Class 12 ISC Physics Refraction of light at Spherical Surfaces Board Questions
Here we provide Class 12 Physics important notes,board questions and predicted questions with Answers for chapter Refraction of light at Spherical Surfaces. These important notes,board questions and predicted questions are based on ISC board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 Physics syllabus. By practising these Class 12 materials, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Board examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
class 12 ISC Physics Refraction of light at Spherical Surfaces BoardQuestions
Refraction of light at Spherical Surfaces BoardQuestions
Q1
2 thin lenses having optical powers of -10 D and + 6 D are placed in contact with each other. The
focal length of the combination is :
(a) + 0.25 cm
(b) - 0.25 cm
(c) + 0.25 m
(d) - 0.25 m
solutions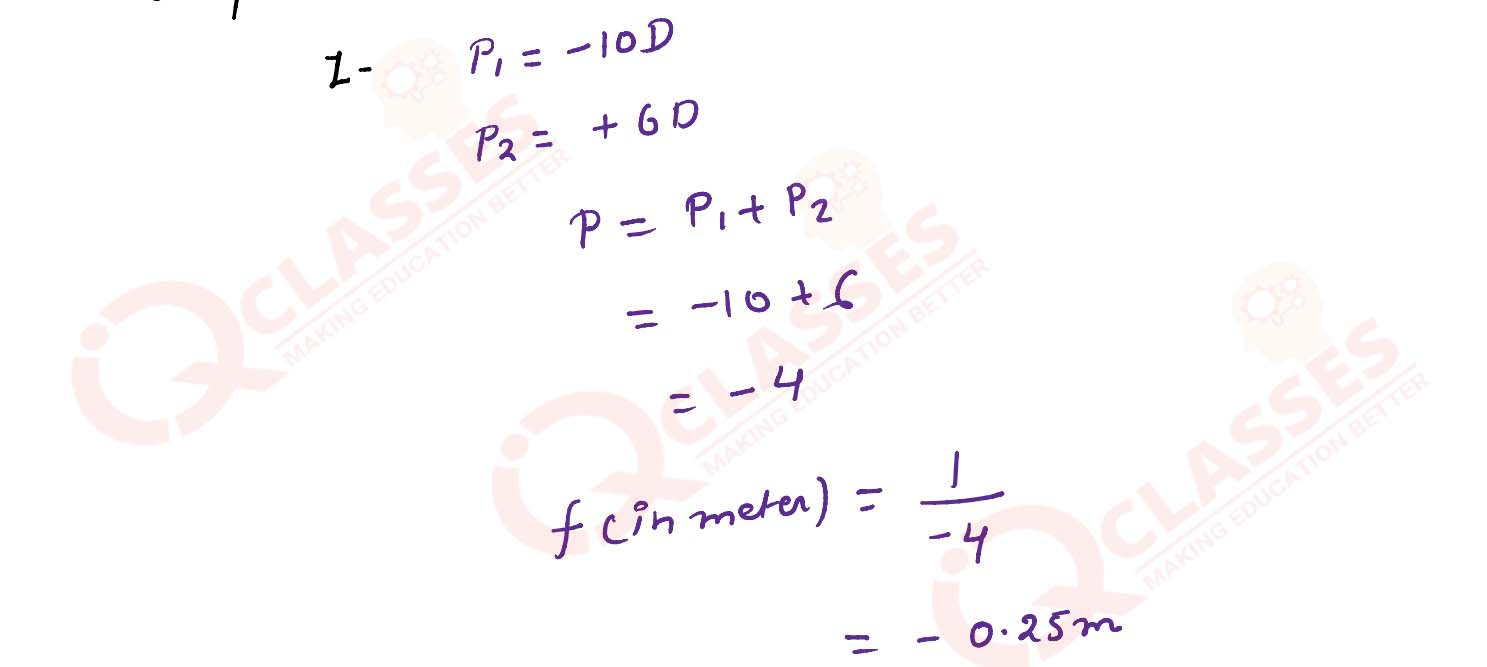
(a) + 0.25 cm
(b) - 0.25 cm
(c) + 0.25 m
(d) - 0.25 m
solutions
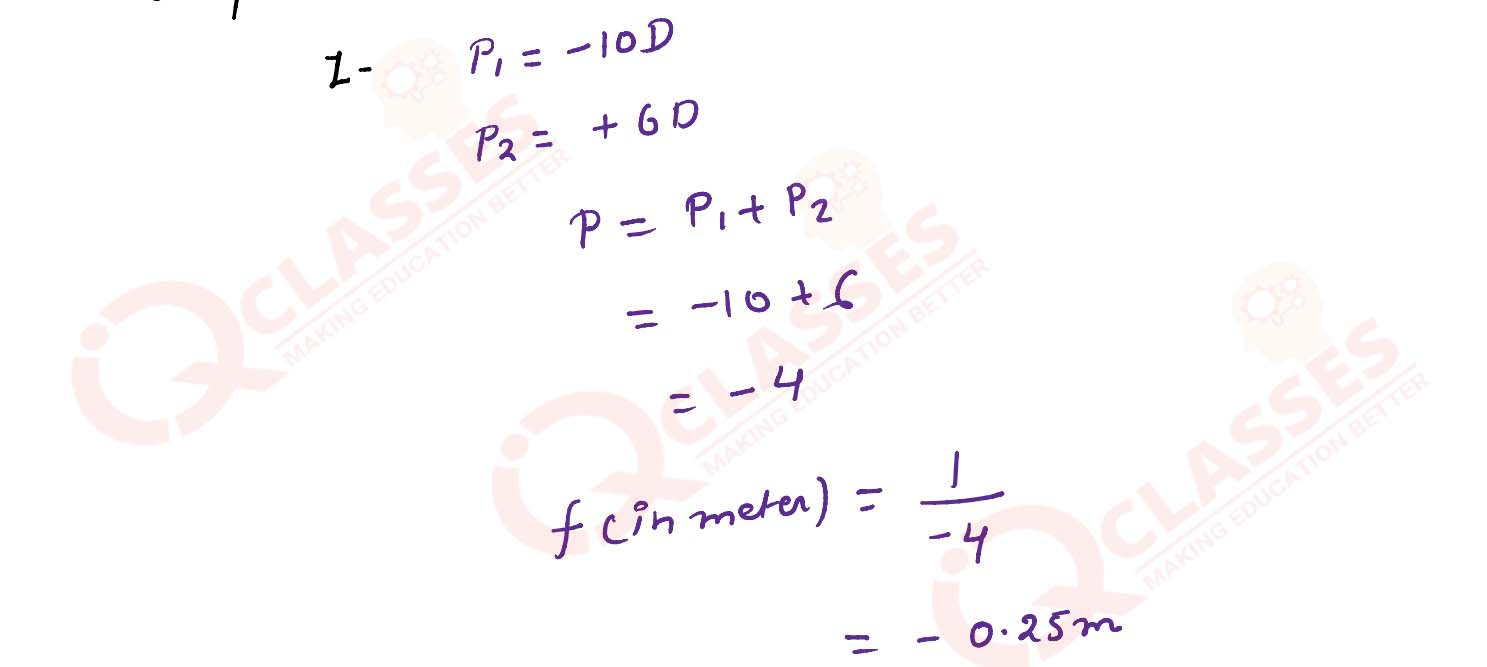
Q2
State how focal length of a glass lens (Refractive index 1.5) changes when it is completely immersed
in :
(a) Water (refractive index 1.33)
(b) A liquid (refractive index 1.65)
solutions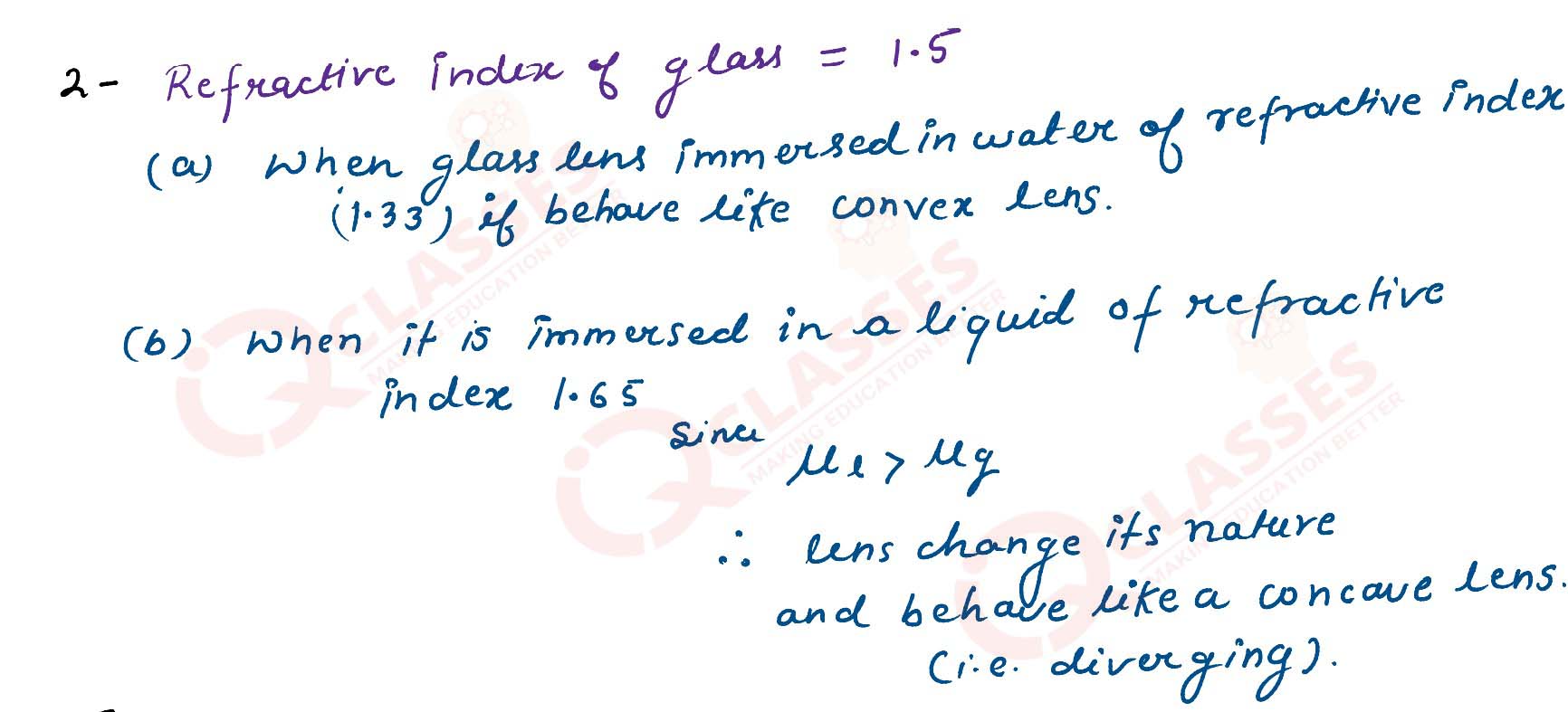
(a) Water (refractive index 1.33)
(b) A liquid (refractive index 1.65)
solutions
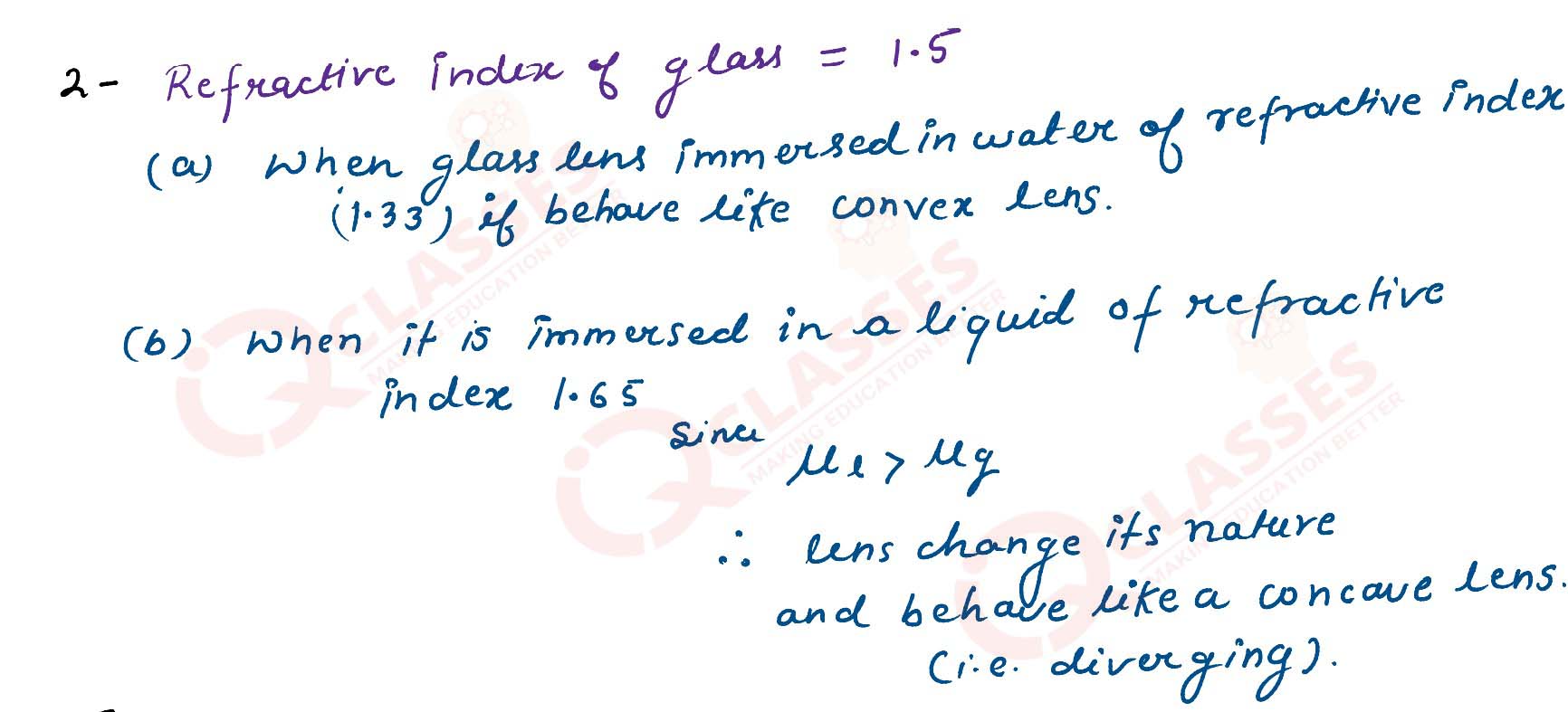
Q3
A biconvex lens made of glass (refractive index 1.5) has 2 spherical surfaces having radii 20 cm and
30 cm calculate its focal length.
solutions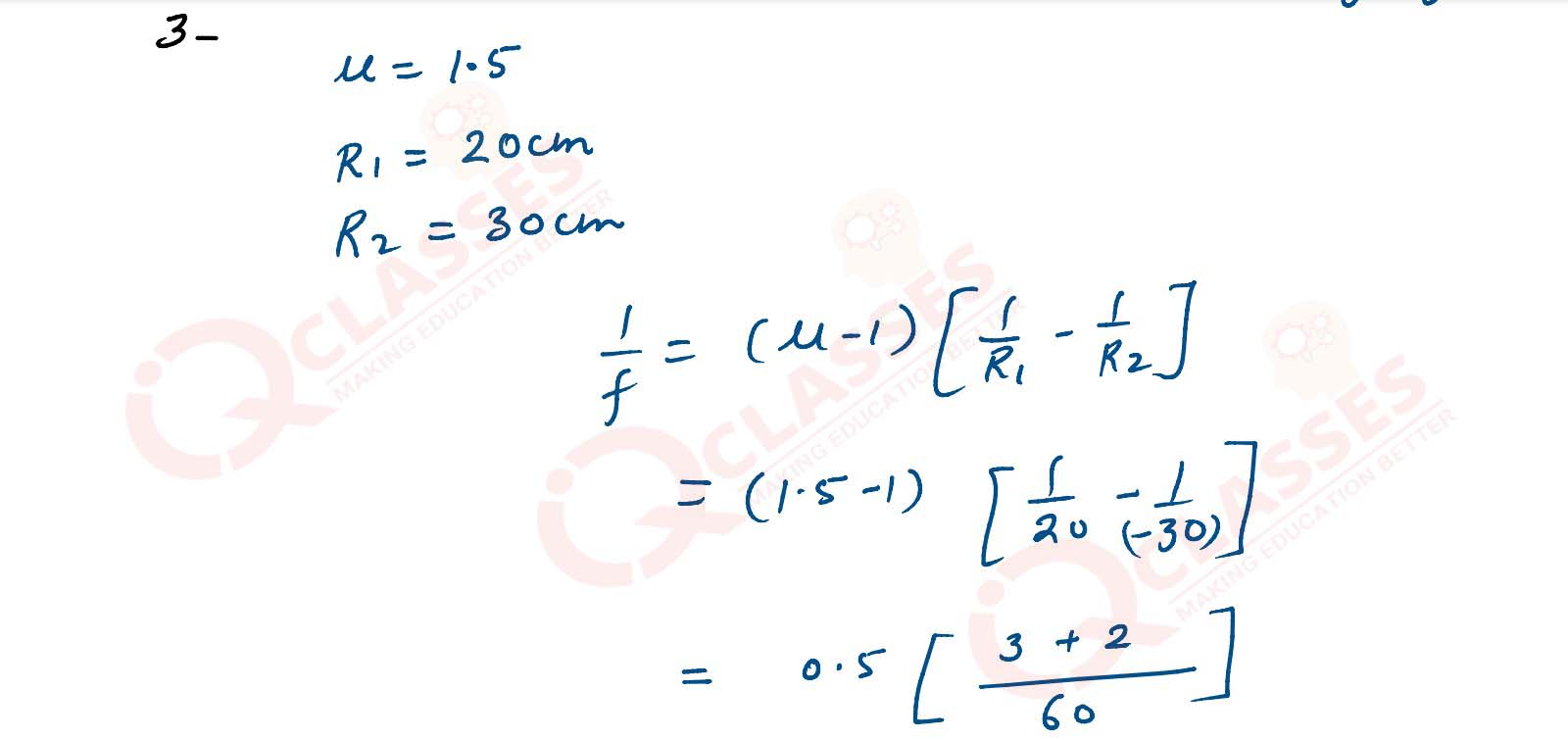
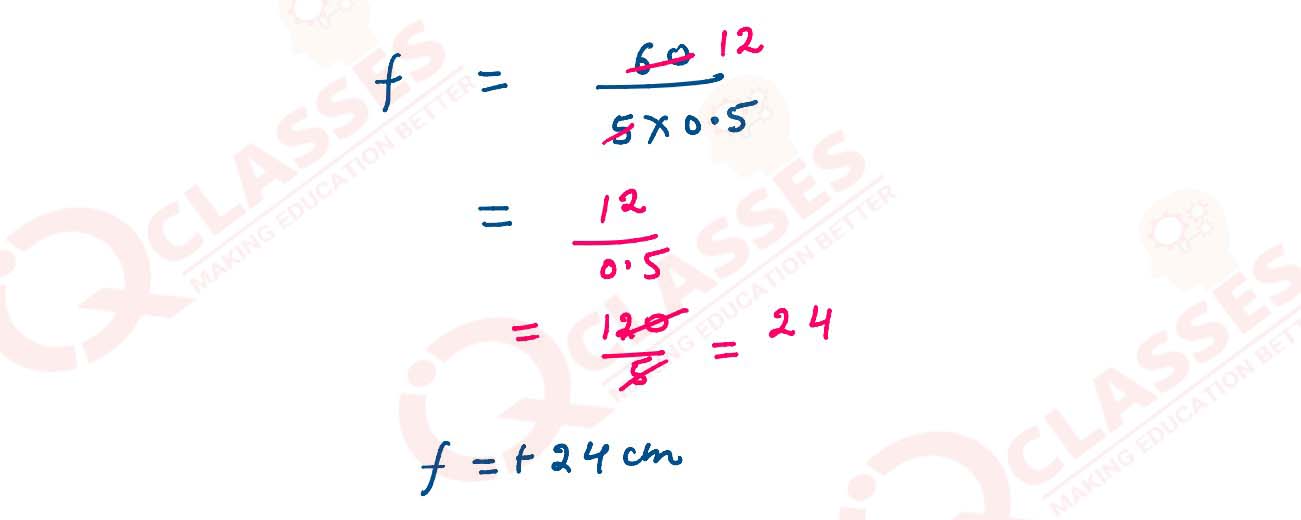
solutions

Q4
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30
cm. Find the focal length of the combination.
solutions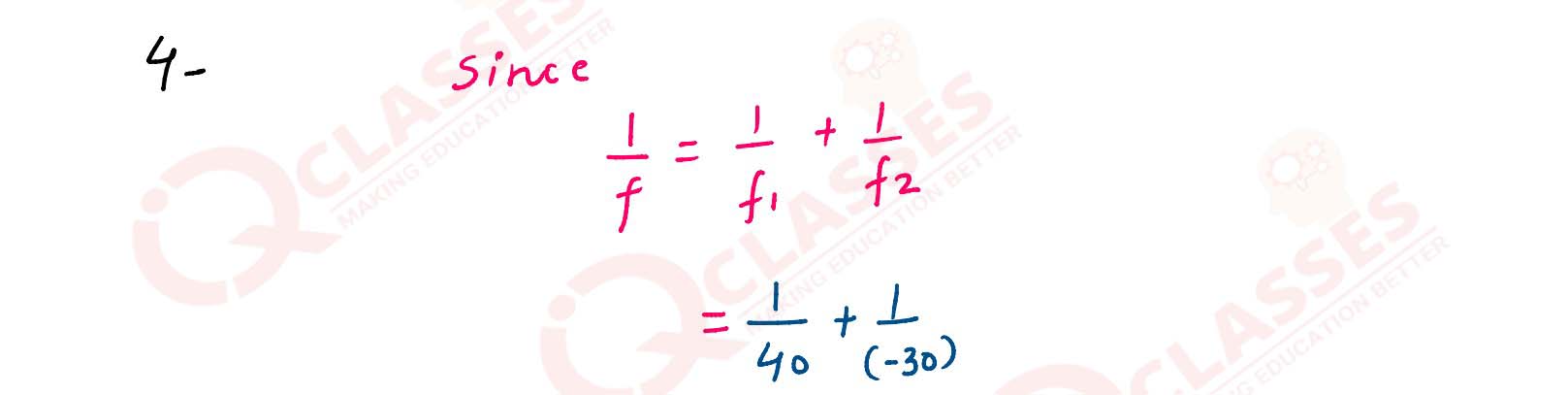

solutions
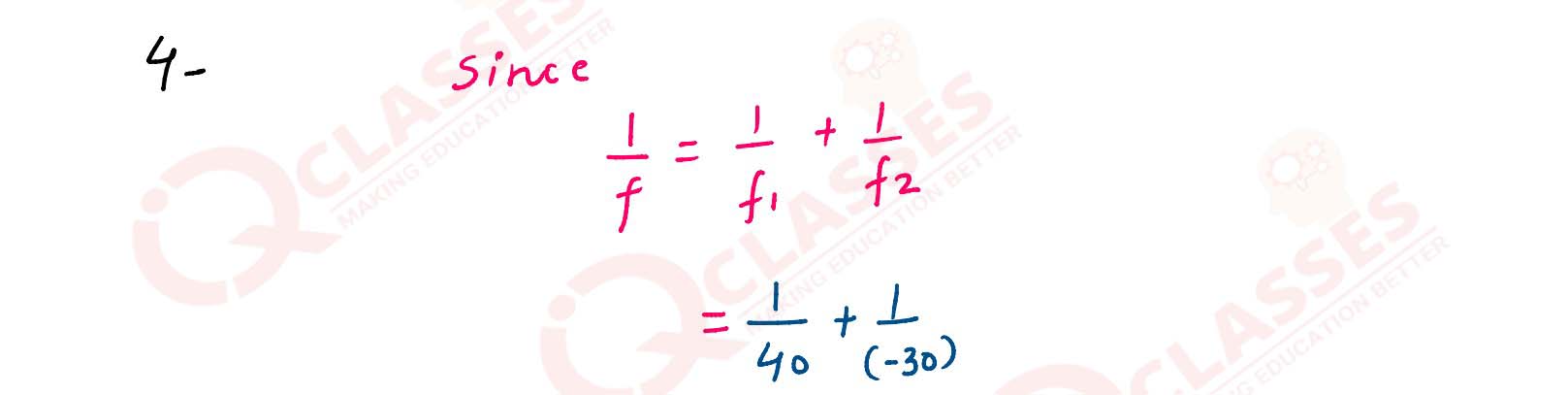

Q5
Starting with an expression for refraction at a single spherical surface, obtain Lens Maker’s
Formula.
solutions
Assumption for lens maker formula,
solutions
Assumption for lens maker formula,
- The lens used is thin so that the distances measured from its surfaces may be taken equal to
those measured from its optical center.
- The object is a point object placed on the principal axis.
- The aperture of lens is small.
- All rays are paraxial.
Lens maker formula for double convex lens. As shown in the figure.Let us consider a thin double
convex lens of refractive index μ1. Here μ1< μ2. Let P1 & P2be the poles, C1&C2 be the centers of
curvature, and R1&R2 be the radii of curvature of the two lens surfaces. Suppose a point object
O is placed on the principal axis in the rarer medium of refractive index μ1. The ray OA is
incident on the first surface.
For refraction at first surface, we can write the relation between the object distance u
, image distance v1 and the radius of curvature R1 as
μ2/v1 - μ1/u= μ2-μ1/R1---------(1)
Therefore CI1=v1
The emergent ray meets the principal axis at pointI
which is the final image of O
formed by the lens. For refraction at second surface, I1 acts as virtual object placed in the
medium of refractive index μ2 and I is a real image formed in the medium of refractive index μ1
. therefore, the relation between the object distance v1, image distance v
and radius of curvature R2 can be written as,

Q6
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens whose radii of curvature of two surface is 10 cm and 15
cm respectively and its refractive index is 1.5.
solutions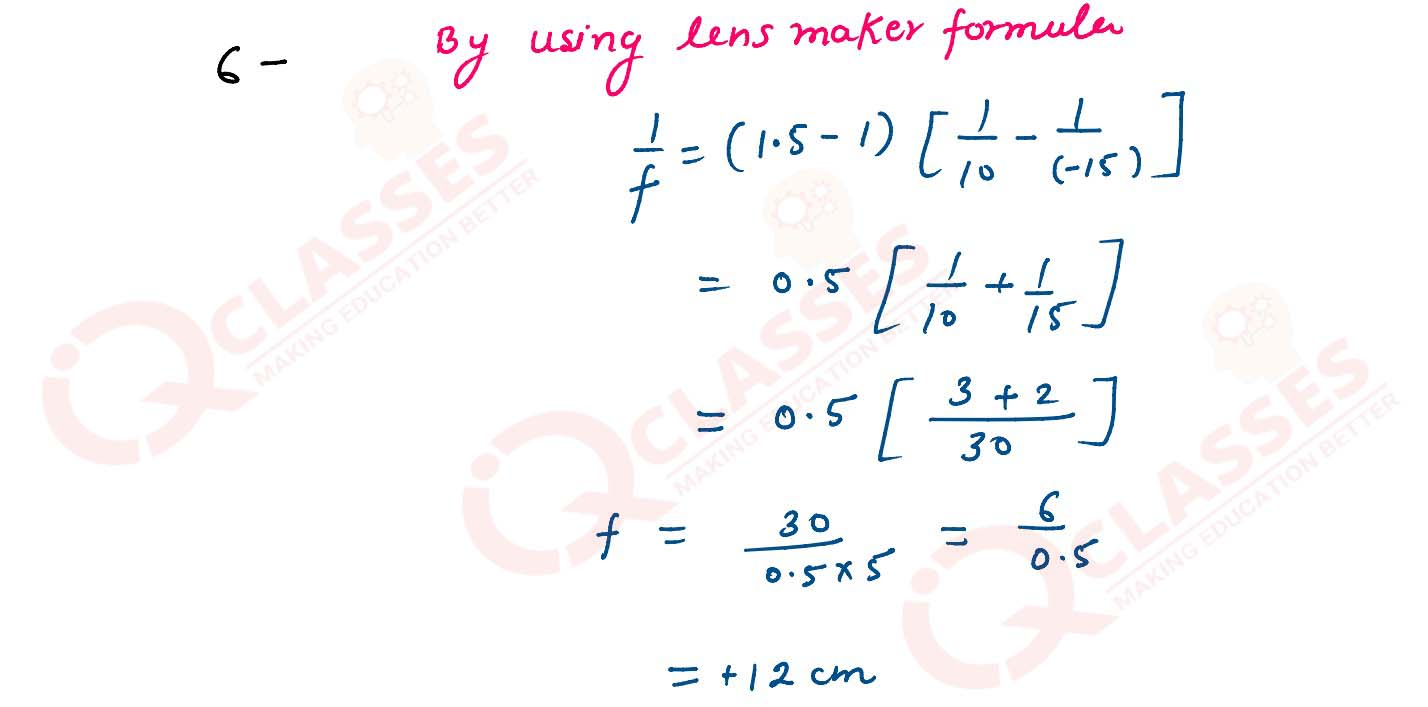
solutions
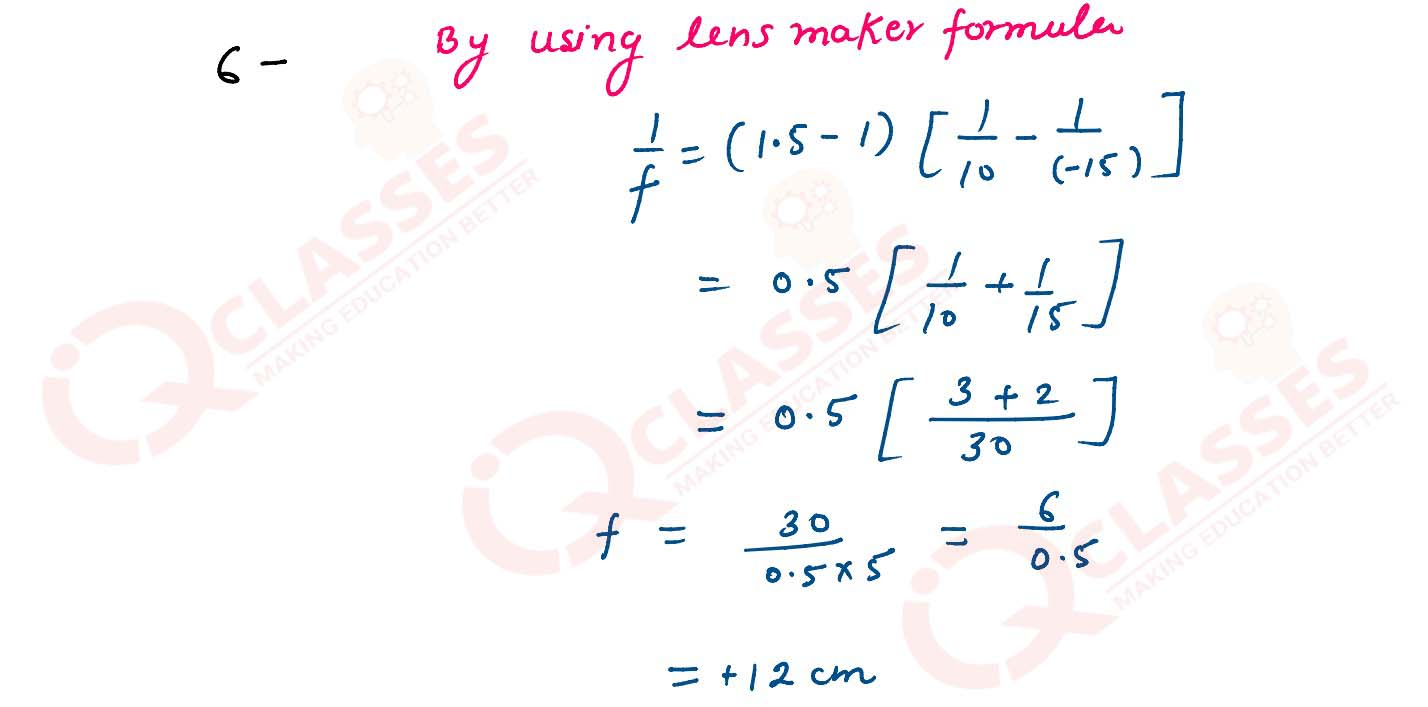
Q7
When 2 thin lenses are kept in contact, prove that their combined or effective focal length F is
given by :
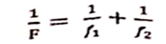
Where the terms have their usual meaning.
solutions
Let us consider two thin convex lenses L1& L2 as shown in the figure of focal lengths f1 & f2
are placed in contact in air having a common principal axis. A point object O
is placed on the principal axis at a distance u
from the first lens L1.
Its image will be formed by the lens L1 alone at I′, the image distance from the lens to the image
I′ is v′.
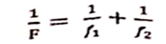
Where the terms have their usual meaning.
solutions
Let us consider two thin convex lenses L1& L2 as shown in the figure of focal lengths f1 & f2
are placed in contact in air having a common principal axis. A point object O
is placed on the principal axis at a distance u
from the first lens L1.
Its image will be formed by the lens L1 alone at I′, the image distance from the lens to the image
I′ is v′.
Using the lens formula for lens L1 is
1/f1=1/v' - 1/u
Lens formula for second convex lens L2 is
1/f2=1/v - 1/v'
Adding equation (1)n & (2) we get,



Add a comment