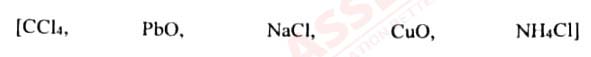Maximum Marks: 80
Time allowed: Two and half hours
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Section-A
(Attempt all questions from this Section.)
Question 1
Choose one correct answer to the questions from the given options:
(i)An element in period3, whose electron affinity is zero:
(a) Neon
(b) Sulphur
(c)Sodium
(d) Argon
View
Solution
(ii) An element with the largest atomic radius among the following is:
(a) Carbon
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Lithium
(d) Beryllium
View
Solution
(iii) The compound that is not an ore of aluminium:
(a) Cryolite
(b) Corundum
(c) Fluorspar
(d) Bauxite
View
Solution
(iv) The vapour density of CH3OH is (At. Wt. C=12, H=1, 0=16)
(a) 32
(b) 18
(c) 16
(d) 34
View
Solution
(v) Which of the following reactions takes place at the anode during the electroplating of an article with
silver?
(a) Ag - 1e- → Ag1+
(6) Ag + 1e- → Ag1-
(c) Ag - 1e- → Ag
(d) None of the above
View
Solution
(vi) The metallic hydroxide which forms a deep inky blue solution with excess
ammonium hydroxide solution is:
(a) Fe(OH)2
(b) Cu(OH)2
(c) Ca(OH)2
(d) Fe(OH)3
View
Solution
(vii) An example of a cyclic organic compound is:
(a) Propene
(6) Pentene
(c) Butene
(d) Benzene
View
Solution
(viii) In the laboratory preparation, HCl gas is dried by passing through:
(a) dilute nitric acid
(b) concentrated sulphuric acid
(c) dilute sulphuric acid
(d) acidified water
View
Solution
(ix) The nitrate which on thermal decomposition leaves behind a residue which is yellow
when hot and white when cold:
(a) Lead nitrate
(6) Ammonium nitrate
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Zinc nitrate
View
Solution
(x) The salt formed when concentrated sulphuric acid reacts with KNO3 above 200°C:
(a) K2SO4
(b) K2SO3
(c) KHSO4
(d) KHSO3
View
Solution
(xi) The property exhibited by concentrated sulphuric acid when it is used to prepare
hydrogen chloride gas from potassium chloride:
(a) Dehydrating property
(b) Drying property
(c) Oxidizing property
(d) Non-volatile acid property
View
Solution
(xii) The hydrocarbon formed when sodium propanoate and soda lime are heated together:
(a) Methane
(b) Ethane
(c)Ethene
(d) Propane
View
Solution
(xiii) The acid which does not form acid salt by a basic radical:
(a) H2CO3
(b) H3PO4
(c) H2SO4
(d) CH3COOH
View
Solution
(xiv) The general formula of hydrocarbons with single covalent bonds is:
(a) CnH2n + 2
(b) CnH2n
(c) CnH2n-2
(d) CnH2n-6
View
Solution
(xv) The indicator which changes to pink colour in an alkaline solution is:
(a) Blue Litmus
(b) Methyl Orange
(c) Red Litmus
(d) Phenolphthalein
View
Solution
Question 2
Section-B
(Attempt any four questions from this Section.)
Question 3
(i) Identify the cation in each of the following cases:
(a) Ammonium hydroxide solution when added to Solution B gives a white
precipitate which does not dissolve in excess of ammonium hydroxide
solution.
(b) Sodium hydroxide solution when added to Solution C gives a white precipitate
which is insoluble in excess of sodium hydroxide solution
(ii) Fill in the blanks by choosing the correct answer from the brackets:
(a) During electrolysis, the compound________ in its molten state liberates
reddish brown fumes at the anode. [NaCl/ PbBr2]
(b)The ion which could be discharged most readily during electrolysis is___________
[Fe2+/Cu2+]
(iii) Arrange the following as per the instruction given in the brackets:
(a) Al, K, Mg, Ca (decreasing order of its reactivity)
(b) N, Be, O, C (increasing order of non-metallic character)
(c) P, Si, E , Be (decreasing order of valence electrons)
(iv) Complete and balance the following equations:
(a) NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 →
(b) CuSO4 + NH4OH →
(c) Cu + Conc. HNO3 →
View
Solution
Section-B
(Attempt any four questions from this Section.)
Question 4
(i) State a relevant reason for the following:
(a) Hydrogen chloride gas cannot be dried over quick lime.
(b) Ammonia gas is not collected over water.
(ii) ldentify the alloy in each case from the given composition:
(a) aluminium, magnesium, manganese, copper
(b) iron, nickel, chromium, carbon
(iii) Solve the following mumerical problem.
Ethane burns in oxygen according to the chemical equation:
2C2H6+7O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O
If 80 ml of ethane is burnt in 300 ml of oxygen, find the composition of the resultant
gaseous mixture when measured at room temperature.
(iv) The following questions are pertaining to the laboratory preparation of Ammonia
gas from Magnesium nitride:
(a) Write a balanced chemical equation for its preparation.
(b) Why is this method seldom used?
(c) How do you identify the gas formed?
View
Solution
Question 5
(i) Write one use of the following alloys:
(a) Bronze
(b) Fuse metal
(ii) Draw the electron dot structure for the following:
(a) Ammonium ion
(b) A molecule of nitrogen
[At. No.: N =7, H = 1]
(iii) Give a balanced chemical equation for the following conversions with conditions:
(a) Ethene from ethanol
(b) Ethyne from calcium carbide
(c) Monochloromethane from methane
(iv) Study the following ohservations and name the anions present in each of the reactions.
(a) When a crystalline solid 'P' is wamed with concentrated H2SO4 and copper
turnings a reddish brown gas is released.
(b) When few drops of dilute sulphuric acid is added to Salt 'R' and heated, a
colourless gas is released which turns moist lead acetate paper silvery black.
(c) When few drops of barium nitrate solution is added to the salt solution 'Q', a
white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in HCl.
View
Solution
Question 6
(i) Define/ State:
(a) Electronegativity
(b) Gay-Lussac's Law of combining volumes
(ii) The Empirical formula of an organic compound is CHCl2.
If its relative molecular mass is 168, what is its molecular formula?
[At. Wt. C= 12, H = 1, Cl = 35.5]
(iii) Choose the substances given in the box below to answer the following questions:

(a) The metal that will not produce hydrogen gas when reacted with dilute acids.
(b)The compound that will produce sulphur dioxide gas when reacted with dilute
HCl.
(c) The solution of this compound produces dirty green precipitate with NaOH.
(iv) State one relevant observation for each of the following:
(a) To the copper nitrate solution, initially few drops of sodium hydroxide solution
is added and then added in excess.
(b) Burning of ammonia in excess of oxygen.
(c) Dry ammonia gas is passed over heated PbO.
View
Solution
Question 7
(i) Name the following:
(a) Organic compounds with same molecular formula but different structural
formula.
(b) Group of organic compounds where the successive members follow a regular
structural pattern, successive compounds differ by a 'CH2' group.
(ii) Give reason for the following:
(a) Ionization potential decreases down a group.
(6) Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in solid state
(iii) Calculate:
(a) The percentage of phosphorus in the fertilizer super phosphate Ca(H2PO4)2
correct to 1 decimal point. [At. Wt. H=1, P=31, 0=16, Ca=40]
(b) Write the empirical formula of C8H18.
(iv) Answer the following questions with reference to electrorefining of copper:
(a) What is the anode made of?
(b) What do you observe at the cathode?
(c) Write the reaction taking place at the cathode
View
Solution
Question 8
(i) Arrange the following according to the instructions given in bracket
(a) C2H2, CH6, CH4, C2H4 (In the increasing
order of the molecular weight)
(b) Cu2+, Na+, Zn2+, Ag+ (The order of Preferential discharge at the
cathode)
(ii) Differentiate between the following pairs bused on the criteria given in the brackets:
(a) Cane sugar and hydrated copper sulphate [using concentrated H2SO4]
(b) Sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid [type of salts formed]
(iii) Convert the following reactions into a balanced chemical equation:
(a) Ammonia to nitric oxide using oxygen and platinum catalyst.
(b) Sodium hydroxide to sodium sulphate using sulphuric acid.
(c) Ferrous sulphide to hydrogen sulphide using hydrochloric acid
(iv) Choose the answer from the list which fits in the description:
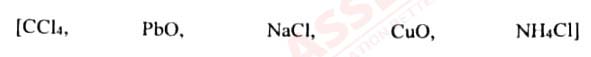
(a) A compound which undergoes thermal dissociation.
(b) An amphoteric oxide.
(c) A compound which is a non-electrolyte.
View
Solution