Maximum Marks: 80
Time allowed: Two and half hours
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Section-A
(Attempt all questions from this Section.)
Question 1
Choose one correct answer to the questions from the given options:
(Do not copy the question,write the correct answers only)
(i) An aqueous solution of copper sulphate turns colourless on electrolysis. Which of the following could be the electrodes?
P. anode: copper; cathode: copper
Q. anode: platinum; cathode: copper
R. anode: copper; cathode: platinum
(a) only P
(b) only Q
(c) only R
(d) both Q andR
View Solution
(ii) A compound P is heated in a test tube with sodium hydroxide solution. A red litmus paper held at the mouth of the test tube turns blue.
Which of the following could compound P be?
(a) zinc sulphate
(b) copper sulphate
(c) ferrous sulphate
(d) ammonium sulphate
View Solution
(iii) Which of the following would weigh the least?
(Atomic masses C=12, O=16, Na=23)
(a) 2 gram atoms of oxygen
(b) one mole of sodium
(c) 22.4 litres of carbon dioxide at STP
(d) 6.023 x 1023 atoms of carbon
View Solution
(iv) The equation below shows the reaction between element ‘X’ and dilute sulphuric acid.
X(s) + H2SO4 (aq.) -> XSO4 (aq.) + H2(g)
Which particles are responsible for conducting electricity in dilute sulphuric acid and compound XSO4?
(a) Electrons
(b) Only positive ions
(c) Only negative ions
(d) Both positive and negative ions
View Solution
(v) Assertion (A): Dry hydrogen chloride gas is collected by the upward displacement of air.
Reason (R): Hydrogen chloride gas is lighter than air.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
View Solution
(vi) The structures of four hydrocarbons are shown below:
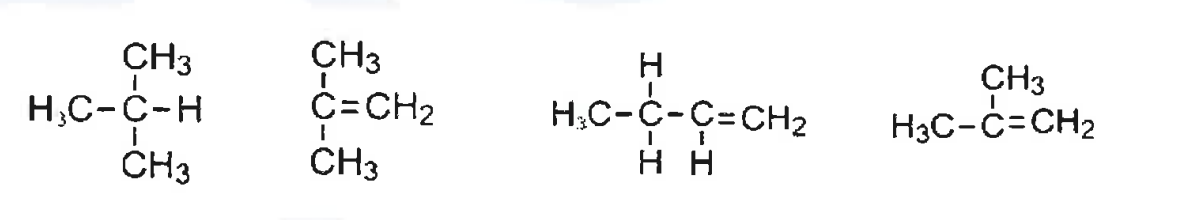
How many isomers of butene are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
View Solution
(vii) Element ‘P’ has electronic configuration 2,8,8,1. The number of chlorine atoms present in the chloride of ‘P’ is:
Reason (R): Rods are sensitive to dim light.
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 4
View Solution
(viii) 1H2 is an isotope of hydrogen. In the modern Periodic Table it will:
(a) be placed before hydrogen
(b) be placed after hydrogen
(c) be placed at the same position as hydrogen
(d) not have any position in the Periodic Table
View Solution
(ix) Anitrate which forms a precipitate with ammonium hydroxide and is also soluble in excess of it:
(a) ferrous nitrate
(b) ferric nitrate
(c) lead nitrate
(d) copper nitrate
View Solution
(x) Which of the following electronic configuration represents the most electropositive element?
(a) 2,1
(b) 2,8, 1
(c) 2,2
(d) 2,8,2
View Solution
(xi) Assertion (A): Alkali metals do not form dipositive ions.
Reason (R): After loss of one electron alkali metals achieve stable electronic configuration of noble gases.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
View Solution
(xii) The ratio between the volumes occupied by 4.4 grams of carbon dioxide and 2 grams of hydrogen gas is:
(a) 2.2:1
(b) 1:2.2
(c) 1:10
(d) 10:1
View Solution
(xiii) Aqueous lead (II) nitrate can be distinguished from aqueous zinc nitrate by adding any of the following solution in excess, except:
(a) aqueous potassium chloride
(b) aqueous sodium sulphate
(c) dilute sulphuric acid
(d) sodium hydroxide solution
View Solution
(xiv) Which of the following about oxides is correct?
(a) A basic oxide is an oxide of a non-metal
(b) Acidic oxides contain ionic bonds
(c) Amphoteric oxides contain a metal
(d) Basic oxides are always gases
View Solution
(xv) A student takes Cu, Al, Fe and Zn strips, separately in four test tubes labeled as I, II, III and IV respectively. He adds 10 ml of freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution to each test tube and observes the colour of the metal residue in each case.
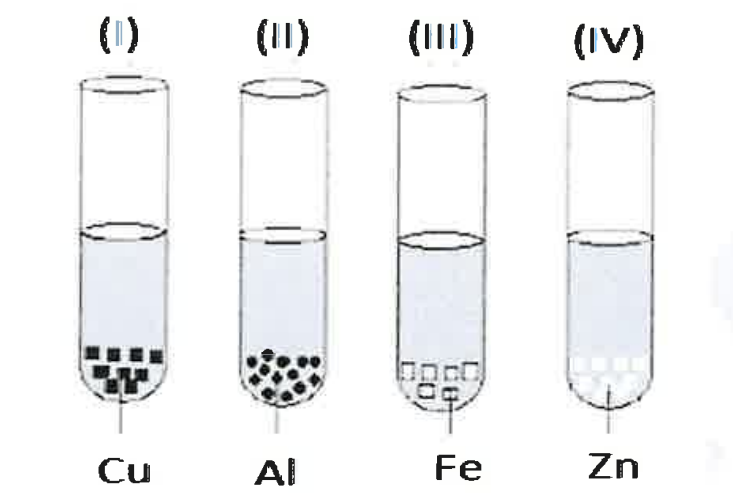
He would observe a black residue in the test tubes:
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) and (II)
(c) (II) and (II)
(d) (II) and (IV)
View Solution
Question 2
Section-B
(Attempt any four questions from this Section.)
Question 3
(i) Identify the reactant and write the balanced equation for the following:
Nitric acid reacts with compound Q to give a salt Ca(NO3)2, water and carbon dioxide.
(ii) What property of Sulphuric acid is exhibited in each of the following cases:
(a) In the preparation of HCl gas when it reacts with Sodium chloride.
(b) When concentrated Sulphuric acid reacts with Copper to produce Sulphur dioxide gas.
(iii) The electron affinity of an element X is greater than that of element Y.
(a) How is the oxidising power of X likely to compare with that of Y?
(b) How is the electronegativity of X likely to compare with that of Y?
(c) State whether X is likely to be placed to the left or to the right of Y in the periodic table?
(iv) You are provided with the list of chemicals mentioned below in the box:

Using suitable chemicals from the list given, write balanced chemical equation for the preparation of the salts mentioned below:
(a) copper sulphate
(b) sodium zincate
(c) ferric chloride
View Solution
Question 4
(i) The following questions relate to the extraction of Aluminium by electrolysis.
(a) Name the other aluminium containing compound added to alumina.
(b) Give a balanced equation for the reaction that takes place at the cathode.
(ii) Pratik heated 11.2 grams of element ‘M’ (atomic weight 56) with 4.8 grams of element ‘N’ (atomic weight 16) to form a compound. Find the empirical formula of the compound obtained by Pratik.
(iii) Give balanced equations for each of the following:
(a) Action of warm water on Aluminium nitride.
(b) Oxidation of carbon with conc. Nitric acid.
(c) Laboratory preparation of ethanol by using chloroethane and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
(iv) The diagram given below is a representation of the Industrial preparation of Nitric acid by Ostwald’s process. With respect to the process answer the following questions:
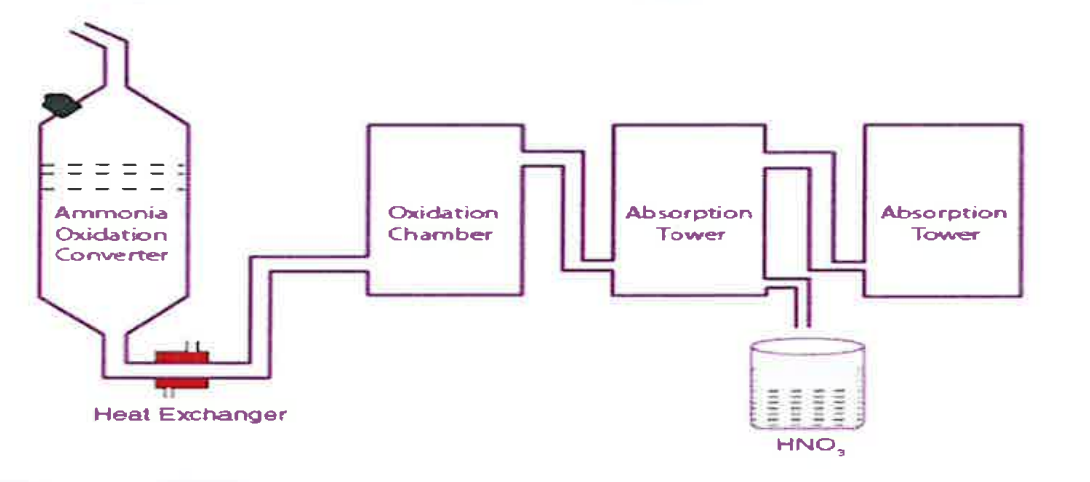
(a) Write the temperature and the catalyst required during the catalytic oxidation of ammonia.
(b) Give balanced chemical equation for the reaction occurring during the conversion of nitrogen dioxide to nitric acid.
View Solution
Question 5
(i) (a) Ranjana wants to prove that ammonia is a reducing agent. To demonstrate this, she passes ammonia gas over heated copper oxide. What will she observe?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the above reaction.
(ii) Name the alloy which is made up of:
(a) Copper, Zinc and Tin
(b) Lead and Tin
(iii) Abhishek was given a salt ‘X’ which was white in colour for analysis. On strong heating it produced a yellow residue, a colourless gas and also a reddish-brown gas. The solution of the salt ‘X’ when tested with excess of ammonium hydroxide produced a chalky white insoluble precipitate.
(a) Name the coloured gas evolved when Abhishek heated the salt strongly.
(b) Which cation was present in the sample given to Abhishek?
(c) Identify the salt given to Abhishek for analysis.
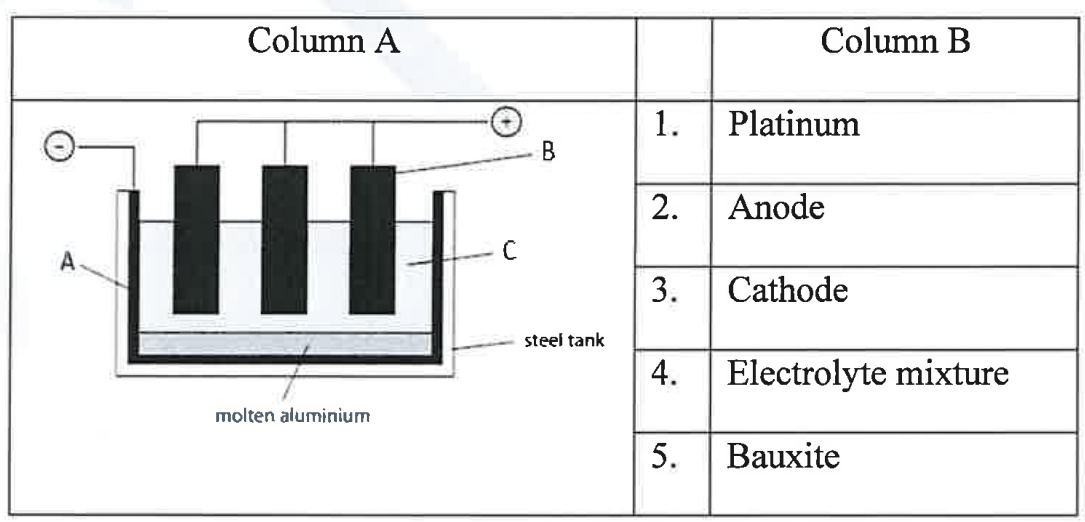
(iv) Given below in column A is a schematic diagram of the electrolytic reduction of alumina. Identify the parts labelled as A, B and C with the correct options from the Column B.
View Solution
Question 6
(i) Element ‘X’ forms an oxide with the formula X203 which is a solid with high melting point. 'X' would most likely be placed in the group of the Periodic Table as:
1. (a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Al
(d) Si
2. Justify your answer in the above question (1).
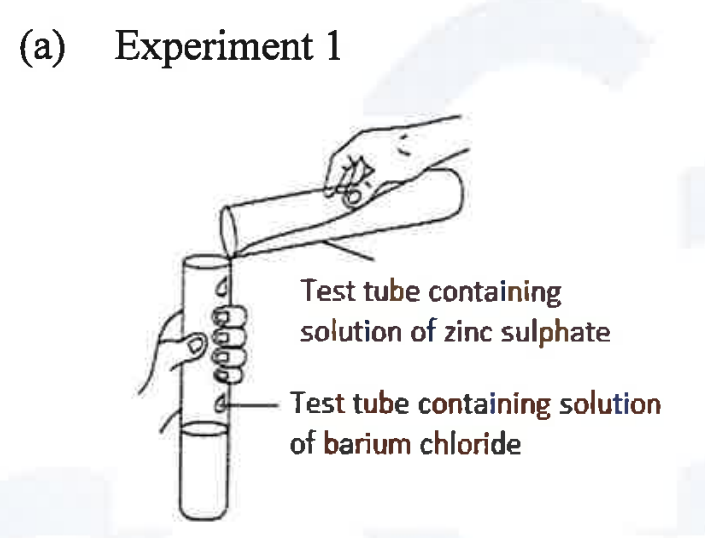
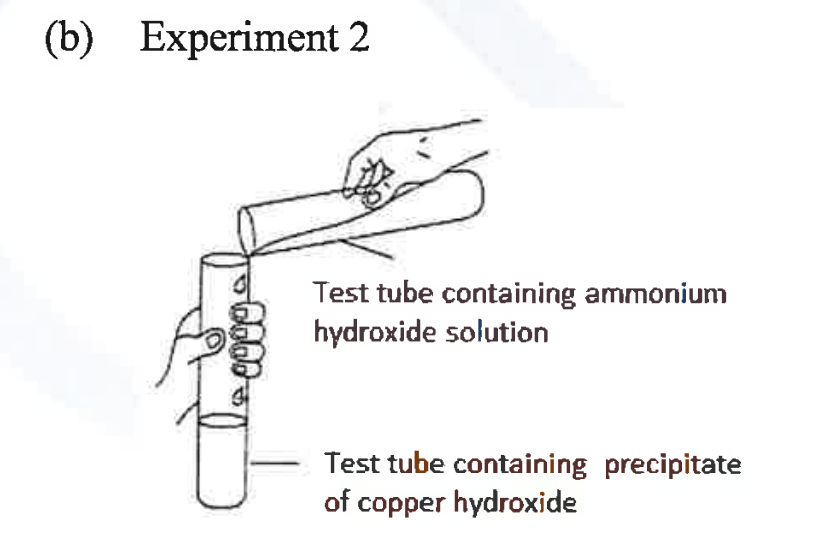
(ii) A student was asked to perform two experiments in the laboratory based [2] on the instructions given:
Observe the picture given below and state one observation for each of the Experiments 1 and 2 that you would notice on mixing the given solutions.
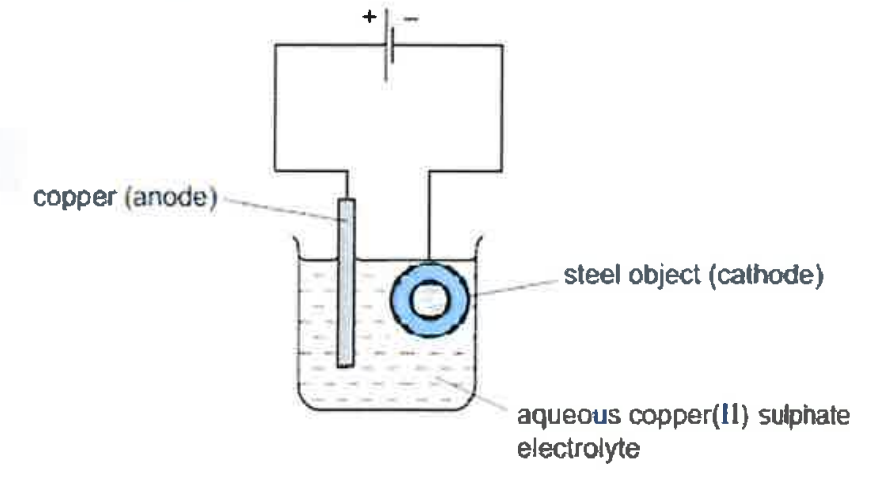
(iii) Copper sulphate solution is electrolysed using copper electrodes.
(a) Which electrode [cathode or anode] is the oxidizing electrode? Why?
(b) Write the equation for the reaction occurring at the above electrode.
(iv) X [2, 8, 7] and Y [2, 8, 2] are two elements. Using this information complete the following:
(a) ______ is the metallic element.
(b) Metal atoms tend to have a maximum of ________ electrons in the outermost shell.
(c) ________ is the reducing agent.
View Solution
Question 7
(i) One variety of household fuel is a mixture of propane (60%) and butane (40%). If 20 litres of this mixture is burnt, find the total volume of carbon dioxide added to the atmosphere. The combination reactions can be represented as:
C3H8 + 5O2 --> 3CO2 + 4H2O
2C4H10 + 13O2 --> 8CO2 + 10H2O
(ii) Rohit has solution X, Y and Z that has pH 2, 7 and 13 respectively. Which solution.
(a) will liberate sulphur dioxide gas when heated with sodium sulphite
(b) will liberate ammonia gas when reacted with ammonium chloride
(c) will not have any effect on litmus paper?
(iii) 8.2 grams of calcium nitrate is decomposed by heating according to the equation
2Ca (NO3)2 --> 2CaO +4NO2 + O2
Calculate the following:
(a) Volume of nitrogen dioxide obtained at STP
(b) Mass of CaO formed
[Atomic weights: Ca—40 , N—14, O—16]
View Solution
Question 8
(i) State giving reasons if:
(a) zinc and aluminium can be distinguished by heating the metal powder with concentrated sodium hydroxide solution.
(b) calcium nitrate and lead nitrate can be distinguished by adding ammonium hydroxide solution to the salt solution.
(ii) Draw the electron dot diagram of ammonium ion.
(iii) Give balanced equations for the following:
(a) Laboratory preparation of ethyne from calcium carbide.
(b) Conversion of acetic acid to ethyl acetate.
(c) Laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
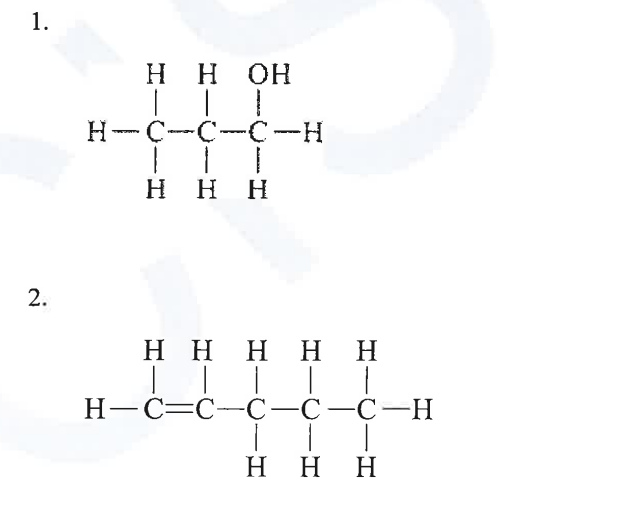
(iv) The structures of six organic compounds are shown:

(a) Identify two of the compounds that are members of the same homologous series but are not isomers.
(b) Which two compounds are isomers of each other?
(c) F can be prepared from D. Give a chemical equation for the reaction.
View Solution