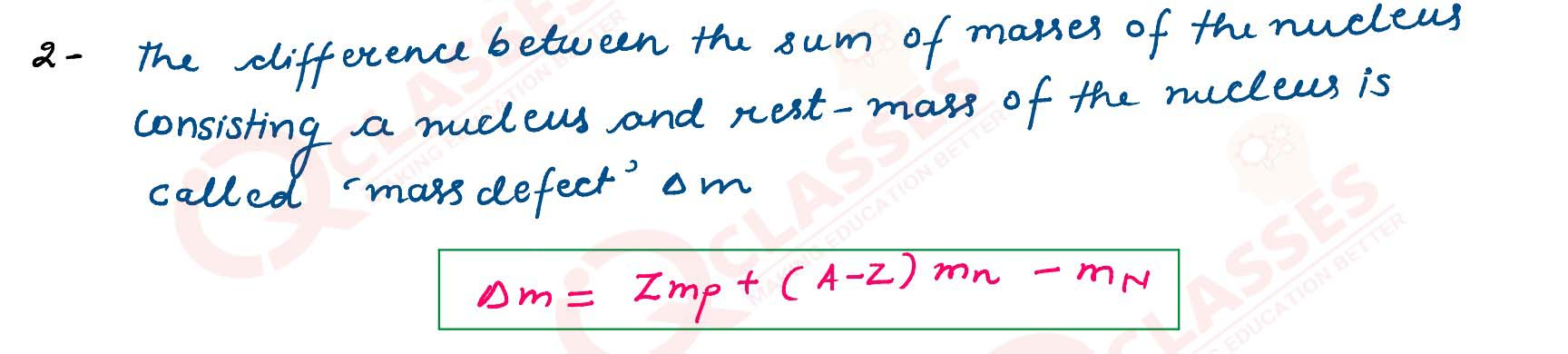
solutions
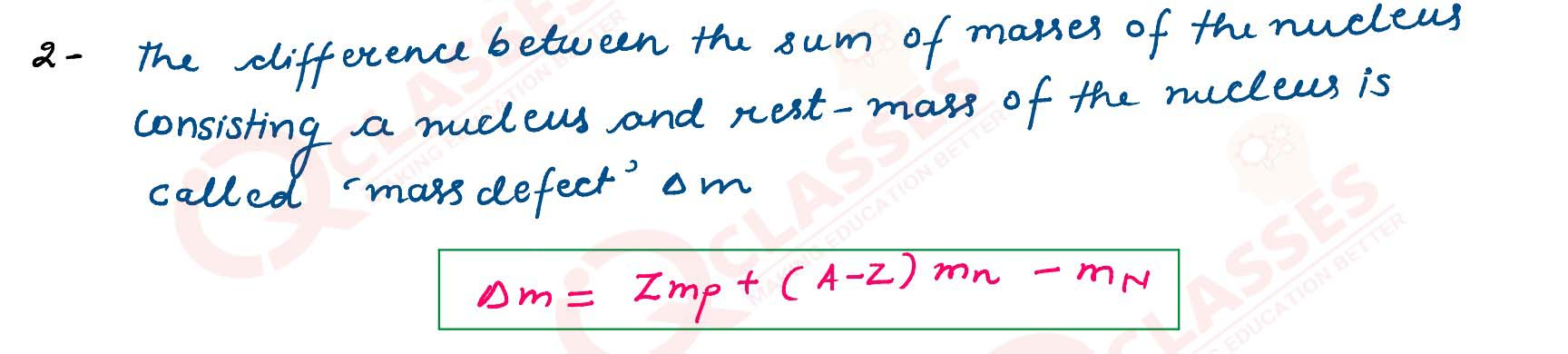
Q3
What is meant by pair annhilation? What is balance equation for the same.
solutions
solutions
- When an electron and positron come close to each other they annihilate each other to produce
two γ−photons.
- Here mass is converted to energy.
- The equation for this process can be given as : -1β0 +
+1β0
=hν(photon)+hν(photon)
- Here, two photons are produced so that both energy and momentum are conserved.
Q4
Sketch a graph showing variation of binding energy per nucleon of a nucleus with its mass number.
solutions
solutions
- The graph between binding energy per nucleon versus mass number explains stability of
nucleus.
- At lower mass number the binding energy per nucleon increases with increasing mass number.
- But, at higher mass number, the binding energy per nucleon decreases with increasing mass
number.
- This decrease is due to the increasing number of protons inside the nucleus in high mass
numbers.
- More protons lead to more Coulomb repulsion, thereby decreasing stability.
- The graph can be given as follows:
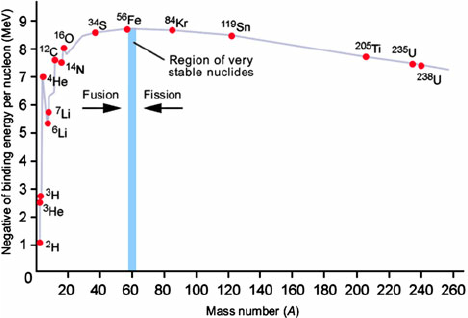
- Here, even-even nuclei such as carbon, helium and oxygen, are more stable than their
immediate neighbours.
- This is evident from the sharp rising peaks present in the graph.

Q5
For a radioactive substance, write the relation between :
(i) Half life (T) and disintegration constant (λ)
(ii) Mean life (τ) and disintegration constant (λ)
solutions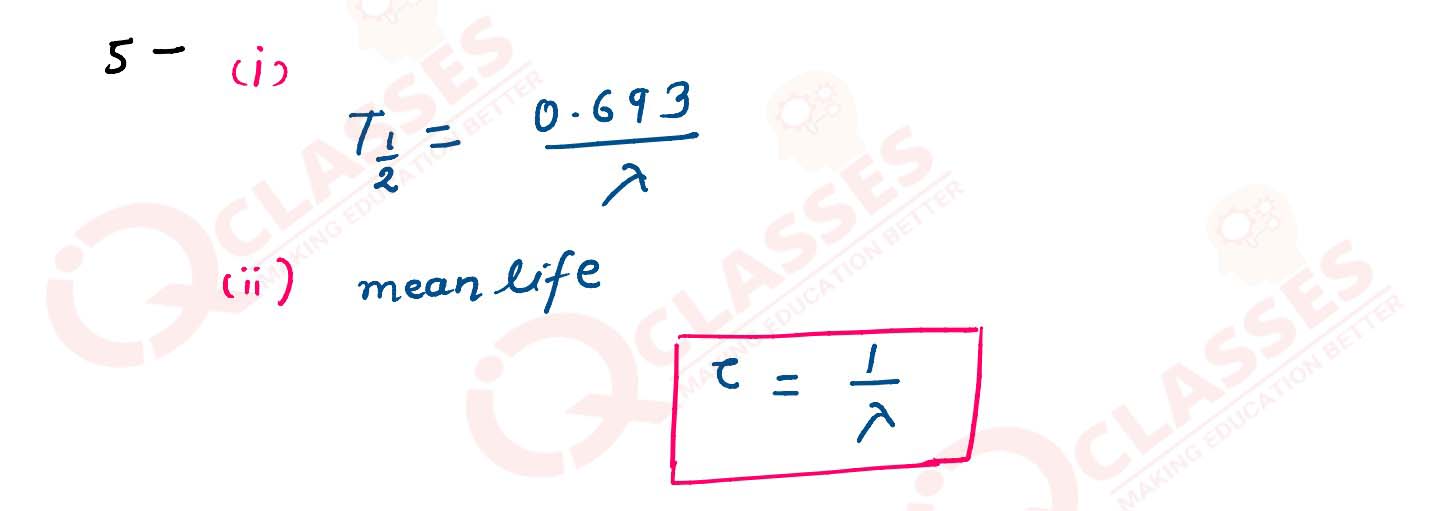
(i) Half life (T) and disintegration constant (λ)
(ii) Mean life (τ) and disintegration constant (λ)
solutions

Q6
Calculate binding energy of oxygen nucleus ((816)O ) from the data given below
:
Mass of proton = 1.007825 u , Mass of neutron = 1.008665 u , Mass of ((816)O )=15.994915 u
solutions
Mass of hydrogen atom is 1.007825 u
Mass of proton = 1.007825 u , Mass of neutron = 1.008665 u , Mass of ((816)O )=15.994915 u
solutions
Mass of hydrogen atom is 1.007825 u
Mass of neutron is 1.008665 u
Atomic mass of 8O16 is 15.994915 u
Now, binding energy is given as:
BE=Δm×931.5MeV
Substituting mass defect :
BE=[8×1.007825+8×1.00865−15.994915]×931.5
BE=0.1368×931.5 MeV
BE=127.42 MeV
Now, total number of nucleons are 16 (since 8 protons and 8 neutrons), so binding energy of nucleus
is 127.42 MeV.
Then, binding energy per nucleon is :
BE per nucleon=127.42/16
BE per nucleon=7.964 MeV
Q7
What is the minimum energy which a gamma ray photon must possess in order to produce
electron-positron pair?
solutions
solutions
1.02MeV
Q8
Calculate mass defect and binding energy per nucleon of 10Ne20 given
Mass of 10Ne20 = 19.992397 u.
Mass of 1H1 = 1.007825 u.
Mass of 0n1 = 1.008665 u.
solutions
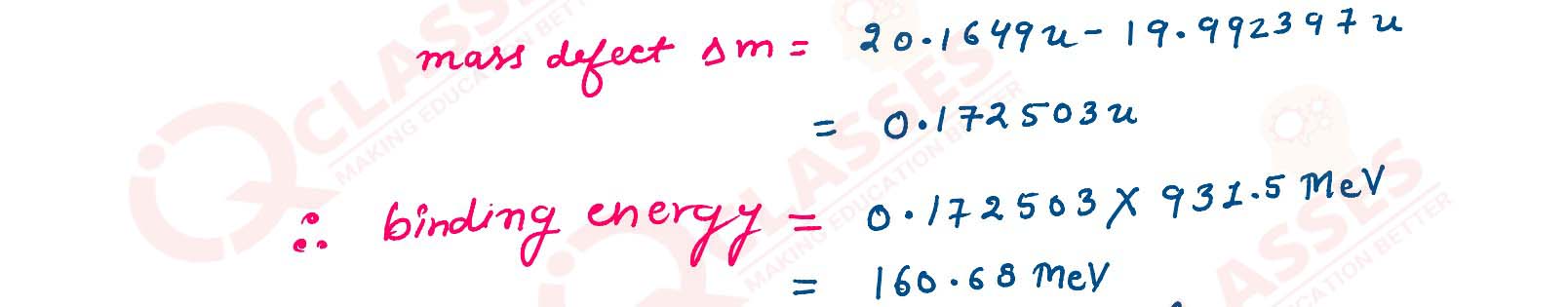
Mass of 10Ne20 = 19.992397 u.
Mass of 1H1 = 1.007825 u.
Mass of 0n1 = 1.008665 u.
solutions

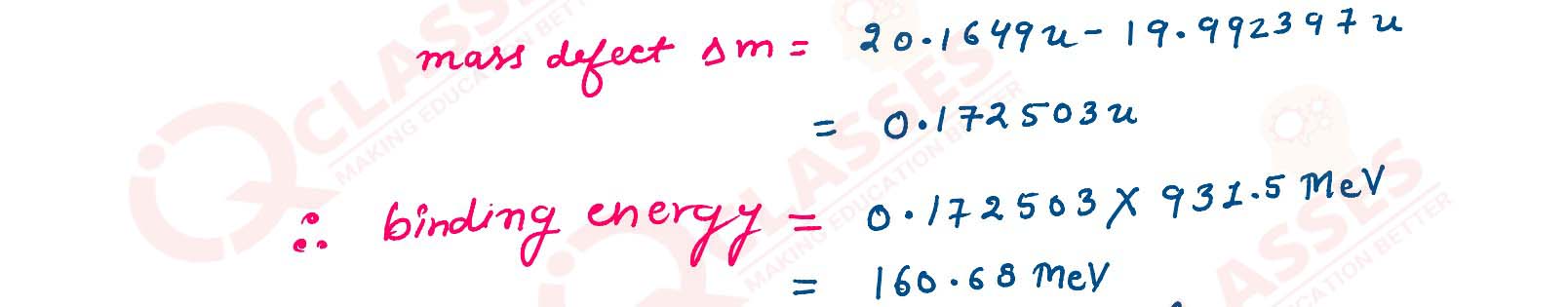


Add a comment